Deck 6: Consumer Choice and Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/170
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Consumer Choice and Demand
1
If marginal utility is negative, total utility is negative.
False
2
The law of diminishing marginal utility implies it is possible that the marginal utility of my tenth pistachio nut is less than the marginal utility of my third pistachio nut, other things constant.
True
3
As a consumer buys more of a good, total utility eventually becomes negative.
False
4
Consumer preferences
A) do not vary from one consumer to another
B) have little to do with personal tastes and income
C) are not influenced by the utility of goods
D) are individual evaluations of goods and services
E) can be objectively measured and compared across individuals
A) do not vary from one consumer to another
B) have little to do with personal tastes and income
C) are not influenced by the utility of goods
D) are individual evaluations of goods and services
E) can be objectively measured and compared across individuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Utility is
A) easily measured because all people derive the same utility from consumption
B) easily measured because it is an objective concept
C) easily measured because it is a subjective concept
D) hard to measure because it is a subjective concept
E) hard to measure because it is an objective concept
A) easily measured because all people derive the same utility from consumption
B) easily measured because it is an objective concept
C) easily measured because it is a subjective concept
D) hard to measure because it is a subjective concept
E) hard to measure because it is an objective concept

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements concerning utility is correct?
A) It is possible to precisely measure the utility an individual receives from consuming a particular good or service
B) It is always possible to determine whether Dalene or Juloy gets more utility from consuming two units of the same good
C) The utility of goods can be measured while the same is not true for services
D) Utility is a subjective measure of satisfaction an individual receives from consuming a good or service
E) It is only useful if there is no scarcity
A) It is possible to precisely measure the utility an individual receives from consuming a particular good or service
B) It is always possible to determine whether Dalene or Juloy gets more utility from consuming two units of the same good
C) The utility of goods can be measured while the same is not true for services
D) Utility is a subjective measure of satisfaction an individual receives from consuming a good or service
E) It is only useful if there is no scarcity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Different people may have different tastes, but their tastes do not change over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Utility is
A) the sense of pleasure or satisfaction derived from consuming goods and services
B) the cost of acquiring goods and services
C) the profit consumers earn from consuming goods and services
D) the monetary value to consumers of goods and services
E) the desire to consume goods and services
A) the sense of pleasure or satisfaction derived from consuming goods and services
B) the cost of acquiring goods and services
C) the profit consumers earn from consuming goods and services
D) the monetary value to consumers of goods and services
E) the desire to consume goods and services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The law of diminishing marginal utility implies that the marginal utility of my fifth hot dog is less than the marginal utility of my second soft drink, other things constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements cannot be made regarding consumer preferences?
A) Pat enjoys her second cotton candy less than her first.
B) Bill enjoys his second cotton candy as much as the first.
C) Arnie enjoys two cotton candies more than one cotton candy.
D) Arnie enjoys two cotton candies more than Pat enjoys one cotton candy.
E) Bill and Arnie enjoy their second cotton candy less than they do their first.
A) Pat enjoys her second cotton candy less than her first.
B) Bill enjoys his second cotton candy as much as the first.
C) Arnie enjoys two cotton candies more than one cotton candy.
D) Arnie enjoys two cotton candies more than Pat enjoys one cotton candy.
E) Bill and Arnie enjoy their second cotton candy less than they do their first.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Marginal utility is the
A) overall satisfaction obtained from consuming a good
B) additional satisfaction obtained from consuming one more unit of a good
C) average satisfaction obtained from consuming a good
D) the change in satisfaction obtained from consuming 1 percent more of a good
E) additional cost of one more unit of a good
A) overall satisfaction obtained from consuming a good
B) additional satisfaction obtained from consuming one more unit of a good
C) average satisfaction obtained from consuming a good
D) the change in satisfaction obtained from consuming 1 percent more of a good
E) additional cost of one more unit of a good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Marginal utility is a measure
A) of total utility derived from consuming a given amount of a good
B) of the total utility gained from consuming an extra unit of a good
C) computed by dividing total utility by the amount of a good consumed
D) determined by production conditions in a market
E) of the cost associated with consuming one more unit of a good
A) of total utility derived from consuming a given amount of a good
B) of the total utility gained from consuming an extra unit of a good
C) computed by dividing total utility by the amount of a good consumed
D) determined by production conditions in a market
E) of the cost associated with consuming one more unit of a good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Total utility can be calculated as the
A) sum of all marginal utilities
B) price paid for one unit of a good
C) product of all marginal utilities
D) total expenditure on all units of a good the consumer buys
E) difference between the marginal utilities of the first and last units of a good
A) sum of all marginal utilities
B) price paid for one unit of a good
C) product of all marginal utilities
D) total expenditure on all units of a good the consumer buys
E) difference between the marginal utilities of the first and last units of a good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Marginal utility can be objectively measured and compared from one individual to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Economists assume people's tastes are
A) determined solely by advertising
B) relatively stable over time
C) quite variable
D) irrelevant to utility analysis
E) identical
A) determined solely by advertising
B) relatively stable over time
C) quite variable
D) irrelevant to utility analysis
E) identical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Utility is determined by an individual's
A) income
B) price
C) relative price
D) profit
E) tastes and preferences
A) income
B) price
C) relative price
D) profit
E) tastes and preferences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Positive marginal utility implies increasing total utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Marginal utility is negative only when quantity demanded is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is true of units of utility?
A) Each unit is worth $1.
B) They cannot be compared across consumers.
C) They apply to goods but not to services.
D) They do not exist for very wealthy individuals.
E) They are negative for inferior goods.
A) Each unit is worth $1.
B) They cannot be compared across consumers.
C) They apply to goods but not to services.
D) They do not exist for very wealthy individuals.
E) They are negative for inferior goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Demand curves usually slope downward because of the income and substitution effects, and because of the law of diminishing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Negative marginal utility means that
A) total utility is also negative
B) marginal utility increases as additional units are consumed
C) the price of the product increases as additional units are consumed
D) the total revenue spent on the product decreases as more of the product is purchased
E) total utility decreases as additional units are consumed
A) total utility is also negative
B) marginal utility increases as additional units are consumed
C) the price of the product increases as additional units are consumed
D) the total revenue spent on the product decreases as more of the product is purchased
E) total utility decreases as additional units are consumed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following sayings describes the concept of diminishing marginal utility?
A) time is money
B) penny wise and pound foolish
C) absence makes the heart grow fonder
D) a penny saved is a penny earned
E) a fool and his money are soon parted
A) time is money
B) penny wise and pound foolish
C) absence makes the heart grow fonder
D) a penny saved is a penny earned
E) a fool and his money are soon parted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that
A) total utility falls as more of a good is consumed, other things constant
B) total utility falls as marginal utility falls, other things constant
C) marginal utility falls as total utility increases, other things constant
D) marginal utility falls as more of a good is consumed, other things constant
E) marginal utility falls as less of a good is consumed, other things constant
A) total utility falls as more of a good is consumed, other things constant
B) total utility falls as marginal utility falls, other things constant
C) marginal utility falls as total utility increases, other things constant
D) marginal utility falls as more of a good is consumed, other things constant
E) marginal utility falls as less of a good is consumed, other things constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
"The marginal utility received from each additional unit of a good consumed declines, other things constant." This is a statement of the law of
A) increasing marginal returns
B) marginal rate of substitution
C) supply
D) diminishing marginal utility
E) demand
A) increasing marginal returns
B) marginal rate of substitution
C) supply
D) diminishing marginal utility
E) demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Carvel advertises a football-shaped ice cream cake for $7; you can buy a second one for only $4. What do they know about consumer preferences?
A) Consumers would never buy a second ice cream cake.
B) Two cakes are worth less to the consumer than one.
C) Marginal utility of ice cream cakes diminishes.
D) Consumers only value the first cake at $4.
E) Consumers value all cakes they eat at $4.
A) Consumers would never buy a second ice cream cake.
B) Two cakes are worth less to the consumer than one.
C) Marginal utility of ice cream cakes diminishes.
D) Consumers only value the first cake at $4.
E) Consumers value all cakes they eat at $4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Newspaper vending machines illustrate that publishers believe
A) the average utility of two identical papers is zero or less
B) the total utility from two identical newspapers is zero or less
C) the marginal utility of a second identical newspaper is zero or less
D) the marginal utility of a second identical newspaper is greater than the marginal utility of the first newspaper
E) the total utility from two identical newspapers is less than the total utility from the first newspaper
A) the average utility of two identical papers is zero or less
B) the total utility from two identical newspapers is zero or less
C) the marginal utility of a second identical newspaper is zero or less
D) the marginal utility of a second identical newspaper is greater than the marginal utility of the first newspaper
E) the total utility from two identical newspapers is less than the total utility from the first newspaper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-1
Exhibit 6-1

In Exhibit 6-1, what is the total utility of three pretzels?
A) 5
B) 15
C) 40
D) 55
E) 70
Exhibit 6-1

In Exhibit 6-1, what is the total utility of three pretzels?
A) 5
B) 15
C) 40
D) 55
E) 70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The reason that you don't drink five cups of coffee at breakfast is that
A) the marginal utility of extra cups of coffee eventually diminishes
B) most people cannot afford five cups
C) the total utility of coffee rises as you consume more cups
D) the price of coffee rises as you buy more cups
E) the marginal satisfaction derived from cups of coffee remains constant
A) the marginal utility of extra cups of coffee eventually diminishes
B) most people cannot afford five cups
C) the total utility of coffee rises as you consume more cups
D) the price of coffee rises as you buy more cups
E) the marginal satisfaction derived from cups of coffee remains constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The law of diminishing marginal utility implies that the marginal utility of my fifth waffle is less than the marginal utility of my friend's second waffle, other things constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If other things constant, as more bananas are consumed, marginal utility eventually
A) decreases at the same rate for all people
B) decreases at the same rate for all goods for a given person
C) increases at the same rate for all people
D) decreases at different rates for different people and for other goods
E) decreases at different rates for different people but at the same rate as other goods for an individual
A) decreases at the same rate for all people
B) decreases at the same rate for all goods for a given person
C) increases at the same rate for all people
D) decreases at different rates for different people and for other goods
E) decreases at different rates for different people but at the same rate as other goods for an individual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Diminishing marginal utility means that
A) as you consume more of a good, other things constant, the total satisfaction you obtain from consuming this good tends to fall
B) as you hire more labor, other things constant, the total amount produced begins to fall
C) as you hire more labor, other things constant, the marginal product begins to fall
D) as you consume more of a good, other things constant, the additional satisfaction you obtain from each additional unit of the good tends to fall
E) as you consume more of a good, other things constant, the extra satisfaction you obtain from each extra good becomes negative
A) as you consume more of a good, other things constant, the total satisfaction you obtain from consuming this good tends to fall
B) as you hire more labor, other things constant, the total amount produced begins to fall
C) as you hire more labor, other things constant, the marginal product begins to fall
D) as you consume more of a good, other things constant, the additional satisfaction you obtain from each additional unit of the good tends to fall
E) as you consume more of a good, other things constant, the extra satisfaction you obtain from each extra good becomes negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-1
Exhibit 6-1

In Exhibit 6-1, what is the marginal utility of the third pretzel?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 15
D) -0.15
E) 55
Exhibit 6-1

In Exhibit 6-1, what is the marginal utility of the third pretzel?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 15
D) -0.15
E) 55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
"I don't feel so good. I shouldn't have had that last doughnut." Which statement best describes this situation?
A) The marginal utility of the last doughnut was positive.
B) The marginal utility of doughnuts is still increasing.
C) The total utility from eating doughnuts is negative.
D) The marginal utility of the last doughnut was negative.
E) The marginal utility of the next doughnut will be positive.
A) The marginal utility of the last doughnut was positive.
B) The marginal utility of doughnuts is still increasing.
C) The total utility from eating doughnuts is negative.
D) The marginal utility of the last doughnut was negative.
E) The marginal utility of the next doughnut will be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following illustrates the law of diminishing marginal utility?
A) The marginal utility of Diane's second Coke is greater than the marginal utility of her third pretzel, other things constant.
B) The marginal utility of Diane's second Coke is greater than the marginal utility of Ken's third pretzel, other things constant.
C) The marginal utility of Diane's second Coke is greater than the marginal utility of her third Coke, other things constant.
D) The total utility of one Coke is greater than the total utility of two Cokes, other things constant.
E) The marginal utility of Diane's second Coke is greater than the marginal utility of Ken's third Coke, other things constant.
A) The marginal utility of Diane's second Coke is greater than the marginal utility of her third pretzel, other things constant.
B) The marginal utility of Diane's second Coke is greater than the marginal utility of Ken's third pretzel, other things constant.
C) The marginal utility of Diane's second Coke is greater than the marginal utility of her third Coke, other things constant.
D) The total utility of one Coke is greater than the total utility of two Cokes, other things constant.
E) The marginal utility of Diane's second Coke is greater than the marginal utility of Ken's third Coke, other things constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
"The second glass of Evian water was very good. May I have another?" Which of the following is necessarily true regarding this statement?
A) The marginal utility of the second glass is negative.
B) The marginal utility of the second glass is less than the marginal utility of the first glass.
C) The marginal utility of the second glass is positive.
D) The water is free.
E) The marginal utility of the third glass is negative.
A) The marginal utility of the second glass is negative.
B) The marginal utility of the second glass is less than the marginal utility of the first glass.
C) The marginal utility of the second glass is positive.
D) The water is free.
E) The marginal utility of the third glass is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Joe the Economist tells his wife, Jane, that he wants to spend a weekend fishing with his friends. She replies, "You don't love me anymore." Just before she hits Joe with a croquet mallet, Joe explains to her that she has confused the concepts of
A) marginal utility and price
B) income and price
C) marginal utility and total utility
D) love and death
E) consumer surplus and utility
A) marginal utility and price
B) income and price
C) marginal utility and total utility
D) love and death
E) consumer surplus and utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The marginal utility of a second copy of today's New York Times is
A) infinite
B) practically zero
C) positive and greater than the marginal utility of the first copy
D) equal to the marginal utility of the first copy
E) 50 cents
A) infinite
B) practically zero
C) positive and greater than the marginal utility of the first copy
D) equal to the marginal utility of the first copy
E) 50 cents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When total utility is falling, marginal utility is
A) increasing
B) decreasing
C) positive
D) negative
E) 0
A) increasing
B) decreasing
C) positive
D) negative
E) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Marginal utility is defined as the
A) average amount of satisfaction gained from consuming a product
B) total amount of satisfaction gained from consuming a product
C) additional satisfaction gained from consuming one more unit of a product
D) total amount of satisfaction gained from consuming a product divided by the number of units consumed
E) total amount of satisfaction gained from consuming a product times the number of units consumed
A) average amount of satisfaction gained from consuming a product
B) total amount of satisfaction gained from consuming a product
C) additional satisfaction gained from consuming one more unit of a product
D) total amount of satisfaction gained from consuming a product divided by the number of units consumed
E) total amount of satisfaction gained from consuming a product times the number of units consumed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as you consume more and more of a good, other things constant,
A) total utility eventually rises
B) marginal utility can become positive
C) marginal utility approaches, but never becomes, zero
D) total utility can never become negative
E) marginal utility eventually declines
A) total utility eventually rises
B) marginal utility can become positive
C) marginal utility approaches, but never becomes, zero
D) total utility can never become negative
E) marginal utility eventually declines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-3
Exhibit 6-3
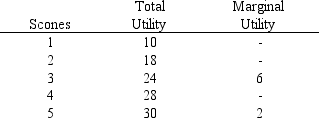
In Exhibit 6-3, the marginal utility of consuming the fourth scone is
A) 4
B) 7
C) 6
D) 24
E) 2
Exhibit 6-3

In Exhibit 6-3, the marginal utility of consuming the fourth scone is
A) 4
B) 7
C) 6
D) 24
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose you go to a wedding reception that has free drinks. What is likely to be the marginal utility of the last drink you had?
A) infinite
B) 0
C) 1
D) less than 0
E) greater than 1
A) infinite
B) 0
C) 1
D) less than 0
E) greater than 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A consumer maximizes utility when the marginal utilities of all goods
A) having positive money prices that are equal to zero
B) are equal
C) are maximized
D) are equal to the opportunity costs for all goods that are considered necessities
E) are exactly proportional to their market prices
A) having positive money prices that are equal to zero
B) are equal
C) are maximized
D) are equal to the opportunity costs for all goods that are considered necessities
E) are exactly proportional to their market prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-3
Exhibit 6-3

In Exhibit 6-3, the total utility of consuming three scones is
A) 34
B) 6
C) 22
D) 12
E) 24
Exhibit 6-3

In Exhibit 6-3, the total utility of consuming three scones is
A) 34
B) 6
C) 22
D) 12
E) 24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose Enid could increase her total utility by purchasing one more book and one less video rental. Which of the following is true?
A) The marginal utility of video rentals exceeds the marginal utility of books.
B) The marginal utility of books exceeds the marginal utility of video rentals.
C) The marginal utility of video rentals is negative.
D) The marginal utility per dollar spent on books exceeds that of video rentals.
E) Total utility is at a maximum.
A) The marginal utility of video rentals exceeds the marginal utility of books.
B) The marginal utility of books exceeds the marginal utility of video rentals.
C) The marginal utility of video rentals is negative.
D) The marginal utility per dollar spent on books exceeds that of video rentals.
E) Total utility is at a maximum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-6
Exhibit 6-6
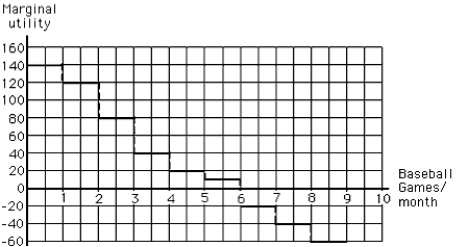
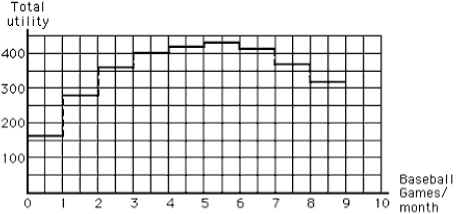
Consider Exhibit 6-6. Which of the following best describes what it reveals about total and marginal utility for baseball game tickets?
A) Marginal utility is constantly pulling total utility down, until eventually it becomes negative.
B) Marginal utility is constantly pulling total utility up and will continue to increase total utility as long as the person consumes more goods.
C) Marginal utility is constantly pulling total utility up, but by less each time.
D) At first marginal utility is positive and pulls total utility up but at a decreasing rate; then marginal utility becomes negative and pulls total utility down.
E) At first marginal utility is positive and pulls total utility up, but then it becomes negative and makes total utility become negative as well.
Exhibit 6-6


Consider Exhibit 6-6. Which of the following best describes what it reveals about total and marginal utility for baseball game tickets?
A) Marginal utility is constantly pulling total utility down, until eventually it becomes negative.
B) Marginal utility is constantly pulling total utility up and will continue to increase total utility as long as the person consumes more goods.
C) Marginal utility is constantly pulling total utility up, but by less each time.
D) At first marginal utility is positive and pulls total utility up but at a decreasing rate; then marginal utility becomes negative and pulls total utility down.
E) At first marginal utility is positive and pulls total utility up, but then it becomes negative and makes total utility become negative as well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the marginal utility of each good a consumer buys does not diminish but remains constant, we should see consumers
A) buying no goods at all
B) spending all of their income on the good with the highest marginal utility
C) buying one unit of each good
D) buying only the least expensive good
E) leaving the store in total confusion
A) buying no goods at all
B) spending all of their income on the good with the highest marginal utility
C) buying one unit of each good
D) buying only the least expensive good
E) leaving the store in total confusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-3
Exhibit 6-3

In Exhibit 6-3, the total utility of consuming five scones is
A) 82
B) 30
C) 34
D) 27
E) 2
Exhibit 6-3

In Exhibit 6-3, the total utility of consuming five scones is
A) 82
B) 30
C) 34
D) 27
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-2
Exhibit 6-2
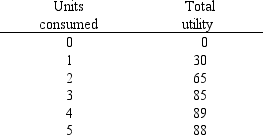
In Exhibit 6-2, where does marginal utility first begin to diminish?
A) sometime after the first unit consumed
B) sometime after the second unit consumed
C) sometime after the third unit consumed
D) sometime after the fourth unit consumed
E) sometime after the fifth unit consumed
Exhibit 6-2

In Exhibit 6-2, where does marginal utility first begin to diminish?
A) sometime after the first unit consumed
B) sometime after the second unit consumed
C) sometime after the third unit consumed
D) sometime after the fourth unit consumed
E) sometime after the fifth unit consumed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-5
Exhibit 6-5
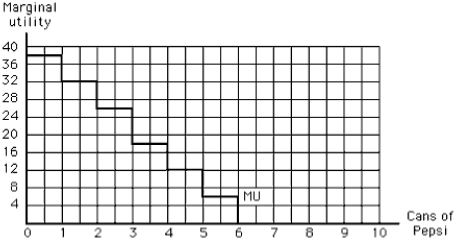
Consider Exhibit 6-5. Which of the following is true?
A) A fourth can of Pepsi increases total utility by 12, to 126.
B) A fourth can of Pepsi increases total utility by 18, to 114.
C) A fourth can of Pepsi increases total utility by 114.
D) All four cans of Pepsi together yield a total utility of 18.
E) All four cans of Pepsi together yield a total utility of 322.
Exhibit 6-5

Consider Exhibit 6-5. Which of the following is true?
A) A fourth can of Pepsi increases total utility by 12, to 126.
B) A fourth can of Pepsi increases total utility by 18, to 114.
C) A fourth can of Pepsi increases total utility by 114.
D) All four cans of Pepsi together yield a total utility of 18.
E) All four cans of Pepsi together yield a total utility of 322.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If marginal utility is positive, then total utility is
A) constant
B) negative
C) increasing
D) decreasing
E) 0
A) constant
B) negative
C) increasing
D) decreasing
E) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If Dalene's marginal benefit from consuming another cookie is greater than the price of the cookie, then
A) Dalene will not purchase any more cookies
B) the opportunity cost of the cookie is lower than the price
C) Dalene's utility will decrease if she purchases the cookie
D) Dalene will increase her total satisfaction by purchasing the additional cookie
E) she has purchased too many cookies
A) Dalene will not purchase any more cookies
B) the opportunity cost of the cookie is lower than the price
C) Dalene's utility will decrease if she purchases the cookie
D) Dalene will increase her total satisfaction by purchasing the additional cookie
E) she has purchased too many cookies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
As long as scarcity exists,
A) product prices play no role in utility maximization
B) income plays no role in utility maximization
C) income and product prices must both be considered in utility maximization
D) consumers maximize utility by consuming all products until their marginal utility is zero
E) product prices will be zero
A) product prices play no role in utility maximization
B) income plays no role in utility maximization
C) income and product prices must both be considered in utility maximization
D) consumers maximize utility by consuming all products until their marginal utility is zero
E) product prices will be zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-3
Exhibit 6-3

In Exhibit 6-3, the marginal utility of consuming the first scone is
A) 0
B) 2
C) 8
D) 9
E) 10
Exhibit 6-3

In Exhibit 6-3, the marginal utility of consuming the first scone is
A) 0
B) 2
C) 8
D) 9
E) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a good is offered to you free of charge, then you
A) never stop consuming it
B) stop consuming it when its marginal utility begins to fall
C) stop consuming it when its marginal utility begins to increase
D) stop consuming it when its marginal utility equals 0
E) stop consuming it when its total utility equals 0
A) never stop consuming it
B) stop consuming it when its marginal utility begins to fall
C) stop consuming it when its marginal utility begins to increase
D) stop consuming it when its marginal utility equals 0
E) stop consuming it when its total utility equals 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-4
Exhibit 6-4
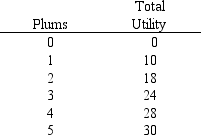
Using Exhibit 6-4, calculate the marginal utility of the third plum consumed.
A) 4
B) 6
C) 24/3
D) 9
E) 24
Exhibit 6-4

Using Exhibit 6-4, calculate the marginal utility of the third plum consumed.
A) 4
B) 6
C) 24/3
D) 9
E) 24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-3
Exhibit 6-3

In Exhibit 6-3, the marginal utility of consuming the second scone is
A) 12
B) 9
C) 8
D) 19
E) 6
Exhibit 6-3

In Exhibit 6-3, the marginal utility of consuming the second scone is
A) 12
B) 9
C) 8
D) 19
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A free good (price = $0) will be consumed up to the point at which its marginal utility is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The fact that the washroom usually has paper towels left (free to the consumer) suggests that the marginal utility of paper towels quickly diminishes to 0 for each consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the price of a good is 0, a consumer will
A) consume all units that have positive total utility
B) consume an infinite quantity
C) consume all units with positive marginal utility
D) consume the entire amount supplied
E) consume until total utility becomes 0
A) consume all units that have positive total utility
B) consume an infinite quantity
C) consume all units with positive marginal utility
D) consume the entire amount supplied
E) consume until total utility becomes 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If by purchasing a little more milk and a little less ice cream you could increase your total utility,
A) the MU of milk must be greater than that of ice cream
B) the MU of ice cream must be greater than that of milk
C) the MU/P of milk must be greater than that of ice cream
D) milk must be cheaper than ice cream
E) the MU of milk will increase
A) the MU of milk must be greater than that of ice cream
B) the MU of ice cream must be greater than that of milk
C) the MU/P of milk must be greater than that of ice cream
D) milk must be cheaper than ice cream
E) the MU of milk will increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Assume that you allocate your income to calzones and juice and that you have not yet spent your entire budget. If the marginal utility of a fourth calzone is 100 and the marginal utility of a third glass of juice is 50, you would
A) eat a fourth calzone because it has a higher marginal utility
B) drink a third glass of juice because you've had less juice
C) consider the total utility received so far from calzones and juice before deciding what to consume next
D) consider the relative prices of calzones and juice before deciding what to consume next
E) consider whether or not marginal utility is diminishing before deciding what to consume next
A) eat a fourth calzone because it has a higher marginal utility
B) drink a third glass of juice because you've had less juice
C) consider the total utility received so far from calzones and juice before deciding what to consume next
D) consider the relative prices of calzones and juice before deciding what to consume next
E) consider whether or not marginal utility is diminishing before deciding what to consume next

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A utility-maximizing consumer equalizes marginal utilities across all goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consumers must understand the law of diminishing marginal utility in order to maximize their satisfaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Sally is allocating her budget between two goods, A and B. If Sally has used up the budget on a combination of A and B for which MUA/PA exceeds MUB/PB, she can increase total utility by buying
A) more A and less B
B) more B and less A
C) more A without changing her consumption of B
D) less B without changing her consumption of A
E) more B and more A
A) more A and less B
B) more B and less A
C) more A without changing her consumption of B
D) less B without changing her consumption of A
E) more B and more A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Your marginal utility of a third waffle is 10 and your marginal utility of a second piece of ham is 30. If you eat the third waffle, which of the following must be true?
A) You are irrational.
B) You prefer waffles.
C) The price of a waffle is less than one third the price of a piece of ham.
D) The price of a waffle is more than the price of a piece of ham.
E) The price of a waffle is three times the price of a piece of ham.
A) You are irrational.
B) You prefer waffles.
C) The price of a waffle is less than one third the price of a piece of ham.
D) The price of a waffle is more than the price of a piece of ham.
E) The price of a waffle is three times the price of a piece of ham.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose you have spent your entire budget and, for all the goods you purchase, the marginal utilities per dollar spent are identical. Which of the following is true?
A) You are being irrational.
B) You can increase your utility by reallocating your income.
C) You will reduce your utility if you allocate income in any other way.
D) You are minimizing your marginal utility.
E) You can avoid diminishing marginal utility.
A) You are being irrational.
B) You can increase your utility by reallocating your income.
C) You will reduce your utility if you allocate income in any other way.
D) You are minimizing your marginal utility.
E) You can avoid diminishing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Assume that you allocate your income to calzones and juice and that you have not yet spent your entire budget. If the marginal utility of a fourth calzone is 100 and the marginal utility of a third glass of juice is 50, you would
A) eat a fourth calzone because it has higher marginal utility
B) drink a third glass of juice
C) drink a third glass of juice if its price is lower than the price of calzones
D) drink a third glass of juice if its price is less than half the price of the calzone
E) drink a third glass of juice because it has lower marginal utility
A) eat a fourth calzone because it has higher marginal utility
B) drink a third glass of juice
C) drink a third glass of juice if its price is lower than the price of calzones
D) drink a third glass of juice if its price is less than half the price of the calzone
E) drink a third glass of juice because it has lower marginal utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In terms of utility theory, "equilibrium" in the real world means that
A) households are consuming as much of every commodity as they would like
B) households have spent their incomes in such a way that their overall satisfaction is maximized
C) households have spent their incomes in such a way that their marginal utility is maximized
D) households have spent their incomes in such a way that their marginal utility is zero for every product consumed
E) households have spent their incomes in such a way that their total utility is zero
A) households are consuming as much of every commodity as they would like
B) households have spent their incomes in such a way that their overall satisfaction is maximized
C) households have spent their incomes in such a way that their marginal utility is maximized
D) households have spent their incomes in such a way that their marginal utility is zero for every product consumed
E) households have spent their incomes in such a way that their total utility is zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A utility-maximizing consumer who is considering two goods, x and y, would allocate her budget in such a way that
A) MUx = MUy
B) MUx > MUy
C) MUx/Px > MUy/Py
D) MUx/Px = MUy/Py
E) MUx/Px < MUy/Py
A) MUx = MUy
B) MUx > MUy
C) MUx/Px > MUy/Py
D) MUx/Px = MUy/Py
E) MUx/Px < MUy/Py

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose you eat at a restaurant that serves clams at a fixed price and crab legs at a price that varies based on market conditions. Each week, the marginal utility you attach to an order of crab legs is 100, and the marginal utility of an order of clams is 50. One week you have crab legs, but the next week you have clams. This means that
A) you are irrational
B) your tastes must have changed
C) the price of clams dropped below the price of crab legs
D) the price of crab legs increased
E) the price of crab legs must have increased to more than twice that of clams
A) you are irrational
B) your tastes must have changed
C) the price of clams dropped below the price of crab legs
D) the price of crab legs increased
E) the price of crab legs must have increased to more than twice that of clams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The law of diminishing marginal utility may be illustrated by a person
A) buying additional goods after getting a pay raise
B) eating more twinkies but enjoying them less
C) giving some of income to a needy person
D) who spends more hours studying than do his fellow students
E) buying goods so long as their marginal utility is greater than zero
A) buying additional goods after getting a pay raise
B) eating more twinkies but enjoying them less
C) giving some of income to a needy person
D) who spends more hours studying than do his fellow students
E) buying goods so long as their marginal utility is greater than zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When a consumer spends income so that the ratio of marginal utilities (MUs) of all goods purchased equals the ratio of their prices, the consumer is
A) maximizing marginal utility
B) spending too much on all goods
C) maximizing total utility
D) beyond the point of diminishing marginal utility
E) behaving in opposition to the principal of rational behavior
A) maximizing marginal utility
B) spending too much on all goods
C) maximizing total utility
D) beyond the point of diminishing marginal utility
E) behaving in opposition to the principal of rational behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-7
Exhibit 6-7
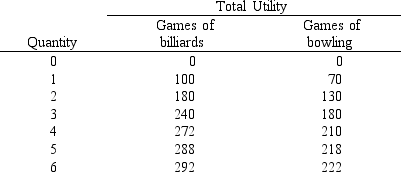
Suppose you have $30 to spend on either bowling or billiards. A game of billiards costs you $4, and bowling costs $2 per game. Using the information in Exhibit 6-7, determine the utility-maximizing combination of bowling and billiards.
A) four billiards games, four games of bowling
B) five billiards games, two games of bowling
C) three billiards games, eight games of bowling
D) five billiards games, five games of bowling
E) twelve games of bowling
Exhibit 6-7

Suppose you have $30 to spend on either bowling or billiards. A game of billiards costs you $4, and bowling costs $2 per game. Using the information in Exhibit 6-7, determine the utility-maximizing combination of bowling and billiards.
A) four billiards games, four games of bowling
B) five billiards games, two games of bowling
C) three billiards games, eight games of bowling
D) five billiards games, five games of bowling
E) twelve games of bowling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If Ellie Mae spends her income on possum and biscuits and the price of possum is three times the price of biscuits, then when Ellie Mae maximizes total utility, she will buy
A) equal quantities of possum and biscuits
B) three times as much possum as biscuits
C) three times as many biscuits as portions of possum
D) biscuits and possum until the marginal utility of possum is three times the marginal utility of biscuits
E) biscuits and possum until the marginal utility of biscuits is three times the marginal utility of possum
A) equal quantities of possum and biscuits
B) three times as much possum as biscuits
C) three times as many biscuits as portions of possum
D) biscuits and possum until the marginal utility of possum is three times the marginal utility of biscuits
E) biscuits and possum until the marginal utility of biscuits is three times the marginal utility of possum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Fernando allocates his lunch money between pizza and Coke. A Coke has a price of $1 and a slice of pizza has a price of $1.50. The marginal utility of the last slice of pizza Fernando ate today was 30, and the marginal utility of his last Coke was 25. Fernando spent all of his lunch money. From this information we can conclude that
A) Fernando allocated his money in a way that maximized his total utility
B) Fernando's total utility would have been greater if he had purchased more Coke and less pizza
C) Fernando's total utility would have been greater if he had purchased more pizza and less Coke
D) Fernando could have increased his total utility by purchasing more Coke but the same quantity of pizza
E) Fernando could have increased his total utility by purchasing more pizza but the same quantity of Coke
A) Fernando allocated his money in a way that maximized his total utility
B) Fernando's total utility would have been greater if he had purchased more Coke and less pizza
C) Fernando's total utility would have been greater if he had purchased more pizza and less Coke
D) Fernando could have increased his total utility by purchasing more Coke but the same quantity of pizza
E) Fernando could have increased his total utility by purchasing more pizza but the same quantity of Coke

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 6-8
Exhibit 6-8
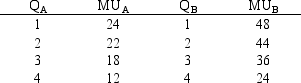
Exhibit 6-8 indicates the marginal utilities that Sharrona receives from consuming different amounts of goods A and B. If the price of A is $2 per unit and the price of B is $4 per unit, what combination of A and B would maximize Sharrona's total utility if her budget is $12?
A) 0 units of A; 3 units of B
B) 4 units of A; 1 unit of B
C) 4 units of each
D) 1 unit of A; 4 units of B
E) 2 units of each
Exhibit 6-8

Exhibit 6-8 indicates the marginal utilities that Sharrona receives from consuming different amounts of goods A and B. If the price of A is $2 per unit and the price of B is $4 per unit, what combination of A and B would maximize Sharrona's total utility if her budget is $12?
A) 0 units of A; 3 units of B
B) 4 units of A; 1 unit of B
C) 4 units of each
D) 1 unit of A; 4 units of B
E) 2 units of each

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
When income is allocated to two goods, x and y, consumer equilibrium occurs when
A) MUx = MUy
B) MUx = MUy, and the budget is exhausted
C) MUx/Py = PUx/Py
D) MUx/Py = PUx/Py, and some money is not spent
E) MUx/Py = PUx/Py, and the budget is exhausted
A) MUx = MUy
B) MUx = MUy, and the budget is exhausted
C) MUx/Py = PUx/Py
D) MUx/Py = PUx/Py, and some money is not spent
E) MUx/Py = PUx/Py, and the budget is exhausted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose that for Jason the marginal utility of $50-per-serving caviar is 100 and the marginal utility of $1-per-serving popcorn is 10. For his snack, Jason should buy
A) the caviar if he has the $50; otherwise the popcorn
B) the caviar if he has the $50; otherwise nothing
C) the popcorn, whether he has the $50 or not
D) one serving each of the caviar and popcorn, if he has $51
E) five servings of popcorn for each serving of caviar
A) the caviar if he has the $50; otherwise the popcorn
B) the caviar if he has the $50; otherwise nothing
C) the popcorn, whether he has the $50 or not
D) one serving each of the caviar and popcorn, if he has $51
E) five servings of popcorn for each serving of caviar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
As a consumer allocates income between good A and good B, total utility is maximized when
A) the marginal utility of A = the marginal utility of B
B) the marginal utility of A = the marginal utility of B = 0
C) the price of A = price of B
D) marginal utility of A/price of A = marginal utility of B/price of B = 0
E) marginal utility of A/price of A = marginal utility of B/price of B
A) the marginal utility of A = the marginal utility of B
B) the marginal utility of A = the marginal utility of B = 0
C) the price of A = price of B
D) marginal utility of A/price of A = marginal utility of B/price of B = 0
E) marginal utility of A/price of A = marginal utility of B/price of B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 170 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



