Deck 9: A: Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/249
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: A: Monopoly
1
Anything that prevents new firms from competing on an equal basis with existing firms in an industry is called a barrier to entry.
True
2
Patent laws
A) reduce incentive to innovate by restricting market entry
B) reduce incentive to innovate by making it difficult to use the patented innovation
C) increase incentive to innovate by restricting entry into a market
D) increase incentive to innovate by giving a firm permanent and exclusive production rights
E) give a firm the right to provide a wide variety of goods or services
A) reduce incentive to innovate by restricting market entry
B) reduce incentive to innovate by making it difficult to use the patented innovation
C) increase incentive to innovate by restricting entry into a market
D) increase incentive to innovate by giving a firm permanent and exclusive production rights
E) give a firm the right to provide a wide variety of goods or services
C
3
Which of the following would probably not be considered a natural monopoly?
A) a municipal water company
B) the local telephone industry
C) the cable television industry
D) natural gas and electric companies
E) the automobile industry
A) a municipal water company
B) the local telephone industry
C) the cable television industry
D) natural gas and electric companies
E) the automobile industry
E
4
U.S. patent laws establish property rights for inventors of new products
A) forever
B) until a superior invention comes along
C) for 3 years
D) for 10 years
E) for 20 years
A) forever
B) until a superior invention comes along
C) for 3 years
D) for 10 years
E) for 20 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the monopoly market structure, new firms
A) cannot profitably enter the industry, even in the long run
B) may freely enter and leave the industry in both the short run and the long run
C) may freely enter and leave the industry in the long run only
D) may freely enter and leave the industry in the short run only
E) have no incentive to enter the industry, even if economic profits are present
A) cannot profitably enter the industry, even in the long run
B) may freely enter and leave the industry in both the short run and the long run
C) may freely enter and leave the industry in the long run only
D) may freely enter and leave the industry in the short run only
E) have no incentive to enter the industry, even if economic profits are present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not considered a barrier to entry?
A) patents
B) government licenses
C) economies of scale
D) diseconomies of scale
E) control over essential resources
A) patents
B) government licenses
C) economies of scale
D) diseconomies of scale
E) control over essential resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Patent laws promote technical progress in all of the following ways except one. Which is the exception?
A) They allow other firms to copy successful products as soon as they are marketed.
B) They prevent duplication of inventions.
C) They provide a stimulus to innovation.
D) They provide the inventor with a temporary monopoly.
E) They increase a firm's incentive to incur the up-front costs of developing new products.
A) They allow other firms to copy successful products as soon as they are marketed.
B) They prevent duplication of inventions.
C) They provide a stimulus to innovation.
D) They provide the inventor with a temporary monopoly.
E) They increase a firm's incentive to incur the up-front costs of developing new products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following could not bar entry into an industry?
A) economies of scale
B) diseconomies of scale
C) patents
D) licenses
E) one firm's control of essential resources
A) economies of scale
B) diseconomies of scale
C) patents
D) licenses
E) one firm's control of essential resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is true of monopoly?
A) There are no barriers to entry.
B) The firm is a price taker.
C) There are no close substitutes for the product being produced.
D) There are many firms in the industry.
E) The firm faces a horizontal demand curve.
A) There are no barriers to entry.
B) The firm is a price taker.
C) There are no close substitutes for the product being produced.
D) There are many firms in the industry.
E) The firm faces a horizontal demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is true?
A) Patents reduce a firm's incentive to develop new products.
B) Patents are given for new works of art or literature.
C) Patents give a permanent exclusive right to produce a new good.
D) Patents give a temporary exclusive right to produce a new good.
E) Patents guarantee economic profits.
A) Patents reduce a firm's incentive to develop new products.
B) Patents are given for new works of art or literature.
C) Patents give a permanent exclusive right to produce a new good.
D) Patents give a temporary exclusive right to produce a new good.
E) Patents guarantee economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Willie Stand obtains a patent on his new invention, the bipod. After twenty years,
A) he can renew his patent
B) new entrants will begin bipod production if price exceeds average variable cost
C) new entrants will drive up the price of the bipod
D) Willie will eventually earn no more than a normal profit
E) Willie will continue to earn a positive economic profit, because entry will not affect the price of bipods
A) he can renew his patent
B) new entrants will begin bipod production if price exceeds average variable cost
C) new entrants will drive up the price of the bipod
D) Willie will eventually earn no more than a normal profit
E) Willie will continue to earn a positive economic profit, because entry will not affect the price of bipods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A natural monopoly is based on economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following could be true of perfect competition but not of monopoly?
A) The government licenses production of the good to a few firms.
B) The government grants a patent for the good.
C) A firm can earn economic profit in the long run.
D) If price falls below average variable cost, it pays to shut down.
E) There are no barriers to entry.
A) The government licenses production of the good to a few firms.
B) The government grants a patent for the good.
C) A firm can earn economic profit in the long run.
D) If price falls below average variable cost, it pays to shut down.
E) There are no barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A monopolist is
A) one of a large number of small firms that produce a homogeneous good
B) one of a small number of large firms that produce a differentiated good
C) a single seller of a product with many close substitutes
D) one of a small number of large firms that produce a homogeneous good
E) a single seller of a product with no close substitutes
A) one of a large number of small firms that produce a homogeneous good
B) one of a small number of large firms that produce a differentiated good
C) a single seller of a product with many close substitutes
D) one of a small number of large firms that produce a homogeneous good
E) a single seller of a product with no close substitutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following describes the market structure of monopoly?
A) many firms with some control over price, and considerable product differentiation
B) many firms with no control over price, producing identical products with no differentiation
C) a few firms with some control over price, producing similar products which are close substitutes
D) a few firms with no control over price, producing highly differentiated products
E) a single firm producing all of the output for the industry
A) many firms with some control over price, and considerable product differentiation
B) many firms with no control over price, producing identical products with no differentiation
C) a few firms with some control over price, producing similar products which are close substitutes
D) a few firms with no control over price, producing highly differentiated products
E) a single firm producing all of the output for the industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following prevents potential competitors from entering a monopolist's market?
A) legal restrictions
B) diseconomies of scale
C) product differentiation
D) stable market demand
E) rising marginal cost
A) legal restrictions
B) diseconomies of scale
C) product differentiation
D) stable market demand
E) rising marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Patents stimulate investment
A) by giving inventors an incentive to incur up-front costs of developing new products
B) by giving tax breaks to inventors
C) by guaranteeing a profit from new products
D) by lowering interest rates
E) through government payments that cover costs of research and development
A) by giving inventors an incentive to incur up-front costs of developing new products
B) by giving tax breaks to inventors
C) by guaranteeing a profit from new products
D) by lowering interest rates
E) through government payments that cover costs of research and development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A natural monopoly results when a firm has
A) a license
B) a patent
C) official approval to produce a product
D) decreasing average costs over the range of market demand
E) exclusive use of a natural resource
A) a license
B) a patent
C) official approval to produce a product
D) decreasing average costs over the range of market demand
E) exclusive use of a natural resource

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Natural monopolies form when
A) small firms merge to form larger firms
B) one firm has control over the entire supply of a basic input required to produce the product
C) one firm's monopoly position is created and enforced by the government
D) one firm receives patent protection for certain basic production processes
E) long-run average cost declines as a firm expands output
A) small firms merge to form larger firms
B) one firm has control over the entire supply of a basic input required to produce the product
C) one firm's monopoly position is created and enforced by the government
D) one firm receives patent protection for certain basic production processes
E) long-run average cost declines as a firm expands output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Innovation is the process of turning an invention into a marketable product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Average revenue, demand, and price are all depicted by the same curve for a monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In order to sell an additional unit of its product, a monopolist must decrease price on all units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Average revenue equals the change in total revenue divided by the change in the quantity of output produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A monopolist has complete control over both price and quantity of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Jewelers are willing to hold large inventories of diamonds
A) because the demand for diamonds is large and growing
B) because that minimizes the fixed cost of producing diamond jewelry
C) because, given monopoly control of the market for diamonds, they are confident that the price of diamonds will not plummet rapidly
D) because, given monopoly control of the market for diamonds, they are confident that the price of diamonds will rise rapidly
E) because that is what their customers expect them to do
A) because the demand for diamonds is large and growing
B) because that minimizes the fixed cost of producing diamond jewelry
C) because, given monopoly control of the market for diamonds, they are confident that the price of diamonds will not plummet rapidly
D) because, given monopoly control of the market for diamonds, they are confident that the price of diamonds will rise rapidly
E) because that is what their customers expect them to do

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For a monopolist, P < MR at all quantities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
DeBeers is a natural monopoly in the world's diamond trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The demand curve a monopolist uses in making an output decision is
A) the same as the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm
B) vertical because there are no close substitutes for its product
C) horizontal because there are no close substitutes for its product
D) the same as the market demand curve
E) perfectly inelastic
A) the same as the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm
B) vertical because there are no close substitutes for its product
C) horizontal because there are no close substitutes for its product
D) the same as the market demand curve
E) perfectly inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a firm is a natural monopoly, its
A) long-run average cost declines over the full range of market demand
B) long-run average cost increases over the full range of market demand
C) fixed cost declines over the full range of market demand
D) fixed cost increases over the full range of market demand
E) long-run average cost declines and marginal cost rises over the full range of market demand
A) long-run average cost declines over the full range of market demand
B) long-run average cost increases over the full range of market demand
C) fixed cost declines over the full range of market demand
D) fixed cost increases over the full range of market demand
E) long-run average cost declines and marginal cost rises over the full range of market demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The demand curve a monopolist faces
A) is more elastic than a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve
B) is the market demand curve
C) is as elastic as a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve
D) is not affected by the prices of complements
E) will not shift in response to a change in consumer tastes
A) is more elastic than a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve
B) is the market demand curve
C) is as elastic as a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve
D) is not affected by the prices of complements
E) will not shift in response to a change in consumer tastes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
De Beers has a monopoly in the market for diamonds because they own a significant portion of the known diamond mines. One important source of challenge to De Beers' control of the diamond market is
A) the additional market supply from Russia, Australia, and Canada
B) the emerging auction markets for diamonds in France and Spain
C) the growing demand for diamonds in industrial uses
D) that its South African mines are not producing as many diamonds as they did decades ago
E) antitrust legislation in the United States
A) the additional market supply from Russia, Australia, and Canada
B) the emerging auction markets for diamonds in France and Spain
C) the growing demand for diamonds in industrial uses
D) that its South African mines are not producing as many diamonds as they did decades ago
E) antitrust legislation in the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
For a monopolist, marginal revenue is
A) equal to price
B) greater than price
C) less than price
D) represented by a horizontal curve
E) equal to average revenue
A) equal to price
B) greater than price
C) less than price
D) represented by a horizontal curve
E) equal to average revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Maximizing total revenue is the same as maximizing profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A monopolist's demand curve is
A) its marginal cost curve
B) its marginal revenue curve
C) identical to the market demand curve
D) the same as the demand curve of a firm in perfect competition
E) nonexistent
A) its marginal cost curve
B) its marginal revenue curve
C) identical to the market demand curve
D) the same as the demand curve of a firm in perfect competition
E) nonexistent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is not a barrier to entry which leads to monopoly power.
A) economies of scale
B) control over key patents
C) control of an essential resource
D) government-imposed barriers to entry
E) homogeneous product
A) economies of scale
B) control over key patents
C) control of an essential resource
D) government-imposed barriers to entry
E) homogeneous product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is true of marginal revenue for a monopolist that charges a single price?
A) P = MR because there are no close substitutes for the monopolist's product.
B) P > MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units sold in order to sell an additional unit.
C) P < MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units sold in order to sell an additional unit.
D) AR = MR because there are no close substitutes for the monopolist's product.
E) P = MR only at the profit-maximizing quantity.
A) P = MR because there are no close substitutes for the monopolist's product.
B) P > MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units sold in order to sell an additional unit.
C) P < MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units sold in order to sell an additional unit.
D) AR = MR because there are no close substitutes for the monopolist's product.
E) P = MR only at the profit-maximizing quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A price searcher is any firm that has no control over price and must accept the market price as given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The demand curve faced by a firm with a patent on a marketable product
A) is horizontal
B) is vertical
C) slopes upward
D) slopes downward
E) is nonexistent
A) is horizontal
B) is vertical
C) slopes upward
D) slopes downward
E) is nonexistent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a monopolist must lower the price on all units in order to sell an additional unit,
A) it is impossible for the monopolist to maximize profit
B) the monopolist will always lose profit when it increases quantity
C) the monopolist will always lose revenue when it increases quantity
D) price will always be greater than marginal revenue
E) price will always be less than marginal revenue
A) it is impossible for the monopolist to maximize profit
B) the monopolist will always lose profit when it increases quantity
C) the monopolist will always lose revenue when it increases quantity
D) price will always be greater than marginal revenue
E) price will always be less than marginal revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A profit-maximizing monopolist will always operate where demand is unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-2
Exhibit 9-2
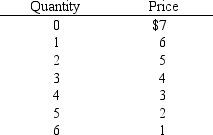
In Exhibit 9-2, the average revenue of the fourth unit is
A) $12
B) $3
C) $4
D) -$4
E) $0
Exhibit 9-2

In Exhibit 9-2, the average revenue of the fourth unit is
A) $12
B) $3
C) $4
D) -$4
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The demand curve facing a monopolist is perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
As a monopolist increases the quantity of output produced, what happens to price (P) and marginal revenue (MR)?
A) both P and MR remain constant
B) P is constant, but MR decreases
C) P decreases, but MR is constant
D) both P and MR decrease, but P falls faster than MR
E) both P and MR decrease, but MR falls faster than P
A) both P and MR remain constant
B) P is constant, but MR decreases
C) P decreases, but MR is constant
D) both P and MR decrease, but P falls faster than MR
E) both P and MR decrease, but MR falls faster than P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For a monopolist,
A) P = MR = AR
B) P = MR > AR
C) P > MR = AR
D) P = MR < AR
E) P = AR > MR
A) P = MR = AR
B) P = MR > AR
C) P > MR = AR
D) P = MR < AR
E) P = AR > MR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-1
Exhibit 9-1
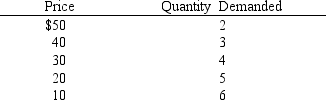
In Exhibit 9-1, total revenue from selling 5 units is
A) $20
B) $140
C) $100
D) $10
E) $5
Exhibit 9-1

In Exhibit 9-1, total revenue from selling 5 units is
A) $20
B) $140
C) $100
D) $10
E) $5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
On a graph, to determine the price a profit-maximizing monopolist would charge, find the quantity at which MC and MR intersect and read up to the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The demand curve facing a single-price monopolist
A) is the same as its average revenue curve
B) is the same as its marginal revenue curve
C) is the same as the perfect competitor's demand curve
D) lies above its average revenue curve
E) lies below its marginal revenue curve
A) is the same as its average revenue curve
B) is the same as its marginal revenue curve
C) is the same as the perfect competitor's demand curve
D) lies above its average revenue curve
E) lies below its marginal revenue curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-1
Exhibit 9-1

In Exhibit 9-1, the marginal revenue of the sixth unit is
A) $10
B) $60
C) $100
D) $40
E) -$40
Exhibit 9-1

In Exhibit 9-1, the marginal revenue of the sixth unit is
A) $10
B) $60
C) $100
D) $40
E) -$40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A monopolist maximizes total revenue at the quantity where marginal revenue equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For a monopolist,
A) marginal revenue and price are constant as quantity increases
B) marginal revenue falls but price is constant as quantity increases
C) marginal revenue is constant but price falls as quantity increases
D) both marginal revenue and price fall as quantity increases, but price falls faster
E) both marginal revenue and price fall as quantity increases, but marginal revenue falls faster
A) marginal revenue and price are constant as quantity increases
B) marginal revenue falls but price is constant as quantity increases
C) marginal revenue is constant but price falls as quantity increases
D) both marginal revenue and price fall as quantity increases, but price falls faster
E) both marginal revenue and price fall as quantity increases, but marginal revenue falls faster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The demand curve facing a monopolist
A) is kinked at the market price
B) is perfectly elastic
C) lies above its marginal revenue curve
D) lies below its marginal revenue curve
E) is the same as its marginal revenue curve
A) is kinked at the market price
B) is perfectly elastic
C) lies above its marginal revenue curve
D) lies below its marginal revenue curve
E) is the same as its marginal revenue curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-2
Exhibit 9-2

The price elasticity of demand between P = $3 and P = $2 in Exhibit 9-2 is
A) 9/5
B) $1.80
C) 5/9
D) $0.56
E) 1
Exhibit 9-2

The price elasticity of demand between P = $3 and P = $2 in Exhibit 9-2 is
A) 9/5
B) $1.80
C) 5/9
D) $0.56
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-2
Exhibit 9-2

Between which quantities in Exhibit 9-2 is demand unit elastic?
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 4 and 5
E) 5 and 6
Exhibit 9-2

Between which quantities in Exhibit 9-2 is demand unit elastic?
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 4 and 5
E) 5 and 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For a monopolist, as output expands, price and marginal revenue become more divergent (i.e., are farther apart).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose that a monopolist must choose between two points on its demand curve; it can sell 100 units for $3 each, or it can sell 160 units for $2 each. Which of the following is true?
A) The monopolist is facing an elastic demand.
B) The monopolist is facing unit elastic demand.
C) The monopolist is facing inelastic demand.
D) The monopolist is facing perfectly elastic demand.
E) The elasticity of demand cannot be determined with the information given.
A) The monopolist is facing an elastic demand.
B) The monopolist is facing unit elastic demand.
C) The monopolist is facing inelastic demand.
D) The monopolist is facing perfectly elastic demand.
E) The elasticity of demand cannot be determined with the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If all of a monopolist's costs are fixed costs, it will produce where demand is unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-2
Exhibit 9-2

In Exhibit 9-2, the marginal revenue of the fourth unit is
A) $12
B) $3
C) $4
D) -$4
E) $0
Exhibit 9-2

In Exhibit 9-2, the marginal revenue of the fourth unit is
A) $12
B) $3
C) $4
D) -$4
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-2
Exhibit 9-2

From the following demand schedule for a monopolist, what is the marginal revenue associated with the sale of the fourth unit?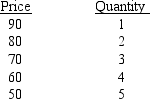
A) $10
B) $30
C) $60
D) $240
E) marginal revenue cannot be determined from the information given
Exhibit 9-2

From the following demand schedule for a monopolist, what is the marginal revenue associated with the sale of the fourth unit?
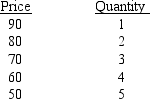
A) $10
B) $30
C) $60
D) $240
E) marginal revenue cannot be determined from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A monopolist's marginal revenue curve is flatter than its demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-1
Exhibit 9-1

In Exhibit 9-1, the marginal revenue of the third unit is
A) $20
B) $120
C) $100
D) $40
E) $0
Exhibit 9-1

In Exhibit 9-1, the marginal revenue of the third unit is
A) $20
B) $120
C) $100
D) $40
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A profit-maximizing monopolist never produces along the __________ portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is __________ there.
A) elastic; positive
B) elastic; negative
C) inelastic; negative
D) inelastic; positive
E) inelastic; zero
A) elastic; positive
B) elastic; negative
C) inelastic; negative
D) inelastic; positive
E) inelastic; zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-3-1
Exhibit 9-3
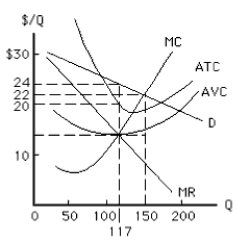
The firm in Exhibit 9-3, which charges the same price to all customers, will produce where
A) MR = 0
B) MR = MC
C) MC < MR
D) MC = ATC
E) P = MC
Exhibit 9-3

The firm in Exhibit 9-3, which charges the same price to all customers, will produce where
A) MR = 0
B) MR = MC
C) MC < MR
D) MC = ATC
E) P = MC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-3-1
Exhibit 9-3

The profit-maximizing output and price for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, which charges the same price to all customers, are
A) 117 and $14
B) 150 and $22
C) 150 and $14
D) 117 and $22
E) 117 and $24
Exhibit 9-3

The profit-maximizing output and price for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, which charges the same price to all customers, are
A) 117 and $14
B) 150 and $22
C) 150 and $14
D) 117 and $22
E) 117 and $24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-4-1
Exhibit 9-4
What is the revenue-maximizing output for the monopolist represented in Exhibit 9-4, assuming it does not price discriminate?
A) 0 units
B) 2 units
C) 3 units
D) 4 units
E) 5 units
Exhibit 9-4
What is the revenue-maximizing output for the monopolist represented in Exhibit 9-4, assuming it does not price discriminate?
A) 0 units
B) 2 units
C) 3 units
D) 4 units
E) 5 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If a firm's demand curve slopes downward, the firm's
A) marginal revenue will rise as price is reduced
B) marginal revenue will generally be less than price
C) total revenue will decline continuously as price is reduced
D) marginal revenue will always be greater than its demand
E) average revenue will increase continuously as output increases
A) marginal revenue will rise as price is reduced
B) marginal revenue will generally be less than price
C) total revenue will decline continuously as price is reduced
D) marginal revenue will always be greater than its demand
E) average revenue will increase continuously as output increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-3-1
Exhibit 9-3

At the profit-maximizing output for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, the single price monopolist will charge _____ per unit of output.
A) $30
B) $24
C) $22
D) $20
E) $10
Exhibit 9-3

At the profit-maximizing output for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, the single price monopolist will charge _____ per unit of output.
A) $30
B) $24
C) $22
D) $20
E) $10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose that a monopolist must choose between two points on its demand curve: it can sell 100 units for $3 each, or it can sell 150 units for $2 each. Which of the following is true?
A) The monopolist is facing elastic demand.
B) The monopolist is facing unit elastic demand.
C) The monopolist is facing inelastic demand.
D) The monopolist is facing perfectly elastic demand.
E) The elasticity of demand cannot be determined with the information given.
A) The monopolist is facing elastic demand.
B) The monopolist is facing unit elastic demand.
C) The monopolist is facing inelastic demand.
D) The monopolist is facing perfectly elastic demand.
E) The elasticity of demand cannot be determined with the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-3-1
Exhibit 9-3

The firm in Exhibit 9-3, a monopolist that maximizes profit by charging all customers the same price, is making a profit of
A) $0
B) $234
C) $482
D) $960
E) $468
Exhibit 9-3

The firm in Exhibit 9-3, a monopolist that maximizes profit by charging all customers the same price, is making a profit of
A) $0
B) $234
C) $482
D) $960
E) $468

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose it costs Minnie's Mini-Golf (a monopolist) not a penny more to let another person on the course. If Minnie's faces a linear (downward-sloping) market demand curve, it will maximize profit by choosing the point on the demand curve at which
A) marginal revenue is greatest
B) price elasticity is unit elastic
C) price elasticity is inelastic
D) price exceeds average total cost by the greatest amount
E) price exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount
A) marginal revenue is greatest
B) price elasticity is unit elastic
C) price elasticity is inelastic
D) price exceeds average total cost by the greatest amount
E) price exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A firm facing a downward-sloping demand curve sells 50 units of output at $10 each. The firm's marginal revenue is
A) $500
B) more than $10 but less than $500
C) $10
D) less than $10
E) zero
A) $500
B) more than $10 but less than $500
C) $10
D) less than $10
E) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-3-1
Exhibit 9-3

The total revenue for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, a monopolist that maximizes profit while charging all customers the same price, is
A) $2,574
B) $2,808
C) $2,100
D) $1,638
E) $3,300
Exhibit 9-3

The total revenue for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, a monopolist that maximizes profit while charging all customers the same price, is
A) $2,574
B) $2,808
C) $2,100
D) $1,638
E) $3,300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the relationship between price elasticity of demand and the monopolist's revenue?
A) marginal revenue is maximized where demand is unit elastic.
B) average revenue is maximized where demand is unit elastic.
C) marginal revenue is negative where demand is inelastic.
D) average revenue is negative where demand is inelastic.
E) marginal revenue is lowest where demand is unit elastic.
A) marginal revenue is maximized where demand is unit elastic.
B) average revenue is maximized where demand is unit elastic.
C) marginal revenue is negative where demand is inelastic.
D) average revenue is negative where demand is inelastic.
E) marginal revenue is lowest where demand is unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A monopolist's demand curve
A) is horizontal at the market price
B) lies above its marginal revenue curve
C) is the same as its marginal cost curve
D) indicates that the firm must raise price to sell additional units
E) lies above the marginal cost curve at all levels of output
A) is horizontal at the market price
B) lies above its marginal revenue curve
C) is the same as its marginal cost curve
D) indicates that the firm must raise price to sell additional units
E) lies above the marginal cost curve at all levels of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-3-1
Exhibit 9-3

At the profit-maximizing quantity, the demand curve facing the firm in Exhibit 9-3 is
A) perfectly elastic
B) price elastic
C) price inelastic
D) unit elastic
E) perfectly inelastic
Exhibit 9-3

At the profit-maximizing quantity, the demand curve facing the firm in Exhibit 9-3 is
A) perfectly elastic
B) price elastic
C) price inelastic
D) unit elastic
E) perfectly inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-4-1
Exhibit 9-4
What is the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing output for the monopolist represented in Exhibit 9-4, assuming it does not price discriminate?
A) 0 units
B) 2 units
C) 3 units
D) 4 units
E) 5 units
Exhibit 9-4
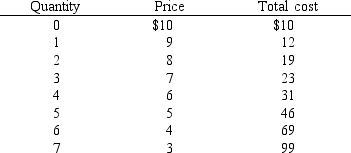
What is the profit-maximizing or loss-minimizing output for the monopolist represented in Exhibit 9-4, assuming it does not price discriminate?
A) 0 units
B) 2 units
C) 3 units
D) 4 units
E) 5 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A profit-maximizing monopolist
A) never produces on the inelastic portion of the demand curve because it can increase profit by increasing output
B) never produces on the inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost
C) always produces on the inelastic portion of the demand curve
D) never produces on the elastic portion of the demand curve because there are no substitutes for the good it produces
E) never produces on the inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is negative there
A) never produces on the inelastic portion of the demand curve because it can increase profit by increasing output
B) never produces on the inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost
C) always produces on the inelastic portion of the demand curve
D) never produces on the elastic portion of the demand curve because there are no substitutes for the good it produces
E) never produces on the inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is negative there

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
For a monopolist, if marginal revenue is $40, total revenue is
A) increasing
B) decreasing
C) zero
D) positive
E) negative
A) increasing
B) decreasing
C) zero
D) positive
E) negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-3-1
Exhibit 9-3

The total cost for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, a monopolist that maximizes profit while charging all customers the same price, is
A) $3,300
B) $3,400
C) $2,808
D) $2,340
E) $1,638
Exhibit 9-3

The total cost for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, a monopolist that maximizes profit while charging all customers the same price, is
A) $3,300
B) $3,400
C) $2,808
D) $2,340
E) $1,638

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose that a monopolist must choose between two points on its demand curve: it can sell 100 units for $3 each, or it can sell 140 units for $2 each. Which of the following is true?
A) The monopolist is facing elastic demand.
B) The monopolist is facing unit elastic demand.
C) The monopolist is facing inelastic demand.
D) The monopolist is facing perfectly elastic demand.
E) The elasticity of demand cannot be determined with the information given.
A) The monopolist is facing elastic demand.
B) The monopolist is facing unit elastic demand.
C) The monopolist is facing inelastic demand.
D) The monopolist is facing perfectly elastic demand.
E) The elasticity of demand cannot be determined with the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
NARRBEGIN: Exhibit 9-3-1
Exhibit 9-3

At the profit-maximizing output for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, the single price monopolist will earn a profit of ______ per unit of output?
A) $10
B) $5
C) $4
D) $0
E) -$5
Exhibit 9-3

At the profit-maximizing output for the firm in Exhibit 9-3, the single price monopolist will earn a profit of ______ per unit of output?
A) $10
B) $5
C) $4
D) $0
E) -$5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 249 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



