Deck 3: Natural Selection
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/47
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Natural Selection
1
Spines, flowers, and a waxy stem coating are all adaptations of cacti because
A) these traits increase the fitness of cacti and arose as a result of natural selection for their current function.
B) these traits arose prior to the diversification of cacti and perform different functions in different cactus species.
C) they develop when the climate is dry, making the cacti a better fit to the environment.
D) they arose by chance and do not provide any benefit to the individuals that have these traits.
A) these traits increase the fitness of cacti and arose as a result of natural selection for their current function.
B) these traits arose prior to the diversification of cacti and perform different functions in different cactus species.
C) they develop when the climate is dry, making the cacti a better fit to the environment.
D) they arose by chance and do not provide any benefit to the individuals that have these traits.
A
2
The figure shows the relationships between oldfield mice populations. Light-colored beach populations are shown with a triangle; dark-colored inland populations are shown with circles. Which of the following statements is consistent with this phylogeny? 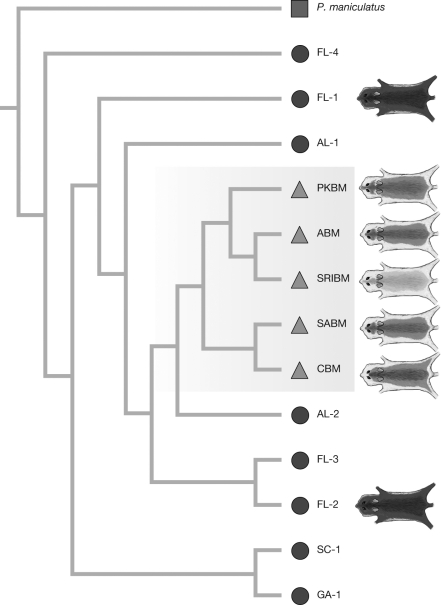
A) Light coat color arose multiple times independently in different beach populations.
B) The light-coat allele arose prior to colonization of beach populations.
C) Natural selection favors light coat color when the Mc1R allele is mutated.
D) Dark-colored populations are derived from migrants from the beach populations.

A) Light coat color arose multiple times independently in different beach populations.
B) The light-coat allele arose prior to colonization of beach populations.
C) Natural selection favors light coat color when the Mc1R allele is mutated.
D) Dark-colored populations are derived from migrants from the beach populations.
C
3
The figure shows the wing length of cliff swallows that died as road kill and of the population at large. What do these data indicate about natural selection acting on wing length in cliff swallows? 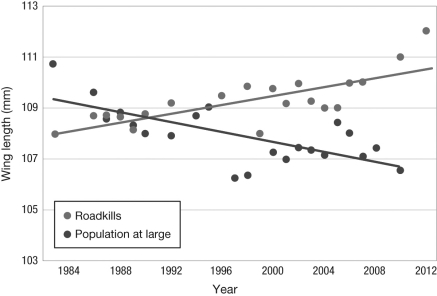
A) Birds with shorter wings die as road kill more often than the population at large; therefore, natural selection will favor birds with longer wings.
B) The probability that a swallow will die as road kill is not affected by its wing length; thus, natural selection is not acting on wing length.
C) Increasing population size in swallows has resulted in an increased number of road kill.
D) Birds with longer wings are more likely to die as road kill, so natural selection favors birds with shorter wings.

A) Birds with shorter wings die as road kill more often than the population at large; therefore, natural selection will favor birds with longer wings.
B) The probability that a swallow will die as road kill is not affected by its wing length; thus, natural selection is not acting on wing length.
C) Increasing population size in swallows has resulted in an increased number of road kill.
D) Birds with longer wings are more likely to die as road kill, so natural selection favors birds with shorter wings.
D
4
The figure indicates a ________ between the number and size of offspring that a female guppy can produce. 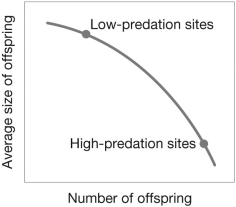
A) fitness curve
B) trade-off
C) positive relationship
D) norm of reaction

A) fitness curve
B) trade-off
C) positive relationship
D) norm of reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a study of life history evolution in response to predation, guppies that were adapted to high predation sites were transplanted to low predation sites. If the hypothesis is correct that producing larger but fewer offspring is an adaptation to low predation sites, then which of the following would we expect?
A) The number and size of offspring will not change in the transplanted guppy population.
B) More, larger offspring will be produced in the transplanted guppy population.
C) More offspring will be produced in the transplanted guppy population, but they will be smaller.
D) Fewer offspring will be produced in the transplanted guppy population, but they will be larger.
A) The number and size of offspring will not change in the transplanted guppy population.
B) More, larger offspring will be produced in the transplanted guppy population.
C) More offspring will be produced in the transplanted guppy population, but they will be smaller.
D) Fewer offspring will be produced in the transplanted guppy population, but they will be larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All of the following are types of traits that evolutionary biologists might study in regard to natural selection EXCEPT
A) traits acquired during the lifetime of an organism.
B) physical characteristics of an organism.
C) behavioral traits.
D) genetic characters.
A) traits acquired during the lifetime of an organism.
B) physical characteristics of an organism.
C) behavioral traits.
D) genetic characters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The formal definition of "fitness" in evolutionary biology
A) pertains to reproductive success relative to other individuals in the population.
B) implies something is well matched or fit to its environment.
C) indicates a general state of good health as a result of exercise and nutrition.
D) is not very useful in understanding natural selection.
A) pertains to reproductive success relative to other individuals in the population.
B) implies something is well matched or fit to its environment.
C) indicates a general state of good health as a result of exercise and nutrition.
D) is not very useful in understanding natural selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In guppy populations that experience low predation by small predators, researchers found that females produced fewer but larger offspring than in populations that experienced high predation by large predators, where females produced many small offspring. Which of the following could explain this observation?
A) In populations with many large predators, the predators can eat guppies no matter the size, so females that produce the most offspring, regardless of size, have the highest fitness.
B) In populations with low predation by small predators, natural selection favors the production of fewer offspring because females that expend fewer resources on reproduction are less likely to be eaten by predators.
C) Regardless of predation risk, it is beneficial for females to produce fewer offspring because this allows the investment of more resources into each offspring, increasing its chances of survival.
D) Under low predation risk, female guppies produce offspring sooner than in populations with high predation; therefore, offspring are larger because they have more time to grow.
A) In populations with many large predators, the predators can eat guppies no matter the size, so females that produce the most offspring, regardless of size, have the highest fitness.
B) In populations with low predation by small predators, natural selection favors the production of fewer offspring because females that expend fewer resources on reproduction are less likely to be eaten by predators.
C) Regardless of predation risk, it is beneficial for females to produce fewer offspring because this allows the investment of more resources into each offspring, increasing its chances of survival.
D) Under low predation risk, female guppies produce offspring sooner than in populations with high predation; therefore, offspring are larger because they have more time to grow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A trait that serves one purpose today but evolved under different selective conditions and previously had a different function
A) is called an exaptation.
B) is called an adaptation.
C) is never favored by natural selection.
D) cannot evolve.
A) is called an exaptation.
B) is called an adaptation.
C) is never favored by natural selection.
D) cannot evolve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The 2000-2004 drought in California dramatically shortened the growing season. What was the consequence of this for the mustard plant, Brassica rapa?
A) The plants were unable to flower in time and therefore went extinct.
B) Natural selection led to earlier flowering time in the plants.
C) The plants had increased reproductive success in those years.
D) Those plants that had longer generation times had higher survival rates.
A) The plants were unable to flower in time and therefore went extinct.
B) Natural selection led to earlier flowering time in the plants.
C) The plants had increased reproductive success in those years.
D) Those plants that had longer generation times had higher survival rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Natural selection acts on _______ differences in a population.
A) phenotypic, not genotypic
B) genotypic, not phenotypic
C) both genotypic and phenotypic
D) neither genotypic nor phenotypic
A) phenotypic, not genotypic
B) genotypic, not phenotypic
C) both genotypic and phenotypic
D) neither genotypic nor phenotypic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Long-term evolution experiments in laboratory populations of E. coli are valuable for all of the following reasons EXCEPT that they allow researchers to
A) precisely replicate natural populations of E. coli evolving in the wild.
B) study evolution over tens of thousands of generations.
C) create replicate populations that start from the same initial conditions.
D) directly complete ancestors to their descendants.
A) precisely replicate natural populations of E. coli evolving in the wild.
B) study evolution over tens of thousands of generations.
C) create replicate populations that start from the same initial conditions.
D) directly complete ancestors to their descendants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Variation is generated in a population primarily by
A) mutation.
B) natural selection.
C) changing environmental conditions.
D) inheritance.
A) mutation.
B) natural selection.
C) changing environmental conditions.
D) inheritance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Natural selection requires that variation exists in a population and that the variation
A) is generated by mechanisms other than mutation.
B) is heritable.
C) does not affect reproductive success.
D) is consistent across environments.
A) is generated by mechanisms other than mutation.
B) is heritable.
C) does not affect reproductive success.
D) is consistent across environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The figure shows the norm of reaction for the number of leaves (B) and the mean leaf area (C) at different light intensities for 10 different genotypes (each shown in a different color) of Persicaria maculosa (A). According to this figure, which of the following statements is true? A

B
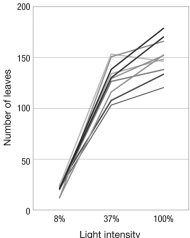
C
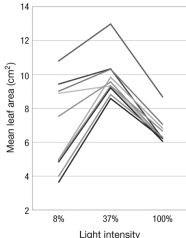
A) Each genotype specifies a fixed leaf size.
B) All genotypes produce the same leaf size for a given light intensity.
C) Genotypes that produce the most leaves also produce the largest leaves.
D) Leaf size specified by a genotype depends on light intensity.

B

C

A) Each genotype specifies a fixed leaf size.
B) All genotypes produce the same leaf size for a given light intensity.
C) Genotypes that produce the most leaves also produce the largest leaves.
D) Leaf size specified by a genotype depends on light intensity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Natural selection is a process that results in
A) the characteristics of individuals changing over time.
B) the characteristics of populations changing over time.
C) no changes in characteristics of individuals or populations.
D) changes in the characteristics of both individuals and populations.
A) the characteristics of individuals changing over time.
B) the characteristics of populations changing over time.
C) no changes in characteristics of individuals or populations.
D) changes in the characteristics of both individuals and populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What does a species' life history strategy refer to?
A) the traits of an individual organism over its lifetime
B) a schedule and manner of investment in survivorship and reproduction over the lifetime of an individual
C) morphological and physiological traits that arise due to the environmental conditions in which an organism develops
D) a strategy for preventing the spread of alleles among populations
A) the traits of an individual organism over its lifetime
B) a schedule and manner of investment in survivorship and reproduction over the lifetime of an individual
C) morphological and physiological traits that arise due to the environmental conditions in which an organism develops
D) a strategy for preventing the spread of alleles among populations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In order for traits to evolve by natural selection, individuals must experience differential reproductive success. This means that
A) individuals differ in the types of mutations that they carry.
B) some individuals are more likely to have a certain trait than others.
C) the number of individuals in a population that are successful at surviving and reproducing increases over time.
D) individuals with certain traits are more successful than others in the population at surviving and reproducing.
A) individuals differ in the types of mutations that they carry.
B) some individuals are more likely to have a certain trait than others.
C) the number of individuals in a population that are successful at surviving and reproducing increases over time.
D) individuals with certain traits are more successful than others in the population at surviving and reproducing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why was it informative for researchers studying evolution of oldfield mouse coat color to find the genes responsible for the light coat color of many beach populations?
A) Natural selection can only result in evolutionary change if variation in the trait of interest has a heritable, genetic component.
B) The only way to understand trait evolution is to determine the molecular mechanism of change.
C) If light coat color is caused by the same gene in all of the beach populations, this would mean that it did not evolve from dark-colored coats.
D) Knowing the genetic basis of coat color in the different populations allowed the researchers to determine the norm of reaction for this trait.
A) Natural selection can only result in evolutionary change if variation in the trait of interest has a heritable, genetic component.
B) The only way to understand trait evolution is to determine the molecular mechanism of change.
C) If light coat color is caused by the same gene in all of the beach populations, this would mean that it did not evolve from dark-colored coats.
D) Knowing the genetic basis of coat color in the different populations allowed the researchers to determine the norm of reaction for this trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The figure shows the number of days to first flowering in populations of mustard plants before the 2000-2004 drought (on the left, in pale gray), after the drought (on the far right, in dark gray), and of hybrids between the before-and-after populations. According to this figure, which of the following statements is true? 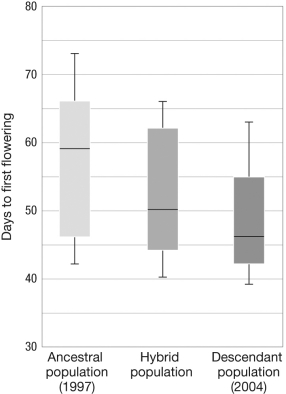
A) After the drought, plants flowered earlier in the season than those from before the drought.
B) After the drought, plants flowered later in the season than those from before the drought.
C) Hybrid plants flowered later in the season than those from before the drought.
D) There was no change in flowering time associated with the drought.

A) After the drought, plants flowered earlier in the season than those from before the drought.
B) After the drought, plants flowered later in the season than those from before the drought.
C) Hybrid plants flowered later in the season than those from before the drought.
D) There was no change in flowering time associated with the drought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Considering the phylogenetic evidence of feather evolution, all of the following might have been original functions of feathers EXCEPT
A) heat retention.
B) flight.
C) waterproofing.
D) shielding from sunlight.
A) heat retention.
B) flight.
C) waterproofing.
D) shielding from sunlight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Describe the three conditions that must be met in order for natural selection to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Richard Lenski and his colleagues' long-term evolution experiments in E. coli provide unprecedented insight into natural selection. In the experiment, 12 parallel E. coli lineages were created and maintained, cells from each line were periodically frozen, and the team followed the lineages for more than 60,000 generations. By using multiple independent lineages started from the same colony, these experiments help determine how predictable evolution is. How can you assess predictability from these experiments, and what did they find about predictability in evolution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The figure below shows the number of leaves produced by Persicaria maculosa genotypes at differing light intensities. Each shade of gray indicates the norm of reaction for a different genotype. Imagine that natural selection always favors plants with the most leaves. If these plants grow in environments that vary in light intensity, why is it difficult to predict which genotype will be favored by selection? 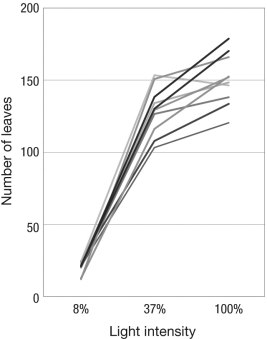


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The figure illustrates a likely scenario for the molecular mechanism of treehopper helmet evolution. This process demonstrates which explanation for the evolution of complex traits? 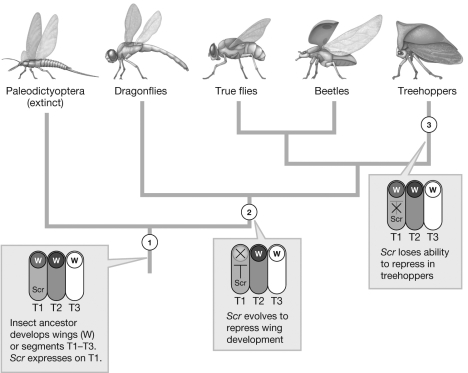
A) Traits arise in gradual steps, each of which is fully functional and adaptive for the same reason as the modern trait.
B) Complex traits cannot evolve if they are adaptive.
C) Complex traits arise by eliminating whole developmental pathways.
D) Traits originally selected for one function are co-opted for a different function.

A) Traits arise in gradual steps, each of which is fully functional and adaptive for the same reason as the modern trait.
B) Complex traits cannot evolve if they are adaptive.
C) Complex traits arise by eliminating whole developmental pathways.
D) Traits originally selected for one function are co-opted for a different function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Imagine you are an evolutionary biologist studying reproductive trade-offs in populations of guppies that have been separated by the formation of barrier waterfalls. The upstream population faces lower predation than the downstream population, and the predators on the downstream side are larger and can eat any guppy offspring, no matter the size. Make a prediction about the reproductive strategies you might find and explain the trade-offs faced by the reproducing female guppies on each side of the barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Organisms may not be perfectly adapted to their environments for all of the following reasons EXCEPT
A) there are physical constraints that cannot be overcome.
B) an organism's surroundings do not present a stationary target to which natural selection can optimize its phenotype.
C) the process of natural selection lacks foresight.
D) natural selection cannot result in novel, complex traits.
A) there are physical constraints that cannot be overcome.
B) an organism's surroundings do not present a stationary target to which natural selection can optimize its phenotype.
C) the process of natural selection lacks foresight.
D) natural selection cannot result in novel, complex traits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
To test the hypothesis that natural selection by predators favors a match between coat color in oldfield mice and the color of their environmental background, Hopi Hoekstra and colleagues made silicone models of mice that were colored either light or dark. These model mice were placed in beach environments that had either light or dark backgrounds. If the hypothesis is correct, what do you predict will happen to the different mice in each background?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Fitness differences among laboratory populations of E. coli are commonly assessed using the Ara +/- marker system, which allows strains to be distinguished based on color. Explain the methods and analyses you would use to determine the fitness of two E. coli strains that are labeled Ara + and Ara +/- .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Populations of cliff swallows in Nebraska have experienced a significant decrease in the number
of road kills over the past 30 years. Describe two alternate hypotheses that could explain this observation, one that relies on natural selection and one that does not, and explain how you would
test these hypotheses.
of road kills over the past 30 years. Describe two alternate hypotheses that could explain this observation, one that relies on natural selection and one that does not, and explain how you would
test these hypotheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Lens crystallins form the transparent lens of the eye. In guinea pigs, lens crystallins also function as alcohol dehydrogenase. What is this an example of?
A) antagonistic pleiotropy
B) gene duplication
C) a trade-off
D) gene sharing
A) antagonistic pleiotropy
B) gene duplication
C) a trade-off
D) gene sharing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An exaptation is a trait
A) originally selected for one function but later co-opted for a different function.
B) of seemingly little importance.
C) that is beneficial in one environment and deleterious in other environments.
D) that was shaped by natural selection to serve the same primary function that makes it beneficial today.
A) originally selected for one function but later co-opted for a different function.
B) of seemingly little importance.
C) that is beneficial in one environment and deleterious in other environments.
D) that was shaped by natural selection to serve the same primary function that makes it beneficial today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Give an example of a trait that provides a good fit to the environment but is not an adaptation. Explain why it is not an adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the term for a simultaneous action of natural selection on each side of the host-pathogen interaction?
A) an evolutionary arms race
B) mutualism
C) antagonistic pleiotropy
D) a trade-off
A) an evolutionary arms race
B) mutualism
C) antagonistic pleiotropy
D) a trade-off

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The figure shows a hypothetical relationship between the growth rates of E. coli at 37 and 42 degrees Celsius. This figure illustrates what type of evolutionary constraint? 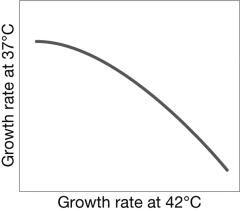
A) Physical constraints make it difficult for natural selection to produce E. coli that are successful at 42 degrees.
B) It illustrates the lack of repeatability in evolution.
C) Alleles that are beneficial in one environment may be deleterious in another environment.
D) Changing environments make it impossible for natural selection to act.

A) Physical constraints make it difficult for natural selection to produce E. coli that are successful at 42 degrees.
B) It illustrates the lack of repeatability in evolution.
C) Alleles that are beneficial in one environment may be deleterious in another environment.
D) Changing environments make it impossible for natural selection to act.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Lenski and Travisano compared what happened to the fitness of cells in 12 replicate lines of E. coli. According to the graph shown, which of the following statements is true? 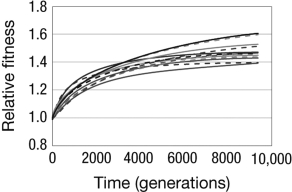
A) Fitness increased in some of the lines and decreased in other lines.
B) Fitness increased initially, but after about 3,000 generations all of the lines reached their maximum fitness and quit evolving.
C) Fitness increased in every line, but to a different degree in each line.
D) Evolution by natural selection cannot be predicted at any level.

A) Fitness increased in some of the lines and decreased in other lines.
B) Fitness increased initially, but after about 3,000 generations all of the lines reached their maximum fitness and quit evolving.
C) Fitness increased in every line, but to a different degree in each line.
D) Evolution by natural selection cannot be predicted at any level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How can gene duplication provide an evolutionary pathway by which a protein can switch functions without loss of the original function?
A) Gene duplication results in two identical genes that both preserve the same function.
B) A pair of duplicated genes initially perform the same functions, but both genes acquire mutations that change their function.
C) When a gene is duplicated, it rapidly acquires mutations that make it no longer functional.
D) An extra copy of a working gene is formed that can gain a new function without changing the function of the original gene.
A) Gene duplication results in two identical genes that both preserve the same function.
B) A pair of duplicated genes initially perform the same functions, but both genes acquire mutations that change their function.
C) When a gene is duplicated, it rapidly acquires mutations that make it no longer functional.
D) An extra copy of a working gene is formed that can gain a new function without changing the function of the original gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Evolutionary change in one species that affects the selective conditions for a second species is known as which of the following?
A) an evolutionary arms race
B) coevolution
C) antagonistic pleiotropy
D) a trade-off
A) an evolutionary arms race
B) coevolution
C) antagonistic pleiotropy
D) a trade-off

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
One constraint on what natural selection can achieve comes from the fact that it lacks foresight. This means that
A) traits that are beneficial in one environment are likely to be costly in another environment.
B) selection cannot adapt organisms perfectly to their surroundings because of physical constraints.
C) traits that increase the probability of higher fitness in the future are favored by selection.
D) selection favors changes that are immediately beneficial, not changes that may be useful sometime in the future.
A) traits that are beneficial in one environment are likely to be costly in another environment.
B) selection cannot adapt organisms perfectly to their surroundings because of physical constraints.
C) traits that increase the probability of higher fitness in the future are favored by selection.
D) selection favors changes that are immediately beneficial, not changes that may be useful sometime in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The exquisite complexity of traits such as the vertebrate eye seems to pose a problem for evolution by natural selection. How do evolutionary biologists think that complex eyes evolved?
A) Complex eyes arose multiple times independently by a single mutation.
B) Intermediate forms of eyes were functional and selected for in the past but were selected for a function other than vision.
C) Eyes evolved in gradual steps, each of which was fully functional and adaptive in improving visual acuity.
D) Precursors to complex eyes were not adaptive and therefore were not subject to evolution by natural selection.
A) Complex eyes arose multiple times independently by a single mutation.
B) Intermediate forms of eyes were functional and selected for in the past but were selected for a function other than vision.
C) Eyes evolved in gradual steps, each of which was fully functional and adaptive in improving visual acuity.
D) Precursors to complex eyes were not adaptive and therefore were not subject to evolution by natural selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The eyes of an owl are positioned in front of the head; the eyes of an ostrich are set on opposite sides of the head. What are the trade-offs in physical constraint that each of these animals face?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Based on the figure, use phylogenetic reasoning to explain whether feathers evolved for flight, and why. What other possible advantages could feathers provide? Is there a way to determine the original selective function? Explain your answer. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
One way that novelty can arise at the molecular level is through the process of gene sharing, where a protein that serves one function is recruited to serve a different function. In what way is gene sharing like an exaptation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An evolutionary arms race occurs when natural selection is acting simultaneously on both sides of a host-pathogen interaction. How does an evolutionary arms race constrain evolution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Your text describes two possible explanations for how complex traits can evolve. These explanations posit that complex traits are either adaptations or exaptations. Describe one way in which these two explanations for the evolution of complex traits are similar and one way in which they differ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Explain what evolutionary biologists mean when they say that there are constraints on what natural selection can achieve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is meant by the statement "Natural selection lacks foresight"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 47 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



