Deck 6: Sterechemistry at Tetrahedral Centers
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Sterechemistry at Tetrahedral Centers
1
Instructions: Consider the structure of streptimidone below to answer the following question(s).
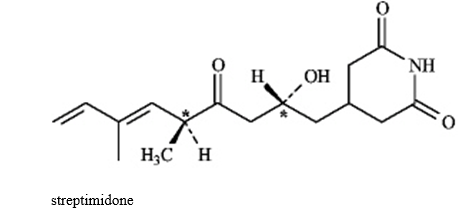 Refer to instructions. Assign R or S configuration to each chirality center indicated in streptimidone.
Refer to instructions. Assign R or S configuration to each chirality center indicated in streptimidone.
 Refer to instructions. Assign R or S configuration to each chirality center indicated in streptimidone.
Refer to instructions. Assign R or S configuration to each chirality center indicated in streptimidone.
2
Which of the following has a plane of symmetry?
A) boot
B) laboratory beaker
C) hammer
D) both b and c
E) none of these
A) boot
B) laboratory beaker
C) hammer
D) both b and c
E) none of these
D
3
The biological importance of enantiomers arises from?
A) Biological reactions involve receptor molecules.
B) Biological receptors are chiral.
C) Biological receptors require a specific enantiomer for reaction.
D) Each enantiomer has different biological properties.
E) all of these
A) Biological reactions involve receptor molecules.
B) Biological receptors are chiral.
C) Biological receptors require a specific enantiomer for reaction.
D) Each enantiomer has different biological properties.
E) all of these
E
4
Which of the following is the definition of a pair of enantiomers?
A) A pair of structures that are superimposable mirror images of one another
B) A pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of one another
C) A pair of stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another
D) A pair of stereoisomers that have equal specific rotations
A) A pair of structures that are superimposable mirror images of one another
B) A pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of one another
C) A pair of stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another
D) A pair of stereoisomers that have equal specific rotations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following physical properties can be used to identify a compound?
A) R
B) S
C) a
D) [a]D
A) R
B) S
C) a
D) [a]D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Instructions: Place asterisks at all the chirality centers in each molecule below.
Place asterisks:
Place asterisks:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Instructions: In the molecules below, assign R, S configurations to the chirality center indicated with an arrow.
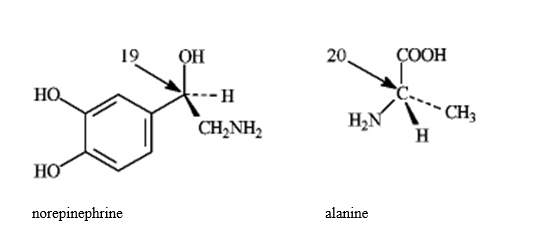 Refer to instructions. The configuration of the carbon atom labeled 19 is _____.
Refer to instructions. The configuration of the carbon atom labeled 19 is _____.
 Refer to instructions. The configuration of the carbon atom labeled 19 is _____.
Refer to instructions. The configuration of the carbon atom labeled 19 is _____.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Instructions: Place asterisks at all the chirality centers in each molecule below.
Place asterisks:

Place asterisks:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Instructions: In the molecules below, assign R, S configurations to the chirality center indicated with an arrow.
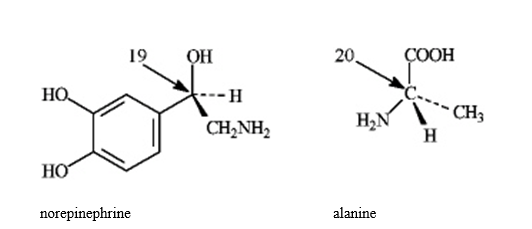 Refer to instructions. The configuration of the carbon atom labeled 20 is _____.
Refer to instructions. The configuration of the carbon atom labeled 20 is _____.
 Refer to instructions. The configuration of the carbon atom labeled 20 is _____.
Refer to instructions. The configuration of the carbon atom labeled 20 is _____.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If (+)-sucrose has a specific rotation of +66.47, what is the specific rotation of (-)-sucrose?
A) +66.47
B) -66.47
C) +33.43
D) -33.43
E) Must be determined with a polarimeter.
A) +66.47
B) -66.47
C) +33.43
D) -33.43
E) Must be determined with a polarimeter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is the definition of a pair of diastereomers?
A) A pair of structures that are superimposable mirror images of one another
B) A pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of one another
C) A pair of stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another
D) A pair of stereoisomers that have equal specific rotations
A) A pair of structures that are superimposable mirror images of one another
B) A pair of stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of one another
C) A pair of stereoisomers that are not mirror images of one another
D) A pair of stereoisomers that have equal specific rotations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Rank the following substituent groups from highest to lowest priority according to the sequencing rules.
CO2CH3 CO2H OH Cl
CO2CH3 CO2H OH Cl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is the definition of a meso compound?
A) A molecule with chirality centers which is chiral
B) A molecule with chirality centers which is not chiral
C) A diastereomer with no chirality centers
D) A chiral compound with more than one chirality center
A) A molecule with chirality centers which is chiral
B) A molecule with chirality centers which is not chiral
C) A diastereomer with no chirality centers
D) A chiral compound with more than one chirality center

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
(-)-cholesterol
A) does not have a chiral center.
B) is dextrorotatory.
C) rotates the plane of polarized light counterclockwise.
D) does not rotate polarized light.
A) does not have a chiral center.
B) is dextrorotatory.
C) rotates the plane of polarized light counterclockwise.
D) does not rotate polarized light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Instructions: Place asterisks at all the chirality centers in each molecule below.
Place asterisks:

Place asterisks:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
2.10 g of an unknown compound was dissolved in 15.00 mL of ethanol. The sample was placed in a 10.0 cm cell in a polarimeter and the angle of rotation was determined to be -18.48 . What is the specific rotation of this unknown and specify if the compound is levorotatory or dextrorotatory?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The numbers on the carbon center of the following molecule represent atomic numbers. 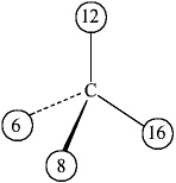 The molecule is in
The molecule is in
A) the R configuration.
B) the S configuration.
C) The carbon is not a chiral center in this molecule.
D) The exact configuration cannot be determined without knowing additional atomic numbers.
 The molecule is in
The molecule is inA) the R configuration.
B) the S configuration.
C) The carbon is not a chiral center in this molecule.
D) The exact configuration cannot be determined without knowing additional atomic numbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Instructions: Consider the structure of streptimidone below to answer the following question(s).
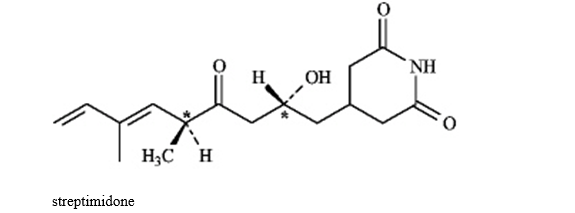 Refer to instructions. Does streptimidone have a meso stereoisomer? Explain.
Refer to instructions. Does streptimidone have a meso stereoisomer? Explain.
 Refer to instructions. Does streptimidone have a meso stereoisomer? Explain.
Refer to instructions. Does streptimidone have a meso stereoisomer? Explain.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is true regarding pairs of enantiomers?
A) They have identical melting points
B) They have identical boiling points.
C) They rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions
D) They produce different products in reactions with chiral reagents
E) all of these
A) They have identical melting points
B) They have identical boiling points.
C) They rotate plane-polarized light in opposite directions
D) They produce different products in reactions with chiral reagents
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following correctly describes a molecule that is achiral?
A) Non-superimposability of the molecule on its mirror image
B) Superimposability of the molecule on its mirror image
C) Contains a carbon atom with four different substituents
D) Does not have a plane of symmetry
E) Both b and d
A) Non-superimposability of the molecule on its mirror image
B) Superimposability of the molecule on its mirror image
C) Contains a carbon atom with four different substituents
D) Does not have a plane of symmetry
E) Both b and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How many stereoisomers of 3-bromo-2-butanol exist? 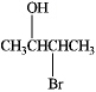
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following have the R configuration? 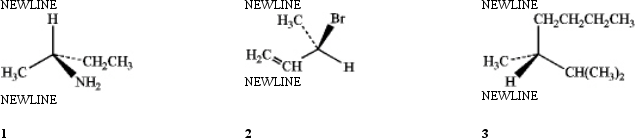
A) only 1
B) only 2
C) only 1 and 2
D) 1, 2 and 3

A) only 1
B) only 2
C) only 1 and 2
D) 1, 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Instructions:
Refer to the structure below to answer the following questions.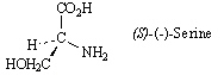 Refer to instructions. Give the complete name of the enantiomer of (S)-(-)-serine.
Refer to instructions. Give the complete name of the enantiomer of (S)-(-)-serine.
Refer to the structure below to answer the following questions.
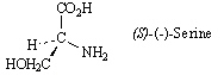 Refer to instructions. Give the complete name of the enantiomer of (S)-(-)-serine.
Refer to instructions. Give the complete name of the enantiomer of (S)-(-)-serine.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following compounds is (are) achiral? 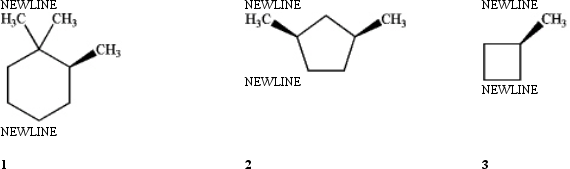
A) only 1
B) only 1 and 2
C) only 2 and 3
D) 1, 2 and 3

A) only 1
B) only 1 and 2
C) only 2 and 3
D) 1, 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the relationship between the following pair of structures? 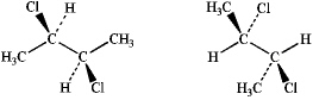
A) They are enantiomers
B) They are diastereomers
C) The are constitutional isomers
D) They are identical
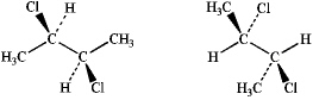
A) They are enantiomers
B) They are diastereomers
C) The are constitutional isomers
D) They are identical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following structures represent the same stereoisomer? 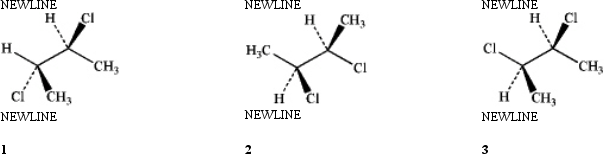
A) only 1 and 2
B) only 1 and 3
C) only 2 and 3
D) 1, 2 and 3

A) only 1 and 2
B) only 1 and 3
C) only 2 and 3
D) 1, 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How many stereoisomers of 2,3-dimethylbutane exist? 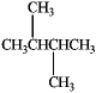
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following structures contain a plane of symmetry? 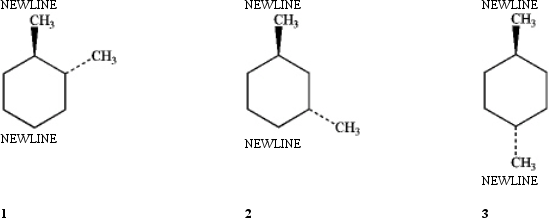
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) All three contain a plane of symmetry

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) All three contain a plane of symmetry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How many stereoisomers of 3-chloro-2-methylbutane exist? 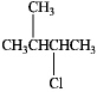
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the relationship between the following pair of structures? 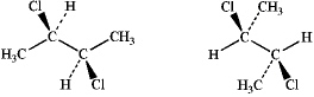
A) They are enantiomers
B) They are diastereomers
C) The are constitutional isomers
D) They are identical
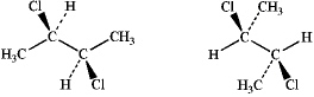
A) They are enantiomers
B) They are diastereomers
C) The are constitutional isomers
D) They are identical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following have the S configuration? 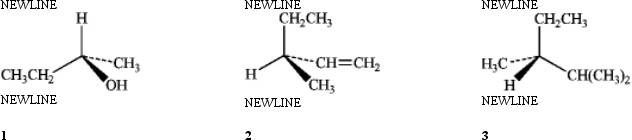
A) only 1
B) only 2
C) only 1 and 2
D) 1, 2 and 3

A) only 1
B) only 2
C) only 1 and 2
D) 1, 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Instructions:
Refer to the structure below to answer the following questions.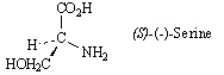 Refer to instructions. Draw the enantiomer of (S)-(-)-serine in a wedge-dash projection.
Refer to instructions. Draw the enantiomer of (S)-(-)-serine in a wedge-dash projection.
Refer to the structure below to answer the following questions.
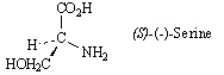 Refer to instructions. Draw the enantiomer of (S)-(-)-serine in a wedge-dash projection.
Refer to instructions. Draw the enantiomer of (S)-(-)-serine in a wedge-dash projection.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A natural product having [a]D = +40.3 has been isolated and purified. This information indicates that the natural product:
a. is racemic
b. doanot rotate plene-polarized light
c. is levaratetary.
d. is dextarotatory.
a. is racemic
b. doanot rotate plene-polarized light
c. is levaratetary.
d. is dextarotatory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



