Deck 2: The Chemical Basis of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/55
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Chemical Basis of Life
1
Isotopes of an element differ in their
A) proton number.
B) electron number.
C) neutron number.
D) type of bonds.
E) atomic number.
A) proton number.
B) electron number.
C) neutron number.
D) type of bonds.
E) atomic number.
C
Explanation: Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. They have the same number of protons, but they have different mass numbers.
Explanation: Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. They have the same number of protons, but they have different mass numbers.
2
An atom that has an electrical charge is called an)
A) ion.
B) molecule.
C) isotope.
D) element.
E) proton.
A) ion.
B) molecule.
C) isotope.
D) element.
E) proton.
A
Explanation: When an atom either loses or gains electrons in a reaction, the resulting atom now bears an overall net charge.This state is called an ion.
Explanation: When an atom either loses or gains electrons in a reaction, the resulting atom now bears an overall net charge.This state is called an ion.
3
The type of bond that would form from the transfer of an electron from one atom to another, shown below, is an) ________ bond. 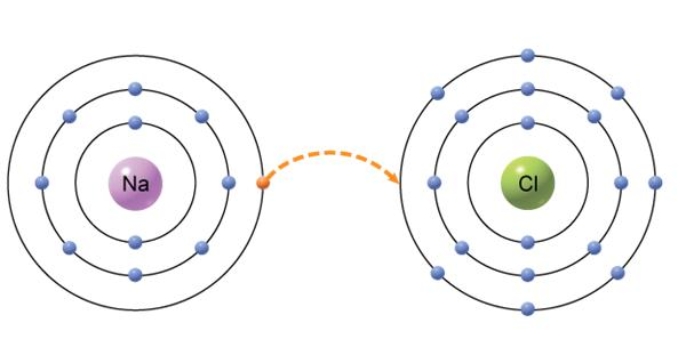
A) covalent
B) ionic
C) hydrogen
D) atomic
E) isotopic

A) covalent
B) ionic
C) hydrogen
D) atomic
E) isotopic
B
Explanation: Ionic bonds are formed when two atoms are held together by an attraction between opposite charges. In this diagram, sodium is transferring a negatively charged electron over to chlorine. The result is sodium having a positive charge Na+) and chlorine now having a negative charge Cl-). These ions have an attraction that creates the ionic bond that holds them together.
Explanation: Ionic bonds are formed when two atoms are held together by an attraction between opposite charges. In this diagram, sodium is transferring a negatively charged electron over to chlorine. The result is sodium having a positive charge Na+) and chlorine now having a negative charge Cl-). These ions have an attraction that creates the ionic bond that holds them together.
4
An atom's valence electron shell
A) is filled when it has three electrons.
B) determines its chemical reactivity.
C) determines its atomic mass.
D) is filled with positively charged particles.
E) is filled identically for every element.
A) is filled when it has three electrons.
B) determines its chemical reactivity.
C) determines its atomic mass.
D) is filled with positively charged particles.
E) is filled identically for every element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An) ________ can be defined as a substance that prevents the pH of a solution from changing by either releasing or absorbing H+ in a solution.
A) equalizer
B) solute
C) buffer
D) acid
E) base
A) equalizer
B) solute
C) buffer
D) acid
E) base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A covalent bond occurs when
A) protons are transferred from one atom to another.
B) neutrons are shared between two atoms to form an isotope.
C) electrons are shared between two atoms to complete their octets.
D) the hydrogen of one water molecule is attracted to the oxygen of another water molecule.
E) electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
A) protons are transferred from one atom to another.
B) neutrons are shared between two atoms to form an isotope.
C) electrons are shared between two atoms to complete their octets.
D) the hydrogen of one water molecule is attracted to the oxygen of another water molecule.
E) electrons are transferred from one atom to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The pH scale is a mathematical indicator of the
A) concentration of H+ present in a solution.
B) concentration of OH- present in a solution.
C) total amount of all ions in a solution.
D) ability of a solution to buffer.
E) ability to dissolve in water.
A) concentration of H+ present in a solution.
B) concentration of OH- present in a solution.
C) total amount of all ions in a solution.
D) ability of a solution to buffer.
E) ability to dissolve in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not a compound?
A) H2O
B) O- 2-
C) NaCl
D) CO2
E) MgCl2
A) H2O
B) O- 2-
C) NaCl
D) CO2
E) MgCl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of these does not occur when a sodium atom transfers an electron to a chlorine atom?
A) The sodium atom becomes a positively charged ion.
B) The positive and negative ions will attract each other, forming a crystal if no water is present.
C) The ions will separate in the presence of water.
D) There is a mutual sharing of the electrons between the sodium and chlorine atoms.
E) The chlorine atom becomes a negatively charged ion.
A) The sodium atom becomes a positively charged ion.
B) The positive and negative ions will attract each other, forming a crystal if no water is present.
C) The ions will separate in the presence of water.
D) There is a mutual sharing of the electrons between the sodium and chlorine atoms.
E) The chlorine atom becomes a negatively charged ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Bases can
A) release only hydrogen ions.
B) take up only hydrogen ions.
C) release only hydroxide ions.
D) both take up hydrogen ions and release hydroxide ions.
E) release hydrogen and release hydroxide.
A) release only hydrogen ions.
B) take up only hydrogen ions.
C) release only hydroxide ions.
D) both take up hydrogen ions and release hydroxide ions.
E) release hydrogen and release hydroxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following would be an example of the value of water's heat capacity?
A) Water is able to travel up a 100-foot tree.
B) Water expands as it freezes causing ice to float on the surface of a lake.
C) Living organisms are able to maintain their internal body temperatures because the water in their cells resists changes in temperature.
D) Small insects can walk on water.
E) Ice cubes float.
A) Water is able to travel up a 100-foot tree.
B) Water expands as it freezes causing ice to float on the surface of a lake.
C) Living organisms are able to maintain their internal body temperatures because the water in their cells resists changes in temperature.
D) Small insects can walk on water.
E) Ice cubes float.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not one of the most common elements in living things?
A) oxygen
B) carbon
C) calcium
D) iron
E) nitrogen
A) oxygen
B) carbon
C) calcium
D) iron
E) nitrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Regarding atoms, identify which statement below is correct.
A) An element may be composed of several types of atoms.
B) The nucleus of an atom contains protons and electrons.
C) The number and arrangement of electrons in an atom governs its chemical activity.
D) The positive charges of an element are carried by the electrons.
E) The neutral charges of an element are carried by the protons.
A) An element may be composed of several types of atoms.
B) The nucleus of an atom contains protons and electrons.
C) The number and arrangement of electrons in an atom governs its chemical activity.
D) The positive charges of an element are carried by the electrons.
E) The neutral charges of an element are carried by the protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The figure below is depicting the interaction of water molecules with one another, which involves the use of 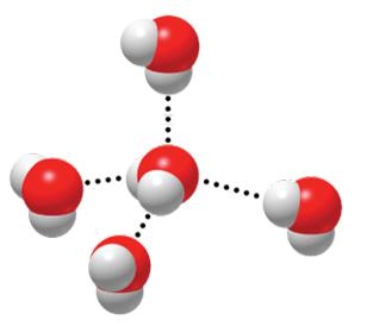
A) covalent bonds.
B) hydrogen bonds.
C) ionic bonds.
D) postive and negative ions.
E) no chemical bonding.

A) covalent bonds.
B) hydrogen bonds.
C) ionic bonds.
D) postive and negative ions.
E) no chemical bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
After drinking a great deal of coffee pH 5), a human's blood buffering system would need to ________ as the coffee was digested to lower the level of acid present in the blood stream.
A) release OH-
B) take up H+
C) release H+
D) take up OH-
E) release OH- and take up H+
A) release OH-
B) take up H+
C) release H+
D) take up OH-
E) release OH- and take up H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A water molecule, as shown here, is polar because of 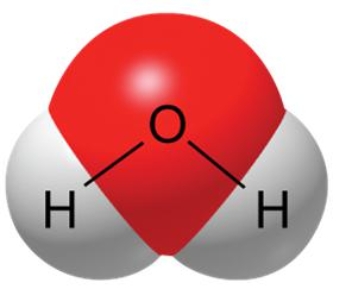
A) the transfer of electrons.
B) unequal sharing of electrons.
C) its ability to freeze.
D) its hydrogen bonds.
E) the negative charge of the molecule.

A) the transfer of electrons.
B) unequal sharing of electrons.
C) its ability to freeze.
D) its hydrogen bonds.
E) the negative charge of the molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is not a property of water?
A) It is a good solvent.
B) It is denser when frozen than when liquid.
C) It is cohesive.
D) It resists temperature changes.
E) It can be found as a solid, liquid, or gas.
A) It is a good solvent.
B) It is denser when frozen than when liquid.
C) It is cohesive.
D) It resists temperature changes.
E) It can be found as a solid, liquid, or gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which one of the following is the smallest unit of matter that has all the properties of an element?
A) molecule
B) proton
C) atom
D) compound
E) electron
A) molecule
B) proton
C) atom
D) compound
E) electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Glucose, C6H12O6, is best described as an)
A) element.
B) isotope.
C) compound.
D) ion.
E) atom.
A) element.
B) isotope.
C) compound.
D) ion.
E) atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Elements differ from each other in their
A) physical properties only.
B) atomic number only.
C) type of subatomic particles.
D) physical properties and atomic number.
E) type of electrons.
A) physical properties only.
B) atomic number only.
C) type of subatomic particles.
D) physical properties and atomic number.
E) type of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What do lemons, tomatoes, and coffee all have in common chemically?
A) They are all foods that people consume.
B) They all produce H+ ions in solution, making them acids.
C) They all are fruits.
D) They all taste bitter.
E) They are all slippery to the touch.
A) They are all foods that people consume.
B) They all produce H+ ions in solution, making them acids.
C) They all are fruits.
D) They all taste bitter.
E) They are all slippery to the touch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An atom with a neutral charge has
A) equal numbers of neutrons and electrons.
B) more neutrons making it more neutral.
C) the same number of protons and neutrons.
D) equal numbers of protons and electrons.
E) more protons than it does electrons.
A) equal numbers of neutrons and electrons.
B) more neutrons making it more neutral.
C) the same number of protons and neutrons.
D) equal numbers of protons and electrons.
E) more protons than it does electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In what ways are radioactive isotopes potentially harmful?
A) Unmonitored release into the environment can make changes in a cell's DNA.
B) They are used to trace molecular changes.
C) They are used to destroy abnormal cells.
D) They are used to determine the age of biological specimens.
E) They are used to trace the path of materials throughout the body.
A) Unmonitored release into the environment can make changes in a cell's DNA.
B) They are used to trace molecular changes.
C) They are used to destroy abnormal cells.
D) They are used to determine the age of biological specimens.
E) They are used to trace the path of materials throughout the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Of the following examples, which best demonstrates the property of water cohesion?
A) Water can move up a 100-foot pine tree, from the roots to the leaves.
B) A rock skipping across the surface of a lake.
C) Water requires a great deal of heat to reach the point of vaporizing.
D) A can of soda bursts when it is placed in the freezer.
E) A large body of fresh water takes a long time to warm up after the winter season.
A) Water can move up a 100-foot pine tree, from the roots to the leaves.
B) A rock skipping across the surface of a lake.
C) Water requires a great deal of heat to reach the point of vaporizing.
D) A can of soda bursts when it is placed in the freezer.
E) A large body of fresh water takes a long time to warm up after the winter season.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following would not be a valuable use for radioactive isotopes?
A) carbon-14 dating
B) destroying abnormal cells as a type of cancer treatment
C) tracing the path of various chemicals in the body for imaging
D) determining the age of biological specimens
E) damaging DNA of healthy cells
A) carbon-14 dating
B) destroying abnormal cells as a type of cancer treatment
C) tracing the path of various chemicals in the body for imaging
D) determining the age of biological specimens
E) damaging DNA of healthy cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The number of neutrons present in the nucleus of an average atom of any given element is best estimated by
A) adding the number of electrons and protons together.
B) subtracting the number of electrons from the number of protons.
C) adding the mass number to the number of electrons.
D) subtracting the number of protons from the mass number.
E) adding the atomic number and atomic mass together.
A) adding the number of electrons and protons together.
B) subtracting the number of electrons from the number of protons.
C) adding the mass number to the number of electrons.
D) subtracting the number of protons from the mass number.
E) adding the atomic number and atomic mass together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The atomic structure of water satisfies the octet rule by having
A) electrons shared between the two oxygen atoms.
B) electrons from hydrogen transferred to the oxygen atom.
C) electrons from oxygen transferred to the hydrogen atoms.
D) oxygen share electrons with two hydrogen atoms.
E) electrons shared between the two hydrogen atoms.
A) electrons shared between the two oxygen atoms.
B) electrons from hydrogen transferred to the oxygen atom.
C) electrons from oxygen transferred to the hydrogen atoms.
D) oxygen share electrons with two hydrogen atoms.
E) electrons shared between the two hydrogen atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Although Oregon and South Dakota are at similar latitudes, winters in Oregon are warmer and summers in Oregon are cooler. Which of the following might explain these differences between the climate of Oregon and the climate of South Dakota?
A) South Dakota has fewer trees.
B) The Pacific Ocean makes Oregon temperatures more moderate.
C) Oregon receives more rainfall.
D) South Dakota has fewer lakes and rivers.
E) South Dakota has more prevailing winds from the west.
A) South Dakota has fewer trees.
B) The Pacific Ocean makes Oregon temperatures more moderate.
C) Oregon receives more rainfall.
D) South Dakota has fewer lakes and rivers.
E) South Dakota has more prevailing winds from the west.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the steam being given off when water boils?
A) oxygen molecules
B) hydrogen molecules
C) water molecules
D) hydroxide OH-) ions
E) hydrogen H+) ions
A) oxygen molecules
B) hydrogen molecules
C) water molecules
D) hydroxide OH-) ions
E) hydrogen H+) ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Baking soda is sometimes used as an antacid. The chemical name for baking soda is sodium bicarbonate. What is the bicarbonate doing to help with stomach upset?
A) It is serving as a buffer to take up excess H+ ions from stomach acid.
B) It is able to coat the stomach lining.
C) The bicarbonate helps to create more acid in the stomach.
D) The bicarbonate acts as a strong acid quickly dissociating into H+ ions.
E) It relaxes the stomach muscles.
A) It is serving as a buffer to take up excess H+ ions from stomach acid.
B) It is able to coat the stomach lining.
C) The bicarbonate helps to create more acid in the stomach.
D) The bicarbonate acts as a strong acid quickly dissociating into H+ ions.
E) It relaxes the stomach muscles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which property of water would help to account for how an individual who is exercising and producing excessive heat can maintain a constant body temperature?
A) Water has high heat capacity.
B) Water is less dense than ice.
C) Water is a good solvent.
D) Water is cohesive.
E) Water molecules form by covalent bonding.
A) Water has high heat capacity.
B) Water is less dense than ice.
C) Water is a good solvent.
D) Water is cohesive.
E) Water molecules form by covalent bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a property of acids?
A) release hydrogen ions when dissolved in a liquid
B) feel slippery when touched
C) taste bitter
D) release hydroxide ions when dissolved in a liquid
E) have a pH reading above 7.0
A) release hydrogen ions when dissolved in a liquid
B) feel slippery when touched
C) taste bitter
D) release hydroxide ions when dissolved in a liquid
E) have a pH reading above 7.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the reaction 6CO2 + 6H2OC6H12O6 + 6O2 carbon dioxide is one of the
A) reactants.
B) products.
C) enzymes.
D) elements.
E) catalysts.
A) reactants.
B) products.
C) enzymes.
D) elements.
E) catalysts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following explains the events occurring when water boils?
A) Hydrogen bonds are broken between neighboring water molecules.
B) Covalent bonds are broken between oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
C) Ionic bonds are broken when the minerals in water are heated.
D) The bond between one water molecule and another is strengthened.
E) The hydrogen atoms break away from the oxygen and escape as vapor.
A) Hydrogen bonds are broken between neighboring water molecules.
B) Covalent bonds are broken between oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
C) Ionic bonds are broken when the minerals in water are heated.
D) The bond between one water molecule and another is strengthened.
E) The hydrogen atoms break away from the oxygen and escape as vapor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
All atoms of the same element have the same
A) number of neutrons.
B) atomic number.
C) number of electrons.
D) atomic mass.
E) number of ions.
A) number of neutrons.
B) atomic number.
C) number of electrons.
D) atomic mass.
E) number of ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Isotopes of an atom differ in their
A) atomic number.
B) atomic mass.
C) number of electrons.
D) atomic radius.
E) number of protons.
A) atomic number.
B) atomic mass.
C) number of electrons.
D) atomic radius.
E) number of protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An element has an atomic number of 78. The number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom of the element are
A) 156 protons and 78 electrons.
B) 39 protons and 39 electrons.
C) 78 protons and 0 electrons.
D) 78 protons and 78 electrons.
E) 78 protons and 39 electrons.
A) 156 protons and 78 electrons.
B) 39 protons and 39 electrons.
C) 78 protons and 0 electrons.
D) 78 protons and 78 electrons.
E) 78 protons and 39 electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Cola has a pH of 3.5. This means that it has an excess of _______ ions and would be called an) ________.
A) H+; acid
B) OH-; acid
C) H+; base
D) OH-; base
E) H+; neutral solution
A) H+; acid
B) OH-; acid
C) H+; base
D) OH-; base
E) H+; neutral solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How does a strong acid differ from a weak acid?
A) A strong acid contains fewer H+ in solution.
B) A weak acid dissociates only partially in water.
C) A strong acid is less likely to remain dissociated.
D) A weak acid dissociates nearly completely in water.
E) A strong acid dissociates only partly in water.
A) A strong acid contains fewer H+ in solution.
B) A weak acid dissociates only partially in water.
C) A strong acid is less likely to remain dissociated.
D) A weak acid dissociates nearly completely in water.
E) A strong acid dissociates only partly in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which property of water causes sugar to dissolve in coffee?
A) Hydrogen bonds are broken between neighboring water molecules.
B) Water is less dense than ice.
C) Water is a good solvent.
D) Water is cohesive.
E) Water is able to change states.
A) Hydrogen bonds are broken between neighboring water molecules.
B) Water is less dense than ice.
C) Water is a good solvent.
D) Water is cohesive.
E) Water is able to change states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why do cells need buffering agents?
A) to minimize the changes in pH of their internal environment
B) to operate at a constant pH of 2.0
C) to carry out life functions in extremely acidic conditions
D) to help transfer electrons from one atom to another
E) to increase the amount of OH- in their surroundings
A) to minimize the changes in pH of their internal environment
B) to operate at a constant pH of 2.0
C) to carry out life functions in extremely acidic conditions
D) to help transfer electrons from one atom to another
E) to increase the amount of OH- in their surroundings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Inside a living cell, which type of bond would be the most stable?
A) hydrogen
B) ionic
C) covalent
D) polar
E) all bonds are equally stable in a living system
A) hydrogen
B) ionic
C) covalent
D) polar
E) all bonds are equally stable in a living system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Sulfur has an atomic number of 16. What would be the valence number of this element?
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
E) Six
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
E) Six

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The subatomic particles that are found in the nucleus of an atom are the
A) protons and electrons.
B) neutrons and protons.
C) electrons only.
D) protons only.
E) electrons and neutrons.
A) protons and electrons.
B) neutrons and protons.
C) electrons only.
D) protons only.
E) electrons and neutrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is not a way in which chemical bonds can be formed?
A) sharing electrons
B) losing electrons
C) splitting electrons
D) gaining electrons
E) attracting opposite charges
A) sharing electrons
B) losing electrons
C) splitting electrons
D) gaining electrons
E) attracting opposite charges

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An ionic bond forms when
A) an atom gives away or takes in an electron.
B) an atom gives away or takes in a proton.
C) a negatively charged ion is attracted to one with a positive charge.
D) two atoms come close enough to share one or more electrons.
E) two atoms come close enough to share one or more protons.
A) an atom gives away or takes in an electron.
B) an atom gives away or takes in a proton.
C) a negatively charged ion is attracted to one with a positive charge.
D) two atoms come close enough to share one or more electrons.
E) two atoms come close enough to share one or more protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following describes how an acid disrupts the chemical bonds of molecules in a cell?
A) The H+ ions can disrupt hydrogen bonds as the slightly negative portion of the molecule is more attracted to H+ ions than to the hydrogen that was part of the bond.
B) The H+ ions can disrupt hydrogen bonds as the slightly positive portion of the molecule is more attracted to H+ ions than to the hydrogen that was part of the bond.
C) The OH- ions can disrupt hydrogen bonds as the slightly positive portion of the molecule is more attracted to H+ ions than to the hydrogen that was part of the bond.
D) The OH- ions can disrupt hydrogen bonds as the slightly negative portion of the molecule is more attracted to H+ ions than to the hydrogen that was part of the bond.
E) The H+ ions disrupt the covalent bonds that hold the molecule together.
A) The H+ ions can disrupt hydrogen bonds as the slightly negative portion of the molecule is more attracted to H+ ions than to the hydrogen that was part of the bond.
B) The H+ ions can disrupt hydrogen bonds as the slightly positive portion of the molecule is more attracted to H+ ions than to the hydrogen that was part of the bond.
C) The OH- ions can disrupt hydrogen bonds as the slightly positive portion of the molecule is more attracted to H+ ions than to the hydrogen that was part of the bond.
D) The OH- ions can disrupt hydrogen bonds as the slightly negative portion of the molecule is more attracted to H+ ions than to the hydrogen that was part of the bond.
E) The H+ ions disrupt the covalent bonds that hold the molecule together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following best describes the structure of how water molecules form and interact?
A) Hydrogen atoms bond with each other to create a stable outer shell of electrons. Then they form a hydrogen bond to an oxygen atom to create the water molecule.
B) Oxygen atoms transfer one electron to each of the hydrogen atoms, forming an ionic bond that attracts other water molecules to it.
Hydrogen bond attractions with other water molecules.
D) Hydrogen bonds are formed between the two hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atom. This water molecule then forms a covalent bond with adjacent water molecules.
E) The oxygen atom is more electronegative than the two hydrogen atoms. Due to this, it removes the electron from each hydrogen atom. This satisfies the outer shell of oxygen. Then hydrogen bonds form between the two remaining hydrogen atoms to hold them near to the oxygen atom.
A) Hydrogen atoms bond with each other to create a stable outer shell of electrons. Then they form a hydrogen bond to an oxygen atom to create the water molecule.
B) Oxygen atoms transfer one electron to each of the hydrogen atoms, forming an ionic bond that attracts other water molecules to it.
Hydrogen bond attractions with other water molecules.
D) Hydrogen bonds are formed between the two hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atom. This water molecule then forms a covalent bond with adjacent water molecules.
E) The oxygen atom is more electronegative than the two hydrogen atoms. Due to this, it removes the electron from each hydrogen atom. This satisfies the outer shell of oxygen. Then hydrogen bonds form between the two remaining hydrogen atoms to hold them near to the oxygen atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The pH of pure water is ________ because ________.
A) 7.0; water dissociates an equal number of H+ ions and OH- ions
B) 14.0; water dissociates and more OH- ions are formed because there are more hydrogen atoms in water
C) 1.0; water dissociates and more H+ ions are formed since hydrogen is smaller and can separate from the oxygen easily
D) 7.0; there are no ions formed in pure water
E) acidic; there are more H+ ions than OH- ions present
A) 7.0; water dissociates an equal number of H+ ions and OH- ions
B) 14.0; water dissociates and more OH- ions are formed because there are more hydrogen atoms in water
C) 1.0; water dissociates and more H+ ions are formed since hydrogen is smaller and can separate from the oxygen easily
D) 7.0; there are no ions formed in pure water
E) acidic; there are more H+ ions than OH- ions present

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The electron arrangement for argon, which has 18 electrons, is
A) 2 in the inner energy shell, 8 in the second energy shell, and 8 in the outer energy shell.
B) 8 in the inner energy shell, 8 in the second energy shell, and 2 in the outer energy shell.
C) 6 in the inner energy shell, 6 in the second energy shell, and 6 in the outer energy shell.
D) 5 in the inner energy shell, 6 in the second energy shell, and 7 in the outer energy shell.
E) 7 in the inner energy shell, 6 in the second energy shell, and 5 in the outer energy shell.
A) 2 in the inner energy shell, 8 in the second energy shell, and 8 in the outer energy shell.
B) 8 in the inner energy shell, 8 in the second energy shell, and 2 in the outer energy shell.
C) 6 in the inner energy shell, 6 in the second energy shell, and 6 in the outer energy shell.
D) 5 in the inner energy shell, 6 in the second energy shell, and 7 in the outer energy shell.
E) 7 in the inner energy shell, 6 in the second energy shell, and 5 in the outer energy shell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Some insects can stride on the surface of water because water
A) has a high specific heat.
B) has lower density when frozen.
C) is a good solvent.
D) has surface tension.
E) resists temperature changes.
A) has a high specific heat.
B) has lower density when frozen.
C) is a good solvent.
D) has surface tension.
E) resists temperature changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A covalent bond involves the sharing of
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) pairs of protons.
D) at least three electrons.
E) pairs of electrons.
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) pairs of protons.
D) at least three electrons.
E) pairs of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Radioactive isotopes are useful in biological studies because
A) an organism will take in a molecule with the isotope and use it normally, but the radioactive decay can be detected.
B) an organism will take in a molecule with the isotope but will only use it in a few specific reactions, not the normal ones.
C ) an organism will take in the molecule with the isotope and then remove the isotope by sending it through the excretory system, while replacing the isotope with a normal atom.
D) they are easily visible and normal atoms are not.
E) they are easy and inexpensive to use in studies.
A) an organism will take in a molecule with the isotope and use it normally, but the radioactive decay can be detected.
B) an organism will take in a molecule with the isotope but will only use it in a few specific reactions, not the normal ones.
C ) an organism will take in the molecule with the isotope and then remove the isotope by sending it through the excretory system, while replacing the isotope with a normal atom.
D) they are easily visible and normal atoms are not.
E) they are easy and inexpensive to use in studies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The reactivity of an atom depends on the number of
A) protons.
B) neutrons.
C) electrons.
D) valence electrons.
E) protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
A) protons.
B) neutrons.
C) electrons.
D) valence electrons.
E) protons and neutrons in the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Chemical bonds involve
A) the giving and taking of electrons.
B) the giving and taking of protons.
C) the giving, taking, or sharing of electrons.
D) the giving, taking, or sharing of protons.
E) the sharing of electrons.
A) the giving and taking of electrons.
B) the giving and taking of protons.
C) the giving, taking, or sharing of electrons.
D) the giving, taking, or sharing of protons.
E) the sharing of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 55 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



