Deck 26: Defenses Against Disease
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Defenses Against Disease
1
_____ cells are nonspecific, destroying cells which do not exhibit "self" proteins.
A) Complement
B) Mast
C) Natural killer
D) Helper T
E) Plasma
A) Complement
B) Mast
C) Natural killer
D) Helper T
E) Plasma
C
Explanation: Natural killer cells are lymphocytes that destroy cells without "self" proteins that they encounter. They do not multiply when exposed to specific pathogens and do not "remember" particular pathogens.
Explanation: Natural killer cells are lymphocytes that destroy cells without "self" proteins that they encounter. They do not multiply when exposed to specific pathogens and do not "remember" particular pathogens.
2
Which of the following is not true regarding B-cell receptors?
A) They bind with specific antigens.
B) They cause B cells to produce plasma cells and memory B cells when activated.
C) They may never encounter the antigen which binds to them.
D) They are identical to the antibodies produced by plasma cells, which they activated.
E) They may be changed by the B cell in response to whatever pathogen is present.
A) They bind with specific antigens.
B) They cause B cells to produce plasma cells and memory B cells when activated.
C) They may never encounter the antigen which binds to them.
D) They are identical to the antibodies produced by plasma cells, which they activated.
E) They may be changed by the B cell in response to whatever pathogen is present.
E
Explanation: When B cells are activated by the presence of a specific antigen, plasma cells and memory B cells are produced. B cells have receptors on their plasma membranes which are specific to the pathogen that activates them. Plasma cells produce antibodies identical to the B cell receptor and which facilitate the destruction of the pathogen. Memory B cells remain in the bloodstream, prepared to jump-start the immune response if that same pathogen enters the body again.
Explanation: When B cells are activated by the presence of a specific antigen, plasma cells and memory B cells are produced. B cells have receptors on their plasma membranes which are specific to the pathogen that activates them. Plasma cells produce antibodies identical to the B cell receptor and which facilitate the destruction of the pathogen. Memory B cells remain in the bloodstream, prepared to jump-start the immune response if that same pathogen enters the body again.
3
When a disease has been fought off by the immune system, what happens to the leftover cells that were produced by the immune system to fight the disease?
A) Apoptosis occurs.
B) They are saved for later use.
C) They are stored in the thymus gland.
D) They are destroyed by bone marrow.
E) They are killed by cytotoxic T cells.
A) Apoptosis occurs.
B) They are saved for later use.
C) They are stored in the thymus gland.
D) They are destroyed by bone marrow.
E) They are killed by cytotoxic T cells.
A
Explanation: After the immune system has successfully fought off an infection, most cells die through a type of self-destruction known as apoptosis. Memory B cells and memory T cells stay around and are responsible for any lasting immunity.
Explanation: After the immune system has successfully fought off an infection, most cells die through a type of self-destruction known as apoptosis. Memory B cells and memory T cells stay around and are responsible for any lasting immunity.
4
When the body responds against its own cells as foreign antigens, this results in
A) allergies.
B) autoimmune disease.
C) passive immunity.
D) anaphylactic shock.
E) active immunity.
A) allergies.
B) autoimmune disease.
C) passive immunity.
D) anaphylactic shock.
E) active immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not correct in describing the spleen?
A) It contains red pulp and white pulp.
B) It is an essential organ for survival.
C) It can be involved in fighting cancer.
D) It is spongy, containing many sinuses.
E) It is easily ruptured by a severe blow or infection.
A) It contains red pulp and white pulp.
B) It is an essential organ for survival.
C) It can be involved in fighting cancer.
D) It is spongy, containing many sinuses.
E) It is easily ruptured by a severe blow or infection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
T lymphocytes
A) migrate from the thymus to the bone marrow where they mature.
B) that recognize "self-cells" leave the thymus and enter lymphatic vessels and organs.
C) must have the antigen presented to them by an antigen-presenting cell.
D) develop into plasma cells once activated.
E) are a component of the body's nonspecific immune defenses.
A) migrate from the thymus to the bone marrow where they mature.
B) that recognize "self-cells" leave the thymus and enter lymphatic vessels and organs.
C) must have the antigen presented to them by an antigen-presenting cell.
D) develop into plasma cells once activated.
E) are a component of the body's nonspecific immune defenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
T-cell receptors will bind with their specific antigens
A) immediately upon encountering them.
B) when presented by an antigen-presenting cell.
C) after antibodies are produced for that antigen.
D) either immediately upon encountering them or when presented by an APC.
E) only in the presence of histamine.
A) immediately upon encountering them.
B) when presented by an antigen-presenting cell.
C) after antibodies are produced for that antigen.
D) either immediately upon encountering them or when presented by an APC.
E) only in the presence of histamine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not an autoimmune disease?
A) myasthenia gravis
B) rheumatoid arthritis
C) multiple sclerosis
D) systemic lupus erythematosus
E) tuberculosis
A) myasthenia gravis
B) rheumatoid arthritis
C) multiple sclerosis
D) systemic lupus erythematosus
E) tuberculosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Antibodies are _____ proteins, while antigens that elicit an immune reaction are _____ proteins.
A) bacterial; self-produced
B) self-produced; foreign
C) self-produced; also self-produced
D) cancer; bacterial
E) viral; self-produced
A) bacterial; self-produced
B) self-produced; foreign
C) self-produced; also self-produced
D) cancer; bacterial
E) viral; self-produced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What type of cells make up the filter seen in lymph nodes and the red pulp of the spleen?
A) T lymphocytes
B) B lymphocytes
C) mast cells
D) macrophages
E) areolar tissue
A) T lymphocytes
B) B lymphocytes
C) mast cells
D) macrophages
E) areolar tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following shows the function of cytotoxic T cells in the correct order?
A) perforin released - cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - granzymes delivered - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell
B) cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - granzymes delivered - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell - perforin released
C) apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell - perforin released - cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - perforin released
D) cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - perforin released - granzymes delivered - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell
E) granzymes delivered - perforin released - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell - cytotoxic T cell binds to
A) perforin released - cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - granzymes delivered - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell
B) cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - granzymes delivered - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell - perforin released
C) apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell - perforin released - cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - perforin released
D) cytotoxic T cell binds to virus-infected cell - perforin released - granzymes delivered - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell
E) granzymes delivered - perforin released - apoptosis occurs in virus-infected cell - cytotoxic T cell binds to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Bacteria that are moved out of the lungs by cilia in the respiratory system are prevented from entering the body because they are often killed by
A) lymphocytes in the saliva.
B) filters lining the pharynx.
C) stomach acid.
D) lymph nodes at the base of the tongue.
E) mucus in the trachea.
A) lymphocytes in the saliva.
B) filters lining the pharynx.
C) stomach acid.
D) lymph nodes at the base of the tongue.
E) mucus in the trachea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
During the inflammatory response, histamine may be released by
A) mast cells.
B) neutrophils.
C) B lymphocytes.
D) macrophages.
E) natural killer cells.
A) mast cells.
B) neutrophils.
C) B lymphocytes.
D) macrophages.
E) natural killer cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A person has type A blood. This means that
A) she has A antigens on her red blood cells and can only receive type A blood in transfusions.
B) she produces A antibodies when type A blood is used in transfusion, causing agglutination.
C) she has A antigens on her red blood cells and will produce antibodies if red blood cells with B antigens are transfused into her body.
D) she has B antigens on her red blood cells and can only receive type O blood.
E) she produces A antibodies when type B blood is used in a transfusion.
A) she has A antigens on her red blood cells and can only receive type A blood in transfusions.
B) she produces A antibodies when type A blood is used in transfusion, causing agglutination.
C) she has A antigens on her red blood cells and will produce antibodies if red blood cells with B antigens are transfused into her body.
D) she has B antigens on her red blood cells and can only receive type O blood.
E) she produces A antibodies when type B blood is used in a transfusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Long-term immunity to diseases such as measles occurs because
A) memory mast cells produce antibodies in response to pathogens entering the body.
B) plasma cells remain in the immune system to protect the body.
C) memory B cells are produced in response to specific pathogens.
D) neutrophils remain in the blood to phagocytize any new measles pathogens.
E) helper T cells continue to produce cytokines indefinitely.
A) memory mast cells produce antibodies in response to pathogens entering the body.
B) plasma cells remain in the immune system to protect the body.
C) memory B cells are produced in response to specific pathogens.
D) neutrophils remain in the blood to phagocytize any new measles pathogens.
E) helper T cells continue to produce cytokines indefinitely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Doctors can easily examine lymph nodes to see if a patient is fighting disease because
A) many lymph nodes are superficial.
B) all lymph nodes are superficial.
C) lymph nodes become hot when fighting disease.
D) lymph nodes secrete pus when fighting an infection.
E) lymph nodes are concentrated in the abdomen.
A) many lymph nodes are superficial.
B) all lymph nodes are superficial.
C) lymph nodes become hot when fighting disease.
D) lymph nodes secrete pus when fighting an infection.
E) lymph nodes are concentrated in the abdomen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is not a lymphatic organ?
A) thymus
B) spleen
C) pancreas
D) bone marrow
E) lymph node
A) thymus
B) spleen
C) pancreas
D) bone marrow
E) lymph node

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Neutrophils and macrophages are different in that
A) neutrophils produce antibodies, while macrophages do not.
B) neutrophils produce histamines, while macrophages produce antibodies.
C) neutrophils travel to the site of injury, while macrophages reside in certain tissues.
D) neutrophils phagocytize pathogens, while macrophages produce holes in a pathogen's membrane.
E) neutrophils are part of the inflammatory response, while macrophages are not.
A) neutrophils produce antibodies, while macrophages do not.
B) neutrophils produce histamines, while macrophages produce antibodies.
C) neutrophils travel to the site of injury, while macrophages reside in certain tissues.
D) neutrophils phagocytize pathogens, while macrophages produce holes in a pathogen's membrane.
E) neutrophils are part of the inflammatory response, while macrophages are not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
One way the complement system acts is by producing
A) proteins that assist neutrophils in recognizing a pathogen.
B) mast cells that attack pathogens'membranes.
C) histamines that stimulate B cell formation.
D) kinins that bind to the surface of pathogens.
E) macrophages that phagocytize bacteria.
A) proteins that assist neutrophils in recognizing a pathogen.
B) mast cells that attack pathogens'membranes.
C) histamines that stimulate B cell formation.
D) kinins that bind to the surface of pathogens.
E) macrophages that phagocytize bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
T lymphocytes mature in the
A) thyroid gland.
B) bone marrow.
C) thymus.
D) spleen.
E) blood.
A) thyroid gland.
B) bone marrow.
C) thymus.
D) spleen.
E) blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The secretions of the structure lettered "A" in the figure shown here
A) contain substances that will weaken or kill some bacteria on the skin.
B) cool the body through evaporative cooling.
C) release white blood cells on the surface of the skin.
D) are part of the body's specific defenses against disease.
E) attract white blood cells to cuts in order to fight infections.
A) contain substances that will weaken or kill some bacteria on the skin.
B) cool the body through evaporative cooling.
C) release white blood cells on the surface of the skin.
D) are part of the body's specific defenses against disease.
E) attract white blood cells to cuts in order to fight infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Natural killer cells can destroy cancer cells that have lost their "self" proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When people are hypersensitive to pollen, they have _____ in response to the antigens on pollen called _____.
A) an autoimmune disease; cytokines
B) immunity; allergens
C) an allergy; allergens
D) an allergy; IgG
E) immunity; antibodies
A) an autoimmune disease; cytokines
B) immunity; allergens
C) an allergy; allergens
D) an allergy; IgG
E) immunity; antibodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Active immunity involves all of the following except
A) exposure to a pathogen either naturally or by vaccination.
B) memory B cells responding to a second exposure to the same pathogen.
C) receiving mother's antibodies through the placenta and breast-feeding.
D) passive or active mechanisms.
E) the stimulation of a nonspecific immune defense.
A) exposure to a pathogen either naturally or by vaccination.
B) memory B cells responding to a second exposure to the same pathogen.
C) receiving mother's antibodies through the placenta and breast-feeding.
D) passive or active mechanisms.
E) the stimulation of a nonspecific immune defense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a person has a genetic defect in the metabolic pathway that produces cytokines, then
A) macrophages will not be produced by the immune system.
B) B cells would not be activated to respond when cells presenting antigens are present.
C) helper T cells would take over the role of activating B cells.
D) the spleen would destroy all red blood cells.
E) histamine will not be produced by mast cells.
A) macrophages will not be produced by the immune system.
B) B cells would not be activated to respond when cells presenting antigens are present.
C) helper T cells would take over the role of activating B cells.
D) the spleen would destroy all red blood cells.
E) histamine will not be produced by mast cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In this figure, "B" represents _____ which is released by "A", _____.
A) histamine; mast cells
B) histamine; neutrophils
C) antibodies; mast cells
D) pathogens; bacteria
E) antibodies; B cells
A) histamine; mast cells
B) histamine; neutrophils
C) antibodies; mast cells
D) pathogens; bacteria
E) antibodies; B cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In this figure, "A" is acting as an)
A) antigen-presenting cell.
B) helper T cell.
C) neutrophil.
D) antibody.
E) plasma cell.
A) antigen-presenting cell.
B) helper T cell.
C) neutrophil.
D) antibody.
E) plasma cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
HIV is contracted mainly by rectal intercourse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is not true about passive immunity?
A) It is temporary.
B) It can be gained by infants through breast milk.
C) It is achieved through the production of antibodies by the person gaining the immunity.
D) It can be achieved through injections of antibodies or immunoglobulins.
E) It can be used to prevent an illness in someone who has been exposed to that illness.
A) It is temporary.
B) It can be gained by infants through breast milk.
C) It is achieved through the production of antibodies by the person gaining the immunity.
D) It can be achieved through injections of antibodies or immunoglobulins.
E) It can be used to prevent an illness in someone who has been exposed to that illness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
This is a graph of antibodies in an immunized person's blood. At point B _____ is given that enhances the immunity to the pathogen. 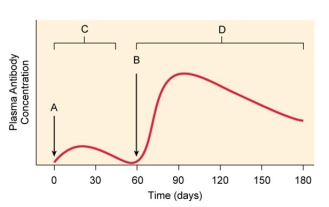
A) a booster
B) the primary exposure to the vaccine
C) a dose of antibodies
D) a live pathogen
E) histamine

A) a booster
B) the primary exposure to the vaccine
C) a dose of antibodies
D) a live pathogen
E) histamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
AIDS is caused by
A) the human immunodeficiency virus that destroys helper T cells.
B) the human immunodeficiency virus that stimulates apoptosis of immune system cells.
C) allergens that stimulate helper T cells to produce cytokines.
D) bacteria that destroy lymphocytes in the bone marrow.
E) the human immunodeficiency virus that destroys macrophages.
A) the human immunodeficiency virus that destroys helper T cells.
B) the human immunodeficiency virus that stimulates apoptosis of immune system cells.
C) allergens that stimulate helper T cells to produce cytokines.
D) bacteria that destroy lymphocytes in the bone marrow.
E) the human immunodeficiency virus that destroys macrophages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Immediate allergic responses occur when
A) IgE antibodies in red blood cells cause destruction of allergens.
B) IgE antibodies in mast cells attach to allergens, releasing histamines.
C) cytotoxic T cells produce histamine in response to allergens.
D) memory T cells release cytokines in response to allergens.
E) memory B cells respond to the presence of an allergen.
A) IgE antibodies in red blood cells cause destruction of allergens.
B) IgE antibodies in mast cells attach to allergens, releasing histamines.
C) cytotoxic T cells produce histamine in response to allergens.
D) memory T cells release cytokines in response to allergens.
E) memory B cells respond to the presence of an allergen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
During an inflammatory response, macrophages consume debris and cause the release of colony-stimulating factors which increase production of white blood cells by the bone marrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The letter "A" in the figure shown here is referring to an)
A) sweat gland.
B) oil sebaceous) gland.
C) salivary gland.
D) blood vessel.
E) lymph node.
A) sweat gland.
B) oil sebaceous) gland.
C) salivary gland.
D) blood vessel.
E) lymph node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
This figure represents
A) the events of the inflammatory response.
B) the first stages of immunity.
C) the complement system.
D) the antibody response.
E) the effects of an immunization on the blood.
A) the events of the inflammatory response.
B) the first stages of immunity.
C) the complement system.
D) the antibody response.
E) the effects of an immunization on the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Red bone marrow in adults produces only white blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which one of the following is a method of treatment for HIV infections?
A) chemotherapy
B) radiation treatment
C) blood transfusion
D) herbal supplements
E) drug therapy
A) chemotherapy
B) radiation treatment
C) blood transfusion
D) herbal supplements
E) drug therapy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The cells labeled "B"
A) produce cytokines that stimulate other types of immune cells.
B) destroy virus-infected cells through phagocytosis.
C) produce perforins and granzymes that destroy cancer cells.
D) produce histamine to induce the inflammatory response.
E) produce specific antibodies.
A) produce cytokines that stimulate other types of immune cells.
B) destroy virus-infected cells through phagocytosis.
C) produce perforins and granzymes that destroy cancer cells.
D) produce histamine to induce the inflammatory response.
E) produce specific antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Macrophages present antigens to T cells by digesting the pathogen and placing the pathogen's antigens on the macrophage plasma membrane along with an MHC "self" protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
After organ transplantation, immunosuppressive drugs are given that
A) stimulate T cell response to cytokines.
B) increase the production of histamines.
C) inhibit T cell response to cytokines.
D) both stimulate T cell response to cytokines and increase the production of histamines.
E) stimulate phagocytosis by macrophages.
A) stimulate T cell response to cytokines.
B) increase the production of histamines.
C) inhibit T cell response to cytokines.
D) both stimulate T cell response to cytokines and increase the production of histamines.
E) stimulate phagocytosis by macrophages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not an autoimmune disease?
A) AIDS
B) myasthenia gravis
C) multiple sclerosis
D) systemic lupus erythematosus
E) rheumatoid arthritis
A) AIDS
B) myasthenia gravis
C) multiple sclerosis
D) systemic lupus erythematosus
E) rheumatoid arthritis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which cell type plays a role in adaptive immunity in the body?
A) lymphocytes
B) red blood cells
C) platelets
D) epithelial cells
E) None of these cell types play a role in adaptive immunity.
A) lymphocytes
B) red blood cells
C) platelets
D) epithelial cells
E) None of these cell types play a role in adaptive immunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following statements is not true regarding the complement proteins?
A) They are blood plasma proteins.
B) Some form the membrane attack complex, which forms a hole in the bacterial plasma membrane.
C) They may amplify the inflammatory response by attracting phagocytes to the site of the infection.
D) They may bind to pathogens already coated with antibodies, ensuring they are phagocytized.
E) Many proteins must be independently activated in order to have a significant impact on the immune response.
A) They are blood plasma proteins.
B) Some form the membrane attack complex, which forms a hole in the bacterial plasma membrane.
C) They may amplify the inflammatory response by attracting phagocytes to the site of the infection.
D) They may bind to pathogens already coated with antibodies, ensuring they are phagocytized.
E) Many proteins must be independently activated in order to have a significant impact on the immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the statistics regarding the number of cases of HIV is not true?
A) Male-to-male contact accounts for the greatest number of new cases each year.
B) As of 2014, there were about 10 million people living worldwide with HIV.
C) In 2014, among the 2 million new HIV infections, nearly 11% were in people under the age of 15.
D) In 2014, HIV/AIDS claimed 1.2 million lives.
E) Heterosexual contact and intravenous drug use together account for a greater percentage of new cases than male-to-male contact.
A) Male-to-male contact accounts for the greatest number of new cases each year.
B) As of 2014, there were about 10 million people living worldwide with HIV.
C) In 2014, among the 2 million new HIV infections, nearly 11% were in people under the age of 15.
D) In 2014, HIV/AIDS claimed 1.2 million lives.
E) Heterosexual contact and intravenous drug use together account for a greater percentage of new cases than male-to-male contact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following bones does not contain red bone marrow in an adult?
A) pelvic bones
B) sternum
C) clavicle
D) vertebrae
E) carpals
A) pelvic bones
B) sternum
C) clavicle
D) vertebrae
E) carpals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which substances are examples of antigens?
A) proteins and carbohydrates
B) nucleic acids and proteins
C) lipids and proteins
D) lipids and carbohydrates
E) nucleic acids and carbohydrates
A) proteins and carbohydrates
B) nucleic acids and proteins
C) lipids and proteins
D) lipids and carbohydrates
E) nucleic acids and carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What organisms are commonly used to mass-produce vaccines?
A) bacteria
B) viruses
C) cattle
D) pigs
E) humans
A) bacteria
B) viruses
C) cattle
D) pigs
E) humans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which statement about delayed allergic reactions is the most accurate?
A) Memory T cells initiate the response at the site in which the allergen contacts the body.
B) Cytotoxic T cells initiate the response at the site in which the allergen contacts the body.
C) Memory T cells initiate the response at the site in which the antibodies contact the body.
D) The response can occur within a matter of seconds.
E) The response can lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure that can be life-threatening.
A) Memory T cells initiate the response at the site in which the allergen contacts the body.
B) Cytotoxic T cells initiate the response at the site in which the allergen contacts the body.
C) Memory T cells initiate the response at the site in which the antibodies contact the body.
D) The response can occur within a matter of seconds.
E) The response can lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure that can be life-threatening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which body system plays the smallest role in preventing and fighting an infection?
A) digestive system
B) skeletal system
C) cardiovascular system
D) lymphatic system
E) integumentary system
A) digestive system
B) skeletal system
C) cardiovascular system
D) lymphatic system
E) integumentary system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which body system plays the greatest role in fighting cancer?
A) immune system
B) cardiovascular system
C) neural system
D) digestive system
E) integumentary system
A) immune system
B) cardiovascular system
C) neural system
D) digestive system
E) integumentary system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements is correct about the usage of a booster?
A) The booster allows the antibody concentration to rise to a level higher than the primary response.
B) The booster will raise the antibody concentration in the individual by 10%.
C) The booster will cause the antibody concentration to rise and then decrease rapidly.
D) The booster will do nothing for the individual's immune response.
E) The booster will initiate the immune response.
A) The booster allows the antibody concentration to rise to a level higher than the primary response.
B) The booster will raise the antibody concentration in the individual by 10%.
C) The booster will cause the antibody concentration to rise and then decrease rapidly.
D) The booster will do nothing for the individual's immune response.
E) The booster will initiate the immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
_____ cells kill virus-infected cells and tumor cells by cell-to-cell contact.
A) Natural killer
B) Plasma
C) Cytotoxic T
D) Memory B
E) Helper T
A) Natural killer
B) Plasma
C) Cytotoxic T
D) Memory B
E) Helper T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which one of the following is not a symptom of an HIV infection?
A) progression into AIDS
B) number of T cells decreases
C) hair loss
D) chronic fever
E) Kaposi sarcoma, a form of cancer
A) progression into AIDS
B) number of T cells decreases
C) hair loss
D) chronic fever
E) Kaposi sarcoma, a form of cancer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the effect of T cells not undergoing apoptosis after the defeat of an infection?
A) An HIV infection may result.
B) Leukemia or lymphoma may result.
C) The future immunity is that much stronger.
D) An autoimmune disease may result.
E) An allergy may result.
A) An HIV infection may result.
B) Leukemia or lymphoma may result.
C) The future immunity is that much stronger.
D) An autoimmune disease may result.
E) An allergy may result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Approximately what percentage of T lymphocytes leave the thymus?
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 24%
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 24%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The immune system plays a significant role in fighting infections and cancer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
During tissue transplant, what is the main reason for the rejection of the transplanted tissue?
A) Cytotoxic T cells and antibodies in the body destroy the transplanted tissue.
B) Helper T cells and antibodies in the body destroy the transplanted tissue.
C) Cytotoxic T cells and antibodies will reroute the blood supply away from the transplanted tissue, starving it to death.
D) The host body's antigens will not allow the transplanted tissue to attach to the host.
E) The host body red blood cells will not carry oxygen to the transplanted tissue.
A) Cytotoxic T cells and antibodies in the body destroy the transplanted tissue.
B) Helper T cells and antibodies in the body destroy the transplanted tissue.
C) Cytotoxic T cells and antibodies will reroute the blood supply away from the transplanted tissue, starving it to death.
D) The host body's antigens will not allow the transplanted tissue to attach to the host.
E) The host body red blood cells will not carry oxygen to the transplanted tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which statement about vaccines is correct?
A) Vaccines will always cause the patient to become ill in order to build the immune system.
B) Vaccines never cause the patient to become ill in order to build the immune system.
C) Vaccines are not intended to cause the patient to become ill in order to build the immune system.
D) Vaccines need to be administered on a continuous basis in order to be effective.
E) It is only necessary to be vaccinated once in order to have immunity for your entire life.
A) Vaccines will always cause the patient to become ill in order to build the immune system.
B) Vaccines never cause the patient to become ill in order to build the immune system.
C) Vaccines are not intended to cause the patient to become ill in order to build the immune system.
D) Vaccines need to be administered on a continuous basis in order to be effective.
E) It is only necessary to be vaccinated once in order to have immunity for your entire life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What structures do the lymphocytes "recognize" in order to participate in active immunity?
A) antigens on the pathogen cell membrane
B) antigens within the DNA of the pathogen
C) protein complexes on the pathogen that bind with the lymphocyte DNA
D) phospholipids of the pathogen cell membrane
E) RNA complexes within the pathogen cell membrane
A) antigens on the pathogen cell membrane
B) antigens within the DNA of the pathogen
C) protein complexes on the pathogen that bind with the lymphocyte DNA
D) phospholipids of the pathogen cell membrane
E) RNA complexes within the pathogen cell membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which autoimmune disorder is characterized by a breakdown of the myelin sheaths on the nerve cells?
A) multiple sclerosis MS)
B) myasthenia gravis
C) systemic lupus erythematosus
D) rheumatoid arthritis
E) leukemia
A) multiple sclerosis MS)
B) myasthenia gravis
C) systemic lupus erythematosus
D) rheumatoid arthritis
E) leukemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



