Deck 22: Life and the Periodic Table
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/95
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Life and the Periodic Table
1
The average person has 15 mg of calcium per gram of body mass. How many pounds of calcium does a person weighing 150 lb contain? (1 lb = 454 g)
A) 22.5 lb
B) 0.225 lb
C) 2.25 lb
D) 10 lb
E) 15 lb
A) 22.5 lb
B) 0.225 lb
C) 2.25 lb
D) 10 lb
E) 15 lb
2.25 lb
2
Stomach acid is 0.16 M HCl. What is the pH of stomach acid?
A) 0.80
B) 8.0
C) -0.80
D) 0.69
E) -8.0
A) 0.80
B) 8.0
C) -0.80
D) 0.69
E) -8.0
0.80
3
Selenium can substitute for sulfur in the amino acid cysteine to make the amino acid selenocysteine because __________
A) sulfur and selenium both begin with s.
B) their atomic symbols are similar.
C) both have about the same atomic radius.
D) both have the same valence electron configuration.
E) both have about the same ionization potential.
A) sulfur and selenium both begin with s.
B) their atomic symbols are similar.
C) both have about the same atomic radius.
D) both have the same valence electron configuration.
E) both have about the same ionization potential.
both have the same valence electron configuration.
4
Radioactive 90Sr can substitute for __________ in the human body.
A) Na+
B) Ca2+
C) K+
D) S2-
E) Se2+
A) Na+
B) Ca2+
C) K+
D) S2-
E) Se2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which element, by mass, is most abundant in the human body?
A) carbon
B) oxygen
C) hydrogen
D) nitrogen
E) calcium
A) carbon
B) oxygen
C) hydrogen
D) nitrogen
E) calcium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which statement describing the mechanisms by which sodium ions pass through cell membranes is not correct?
A) Groups of proteins form ion channels for sodium ions.
B) Sodium ions can be transported by Na+ - K+ pumps.
C) Membrane proteins pump sodium ions through the membrane.
D) Sodium ions form complexes with nonpolar ligands that can diffuse through the membrane.
E) Sodium ions can diffuse directly through the membrane.
A) Groups of proteins form ion channels for sodium ions.
B) Sodium ions can be transported by Na+ - K+ pumps.
C) Membrane proteins pump sodium ions through the membrane.
D) Sodium ions form complexes with nonpolar ligands that can diffuse through the membrane.
E) Sodium ions can diffuse directly through the membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The concentration of an ultratrace essential element in the body is less than __________ per gram of body mass.
A) 1 g
B) 10 mg
C) 1 mg
D) 10 g
E) 1 g
A) 1 g
B) 10 mg
C) 1 mg
D) 10 g
E) 1 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Selenium, an ultratrace element, is used in the synthesis of selenocysteine, which is __________
A) an antioxidant.
B) a lipid.
C) a fatty acid.
D) a carbohydrate.
E) a nucleic acid base
A) an antioxidant.
B) a lipid.
C) a fatty acid.
D) a carbohydrate.
E) a nucleic acid base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The concentration of a major essential element in the body is greater than __________ per gram of body mass.
A) 1 g
B) 10 mg
C) 1 mg
D) 10 g
E) 1 g
A) 1 g
B) 10 mg
C) 1 mg
D) 10 g
E) 1 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Cell membranes are formed by __________
A) a lipid layer.
B) a lipid bilayer.
C) a phospholipid bilayer.
D) cellulose.
E) starch.
A) a lipid layer.
B) a lipid bilayer.
C) a phospholipid bilayer.
D) cellulose.
E) starch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Magnesium is found in which one of the following important biological molecules?
A) chlorophyll
B) hemoglobin
C) cytochrome C
D) ferridoxin
E) ATP
A) chlorophyll
B) hemoglobin
C) cytochrome C
D) ferridoxin
E) ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The release of radioactive cesium-137 into the environment by the nuclear accident at Chernobyl produced a health hazard because cesium ions can substitute for __________ in plants, making them unsafe for human consumption.
A) Mg2+
B) K+
C) Ca2+
D) Li+
E) H+
A) Mg2+
B) K+
C) Ca2+
D) Li+
E) H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which element, by the number of atoms, is most abundant in the human body?
A) carbon
B) oxygen
C) hydrogen
D) nitrogen
E) calcium
A) carbon
B) oxygen
C) hydrogen
D) nitrogen
E) calcium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which element, by the number of atoms, is least abundant in the human body?
A) sodium
B) calcium
C) potassium
D) magnesium
E) nitrogen
A) sodium
B) calcium
C) potassium
D) magnesium
E) nitrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Selenocysteine is an amino acid that gets incorporated into proteins that serve as antioxidants. Evidence points to a need for a minimum daily dose of selenium of 55 g. How many moles of selenocysteine (C3H7NO2Se, 168 g/mol) can be synthesized using this amount of selenium?
A) 3.3 *10-7 mol
B) 7.0*10-7 mol
C) 3.3 * 10-4 mol
D) 7.0 * 10-4 mol
E) 3.7* 10-7 mol
A) 3.3 *10-7 mol
B) 7.0*10-7 mol
C) 3.3 * 10-4 mol
D) 7.0 * 10-4 mol
E) 3.7* 10-7 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Plants convert nitrate into ammonia by using enzymes called __________
A) peptidases.
B) amylases.
C) anhydrases.
D) oxidases.
E) reductases.
A) peptidases.
B) amylases.
C) anhydrases.
D) oxidases.
E) reductases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Stomach acid has a pH of 0.80. What is the molar concentration of the acid, HCl?
A) 0.55 M
B) 0.25 M
C) 3.98 M
D) 1.82 M
E) 0.16 M
A) 0.55 M
B) 0.25 M
C) 3.98 M
D) 1.82 M
E) 0.16 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The concentration of a trace essential element in the body is typically in the range of __________ per gram of body mass.
A) 1 g to 1 mg
B) 1 g to 10 mg
C) 10 g to 10 mg
D) 10 g to 100 mg
E) 100 g to 100 mg
A) 1 g to 1 mg
B) 1 g to 10 mg
C) 10 g to 10 mg
D) 10 g to 100 mg
E) 100 g to 100 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Tooth enamel is composed of the calcium compound called __________
A) hydrophilite.
B) apatite.
C) hydroxyapatite.
D) calcite.
E) andradite.
A) hydrophilite.
B) apatite.
C) hydroxyapatite.
D) calcite.
E) andradite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Selenium is an ultratrace element that is essential for life. It is used in the synthesis of __________, which is __________
A) selenocysteine; a lipid.
B) cysteine; an amino acid.
C) selenocysteine; an amino acid.
D) selenocysteine; a fatty acid.
E) selenothymine; a nucleic acid base.
A) selenocysteine; a lipid.
B) cysteine; an amino acid.
C) selenocysteine; an amino acid.
D) selenocysteine; a fatty acid.
E) selenothymine; a nucleic acid base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An essential biological element __________
A) is any element detected in the organism.
B) stimulates essential biological functions.
C) is found in all organisms.
D) has beneficial physiological effects, and its absence impairs function of the organism.
E) is expensive.
A) is any element detected in the organism.
B) stimulates essential biological functions.
C) is found in all organisms.
D) has beneficial physiological effects, and its absence impairs function of the organism.
E) is expensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Nickel-cadmium batteries thrown into landfills can introduce cadmium ions into the ground water. Cadmium ions can replace __________ in bones, which can weaken them.
A) Na+
B) K+
C) Zn2+
D) Ca2+
E) Mg2+
A) Na+
B) K+
C) Zn2+
D) Ca2+
E) Mg2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Hydroxyapatite, which is a component of tooth enamel, is very insoluble in water. For the following reaction, Ksp = 2.3 *10-59. Ca5(PO4)3(OH)(s) Ca5(PO4)3+(aq) + OH-(aq)
What is the molar concentration of Ca5(PO4)3+ when the pH of the mouth is 4.0?
A) 2.3 * 10-49 M
B) 2.3* 10-59 M
C) 2.3 * 10-55 M
D) 2.3 * 10-63 M
E) 0, teeth don't dissolve!
What is the molar concentration of Ca5(PO4)3+ when the pH of the mouth is 4.0?
A) 2.3 * 10-49 M
B) 2.3* 10-59 M
C) 2.3 * 10-55 M
D) 2.3 * 10-63 M
E) 0, teeth don't dissolve!

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Shape memory alloys are used in __________
A) artificial joints.
B) stents to prop open arteries.
C) sutures to close wounds.
D) braces for teeth.
E) screws to connect broken bones.
A) artificial joints.
B) stents to prop open arteries.
C) sutures to close wounds.
D) braces for teeth.
E) screws to connect broken bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a nonessential biological element?
A) detected in the body but has no clear biological function
B) has a stimulatory effect on biological functions
C) often are incorporated into biological compounds because they are similar to essential elements
D) has clear biological functions
E) organisms require them for survival
A) detected in the body but has no clear biological function
B) has a stimulatory effect on biological functions
C) often are incorporated into biological compounds because they are similar to essential elements
D) has clear biological functions
E) organisms require them for survival

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Plants react urea with water to produce ammonia and carbon dioxide. This reaction is an example of a __________ reaction.
A) redox
B) metathesis
C) hydrolysis
D) combustion
E) precipitation
A) redox
B) metathesis
C) hydrolysis
D) combustion
E) precipitation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Enzymes in plants convert nitrate into ammonia. The unbalanced half-reaction equation is given below. What is the change in oxidation number of nitrogen in this reaction? NO3-(aq) + H2O(  ) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)
) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)
A) 0
B) +5
C) +3
D) -2
E) -3
 ) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)
) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)A) 0
B) +5
C) +3
D) -2
E) -3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The isotope 201Th is used in the diagnosis of heart disease. It has a first-order rate constant, k, of 9.49 *10-3 h-1. What is the half-life for 201Th?
A) 73 hr
B) 0.014 hr
C) 9.49 * 10-3 hr
D) 7.3 hr
E) 1.4 hr
A) 73 hr
B) 0.014 hr
C) 9.49 * 10-3 hr
D) 7.3 hr
E) 1.4 hr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Urea is a waste product produced when the body metabolizes protein. What is the oxidation number of nitrogen in urea, (NH2)2CO?
A) +3
B) -3
C) 1
D) -1
E) -4
A) +3
B) -3
C) 1
D) -1
E) -4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Adding fluoride ions to toothpaste and drinking water converts the mineral in tooth enamel, hydroxyapatite, to fluoroapatite. This conversion is beneficial in preventing tooth decay because fluoroapatite __________
A) solubility is less pH dependent.
B) makes strong hydrogen bonds.
C) prevents halitosis.
D) repels decay-producing bacteria.
E) kills decay-producing bacteria.
A) solubility is less pH dependent.
B) makes strong hydrogen bonds.
C) prevents halitosis.
D) repels decay-producing bacteria.
E) kills decay-producing bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Adding fluoride ions to toothpaste and drinking water to prevent tooth decay is effective because fluoride __________
A) kills decay producing bacteria.
B) produces stronger teeth.
C) reduces the solubility of tooth enamel at low pH.
D) reduces the solubility of tooth enamel at high pH.
E) prevents halitosis.
A) kills decay producing bacteria.
B) produces stronger teeth.
C) reduces the solubility of tooth enamel at low pH.
D) reduces the solubility of tooth enamel at high pH.
E) prevents halitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Plants convert nitrogen into ammonia. This biological nitrogen fixation is effected by enzymes called nitrogenases. The enzymes assist in the transfer of electrons. The unbalanced reaction equation is N2(g) + H+(aq) + e- H2(g) + NH3(aq)
What is the change in the oxidation number of nitrogen in this reaction?
A) +1
B) -3
C) +3
D) +2
E) -1
What is the change in the oxidation number of nitrogen in this reaction?
A) +1
B) -3
C) +3
D) +2
E) -1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Iodine's role is very specific. It is incorporated into a hormone, __________, which regulates energy production and use.
A) melatonin
B) thyroxine
C) dopamine
D) insulin
E) iodocin
A) melatonin
B) thyroxine
C) dopamine
D) insulin
E) iodocin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Enzymes in plants convert nitrate into ammonia. The unbalanced half-reaction equation is given below. What is the stoichiometric coefficient of the hydroxide in the balanced reaction equation? NO3-(aq) + H2O(  ) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)
) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
 ) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)
) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Thallium-201 is used in cardiac imaging. It decays by electron capture. What isotope is produced when thallium-201 captures an electron?
A) thallium-202
B) lead-201
C) lead-202
D) mercury-201
E) mercury-202
A) thallium-202
B) lead-201
C) lead-202
D) mercury-201
E) mercury-202

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Rhenium-186 has medical applications. It decays by emission. What isotope is formed from this decay?
A)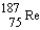
B)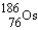
C)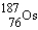
D)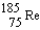
E)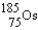
A)
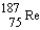
B)
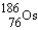
C)
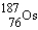
D)
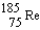
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Plants convert nitrogen into ammonia. This biological nitrogen fixation is effected by enzymes called nitrogenases. The enzymes assist in the transfer of electrons. The unbalanced reaction equation is N2(g) + H+(aq) + e- H2(g) + NH3(aq)
What is the stoichiometric coefficient for the electrons in the balanced reaction equation?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
What is the stoichiometric coefficient for the electrons in the balanced reaction equation?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Enzymes in plants convert nitrate into ammonia. The unbalanced half-reaction equation is given below. What is the stoichiometric coefficient of the electrons, e-, in the balanced reaction equation? NO3-(aq) + H2O( 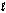 ) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)
) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
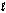 ) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)
) + e- NO2-(aq) + OH-(aq)A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Technetium can be produced in a nuclear reactor for medical applications and is given the symbol 99mTc. What does the m stand for?
A) microstate
B) metastable excited state
C) microstable excited state
D) medical isotope
E) massive isotope
A) microstate
B) metastable excited state
C) microstable excited state
D) medical isotope
E) massive isotope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Plants convert nitrogen into ammonia. This biological nitrogen fixation is effected by enzymes called nitrogenases. The enzymes assist in the transfer of electrons. The unbalanced reaction equation is N2(g) + H+(aq) + e- H2(g) + NH3(aq)
What is the stoichiometric coefficient for ammonia in the balanced reaction equation?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
What is the stoichiometric coefficient for ammonia in the balanced reaction equation?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Chromium is an ultratrace metal in the human body with a typical concentration of 5.0 mg in 75 kg of body mass. What is this concentration in units of parts per billion (ppb)?
A) 6.7 *107 ppb
B) 6.7 * 104 ppb
C) 67 ppb
D) 0.067 ppb
E) 0.67 ppb
A) 6.7 *107 ppb
B) 6.7 * 104 ppb
C) 67 ppb
D) 0.067 ppb
E) 0.67 ppb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Iron accumulation in the human body has been implicated in some diseases. A chelating ligand sometimes is administered to treat these diseases. This treatment works because the ligand __________
A) oxidizes iron(II) to iron(III).
B) reduces iron(III) to iron(II).
C) precipitates the iron.
D) binds the iron to a protein.
E) forms a complex with the iron, which then is eliminated from the blood.
A) oxidizes iron(II) to iron(III).
B) reduces iron(III) to iron(II).
C) precipitates the iron.
D) binds the iron to a protein.
E) forms a complex with the iron, which then is eliminated from the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Hearing aid batteries utilize a zinc/air electrochemical cell. The reduction half-reactions and standard reduction potentials for this cell are given below. What species are oxidized and reduced in the cell reaction? Zn(OH)2(s) + 2e- Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq)
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O(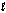 ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
+0)401 V
A) Oxygen is reduced and zinc is oxidized.
B) Zinc is reduced and oxygen is oxidized.
C) Zinc hydroxide is reduced and oxygen is oxidized.
D) Zinc hydroxide is reduced and hydroxide is oxidized.
E) Water is reduced and zinc is oxidized.
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O(
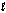 ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)+0)401 V
A) Oxygen is reduced and zinc is oxidized.
B) Zinc is reduced and oxygen is oxidized.
C) Zinc hydroxide is reduced and oxygen is oxidized.
D) Zinc hydroxide is reduced and hydroxide is oxidized.
E) Water is reduced and zinc is oxidized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The average concentration of calcium in the human body is 15 mg/g of body mass. What is the mass of calcium in the body of a person weighing 150 lbs? (1 lb = 454 g)
A) 1.0 lbs
B) 0.023 lbs
C) 23 lbs
D) 100 lbs
E) 2.3 lbs
A) 1.0 lbs
B) 0.023 lbs
C) 23 lbs
D) 100 lbs
E) 2.3 lbs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Hearing aid batteries utilize a zinc/air electrochemical cell. The reduction half-reactions and standard reduction potentials for this cell are given below. What is the reducing agent in the cell reaction? Zn(OH)2(s) + 2e- Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq)
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O(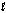 ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
+0)401 V
A) oxygen
B) zinc
C) zinc hydroxide
D) hydroxide
E) water
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O(
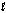 ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)+0)401 V
A) oxygen
B) zinc
C) zinc hydroxide
D) hydroxide
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Calcium carbonate is used to form exoskeletons. It has a solubility-product constant of 5.0 *10-9. What is the molar concentration of calcium ions in a saturated solution of calcium carbonate?
A) 2.5 * 10-9 M
B) 7.1 *10-5 M
C) 3.5 *10-5 M
D) 5.0 * 10-9 M
E) 4.7 *10-7 M
A) 2.5 * 10-9 M
B) 7.1 *10-5 M
C) 3.5 *10-5 M
D) 5.0 * 10-9 M
E) 4.7 *10-7 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Copper is a trace metal in the human body with a typical concentration of 110 mg in 75 kg of body mass. What is this concentration in units of parts per million (ppm)?
A) 1.5 * 10-6 ppm
B) 1.5 ppm
C) 1.1 * 10-5 ppm
D) 1.1 *10-7 ppm
E) 150 ppm
A) 1.5 * 10-6 ppm
B) 1.5 ppm
C) 1.1 * 10-5 ppm
D) 1.1 *10-7 ppm
E) 150 ppm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Pacemakers implanted in the chests of patients with certain heart conditions are powered by a lithium/iodine PVP battery, where PVP represents polyvinylpyridine. The cell reaction and standard cell potential are given below. The standard reduction potential for Li/Li+ is -3.05 V. What is the standard reduction potential for the iodine PVP half-reaction? 2Li(s) + I2:PVP(s) 2LiI(s) + PVP(s)
3)59 V
A) +1.50 V
B) -6.64 V
C) -0.54 V
D) +6.64 V
E) +0.54 V
3)59 V
A) +1.50 V
B) -6.64 V
C) -0.54 V
D) +6.64 V
E) +0.54 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Different concentrations of ions on either side of a cell membrane constitute a concentration cell, which is described by the Nernst equation given below. What is the electrochemical potential across a membrane when the sodium ion concentration is 0.10 M on one side of the membrane and 0.010 M on the other side, and the temperature is 37°C (body temperature)? (Given: Na+ + e- Na, 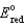 = -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K)
= -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K) 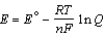
A) 61.5 mV
B) 26.7 mV
C) 2.65 V
D) 2.68 V
E) 2.98 V
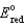 = -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K)
= -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K) 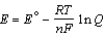
A) 61.5 mV
B) 26.7 mV
C) 2.65 V
D) 2.68 V
E) 2.98 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Pacemakers implanted in the chests of patients with certain heart conditions are powered by a lithium/iodine PVP battery, where PVP represents polyvinylpyridine. The cell reaction and standard cell potential are given below. The standard reduction potential for Li/Li+ is -3.05 V. What species is oxidized in this reaction? 2Li(s) + I2:PVP(s) 2LiI(s) + PVP(s)
3)59 V
A) Li
B) I2
C) I2:PVP
D) PVP
E) LiI
3)59 V
A) Li
B) I2
C) I2:PVP
D) PVP
E) LiI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
How much energy must be expended by a cell to transport 1 mole of sodium ions across a membrane with an electrochemical potential of 62 mV in order to maintain this potential?
A) 50 kJ
B) 260 kJ
C) 6.0 kJ
D) 250 kJ
E) 6000 kJ
A) 50 kJ
B) 260 kJ
C) 6.0 kJ
D) 250 kJ
E) 6000 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Radioactive tritium, 3H, is used as a tracer in many biological experiments. It decays by emission. What is the product of this decay?
A)(3He)
B)(4He)
C)(2H)
D)(14C)
E)("2H")
A)(3He)
B)(4He)
C)(2H)
D)(14C)
E)("2H")

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Different concentrations of ions on either side of a cell membrane constitute a concentration cell, which is described by the Nernst equation given below. A cell must expend energy to maintain this concentration gradient by moving ions from one side of the membrane to the other. How much energy must be expended to transport 1 mole of sodium ions across a membrane when the sodium ion concentration is 0.10 M on one side of the membrane and 0.010 M on the other side, and the temperature is 37°C (body temperature)? (Given: Na+ + e- Na, 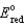 = -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K)
= -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K) 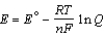
A) 50 kJ
B) 260 kJ
C) 6.0 kJ
D) 250 kJ
E) 6000 kJ
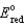 = -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K)
= -2.71 V; F = 96,485 C; 1 J = 1 C V; R = 8.315 J / mol K) 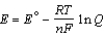
A) 50 kJ
B) 260 kJ
C) 6.0 kJ
D) 250 kJ
E) 6000 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The concentration of sodium in the human body is approximately 1.5 mg/g of body mass. What is this concentration in ppm (parts per million)?
A) 1.5 *106 ppm
B) 1.5 *10-3 ppm
C) 0.015 ppm
D) 1500 ppm
E) 150 ppm
A) 1.5 *106 ppm
B) 1.5 *10-3 ppm
C) 0.015 ppm
D) 1500 ppm
E) 150 ppm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Hearing aid batteries utilize a zinc/air electrochemical cell. The reduction half-reactions and standard reduction potentials for this cell are given below. What is the oxidizing agent in the cell reaction? Zn(OH)2(s) + 2e- Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq)
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O(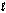 ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
+0)401 V
A) oxygen
B) zinc
C) zinc hydroxide
D) hydroxide
E) water
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O(
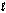 ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)+0)401 V
A) oxygen
B) zinc
C) zinc hydroxide
D) hydroxide
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Hearing aid batteries utilize a zinc/air electrochemical cell. The reduction half-reactions and standard reduction potentials for this cell are given below. Write the balanced reaction equation for the cell and report the sum of the stoichiometric coefficients. Zn(OH)2(s) + 2e- Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq)
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O(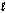 ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
+0)401 V
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 8
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O(
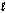 ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)+0)401 V
A) 4
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Fluoridation to prevent tooth decay replaces __________ with fluoride in hydroxyapatite.
A) hydroxide
B) phosphate
C) phosphide
D) calcium
E) water
A) hydroxide
B) phosphate
C) phosphide
D) calcium
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The concentration of Li in the human body is approximately 30 ng/g body mass. How many g of Li are there in a person weighing 170 lb? 1 lb = 454 g
A) 2.3 * 106 g
B) 5100 g
C) 2.3 103 g
D) 1.1 10-2 g
E) 2.3 10-3 g
A) 2.3 * 106 g
B) 5100 g
C) 2.3 103 g
D) 1.1 10-2 g
E) 2.3 10-3 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Hearing aid batteries utilize a zinc/air electrochemical cell. The reduction half-reactions and standard reduction potentials for this cell are given below. What is the standard cell potential of a zinc/air cell? Zn(OH)2(s) + 2e- Zn(s) + 2OH-(aq)
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O( ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
+0)401 V
A) -0.848 V
B) +1.500 V
C) 0.848 V
D) +1.650 V
E) -1.650 V
-1)249 V
O2(g) + 2H2O(
 ) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)
) + 4e- 4OH-(aq)+0)401 V
A) -0.848 V
B) +1.500 V
C) 0.848 V
D) +1.650 V
E) -1.650 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
One reason some metals have toxic effects is that they can replace other metals in a biomolecule and thereby inhibit or destroy the function of the biomolecule. Such replacement depends on the charge and size of the metal ion. For each of the following pairs of metal ions, identify the one that is larger. (Ca2+, Mg2+)
(Ca2+, Zn2+)
(P3+, As3+)
A) Ca2+; Ca2+; P3+
B) Ca2+; Ca2+; As3+
C) Mg2+; Ca2+; As3+
D) Ca2+; Zn2+; P3+
E) Ca2+; Zn2+; As3+
(Ca2+, Zn2+)
(P3+, As3+)
A) Ca2+; Ca2+; P3+
B) Ca2+; Ca2+; As3+
C) Mg2+; Ca2+; As3+
D) Ca2+; Zn2+; P3+
E) Ca2+; Zn2+; As3+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the dominant role played by iodine in the body?
A) maintains osmotic pressure
B) transmits nerve impulses
C) forms structural materials
D) a key component in enzymes
E) important in the function of the thyroid gland
A) maintains osmotic pressure
B) transmits nerve impulses
C) forms structural materials
D) a key component in enzymes
E) important in the function of the thyroid gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Nitrogen is a major essential element in the human body. Which biomolecules incorporate nitrogen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Urease is an enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide. The rate constant for the uncatalyzed reaction is 4.0 *10-11/s at 22°C. Urease increases the rate constant to a value of 8.0 * 10-5/s. Use the Arrhenius equation, which is given below, to determine the difference in the activation energies Euncatalyzed - Ecatalyzed. (R = 8.315 J/mol K) 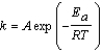
A) 23 kJ/mol
B) 2.3 kJ/mol
C) 15 kJ/mol
D) 36 kJ/mol
E) 51 kJ/mol
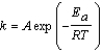
A) 23 kJ/mol
B) 2.3 kJ/mol
C) 15 kJ/mol
D) 36 kJ/mol
E) 51 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Calcium carbonate is used to form exoskeletons. It has a solubility-product constant of 5.0 *10-9. What is the mass of calcium ions dissolved in 1.0 L of a saturated solution of calcium carbonate?
A) 101 ng
B) 2.8 mg
C) 1.4 mg
D) 201 ng
E) 16 g
A) 101 ng
B) 2.8 mg
C) 1.4 mg
D) 201 ng
E) 16 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the dominant role played by calcium in the body?
A) maintains osmotic pressure
B) transmits nerve impulses
C) forms structural materials
D) a key component in enzymes
E) important in the function of the thyroid gland
A) maintains osmotic pressure
B) transmits nerve impulses
C) forms structural materials
D) a key component in enzymes
E) important in the function of the thyroid gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which statement regarding mercury poisoning is not correct?
A) Mercury is readily transformed into methylmercury(II).
B) Methylmercury(II) is highly toxic because it can readily diffuse through the lipid bilayer of membranes.
C) Mercury(II) ions bind to sulfur-containing amino acids.
D) Mercury is stabilized and is not leached from amalgams used in dentistry.
E) Methylmercury(II) is a +2 cation.
A) Mercury is readily transformed into methylmercury(II).
B) Methylmercury(II) is highly toxic because it can readily diffuse through the lipid bilayer of membranes.
C) Mercury(II) ions bind to sulfur-containing amino acids.
D) Mercury is stabilized and is not leached from amalgams used in dentistry.
E) Methylmercury(II) is a +2 cation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The active site of an enzyme typically contains __________
A) an alkali metal.
B) an alkaline earth metal.
C) a transition metal.
D) an actinide metal.
E) a lanthanide metal.
A) an alkali metal.
B) an alkaline earth metal.
C) a transition metal.
D) an actinide metal.
E) a lanthanide metal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Barium is a nonessential element in the human body, but some organisms build exoskeletons using barium sulfate, which has a Ksp of 1.1 *10-10 at 25°C. How many grams of barium are there in 1.0 L of a saturated solution of barium sulfate at 25°C?
A) 4.1 g
B) 1.4 mg
C) 3.7 mg
D) 7.3 g
E) 15 ng
A) 4.1 g
B) 1.4 mg
C) 3.7 mg
D) 7.3 g
E) 15 ng

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Tooth enamel is composed of the mineral hydroxyapatite. It is essentially insoluble in water with Ksp = 2.3 * 10-59, but it reacts with weak acids in the mouth as described by one of the reaction equations below. You can determine the equilibrium constant, K, for this reaction from Ksp and Kw (the equilibrium constant for water autoionization). How do you do this? Ca5 (PO4)3(OH)(s) Ca5 (PO4)3+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Ca5 (PO4)3(OH)(s) + H+(aq) Ca5 (PO4)3+(aq) + H2O(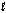 )
)
A) K = KwKsp
B) K = Kw /Ksp
C) K = Ksp /Kw
D) K = Kw - Ksp
E) K = Kw + Ksp
Ca5 (PO4)3(OH)(s) + H+(aq) Ca5 (PO4)3+(aq) + H2O(
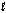 )
)A) K = KwKsp
B) K = Kw /Ksp
C) K = Ksp /Kw
D) K = Kw - Ksp
E) K = Kw + Ksp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Tooth enamel is composed of the mineral hydroxyapatite. It is essentially insoluble in water with Ksp = 2.3 *10-59, but it reacts with weak acids in the mouth as described by one of the reaction equations below. You can determine the equilibrium constant, K, for this reaction from Ksp and Kw (the equilibrium constant for water autoionization, Kw = 1.0 * 10-14). What is its value? Ca5 (PO4)3(OH)(s) Ca5 (PO4)3+(aq) + OH-(aq)
Ca5 (PO4)3(OH)(s) + H+(aq) Ca5 (PO4)3+(aq) + H2O(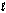 )
)
A) 2.3*10-73
B) 4.3 * 1045
C) 2.3 * 10-45
D) 1.1 * 10-14
E) 9.9 *10-15
Ca5 (PO4)3(OH)(s) + H+(aq) Ca5 (PO4)3+(aq) + H2O(
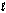 )
)A) 2.3*10-73
B) 4.3 * 1045
C) 2.3 * 10-45
D) 1.1 * 10-14
E) 9.9 *10-15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The cation BiO+ is found in some over-the-counter antacids. Draw the Lewis structure of this cation that satisfies the octet rule for both atoms. Based on this Lewis structure, this cation has __________ of nonbonding electrons.
A) a triple bond and two pairs
B) a single bond and six pairs
C) a double bond and three pairs
D) a single bond and four pairs
E) a quadruple bond and one pair
A) a triple bond and two pairs
B) a single bond and six pairs
C) a double bond and three pairs
D) a single bond and four pairs
E) a quadruple bond and one pair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The essential elements found in the human body are classified as major, trace, and ultratrace based on their concentration levels. What are the concentration ranges that define each of these classifications?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A patient is injected with a 5.0 M solution of gallium citrate containing radioactive gallium-68 for a PET study. The half-life of gallium-68 is 9.4 hr. How long does it take for the activity of this isotope to drop to 1% of its initial value?
A) 18 hr
B) 25 hr
C) 32 hr
D) 41 hr
E) 62 hr
A) 18 hr
B) 25 hr
C) 32 hr
D) 41 hr
E) 62 hr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An enzyme catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide at 20°C. The activation energy for the uncatalyzed reaction is 75.3 kJ/mol. The activation energy for the catalyzed reaction is 29.3 kJ/mol. By what factor is the rate of the reaction increased by the enzyme? Use the Arrhenius equation, which is given below, to determine the ratio of rate constants, kcatalyzed/kuncatalyzed. (R = 8.315 J/mol K) 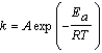
A) 1.6 *105
B) 1.6 *1011
C) 1.6 * 108
D) 7.6
E) 6100
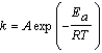
A) 1.6 *105
B) 1.6 *1011
C) 1.6 * 108
D) 7.6
E) 6100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which ion is important in transmitting nerve impulses?
A) Na+
B) Mg2+
C) Fe2+
D) Zn2+
E) Li+
A) Na+
B) Mg2+
C) Fe2+
D) Zn2+
E) Li+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A radioactive isotope that emits the shortest range particles and therefore would be a good choice for implantation therapy most likely decays via __________
A) alpha particles.
B) beta particles.
C) positrons.
D) gamma rays.
E) X-rays.
A) alpha particles.
B) beta particles.
C) positrons.
D) gamma rays.
E) X-rays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The ion found in chlorophyll is __________
A) Zn2+
B) Mg2+
C) Ca2+
D) Fe2+
E) Cu2+
A) Zn2+
B) Mg2+
C) Ca2+
D) Fe2+
E) Cu2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Ions need to move in and out of cells through cell membranes. Direct diffusion of ions through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane is difficult because ions are not soluble in these nonpolar regions. Describe three mechanisms by which ions are transported through cell membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Calcium is a major essential element in the human body. What is the dominant role played by calcium?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Chromium is an ultratrace metal in the human body. The typical concentration is 5.0 mg in 70.0 kg of body mass. This concentration can be expressed as __________
A) 0.071 ppm or 71 ppb.
B) 71 ppm or 0.071 ppb.
C) 14 ppm or 14,000 ppb
D) 0.71 ppm or 710 ppb
E) 5.0 ppm or 500 ppb
A) 0.071 ppm or 71 ppb.
B) 71 ppm or 0.071 ppb.
C) 14 ppm or 14,000 ppb
D) 0.71 ppm or 710 ppb
E) 5.0 ppm or 500 ppb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



