Deck 20: Biochemistry: the Compounds of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Biochemistry: the Compounds of Life
1
Which of the following statements is not correct? Triglycerides __________
A) have both structural isomers and stereoisomers.
B) are soluble in water.
C) are made from glycerol combining with three fatty acids.
D) are lipids.
E) have ester groups.
A) have both structural isomers and stereoisomers.
B) are soluble in water.
C) are made from glycerol combining with three fatty acids.
D) are lipids.
E) have ester groups.
are soluble in water.
2
Which of the following compounds is an -amino acid?
A)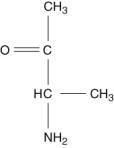
B)
C)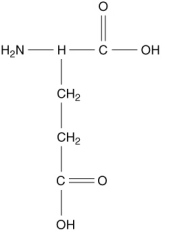
D)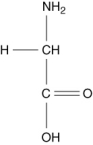
A)

B)

C)

D)


3
How many different nucleotides are used to create DNA and RNA?
A) 2
B) 5
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6
A) 2
B) 5
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6
5
4
At a physiological pH of 7.4, amino acids exist as zwitterions. At a very low pH (in an acid solution), both the amine group and the carboxylic acid group on an amino acid are protonated. Which acid group is the stronger acid?
A) -NH2
B) -NH3+
C) -COOH
D) -COO-
E) -H3O+
A) -NH2
B) -NH3+
C) -COOH
D) -COO-
E) -H3O+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not a lipid?
A) fatty acid esters
B) cholesterol
C) fats
D) cellulose
E) oils
A) fatty acid esters
B) cholesterol
C) fats
D) cellulose
E) oils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many different nucleic acid bases are found in DNA and RNA?
A) 2
B) 5
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6
A) 2
B) 5
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
At a physiological pH of 7.4, amino acids exist as zwitterions. At a very low pH (in an acid solution), both the amine group and the carboxylic acid group on an amino acid are protonated. Therefore, the following must be true: the pKa of the __________ group is larger than the pKa of the __________ group.
A) protonated amine group / carboxylic acid group
B) carboxylic acid group / protonated amine group
C) amine group / carbonate group
D) hydronium ion group / hydroxyl ion group
E) carbonate group / amine group
A) protonated amine group / carboxylic acid group
B) carboxylic acid group / protonated amine group
C) amine group / carbonate group
D) hydronium ion group / hydroxyl ion group
E) carbonate group / amine group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following are amino acids?
I.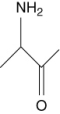
II.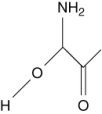
III.
IV.
A) III and IV
B) I and II
C) I only
D) II only
E) III only
I.

II.

III.

IV.

A) III and IV
B) I and II
C) I only
D) II only
E) III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An α-amino acid is one in which the amine group and the carboxylic acid group are attached to __________
A) different carbon atoms.
B) different nitrogen atoms.
C) the same carbon atom.
D) the first and third carbon of the molecule.
E) neighboring carbon atoms.
A) different carbon atoms.
B) different nitrogen atoms.
C) the same carbon atom.
D) the first and third carbon of the molecule.
E) neighboring carbon atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which statement about amino acid enantiomers is not correct?
A) An enantiomer cannot be superimposed on its mirror image.
B) Enantiomers are examples of stereoisomers.
C) A solution of an enantiomer rotates the plane of polarized light.
D) Enantiomers are designated by the prefixes D and L.
E) All the chiral amino acids in our bodies are mixtures of enantiomers.
A) An enantiomer cannot be superimposed on its mirror image.
B) Enantiomers are examples of stereoisomers.
C) A solution of an enantiomer rotates the plane of polarized light.
D) Enantiomers are designated by the prefixes D and L.
E) All the chiral amino acids in our bodies are mixtures of enantiomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An amino acid is composed of __________
A) ammonia and a carboxylic acid group.
B) an amine and a carboxylic acid group.
C) an amine and an alcohol group.
D) an amine and a sulfonic acid group.
E) an amide and a hydrochloric acid group.
A) ammonia and a carboxylic acid group.
B) an amine and a carboxylic acid group.
C) an amine and an alcohol group.
D) an amine and a sulfonic acid group.
E) an amide and a hydrochloric acid group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
At a physiological pH of 7.4, amino acids exist as zwitterions because the pKa of the -NH3+ group is __________ 7.4, and the pKa of the -COOH group is __________ 7.4.
A) greater than / less than
B) less than / greater than
C) greater than / greater than
D) less than / less than
E) equal to / equal to
A) greater than / less than
B) less than / greater than
C) greater than / greater than
D) less than / less than
E) equal to / equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Isomers that cannot be superimposed on their mirror images are called __________
A) geometric isomers.
B) structural isomers.
C) enantiomers.
D) isotopes.
E) constitutional isomers.
A) geometric isomers.
B) structural isomers.
C) enantiomers.
D) isotopes.
E) constitutional isomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a monosaccharide?
A) sucrose
B) glucose
C) starch
D) cellulose
E) cellobiose
A) sucrose
B) glucose
C) starch
D) cellulose
E) cellobiose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The following reaction produces a peptide. Which statement about this reaction is not correct? 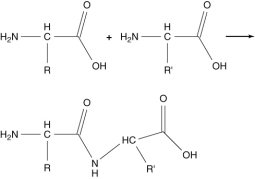
A) The peptide shown is the only product produced by this reaction.
B) This condensation reaction produces a peptide bond.
C) An amide group is formed in this reaction.
D) An amino group reacts with a carboxylic acid group.
E) Two amino acids are linked together by this reaction.

A) The peptide shown is the only product produced by this reaction.
B) This condensation reaction produces a peptide bond.
C) An amide group is formed in this reaction.
D) An amino group reacts with a carboxylic acid group.
E) Two amino acids are linked together by this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which statement about chirality is not correct?
A) A molecule is chiral if it has a carbon atom bonded to four different groups.
B) A molecule is chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image.
C) Almost all amino acids are chiral.
D) In an amino acid, the alpha carbon is the chiral center.
E) Chiral amino acids each have three enantiomers.
A) A molecule is chiral if it has a carbon atom bonded to four different groups.
B) A molecule is chiral if it cannot be superimposed on its mirror image.
C) Almost all amino acids are chiral.
D) In an amino acid, the alpha carbon is the chiral center.
E) Chiral amino acids each have three enantiomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following are not amino acids?
I.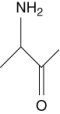
II.
III.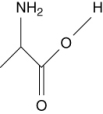
IV.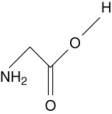
A) III and IV
B) I and II
C) I only
D) II only
E) III only
I.

II.

III.

IV.

A) III and IV
B) I and II
C) I only
D) II only
E) III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is not part of a nucleotide?
A) a five-carbon sugar
B) a phosphate group
C) a nitrogen-containing base
D) an amine group
E) a carboxylic acid group
A) a five-carbon sugar
B) a phosphate group
C) a nitrogen-containing base
D) an amine group
E) a carboxylic acid group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Triglycerides are formed between __________
A) glycerol and inorganic acids.
B) glucose and long-chain fatty acids.
C) glycerol and long-chain fatty acids.
D) glycerol and any carboxylic acid.
E) glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
A) glycerol and inorganic acids.
B) glucose and long-chain fatty acids.
C) glycerol and long-chain fatty acids.
D) glycerol and any carboxylic acid.
E) glucose, fructose, and sucrose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which statement is not correct? A chiral molecule __________
A) is an enantiomer.
B) rotates the plane of polarized light.
C) has four different groups bonded to the same carbon atom.
D) has properties different from those of its mirror image.
E) can be superimposed on its mirror image.
A) is an enantiomer.
B) rotates the plane of polarized light.
C) has four different groups bonded to the same carbon atom.
D) has properties different from those of its mirror image.
E) can be superimposed on its mirror image.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The ordering of subunits, such as amino acids, in a polymer, is called __________
A) the primary structure.
B) the secondary structure.
C) the tertiary structure.
D) the ordering structure.
E) the quaternary structure.
A) the primary structure.
B) the secondary structure.
C) the tertiary structure.
D) the ordering structure.
E) the quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The cyclization of glucose forms a __________
A) four-membered ring.
B) five-membered ring.
C) six-membered ring.
D) seven-membered ring.
E) double ring.
A) four-membered ring.
B) five-membered ring.
C) six-membered ring.
D) seven-membered ring.
E) double ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The active ingredient, sucralose, in an artificial sweetener, Splenda, is shown below. Sucralose is advertised as being made from table sugar. What is the main difference between sucrose (table sugar) and sucralose? 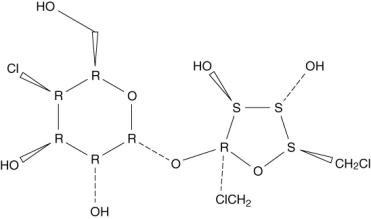
A) Sucralose is a disaccharide while sucrose is a monosaccharide.
B) Sucralose has a six-membered and a five-membered ring, unlike the two six-membered rings in sucrose.
C) Sucralose has a glycosidic bond between the two saccharide units, unlike the C-C bond in sucrose.
D) Some hydroxyl groups in sucrose are replaced by chlorine atoms in sucralose.
E) Sucralose has a six-membered and a five-membered ring, unlike the two five-membered rings in sucrose.

A) Sucralose is a disaccharide while sucrose is a monosaccharide.
B) Sucralose has a six-membered and a five-membered ring, unlike the two six-membered rings in sucrose.
C) Sucralose has a glycosidic bond between the two saccharide units, unlike the C-C bond in sucrose.
D) Some hydroxyl groups in sucrose are replaced by chlorine atoms in sucralose.
E) Sucralose has a six-membered and a five-membered ring, unlike the two five-membered rings in sucrose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The primary structure of a protein is __________
A) the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
B) the -helix structure of the protein.
C) the -pleated sheet structure of the protein.
D) a list of the amino acids in the protein along with the number of times each occurs.
E) the arrangement of -helices and -pleated sheets in the protein.
A) the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
B) the -helix structure of the protein.
C) the -pleated sheet structure of the protein.
D) a list of the amino acids in the protein along with the number of times each occurs.
E) the arrangement of -helices and -pleated sheets in the protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The cyclization of fructose forms a __________
A) four-membered ring.
B) five-membered ring.
C) six-membered ring.
D) seven-membered ring.
E) double ring.
A) four-membered ring.
B) five-membered ring.
C) six-membered ring.
D) seven-membered ring.
E) double ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Table sugar is __________
A) glucose.
B) fructose.
C) cellobiose.
D) a monosaccharide.
E) a disaccharide of glucose and fructose.
A) glucose.
B) fructose.
C) cellobiose.
D) a monosaccharide.
E) a disaccharide of glucose and fructose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The Krebs cycle __________
A) produces carbohydrates in photosynthesis.
B) is a series of chemical reactions that assist in extracting energy from glucose.
C) serves to break down cellulose to produce glucose.
D) describes how enzymes act as catalysts.
E) has one more wheel than a tricycle.
A) produces carbohydrates in photosynthesis.
B) is a series of chemical reactions that assist in extracting energy from glucose.
C) serves to break down cellulose to produce glucose.
D) describes how enzymes act as catalysts.
E) has one more wheel than a tricycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which statement is not correct? Sucrose is __________
A) used for table sugar.
B) is a disaccharide.
C) consists of glucose and fructose with a glycosidic bond.
D) formed in a condensation reaction that eliminates water.
E) a synonym for glucose.
A) used for table sugar.
B) is a disaccharide.
C) consists of glucose and fructose with a glycosidic bond.
D) formed in a condensation reaction that eliminates water.
E) a synonym for glucose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Amino acids bond together via __________ bonds.
A) ionic
B) coordinate covalent
C) hydrogen
D) peptide
E) van der Waals
A) ionic
B) coordinate covalent
C) hydrogen
D) peptide
E) van der Waals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Aspartame exists as a zwitterion with a __________ amine group and a __________ carboxylic acid group.
A) deprotonated; protonated
B) protonated; deprotonated
C) protonated; protonated
D) deprotonated; deprotonated
E) functionalized; defunctionalized
A) deprotonated; protonated
B) protonated; deprotonated
C) protonated; protonated
D) deprotonated; deprotonated
E) functionalized; defunctionalized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is not a description of the secondary structure of a protein?
A) '' -helix''
B) '' -pleated sheets''
C) random coil
D) sequence of amino acids in the protein
E) geometric patterns formed by amino acids
A) '' -helix''
B) '' -pleated sheets''
C) random coil
D) sequence of amino acids in the protein
E) geometric patterns formed by amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An oligopeptide consists of up to __________ amino acids that bond together.
A) 5
B) 20
C) 10
D) 15
E) 50
A) 5
B) 20
C) 10
D) 15
E) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A peptide bond is the result of a condensation reaction between __________
A) two carboxylic acid groups on different amino acids.
B) an amino group on one amino acid and the carboxylic acid group on another.
C) two amino groups on different amino acids.
D) an amino group and a carboxylic acid group on the same amino acid.
E) an amino group and a carboxylic acid group producing a zwitterion.
A) two carboxylic acid groups on different amino acids.
B) an amino group on one amino acid and the carboxylic acid group on another.
C) two amino groups on different amino acids.
D) an amino group and a carboxylic acid group on the same amino acid.
E) an amino group and a carboxylic acid group producing a zwitterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Table sugar is __________
A) glucose.
B) fructose.
C) cellobiose.
D) a monosaccharide.
E) a disaccharide.
A) glucose.
B) fructose.
C) cellobiose.
D) a monosaccharide.
E) a disaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The assembly and interaction of coils and sheets in a polypeptide to produce the overall three-dimensional shape are described by the term __________
A) primary structure.
B) secondary structure.
C) tertiary structure.
D) long-range structure.
E) quaternary structure.
A) primary structure.
B) secondary structure.
C) tertiary structure.
D) long-range structure.
E) quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The -helix and -pleated sheet are examples of __________
A) primary structure.
B) secondary structure.
C) tertiary structure.
D) arrangement structure.
E) quaternary structure.
A) primary structure.
B) secondary structure.
C) tertiary structure.
D) arrangement structure.
E) quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In glycolysis, __________ is converted into pyruvic acid.
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) galactose
D) glucose
E) glycolase
A) sucrose
B) fructose
C) galactose
D) glucose
E) glycolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Table sugar is __________
A) glucose.
B) fructose.
C) cellobiose.
D) a monosaccharide.
E) sucrose.
A) glucose.
B) fructose.
C) cellobiose.
D) a monosaccharide.
E) sucrose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Glucose is shown below. Number the carbon atoms 1-6 from top to bottom. In the cyclization reaction, a bond is formed to C-1 by an oxygen lone pair on the OH bonded to __________ 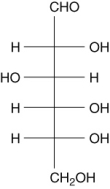
A) C-2.
B) C-4.
C) C-5.
D) C-6.
E) C-3.

A) C-2.
B) C-4.
C) C-5.
D) C-6.
E) C-3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The cyclization reaction of fructose is different from that of glucose because __________
A) a five-membered ring instead of a six-membered ring is formed.
B) a bond is formed to a carbonyl carbon instead of to a methyl carbon.
C) the aldehyde group migrates to a new position.
D) a ketone is formed.
E) fructose has only 5 carbon atoms total instead of 6 as in sucrose.
A) a five-membered ring instead of a six-membered ring is formed.
B) a bond is formed to a carbonyl carbon instead of to a methyl carbon.
C) the aldehyde group migrates to a new position.
D) a ketone is formed.
E) fructose has only 5 carbon atoms total instead of 6 as in sucrose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Mountain folk in Kentucky and Tennessee were sometimes stereotyped for their "corn-liquor" stills that they hid from the "revenue-ers." What is the first step in making corn liquor (ethanol) from corn?
A) fermentation
B) distillation
C) hydrolysis
D) intoxication
E) celebration
A) fermentation
B) distillation
C) hydrolysis
D) intoxication
E) celebration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which one of the following is a saturated fatty acid?
A)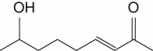
B)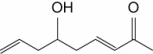
C)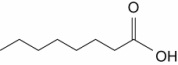
D)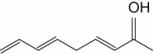
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A disaccharide has a molecular formula of __________
A) CH2O.
B) C6H10O5.
C) C12H22O11.
D) C2H4O2.
E) C12H24O12.
A) CH2O.
B) C6H10O5.
C) C12H22O11.
D) C2H4O2.
E) C12H24O12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A carbohydrate has a molecular formula of __________
A) CH2O.
B) C6H12O6.
C) C12H22O11.
D) C2H4O2.
E) C3H6O3.
A) CH2O.
B) C6H12O6.
C) C12H22O11.
D) C2H4O2.
E) C3H6O3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Glucose and fructose undergo a __________ reaction in the formation of sucrose.
A) sugarization
B) precipitation
C) condensation
D) neutralization
E) addition
A) sugarization
B) precipitation
C) condensation
D) neutralization
E) addition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
To produce ethanol from corn (i.e., starch) to use as fuel or drink, the starch first must be decomposed to glucose through a process called __________
A) fermentation.
B) distillation.
C) hydrolysis.
D) combustion.
E) oxidation.
A) fermentation.
B) distillation.
C) hydrolysis.
D) combustion.
E) oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the linkage that forms between two monosaccharides in a polysaccharide?
A) C- CH2 - C
B) C- O - O - C
C) C- O - C
D) C- C C
C  C
C
E) C - N - C
A) C- CH2 - C
B) C- O - O - C
C) C- O - C
D) C- C
 C
C  C
CE) C - N - C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Converting renewable biomass into fuel to reduce our need to import petroleum and release carbon dioxide from fossil fuels is a great idea. But, to be viable, the process must be cost effective, not subsidized by taxpayer support, and not reduce our supply of food! It also must be recognized that the amount of energy produced through biomass conversion will always be small compared to our total needs. In any case, Professor Popsnorkle's research students at PC University have projects dealing with these issues. Amy's project deals with -glucoside hydrolysis of starches, and Brad's project deals with -glucoside hydrolysis of cellulose. What do you see as the value of these projects and why?
A) Amy's is more valuable because improving the efficiency of starch hydrolysis will increase the effectiveness of our edible corn for fuel program and reduce the need for taxpayer subsidies.
B) Brad's is more valuable because the hydrolysis of cellulose, which is not edible, to produce glucose and ethanol currently is not economically viable.
C) Both are valuable because anything we can do along these lines merits equitable support.
D) Neither is valuable because these ideas are promoted only to enrich farmers in the Midwest.
E) I have a neutral position on the value of these projects because I do not know enough about these issues.
A) Amy's is more valuable because improving the efficiency of starch hydrolysis will increase the effectiveness of our edible corn for fuel program and reduce the need for taxpayer subsidies.
B) Brad's is more valuable because the hydrolysis of cellulose, which is not edible, to produce glucose and ethanol currently is not economically viable.
C) Both are valuable because anything we can do along these lines merits equitable support.
D) Neither is valuable because these ideas are promoted only to enrich farmers in the Midwest.
E) I have a neutral position on the value of these projects because I do not know enough about these issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Glucose is to cellulose as __________
A) pure gold is to 14 karat gold.
B) a link is to a chain.
C) a leaf is to a tree.
D) a trumpet is to a tuba.
E) a tomato is to a potato.
A) pure gold is to 14 karat gold.
B) a link is to a chain.
C) a leaf is to a tree.
D) a trumpet is to a tuba.
E) a tomato is to a potato.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In its linear form, which functional groups are present in glucose?
A) aldehyde and alcohol
B) aldehyde and carboxyl
C) alcohol and ketone
D) amino and alcohol
E) amino and aldehyde
A) aldehyde and alcohol
B) aldehyde and carboxyl
C) alcohol and ketone
D) amino and alcohol
E) amino and aldehyde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Glucose is to starch as __________
A) pure gold is to 14 karat gold.
B) a link is to a chain.
C) a leaf is to a tree.
D) a trumpet is to a tuba.
E) a tomato is to a potato.
A) pure gold is to 14 karat gold.
B) a link is to a chain.
C) a leaf is to a tree.
D) a trumpet is to a tuba.
E) a tomato is to a potato.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A carbohydrate has an empirical formula of __________
A) CH2O.
B) C6H12O6.
C) C12H22O11.
D) C2H4O2.
E) C3H6O3.
A) CH2O.
B) C6H12O6.
C) C12H22O11.
D) C2H4O2.
E) C3H6O3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How many different nucleic acid bases are found altogether in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which base is not present in DNA?
A) adenine
B) cytosine
C) guanine
D) thymine
E) uracil
A) adenine
B) cytosine
C) guanine
D) thymine
E) uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In its ring structure, which functional groups are present in glucose?
A) ether and alcohol
B) aldehyde and carboxyl
C) alcohol and ketone
D) amino and alcohol
E) amino and aldehyde
A) ether and alcohol
B) aldehyde and carboxyl
C) alcohol and ketone
D) amino and alcohol
E) amino and aldehyde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A saturated fatty acid has __________
A) more than one carboxyl group.
B) a long hydrocarbon chain containing C C and C- C bonds.
C and C- C bonds.
C) a long hydrocarbon chain containing only C - C bonds.
D) a long hydrocarbon chain containing only C C bonds.
C bonds.
E) cis and trans isomers.
A) more than one carboxyl group.
B) a long hydrocarbon chain containing C
 C and C- C bonds.
C and C- C bonds.C) a long hydrocarbon chain containing only C - C bonds.
D) a long hydrocarbon chain containing only C
 C bonds.
C bonds.E) cis and trans isomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A monosaccharide has a molecular formula of __________
A) CH2O.
B) C6H10O5.
C) C12H22O11.
D) C2H4O2.
E) C6H12O6.
A) CH2O.
B) C6H10O5.
C) C12H22O11.
D) C2H4O2.
E) C6H12O6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Hydrolysis is __________
A) any reaction involving hydrogen.
B) breaking a bond by the addition of water.
C) the process of dissolving a solute to make a solution.
D) breaking a bond to produce hydrogen gas.
E) forming a bond by adding hydrogen gas.
A) any reaction involving hydrogen.
B) breaking a bond by the addition of water.
C) the process of dissolving a solute to make a solution.
D) breaking a bond to produce hydrogen gas.
E) forming a bond by adding hydrogen gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which base is not present in RNA?
A) adenine
B) cytosine
C) guanine
D) thymine
E) uracil
A) adenine
B) cytosine
C) guanine
D) thymine
E) uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which statement is not correct? Starch and cellulose __________
A) are polysaccharides.
B) have monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds.
C) are equally easily hydrolyzed to produce glucose.
D) are stereoisomers made from glucose monomers.
E) are a major source of biomass.
A) are polysaccharides.
B) have monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds.
C) are equally easily hydrolyzed to produce glucose.
D) are stereoisomers made from glucose monomers.
E) are a major source of biomass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
DNA contains the sugar __________ and the base __________.
A) ribose; uracil
B) deoxyribose; uracil
C) fructose; uracil
D) ribose; thymine
E) deoxyribose; thymine
A) ribose; uracil
B) deoxyribose; uracil
C) fructose; uracil
D) ribose; thymine
E) deoxyribose; thymine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
This molecule, like cholesterol, is __________ 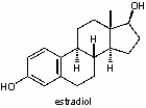
A) a nucleic acid base.
B) an amino acid.
C) a carbohydrate.
D) a fatty acid.
E) a lipid.

A) a nucleic acid base.
B) an amino acid.
C) a carbohydrate.
D) a fatty acid.
E) a lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
RNA contains the sugar __________ and the base __________.
A) ribose; uracil
B) deoxyribose; uracil
C) fructose; uracil
D) ribose; thymine
E) Deoxyribose; uracil
A) ribose; uracil
B) deoxyribose; uracil
C) fructose; uracil
D) ribose; thymine
E) Deoxyribose; uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which one of the following is best associated with carbohydrates?
A) amino acids
B) saccharides
C) hydrocarbon chains
D) phosphate linkages
E) hydrocarbon rings
A) amino acids
B) saccharides
C) hydrocarbon chains
D) phosphate linkages
E) hydrocarbon rings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The molecule drawn below is an example of __________ 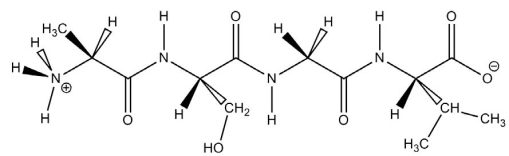
A) a nucleic acid base.
B) a peptide.
C) a carbohydrate.
D) a fatty acid.
E) an amino acid.

A) a nucleic acid base.
B) a peptide.
C) a carbohydrate.
D) a fatty acid.
E) an amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An ether linkage connects monomers in __________
A) proteins.
B) nucleic acids.
C) carbohydrates.
D) lipids.
E) steroids.
A) proteins.
B) nucleic acids.
C) carbohydrates.
D) lipids.
E) steroids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The molecule drawn below is an example of __________ 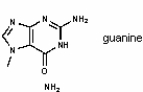
A) a nucleic acid base
B) an amino acid
C) a carbohydrate
D) a fatty acid
E) a lipid

A) a nucleic acid base
B) an amino acid
C) a carbohydrate
D) a fatty acid
E) a lipid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following triglycerides would you most expect to be a liquid at room temperature?
A) saturated fat
B) trans mono-unsaturated fat
C) trans poly-unsaturated fat
D) cis mono-unsaturated fat
E) cis poly-unsaturated fat
A) saturated fat
B) trans mono-unsaturated fat
C) trans poly-unsaturated fat
D) cis mono-unsaturated fat
E) cis poly-unsaturated fat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which one of the following is best associated with nucleic acids?
A) amino acids
B) saccharides
C) hydrocarbon chains
D) phosphate linkages
E) hydrocarbon rings
A) amino acids
B) saccharides
C) hydrocarbon chains
D) phosphate linkages
E) hydrocarbon rings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which one of the following is best associated with proteins?
A) amino acids
B) saccharides
C) hydrocarbon chains
D) phosphate linkages
E) hydrocarbon rings
A) amino acids
B) saccharides
C) hydrocarbon chains
D) phosphate linkages
E) hydrocarbon rings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following triglycerides would you most expect to be a liquid and the most healthy to use in cooking?
A) saturated fat
B) trans mono-unsaturated fat
C) trans poly-unsaturated fat
D) cis mono-unsaturated fat
E) cis poly-unsaturated fat
A) saturated fat
B) trans mono-unsaturated fat
C) trans poly-unsaturated fat
D) cis mono-unsaturated fat
E) cis poly-unsaturated fat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
mRNA and tRNA are responsible for the synthesis of __________
A) carbohydrates.
B) lipids.
C) proteins.
D) phospholipids.
E) cells.
A) carbohydrates.
B) lipids.
C) proteins.
D) phospholipids.
E) cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which type of noncovalent interaction supports the double helix of DNA and produces the base pairings A-T and G-C?
A) hydrogen bonding
B) London dispersion forces
C) dipole-dipole forces
D) ion-ion interactions
E) ion-dipole interactions
A) hydrogen bonding
B) London dispersion forces
C) dipole-dipole forces
D) ion-ion interactions
E) ion-dipole interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The molecule drawn below is an example of __________ 
A) a nucleic acid base.
B) an amino acid.
C) a carbohydrate.
D) a fatty acid.
E) a lipid.

A) a nucleic acid base.
B) an amino acid.
C) a carbohydrate.
D) a fatty acid.
E) a lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which one of the following statements about biomolecules is not correct?
A) Table sugar (sucrose) is a disaccharide made of glucose and fructose.
B) Starch and cellulose are polysaccharides made from glucose.
C) A glycosidic linkage in polysaccharides is an ether group.
D) Cellobiose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose monomers.
E) Maltose is a disaccharide composed of two fructose monomers.
A) Table sugar (sucrose) is a disaccharide made of glucose and fructose.
B) Starch and cellulose are polysaccharides made from glucose.
C) A glycosidic linkage in polysaccharides is an ether group.
D) Cellobiose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose monomers.
E) Maltose is a disaccharide composed of two fructose monomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following saccharides, if any, can be found in a nucleic acid?
A) sucrose
B) glucose
C) fructose
D) ribose
E) None, a nucleic acid is not a carbohydrate.
A) sucrose
B) glucose
C) fructose
D) ribose
E) None, a nucleic acid is not a carbohydrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The molecule drawn below is an example of __________ 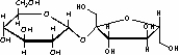
A) a nucleic acid base.
B) an amino acid.
C) a disaccharide.
D) a fatty acid.
E) a lipid.

A) a nucleic acid base.
B) an amino acid.
C) a disaccharide.
D) a fatty acid.
E) a lipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following sugars is glucose?
A)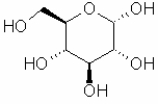
B)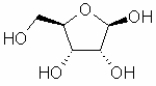
C)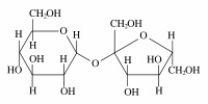
D)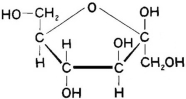
E)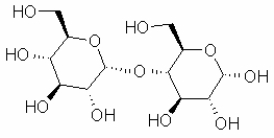
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The molecules drawn below are examples of __________ 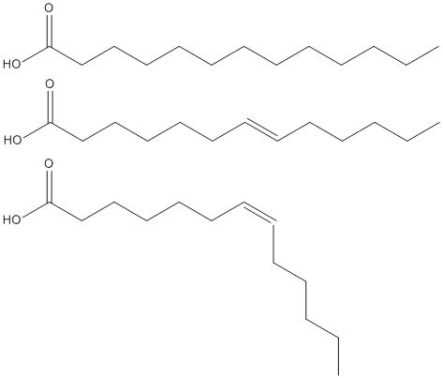
A) nucleic acids.
B) amino acids.
C) carbohydrates.
D) fatty acids.
E) steroidal acids.

A) nucleic acids.
B) amino acids.
C) carbohydrates.
D) fatty acids.
E) steroidal acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which one of the following is best associated with lipids?
A) amino acids
B) saccharides
C) ribose units
D) phosphate linkages
E) fatty acids
A) amino acids
B) saccharides
C) ribose units
D) phosphate linkages
E) fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



