Deck 16: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Chemical Equilibrium
1
Which of the following is true for a chemical reaction at equilibrium regarding the concentration of products?
A) They will not change because there are no more reactants.
B) They will not change because the limiting reagent is gone.
C) They will not change because this is a constant for each reaction.
D) They will not change because the forward and reverse rates are equal.
E) They will change continually because of reversibility.
A) They will not change because there are no more reactants.
B) They will not change because the limiting reagent is gone.
C) They will not change because this is a constant for each reaction.
D) They will not change because the forward and reverse rates are equal.
E) They will change continually because of reversibility.
They will not change because the forward and reverse rates are equal.
2
Which choice A-D includes quantities that may have only positive values?
A) K, Q, and S°
B) " G", " H", and " S"
C) lnK and lnQ
D) K and " G°"
E) none of the above
A) K, Q, and S°
B) " G", " H", and " S"
C) lnK and lnQ
D) K and " G°"
E) none of the above
K, Q, and S°
3
The forward rate constant, kf, and reverse rate constant, kr, for a chemical reaction are not equal. Which of the following must be true?
A) The reaction will be unable to achieve equilibrium.
B) kf and kr will become equal as equilibrium is approached owing to concentration changes.
C) kf and kr will become equal as equilibrium is approached owing to temperature changes.
D) kf and kr will remain unequal but the rates will become equal owing to concentration changes.
E) kf and kr will remain unequal but the rates will become equal owing to temperature changes.
A) The reaction will be unable to achieve equilibrium.
B) kf and kr will become equal as equilibrium is approached owing to concentration changes.
C) kf and kr will become equal as equilibrium is approached owing to temperature changes.
D) kf and kr will remain unequal but the rates will become equal owing to concentration changes.
E) kf and kr will remain unequal but the rates will become equal owing to temperature changes.
kf and kr will remain unequal but the rates will become equal owing to concentration changes.
4
Write the equilibrium expression for the following reaction, assuming homogeneity: fool(money) 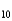
 fool + 10 money
fool + 10 money
A)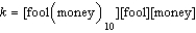
B)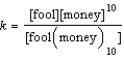
C)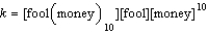
D)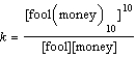
E)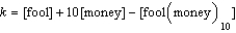
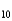
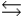 fool + 10 money
fool + 10 moneyA)
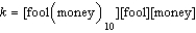
B)
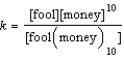
C)
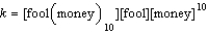
D)
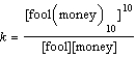
E)
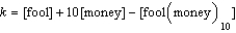

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the equilibrium A + B ![<strong>Consider the equilibrium A + B C. What is significant about the equilibrium state in which [B] = [C]?</strong> A) [A] = K B) [A] = [B] = [C] C) [B] = [C] = K D) [A] = 1/K E) [C]/[B] = K](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_3731_95d8_41e272859d2d_TB3833_11.jpg) C. What is significant about the equilibrium state in which [B] = [C]?
C. What is significant about the equilibrium state in which [B] = [C]?
A) [A] = K
B) [A] = [B] = [C]
C) [B] = [C] = K
D) [A] = 1/K
E) [C]/[B] = K
![<strong>Consider the equilibrium A + B C. What is significant about the equilibrium state in which [B] = [C]?</strong> A) [A] = K B) [A] = [B] = [C] C) [B] = [C] = K D) [A] = 1/K E) [C]/[B] = K](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_3731_95d8_41e272859d2d_TB3833_11.jpg) C. What is significant about the equilibrium state in which [B] = [C]?
C. What is significant about the equilibrium state in which [B] = [C]?A) [A] = K
B) [A] = [B] = [C]
C) [B] = [C] = K
D) [A] = 1/K
E) [C]/[B] = K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A chemical equilibrium 2 A ![<strong>A chemical equilibrium 2<sub> </sub>A B Has a forward rate constant, k<sub>f </sub>= 10 M <sup>-</sup><sup>1 </sup>s<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>, and a reverse rate constant, k<sub>r</sub> = 5 s<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>. If the system has a concentration of [A] = 0.10 M at equilibrium, what must be the concentration of B at equilibrium?</strong> A) 20.0 B) 2.0 C) 0.20 D) 0.020 E) 200](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0893_4cbd_95d8_65821319a634_TB3833_11.jpg) B
B
Has a forward rate constant, kf = 10 M -1 s-1, and a reverse rate constant, kr = 5 s-1. If the system has a concentration of [A] = 0.10 M at equilibrium, what must be the concentration of B at equilibrium?
A) 20.0
B) 2.0
C) 0.20
D) 0.020
E) 200
![<strong>A chemical equilibrium 2<sub> </sub>A B Has a forward rate constant, k<sub>f </sub>= 10 M <sup>-</sup><sup>1 </sup>s<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>, and a reverse rate constant, k<sub>r</sub> = 5 s<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup>. If the system has a concentration of [A] = 0.10 M at equilibrium, what must be the concentration of B at equilibrium?</strong> A) 20.0 B) 2.0 C) 0.20 D) 0.020 E) 200](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0893_4cbd_95d8_65821319a634_TB3833_11.jpg) B
BHas a forward rate constant, kf = 10 M -1 s-1, and a reverse rate constant, kr = 5 s-1. If the system has a concentration of [A] = 0.10 M at equilibrium, what must be the concentration of B at equilibrium?
A) 20.0
B) 2.0
C) 0.20
D) 0.020
E) 200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A chemical equilibrium 2 A  B
B
Has a forward rate constant, kf = 10 M -1s-1, and a reverse rate constant, kr = 5.0 s-1. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for this system?
A) 0.5
B) 2.0
C) 20
D) 0.050
E) 5.0
 B
BHas a forward rate constant, kf = 10 M -1s-1, and a reverse rate constant, kr = 5.0 s-1. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for this system?
A) 0.5
B) 2.0
C) 20
D) 0.050
E) 5.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify the equilibrium expression for the following reaction, assuming homogeneity: boy + girl 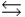 couple
couple
A)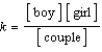
B)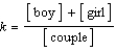
C)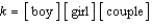
D)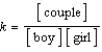
E)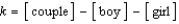
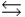 couple
coupleA)
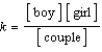
B)
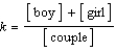
C)
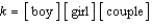
D)
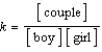
E)
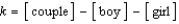

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
For an equilibrium reaction with K = 1.2 *108, the forward rate constant was found to be 3.5 * 105. What is the value of the reverse rate constant?
A) 3.5 * 105
B) 3.4 *102
C) 4.2 * 1013
D) 2.9 * 10-3
E) 6.0 * 10-5
A) 3.5 * 105
B) 3.4 *102
C) 4.2 * 1013
D) 2.9 * 10-3
E) 6.0 * 10-5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The equilibrium constant for the acid ionization of mercaptoethanol (HSCH2CH2OH ) is 1.91 *10-10. HSCH2CH2OH(aq) 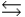 H+(aq) + SCH2CH2OH-(aq)
H+(aq) + SCH2CH2OH-(aq)
Which of the following is true regarding this equilibrium?
(I)The reaction is product favored.
(II)The reaction is reactant favored.
(III)Equilibrium lies far to the right.
(IV)Equilibrium lies far to the left.
A) I and III
B) I and IV
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) None are true, as the concentrations of reactants and products are comparable.
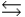 H+(aq) + SCH2CH2OH-(aq)
H+(aq) + SCH2CH2OH-(aq)Which of the following is true regarding this equilibrium?
(I)The reaction is product favored.
(II)The reaction is reactant favored.
(III)Equilibrium lies far to the right.
(IV)Equilibrium lies far to the left.
A) I and III
B) I and IV
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) None are true, as the concentrations of reactants and products are comparable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An equilibrium that strongly favors products has __________
A) a value of K << 1.
B) a value of K >> 1.
C) a value of Q >> 1.
D) a value of Q << 1.
E) K = Q.
A) a value of K << 1.
B) a value of K >> 1.
C) a value of Q >> 1.
D) a value of Q << 1.
E) K = Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of A-D is equal in an equilibrium? If all are equal, answer E.
A) the concentrations of reactant and products
B) the rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions
C) the time that a particular atom or molecule spends as a reactant and product
D) the rate of the forward and reverse reaction
E) all of the above are equal
A) the concentrations of reactant and products
B) the rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions
C) the time that a particular atom or molecule spends as a reactant and product
D) the rate of the forward and reverse reaction
E) all of the above are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Under what conditions are the values of Kc and Kp for a given gas-phase equilibrium the same?
A) there is no change in the moles of gas in the reaction
B) there is no change in the temperature during the reaction
C) if the coefficients of the reactants and products are the same
D) if the pressure remains constant
E) if either Kc or Kp = 1
A) there is no change in the moles of gas in the reaction
B) there is no change in the temperature during the reaction
C) if the coefficients of the reactants and products are the same
D) if the pressure remains constant
E) if either Kc or Kp = 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A chemical equilibrium may be established by starting a reaction with __________
A) reactants only.
B) products only.
C) equal quantities of reactants and products.
D) any quantities of reactants and products.
E) all the above
A) reactants only.
B) products only.
C) equal quantities of reactants and products.
D) any quantities of reactants and products.
E) all the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is true for a chemical reaction at equilibrium?
A) only the forward reaction stops
B) only the reverse reaction stops
C) both the forward and reverse reactions stop
D) the rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions are equal
E) the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
A) only the forward reaction stops
B) only the reverse reaction stops
C) both the forward and reverse reactions stop
D) the rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions are equal
E) the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the equilibrium that exists between Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in solution. The extra electron originally on one Fe2+ ion can be transferred to an Fe3+ ion. This amounts to no net reaction because iron(II) becomes iron(III) and iron(III) becomes iron(II). What is true about this equilibrium?
A) There is no activation energy for this reaction.
B) K = 1.
C) K = 0.
D) There is no net reaction, so there is no value for K.
E) The concentrations of iron(II) and iron(III) change because of the electron transfer.
A) There is no activation energy for this reaction.
B) K = 1.
C) K = 0.
D) There is no net reaction, so there is no value for K.
E) The concentrations of iron(II) and iron(III) change because of the electron transfer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For the following hypothetical equilibrium, what is the value of the equilibrium constant if the concentrations at equilibrium are as shown? A + 2 B ![<strong>For the following hypothetical equilibrium, what is the value of the equilibrium constant if the concentrations at equilibrium are as shown? <sub> </sub>A + 2<sub> </sub>B C [A] = 4.5 *10<sup>-</sup><sup>5</sup> [B] = 2.2 * 10<sup>-</sup><sup>2</sup> [C] = 9.4 *10<sup>-</sup><sup>3</sup></strong> A) 0.22 B) 9.9 C) 4.3 * 10<sup>5</sup> D) 2.3 * 10<sup>8</sup> E) 9.5 * 10<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_3732_95d8_79e65db5757c_TB3833_11.jpg) C
C
[A] = 4.5 *10-5
[B] = 2.2 * 10-2
[C] = 9.4 *10-3
A) 0.22
B) 9.9
C) 4.3 * 105
D) 2.3 * 108
E) 9.5 * 103
![<strong>For the following hypothetical equilibrium, what is the value of the equilibrium constant if the concentrations at equilibrium are as shown? <sub> </sub>A + 2<sub> </sub>B C [A] = 4.5 *10<sup>-</sup><sup>5</sup> [B] = 2.2 * 10<sup>-</sup><sup>2</sup> [C] = 9.4 *10<sup>-</sup><sup>3</sup></strong> A) 0.22 B) 9.9 C) 4.3 * 10<sup>5</sup> D) 2.3 * 10<sup>8</sup> E) 9.5 * 10<sup>3</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_3732_95d8_79e65db5757c_TB3833_11.jpg) C
C[A] = 4.5 *10-5
[B] = 2.2 * 10-2
[C] = 9.4 *10-3
A) 0.22
B) 9.9
C) 4.3 * 105
D) 2.3 * 108
E) 9.5 * 103

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The law of mass action is a result of __________
A) the law of conservation of matter.
B) the law of conservation of energy.
C) kinetics of reversible reactions.
D) limiting reagent stoichiometry.
E) the third law of thermodynamics.
A) the law of conservation of matter.
B) the law of conservation of energy.
C) kinetics of reversible reactions.
D) limiting reagent stoichiometry.
E) the third law of thermodynamics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Write the equilibrium expression for the reaction Zn2+(aq) + 2 NH3(aq) 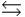 Zn(NH3)2+(aq)
Zn(NH3)2+(aq)
A)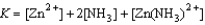
B)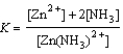
C)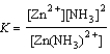
D)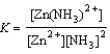
E)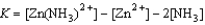
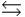 Zn(NH3)2+(aq)
Zn(NH3)2+(aq)A)
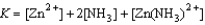
B)
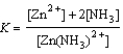
C)
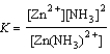
D)
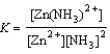
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The equilibrium constant for the formation of hydrogen iodide from hydrogen and iodine is 45.0 at a certain temperature. H2(g) + I2(s) 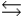 2 HI(g)
2 HI(g)
Which of the following is true regarding this equilibrium?
(I)The reaction is product favored.
(II)The reaction is reactant favored.
(III)Equilibrium lies to the right.
(IV)Equilibrium lies to the left.
A) I and III
B) I and IV
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) None are true, as the concentrations of reactants and products are essentially the same.
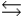 2 HI(g)
2 HI(g)Which of the following is true regarding this equilibrium?
(I)The reaction is product favored.
(II)The reaction is reactant favored.
(III)Equilibrium lies to the right.
(IV)Equilibrium lies to the left.
A) I and III
B) I and IV
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) None are true, as the concentrations of reactants and products are essentially the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the reaction quotient Q has a larger value than the related equilibrium constant, K, __________
A) the reaction is at equilibrium.
B) the reaction will continue to make more products.
C) the reaction will consume products and make reactants.
D) the reaction will release heat to achieve equilibrium.
E) the value of K will increase until it is equal to Q.
A) the reaction is at equilibrium.
B) the reaction will continue to make more products.
C) the reaction will consume products and make reactants.
D) the reaction will release heat to achieve equilibrium.
E) the value of K will increase until it is equal to Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In equilibrium expressions, the concentrations of pure solids and liquids __________
A) have the assigned value of one.
B) have the assigned value of zero.
C) have constant values, cS and c1.
D) are determined from the density and molar mass.
E) are treated as any other solute.
A) have the assigned value of one.
B) have the assigned value of zero.
C) have constant values, cS and c1.
D) are determined from the density and molar mass.
E) are treated as any other solute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For the chemical equilibrium aA + bB  cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 2cC
cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 2cC  2aA + 2bB
2aA + 2bB
A) 0.10
B) 0.20
C) 0.010
D) 20
E) 10
 cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 2cC
cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 2cC  2aA + 2bB
2aA + 2bBA) 0.10
B) 0.20
C) 0.010
D) 20
E) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is the equilibrium expression for the scrubbing reaction of calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide to make calcium sulfite? CaO(s) + SO2(g) ![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium expression for the scrubbing reaction of calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide to make calcium sulfite? CaO(s) + SO<sub>2</sub>(g) CaSO<sub>3</sub>(s)</strong> A) K<sub>c</sub> = [SO<sub>2</sub>] B) C) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaO] + [SO<sub>2</sub>] D) E) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaSO<sub>3</sub>] -[CaO] - [SO<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0896_8041_95d8_7f51c6e20301_TB3833_11.jpg) CaSO3(s)
CaSO3(s)
A) Kc = [SO2]
B)![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium expression for the scrubbing reaction of calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide to make calcium sulfite? CaO(s) + SO<sub>2</sub>(g) CaSO<sub>3</sub>(s)</strong> A) K<sub>c</sub> = [SO<sub>2</sub>] B) C) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaO] + [SO<sub>2</sub>] D) E) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaSO<sub>3</sub>] -[CaO] - [SO<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0896_8042_95d8_e100e4044ab4_TB3833_11.jpg)
C) Kc = [CaO] + [SO2]
D)![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium expression for the scrubbing reaction of calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide to make calcium sulfite? CaO(s) + SO<sub>2</sub>(g) CaSO<sub>3</sub>(s)</strong> A) K<sub>c</sub> = [SO<sub>2</sub>] B) C) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaO] + [SO<sub>2</sub>] D) E) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaSO<sub>3</sub>] -[CaO] - [SO<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0896_a753_95d8_b15c52f8447f_TB3833_11.jpg)
E) Kc = [CaSO3] -[CaO] - [SO2]
![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium expression for the scrubbing reaction of calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide to make calcium sulfite? CaO(s) + SO<sub>2</sub>(g) CaSO<sub>3</sub>(s)</strong> A) K<sub>c</sub> = [SO<sub>2</sub>] B) C) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaO] + [SO<sub>2</sub>] D) E) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaSO<sub>3</sub>] -[CaO] - [SO<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0896_8041_95d8_7f51c6e20301_TB3833_11.jpg) CaSO3(s)
CaSO3(s)A) Kc = [SO2]
B)
![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium expression for the scrubbing reaction of calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide to make calcium sulfite? CaO(s) + SO<sub>2</sub>(g) CaSO<sub>3</sub>(s)</strong> A) K<sub>c</sub> = [SO<sub>2</sub>] B) C) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaO] + [SO<sub>2</sub>] D) E) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaSO<sub>3</sub>] -[CaO] - [SO<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0896_8042_95d8_e100e4044ab4_TB3833_11.jpg)
C) Kc = [CaO] + [SO2]
D)
![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium expression for the scrubbing reaction of calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide to make calcium sulfite? CaO(s) + SO<sub>2</sub>(g) CaSO<sub>3</sub>(s)</strong> A) K<sub>c</sub> = [SO<sub>2</sub>] B) C) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaO] + [SO<sub>2</sub>] D) E) K<sub>c</sub> = [CaSO<sub>3</sub>] -[CaO] - [SO<sub>2</sub>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0896_a753_95d8_b15c52f8447f_TB3833_11.jpg)
E) Kc = [CaSO3] -[CaO] - [SO2]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For the chemical equilibrium aA + bB  cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? cC
cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? cC  aA + bB
aA + bB
A) 0.10
B) 10
C) 1
D) 100
E) -10
 cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? cC
cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? cC  aA + bB
aA + bBA) 0.10
B) 10
C) 1
D) 100
E) -10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Sulfur dioxide emitted in the burning of coal is "scrubbed" from the effluent using __________
A) limestone (CaCO3).
B) lime (CaO).
C) calcium metal (Ca).
D) calcium hydride (CaH2).
E) calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2].
A) limestone (CaCO3).
B) lime (CaO).
C) calcium metal (Ca).
D) calcium hydride (CaH2).
E) calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Write the expression for the reaction quotient for the reaction Zn2+(aq) + 2NH3(aq) 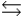 Zn(NH3)2+(aq)
Zn(NH3)2+(aq)
A)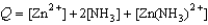
B)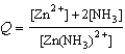
C)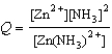
D)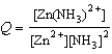
E)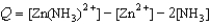
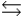 Zn(NH3)2+(aq)
Zn(NH3)2+(aq)A)
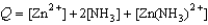
B)
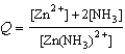
C)
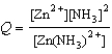
D)
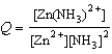
E)
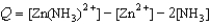

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following occurs when reactants are added to a chemical reaction in solution or the gas phase at equilibrium?
A) Q increases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more products.
B) Q increases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more reactants.
C) Q decreases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more products.
D) Q decreases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more reactants.
E) Q is unchanged by the addition of reactants.
A) Q increases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more products.
B) Q increases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more reactants.
C) Q decreases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more products.
D) Q decreases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more reactants.
E) Q is unchanged by the addition of reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu2+ + 4NH3 ![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_fa8a_95d8_f957eeac85fc_TB3833_11.jpg) [Cu(NH3)4]2+
[Cu(NH3)4]2+
Koverall
Cu2+ + NH3![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_fa8b_95d8_6782084c4b4a_TB3833_11.jpg) [Cu(NH3)]2+
[Cu(NH3)]2+
K1
[Cu(NH3)]2+ + NH3![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_fa8c_95d8_172064c54a4f_TB3833_11.jpg) [Cu(NH3)2]2+
[Cu(NH3)2]2+
K2
Etc)
What is true about K4?
A) K4 = Koverall
B) K4 = K1K2K3
C)![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_219d_95d8_15d7c22bb974_TB3833_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_219e_95d8_458d76d05239_TB3833_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_219f_95d8_691d7c0e4e9e_TB3833_11.jpg)
![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_fa8a_95d8_f957eeac85fc_TB3833_11.jpg) [Cu(NH3)4]2+
[Cu(NH3)4]2+Koverall
Cu2+ + NH3
![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_fa8b_95d8_6782084c4b4a_TB3833_11.jpg) [Cu(NH3)]2+
[Cu(NH3)]2+K1
[Cu(NH3)]2+ + NH3
![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0894_fa8c_95d8_172064c54a4f_TB3833_11.jpg) [Cu(NH3)2]2+
[Cu(NH3)2]2+K2
Etc)
What is true about K4?
A) K4 = Koverall
B) K4 = K1K2K3
C)
![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_219d_95d8_15d7c22bb974_TB3833_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_219e_95d8_458d76d05239_TB3833_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>A series of four equilibrium steps can be defined for the following overall reaction: Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub> Cu<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>1</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)]<sup>2+</sup> + NH<sub>3</sub> [Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2+</sup> K<sub>2</sub> Etc) What is true about K<sub>4</sub>?</strong> A) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>overall</sub> B) K<sub>4</sub> = K<sub>1</sub>K<sub>2</sub>K<sub>3</sub> C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_219f_95d8_691d7c0e4e9e_TB3833_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Addition of reactants to a chemical reaction in solution or gas phase at equilibrium results in __________
A) an increase in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more products.
B) an increase in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more reactants.
C) a decrease in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more products.
D) a decrease in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more reactants.
E) no change in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more products.
A) an increase in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more products.
B) an increase in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more reactants.
C) a decrease in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more products.
D) a decrease in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more reactants.
E) no change in K and a shift in equilibrium to produce more products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An increase in the number of moles of gas as the reaction goes from reactants to products in a gas-phase equilibrium results in __________
A) Kp > Kc.
B) Kp < Kc.
C) Kp = Kc.
D) Kp + Kc = (RT) n.
E) KpKc = (RT) n.
A) Kp > Kc.
B) Kp < Kc.
C) Kp = Kc.
D) Kp + Kc = (RT) n.
E) KpKc = (RT) n.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the equilibrium A + B ![<strong>Consider the equilibrium A + B C. What is significant about the reaction quotient when [B] = [C]?</strong> A) only that [B] = [C] B) [A] = [B] = [C] C) [B] = [C] = K D) [A] = K E) The reaction must run in the forward direction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0896_5930_95d8_457a451c1813_TB3833_11.jpg) C. What is significant about the reaction quotient when [B] = [C]?
C. What is significant about the reaction quotient when [B] = [C]?
A) only that [B] = [C]
B) [A] = [B] = [C]
C) [B] = [C] = K
D) [A] = K
E) The reaction must run in the forward direction.
![<strong>Consider the equilibrium A + B C. What is significant about the reaction quotient when [B] = [C]?</strong> A) only that [B] = [C] B) [A] = [B] = [C] C) [B] = [C] = K D) [A] = K E) The reaction must run in the forward direction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0896_5930_95d8_457a451c1813_TB3833_11.jpg) C. What is significant about the reaction quotient when [B] = [C]?
C. What is significant about the reaction quotient when [B] = [C]?A) only that [B] = [C]
B) [A] = [B] = [C]
C) [B] = [C] = K
D) [A] = K
E) The reaction must run in the forward direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of A through D is not a perturbation or stress to the equilibrium position of an endothermic chemical reaction that involves one or more gases? If all are perturbations, choose E.
A) adding reactants to a gas or solution reaction
B) removing products from a gas or solution reaction
C) decreasing the temperature
D) increasing pressure by adding an inert gas to a reaction in the gas phase
E) All of the above are perturbations to chemical equilibrium.
A) adding reactants to a gas or solution reaction
B) removing products from a gas or solution reaction
C) decreasing the temperature
D) increasing pressure by adding an inert gas to a reaction in the gas phase
E) All of the above are perturbations to chemical equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The equilibrium constants for the two reactions are known: Mm+ + 4L- ![<strong>The equilibrium constants for the two reactions are known: M<sup>m+</sup> + 4L<sup>-</sup> [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> K<sub>a</sub> HL H<sup>+</sup> + L<sup>-</sup> K<sub>b</sub> What must be the value of the equilibrium constant, K<sub>overall</sub> for the following overall reaction? M<sup>m+</sup> + 4HL [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> + 4H<sup>+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub></strong> A) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub> B) K<sub>a</sub> + 4K<sub>b</sub> C) K<sub>a</sub> + K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> D) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> E) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>1/4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_e3f7_95d8_29704e663389_TB3833_11.jpg) [ML4]m-4 Ka
[ML4]m-4 Ka
HL![<strong>The equilibrium constants for the two reactions are known: M<sup>m+</sup> + 4L<sup>-</sup> [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> K<sub>a</sub> HL H<sup>+</sup> + L<sup>-</sup> K<sub>b</sub> What must be the value of the equilibrium constant, K<sub>overall</sub> for the following overall reaction? M<sup>m+</sup> + 4HL [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> + 4H<sup>+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub></strong> A) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub> B) K<sub>a</sub> + 4K<sub>b</sub> C) K<sub>a</sub> + K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> D) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> E) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>1/4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_e3f8_95d8_c9c728fd3e81_TB3833_11.jpg) H+ + L- Kb
H+ + L- Kb
What must be the value of the equilibrium constant, Koverall for the following overall reaction?
Mm+ + 4HL![<strong>The equilibrium constants for the two reactions are known: M<sup>m+</sup> + 4L<sup>-</sup> [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> K<sub>a</sub> HL H<sup>+</sup> + L<sup>-</sup> K<sub>b</sub> What must be the value of the equilibrium constant, K<sub>overall</sub> for the following overall reaction? M<sup>m+</sup> + 4HL [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> + 4H<sup>+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub></strong> A) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub> B) K<sub>a</sub> + 4K<sub>b</sub> C) K<sub>a</sub> + K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> D) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> E) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>1/4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_e3f9_95d8_7f78a4b20384_TB3833_00.jpg) [ML4]m-4 + 4H+ Koverall
[ML4]m-4 + 4H+ Koverall
A) KaKb
B) Ka + 4Kb
C) Ka + Kb4
D) KaKb4
E) KaKb1/4
![<strong>The equilibrium constants for the two reactions are known: M<sup>m+</sup> + 4L<sup>-</sup> [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> K<sub>a</sub> HL H<sup>+</sup> + L<sup>-</sup> K<sub>b</sub> What must be the value of the equilibrium constant, K<sub>overall</sub> for the following overall reaction? M<sup>m+</sup> + 4HL [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> + 4H<sup>+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub></strong> A) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub> B) K<sub>a</sub> + 4K<sub>b</sub> C) K<sub>a</sub> + K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> D) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> E) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>1/4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_e3f7_95d8_29704e663389_TB3833_11.jpg) [ML4]m-4 Ka
[ML4]m-4 KaHL
![<strong>The equilibrium constants for the two reactions are known: M<sup>m+</sup> + 4L<sup>-</sup> [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> K<sub>a</sub> HL H<sup>+</sup> + L<sup>-</sup> K<sub>b</sub> What must be the value of the equilibrium constant, K<sub>overall</sub> for the following overall reaction? M<sup>m+</sup> + 4HL [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> + 4H<sup>+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub></strong> A) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub> B) K<sub>a</sub> + 4K<sub>b</sub> C) K<sub>a</sub> + K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> D) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> E) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>1/4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_e3f8_95d8_c9c728fd3e81_TB3833_11.jpg) H+ + L- Kb
H+ + L- KbWhat must be the value of the equilibrium constant, Koverall for the following overall reaction?
Mm+ + 4HL
![<strong>The equilibrium constants for the two reactions are known: M<sup>m+</sup> + 4L<sup>-</sup> [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> K<sub>a</sub> HL H<sup>+</sup> + L<sup>-</sup> K<sub>b</sub> What must be the value of the equilibrium constant, K<sub>overall</sub> for the following overall reaction? M<sup>m+</sup> + 4HL [ML<sub>4</sub>]<sup>m</sup><sup>-</sup><sup>4</sup> + 4H<sup>+</sup> K<sub>overall</sub></strong> A) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub> B) K<sub>a</sub> + 4K<sub>b</sub> C) K<sub>a</sub> + K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> D) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>4</sup> E) K<sub>a</sub>K<sub>b</sub><sup>1/4</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0895_e3f9_95d8_7f78a4b20384_TB3833_00.jpg) [ML4]m-4 + 4H+ Koverall
[ML4]m-4 + 4H+ KoverallA) KaKb
B) Ka + 4Kb
C) Ka + Kb4
D) KaKb4
E) KaKb1/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the reaction quotient Q has a smaller value than the related equilibrium constant, K, __________
A) the reaction is at equilibrium.
B) the reaction will continue to make more products.
C) the reaction will consume products and make reactants.
D) the reaction will release heat to achieve equilibrium.
E) the value of K will decrease until it is equal to Q.
A) the reaction is at equilibrium.
B) the reaction will continue to make more products.
C) the reaction will consume products and make reactants.
D) the reaction will release heat to achieve equilibrium.
E) the value of K will decrease until it is equal to Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Two students measured an equilibrium constant for the same chemical reaction. Ken obtained a value of 130 for the equilibrium constant, but Barbie obtained a value of 11.4. The instructor checked their results and said they were both correct. How can that be?
A) The values vary according to the way the measurement is made. Ken must have measured product concentrations, while Barbie measured reactant concentrations.
B) The values vary according to the starting conditions of the reaction prior to equilibrium. Ken must have started with all reactants, while Barbie must have started with all products.
C) The values vary according to the stoichiometric coefficients that are used. The balancing coefficients that Ken used must have been twice those that Barbie used.
D) The values vary according to direction of the reaction. Ken must have used the reverse reaction.
E) The instructor must have made a mistake as the equilibrium constant for a reaction must always be the same.
A) The values vary according to the way the measurement is made. Ken must have measured product concentrations, while Barbie measured reactant concentrations.
B) The values vary according to the starting conditions of the reaction prior to equilibrium. Ken must have started with all reactants, while Barbie must have started with all products.
C) The values vary according to the stoichiometric coefficients that are used. The balancing coefficients that Ken used must have been twice those that Barbie used.
D) The values vary according to direction of the reaction. Ken must have used the reverse reaction.
E) The instructor must have made a mistake as the equilibrium constant for a reaction must always be the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For the chemical equilibrium aA + bB  cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 2aA + 2 bB
cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 2aA + 2 bB  2cC
2cC
A) 10
B) 20
C) 40
D) 100
E) 400
 cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 2aA + 2 bB
cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 2aA + 2 bB  2cC
2cCA) 10
B) 20
C) 40
D) 100
E) 400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Lime is obtained __________
A) by heating calcium sulfite at 900 C.
B) as a by-product of burning coal.
C) from the reaction between calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide.
D) by heating calcium carbonate at 900 C.
E) from sweet soil.
A) by heating calcium sulfite at 900 C.
B) as a by-product of burning coal.
C) from the reaction between calcium oxide and sulfur dioxide.
D) by heating calcium carbonate at 900 C.
E) from sweet soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For the chemical equilibrium aA +bB 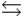 cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 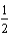
CC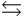
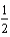
AA +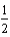
BB
A) 0.32
B) 10
C) 3.2
D) 3.1
E) 32
 cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
cC, the value of the equilibrium constant, K, is 10. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? 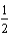
CC
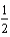
AA +
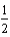
BB
A) 0.32
B) 10
C) 3.2
D) 3.1
E) 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The equilibrium constant for the formation of calcium carbonate from the ions in solution is 2.2*108 according to the reaction: Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq)  CaCO3(s)
CaCO3(s)
What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reverse of this reaction?
A) the same, 2.2 * 108
B) -2.2 * 108
C) 2.2 * 10-8
D) 4.5 * 10-9
E) 4.5*109
 CaCO3(s)
CaCO3(s)What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reverse of this reaction?
A) the same, 2.2 * 108
B) -2.2 * 108
C) 2.2 * 10-8
D) 4.5 * 10-9
E) 4.5*109

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is true regarding the effect of a catalyst on chemical equilibrium?
A) Only the forward rate increases so the quantity of products increases.
B) Only the forward rate increases but the quantity of products remains the same.
C) Both the forward and reverse rates increase and the quantity of products increases.
D) Both the forward and reverse rates increase but the quantity of products is unchanged.
E) The effect varies depending on whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
A) Only the forward rate increases so the quantity of products increases.
B) Only the forward rate increases but the quantity of products remains the same.
C) Both the forward and reverse rates increase and the quantity of products increases.
D) Both the forward and reverse rates increase but the quantity of products is unchanged.
E) The effect varies depending on whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The sulfide ion, S2-, reacts with water as a weak base: S2- + H2O  SH- + OH- K = 1.0
SH- + OH- K = 1.0
If sodium sulfide were dissolved in water to make a solution of 0.50 M, what would be the resulting concentration of OH-?
A) 0.50 M
B) 0.37 M
C) 0.63 M
D) 1.0 M
E) 0.19 M
 SH- + OH- K = 1.0
SH- + OH- K = 1.0If sodium sulfide were dissolved in water to make a solution of 0.50 M, what would be the resulting concentration of OH-?
A) 0.50 M
B) 0.37 M
C) 0.63 M
D) 1.0 M
E) 0.19 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Cylinders of NO gas may contain small quantities of oxygen as impurities, leading to the formation of NO2 in equilibrium with the NO and oxygen. Is this contamination by NO2 dependent on pressure in the tank?
A) Yes, there will be more NO2 at higher pressures.
B) Yes, there will be less NO2 at higher pressures.
C) No, the amount of NO2 has nothing to do with pressure.
D) No, the amount of NO2 depends on the partial pressure, not the total pressure.
E) There is no way to tell without additional information.
A) Yes, there will be more NO2 at higher pressures.
B) Yes, there will be less NO2 at higher pressures.
C) No, the amount of NO2 has nothing to do with pressure.
D) No, the amount of NO2 depends on the partial pressure, not the total pressure.
E) There is no way to tell without additional information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following relationships are sufficient to assure that reactants and products will be in their standard state at equilibrium?
(I) G = 0
(II) G° = 0
(III) K = 1
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
E) Reactants and products can never be in equilibrium in their standard states.
(I) G = 0
(II) G° = 0
(III) K = 1
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
E) Reactants and products can never be in equilibrium in their standard states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What happens to the equilibrium between NO2(g) and N2O4(g) in inert argon when the volume is increased and additional argon is added to maintain a constant total pressure?
A) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 increases solely because of the increase in volume.
B) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 increases solely because of the addition of argon.
C) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 decreases solely because of the increase in volume.
D) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 decreases solely because of the addition of argon.
E) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 remains the same, as the effects of the two processes cancel.
A) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 increases solely because of the increase in volume.
B) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 increases solely because of the addition of argon.
C) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 decreases solely because of the increase in volume.
D) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 decreases solely because of the addition of argon.
E) The ratio of NO2 to N2O4 remains the same, as the effects of the two processes cancel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The gas-phase equilibrium of the oxidation of sulfur dioxide, shown here, has an equilibrium constant, Kp, value of 4.17 *102 at 200 C. If a closed vessel was filled with sulfur trioxide and the initial pressure of SO3 was 0.033 atm at 200 C, what would be the final partial pressure of SO3? 2SO2(g) + O2(g)  2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)
A) more than 0.033 atm
B) less than 0.033 atm
C) 0.033 atm exactly
D) there is no way to tell
 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)A) more than 0.033 atm
B) less than 0.033 atm
C) 0.033 atm exactly
D) there is no way to tell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A student determined the equilibrium concentration in the following equation by neglecting the x term in the denominator. Was she justified or not in this approximation and why? K = 4.0 * 10-2 = 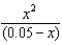
A) Yes, the concentration > K, so the x can be ignored.
B) Yes, the value of x determined in this way is less than 0.05, so it can be ignored.
C) No, the value of x determined in this way significantly reduces the denominator.
D) No, the value of x can never be ignored in solving an algebra problem.
E) No, the value of K is much less than 1 so x cannot be ignored.
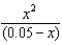
A) Yes, the concentration > K, so the x can be ignored.
B) Yes, the value of x determined in this way is less than 0.05, so it can be ignored.
C) No, the value of x determined in this way significantly reduces the denominator.
D) No, the value of x can never be ignored in solving an algebra problem.
E) No, the value of K is much less than 1 so x cannot be ignored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the ICE table started for calculating equilibrium concentrations of the reaction shown, the terms in the "change" column are __________ M2+ + 4L ![<strong>In the ICE table started for calculating equilibrium concentrations of the reaction shown, the terms in the change column are __________ M<sup>2+</sup> + 4L ML<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup> [M<sup>2+</sup>] [L] [ML<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] I 0.10 M 0.32 M 0 M C ______ ______ ______ E</strong> A) -x, -x, +x B) +x, +x, -x C) -x, -4x, +x D) +x, +4x, +x E) +x, +4x, -x](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0897_1c85_95d8_578e31f2b486_TB3833_11.jpg) ML4+
ML4+
[M2+] [L] [ML4+]
I 0.10 M 0.32 M 0 M
C ______ ______ ______
E
A) -x, -x, +x
B) +x, +x, -x
C) -x, -4x, +x
D) +x, +4x, +x
E) +x, +4x, -x
![<strong>In the ICE table started for calculating equilibrium concentrations of the reaction shown, the terms in the change column are __________ M<sup>2+</sup> + 4L ML<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup> [M<sup>2+</sup>] [L] [ML<sub>4</sub><sup>+</sup>] I 0.10 M 0.32 M 0 M C ______ ______ ______ E</strong> A) -x, -x, +x B) +x, +x, -x C) -x, -4x, +x D) +x, +4x, +x E) +x, +4x, -x](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_0897_1c85_95d8_578e31f2b486_TB3833_11.jpg) ML4+
ML4+[M2+] [L] [ML4+]
I 0.10 M 0.32 M 0 M
C ______ ______ ______
E
A) -x, -x, +x
B) +x, +x, -x
C) -x, -4x, +x
D) +x, +4x, +x
E) +x, +4x, -x

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the equation relating equilibrium to thermodynamics, a = -RTb,
A) a = G and b = lnK.
B) a = G and b = K.
C) a = G and b = lnK.
D) a = G and b = K
E) a = ln G and b = K
A) a = G and b = lnK.
B) a = G and b = K.
C) a = G and b = lnK.
D) a = G and b = K
E) a = ln G and b = K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the difference between " G" and " G "?
A) " G " refers to the formation of a compound from its elements; " G" can be defined for any reaction.
B) " G " refers to the formation of a pure compound; " G" can be defined for an impure compound.
C) " G " refers to a reaction that goes to completion; " G" is defined for a reaction that goes to any extent.
D) " G " refers to the conversion of reactants in their standard state to products in their standard state; " G" is defined for a reaction under any conditions.
E) " G " refers to reactions of one mole quantities of reactants; " G" is defined for any quantity of reactants.
A) " G " refers to the formation of a compound from its elements; " G" can be defined for any reaction.
B) " G " refers to the formation of a pure compound; " G" can be defined for an impure compound.
C) " G " refers to a reaction that goes to completion; " G" is defined for a reaction that goes to any extent.
D) " G " refers to the conversion of reactants in their standard state to products in their standard state; " G" is defined for a reaction under any conditions.
E) " G " refers to reactions of one mole quantities of reactants; " G" is defined for any quantity of reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following must be true for a reaction to proceed to form products?
A) Q > K, G < 0, and G° < 0
B) Q > K and G < 0, G° can be anything
C) Q > K and G° < 0, G can be anything
D) Q < K, G < 0, G° < 0
E) Q < K and G° < 0, G can be anything
A) Q > K, G < 0, and G° < 0
B) Q > K and G < 0, G° can be anything
C) Q > K and G° < 0, G can be anything
D) Q < K, G < 0, G° < 0
E) Q < K and G° < 0, G can be anything

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the temperature of an endothermic reaction at equilibrium could be increased instantaneously, what would be the instantaneous effect on Q and K before equilibrium was again achieved?
A) Q would increase and K would stay the same.
B) Q would decrease and K would stay the same.
C) Q would stay the same and K would increase.
D) Q would stay the same and K would decrease.
E) Both Q and K would stay the same.
A) Q would increase and K would stay the same.
B) Q would decrease and K would stay the same.
C) Q would stay the same and K would increase.
D) Q would stay the same and K would decrease.
E) Both Q and K would stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The reaction of bromine gas with chlorine gas, shown here, has a Kp value of 7.20. If a closed vessel was charged with the two reactants, each at an initial partial pressure of 0.500 atm, and the product also at 0.500 atm, what would be the equilibrium partial pressure of BrCl(g)? Br2(g) + Cl2(g)  2BrCl(g)
2BrCl(g)
A) 0.500 atm
B) 0.680 atm
C) 0.859 atm
D) 0.029 atm
E) 0.987 atm
 2BrCl(g)
2BrCl(g)A) 0.500 atm
B) 0.680 atm
C) 0.859 atm
D) 0.029 atm
E) 0.987 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In a simple equilibrium A + B 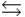 C, will there be any stress to the system if both B and C were added to the equilibrium system simultaneously and in the same amount?
C, will there be any stress to the system if both B and C were added to the equilibrium system simultaneously and in the same amount?
A) No, these two stresses will always cancel each other out.
B) No, these two stresses will cancel each other out unless the initial concentrations of B and C are also the same.
C) Yes, the same amount of A is also required for the stresses to cancel.
D) Yes, unless the initial concentrations of B and C are also the same.
E) More than two of the above statements are correct.
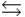 C, will there be any stress to the system if both B and C were added to the equilibrium system simultaneously and in the same amount?
C, will there be any stress to the system if both B and C were added to the equilibrium system simultaneously and in the same amount?A) No, these two stresses will always cancel each other out.
B) No, these two stresses will cancel each other out unless the initial concentrations of B and C are also the same.
C) Yes, the same amount of A is also required for the stresses to cancel.
D) Yes, unless the initial concentrations of B and C are also the same.
E) More than two of the above statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The reaction of bromine gas with chlorine gas, shown here, has a Kp value of 7.20. If a closed vessel was charged with the two reactants, each at an initial partial pressure of 0.500 atm, what would be the equilibrium partial pressure of BrCl(g)? Br2(g) + Cl2(g) 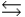 2BrCl(g)
2BrCl(g)
A) 1.9 atm
B) 1.4 atm
C) 0.84 atm
D) 0.29 atm
E) 0.57 atm
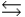 2BrCl(g)
2BrCl(g)A) 1.9 atm
B) 1.4 atm
C) 0.84 atm
D) 0.29 atm
E) 0.57 atm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A reaction X + 2Y 3Z is started with 1.0 M Z and no X or Y. To calculate the equilibrium concentrations of all species using an ICE table, which of the following would you enter in the Z column for the C row?
A) 1.0 M
B) 1.0 M - x
C) 1.0 M - 3x
D) 1.0 M + 3x
E) -3x
A) 1.0 M
B) 1.0 M - x
C) 1.0 M - 3x
D) 1.0 M + 3x
E) -3x

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When can an x be ignored in solving an equilibrium expression derived from an ICE table?
A) whenever it simplifies the calculation
B) whenever it is very much smaller than the term it is added to or subtracted from
C) whenever the equilibrium concentration for that species is relatively very small
D) whenever it is raised to any power higher than 1
E) never
A) whenever it simplifies the calculation
B) whenever it is very much smaller than the term it is added to or subtracted from
C) whenever the equilibrium concentration for that species is relatively very small
D) whenever it is raised to any power higher than 1
E) never

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Increasing the temperature of an exothermic reaction results in __________
A) more products and fewer reactants.
B) more reactants and fewer products.
C) more reactants and products.
D) fewer reactants and products.
E) no change in the quantities of reactants and products.
A) more products and fewer reactants.
B) more reactants and fewer products.
C) more reactants and products.
D) fewer reactants and products.
E) no change in the quantities of reactants and products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following occurs when products are removed from a chemical reaction in solution or the gas phase at equilibrium?
A) Q increases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more products.
B) Q increases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more reactants.
C) Q decreases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more products.
D) Q decreases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more reactants.
E) Q is unchanged by the addition of reactants.
A) Q increases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more products.
B) Q increases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more reactants.
C) Q decreases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more products.
D) Q decreases and the equilibrium shifts to produce more reactants.
E) Q is unchanged by the addition of reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
To solve an equation of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0 for values of x, use __________
A)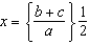
B)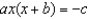
C)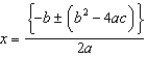
D)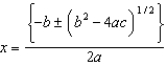
E)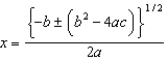
A)
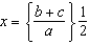
B)
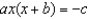
C)
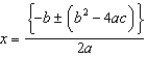
D)
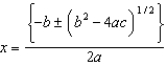
E)
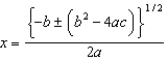

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
As the temperature of a reaction with S° > 0 is increased, the equilibrium constant __________
A) always increases.
B) always decreases.
C) always stays the same.
D) only increases when H° > 0.
E) only increases when H° < 0.
A) always increases.
B) always decreases.
C) always stays the same.
D) only increases when H° > 0.
E) only increases when H° < 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A sketch of the free energy for a hypothetical chemical equilibrium is shown here. Which sketch shows the equilibrium position labeled with an asterisk (*)?
A)
B)
C)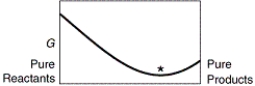
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The G  of atomic oxygen is 230.1 kJ/mol. Determine the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at standard thermodynamic conditions. O2(g)
of atomic oxygen is 230.1 kJ/mol. Determine the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at standard thermodynamic conditions. O2(g)  2O(g)
2O(g)
A) 4.7 * 10-41
B) 2.3 *10-61
C) 2.2 * 10-81
D) 2.1 * 1040
E) 4.5 * 1080
 of atomic oxygen is 230.1 kJ/mol. Determine the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at standard thermodynamic conditions. O2(g)
of atomic oxygen is 230.1 kJ/mol. Determine the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at standard thermodynamic conditions. O2(g) 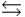 2O(g)
2O(g)A) 4.7 * 10-41
B) 2.3 *10-61
C) 2.2 * 10-81
D) 2.1 * 1040
E) 4.5 * 1080

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If K for a reaction is large,
A) " G "is definitely negative.
B) " G "is definitely positive.
C) " G "is equal to zero.
D) " G "is definitely negative
E) " G "is definitely positive
A) " G "is definitely negative.
B) " G "is definitely positive.
C) " G "is equal to zero.
D) " G "is definitely negative
E) " G "is definitely positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When plotting lnK vs. 1/T, a linear relationship is obtained __________
A) with a slope of - H/R and an intercept of + S /R.
B) with a slope of - H/R and an intercept of - S /R.
C) with a slope of + H/R and an intercept of + S /R.
D) with a slope of + H/R and an intercept of - S /R.
E) never, as logarithmic relationships are intrinsically nonlinear.
A) with a slope of - H/R and an intercept of + S /R.
B) with a slope of - H/R and an intercept of - S /R.
C) with a slope of + H/R and an intercept of + S /R.
D) with a slope of + H/R and an intercept of - S /R.
E) never, as logarithmic relationships are intrinsically nonlinear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A sketch of the free energy for a hypothetical chemical equilibrium is shown here. What part of the plot on the axis representing the relative quantities of reactants and products corresponds to a value of G that is greater than zero? 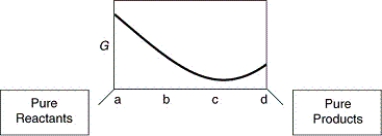
A) a to c
B) c only
C) c to d
D) b to d
E) none of these

A) a to c
B) c only
C) c to d
D) b to d
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The equilibrium constant for a given reaction __________
A) does not change with temperature.
B) always increases with temperature.
C) always decreases with temperature.
D) increases with temperature for exothermic reactions only.
E) increases with temperature for endothermic reactions only.
A) does not change with temperature.
B) always increases with temperature.
C) always decreases with temperature.
D) increases with temperature for exothermic reactions only.
E) increases with temperature for endothermic reactions only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The prediction of linearity in a van't Hoff plot assumes __________
A) that the reaction is run under ideal conditions.
B) that H and S are independent of temperature.
C) that G is independent of temperature.
D) that lnK is independent of temperature.
E) none of the above.
A) that the reaction is run under ideal conditions.
B) that H and S are independent of temperature.
C) that G is independent of temperature.
D) that lnK is independent of temperature.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A qualitative interpretation of the effect of temperature on equilibrium views heat as a reactant or product and explains shifts in equilibrium with temperature as responses to stress to the equilibrium. How does van't Hoff's equation refine this view?
A) It incorporates the heat into an ICE table calculation.
B) It accounts for the shift in terms of the temperature dependence of K.
C) It uses stoichiometry to interpret heat quantitatively as a reactant or product.
D) It uses a statistical-mechanical interpretation of heat.
E) It enables Q to be calculated from H° and S°.
A) It incorporates the heat into an ICE table calculation.
B) It accounts for the shift in terms of the temperature dependence of K.
C) It uses stoichiometry to interpret heat quantitatively as a reactant or product.
D) It uses a statistical-mechanical interpretation of heat.
E) It enables Q to be calculated from H° and S°.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A sketch of the free energy versus Q for a hypothetical chemical equilibrium is shown here. The stress to the equilibrium by adding more reactants is shown by which arrow? 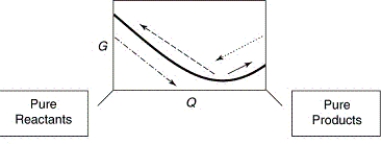
A)
B)
C)
D)

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
As the temperature of an endothermic reaction is increased, the equilibrium constant __________
A) always increases.
B) always decreases.
C) always stays the same.
D) only increases when S° > 0.
E) only increases when S° < 0.
A) always increases.
B) always decreases.
C) always stays the same.
D) only increases when S° > 0.
E) only increases when S° < 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following figures illustrates best the sequence of the free-energy values (shown with the star) for a chemical reaction at equilibrium to the removal of products, followed by the response of the equilibrium to this stress?
A)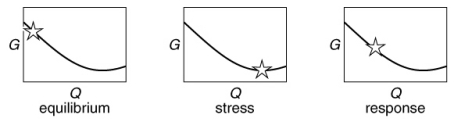
B)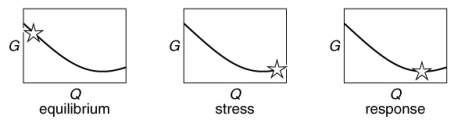
C)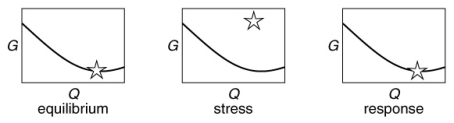
D)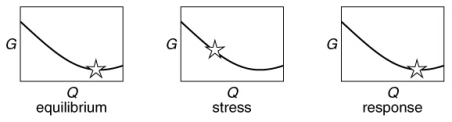
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A sketch of the free energy for a hypothetical chemical equilibrium is shown here. What part of the plot on the axis representing the relative quantities of reactants and products corresponds to a value of Q that is less than K? 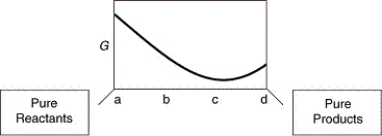
A) a to b
B) b to c
C) a to c
D) b to d
E) c to d

A) a to b
B) b to c
C) a to c
D) b to d
E) c to d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Jane can accept that " G " = -RTlnK, but she cannot reconcile the relationship between " S " and lnK. Please explain it to her.
A) " S " = R lnK - " H "/T
B) " S " = +ln(K/R) + " H "/T
C) " S " = +R ln(K/T) + " H "
D) " S " = +R ln(K) + " H "/T
E) " S " = -R ln(K) + " H "/T
A) " S " = R lnK - " H "/T
B) " S " = +ln(K/R) + " H "/T
C) " S " = +R ln(K/T) + " H "
D) " S " = +R ln(K) + " H "/T
E) " S " = -R ln(K) + " H "/T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A perturbation or stress to a chemical reaction at equilibrium _________
A) increases the free energy of the system.
B) decreases the free energy of the system.
C) neither increases nor decreases the free energy of the system.
D) may increase or decrease the free energy of they system depending on the nature of the stress.
E) causes the free energy of the system to become zero.
A) increases the free energy of the system.
B) decreases the free energy of the system.
C) neither increases nor decreases the free energy of the system.
D) may increase or decrease the free energy of they system depending on the nature of the stress.
E) causes the free energy of the system to become zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
For a particular hypothetical reaction, 2A + B C, the value of G is 250 kJ/mol. What is the value of G for this reaction at 298 K when [A] = 0.60 M, [B] = 0.10 M, and [C] = 4.0 * 10-3 M?
A) 248 kJ/mol
B) 245 kJ/mol
C) 2775 kJ/mol
D) 250 kJ/mol
E) 255 kJ/mol
A) 248 kJ/mol
B) 245 kJ/mol
C) 2775 kJ/mol
D) 250 kJ/mol
E) 255 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What is the value of the equilibrium constant at 500 K for a chemical equilibrium that has a H value of 250 kJ/mol and a S value of 48 J/mol · K?
A) 4.22 *1028
B) -3.01 * 104
C) -54.36
D) 2.45 * 10-24
E) 7.58
A) 4.22 *1028
B) -3.01 * 104
C) -54.36
D) 2.45 * 10-24
E) 7.58

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
As T approaches infinity, lnK approaches __________
A) infinity.
B) zero.
C)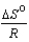 .
.
D)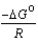 .
.
E)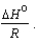
A) infinity.
B) zero.
C)
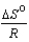 .
.D)
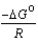 .
.E)
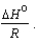

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Several groups of general chemistry lab students measured the equilibrium constant for the same chemical equilibrium. In comparing their results, they found that they had different values because the temperatures of the experiments were different. Everyone was disappointed by the inconsistency, except for Dexter when he realized the measurements were made at different measured temperatures: "My esteemed colleagues," he said, "together we have sufficient data to determine two additional thermodynamic parameters and show the lab instructor what we know!" What two parameters did Dexter have in mind?
A) " G " and " H "
B) " G " and " S "
C) " H " and " S "
D) " E " and " S "
E) This cannot be determined as there are no two thermodynamic parameters related to K and T.
A) " G " and " H "
B) " G " and " S "
C) " H " and " S "
D) " E " and " S "
E) This cannot be determined as there are no two thermodynamic parameters related to K and T.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Using the thermodynamic data below, determine the equilibrium constant for the conversion of oxygen to ozone at 2000 K. Substance H  (kJ/mol) G
(kJ/mol) G  (kJ/mol) S (J/mol · K)
(kJ/mol) S (J/mol · K)
O2(g) 0 0 205.0
O3(g) 142.3 163.4 237.6
3O2(g) 2O3(g)
2O3(g)
A) 2.04 * 107
B) 5.44 *10-14
C) 2.67 * 10-8
D) 2.91 * 10-9
E) 3.65 *10-12
 (kJ/mol) G
(kJ/mol) G  (kJ/mol) S (J/mol · K)
(kJ/mol) S (J/mol · K)O2(g) 0 0 205.0
O3(g) 142.3 163.4 237.6
3O2(g)
 2O3(g)
2O3(g)A) 2.04 * 107
B) 5.44 *10-14
C) 2.67 * 10-8
D) 2.91 * 10-9
E) 3.65 *10-12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



