Deck 13: Organic Chemistry: Fuels, Pharmaceuticals, and Materials
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/112
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Organic Chemistry: Fuels, Pharmaceuticals, and Materials
1
Iso-octane has the following structure. In this structure, how many carbon atoms are bonded to three other carbon atoms? 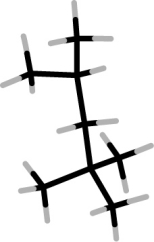
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
1
2
A saturated compound composed solely of carbon and hydrogen must be __________
A) an alkane.
B) an alkene.
C) an alkyne.
D) either an alkane or an alkene.
E) either an alkene or an alkyne.
A) an alkane.
B) an alkene.
C) an alkyne.
D) either an alkane or an alkene.
E) either an alkene or an alkyne.
an alkane.
3
A subunit of an organic compound that confers particular chemical and physical properties is termed __________
A) a monomer.
B) an oligomer.
C) a functional group.
D) a synthetic unit.
E) an isomer.
A) a monomer.
B) an oligomer.
C) a functional group.
D) a synthetic unit.
E) an isomer.
a functional group.
4
Organic chemistry encompasses the chemistry of all __________
A) hydrocarbons.
B) functional groups.
C) monomers, oligomers, and polymers.
D) naturally occurring compounds.
E) carbon compounds.
A) hydrocarbons.
B) functional groups.
C) monomers, oligomers, and polymers.
D) naturally occurring compounds.
E) carbon compounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Where is the carbon-carbon double bond in the hydrocarbon shown? 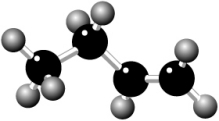
A) on the left
B) in the middle
C) on the right
D) on each bond
E) spread over all three bonds because of resonance

A) on the left
B) in the middle
C) on the right
D) on each bond
E) spread over all three bonds because of resonance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following are true regarding cyclohexane, whose carbon skeleton is shown? 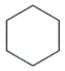
(I) The molecule is flat.
(II) Each carbon is bonded to four other atoms.
(III) Each carbon is sp3 hybridized.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
E) I, II, and III are all true.

(I) The molecule is flat.
(II) Each carbon is bonded to four other atoms.
(III) Each carbon is sp3 hybridized.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
E) I, II, and III are all true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which is not true about n-alkanes?
A) Their formulas are all CnH2n+2.
B) All of the carbon atoms are centers of tetrahedral geometry.
C) Their melting points increase with the number of carbon atoms.
D) Their vapor pressures increase with the number of carbon atoms.
E) All of the carbons are sp3 hybridized.
A) Their formulas are all CnH2n+2.
B) All of the carbon atoms are centers of tetrahedral geometry.
C) Their melting points increase with the number of carbon atoms.
D) Their vapor pressures increase with the number of carbon atoms.
E) All of the carbons are sp3 hybridized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the molecular formula for the compound illustrated below? 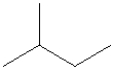
A) C5H8
B) C5H9
C) C5H10
D) C5H11
E) C5H12

A) C5H8
B) C5H9
C) C5H10
D) C5H11
E) C5H12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The basic building block of a polymer is called ___________
A) a functional group.
B) a monomer.
C) a monotone.
D) an oligomer.
E) an addition.
A) a functional group.
B) a monomer.
C) a monotone.
D) an oligomer.
E) an addition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is true about normal alkanes?
A) They all exhibit strong hydrogen bonding with one another and with water.
B) They all contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in consistent ratios.
C) Some are gases, some are liquids, and some are solids at room temperature.
D) Some are yellow, some are red, and some are blue, depending on the chain length.
E) They have the formula CnH2n+2 if they are linear or branched or CnH2n if they are cyclic.
A) They all exhibit strong hydrogen bonding with one another and with water.
B) They all contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in consistent ratios.
C) Some are gases, some are liquids, and some are solids at room temperature.
D) Some are yellow, some are red, and some are blue, depending on the chain length.
E) They have the formula CnH2n+2 if they are linear or branched or CnH2n if they are cyclic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A compound composed solely of carbon and hydrogen that is unsaturated must be __________
A) an alkane.
B) an alkene.
C) an alkyne.
D) either an alkane or an alkene.
E) either an alkene or an alkyne.
A) an alkane.
B) an alkene.
C) an alkyne.
D) either an alkane or an alkene.
E) either an alkene or an alkyne.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The C - C - C bond angles in octane (CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3) are ___________
A) 180°.
B) 120°.
C) 90°.
D) 109.5°.
E) 60°.
A) 180°.
B) 120°.
C) 90°.
D) 109.5°.
E) 60°.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A hydrocarbon is a compound that contains __________
A) carbon with hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio 2:1.
B) carbon with hydrogen and oxygen in any ratio.
C) only carbon and hydrogen.
D) carbon, hydrogen, and any functional groups.
E) carbon and any other elements.
A) carbon with hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio 2:1.
B) carbon with hydrogen and oxygen in any ratio.
C) only carbon and hydrogen.
D) carbon, hydrogen, and any functional groups.
E) carbon and any other elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The -CH2- unit is known as
A) a methyl group.
B) a methylene group.
C) an acetylene group.
D) an alkyne group.
E) an alkene group.
A) a methyl group.
B) a methylene group.
C) an acetylene group.
D) an alkyne group.
E) an alkene group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is not likely to be a component of a natural gas deposit?
A) CH4
B) C3H8
C) C4H8
D) C4H10
E) C8H18
A) CH4
B) C3H8
C) C4H8
D) C4H10
E) C8H18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the degree of unsaturation of CH2  CH - C
CH - C  CH?
CH?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
 CH - C
CH - C  CH?
CH?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When 1 mol of an alkene with one degree of unsaturation is hydrogenated, how many moles of hydrogen gas react?
A) 0 mol
B) 1.5 mol
C) 0.5 mol
D) 1.0 mol
E) 2.0 mol
A) 0 mol
B) 1.5 mol
C) 0.5 mol
D) 1.0 mol
E) 2.0 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a methyl group?
A) -CH2
B) =CH2
C) -CH2-
D) =CH=
E) -CH3
A) -CH2
B) =CH2
C) -CH2-
D) =CH=
E) -CH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following tends to be true of polymers but not small molecules?
(I)Variable instead of constant composition
(II)A poorly defined melting point
(III)Solid state regions that are disordered
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I, II, and III
E) None of these, as polymers are molecules just like small molecules only bigger.
(I)Variable instead of constant composition
(II)A poorly defined melting point
(III)Solid state regions that are disordered
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I, II, and III
E) None of these, as polymers are molecules just like small molecules only bigger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following structures is an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
A)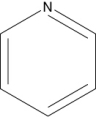
B)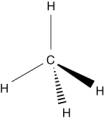
C)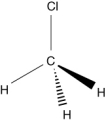
D)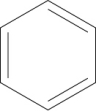
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider the 1,2-dichloro derivative of ethylene in which one of the hydrogen atoms on each of the carbon atoms in ethylene is substituted with a chlorine atom, giving the structural formula CHClCHCl. Which of the following is true?
A) The cis isomer is more polar.
B) The trans isomer is more polar.
C) Neither cis nor trans isomers are polar.
D) Both cis and trans isomers are equally polar.
E) There are no isomers for this molecule.
A) The cis isomer is more polar.
B) The trans isomer is more polar.
C) Neither cis nor trans isomers are polar.
D) Both cis and trans isomers are equally polar.
E) There are no isomers for this molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the molecular formula for the following compound? 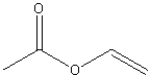
A) C4H5O2
B) C4H6O2
C) C4H7O2
D) C4H8O2
E) C4H10O2

A) C4H5O2
B) C4H6O2
C) C4H7O2
D) C4H8O2
E) C4H10O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Name the compound. 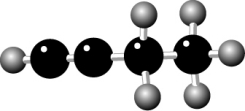
A) 1-butene
B) 1-butyne
C) 2-butene
D) 2-butyne
E) butane

A) 1-butene
B) 1-butyne
C) 2-butene
D) 2-butyne
E) butane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following pairs has the same molecular formula?
A) hexene and cyclohexane
B) octane and cyclooctane
C) hexane and benzene
D) hexane and cylcohexene
E) methyl and methylene
A) hexene and cyclohexane
B) octane and cyclooctane
C) hexane and benzene
D) hexane and cylcohexene
E) methyl and methylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For each of the bonds in the figure below, identify whether the bond is cis, trans, or neither cis nor trans. 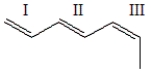
A) I-cis; II-trans; III-cis
B) I-trans; II-cis; III-trans
C) I-neither; II-trans; III-cis
D) I-neither; II-cis; III-trans
E) I-neither; II-cis; III-cis

A) I-cis; II-trans; III-cis
B) I-trans; II-cis; III-trans
C) I-neither; II-trans; III-cis
D) I-neither; II-cis; III-trans
E) I-neither; II-cis; III-cis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the formula for n-nonane?
A) CH3(CH2)9CH3
B) CH3(CH2)7CH3
C) CH3(CH2)17CH3
D) CH3(CH2)5CH3
E) CH3(CH2)8CH3
A) CH3(CH2)9CH3
B) CH3(CH2)7CH3
C) CH3(CH2)17CH3
D) CH3(CH2)5CH3
E) CH3(CH2)8CH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the molecular formula for the following compound? 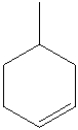
A) C6H11
B) C6H12
C) C7H11
D) C7H12
E) C7H14

A) C6H11
B) C6H12
C) C7H11
D) C7H12
E) C7H14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Without working out all the structures, which has the larger number of structural isomers, C14H30 or C15H32?
A) C14H30
B) C15H32
C) They have the same number of isomers.
D) There is no way to tell without working out all the structures.
A) C14H30
B) C15H32
C) They have the same number of isomers.
D) There is no way to tell without working out all the structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Name this molecule. 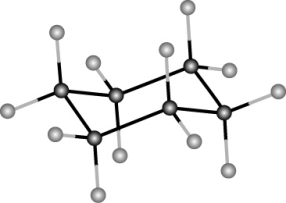
A) dodecane
B) cyclohexane (boat conformation)
C) cyclohexane (chair conformation)
D) puckerane
E) trans-cyclohexane

A) dodecane
B) cyclohexane (boat conformation)
C) cyclohexane (chair conformation)
D) puckerane
E) trans-cyclohexane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Cyclic alkanes differ from normal alkanes in ___________
A) the ratio of hydrogen to carbon.
B) their utility as a combustible fuel.
C) the orbital hybridization on the carbon atoms.
D) the number of hydrogens bonded to non-terminal carbon atoms.
E) the degree to which electrons are delocalized.
A) the ratio of hydrogen to carbon.
B) their utility as a combustible fuel.
C) the orbital hybridization on the carbon atoms.
D) the number of hydrogens bonded to non-terminal carbon atoms.
E) the degree to which electrons are delocalized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Most simple ionic compounds that are soluble in water are not soluble in organic solvents. However, replacing a common cation such as Na+ with an alkyl ammonium ion with four alkyl groups greatly enhances solubility of the ionic compound in many organic solvents. Which formula represents the tetrabutylammonium ion that is found in tetrabutylammonium bromide?
A) [(CH3)4N]+
B) [(CH3CH2)4N]+
C) [(CH3(CH2)2)4N]+
D) [(CH3(CH2)3)4N]+
E) [C(CH3)3NH2]+
A) [(CH3)4N]+
B) [(CH3CH2)4N]+
C) [(CH3(CH2)2)4N]+
D) [(CH3(CH2)3)4N]+
E) [C(CH3)3NH2]+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Does this molecule have both cis and trans isomers? 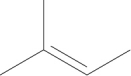
A) Yes, this is the cis isomer.
B) Yes, this is the trans isomer.
C) No, it has only the cis isomer.
D) No, it has only the trans isomer.
E) No, this molecule does not have cis-trans isomerism.

A) Yes, this is the cis isomer.
B) Yes, this is the trans isomer.
C) No, it has only the cis isomer.
D) No, it has only the trans isomer.
E) No, this molecule does not have cis-trans isomerism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Name the compound. 
A) cis-3-octene
B) trans-3-octene
C) cis-5-octene
D) trans-5-octene
E) 1-ethyl-2-butyl ethylene

A) cis-3-octene
B) trans-3-octene
C) cis-5-octene
D) trans-5-octene
E) 1-ethyl-2-butyl ethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the molecular formula for the compound illustrated below? 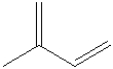
A) C5H7
B) C5H8
C) C5H9
D) C5H10
E) C5H23

A) C5H7
B) C5H8
C) C5H9
D) C5H10
E) C5H23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A molecule with the formula C7H14 was found to have carbons that were all identical in terms of structure. That is, each carbon atom was bonded to exactly the same kinds of atoms as all the rest. What is a reasonable structure for this molecule?
A) CH3(CH2)5CH3
B)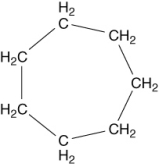
C) CH2(CH2)5CH2
D)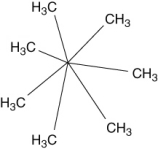
A) CH3(CH2)5CH3
B)

C) CH2(CH2)5CH2
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consider the 1,2-dichloro derivative of ethylene in which one of the hydrogen atoms on each of the carbon atoms in ethylene is substituted with a chlorine atom, giving the structural formula CHClCHCl. Does this molecule have geometrical isomers? Remember that ethylene does not.
A) yes, because the chlorines can be placed on the same or opposite sides of the double bond
B) yes, because the chlorines can be placed on either one or both of the carbons
C) no, because both the formula and bonds are the same in all skeletal structures
D) no, because the two structures can interconvert through bond rotation
E) no, because there are less than four atoms bound to each carbon
A) yes, because the chlorines can be placed on the same or opposite sides of the double bond
B) yes, because the chlorines can be placed on either one or both of the carbons
C) no, because both the formula and bonds are the same in all skeletal structures
D) no, because the two structures can interconvert through bond rotation
E) no, because there are less than four atoms bound to each carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Crude oil is composed mostly of
A) liquefied carbon.
B) liquefied rock and soil.
C) compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen.
D) decomposed anaerobic bacteria.
E) compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
A) liquefied carbon.
B) liquefied rock and soil.
C) compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen.
D) decomposed anaerobic bacteria.
E) compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How many structural (constitutional) isomers are there for propylene, and why?
A) two, because of resonance
B) two, because of geometrical isomerism
C) two, because the double bond can be in either one of two locations
D) none, because the two skeletal structures can be superimposed
E) none, because double bonds always occur on the right in alkenes
A) two, because of resonance
B) two, because of geometrical isomerism
C) two, because the double bond can be in either one of two locations
D) none, because the two skeletal structures can be superimposed
E) none, because double bonds always occur on the right in alkenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Name the compound with the structural formula CH3(CH2)16CH3.
A) n-octane
B) n-hexadecane
C) n-octadecane
D) n-decane
E) 1,16-dimethylhexadecane
A) n-octane
B) n-hexadecane
C) n-octadecane
D) n-decane
E) 1,16-dimethylhexadecane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the systematic name of the molecule shown? 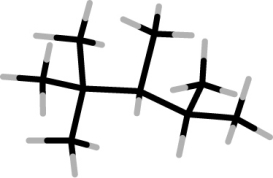
A) 2,2,3,4-tetramethylpentane
B) 2,3,4,4-tetramethylpentane
C) 1,2,3,4,4-pentamethylbutane
D) 1,1,1,2,3,3-hexamethylpropane
E) 2-tert-butyl-3-methylbutane

A) 2,2,3,4-tetramethylpentane
B) 2,3,4,4-tetramethylpentane
C) 1,2,3,4,4-pentamethylbutane
D) 1,1,1,2,3,3-hexamethylpropane
E) 2-tert-butyl-3-methylbutane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How many structural isomers does toluene (C6H5CH3) have?
A) None, i.e., there is only 1 molecule
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) None, i.e., there is only 1 molecule
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The monomer for polystyrene is shown below. Which of the bonds is involved in the polymerization process? 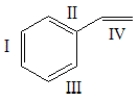
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) IV only
E) Bonds I-IV are all involved in polymerization.

A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) IV only
E) Bonds I-IV are all involved in polymerization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following shows a small section of polyethylene?
A)
B)
C)
D)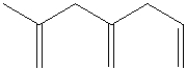
E)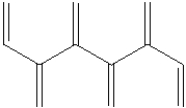
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Aldrich Chemical Company catalogue lists the three isomers of xylene as having boiling points of 143-145°C, 138-139°C, and 138°C. Which isomer has the highest boiling point, and why?
A) o-xylene (1,2-dimethylbenzene) because of its polarity
B) p-xylene (1,4-dimethylbenzene) because of its polarity
C) p-xylene (1,4-dimethylbenzene) because of its para-normalcy
D) m-xylene (1,3-dimethylbenzene) because of its C2 symmetry
E) o,m,p-xylene (1,2,3,4-tetramethylbenzene) because of its molar mass
A) o-xylene (1,2-dimethylbenzene) because of its polarity
B) p-xylene (1,4-dimethylbenzene) because of its polarity
C) p-xylene (1,4-dimethylbenzene) because of its para-normalcy
D) m-xylene (1,3-dimethylbenzene) because of its C2 symmetry
E) o,m,p-xylene (1,2,3,4-tetramethylbenzene) because of its molar mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Name the compound. 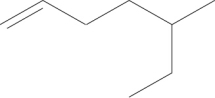
A) 3-methyl-6-heptene
B) 5-ethyl-1-hexene
C) 5-methyl-1-heptene
D) 2-ethyl-5-hexene
E) 3-methylpentylethylene

A) 3-methyl-6-heptene
B) 5-ethyl-1-hexene
C) 5-methyl-1-heptene
D) 2-ethyl-5-hexene
E) 3-methylpentylethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What functional group is found in the following molecule? 
A) amine
B) amide
C) ammonia
D) ammonium
E) amonyl

A) amine
B) amide
C) ammonia
D) ammonium
E) amonyl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Name the compound. 
A) trans-3-hexene
B) cis-3-hexene
C) trans-4-hexene
D) cis-4-hexene
E) 1,2-diethylethylene

A) trans-3-hexene
B) cis-3-hexene
C) trans-4-hexene
D) cis-4-hexene
E) 1,2-diethylethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How many structural isomers does xylene have?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Naphthalene, a polyaromatic hydrocarbon, is used for mothballs. Its molecular formula is C10H8. How many fused aromatic rings does naphthalene have in its molecular structure?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A homopolymer is a polymer in which ___________
A) each polymer has the same mass.
B) each polymer has the same mass and structure.
C) the monomers are distributed uniformly throughout the polymer.
D) the polymers are distributed uniformly throughout the solution.
E) there is only one monomer unit.
A) each polymer has the same mass.
B) each polymer has the same mass and structure.
C) the monomers are distributed uniformly throughout the polymer.
D) the polymers are distributed uniformly throughout the solution.
E) there is only one monomer unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is not a difference between cyclohexane and benzene?
A) Cyclohexane is puckered, but benzene is planar.
B) Cyclohexane carbons are sp3 hybridized, but benzene carbons are sp2 hybridized.
C) Cyclohexane is a combustible hydrocarbon, but benzene has such a stable aromatic structure that it does not burn.
D) Cyclohexane has 12 hydrogen atoms in its structure, but benzene has 6 hydrogen atoms in its structure.
E) Cyclohexane is not aromatic, but benzene is.
A) Cyclohexane is puckered, but benzene is planar.
B) Cyclohexane carbons are sp3 hybridized, but benzene carbons are sp2 hybridized.
C) Cyclohexane is a combustible hydrocarbon, but benzene has such a stable aromatic structure that it does not burn.
D) Cyclohexane has 12 hydrogen atoms in its structure, but benzene has 6 hydrogen atoms in its structure.
E) Cyclohexane is not aromatic, but benzene is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What type of amine is adrenaline, which is depicted below? 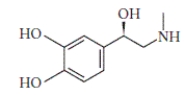
A) aromatic
B) auxiliary
C) primary
D) secondary
E) tertiary

A) aromatic
B) auxiliary
C) primary
D) secondary
E) tertiary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Are the methyl groups in xylene included in the aromatic part of the molecular structure?
A) Yes, the aromatic bonding extends throughout the molecule.
B) Yes, but only when the resonance form with double bonds to the methyl groups exists.
C) No, only the carbons in the ring are involved in aromatic bonding.
D) No, only the hydrogens in the ring are involved in the aromatic bonding.
E) No, only the carbon atoms in xylene are involved in aromatic bonding, not the hydrogens.
A) Yes, the aromatic bonding extends throughout the molecule.
B) Yes, but only when the resonance form with double bonds to the methyl groups exists.
C) No, only the carbons in the ring are involved in aromatic bonding.
D) No, only the hydrogens in the ring are involved in the aromatic bonding.
E) No, only the carbon atoms in xylene are involved in aromatic bonding, not the hydrogens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is/are true regarding aromatic hydrocarbons?
(I)They are particularly stable because of delocalized bonding.
(II)They are particularly stable because of their covalent network bonding.
(III)They are particularly unstable as evidenced by their tendency to evaporate.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) I and III only
(I)They are particularly stable because of delocalized bonding.
(II)They are particularly stable because of their covalent network bonding.
(III)They are particularly unstable as evidenced by their tendency to evaporate.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) I and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following monomers is used in making the polymer illustrated below? 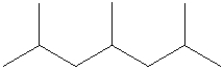
A)
B)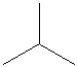
C)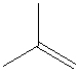
D)
E)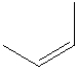

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Do carbon atoms in aromatic hydrocarbon molecules (not ions) obey the octet rule?
A) No, each carbon is bonded to only three atoms, and there are no lone pairs.
B) No, each carbon has one single bond and one double bond for a total of only six electrons.
C) Yes, each carbon obeys the octet rule.
D) Yes, but only because the double bond is counted twice owing to the resonance structures.
E) Yes, but only when one or the other resonance form dominates, not when the structure is an average of the two.
A) No, each carbon is bonded to only three atoms, and there are no lone pairs.
B) No, each carbon has one single bond and one double bond for a total of only six electrons.
C) Yes, each carbon obeys the octet rule.
D) Yes, but only because the double bond is counted twice owing to the resonance structures.
E) Yes, but only when one or the other resonance form dominates, not when the structure is an average of the two.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following structures represents cyclohexene?
A)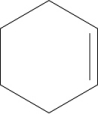
B)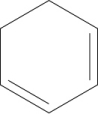
C)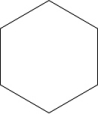
D)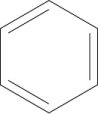
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Delocalized bonding in aromatic hydrocarbons is possible because of ___________
A) the fact that electrons can move very quickly from one resonance form to another.
B) adjacent 2pz orbitals each having one electron.
C) Wade's rules.
D) double-headed arrows.
E) Cooper pairs.
A) the fact that electrons can move very quickly from one resonance form to another.
B) adjacent 2pz orbitals each having one electron.
C) Wade's rules.
D) double-headed arrows.
E) Cooper pairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is another name for methylbenzene?
A) toluene
B) xylene
C) naphthalene
D) Jolene
E) 1-methyl-2,4,6-cyclohexene
A) toluene
B) xylene
C) naphthalene
D) Jolene
E) 1-methyl-2,4,6-cyclohexene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is an amine functional group?
A) -COOH
B) -OH
C) -NH
D) -NH2
E) -CONH2
A) -COOH
B) -OH
C) -NH
D) -NH2
E) -CONH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The alcohol functional group has the bonding arrangement ___________
A) C -O -H.
B) C -O -C.
C) Al -O -H.
D) C -O -O -H.
E) R -O -H, where R is any element.
A) C -O -H.
B) C -O -C.
C) Al -O -H.
D) C -O -O -H.
E) R -O -H, where R is any element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Rank the following according to their fuel values in order of increasing energy/mass. C8H18; CO; CH3OH; CH3OCH3
A) CO < CH3OCH3 < CH3OH < C8H18
B) CH3OCH3 < CO < CH3OH < C8H18
C) CO < CH3OH < CH3OCH3 < C8H18
D) C8H18 < CO < CH3OH < CH3OCH3
E) C8H18 < CH3OCH3 < CH3OH < CO
A) CO < CH3OCH3 < CH3OH < C8H18
B) CH3OCH3 < CO < CH3OH < C8H18
C) CO < CH3OH < CH3OCH3 < C8H18
D) C8H18 < CO < CH3OH < CH3OCH3
E) C8H18 < CH3OCH3 < CH3OH < CO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which functional group is found in the following molecule? 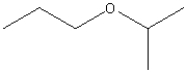
A) alcohol
B) aldehyde
C) carbonyl
D) ester
E) ether

A) alcohol
B) aldehyde
C) carbonyl
D) ester
E) ether

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What functional group is found in the following molecule? 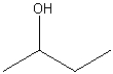
A) alcohol
B) aldehyde
C) aquo
D) carbonyl
E) hydroxyl

A) alcohol
B) aldehyde
C) aquo
D) carbonyl
E) hydroxyl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following illustrates the aldehyde functional group?
A)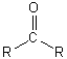
B)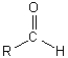
C)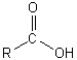
D)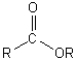
E) All of the above illustrate the aldehyde functional group.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) All of the above illustrate the aldehyde functional group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The characteristic "fishy" odor comes from methylamine (CH3NH2), which is similar to ammonia (NH3) in structure and also in its ability to react with acids as a weak base. Why would the acid form of methylamine not have as strong an odor as methylamine?
A) because it would decompose to methane and ammonia
B) because it would not be volatile as a polyatomic ion
C) because it would melt in the acid
D) because it would decompose to carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen
E) because it would have a different three-dimensional structure
A) because it would decompose to methane and ammonia
B) because it would not be volatile as a polyatomic ion
C) because it would melt in the acid
D) because it would decompose to carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen
E) because it would have a different three-dimensional structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
MTBE (methyl tert-butyl ether) is:
A)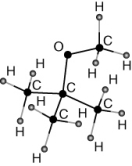
B)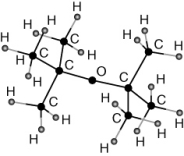
C)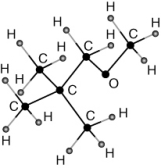
D)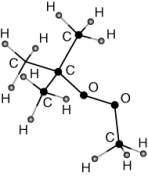
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Gasoline additives like ethanol are employed to
A) decrease odor.
B) promote complete combustion.
C) decrease octane rating.
D) make the fuel less volatile.
E) increase fuel value.
A) decrease odor.
B) promote complete combustion.
C) decrease octane rating.
D) make the fuel less volatile.
E) increase fuel value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following class of compounds is not used in gasoline?
A) alcohols
B) ethers
C) thiols
D) alkanes
E) octanes
A) alcohols
B) ethers
C) thiols
D) alkanes
E) octanes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Rank these molecules with respect to the increasing oxidation number of the carbon atom: formic acid (HCOOH); methane (CH4); methanol (CH3OH); carbon dioxide (CO2); graphite (C).
A) formic acid; carbon dioxide; methanol; methane; graphite
B) methanol; methane; graphite; carbon dioxide; formic acid
C) methane; methanol; graphite; formic acid; carbon dioxide
D) carbon dioxide; formic acid; graphite; methanol; methane
E) The oxidation number of carbon is the same in all of these compounds.
A) formic acid; carbon dioxide; methanol; methane; graphite
B) methanol; methane; graphite; carbon dioxide; formic acid
C) methane; methanol; graphite; formic acid; carbon dioxide
D) carbon dioxide; formic acid; graphite; methanol; methane
E) The oxidation number of carbon is the same in all of these compounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of these functional groups does not contain a carbonyl group?
A) aldehyde
B) carboxylic acid
C) ester
D) ether
E) ketone
A) aldehyde
B) carboxylic acid
C) ester
D) ether
E) ketone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which functional group is found in the following molecule? 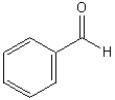
A) aldehyde
B) carboxylic acid
C) ester
D) ether
E) ketone

A) aldehyde
B) carboxylic acid
C) ester
D) ether
E) ketone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Methane used for fuel and commonly called natural gas is odorless, but for safety it has a small quantity of foul-smelling methylmercaptan (CH3SH) added. The "mercaptan" functional group is most similar to which of the following?
A) carboxylic acid
B) amine
C) alcohol
D) aldehyde
E) ether
A) carboxylic acid
B) amine
C) alcohol
D) aldehyde
E) ether

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which functional group is found in the following molecule? 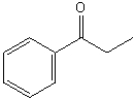
A) aldehyde
B) carboxylic acid
C) ester
D) ether
E) ketone

A) aldehyde
B) carboxylic acid
C) ester
D) ether
E) ketone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Alcohols used as a gasoline additive or substitute are often called biofuels. Similar organic compounds derived from vegetable oils and fats are called biodiesels, which are not alcohols but another class of organic chemicals called esters. Qualitatively compare the combustion energy content (kJ/g) of the four-carbon alcohol, butanol (CH3CH2CH2CH2OH), with the energy content (kJ/g) of the four-carbon ester, ethyl acetate (CH3COOCH2CH3).
A) Ethyl acetate has less energy/mass than butanol.
B) Ethyl acetate has more energy/mass than butanol.
C) The two compounds have roughly the same energy/mass.
D) These are not two different compounds and so must have the same energy/mass.
E) There is no basis for determining this without some form of enthalpy values.
A) Ethyl acetate has less energy/mass than butanol.
B) Ethyl acetate has more energy/mass than butanol.
C) The two compounds have roughly the same energy/mass.
D) These are not two different compounds and so must have the same energy/mass.
E) There is no basis for determining this without some form of enthalpy values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The C - O - C bonding arrangement is called the _____ functional group.
A) alcohol
B) ester
C) amine
D) ether
E) carbonyl
A) alcohol
B) ester
C) amine
D) ether
E) carbonyl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the following structure of tert-butyl alcohol, identify the tertiary carbon. 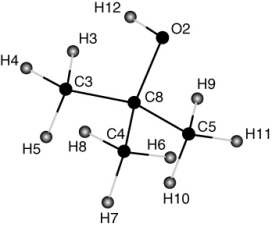
A) C3
B) C4
C) C5
D) C6
E) C8

A) C3
B) C4
C) C5
D) C6
E) C8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Ethanol is a renewable chemical energy source, but there are presently some barriers to its use as the primary fuel for cars. Which of the following is not among these barriers?
A) It is more expensive than gasoline.
B) It has a lower fuel value than gasoline.
C) Much of the energy it can produce is expended in its production.
D) It is a greater contributor to global warming than gasoline because it produces more carbon dioxide per carbon atom than gasoline.
E) All of the above are barriers to its use as a primary fuel.
A) It is more expensive than gasoline.
B) It has a lower fuel value than gasoline.
C) Much of the energy it can produce is expended in its production.
D) It is a greater contributor to global warming than gasoline because it produces more carbon dioxide per carbon atom than gasoline.
E) All of the above are barriers to its use as a primary fuel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following is the ketone functional group?
A)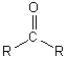
B)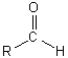
C)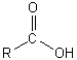
D)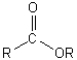
E) All of the above illustrate the ketone functional group.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) All of the above illustrate the ketone functional group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Ethanol is water soluble. Which of the following sketches properly illustrates the strongest interaction between water and ethanol that is responsible for this solubility?
A)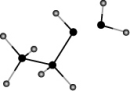
B)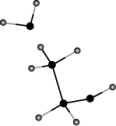
C)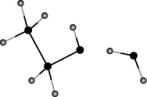
D)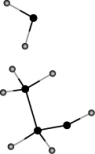
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



