Deck 12: The Chemistry of Solids
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: The Chemistry of Solids
1
The bonding in solid-state metals can be described as __________
A) nonexistent.
B) a covalent network.
C) an electron sea.
D) highly directional.
E) ionic.
A) nonexistent.
B) a covalent network.
C) an electron sea.
D) highly directional.
E) ionic.
an electron sea.
2
At a historic Civil War battleground, a stack of cannonballs looked like the picture below on the far left. Removing the top cannonball resulted in the middle view, and removing the next layer resulted in the view on the right. What sort of packing was used in stacking the cannonballs? 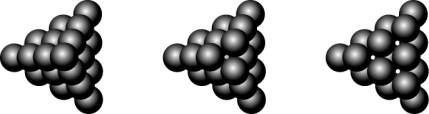
A) cannonball closest-packed
B) hexagonal closest-packed
C) cubic closest-packed
D) random packed
E) body-centered closest-packed

A) cannonball closest-packed
B) hexagonal closest-packed
C) cubic closest-packed
D) random packed
E) body-centered closest-packed
cubic closest-packed
3
A cubic closest-packed structure has hexagonally arranged layers of atoms in the series __________
A) ababab.
B) abcabcabc.
C) abcbabcbabcba.
D) abacabacaba.
E) aaaaaa.
A) ababab.
B) abcabcabc.
C) abcbabcbabcba.
D) abacabacaba.
E) aaaaaa.
abcabcabc.
4
The two types of closest-packed lattices are __________
A) cubic closest-packed and face-centered cubic.
B) cubic closest-packed and hexagonal closest-packed.
C) cubic closest-packed and random closest-packed.
D) cubic closest-packed and pyramidal closest-packed.
E) simple cubic and hexagonal closest-packed.
A) cubic closest-packed and face-centered cubic.
B) cubic closest-packed and hexagonal closest-packed.
C) cubic closest-packed and random closest-packed.
D) cubic closest-packed and pyramidal closest-packed.
E) simple cubic and hexagonal closest-packed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When silicon is doped with gallium, electrical conduction increases because __________
A) gallium has fewer valence electrons than silicon so holes are created in the valence band of silicon.
B) gallium has more valence electrons than silicon so electrons are added to the conduction band of silicon.
C) gallium causes electrons to be transferred from the valence band of silicon to the conduction band of silicon.
D) gallium causes electrons to be transferred from the conduction band of silicon to the valence band of silicon.
E) gallium is a better conductor of electricity than silicon.
A) gallium has fewer valence electrons than silicon so holes are created in the valence band of silicon.
B) gallium has more valence electrons than silicon so electrons are added to the conduction band of silicon.
C) gallium causes electrons to be transferred from the valence band of silicon to the conduction band of silicon.
D) gallium causes electrons to be transferred from the conduction band of silicon to the valence band of silicon.
E) gallium is a better conductor of electricity than silicon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following elements are semiconductors? C, Si, Ge, Sn
A) C and Si only
B) Si and Ge only
C) Ge and Sn only
D) None of these elements are semiconductors unless a dopant is added.
E) All of these elements are semiconductors.
A) C and Si only
B) Si and Ge only
C) Ge and Sn only
D) None of these elements are semiconductors unless a dopant is added.
E) All of these elements are semiconductors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The molecular orbital description for metal bonding is different from that for diatomic molecules in that __________
A) there are no antibonding orbitals in the metal bonding description.
B) quantum theory no longer applies as the orbitals are continuous.
C) the orbitals are so close in energy that they are referred to as bands.
D) the increased number of electrons results in each bond being stronger.
E) All the above are true.
A) there are no antibonding orbitals in the metal bonding description.
B) quantum theory no longer applies as the orbitals are continuous.
C) the orbitals are so close in energy that they are referred to as bands.
D) the increased number of electrons results in each bond being stronger.
E) All the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The band structure of semiconductors differs from that of metal conductors in that __________
A) metal bands are relatively empty while semiconductor bands are nearly full.
B) metal bands are nearly full while semiconductor bands are relatively empty.
C) metal conduction bands are lower in energy than valence bands while semiconductor conduction bands are higher in energy than valence bands.
D) metal conduction bands are higher in energy than valence bands while semiconductor conduction bands are lower in energy than valence bands.
E) valence bands in metals are either partially empty or overlap with conduction bands while these bands in semiconductors are separated by a small gap.
A) metal bands are relatively empty while semiconductor bands are nearly full.
B) metal bands are nearly full while semiconductor bands are relatively empty.
C) metal conduction bands are lower in energy than valence bands while semiconductor conduction bands are higher in energy than valence bands.
D) metal conduction bands are higher in energy than valence bands while semiconductor conduction bands are lower in energy than valence bands.
E) valence bands in metals are either partially empty or overlap with conduction bands while these bands in semiconductors are separated by a small gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Molecular orbital theory can be applied __________
A) only to two adjacent metal atoms.
B) only to a few metal atoms that are very close to each other.
C) to any number of metal atoms.
D) to nonmetals only-not to metals.
E) to nonmetals and ionic bonds only-not to metals.
A) only to two adjacent metal atoms.
B) only to a few metal atoms that are very close to each other.
C) to any number of metal atoms.
D) to nonmetals only-not to metals.
E) to nonmetals and ionic bonds only-not to metals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Light-emitting diodes are semiconductors that emit light when a current is passed through them. What is the key factor that must be changed to change the wavelength of the emitted light in an LED?
A) the width of the valence band
B) the width of the conduction band
C) the width of the band gap
D) the magnitude of the current
E) the type of semiconductor (p vs. n)
A) the width of the valence band
B) the width of the conduction band
C) the width of the band gap
D) the magnitude of the current
E) the type of semiconductor (p vs. n)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following can be used to increase the conductivity of any semimetal?
(I)Adding an element with one additional valence electron
(II)Adding an element with one fewer valence electron
(III)Lowering the temperature
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) I, II and III.
(I)Adding an element with one additional valence electron
(II)Adding an element with one fewer valence electron
(III)Lowering the temperature
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) I, II and III.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which element would be used to dope silicon to produce a p-type semiconductor?
A) boron (B)
B) carbon (C)
C) aluminum (Al)
D) phosphorus (P)
E) germanium (Ge)
A) boron (B)
B) carbon (C)
C) aluminum (Al)
D) phosphorus (P)
E) germanium (Ge)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The face-centered cubic structure is also known as __________
A) cubic closest-packed.
B) hexagonal closest-packed.
C) square closest-packed.
D) spherical closest-packed.
E) none of the above as it is not a closest-packed pattern.
A) cubic closest-packed.
B) hexagonal closest-packed.
C) square closest-packed.
D) spherical closest-packed.
E) none of the above as it is not a closest-packed pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Electrical and thermal conductivity in metals __________
A) is explained by a dipolar coupling model.
B) is explained by band theory.
C) is explained by matrix isolation techniques.
D) is explained by temporary ionization.
E) is a function of the level of contamination by excess electrons.
A) is explained by a dipolar coupling model.
B) is explained by band theory.
C) is explained by matrix isolation techniques.
D) is explained by temporary ionization.
E) is a function of the level of contamination by excess electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
GaAs and AlGaAs2 are examples of __________ semiconductors.
A) light-emitting diode (LED)
B) sound-emitting
C) np
D) non-
E) dual voltage
A) light-emitting diode (LED)
B) sound-emitting
C) np
D) non-
E) dual voltage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When Ge is doped with Ga, it produces a(n) __________ -type semiconductor.
A) p
B) n
C) q
D) np
E) No semiconductor will be produced.
A) p
B) n
C) q
D) np
E) No semiconductor will be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Metal solids are good conductors of electricity because __________
A) they are easily ionized.
B) their valence electrons are not localized.
C) they are easily reduced and oxidized.
D) they can be drawn into wires.
E) they are ductile.
A) they are easily ionized.
B) their valence electrons are not localized.
C) they are easily reduced and oxidized.
D) they can be drawn into wires.
E) they are ductile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which element would be used to dope germanium to produce an n-type semiconductor?
A) Ga
B) Sn
C) Si
D) As
E) Cu
A) Ga
B) Sn
C) Si
D) As
E) Cu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When Si is doped with P, it produces a(n) __________ -type semiconductor.
A) p
B) n
C) q
D) np
E) No semiconductor will be produced.
A) p
B) n
C) q
D) np
E) No semiconductor will be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Band theory of bonding in solids __________
A) is an extension of molecular orbital theory.
B) describes bonds as rubber bands.
C) does not apply to any type of solid other than metals.
D) explains bond formation in metals, but not their physical properties.
E) All of the above are correct.
A) is an extension of molecular orbital theory.
B) describes bonds as rubber bands.
C) does not apply to any type of solid other than metals.
D) explains bond formation in metals, but not their physical properties.
E) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How many nearest neighbor atoms are there around each atom in a body-centered cubic unit cell?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Iron (Fe) has a density of 7.874 g/cm3 and crystallizes in a body-centered cubic structure. What is the atomic radius of iron?
A) 99 pm
B) 114 pm
C) 124 pm
D) 143 pm
E) 255 pm
A) 99 pm
B) 114 pm
C) 124 pm
D) 143 pm
E) 255 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How many nearest neighbor atoms are there around each atom in a face-centered cubic unit cell?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Polonium crystallizes in a simple cubic pattern. How many polonium atoms are in each unit cell?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The alpha form of polonium (Po) crystallizes as a simple cubic unit cell with an edge length of 335 pm. What is the atomic radius of polonium?
A) 84 pm
B) 168 pm
C) 335 pm
D) 175 pm
E) 808 pm
A) 84 pm
B) 168 pm
C) 335 pm
D) 175 pm
E) 808 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Pure solid metals __________
A) do not crystallize.
B) are amorphous.
C) often crystallize in closest-packed structures.
D) often crystallize in very complex unit cells.
E) are like liquids with the nuclei flowing through a sea of electrons.
A) do not crystallize.
B) are amorphous.
C) often crystallize in closest-packed structures.
D) often crystallize in very complex unit cells.
E) are like liquids with the nuclei flowing through a sea of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the sodium chloride unit cell, the chloride ions form a cube in which each side is arranged like the following figure. The circles represent the positions of the chloride ions on one square face of the cube. All the other faces are the same. What is the name of this unit cell? 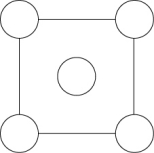
A) cubic
B) chloride-centered cubic
C) face-centered cubic
D) x-face cubic
E) body-centered cubic

A) cubic
B) chloride-centered cubic
C) face-centered cubic
D) x-face cubic
E) body-centered cubic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Gold has a face-centered cubic structure with a unit cell edge length of 407.8 pm. What is the density of each individual gold atom?
A) 21.44 g/cm3
B) 26.20 g/cm3
C) 13.1 g/cm3
D) 6.55 g/cm3
E) 19.28 g/cm3
A) 21.44 g/cm3
B) 26.20 g/cm3
C) 13.1 g/cm3
D) 6.55 g/cm3
E) 19.28 g/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which is not true about a crystallographic unit cell?
A) It repeats throughout a crystalline structure in three dimensions.
B) It fills all the space in the crystalline lattice.
C) Its dimensions can be measured with X-rays.
D) It always has corners with 90° angles.
E) It represents the smallest repeating unit in the crystal.
A) It repeats throughout a crystalline structure in three dimensions.
B) It fills all the space in the crystalline lattice.
C) Its dimensions can be measured with X-rays.
D) It always has corners with 90° angles.
E) It represents the smallest repeating unit in the crystal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which unit cell contains the most atoms?
A) fcc
B) bcc
C) cubic
D) both fcc and bcc
E) None of the above, as fcc, bcc, and cubic contain the same number of atoms.
A) fcc
B) bcc
C) cubic
D) both fcc and bcc
E) None of the above, as fcc, bcc, and cubic contain the same number of atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many nearest neighbor atoms are there around each atom in a simple cubic unit cell?
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 10
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Aluminum (Al) crystallizes as a face-centered unit cell with an edge length of 404 pm. What is the atomic radius of aluminum?
A) 143 pm
B) 202 pm
C) 286 pm
D) 175 pm
E) 808 pm
A) 143 pm
B) 202 pm
C) 286 pm
D) 175 pm
E) 808 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a body-centered cubic unit cell has a volume of 1.447 * 108 pm3, what must be the dimension of the cube's edge?
A) 1.131* 108 pm
B) 110 pm
C) 1.20 *104 pm
D) 525 pm
E) 367 pm
A) 1.131* 108 pm
B) 110 pm
C) 1.20 *104 pm
D) 525 pm
E) 367 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a face-centered cubic unit cell has a volume of 1.447 * 108 pm3 and the ions at the corners touch the ion on the face, what must be the ion's radius?
A) 186 pm
B) 388 pm
C) 4243 pm
D) 125 pm
E) 1050 pm
A) 186 pm
B) 388 pm
C) 4243 pm
D) 125 pm
E) 1050 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Iron (Fe) crystallizes as a body-centered unit cell with an edge length of 287 pm. What is the atomic radius of iron?
A) 99 pm
B) 114 pm
C) 124 pm
D) 143 pm
E) 256 pm
A) 99 pm
B) 114 pm
C) 124 pm
D) 143 pm
E) 256 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The alpha form of polonium (Po) has a density of 9.196 g/cm3 and crystallizes in a simple cubic structure. What is the atomic radius of polonium?
A) 119 pm
B) 168 pm
C) 266 pm
D) 335 pm
E) 419 pm
A) 119 pm
B) 168 pm
C) 266 pm
D) 335 pm
E) 419 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Iron crystallizes in a body-centered cubic pattern. How many iron atoms are in each unit cell?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 9
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Copper crystallizes in a face-centered cubic pattern. How many copper atoms are in each unit cell?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 12
E) 14
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 12
E) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Gold (Au) has a face-centered cubic structure with a unit cell edge length of 407.8 pm. What is the calculated value of the density of gold based on this information?
A) 15.78 g/cm3
B) 19.28 g/cm3
C) 9.64 g/cm3
D) 4.82 g/cm3
E) 11.6 g/cm3
A) 15.78 g/cm3
B) 19.28 g/cm3
C) 9.64 g/cm3
D) 4.82 g/cm3
E) 11.6 g/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Aluminum (Al) has a density of 2.70 g/cm3 and crystallizes in a face-centered cubic structure. What is the unit-cell edge length?
A) 2.47 *10-3 pm
B) 40.0 pm
C) 405 pm
D) 321 pm
E) 255 pm
A) 2.47 *10-3 pm
B) 40.0 pm
C) 405 pm
D) 321 pm
E) 255 pm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a two-component alloy the more abundant metal can be thought of as the solvent while the less abundant metal can be thought of as the solute. Which of the following would not change the orientation of atoms in the solvent's unit cell?
(I)a solute with the same atomic radius as the solvent
(II)a solute that was sufficiently small to fit into holes in the solvent's unit cell
(III)a solvent that was sufficiently small to fit into holes in the solute's unit cell
A) only I
B) only II
C) only III
D) I or II
E) I, II, or III
(I)a solute with the same atomic radius as the solvent
(II)a solute that was sufficiently small to fit into holes in the solvent's unit cell
(III)a solvent that was sufficiently small to fit into holes in the solute's unit cell
A) only I
B) only II
C) only III
D) I or II
E) I, II, or III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Aluminum is resistant to corrosion because of __________
A) its positive oxidation potential.
B) its low density.
C) the formation of a protective surface film of aluminum oxide.
D) the formation of a protective surface film of aluminum nitride.
E) its lack of reactivity toward oxygen.
A) its positive oxidation potential.
B) its low density.
C) the formation of a protective surface film of aluminum oxide.
D) the formation of a protective surface film of aluminum nitride.
E) its lack of reactivity toward oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following refers to an alloy in which the composition is variable and the elements have comparable radii?
A) intermetallic
B) interstitial
C) stoichiometric
D) substitutional
E) homogeneous
A) intermetallic
B) interstitial
C) stoichiometric
D) substitutional
E) homogeneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following elements are found as a covalent network solid?
(I)beryllium
(II)carbon
(III)phosphorus
(IV)sulfur
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) III and IV
(I)beryllium
(II)carbon
(III)phosphorus
(IV)sulfur
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following can be varied to change the physical properties of an alloy?
(I)The elements used
(II)The proportions used
(III)The type of hole each element occupies
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) I, II, and III
(I)The elements used
(II)The proportions used
(III)The type of hole each element occupies
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How many carbons are bonded to each carbon in graphite?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) some have 2 and some have 3
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) some have 2 and some have 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Bronze that is composed of 10% tin and 90% copper is __________
A) a substitutional alloy.
B) an interstitial alloy.
C) a doped semiconductor.
D) a colloidal alloy.
E) an intermetallic compound.
A) a substitutional alloy.
B) an interstitial alloy.
C) a doped semiconductor.
D) a colloidal alloy.
E) an intermetallic compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Different structural forms of the elements are called __________
A) polymers.
B) allotropes.
C) isotopes.
D) isoforms.
E) polymorphs.
A) polymers.
B) allotropes.
C) isotopes.
D) isoforms.
E) polymorphs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In addition to carbon and iron, stainless steel contains __________
A) teflon and polyethylene.
B) gold and silver.
C) copper and nickel.
D) chromium and nickel.
E) platinum.
A) teflon and polyethylene.
B) gold and silver.
C) copper and nickel.
D) chromium and nickel.
E) platinum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which two of the following elements are not found as a covalent network solid?
(I)beryllium
(II)carbon
(III)phosphorus
(IV)sulfur
A) I and III
B) I and II
C) I and IV
D) II and III
E) II and IV
(I)beryllium
(II)carbon
(III)phosphorus
(IV)sulfur
A) I and III
B) I and II
C) I and IV
D) II and III
E) II and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The hybridization of atomic orbitals in diamond is __________
A) none, since it is the element.
B) sp.
C) sp2.
D) sp3.
E) dsp3.
A) none, since it is the element.
B) sp.
C) sp2.
D) sp3.
E) dsp3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Aluminum alloys are more desirable than steel in some applications because of their relatively __________
A) low density.
B) low cost.
C) high luster.
D) high warmth to touch.
E) high conductivity.
A) low density.
B) low cost.
C) high luster.
D) high warmth to touch.
E) high conductivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following refers to an alloy in which the composition of the elements is variable and one element must have a much smaller radius than the other?
A) intermetallic
B) interstitial
C) stoichiometric
D) substitutional
E) inhomogeneous
A) intermetallic
B) interstitial
C) stoichiometric
D) substitutional
E) inhomogeneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following unit cells has the lowest packing efficiency?
A) simple cubic
B) face-centered cubic
C) body-centered cubic
D) both face-centered and body-centered cubic
E) Simple, face-centered, and body-centered cubic all have the same packing efficiency.
A) simple cubic
B) face-centered cubic
C) body-centered cubic
D) both face-centered and body-centered cubic
E) Simple, face-centered, and body-centered cubic all have the same packing efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Stainless steel is less susceptible to rusting than iron because __________
A) it is coated with plastic.
B) the metals other than iron in the alloy are oxidized more easily, forming protective oxides.
C) the carbon within the alloy polymerizes to form a protective film.
D) the silicon within the alloy oxidizes to form a protective silicate layer.
E) the intermetallic compound formed is less reactive.
A) it is coated with plastic.
B) the metals other than iron in the alloy are oxidized more easily, forming protective oxides.
C) the carbon within the alloy polymerizes to form a protective film.
D) the silicon within the alloy oxidizes to form a protective silicate layer.
E) the intermetallic compound formed is less reactive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The higher the carbon content in steel, __________
A) the stronger and more malleable it is.
B) the stronger and more brittle it is.
C) the weaker and more malleable it is.
D) the weaker and more brittle it is.
E) Any of these, depending on the formula of the interstitial compound.
A) the stronger and more malleable it is.
B) the stronger and more brittle it is.
C) the weaker and more malleable it is.
D) the weaker and more brittle it is.
E) Any of these, depending on the formula of the interstitial compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following unit cells has the highest packing efficiency?
A) simple cubic
B) face-centered cubic
C) body-centered cubic
D) both face-centered and body-centered cubic
E) Simple, face-centered, and body-centered cubic all have the same packing efficiency.
A) simple cubic
B) face-centered cubic
C) body-centered cubic
D) both face-centered and body-centered cubic
E) Simple, face-centered, and body-centered cubic all have the same packing efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following refers to an alloy in which the composition of the elements is constant?
A) intermetallic
B) interstitial
C) stoichiometric
D) substitutional
E) homogeneous
A) intermetallic
B) interstitial
C) stoichiometric
D) substitutional
E) homogeneous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In comparing the density of bronze composed of 20% tin to the density of pure copper, __________
A) the density of the bronze is higher.
B) the density of the bronze is lower.
C) the density of the bronze is the same.
D) the density of the bronze depends on whether the tin or the copper occupies holes.
E) It cannot be determined as only the 1:1 intermetallic compound of tin and copper has ever been observed.
A) the density of the bronze is higher.
B) the density of the bronze is lower.
C) the density of the bronze is the same.
D) the density of the bronze depends on whether the tin or the copper occupies holes.
E) It cannot be determined as only the 1:1 intermetallic compound of tin and copper has ever been observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The most common allotrope of carbon is __________
A) coal.
B) graphite.
C) soot.
D) diamond.
E) carbon steel.
A) coal.
B) graphite.
C) soot.
D) diamond.
E) carbon steel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An approximately spherical allotrope of carbon containing 60 or 70 atoms is __________
A) spherohexadecalene and spheroheptadecalene.
B) spheralene-60 and spheralene-70.
C) fullerene.
D) graphitolene.
E) soccerene.
A) spherohexadecalene and spheroheptadecalene.
B) spheralene-60 and spheralene-70.
C) fullerene.
D) graphitolene.
E) soccerene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the solid-state structure of sodium chloride, the closest distance between the centers of ions is observed __________
A) between adjacent sodium ions on the edge of the unit cell.
B) between adjacent chloride ions on the edge of the unit cell.
C) between adjacent sodium ions on the face and one corner of the unit cell.
D) between adjacent chloride ions on the face and one corner of the unit cell.
E) between all adjacent sodium and chloride ions.
A) between adjacent sodium ions on the edge of the unit cell.
B) between adjacent chloride ions on the edge of the unit cell.
C) between adjacent sodium ions on the face and one corner of the unit cell.
D) between adjacent chloride ions on the face and one corner of the unit cell.
E) between all adjacent sodium and chloride ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
How many tennis balls will fit within the interstitial holes between a truckload of basketballs perfectly placed in a closest-packed arrangement? Assume that the tennis balls have a radius that is 20% that of a basketball.
A) equal number of tennis balls and basketballs
B) twice as many tennis balls as basketballs
C) three times as many tennis balls as basketballs
D) four times as many tennis balls as basketballs
E) five times as many tennis balls as basketballs
A) equal number of tennis balls and basketballs
B) twice as many tennis balls as basketballs
C) three times as many tennis balls as basketballs
D) four times as many tennis balls as basketballs
E) five times as many tennis balls as basketballs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A face-centered cubic unit cell contains __________ octahedral holes.
A) 1
B) 4
C) 8
D) 13
E) "13"
A) 1
B) 4
C) 8
D) 13
E) "13"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is true regarding the attractive force that holds sodium chloride in the solid state?
(I)It is electrostatic.
(II)It is termed ionic bonding.
(III)It depends on the distance between the sodium and chloride.
(IV)It only operates between adjacent sodium and chloride.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III only
D) II and IV only
E) I-IV are all true statements.
(I)It is electrostatic.
(II)It is termed ionic bonding.
(III)It depends on the distance between the sodium and chloride.
(IV)It only operates between adjacent sodium and chloride.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III only
D) II and IV only
E) I-IV are all true statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the cubic closest-packed structure of sodium chloride, what ions are touching or nearly touching?
(I)Sodium ions and sodium ions
(II)Chloride ions and chloride ions
(III)Sodium ions and chloride ions
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
E) I and III only
(I)Sodium ions and sodium ions
(II)Chloride ions and chloride ions
(III)Sodium ions and chloride ions
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
E) I and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following figures best represents a common structure within crystalline sulfur? (A sulfur atom lies at each vertex.)
A)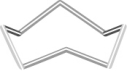
B)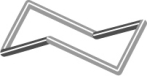
C)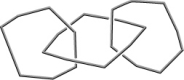
D)
E) None of these as sulfur is a network covalent solid.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) None of these as sulfur is a network covalent solid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Boron nitride, BN, is solid under standard conditions. Which of the following structures would you expect it to most resemble?
A) S8
B) white phosphorus
C) graphite
D) carbon dioxide
E) kaolinite
A) S8
B) white phosphorus
C) graphite
D) carbon dioxide
E) kaolinite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Compare the packing efficiency of face-centered cubic gold and face-centered cubic sodium chloride.
A) The efficiency of packing in the gold unit cell is higher.
B) The efficiency of packing in the sodium chloride unit cell is higher.
C) The efficiencies of packing in the two lattices are the same.
D) Packing efficiencies cannot be defined for one or both of these.
E) There is no way to compare without further information.
A) The efficiency of packing in the gold unit cell is higher.
B) The efficiency of packing in the sodium chloride unit cell is higher.
C) The efficiencies of packing in the two lattices are the same.
D) Packing efficiencies cannot be defined for one or both of these.
E) There is no way to compare without further information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
As an analog of graphite, a material composed of boron and nitrogen (B-N) has been prepared. Why do these elements make a good substitute for the element in graphite?
(I)They are all elements with electrons in the 2p subshell.
(II)The sum of the valence electrons of one boron atom and one nitrogen atom is the same as the number of valence electrons on two carbon atoms.
(III)Boron and nitrogen have suitable 2p orbital overlap.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) I, II, and III
(I)They are all elements with electrons in the 2p subshell.
(II)The sum of the valence electrons of one boron atom and one nitrogen atom is the same as the number of valence electrons on two carbon atoms.
(III)Boron and nitrogen have suitable 2p orbital overlap.
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
E) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A rock salt structure has smaller ions in __________
A) cubic holes.
B) tetrahedral holes.
C) hexagonal holes.
D) octahedral holes.
E) the usual atomic positions in the unit cell, i.e., not in holes.
A) cubic holes.
B) tetrahedral holes.
C) hexagonal holes.
D) octahedral holes.
E) the usual atomic positions in the unit cell, i.e., not in holes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following contribute to the arrangement of ions in the unit cells of an ionic solid?
(I)The empirical formula
(II)The relative radii of the ions
(III)The shape of polyatomic ions
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I only
E) I, II, and III
(I)The empirical formula
(II)The relative radii of the ions
(III)The shape of polyatomic ions
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I only
E) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The sheet structure of carbon is __________
A) diamond.
B) graphite.
C) fullerene.
D) industrial diamond.
E) rolled carbon steel.
A) diamond.
B) graphite.
C) fullerene.
D) industrial diamond.
E) rolled carbon steel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A face-centered cubic unit cell has a(n) __________ in its center.
A) tetrahedral hole
B) octahedral hole
C) atom
D) square planar hole
E) cubic hole
A) tetrahedral hole
B) octahedral hole
C) atom
D) square planar hole
E) cubic hole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The face-centered cubic unit cell has __________ tetrahedral holes.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 4
D) 8
E) 12
A) 0
B) 1
C) 4
D) 8
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Would you expect the linear allotrope of carbon to conduct electricity? (Fragments of it were first prepared and characterized in 1998.)
A) No, the linear carbon chains would have no free electrons for carrying electricity.
B) Yes, this allotrope would be ionic and would therefore conduct electricity.
C) No, linear carbon chains would easily break under any electrical potential difference.
D) Yes, electrons can move through the delocalized network.
E) No, only metals conduct electricity.
A) No, the linear carbon chains would have no free electrons for carrying electricity.
B) Yes, this allotrope would be ionic and would therefore conduct electricity.
C) No, linear carbon chains would easily break under any electrical potential difference.
D) Yes, electrons can move through the delocalized network.
E) No, only metals conduct electricity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A tetrahedral hole in a crystal lattice is defined as __________
A) one-half of an octahedral hole.
B) the space between any number of atoms having tetrahedral edges.
C) the space between a cage of sp3 hybridized atoms such as in diamond.
D) the space between a cluster of four adjacent atoms arranged in a tetrahedron.
E) a large hole having four flat sides arranged in a tetrahedral shape.
A) one-half of an octahedral hole.
B) the space between any number of atoms having tetrahedral edges.
C) the space between a cage of sp3 hybridized atoms such as in diamond.
D) the space between a cluster of four adjacent atoms arranged in a tetrahedron.
E) a large hole having four flat sides arranged in a tetrahedral shape.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of these is the best conductor of electricity?
A) diamond
B) graphite
C) water
D) glass
E) fullerene
A) diamond
B) graphite
C) water
D) glass
E) fullerene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Researchers at the University of Texas at Austin prepared a linear allotrope of carbon in 1998. What is the hybridization of its atomic orbitals?
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) dsp3
E) Cannot be determined from the information provided.
A) sp
B) sp2
C) sp3
D) dsp3
E) Cannot be determined from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Why does a pure metal not crystallize in a fluorite or antifluorite unit cell?
A) They can and do.
B) These unit cells require two types of atoms or ions with differing radii.
C) Pure metals do not crystallize; they are amorphous.
D) The atoms in pure metals move about in a sea of electrons.
E) The radius of the metal is too large.
A) They can and do.
B) These unit cells require two types of atoms or ions with differing radii.
C) Pure metals do not crystallize; they are amorphous.
D) The atoms in pure metals move about in a sea of electrons.
E) The radius of the metal is too large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



