Deck 5: Thermochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/101
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Thermochemistry
1
From year to year, the water level in a lake varies, as shown below. At which time is the potential energy of the water behind the dam greatest?
A)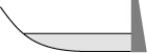
B)
C)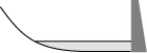
D)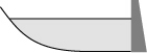
A)

B)

C)

D)


2
Assuming that the distances between the two ions are the same in all cases, which of the following ion pairs has the greatest electrostatic potential energy?
A) Na+ - Cl-
B) Na+ - O2-
C) Mg2+ - O2-
D) Al3+ - O2-
E) Na+ - Mg2+
A) Na+ - Cl-
B) Na+ - O2-
C) Mg2+ - O2-
D) Al3+ - O2-
E) Na+ - Mg2+
Al3+ - O2-
3
Heat is best defined as __________
A) a substance that increases the temperature and causes water to boil.
B) a form of potential energy.
C) a form of work.
D) the total energy that a substance has.
E) energy transferred as the result of a temperature difference.
A) a substance that increases the temperature and causes water to boil.
B) a form of potential energy.
C) a form of work.
D) the total energy that a substance has.
E) energy transferred as the result of a temperature difference.
energy transferred as the result of a temperature difference.
4
Thermochemistry is the study of how __________ is produced and consumed during chemical reactions.
A) kinetic energy
B) temperature
C) energy
D) work
E) potential energy
A) kinetic energy
B) temperature
C) energy
D) work
E) potential energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A balanced reaction equation with a H value is called __________
A) Hess's law.
B) a thermochemical equation.
C) the first law of thermodynamics.
D) a combustion reaction.
E) a chemical equation.
A) Hess's law.
B) a thermochemical equation.
C) the first law of thermodynamics.
D) a combustion reaction.
E) a chemical equation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
During a(n) __________ process, energy is transferred from the system to the surroundings.
A) exothermic
B) endothermic
C) thermodynamic
D) thermochemical
E) physical
A) exothermic
B) endothermic
C) thermodynamic
D) thermochemical
E) physical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The capacity to do work is a definition of __________
A) heat.
B) thermochemistry.
C) work.
D) energy.
E) ambition.
A) heat.
B) thermochemistry.
C) work.
D) energy.
E) ambition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The kinetic energy associated with the random motion of molecules is called __________
A) motional energy.
B) work.
C) heat.
D) microscopic energy.
E) thermal energy.
A) motional energy.
B) work.
C) heat.
D) microscopic energy.
E) thermal energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following diagrams illustrate the flow of energy (q) and work (w) in different processes. Which one is definitely an exothermic process?
A)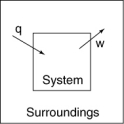
B)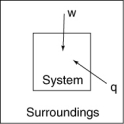
C)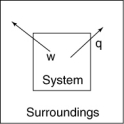
D)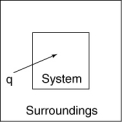
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is an endothermic process for the system? In each case, the "system" is underlined.
A) a block of cheese being cooled in a refrigerator
B) a hot pack being used to warm a sore muscle
C) a heat pump being used to warm a house
D) a candle burning at a dinner table
E) ice cubes freezing in the refrigerator
A) a block of cheese being cooled in a refrigerator
B) a hot pack being used to warm a sore muscle
C) a heat pump being used to warm a house
D) a candle burning at a dinner table
E) ice cubes freezing in the refrigerator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The first law of thermodynamics implies that __________
A) energy is transferred from the surroundings to the system during a combustion reaction.
B) if a system loses energy to the surroundings, then the surroundings must do an equal amount of work on the system.
C) if the surroundings gain energy from the system, then the system must lose an equal amount of energy.
D) energy is transferred from the system to the surroundings during a combustion reaction.
E) if a system does work on the surroundings, then the surroundings must transfer an equal amount of energy to the system.
A) energy is transferred from the surroundings to the system during a combustion reaction.
B) if a system loses energy to the surroundings, then the surroundings must do an equal amount of work on the system.
C) if the surroundings gain energy from the system, then the system must lose an equal amount of energy.
D) energy is transferred from the system to the surroundings during a combustion reaction.
E) if a system does work on the surroundings, then the surroundings must transfer an equal amount of energy to the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In addition to identifying the reactants and products, a thermochemical reaction equation provides __________
A) the amount of energy released or absorbed.
B) the temperature.
C) the work needed to drive the reaction.
D) the cost of the reactants.
E) the energy of the products.
A) the amount of energy released or absorbed.
B) the temperature.
C) the work needed to drive the reaction.
D) the cost of the reactants.
E) the energy of the products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
During a(n) __________ process, energy is transferred to the system from the surroundings.
A) exothermic
B) endothermic
C) thermodynamic
D) thermochemical
E) physical
A) exothermic
B) endothermic
C) thermodynamic
D) thermochemical
E) physical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Energy that an object has by virtue of its position is called __________
A) kinetic energy.
B) thermal energy.
C) potential energy.
D) heat.
E) mechanical energy.
A) kinetic energy.
B) thermal energy.
C) potential energy.
D) heat.
E) mechanical energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When solid sodium hydroxide (NaOH) pellets are dissolved in water, the temperature of the water and beaker rises. This is an example of __________
A) an exothermic process.
B) an endothermic process.
C) a combustion reaction.
D) a thermodynamic cycle.
E) all solvation processes.
A) an exothermic process.
B) an endothermic process.
C) a combustion reaction.
D) a thermodynamic cycle.
E) all solvation processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Work requires __________
A) a use of potential energy.
B) a release of kinetic energy.
C) that a force moves an object.
D) a change in temperature.
E) the application of a force.
A) a use of potential energy.
B) a release of kinetic energy.
C) that a force moves an object.
D) a change in temperature.
E) the application of a force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Energy that an object has by virtue of its motion is called __________
A) kinetic energy.
B) thermal energy.
C) potential energy.
D) orbital energy.
E) mechanical energy.
A) kinetic energy.
B) thermal energy.
C) potential energy.
D) orbital energy.
E) mechanical energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the kinetic energy of a skier weighing 175 lb traveling 60 mph? (2.205 lb = 1 kg, 1 mi = 1.609 km, 1 J = 1 kg m2s-2)
A) 29 kJ
B) 57 kJ
C) 2.1 kJ
D) 1.1 kJ
E) 130 kJ
A) 29 kJ
B) 57 kJ
C) 2.1 kJ
D) 1.1 kJ
E) 130 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a mass of 100.0 g moves through a distance of 50.0 m with an acceleration of 25.0 m s-2, how much work was necessary to move the mass? F = ma, where F is force, m is mass, and a is acceleration. (1 J = 1 kg m2s-2)
A) 125 kJ
B) 12.5 kJ
C) 125 J
D) 12.5 J
E) 2.5 J
A) 125 kJ
B) 12.5 kJ
C) 125 J
D) 12.5 J
E) 2.5 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A student dissolving some ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) in water notices that the beaker gets cooler as the solid dissolves. This is an example of __________
A) an exothermic process.
B) an endothermic process.
C) a combustion reaction.
D) a thermodynamic cycle.
E) all solvation processes.
A) an exothermic process.
B) an endothermic process.
C) a combustion reaction.
D) a thermodynamic cycle.
E) all solvation processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A heating curve for some substance is shown below. Which of the line segments (I-V) represents heating of the liquid? 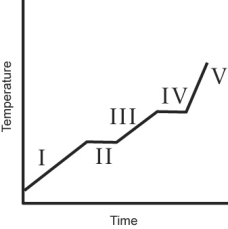
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How much energy is needed to change the temperature of 25.00 mL of water from 10.0°C to 95.0°C? (CP = 75.38 J/(mol · °C), d = 1.00 g/mL)
A) 160 kJ
B) 2880 kJ
C) 8.9 kJ
D) 6.4 kJ
E) 105 kJ
A) 160 kJ
B) 2880 kJ
C) 8.9 kJ
D) 6.4 kJ
E) 105 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the changes, A-D, will always increase the internal energy of a system?
A) The system gains energy and performs work.
B) The system gains energy and work is performed on it.
C) The system loses energy and performs work.
D) The system loses energy and work is performed on it.
E) None of the changes A-D will always increase the internal energy of a system.
A) The system gains energy and performs work.
B) The system gains energy and work is performed on it.
C) The system loses energy and performs work.
D) The system loses energy and work is performed on it.
E) None of the changes A-D will always increase the internal energy of a system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At a certain elevation, the boiling point of water is 98.5°C. How much energy is needed to heat 35.0 mL of water to the boiling point at this elevation if the water initially was at 23.4°C? (CP = 75.38 J/(mol · °C), d = 1.00 g/mL)
A) 8.5 kJ
B) 11.0 kJ
C) 0.93 kJ
D) 1.0 kJ
E) 25.6 kJ
A) 8.5 kJ
B) 11.0 kJ
C) 0.93 kJ
D) 1.0 kJ
E) 25.6 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The inside of a perfectly insulated capped thermos bottle is an example of __________
A) an open system.
B) a closed system.
C) an isolated system.
D) an undefined system.
E) a system plus surroundings.
A) an open system.
B) a closed system.
C) an isolated system.
D) an undefined system.
E) a system plus surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Internal energy is defined as __________
A) the total kinetic energy of all the system components.
B) the total potential energy of all the system components.
C) the total of the potential and kinetic energies of all the system components.
D) the total potential energy minus the total kinetic energy of all the system components.
E) the total kinetic energy minus the total potential energy of all the system components.
A) the total kinetic energy of all the system components.
B) the total potential energy of all the system components.
C) the total of the potential and kinetic energies of all the system components.
D) the total potential energy minus the total kinetic energy of all the system components.
E) the total kinetic energy minus the total potential energy of all the system components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The heating curve for a substance is shown below. The substance initially is a solid. It then becomes a liquid and a gas. Which of the line segments (I-V) represents the solid to liquid phase transition? 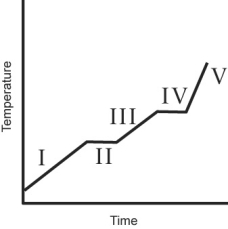
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The enthalpy change is defined as __________
A) the energy that is transferred into or out of a system when the pressure is constant and only PV work is done.
B) the change in internal energy of a system when the pressure is constant.
C) the change in internal energy of a system when the volume is constant.
D) the energy that is transferred into or out of a system when the pressure is constant and no work is done.
E) the change in internal energy of a system when the pressure is constant and no work is done.
A) the energy that is transferred into or out of a system when the pressure is constant and only PV work is done.
B) the change in internal energy of a system when the pressure is constant.
C) the change in internal energy of a system when the volume is constant.
D) the energy that is transferred into or out of a system when the pressure is constant and no work is done.
E) the change in internal energy of a system when the pressure is constant and no work is done.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
During an exothermic process, __________ for the system.
A) q > 0
B) w > 0
C) " H" > 0
D) " H" < 0
E) q + w = 0
A) q > 0
B) w > 0
C) " H" > 0
D) " H" < 0
E) q + w = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
You heat a cup of coffee in a microwave oven. It absorbs 40 kJ of energy from the microwave, and the volume expands. Which one of the following statements correctly describes the relationship between the change in enthalpy H and the change in internal energy E of the coffee? (> means greater than, < means less than)
A) " H" = 40 kJ, " E" < 40 kJ
B) " H" = 40 kJ, " E" > 40 kJ
C) " H" < 40 kJ, " E" = 40 kJ
D) " H" > 40 kJ, " E" = 40 kJ
E) " H" = 40 kJ, " E" = 40 kJ
A) " H" = 40 kJ, " E" < 40 kJ
B) " H" = 40 kJ, " E" > 40 kJ
C) " H" < 40 kJ, " E" = 40 kJ
D) " H" > 40 kJ, " E" = 40 kJ
E) " H" = 40 kJ, " E" = 40 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A pot of water is heated with 10 J of energy at constant pressure. What is the enthalpy change ( H) for this process?
A) -10 J
B) >10 J
C) +10 J
D) <10 J
E) 0
A) -10 J
B) >10 J
C) +10 J
D) <10 J
E) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which one of the following statements is not correct?
A) When dry ice sublimes to form CO2(g), the internal energy of the surroundings decreases.
B) In any physical process, such as dew forming on grass or carbon dioxide subliming, the internal energy of the system does not change.
C) When dew forms on grass overnight, the energy of the water molecules decreases.
D) When dew forms on grass overnight, the energy of the surroundings (grass, air, etc.) increases.
E) When dry ice sublimes to form CO2(g), the energy of the carbon dioxide increases.
A) When dry ice sublimes to form CO2(g), the internal energy of the surroundings decreases.
B) In any physical process, such as dew forming on grass or carbon dioxide subliming, the internal energy of the system does not change.
C) When dew forms on grass overnight, the energy of the water molecules decreases.
D) When dew forms on grass overnight, the energy of the surroundings (grass, air, etc.) increases.
E) When dry ice sublimes to form CO2(g), the energy of the carbon dioxide increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How much work does a gas do when it expands against a constant pressure of 0.500 atm from a volume of 50.00 mL to a volume of 350.00 mL? (101.3 J = 1 L atm)
A) 15.2 J
B) 0.150 J
C) -15.2 J
D) -0.152 J
A) 15.2 J
B) 0.150 J
C) -15.2 J
D) -0.152 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the change in internal energy of a system when it loses 10 kJ of energy and 5000 J of work is done on the system?
A) +15 kJ
B) -10 kJ
C) -5 kJ
D) +5010 J
E) +4990 J
A) +15 kJ
B) -10 kJ
C) -5 kJ
D) +5010 J
E) +4990 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What will be the final temperature of a 10.0 g piece of iron (CP = 25.09 J/(mol · °C)) initially at 25°C, if it is supplied with 9.5 J from a stove?
A) 25°C
B) 27°C
C) 23°C
D) 1356°C
E) 20°C
A) 25°C
B) 27°C
C) 23°C
D) 1356°C
E) 20°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following bar charts shows the correct internal energy changes that occur when a propane grill is used to cook a steak? (Consider the propane combustion reaction to be the system. Consider the grill, steak, and everything else to be the surroundings.)
A)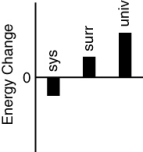
B)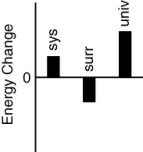
C)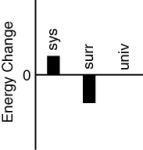
D)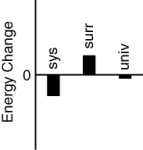
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the change in internal energy ( E) when a system is heated with 35 J of energy while it does 15 J of work?
A) +50 J
B) +20 J
C) -20 J
D) -50 J
E) +35 K
A) +50 J
B) +20 J
C) -20 J
D) -50 J
E) +35 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following bar charts shows the correct internal energy changes that occur in a pitcher of iced tea (system), the refrigerator (surroundings), and the universe, as the iced tea in the refrigerator cools?
A)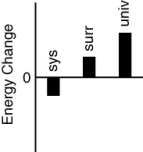
B)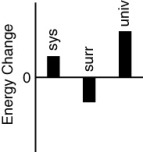
C)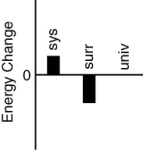
D)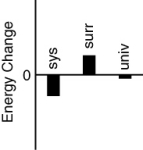
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In a steam engine, steam in a cylinder expands against a piston exerting 10 atm of external pressure. The volume of the cylinder increases by 10 L and simultaneously the steam cools, losing 3000 kJ of energy to the surroundings. What is the change in energy of the steam? (101.3 J = 1 L atm)
A) -3,010 kJ
B) -3,001 kJ
C) -3,100 kJ
D) -13,135 kJ
E) -2,990 kJ
A) -3,010 kJ
B) -3,001 kJ
C) -3,100 kJ
D) -13,135 kJ
E) -2,990 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a chemical reaction causes the temperature of the container to drop, it is a(n) __________ reaction.
A) endothermic
B) exothermic
C) spontaneous
D) fast
E) slow
A) endothermic
B) exothermic
C) spontaneous
D) fast
E) slow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A 150 g piece of iron (CP = 25.09 J/(mol · °C)) was heated to a temperature of 47°C and then placed in contact with a 275 g piece of copper at 20°C (CP = 25.46 J/(mol · °C)). What was the final temperature of the two pieces of metal?
A) 25°C
B) 20°C
C) 30°C
D) 47°C
E) 33°C
A) 25°C
B) 20°C
C) 30°C
D) 47°C
E) 33°C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 15 g piece of iron (CP = 25.09 J/(mol · °C)) is heated to a temperature of 95°C and placed into a bucket containing 4.5 gal of water (CP = 75.38 J/(mol · °C)) initially at 25°C. Eventually,
A) the water will be warmer than the iron.
B) the iron will be warmer than the water.
C) the iron will be colder than the water.
D) the iron and the water will be at the same temperature.
E) the temperature will be the average of 98°C and 25°C.
A) the water will be warmer than the iron.
B) the iron will be warmer than the water.
C) the iron will be colder than the water.
D) the iron and the water will be at the same temperature.
E) the temperature will be the average of 98°C and 25°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
You have a summer job in a lead foundry. Your task is to identify how energy efficiency can be improved. You therefore need to know the minimum amount of energy it takes to raise 1 pound of lead (454 g) from room temperature (25°C) to its melting point (327°C) and then melt it. The specific heat capacity of lead is 0.159 J/(g °C), the enthalpy of fusion is 24.7 J/g, and the molar mass is 207 g/mol.
A) 3.39 MJ
B) 21.9 kJ
C) 21.0 kJ
D) 33.0 kJ
E) 11.0 kJ
A) 3.39 MJ
B) 21.9 kJ
C) 21.0 kJ
D) 33.0 kJ
E) 11.0 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In terms of the enthalpy of formation, which of the following compounds is the most unstable compared to its elements under standard conditions?
A) KCl(s), H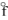 = - 435.9 kJ/mol
= - 435.9 kJ/mol
B) PH3(g), H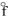 = +5.4 kJ/mol
= +5.4 kJ/mol
C) Fe3O4(s), H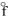 = - 1117.1 kJ/mol
= - 1117.1 kJ/mol
D) NiO(s), H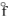 = - 239.7 kJ/mol
= - 239.7 kJ/mol
E) ICl(g), H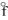 = + 17.8 kJ/mol
= + 17.8 kJ/mol
A) KCl(s), H
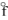 = - 435.9 kJ/mol
= - 435.9 kJ/molB) PH3(g), H
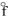 = +5.4 kJ/mol
= +5.4 kJ/molC) Fe3O4(s), H
 = - 1117.1 kJ/mol
= - 1117.1 kJ/molD) NiO(s), H
 = - 239.7 kJ/mol
= - 239.7 kJ/molE) ICl(g), H
 = + 17.8 kJ/mol
= + 17.8 kJ/mol
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following objects will cool the fastest from the same initial temperature, assuming you had equal masses of each?
A) an aluminum pan (cs = 0.90 J/(g · °C))
B) a copper pot (cs = 0.39 J/(g · °C))
C) an iron skillet (cs = 0.45 J/(g · °C))
D) a container of water (4.2 J/(g · °C)
E) a container of ethanol (2.5 J/(g · °C)
A) an aluminum pan (cs = 0.90 J/(g · °C))
B) a copper pot (cs = 0.39 J/(g · °C))
C) an iron skillet (cs = 0.45 J/(g · °C))
D) a container of water (4.2 J/(g · °C)
E) a container of ethanol (2.5 J/(g · °C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The energy content of a Big Mac is 540 Cal. How much water can be heated from 20°C to 90°C by this amount of energy? (cP(water) = 1.00 g/mL, cs(water) = 4.18 J/(g · °C), 1 Cal = 1000 cal = 4.184 kJ)
A) 2.2 mL
B) 6.0 L
C) 7.7 mL
D) 7.7 L
E) 6.0 mL
A) 2.2 mL
B) 6.0 L
C) 7.7 mL
D) 7.7 L
E) 6.0 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When a 13.0 g sample of NaOH(s) dissolves in 400.0 mL of water to produce 413.0 g of solution in a constant pressure calorimeter, the temperature of the water and reaction vessel changes from 22.6°C to 30.6°C. Assume that the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.20 J/(g · °C), and that the heat capacity of the reaction vessel is 1.00 J/°C. What is the molar enthalpy of solution of sodium hydroxide (40.00 g/mol)?
A) 34 kJ/mol
B) 54 kJ/mol
C) 17 kJ/mol
D) 43 kJ/mol
E) 14 kJ/mol
A) 34 kJ/mol
B) 54 kJ/mol
C) 17 kJ/mol
D) 43 kJ/mol
E) 14 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Indicate which of the following is not an element in its standard state at 25°C and 1 atm.
A) O2(g)
B) H2(g)
C) Ne(g)
D) N(g)
E) C(s, graphite)
A) O2(g)
B) H2(g)
C) Ne(g)
D) N(g)
E) C(s, graphite)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
You hold a 50 g sphere of copper (cs= 0.4 J/(g · °C)) in one hand and a 25 g sphere of aluminum (cs = 0.9 J/(g · °C)) in the other hand. If both absorb energy at the same rate, which will come to your body temperature first and why?
A) copper, because the specific heat is smaller
B) aluminum, because the specific heat is larger
C) aluminum, because the mass is smaller
D) copper, because the heat capacity is smaller
E) Both reach body temperature at the same time because they absorb energy at the same rate.
A) copper, because the specific heat is smaller
B) aluminum, because the specific heat is larger
C) aluminum, because the mass is smaller
D) copper, because the heat capacity is smaller
E) Both reach body temperature at the same time because they absorb energy at the same rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Determine the change in enthalpy for the following reaction from the enthalpies of formation for the reactants and products. (C2H2Cl2, +4.27 kJ/mol; C2H2Cl4, -155.6 kJ/mol) Cl2(g) + C2H2Cl2(g) C2H2Cl4(g)
A) +159.9 kJ/mol
B) -159.9 kJ/mol
C) -151.3 kJ/mol
D) +151.3 kJ/mol
E) +153.1 kJ/mol
A) +159.9 kJ/mol
B) -159.9 kJ/mol
C) -151.3 kJ/mol
D) +151.3 kJ/mol
E) +153.1 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In terms of the enthalpy of formation, which of the following compounds is most stable relative to its elements under standard conditions?
A) PbBr2(s), H = -277.4 kJ/mol
= -277.4 kJ/mol
B) O3(g), H = +142.3 kJ/mol
= +142.3 kJ/mol
C) SO2(g), H = -269.9 kJ/mol
= -269.9 kJ/mol
D) H2Se(g), H = +29.7 kJ/mol
= +29.7 kJ/mol
E) ICl(g), H = +17.8 kJ/mol
= +17.8 kJ/mol
A) PbBr2(s), H
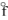 = -277.4 kJ/mol
= -277.4 kJ/molB) O3(g), H
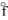 = +142.3 kJ/mol
= +142.3 kJ/molC) SO2(g), H
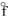 = -269.9 kJ/mol
= -269.9 kJ/molD) H2Se(g), H
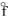 = +29.7 kJ/mol
= +29.7 kJ/molE) ICl(g), H
 = +17.8 kJ/mol
= +17.8 kJ/mol
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Isooctane is a good model for gasoline. When 1.14 g of isooctane (C8H18, molar mass = 114 g/mol) reacted with excess oxygen in a constant volume calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increased by 5.83°C. The calorimeter consisted of two components: a steel vessel with a heat capacity of 1.00 kJ/ °C and 2.00 L of water surrounding it. The density and specific heat capacity of water are 1.00 g/mL and 4.184 J/(g · °C), respectively. Use these data to determine the molar enthalpy of combustion of isooctane.
A) 5.83 kJ
B) 54.6 kJ
C) 5460 kJ
D) 48,800 J
E) 48,800 kJ
A) 5.83 kJ
B) 54.6 kJ
C) 5460 kJ
D) 48,800 J
E) 48,800 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When 1.14 g of octane (molar mass = 114 g/mol) reacts with excess oxygen in a constant volume calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases by 10.0°C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 6.97 kJ/°C. Determine the energy flow, q (reaction).
A) +69.7 kJ
B) +6970 kJ
C) -69.7 kJ
D) -6970 kJ
E) +6.97 kJ
A) +69.7 kJ
B) +6970 kJ
C) -69.7 kJ
D) -6970 kJ
E) +6.97 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which statement regarding combustion of a sample of gasoline in a bomb calorimeter is correct?
A) Work is done by the system on the surroundings.
B) Work is done by the surroundings on the system.
C) No work is done because the pressure is constant.
D) The work done by the system equals the energy produced by the system.
E) The experiment provides an accurate value for the change in energy, not the change in enthalpy.
A) Work is done by the system on the surroundings.
B) Work is done by the surroundings on the system.
C) No work is done because the pressure is constant.
D) The work done by the system equals the energy produced by the system.
E) The experiment provides an accurate value for the change in energy, not the change in enthalpy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The cooling system in an automobile holds 10.0 L of ethylene glycol antifreeze. How much energy is absorbed when the temperature of the ethylene glycol goes from 20°C to 100°C? The density and specific heat capacity of ethylene glycol are 1.11 g/mL and 2.42 J/(g · °C), respectively.
A) 2150 J
B) 2150 kJ
C) 1940 kJ
D) 1940 J
E) 215 J
A) 2150 J
B) 2150 kJ
C) 1940 kJ
D) 1940 J
E) 215 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A food sample was burned in a bomb calorimeter containing 524 mL water. How much thermal energy was produced when the temperature of the water and the calorimeter rose from 20.0°C to 25.0°C? The metal calorimeter had a heat capacity of 725 J/°C without the water.
A) 3.63 kJ
B) 14.6 kJ
C) 58.4 kJ
D) 45.8 kJ
E) 46.1 kJ
A) 3.63 kJ
B) 14.6 kJ
C) 58.4 kJ
D) 45.8 kJ
E) 46.1 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A 300 kg black bear hibernates in the winter. During hibernation the bear's body temperature drops from 37 to 31°C. How many grams of glucose must the bear metabolize in order to restore its body temperature to normal? Assume the bear's body is mostly water with a specific heat capacity of 4.2 J/(g · °C) and that all the energy from the combustion of glucose is used to raise the bear's body temperature. (Glucose: H(combustion) = -2830 kJ/mol, molar mass = 180 g/mol)
A) 7560 g
B) 2.67 g
C) 2975 g
D) 481 g
E) 16.5 g
A) 7560 g
B) 2.67 g
C) 2975 g
D) 481 g
E) 16.5 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In an experiment, 10.0 g of ice at -20°C is converted into steam with a temperature of 110°C. How much energy is required for this process? Hvap = 2260 J/g; Hfus = 334 J/g; cs(ice) = 2.06 J/(g · °C); cs(water) = 4.18 J/(g · °C);
Cs(steam) = 1.99 J/(g · °C))
A) 30.7 kJ
B) 26.8 kJ
C) 34.9 kJ
D) 30.3 kJ
E) 38.7 kJ
Cs(steam) = 1.99 J/(g · °C))
A) 30.7 kJ
B) 26.8 kJ
C) 34.9 kJ
D) 30.3 kJ
E) 38.7 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which statement regarding combustion of a sample of gasoline in a bomb calorimeter is correct?
A) Work is done by the system on the surroundings.
B) Work is done by the surroundings on the system.
C) No work is done because the volume cannot change.
D) The work done by the system equals the energy produced by the system.
E) The experiment provides a very accurate value for the enthalpy of combustion of gasoline.
A) Work is done by the system on the surroundings.
B) Work is done by the surroundings on the system.
C) No work is done because the volume cannot change.
D) The work done by the system equals the energy produced by the system.
E) The experiment provides a very accurate value for the enthalpy of combustion of gasoline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In an experiment, 30.0 g of metal was heated to 98.0°C and then quickly transferred to 50.0 g of water in a calorimeter. The heat capacity of the calorimeter with the water was 211 J/°C. The initial temperature of the calorimeter was 27.0°C, and the final temperature after addition of the metal was 32.5°C. What is the value of the specific heat capacity of the metal?
A) 0.140 J/(g · °C)
B) 83.0 J/(g · °C)
C) 0.540 J/(g · °C)
D) 0.591 J/(g · °C)
E) 29.5 J/(g · °C)
A) 0.140 J/(g · °C)
B) 83.0 J/(g · °C)
C) 0.540 J/(g · °C)
D) 0.591 J/(g · °C)
E) 29.5 J/(g · °C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Fuel density is __________
A) the cost of energy in kJ/$.
B) the amount of energy contained in 1 mol of a substance (kJ/mol).
C) the energy released when 1 g of a substance is burned (kJ/g).
D) the energy released when 1 g of a substance is formed (kJ/g).
E) the energy released when 1 L of a substance is burned (kJ/L).
A) the cost of energy in kJ/$.
B) the amount of energy contained in 1 mol of a substance (kJ/mol).
C) the energy released when 1 g of a substance is burned (kJ/g).
D) the energy released when 1 g of a substance is formed (kJ/g).
E) the energy released when 1 L of a substance is burned (kJ/L).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) has been suggested as an alternative fuel source. Ethanol's enthalpy of combustion is Hcomb = -1368 kJ/mol, and its density is 0.789 g/mL. What is the fuel value of ethanol (kJ/g)?
A) 3.75 kJ/g
B) 1079 kJ/g
C) 1734 kJ/g
D) 23.4 kJ/g
E) 29.7 kJ/g
A) 3.75 kJ/g
B) 1079 kJ/g
C) 1734 kJ/g
D) 23.4 kJ/g
E) 29.7 kJ/g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following substances, A-D, will release the most energy during combustion in air?
A) 1 mol of C6H14
B) 1 mol of C2H6
C) 1 g of C6H14
D) 1 g of C2H6
E) Cannot answer without more information.
A) 1 mol of C6H14
B) 1 mol of C2H6
C) 1 g of C6H14
D) 1 g of C2H6
E) Cannot answer without more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following fuels has the highest fuel value (kJ/g)?
A) natural gas, CH4(g); 16.0 g/mol, Hcomb = -801 kJ/mol
B) ethanol, CH3CH2OH( ); 46.1 g/mol, Hcomb = -1,368 kJ/mol
); 46.1 g/mol, Hcomb = -1,368 kJ/mol
C) heating oil, C16H34( ), 226 g/mol, Hcomb = -10,800 kJ/mol
), 226 g/mol, Hcomb = -10,800 kJ/mol
D) coal, C135H96O9NS(l), 1906 g/mol, Hcomb = - 44,000 kJ/mol
E) wood, C6H12O6(l), 180 g/mol, DHcomb = -2,540 kJ/mol
A) natural gas, CH4(g); 16.0 g/mol, Hcomb = -801 kJ/mol
B) ethanol, CH3CH2OH(
 ); 46.1 g/mol, Hcomb = -1,368 kJ/mol
); 46.1 g/mol, Hcomb = -1,368 kJ/molC) heating oil, C16H34(
 ), 226 g/mol, Hcomb = -10,800 kJ/mol
), 226 g/mol, Hcomb = -10,800 kJ/molD) coal, C135H96O9NS(l), 1906 g/mol, Hcomb = - 44,000 kJ/mol
E) wood, C6H12O6(l), 180 g/mol, DHcomb = -2,540 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Assume gasoline has an energy density of 129 MJ/gal, and diesel fuel has an energy density of 145 MJ/gal. If gasoline costs $3.00 per gallon, how much should a gallon of diesel fuel cost so they have the same economic value (MJ/$)?
A) $3.00
B) $3.37
C) $3.53
D) $2.75
E) $2.67
A) $3.00
B) $3.37
C) $3.53
D) $2.75
E) $2.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose you eat a one-third pound hamburger without bread, cheese, or other items. Approximately how long would you need to walk to use up the calories in the hamburger? Assume the mass of the hamburger is 150 g with 3.6 Cal/g and that walking requires 2.5 times a basal metabolic rate of 280 kJ/hr.
A) 2 hours
B) 3 hours
C) 4 hours
D) 5 hours
E) 6 hours
A) 2 hours
B) 3 hours
C) 4 hours
D) 5 hours
E) 6 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Lightweight camping stoves typically use a mixture of C5 and C6 hydrocarbons, which is called white gas. Assuming white gas is 100% C6H14 with an enthalpy of combustion of -4150 kJ/mol, how many grams of it must be used to heat 1.50 L of water from 20°C to 90°C? Assume all the energy is used to heat the water.
A) 8.96 g
B) 9.65 g
C) 9.11 g
D) 7.64 g
E) 10.73 g
A) 8.96 g
B) 9.65 g
C) 9.11 g
D) 7.64 g
E) 10.73 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How much energy is needed to change the temperature of 25.00 mL of water from 10.0°C to 95.0°C? (cs = 4.184 J/(g · °C), d = 1.00 g/mL)
A) 160 kJ
B) 2880 kJ
C) 8.9 kJ
D) 6.4 kJ
E) 105 kJ
A) 160 kJ
B) 2880 kJ
C) 8.9 kJ
D) 6.4 kJ
E) 105 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
There is concern that the combustion of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum contributes to climate change by adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. Electric cars are being promoted as a way to address this situation by reducing the use of gasoline. Yet most electricity is produced by coal-fired power plants. Several factors need to be considered in determining whether electric cars actually are helpful in this regard. One is the environmental values of these fuels. Estimate the environmental value of coal compared to gasoline from the following information. The environmental value is defined as the amount of energy obtained per mole of carbon dioxide produced, so a larger environmental value is better. Substance
Model Compound
Molar Mass
Hocombustion
Coal
C135H96O9NS
1906 g/mol
44,000 kJ/mol
Gasoline
C8H18
114 g/mol
5,460 kJ/mol
A) coal = 23.1 kJ/mol, gasoline = 47.9 kJ/mol is better
B) coal = 386 kJ/mol is better, gasoline = 2.86 kJ/mol
C) coal = 182 kJ/mol is better, gasoline = 152 kJ/mol
D) coal = 325 kJ/mol, gasoline = 683 kJ/mol is better
E) coal = 527 kJ/mol is better, gasoline = 224 kJ/mol
Model Compound
Molar Mass
Hocombustion
Coal
C135H96O9NS
1906 g/mol
44,000 kJ/mol
Gasoline
C8H18
114 g/mol
5,460 kJ/mol
A) coal = 23.1 kJ/mol, gasoline = 47.9 kJ/mol is better
B) coal = 386 kJ/mol is better, gasoline = 2.86 kJ/mol
C) coal = 182 kJ/mol is better, gasoline = 152 kJ/mol
D) coal = 325 kJ/mol, gasoline = 683 kJ/mol is better
E) coal = 527 kJ/mol is better, gasoline = 224 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) has been suggested as an alternative fuel source. Ethanol's enthalpy of combustion is Hcomb = -1368 kJ/mol, and its density is 0.789 g/mL. What is the fuel density of ethanol (kJ/mL)?
A) 3.75 kJ/mL
B) 12.8 kJ/mL
C) 1.28 kJ/mL
D) 23.4 kJ/mL
E) 37.5 kJ/mL
A) 3.75 kJ/mL
B) 12.8 kJ/mL
C) 1.28 kJ/mL
D) 23.4 kJ/mL
E) 37.5 kJ/mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following fuels has the lowest fuel value (kJ/g)?
A) natural gas, CH4(g); 16.0 g/mol, Hcomb = -801 kJ/mol
B) ethanol, CH3CH2OH( ); 46.1 g/mol, Hcomb = -1,368 kJ/mol
); 46.1 g/mol, Hcomb = -1,368 kJ/mol
C) heating oil, C16H34( ), 226 g/mol, Hcomb = -10,800 kJ/mol
), 226 g/mol, Hcomb = -10,800 kJ/mol
D) coal, C135H96O9NS(s), 1906 g/mol, DHcomb = - 44,000 kJ/mol
E) wood, C6H12O6(s), 180 g/mol, Hcomb = -2,540 kJ/mol
A) natural gas, CH4(g); 16.0 g/mol, Hcomb = -801 kJ/mol
B) ethanol, CH3CH2OH(
 ); 46.1 g/mol, Hcomb = -1,368 kJ/mol
); 46.1 g/mol, Hcomb = -1,368 kJ/molC) heating oil, C16H34(
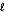 ), 226 g/mol, Hcomb = -10,800 kJ/mol
), 226 g/mol, Hcomb = -10,800 kJ/molD) coal, C135H96O9NS(s), 1906 g/mol, DHcomb = - 44,000 kJ/mol
E) wood, C6H12O6(s), 180 g/mol, Hcomb = -2,540 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In a Reuters news report dated February 3, 2010, President Obama is quoted as saying, "By 2022 we will more than double the amount of biofuels we produce to 36 billion gallons, which will decrease our dependence on foreign oil by hundreds of millions of barrels per year." Use the following information to determine the fraction of our projected 2022 total energy demand this target represents in order to assess its significance. (M = mega = 106) US projected annual energy demand in 2022: equivalent of 22 *103 Mbarrels of oil
Energy density of oil: 5.9 *103 MJ/barrel
Energy density of biofuels: 100 MJ/gal
Mass density of petroleum: 900 g/L
Mass density of biofuels: 800 g/L
1 gal = 3.785 L
A) 2.8%
B) 3.6%
C) 9.2%
D) 4.5%
E) 1.8%
Energy density of oil: 5.9 *103 MJ/barrel
Energy density of biofuels: 100 MJ/gal
Mass density of petroleum: 900 g/L
Mass density of biofuels: 800 g/L
1 gal = 3.785 L
A) 2.8%
B) 3.6%
C) 9.2%
D) 4.5%
E) 1.8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The integrated circuits in your cell phone and computer are made from the semiconductor silicon. The silicon is obtained from a really inexpensive starting material, sand, which is primarily SiO2. One step in the purification of silicon is to separate it from solid impurities by forming the gas silicon tetrachloride. Given the following reactions, what is the overall enthalpy change in converting 1.00 mol of silicon dioxide into pure silicon? Reaction
H° (kJ)
SiO2(s) + 2C(s) Si(impure s) + 2CO(g)
+690
Si(impure s) + 2Cl2(g) SiCl4(g)
-657
SiCl4(g) + 2Mg(s) 2MgCl2(s) + Si(s)
-625
A) +1972 kJ
B) -1972 kJ
C) -592 kJ
D) +592 kJ
E) -625 kJ
H° (kJ)
SiO2(s) + 2C(s) Si(impure s) + 2CO(g)
+690
Si(impure s) + 2Cl2(g) SiCl4(g)
-657
SiCl4(g) + 2Mg(s) 2MgCl2(s) + Si(s)
-625
A) +1972 kJ
B) -1972 kJ
C) -592 kJ
D) +592 kJ
E) -625 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) has been suggested as an alternative fuel source. Ethanol's enthalpy of combustion is Hcomb = -1368 kJ/mol. What volume of ethanol (d = 0.789 g/mL) is required to produce the same amount of energy as 1 gallon of gasoline, which can be modeled as isooctane (C8H18) with an energy density of 32.9 kJ/mL? (1 gal = 3.785 L; d = 0.703 g/mL)
A) 1.41 gal
B) 1.00 gal
C) 0.90 gal
D) 0.85 gal
E) 1.15 gal
A) 1.41 gal
B) 1.00 gal
C) 0.90 gal
D) 0.85 gal
E) 1.15 gal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following hydrocarbons has the greatest fuel value?
A) C5H12
B) C7H16
C) C6H12
D) C6H14
E) C10H8
A) C5H12
B) C7H16
C) C6H12
D) C6H14
E) C10H8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a Reuters news report dated February 3, 2010, President Obama is quoted as saying, "By 2022 we will more than double the amount of biofuels we produce to 36 billion gallons, which will decrease our dependence on foreign oil by hundreds of millions of barrels per year." Use the following information to estimate the fraction of farmland in the U.S. that will be needed to meet this target in order to assess the impact on other uses of farmland, such as the production of food. (M = mega = 106) Farmland in the U.S. = 1.4 * 106 square miles
Energy density of biofuels = 100 MJ/gal
Annual biofuel production from farmland = 1000 gal/acre
640 acres = 1 square mile
1 gal = 3.785 L
Mass density of biofuels: 800 g/L
A) 0.4%
B) 1.0%
C) 4.0%
D) 10%
E) 40%
Energy density of biofuels = 100 MJ/gal
Annual biofuel production from farmland = 1000 gal/acre
640 acres = 1 square mile
1 gal = 3.785 L
Mass density of biofuels: 800 g/L
A) 0.4%
B) 1.0%
C) 4.0%
D) 10%
E) 40%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following information to determine the standard enthalpy change when 1 mol of PbO(s) is formed from lead metal and oxygen gas. PbO(s) + C(graphite) Pb(s) + CO(g) Ho = 107 kJ
2C(graphite) + O2(g) 2CO(g) Ho = -222 kJ
A) - 436 kJ
B) +436 kJ
C) -218 kJ
D) -329 kJ
E) -115 kJ
2C(graphite) + O2(g) 2CO(g) Ho = -222 kJ
A) - 436 kJ
B) +436 kJ
C) -218 kJ
D) -329 kJ
E) -115 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Lightweight camping stoves typically use a mixture of C5 and C6 hydrocarbons, which is called white gas. Assuming white gas is 100% C5H12 with an enthalpy of combustion of -3550 kJ/mol, how many grams of it must be used to heat 1.50 L of water from 20°C to 80°C? Assume all the energy is used to heat the water.
A) 8.96 g
B) 7.64 g
C) 9.65 g
D) 6.99 g
E) 10.73 g
A) 8.96 g
B) 7.64 g
C) 9.65 g
D) 6.99 g
E) 10.73 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The enthalpy of combustion of table sugar (sucrose, C12H22O11, 342.3 g/mol) is -5643 kJ/mol. What is the food value (Cal/g) of sucrose? (1 Cal = 4.184 kJ)
A) 3.94 Cal/g
B) 11.1 Cal/g
C) 16.5 Cal/g
D) 2.92 Cal/g
E) 1350 Cal/g
A) 3.94 Cal/g
B) 11.1 Cal/g
C) 16.5 Cal/g
D) 2.92 Cal/g
E) 1350 Cal/g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Fuel value is __________
A) the cost of energy in kJ/$.
B) the amount of energy contained in 1 mol of a substance (kJ/mol).
C) the energy released when 1 g of a substance is burned (kJ/g).
D) the energy released when 1 g of a substance is formed (kJ/g).
E) the energy released when 1 L of a substance is burned (kJ/L).
A) the cost of energy in kJ/$.
B) the amount of energy contained in 1 mol of a substance (kJ/mol).
C) the energy released when 1 g of a substance is burned (kJ/g).
D) the energy released when 1 g of a substance is formed (kJ/g).
E) the energy released when 1 L of a substance is burned (kJ/L).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



