Deck 14: Differential Analysis, Profitability Analysis and Capital Budgeting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Differential Analysis, Profitability Analysis and Capital Budgeting
1
The purpose of incremental analysis is to find the alternative:
A) with the lowest fixed costs.
B) that brings in the most income.
C) with the least direct costs.
D) that contributes the most to profit.
A) with the lowest fixed costs.
B) that brings in the most income.
C) with the least direct costs.
D) that contributes the most to profit.
D
2
Petnet Corporation purchased capital equipment two years ago for $50 000. The firm is considering selling the equipment outright for $20 000 or, alternatively, trading it in on new equipment for an allowance of $24 000 The sunk cost associated with the equipment is:
A) $20 000.
B) $50 000.
C) $24 000.
D) $26 000.
A) $20 000.
B) $50 000.
C) $24 000.
D) $26 000.
B
3
Which of these is not relevant in the evaluation of a make-or-buy decision?
A) Quality control
B) Alternative uses of the unused capacity
C) Unavoidable costs
D) Potential adverse effects on business relationships
A) Quality control
B) Alternative uses of the unused capacity
C) Unavoidable costs
D) Potential adverse effects on business relationships
C
4
Sunk costs are omitted from decision analysis:
A) sometimes.
B) only if immaterial.
C) always.
D) never.
A) sometimes.
B) only if immaterial.
C) always.
D) never.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A sunk cost is a:
A) cost that cannot be changed and is therefore not relevant to decision making.
B) fixed cost.
C) cost which may be saved by not adopting an alternative.
D) potential benefit forgone.
A) cost that cannot be changed and is therefore not relevant to decision making.
B) fixed cost.
C) cost which may be saved by not adopting an alternative.
D) potential benefit forgone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A cost which differs between alternative courses of action is a:
A) relevant cost.
B) sunk cost.
C) controllable cost.
D) non-joint cost.
A) relevant cost.
B) sunk cost.
C) controllable cost.
D) non-joint cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
List the following steps in the decision-making process in the order in which they are carried out.
I Gather information
II Evaluate the alternatives
III Define the problem
IV Choose a course of action
A) I, III, II, IV
B) III, II, I, IV
C) III, I, II, IV
D) IV, III, I, II
I Gather information
II Evaluate the alternatives
III Define the problem
IV Choose a course of action
A) I, III, II, IV
B) III, II, I, IV
C) III, I, II, IV
D) IV, III, I, II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The term incremental cost refers to:
A) the difference in total costs between alternatives.
B) the operating profit forgone by selecting one choice instead of another.
C) a cost that continues to be incurred even though there is no activity.
D) a cost that is directly traceable to a specific cost object.
A) the difference in total costs between alternatives.
B) the operating profit forgone by selecting one choice instead of another.
C) a cost that continues to be incurred even though there is no activity.
D) a cost that is directly traceable to a specific cost object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The point in the production process at which joint products become separate products is called the:
A) constraint point.
B) split-off point.
C) differential point.
D) acceptance point.
A) constraint point.
B) split-off point.
C) differential point.
D) acceptance point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of these is irrelevant in the evaluation of a special order?
A) Differential income
B) Differential cost
C) Average production cost
D) Idle capacity
A) Differential income
B) Differential cost
C) Average production cost
D) Idle capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In relation to joint products the objective of the sell or process further decision is to:
A) maximise profit.
B) maximise production.
C) maximise joint costs.
D) minimise processing.
A) maximise profit.
B) maximise production.
C) maximise joint costs.
D) minimise processing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

A) $800.
B) $2400.
C) $4800.
D) $15 200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In differential analysis irrelevant costs include costs that are:
A) avoidable.
B) different among alternatives.
C) sunk.
D) opportunity costs.
A) avoidable.
B) different among alternatives.
C) sunk.
D) opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a firm has limited production capacity in one part of a sequential production operation, it can maximise profits by producing those items having the highest:
A) selling price.
B) profit.
C) contribution margin per unit of the scarce resource.
D) gross profit.
A) selling price.
B) profit.
C) contribution margin per unit of the scarce resource.
D) gross profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The decision to further process a joint product is influenced by the:
A) amount of fixed overhead which has been absorbed by the product.
B) amount of costs already incurred for the product.
C) increased costs of further processing.
D) method used to allocate joint costs.
A) amount of fixed overhead which has been absorbed by the product.
B) amount of costs already incurred for the product.
C) increased costs of further processing.
D) method used to allocate joint costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The decision to process a joint product further is influenced by:
A) common costs allocated to the product.
B) the costs of further processing.
C) the amount of fixed overhead which has been absorbed by the product.
D) the amount of costs already incurred for the product.
A) common costs allocated to the product.
B) the costs of further processing.
C) the amount of fixed overhead which has been absorbed by the product.
D) the amount of costs already incurred for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Top managers of Arctic Cruises are alarmed at the firm's latest income statement which shows a continuing decline in profits. In approaching this situation what is the first step management should take?
A) Make key personnel changes in the marketing department.
B) Do a better job of scheduling entertainment on the ships.
C) Train the ships employees in more courteous behaviour to customers.
D) Define the problem with an emphasis on the objective to be accomplished.
A) Make key personnel changes in the marketing department.
B) Do a better job of scheduling entertainment on the ships.
C) Train the ships employees in more courteous behaviour to customers.
D) Define the problem with an emphasis on the objective to be accomplished.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

A) $21
B) $25
C) $27
D) $28.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In incremental analysis estimated future costs that differ between alternative courses of action are called:
A) relevant costs.
B) absorption costs.
C) variable overhead costs.
D) joint costs.
A) relevant costs.
B) absorption costs.
C) variable overhead costs.
D) joint costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The difference in total costs between two alternatives is referred to as the:
A) direct cost.
B) incremental cost.
C) opportunity cost.
D) sunk cost.
A) direct cost.
B) incremental cost.
C) opportunity cost.
D) sunk cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Using the following information, calculate the residual profit.
Sales $500 000
Profit 40 000
Average operating assets 180 000
Shareholders' equity 50 000
Minimum required rate of return 15%
A) $13 000
B) $25 000
C) $16 000
D) $15 000
Sales $500 000
Profit 40 000
Average operating assets 180 000
Shareholders' equity 50 000
Minimum required rate of return 15%
A) $13 000
B) $25 000
C) $16 000
D) $15 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22

A) $12 200
B) $12 800
C) $17 000
D) $4400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What amount must be deposited today at 8% p.a. to grow to $1200 in three years?
A) $400.00
B) $947.28
C) $952.56
D) $981.22
A) $400.00
B) $947.28
C) $952.56
D) $981.22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of these represents the number of sales dollars generated by each dollar invested in assets?
A) Assets invested
B) Profit margin
C) Number of sales
D) Asset turnover
A) Assets invested
B) Profit margin
C) Number of sales
D) Asset turnover

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Using the following information, calculate the return on investment.
Sales $100 000
Operating profit $6000
Profit margin 8%
Equity $25 000
Minimum required rate of return 10%
Turnover of assets 1.5 times p.a.
A) 10%
B) 22%
C) 8%
D) 12%
Sales $100 000
Operating profit $6000
Profit margin 8%
Equity $25 000
Minimum required rate of return 10%
Turnover of assets 1.5 times p.a.
A) 10%
B) 22%
C) 8%
D) 12%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
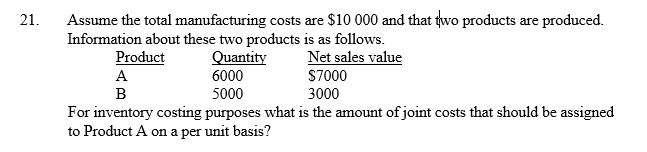
A) $0.75
B) $0.91
C) $1.00
D) $1.06

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Discounting calculates which value of an amount to be received?
A) Present
B) Future
C) Payback
D) Historical
A) Present
B) Future
C) Payback
D) Historical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What amount must be deposited today at 6% to grow to $900 in three years?
A) $405.70
B) $755.64
C) $817.22
D) $456.79
A) $405.70
B) $755.64
C) $817.22
D) $456.79

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
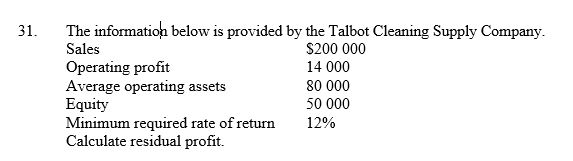
A) $8000
B) $4400
C) $5000
D) $4000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Capital investment proposals should be ranked in decreasing order of:
A) rate of return.
B) dollar amount required.
C) salvage value.
D) residual value expected.
A) rate of return.
B) dollar amount required.
C) salvage value.
D) residual value expected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If $100 is invested at 6%, which calculation will provide the answer to how much will it grow to at the end of three years?
A) $100 x 0.9434 x 3
B) ($100 / 2.6730) x 3
C) $100 / 0.8396
D) $100 x 2.6730
A) $100 x 0.9434 x 3
B) ($100 / 2.6730) x 3
C) $100 / 0.8396
D) $100 x 2.6730

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

A) product b, since it has the highest contribution margin per unit.
B) product b, since it has the highest price.
C) product a, since it has the highest contribution margin per labour hour.
D) product B, since it has the lowest costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Using the information provided by Tasco Sales, calculate the return on investment.
Sales $1 900 000
Operating profit 30 000
Average operating assets 600 000
Shareholders' equity 50 000
Minimum required rate of return 10%
A) 4%
B) 9%
C) 5%
D) 6%
Sales $1 900 000
Operating profit 30 000
Average operating assets 600 000
Shareholders' equity 50 000
Minimum required rate of return 10%
A) 4%
B) 9%
C) 5%
D) 6%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of these is not a capital investment decision?
A) Replace old equipment
B) Acquire a new company
C) Downsize the workforce
D) Add a new product line
A) Replace old equipment
B) Acquire a new company
C) Downsize the workforce
D) Add a new product line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The time value of money concept is given consideration in long-range investment decisions by:
A) investing only in short term projects.
B) assigning greater value to more immediate cash flows.
C) assuming equal annual cash flow patterns.
D) using the payback method and at least one other method to make an evaluation.
A) investing only in short term projects.
B) assigning greater value to more immediate cash flows.
C) assuming equal annual cash flow patterns.
D) using the payback method and at least one other method to make an evaluation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A manager can improve return on assets by how many of the following actions?
Increasing sales
Decreasing costs
Decreasing assets
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
Increasing sales
Decreasing costs
Decreasing assets
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Milam Company requires a 12% return on all investments. How much will the company be willing to pay for machine A if the machine will pay $8000 per year for 10 years?
A) $2576
B) $8000
C) $45 202
D) $80 000
A) $2576
B) $8000
C) $45 202
D) $80 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of these is not a reason why capital budgeting decisions must be carefully considered?
A) They involve large sums of money.
B) Resources are committed for long periods.
C) Cash flows must be discounted.
D) Because they are long-term there is greater risk that external conditions may alter.
A) They involve large sums of money.
B) Resources are committed for long periods.
C) Cash flows must be discounted.
D) Because they are long-term there is greater risk that external conditions may alter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Return on investment equals:
A) profit margin x return on equity.
B) asset turnover x residual profit.
C) selling price x cost of investment.
D) profit margin x asset turnover.
A) profit margin x return on equity.
B) asset turnover x residual profit.
C) selling price x cost of investment.
D) profit margin x asset turnover.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
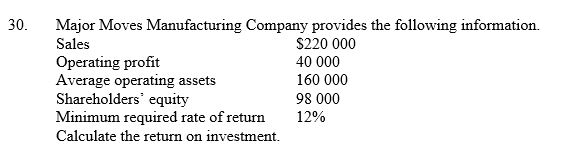
A) 12%
B) 18%
C) 25%
D) 41%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Anton Wine Company is considering a project with annual after-tax cash flows of $4000 per year for 5 years. The company's cost of capital is 5%. Using the net present value method, what is the maximum amount that the company should invest?
A) $16 316
B) $14 556
C) $17 318
D) $13 434
A) $16 316
B) $14 556
C) $17 318
D) $13 434

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is not a component of the cost of capital?
A) Preference shares
B) Retained earnings
C) Debt
D) Cost of sales
A) Preference shares
B) Retained earnings
C) Debt
D) Cost of sales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An increase in the discount rate:
A) will increase present values.
B) will have no effect on net present value.
C) may either increase or decrease present values, depending on the state of the economy.
D) will reduce present values.
A) will increase present values.
B) will have no effect on net present value.
C) may either increase or decrease present values, depending on the state of the economy.
D) will reduce present values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Always Rite Corporation is considering a project with annual after-tax cash flows of $8000 per year for 5 years. The company's cost of capital is 5%. Using the net present value method, what is the maximum amount that the company should invest?
A) $22 985
B) $27 472
C) $34 636
D) $33 908
A) $22 985
B) $27 472
C) $34 636
D) $33 908

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Darwin Limited is considering purchasing a new asset with an initial cost of $75 000 and an estimated annual income of $20 000. Cash operating expenses are expected to be $11 500 per year. Straight-line depreciation will be used over the five-year life of the asset and salvage value of $15 000 is to be considered in computing depreciation. Assuming that the income tax rate is 30%, what is the amount of annual tax savings from depreciation? (Assume the straight-line depreciation method is used for both accounting and tax purposes.)
A) $3600
B) $4500
C) $9150
D) $12 750
A) $3600
B) $4500
C) $9150
D) $12 750

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Rank these investments in order of profitability, showing the best project first.
Investment A - NPV, $114 561
Investment B - NPV, $145 000
Investment C - NPV, $72 634
Investment D - NPV, $0
A) D, C, A, B
B) D, A, B, C
C) B, A, C, D
D) B, C, A, D
Investment A - NPV, $114 561
Investment B - NPV, $145 000
Investment C - NPV, $72 634
Investment D - NPV, $0
A) D, C, A, B
B) D, A, B, C
C) B, A, C, D
D) B, C, A, D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

A) $1039
B) $2892
C) $4417
D) $4745

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of these is not an advantage of the payback method of capital budgeting?
A) It can be used to separate investments when other methods show similar returns.
B) The sooner cash is recovered the sooner it can be reinvested.
C) It looks at returns over the whole life of the investment.
D) A quick payback period reduces the risk of the investment.
A) It can be used to separate investments when other methods show similar returns.
B) The sooner cash is recovered the sooner it can be reinvested.
C) It looks at returns over the whole life of the investment.
D) A quick payback period reduces the risk of the investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The cost of capital is the:
A) cost of borrowing from a bank.
B) cost involved in issuing new shares.
C) rate of interest on government bonds.
D) weighted average of the cost of obtaining funds in the form of debt and/or equity.
A) cost of borrowing from a bank.
B) cost involved in issuing new shares.
C) rate of interest on government bonds.
D) weighted average of the cost of obtaining funds in the form of debt and/or equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Hot Rocks Corporation estimates that it can save $2800 a year in cash operating costs for the next ten years if it buys a special purpose machine at a cost of $11 000. No residual value is expected. The firm's minimum desired rate of return is 12%. Compute the net present value.
A) $6289.66
B) $4314.00
C) $2850.29
D) $4820.56
A) $6289.66
B) $4314.00
C) $2850.29
D) $4820.56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The method of project selection that brings the time value of money into capital investment analysis is the:
A) accounting rate of return method.
B) net present value method.
C) payback method.
D) return on average investment method.
A) accounting rate of return method.
B) net present value method.
C) payback method.
D) return on average investment method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The net present value method of evaluating proposed investments:
A) measures a project's time adjusted rate of return.
B) ignores cash flows beyond the payback period.
C) applies to only mutually exclusive investment proposals.
D) discounts cash flows at the minimum rate of return.
A) measures a project's time adjusted rate of return.
B) ignores cash flows beyond the payback period.
C) applies to only mutually exclusive investment proposals.
D) discounts cash flows at the minimum rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Select the incorrect statement concerning the return on average investment method of capital budgeting.
A) It measures profit in the same way as the income statement.
B) It is easy to use.
C) It distinguishes between investments requiring an immediate payment of cash and those where payment is in the future.
D) It considers profits over the useful life of the investment.
A) It measures profit in the same way as the income statement.
B) It is easy to use.
C) It distinguishes between investments requiring an immediate payment of cash and those where payment is in the future.
D) It considers profits over the useful life of the investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Lamb Ltd is evaluating an investment proposal using the payback method. Cash inflows are expected to be $3000 in year 1, $3500 in year 2, $5000 in year 3, and $4500 in year 4. The initial investment required is $7000. Assuming even cash inflows within each year what is the payback period?
A) 1.8 years
B) 2.1 years
C) 2.3 years
D) 3.1 years
A) 1.8 years
B) 2.1 years
C) 2.3 years
D) 3.1 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An investment will return net after-tax cash inflows of $5000 per year for 5 years. The desired rate of return is 10%. What is the total present value of the future cash flows?
A) $12 622
B) $10 891
C) $18 954
D) $13 923
A) $12 622
B) $10 891
C) $18 954
D) $13 923

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Ignoring tax effects which item is not relevant to capital investment?
A) Cost savings
B) Net income
C) Disposal value
D) Depreciation
A) Cost savings
B) Net income
C) Disposal value
D) Depreciation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is irrelevant to capital investment analysis?
A) Residual value
B) Carrying value
C) Net cash flows
D) Investment cost
A) Residual value
B) Carrying value
C) Net cash flows
D) Investment cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Rank these investments in order payback period showing the best project first.
Investment A - 4.7 years
Investment B - 3.8 years
Investment C - 4 years
Investment D - 3.2 years
A) D, C, A, B
B) D, B, C, A
C) B, A, C, D
D) A, C, B, D
Investment A - 4.7 years
Investment B - 3.8 years
Investment C - 4 years
Investment D - 3.2 years
A) D, C, A, B
B) D, B, C, A
C) B, A, C, D
D) A, C, B, D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which item is a non-cash expense?
A) Depreciation
B) Salaries
C) Rates
D) Income taxes
A) Depreciation
B) Salaries
C) Rates
D) Income taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How does depreciation affect net cash flows?
A) Increases taxation payable
B) Reduces taxation payable
C) Reduces cash inflows
D) Increases cash outflows
A) Increases taxation payable
B) Reduces taxation payable
C) Reduces cash inflows
D) Increases cash outflows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A piece of equipment costing $108 000 is expected to generate $16 000 annually in cash inflows during its life of 6 years. The payback in years is:
A) 6.25 years.
B) 6.75 years.
C) 9.60 years.
D) 2.34 years.
A) 6.25 years.
B) 6.75 years.
C) 9.60 years.
D) 2.34 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which statement concerning the internal rate of return method of capital budgeting is true?
A) The interest rate that will discount future cash flows so that their present value is exactly equal to the cost of the investment is the cost of capital.
B) When the internal rate of return method is employed a direct relationship will exist between the interest rate chosen and the present value of future cash flows.
C) When the net present value is equal to zero, the cost of capital (discount rate) and the internal rate of return are equal.
D) The internal rate of return is the discount rate that will produce a positive net present value for the investment.
A) The interest rate that will discount future cash flows so that their present value is exactly equal to the cost of the investment is the cost of capital.
B) When the internal rate of return method is employed a direct relationship will exist between the interest rate chosen and the present value of future cash flows.
C) When the net present value is equal to zero, the cost of capital (discount rate) and the internal rate of return are equal.
D) The internal rate of return is the discount rate that will produce a positive net present value for the investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of these is not true for the payback method of investment analysis?
A) It does not consider the time value of money.
B) It does not consider project profitability.
C) It is relatively simple to calculate.
D) The longer the payback period the better.
A) It does not consider the time value of money.
B) It does not consider project profitability.
C) It is relatively simple to calculate.
D) The longer the payback period the better.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Equipment A costing $80 000 is expected to generate $12 000 annually in cash inflows during its life of 8 years. Equipment B costing $120 000 is expected to generate $17 000 annually in cash inflows during its life of 8 years. Equipment C costing $60 000 is expected to generate $8000 annually in cash inflows during its life of 9 years. Rank the three investments in terms of payback period.
A) A1, B2, C3
B) B1, A2, C3
C) A1, B2, C3
D) C1, A2, B3
A) A1, B2, C3
B) B1, A2, C3
C) A1, B2, C3
D) C1, A2, B3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Aston Advertising is considering the purchase of a special purpose machine for $22 000. It is expected to have a useful life of ten years with no salvage value. The firm's accountant estimates savings in cash operating costs of $5000 per year. Compute the pay-back period.
A) 4.6 years
B) 4.4 years
C) 6.2 years
D) 5.6 years
A) 4.6 years
B) 4.4 years
C) 6.2 years
D) 5.6 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



