Deck 27: Reactions of Organic Compounds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/94
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: Reactions of Organic Compounds
1
The step reaction polymerizations are fast polymerization reactions
False
2
SN2 reactions are nucleophilic substitution reactions for which the rate determining step is bimolecular.
True
3
The alkanes are known for their reactivity
False
4
The following can be said about the reaction profile of an SN1 reaction:
I. The rate determining step is formation of carbocation.
II. The reaction profile has one transition state.
III. The slow step is the first transition state.
IV. The second step is attack of electrophile on carbocation.
V.The reaction proceeds in a polar aprotic solvent.
A) I, III, and IV
B) I, II and IV
C) II, III and IV
D) I, II and V
E) II, IV and V
I. The rate determining step is formation of carbocation.
II. The reaction profile has one transition state.
III. The slow step is the first transition state.
IV. The second step is attack of electrophile on carbocation.
V.The reaction proceeds in a polar aprotic solvent.
A) I, III, and IV
B) I, II and IV
C) II, III and IV
D) I, II and V
E) II, IV and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements correctly describe SN2 and SN1 reactions?
I. SN2 reactions proceed with retention of configuration.
II. SN1 reactions prefer polar protic solvents
III. SN1 reactions produce racemic products
IV. SN2 reactions are promoted in the presence of a substrate that produces a very stable carbocation
V.SN1 reactions have a unimolecular rate-determining step.
A) I, II and V
B) II, III, and IV
C) III, IV and V
D) II, III and V
E) I, III, and IV
I. SN2 reactions proceed with retention of configuration.
II. SN1 reactions prefer polar protic solvents
III. SN1 reactions produce racemic products
IV. SN2 reactions are promoted in the presence of a substrate that produces a very stable carbocation
V.SN1 reactions have a unimolecular rate-determining step.
A) I, II and V
B) II, III, and IV
C) III, IV and V
D) II, III and V
E) I, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In a substitution reaction an atom, an ion or a group in one molecule is replaced by another atom, ion or group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following trends in nucleophilicity are correct?
I. Everything else being equal, a negatively charged nucleophile will react faster than a neutral one.
II. Generally, species containing elements of high electronegativity are good nucleophiles.
III. Anionic nucleophiles are more reactive in polar and aprotic solvents than in polar and protic solvents
IV. Generally, nucleophilicity is increasing with the increase in size of an atom.
V. Bulky groups adjacent to the nucleophilic atom enhance the nucleophilicity and reactivity of the species.
A) I, III, and V
B) II, III and V
C) I, II and IV
D) II, III and V.
E) III, IV and V
I. Everything else being equal, a negatively charged nucleophile will react faster than a neutral one.
II. Generally, species containing elements of high electronegativity are good nucleophiles.
III. Anionic nucleophiles are more reactive in polar and aprotic solvents than in polar and protic solvents
IV. Generally, nucleophilicity is increasing with the increase in size of an atom.
V. Bulky groups adjacent to the nucleophilic atom enhance the nucleophilicity and reactivity of the species.
A) I, III, and V
B) II, III and V
C) I, II and IV
D) II, III and V.
E) III, IV and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Synthesis of alkanes from alkyl halides is a typical example of E2 reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following steps can be found in E1 reaction mechanism?
I. Formation of a carbocation
II. Attack of the base and removal of a proton from carbocation
III. Attack of a nucleophile
IV. Formation of a carboanion
A) I and II
B) only II
C) I and III
D) III and IV
E) only III
I. Formation of a carbocation
II. Attack of the base and removal of a proton from carbocation
III. Attack of a nucleophile
IV. Formation of a carboanion
A) I and II
B) only II
C) I and III
D) III and IV
E) only III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
We can promote SN2 over SN1 reactions if we:
I. use a substrate that gives a primary carbocation and not tertiary carbocation
II. use a sterically hindered substrate
III. use a polar protic solvent
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and III
E) II and III
I. use a substrate that gives a primary carbocation and not tertiary carbocation
II. use a sterically hindered substrate
III. use a polar protic solvent
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and III
E) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Arrange the following carbocations in order of decreasing stability: 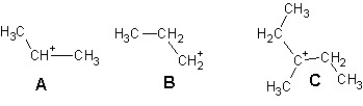
A) A > B > C.
B) C > B > A
C) A > B > C
D) C > A > B.
E) B > A > C.

A) A > B > C.
B) C > B > A
C) A > B > C
D) C > A > B.
E) B > A > C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Organic reactions in which atoms or groups that are bonded to adjacent carbon atoms are eliminated are called elimination reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Molecules add across multiple bonds in another molecule in addition reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Arrange the following in the order of decreasing nucleophilicity: H2N-, HO-, HCOO-, CH3O-
A) H2N- > HO- > HCOO- > CH3O-
B) H2N- > CH3O- > HO- > HCOO-
C) H2N- > HO- > CH3O- > HCOO-
D) HO- > H2N- > CH3O- > HCOO-
E) CH3O- > HO- > H2N- > HCOO-
A) H2N- > HO- > HCOO- > CH3O-
B) H2N- > CH3O- > HO- > HCOO-
C) H2N- > HO- > CH3O- > HCOO-
D) HO- > H2N- > CH3O- > HCOO-
E) CH3O- > HO- > H2N- > HCOO-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Finish the sentence: "Elimination reactions....
A) ...can follow two different mechanisms."
B) ...do not compete with other reaction types."
C) ...usually give a saturated product."
D) ...always give only one product."
E) ...have only one mechanistic path."
A) ...can follow two different mechanisms."
B) ...do not compete with other reaction types."
C) ...usually give a saturated product."
D) ...always give only one product."
E) ...have only one mechanistic path."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Nucleophiles are electron poor atoms, ions or groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Find the combination of conditions that are the best for SN2 reactions.
A) The substrate is a tertiary alkyl iodide, solvent is aprotic, polar and the nucleophile is a strong base.
B) The substrate is a primary alkyl iodide, solvent is aprotic, polar and the nucleophile is a strong base.
C) The substrate is a primary alkyl fluoride, solvent is protic, polar and the nucleophile is a strong base.
D) The substrate is a primary alkyl iodide, solvent is non-polar and the nucleophile is a weak base
E) The substrate is a tertiary alkyl iodide, solvent is non-polar and the nucleophile is a strong base.
A) The substrate is a tertiary alkyl iodide, solvent is aprotic, polar and the nucleophile is a strong base.
B) The substrate is a primary alkyl iodide, solvent is aprotic, polar and the nucleophile is a strong base.
C) The substrate is a primary alkyl fluoride, solvent is protic, polar and the nucleophile is a strong base.
D) The substrate is a primary alkyl iodide, solvent is non-polar and the nucleophile is a weak base
E) The substrate is a tertiary alkyl iodide, solvent is non-polar and the nucleophile is a strong base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
For which type of reaction is the following an example? 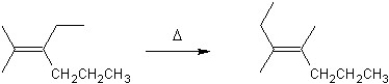
A) substitution
B) elimination
C) polymerization
D) rearrangement
E) addition

A) substitution
B) elimination
C) polymerization
D) rearrangement
E) addition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Reactions between alkanes and HX compounds are typical examples of addition reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Electrophilic substitution reactions are typical reactions of aromatic compounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The rate of E2 reaction between an alkyl halide RX and a base B is given by the following expression (k is a rate constant):
A) k[RX}
B) k[B]
C) k[RX]{B]
D) k{RX]2
E) k{RX]2[B]
A) k[RX}
B) k[B]
C) k[RX]{B]
D) k{RX]2
E) k{RX]2[B]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Hyperconjugation is best described as:
A) an interaction between the orbitals on a substrate and orbitals on a nucleophile
B) an interaction between σ bonds and π network
C) a resonance structure with separated charges
D) an interaction between two π networks
E) an electrostatic interaction between an electrophile and a nucleophile
A) an interaction between the orbitals on a substrate and orbitals on a nucleophile
B) an interaction between σ bonds and π network
C) a resonance structure with separated charges
D) an interaction between two π networks
E) an electrostatic interaction between an electrophile and a nucleophile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Find a group that is a ortho,para director in electrophilic aromatic substitution.
A) -NO2
B) -SO3H
C) -OH
D) -COH
E) -COOCH3
A) -NO2
B) -SO3H
C) -OH
D) -COH
E) -COOCH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Arrange the following alkenes according to their increasing stability: 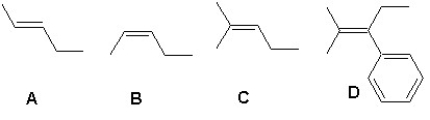
A) A < B < C < D
B) B < C < A < D
C) B < A < C < D
D) C < B < A < D
E) C < A < B < D

A) A < B < C < D
B) B < C < A < D
C) B < A < C < D
D) C < B < A < D
E) C < A < B < D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Markovnikof's rule predicts that when HBr is added to an unsymmetrical alkene or alkyne, the H atom will add to which carbon atom?
A) the carbon with the fewest attached hydrogens
B) the carbon with the Br
C) the carbon with the most attached hydrogens
D) the carbon next to the double or triple bond
E) HBr does not react with unsymmetrical alkenes or alkynes.
A) the carbon with the fewest attached hydrogens
B) the carbon with the Br
C) the carbon with the most attached hydrogens
D) the carbon next to the double or triple bond
E) HBr does not react with unsymmetrical alkenes or alkynes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following could be added across carbon-carbon multiple bonds?
I. H2SO4
II. H2
III. H2O
IV. NO2
V. HBr
A) II, III, and V
B) II, III, and IV
C) I, III, and V
D) I, III, and IV
E) I, II, and III
I. H2SO4
II. H2
III. H2O
IV. NO2
V. HBr
A) II, III, and V
B) II, III, and IV
C) I, III, and V
D) I, III, and IV
E) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
During the nitration of a benzene ring in a mixture of HNO3 and H2SO4 the following species reacts as an electrophile:
A) H3O+
B) H3SO4+
C) H2NO3+
D) H+
E) NO2+
A) H3O+
B) H3SO4+
C) H2NO3+
D) H+
E) NO2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What product would you expect to obtain from a reaction between one isomer of 3-methyl-1-pentanol and HI?
A) a substitution product with retention of configuration
B) only one elimination product
C) a substitution product with inversion of configuration
D) two elimination products
E) a racemic mixture of substitution products
A) a substitution product with retention of configuration
B) only one elimination product
C) a substitution product with inversion of configuration
D) two elimination products
E) a racemic mixture of substitution products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A hydrocarbon has a molecular weight 56 g/mol and contains 85.7% carbon. It easily adds one mol of HBr to produce a chiral alkyl bromide. Which of the following structures could be our hydrocarbon?
A)
B)
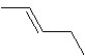
C)
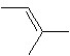
D)
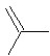
E)

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following mechanistic steps do you expect in bromination of benzene with Br2 and FeBr3 as a catalyst?
I. Formation of Br+[FeBr4]-
II. Attack of [FeBr4]- on benzene ring
III. Formation of arenium ion
IV. Deprotonation of arenium ion
V. Nucleophilic attack of Br+
A) I), III), and IV)
B) I), II), and IV)
C) II), III), and V)
D) III), IV), and V)
E) II), IV), and V)
I. Formation of Br+[FeBr4]-
II. Attack of [FeBr4]- on benzene ring
III. Formation of arenium ion
IV. Deprotonation of arenium ion
V. Nucleophilic attack of Br+
A) I), III), and IV)
B) I), II), and IV)
C) II), III), and V)
D) III), IV), and V)
E) II), IV), and V)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The chlorination of benzaldehyde is producing:
A) m-chlorobenzaldehyde
B) a mixture of o and p- chlorobenzaldehyde
C) o -chlorobenzaldehyde
D) p-chlorobenzaldehyde
E) a mixture of m- and p-chlorobenzaldehyde
A) m-chlorobenzaldehyde
B) a mixture of o and p- chlorobenzaldehyde
C) o -chlorobenzaldehyde
D) p-chlorobenzaldehyde
E) a mixture of m- and p-chlorobenzaldehyde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is a dehydration reaction?
A) Dehydration is elimination of water molecule from an alcohol molecule to produce alkene.
B) Dehydration reaction is removal of one equivalent of H2 from an alkane to produce alkene.
C) Dehydration reaction is one of the steps in chain-reaction polymerization.
D) Dehydration reaction is removal of crystalline water.
E) Dehydration reaction is deprotonation of a substrate with a strong base in E2 mechanism.
A) Dehydration is elimination of water molecule from an alcohol molecule to produce alkene.
B) Dehydration reaction is removal of one equivalent of H2 from an alkane to produce alkene.
C) Dehydration reaction is one of the steps in chain-reaction polymerization.
D) Dehydration reaction is removal of crystalline water.
E) Dehydration reaction is deprotonation of a substrate with a strong base in E2 mechanism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following steps would you expect to occur in the addition reaction mechanism?
I. Electrophilic attack on the unsaturated bond
II. Formation of carboanion
III. Formation of carbocation
IV. Nucleophilic attack on the carbocation
V. Elimination of a base
A) I, III, and IV
B) I, II, and V
C) II, III and IV
D) III, IV and V
E) II, IV and V
I. Electrophilic attack on the unsaturated bond
II. Formation of carboanion
III. Formation of carbocation
IV. Nucleophilic attack on the carbocation
V. Elimination of a base
A) I, III, and IV
B) I, II, and V
C) II, III and IV
D) III, IV and V
E) II, IV and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following groups is a meta director during electrophilic aromatic substitution?
A) -NH2
B) -OCH3
C) -Br
D) -C≡N
E) -OCOC2H5
A) -NH2
B) -OCH3
C) -Br
D) -C≡N
E) -OCOC2H5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
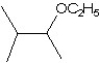
What is the major product in the reaction between 2-bromo-3-methylbutane and KOtBu in ethanol?
A)
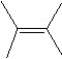
B)
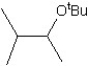
C)
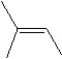
D)
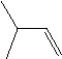
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following roles can alcohols have in organic reactions?
I. electrophile
II. solvent
III. base
IV. substrate
V. acid
A) II, III and IV
B) I, II, and III
C) I, III and V
D) II, III and V
E) II, IV and V
I. electrophile
II. solvent
III. base
IV. substrate
V. acid
A) II, III and IV
B) I, II, and III
C) I, III and V
D) II, III and V
E) II, IV and V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is arenium ion?
A) a carbocation formed after the electrophilic attack on the benzene ring
B) a carbocation formed from a molecule containing an arene ring
C) a carbocation formed during the elimination reaction from an aromatic molecule
D) a carboanion formed from deprotonation of benzene ring
E) a carboanion formed after nucleophilic attack on the benzene ring
A) a carbocation formed after the electrophilic attack on the benzene ring
B) a carbocation formed from a molecule containing an arene ring
C) a carbocation formed during the elimination reaction from an aromatic molecule
D) a carboanion formed from deprotonation of benzene ring
E) a carboanion formed after nucleophilic attack on the benzene ring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is an unsymmetrical reagent?
A) Cl2
B) H2O
C) H2O and HCl
D) HCl
E) I2
A) Cl2
B) H2O
C) H2O and HCl
D) HCl
E) I2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following compounds could be used as catalysts in halogenation of benzene?
I. AlCl3
II. NaCl
III. FeBr3
IV. MgCl2
V. PbCl2
A) I) and V)
B) II) and III)
C) II) and IV)
D) I) and III)
E) III) and V)
I. AlCl3
II. NaCl
III. FeBr3
IV. MgCl2
V. PbCl2
A) I) and V)
B) II) and III)
C) II) and IV)
D) I) and III)
E) III) and V)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In which of the following reactions can alcohol participate?
I. oxidation reactions
II. elimination reactions
III. amide synthesis
IV. peptide synthesis
V. ester synthesis
A) I, III and V
B) I, II and V
C) II, III and V
D) I, II and IV
E) II, III and IV
I. oxidation reactions
II. elimination reactions
III. amide synthesis
IV. peptide synthesis
V. ester synthesis
A) I, III and V
B) I, II and V
C) II, III and V
D) I, II and IV
E) II, III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The initiation step in chain reaction for alkene substitution produces:
A) free halogen radicals
B) free alkyl radicals
C) both free halogen and alkyl radicals
D) free halonium ions
E) free halide ions
A) free halogen radicals
B) free alkyl radicals
C) both free halogen and alkyl radicals
D) free halonium ions
E) free halide ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Complete the following reaction: NH3 + CH3Br →
A) CH4 + NH2Br
B) CH2=NH + H2 + HBr
C) CH3NH2 + NH4+Br-
D) CH3NH3+Br-
E) There is no reaction.
A) CH4 + NH2Br
B) CH2=NH + H2 + HBr
C) CH3NH2 + NH4+Br-
D) CH3NH3+Br-
E) There is no reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The physical properties of polymers depend on:
I. the average molecular mass of a chain
II. the strength of intermolecular forces between the chains
III. the reaction temperature applied during synthesis
IV. the degree of crystallinity
V. the reaction pressure
A) I), II), and IV)
B) II), III), and IV)
C) I), II), and V)
D) III), IV), and V)
E) II), IV), and V)
I. the average molecular mass of a chain
II. the strength of intermolecular forces between the chains
III. the reaction temperature applied during synthesis
IV. the degree of crystallinity
V. the reaction pressure
A) I), II), and IV)
B) II), III), and IV)
C) I), II), and V)
D) III), IV), and V)
E) II), IV), and V)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Chain reaction polymerization is typical for:
A) monomers with carbon-carbon double bonds
B) monomers with carbon oxygen double bonds
C) monomers containing aromatic rings
D) monomeric alkanes
E) monomeric alcohols
A) monomers with carbon-carbon double bonds
B) monomers with carbon oxygen double bonds
C) monomers containing aromatic rings
D) monomeric alkanes
E) monomeric alcohols

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
H3C∙ + ∙Cl → H3CCl is an example of:
A) polymerization
B) neutralization reaction
C) termination step in alkane chlorination
D) addition reaction
E) reforming reaction
A) polymerization
B) neutralization reaction
C) termination step in alkane chlorination
D) addition reaction
E) reforming reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suggest possible compounds for A and B in the following scheme: CH3CH2I + A → CH3CH2SH + B
A) A is HS- and B is I-
B) A is H2S and B is I2
C) A is H2S and B is HI
D) A is S2- and B is I-
E) A is H2S and B is I-
A) A is HS- and B is I-
B) A is H2S and B is I2
C) A is H2S and B is HI
D) A is S2- and B is I-
E) A is H2S and B is I-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which type of polymerization and which monomer(s) would you use to prepare poly(1,4-phenylenediformamide) with the following structure? 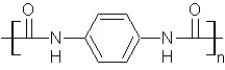
A)
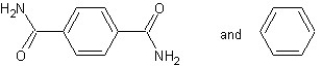
With chain reaction polymerization
B)
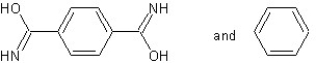
With condensation polymerization
C)
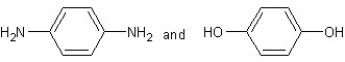
With chain reaction polymerization
D)
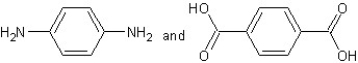
With step-reaction polymerization
E)
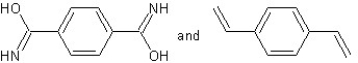
With chain reaction polymerization

A)

With chain reaction polymerization
B)

With condensation polymerization
C)
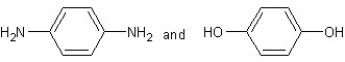
With chain reaction polymerization
D)

With step-reaction polymerization
E)
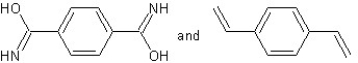
With chain reaction polymerization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Predict the product and mechanism type for the following reaction: 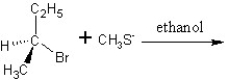
A)
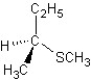
SN2 mechanism
B)
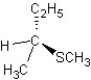
SN2 mechanism
C)
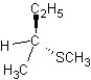
SN1 mechanism
D)
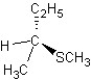
SN1 mechanism
E)
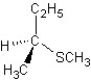
SN1 mechanism
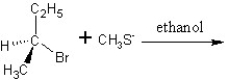
A)

SN2 mechanism
B)

SN2 mechanism
C)

SN1 mechanism
D)

SN1 mechanism
E)

SN1 mechanism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is "retrosynthesis"?
A) a chemical analysis followed by chemical synthesis
B) a chemical synthesis followed by chemical analysis
C) a synthetic procedure designed to check old synthetic procedure
D) a synthetic strategy that works from the desired compound towards starting materials
E) a synthetic strategy that works from the starting materials towards desired product
A) a chemical analysis followed by chemical synthesis
B) a chemical synthesis followed by chemical analysis
C) a synthetic procedure designed to check old synthetic procedure
D) a synthetic strategy that works from the desired compound towards starting materials
E) a synthetic strategy that works from the starting materials towards desired product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following steps are a part of chain reaction during alkane substitution?
I. Propagation
II. Initiation
III. Competition
IV. Dehalogenation
V. Termination
A) I), II) and V)
B) I), III) and V)
C) II), III) and V)
D) I), II) and IV)
E) III), IV) and V)
I. Propagation
II. Initiation
III. Competition
IV. Dehalogenation
V. Termination
A) I), II) and V)
B) I), III) and V)
C) II), III) and V)
D) I), II) and IV)
E) III), IV) and V)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Identify the product(s) and mechanism for the following reaction: 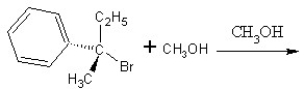
A)
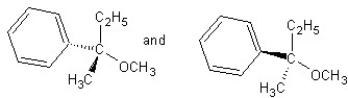
SN1 mechanism
B)
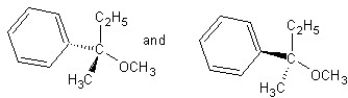
SN2 mechanism
C)
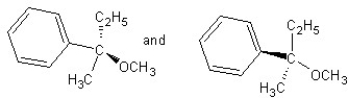
SN1 mechanism
D)
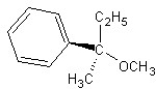
SN2 mechanism
E)
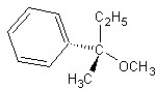
SN2 mechanism

A)

SN1 mechanism
B)

SN2 mechanism
C)

SN1 mechanism
D)

SN2 mechanism
E)

SN2 mechanism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Arrange the following radicals in the order of increasing stability: 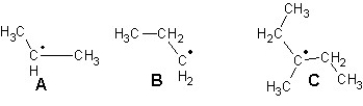
A) B < A < C
B) C < A < B
C) A < B < C
D) C < B < A
E) B < C < A

A) B < A < C
B) C < A < B
C) A < B < C
D) C < B < A
E) B < C < A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The formation of isopropanol (rubbing alcohol) through the following hydrolysis is known as what type of general reaction? 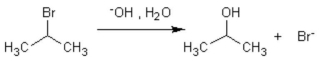
A) oxidation
B) aromatic substitution
C) addition reaction
D) elimination
E) substitution reaction

A) oxidation
B) aromatic substitution
C) addition reaction
D) elimination
E) substitution reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements correctly describe the step-reaction polymerization?
I. It is also called condensation polymerization.
II. It produces polymers of moderately high molecular masses.
III. It requires that monomers have functional groups that can join together.
IV. This type of polymerization is fast.
V. It is accompanied with the addition of a small molecule.
A) I), II) and III)
B) I), and II)
C) II), III) and IV)
D) III), IV) and V)
E) II), IV) and V)
I. It is also called condensation polymerization.
II. It produces polymers of moderately high molecular masses.
III. It requires that monomers have functional groups that can join together.
IV. This type of polymerization is fast.
V. It is accompanied with the addition of a small molecule.
A) I), II) and III)
B) I), and II)
C) II), III) and IV)
D) III), IV) and V)
E) II), IV) and V)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following are electrophiles? I. CH3CH2NH2 II. CH3CH2I III. CH3OH
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I + II
E) I + III
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I + II
E) I + III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following are nucleophiles? I. CH3C(O)CH3 II. CH3Br III. CH3CH2C≡C-
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I + II
E) I + III
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I + II
E) I + III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the rate law for the SN1 reactions (S is substrate and N is nucleophile) ?
A) rate = k[S][N]
B) rate = k[S]
C) rate = k[N}
D) rate = k[S]2
E) rate = k[S][N}2
A) rate = k[S][N]
B) rate = k[S]
C) rate = k[N}
D) rate = k[S]2
E) rate = k[S][N}2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suggest possible compounds for A, B and C in the following scheme: 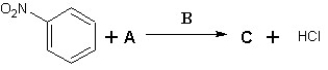
A) A is Cl2, B is AlCl3 and C is meta chloronitrobenzene
B) A is Cl2, B is FeCl3 and C is ortho chloronitrobenzene
C) A is Cl2, B is FeBr3 and C is meta chloronitrobenzene
D) A is HCl, B is AlCl3 and C is para chloronitrobenzene
E) A is Cl2, B is AlBr3 and C is meta chloronitrobenzene
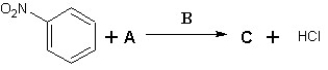
A) A is Cl2, B is AlCl3 and C is meta chloronitrobenzene
B) A is Cl2, B is FeCl3 and C is ortho chloronitrobenzene
C) A is Cl2, B is FeBr3 and C is meta chloronitrobenzene
D) A is HCl, B is AlCl3 and C is para chloronitrobenzene
E) A is Cl2, B is AlBr3 and C is meta chloronitrobenzene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Classify the following polymers as atactic, isotactic or syndiotactic: 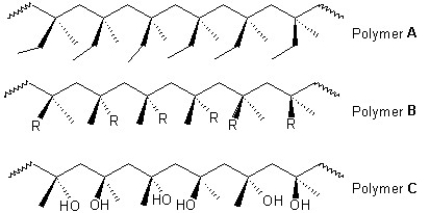
A) Polymer A is isotactic, polymer B is atactic and polymer C is syndiotactic
B) Polymer A is atactic, polymer B is isotactic and polymer C is syndiotactic
C) Polymers A and B are isotactic and polymer C is syndiotactic
D) Polymer A is isotactic and polymers B and C is syndiotactic
E) Polymer A is syndiotactic, polymer B is isotactic and polymer C is atactic

A) Polymer A is isotactic, polymer B is atactic and polymer C is syndiotactic
B) Polymer A is atactic, polymer B is isotactic and polymer C is syndiotactic
C) Polymers A and B are isotactic and polymer C is syndiotactic
D) Polymer A is isotactic and polymers B and C is syndiotactic
E) Polymer A is syndiotactic, polymer B is isotactic and polymer C is atactic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What are the three characteristic steps in a chain-reaction polymerization?
A) initiation, elongation and termination
B) initiation, propagation and termination
C) racemization, propagation and quenching
D) propagation, formation and termination
E) breaking, elongation and quenching
A) initiation, elongation and termination
B) initiation, propagation and termination
C) racemization, propagation and quenching
D) propagation, formation and termination
E) breaking, elongation and quenching

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Lindlar's catalyst is used when ________.
A) we want to reduce alkynes to alkanes
B) we want to speed up HX addition reactions
C) we have to promote elimination reactions over substitution reactions
D) we need to activate Pd hydrogenation catalyst
E) we want to reduce alkynes to Z alkenes
A) we want to reduce alkynes to alkanes
B) we want to speed up HX addition reactions
C) we have to promote elimination reactions over substitution reactions
D) we need to activate Pd hydrogenation catalyst
E) we want to reduce alkynes to Z alkenes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Give the product(s) of the reaction: CH2CHCH3 + HCl → product(s)
A) CH3CH2CH3 + H2
B) CH2ClCHClCH3 + H2
C) CH3CHClCH3
D) CH2ClCH2CH3
E) none of these
A) CH3CH2CH3 + H2
B) CH2ClCHClCH3 + H2
C) CH3CHClCH3
D) CH2ClCH2CH3
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Oxidation of the following alcohol via the conditions below yields spearmint oil. What new functional group is formed in the reaction to yield spearmint? 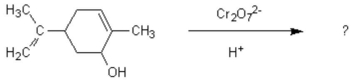
A) aldehyde
B) carboxylic acid
C) ketone
D) amine
E) ester

A) aldehyde
B) carboxylic acid
C) ketone
D) amine
E) ester

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suggest reagents for the synthesis of meta-chloronitrobenzene from nitrobenzene.
A) Cl2 and AlCl3
B) HCl and AlCl3
C) Cl2 and H2SO4
D) HCl and HNO3
E) Cl2 and FeBr3
A) Cl2 and AlCl3
B) HCl and AlCl3
C) Cl2 and H2SO4
D) HCl and HNO3
E) Cl2 and FeBr3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
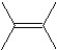
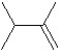
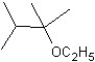
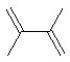
What is the major product in the following transformation? 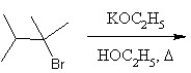
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
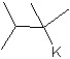

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Identify the product for the following reaction: 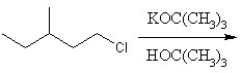
A) 3-methyl-1-pentene
B) 3-methyl-2-pentene
C) 3-methyl-1-pentane
D) 3-methyl-1-tert-butylpentante
E) 3-methylpentane

A) 3-methyl-1-pentene
B) 3-methyl-2-pentene
C) 3-methyl-1-pentane
D) 3-methyl-1-tert-butylpentante
E) 3-methylpentane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Order the following substrates according to the increase in SN2 reaction rate: (CH3)2CHBr, (CH3)3CBr, CH3CH2Br, CH3Br
A) (CH3)2CHBr < (CH3)3CBr < CH3CH2Br < CH3Br
B) (CH3)3CBr < (CH3)2CHBr < CH3CH2Br < CH3Br
C) (CH3)3CBr < (CH3)2CHBr < CH3Br < CH3CH2Br
D) (CH3)3CBr < CH3CH2Br < (CH3)2CHBr < CH3Br
E) CH3CH2Br < (CH3)3CBr < (CH3)2CHBr < CH3Br
A) (CH3)2CHBr < (CH3)3CBr < CH3CH2Br < CH3Br
B) (CH3)3CBr < (CH3)2CHBr < CH3CH2Br < CH3Br
C) (CH3)3CBr < (CH3)2CHBr < CH3Br < CH3CH2Br
D) (CH3)3CBr < CH3CH2Br < (CH3)2CHBr < CH3Br
E) CH3CH2Br < (CH3)3CBr < (CH3)2CHBr < CH3Br

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Predict the major product for the reaction: CH3C≡CH + 2HBr →
A) CH3CBr2CH3
B) CH3CH2CHBr2
C) CH3CHBrCH2Br
D) CH2=CBrCH2Br
E) no reaction
A) CH3CBr2CH3
B) CH3CH2CHBr2
C) CH3CHBrCH2Br
D) CH2=CBrCH2Br
E) no reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the main product of the following reaction? 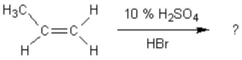
A) 1-bromopropane
B) 2-bromopropane
C) propyl alcohol
D) 2-bromopropene
E) 1-bromo-2-methylethane
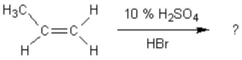
A) 1-bromopropane
B) 2-bromopropane
C) propyl alcohol
D) 2-bromopropene
E) 1-bromo-2-methylethane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Give the correct mathematical expression for the rate law for E2 reactions (S is a substrate and B is a base).
A) rate = k[S]
B) rate = k[B]
C) rate = k[S][B]
D) rate = k[S]1/2
E) rate = k[S]2
A) rate = k[S]
B) rate = k[B]
C) rate = k[S][B]
D) rate = k[S]1/2
E) rate = k[S]2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What alkene(s) would be produced in the following reaction? 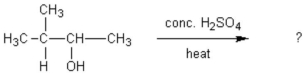
A) 3-methyl-2-pentene
B) 2-methyl-2-butene
C) 3-methylbutene
D) pentene and 1-methylpentene
E) 2-methyl-2-butene and 3-methylbutene

A) 3-methyl-2-pentene
B) 2-methyl-2-butene
C) 3-methylbutene
D) pentene and 1-methylpentene
E) 2-methyl-2-butene and 3-methylbutene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When (CH3)3CBr reacts with CH3ONa in methanol, two products are formed: a major one is an alkene and minor one is an ether. Identify the two products and by what mechanism(s) they are formed?
A)
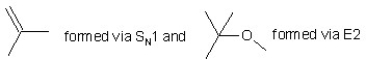
B)

C)
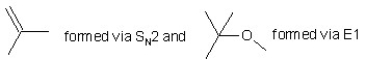
D)
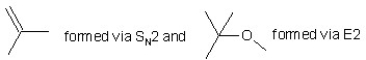
E)
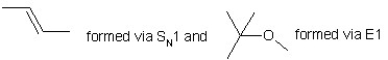
A)
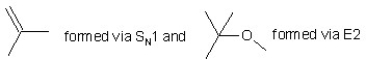
B)

C)
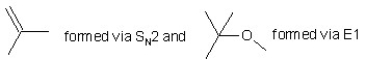
D)
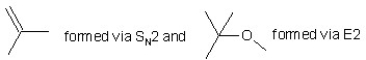
E)
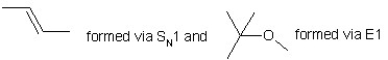

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following alcohols can eliminate water to produce alkene? I) phenol
II) HOC(CH3)3
III) HOCH(CH3)2
A) II) and III)
B) I), II) and III)
C) III) only
D) I) and II)
E) II) only
II) HOC(CH3)3
III) HOCH(CH3)2
A) II) and III)
B) I), II) and III)
C) III) only
D) I) and II)
E) II) only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which are the most probable reactions and mechanisms in which tertiary haloalkanes participate?
I Substitution, SN1
II. Substitution SN2
III. Elimination E1
IV. Elimination E2
V. Addition
A) II), III) and IV)
B) I), IV) and V)
C) II), III) and V)
D) I), III) and IV)
E) III), IV), V)
I Substitution, SN1
II. Substitution SN2
III. Elimination E1
IV. Elimination E2
V. Addition
A) II), III) and IV)
B) I), IV) and V)
C) II), III) and V)
D) I), III) and IV)
E) III), IV), V)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Predict the major product for the reaction: 1-butene + HI →
A) CH2ICH2CH2CH3
B) CH2ICH=CHCH3
C) CH2=CICH2CH3
D) CH3CHICH2CH3
E) CH3CI2CH2CH3
A) CH2ICH2CH2CH3
B) CH2ICH=CHCH3
C) CH2=CICH2CH3
D) CH3CHICH2CH3
E) CH3CI2CH2CH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The common general anesthetic neothyl can be produced by the following dehydration reaction. What is the systematic name of neothyl? 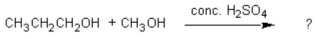
A) propanone
B) propanal
C) methyl propanoate
D) methyl propyl ether
E) ethyl methyl ether

A) propanone
B) propanal
C) methyl propanoate
D) methyl propyl ether
E) ethyl methyl ether

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Give the product(s) of the reaction (in H2SO4) : CH2CHCH3 + H2O → product(s)
A) CH2OHCH(OH)CH3
B) CH2OHCH2CH3
C) CH2OHCHOHCH3 + H2
D) CH3CH2CH3 + H2O2
E) CH3CH(OH)CH3
A) CH2OHCH(OH)CH3
B) CH2OHCH2CH3
C) CH2OHCHOHCH3 + H2
D) CH3CH2CH3 + H2O2
E) CH3CH(OH)CH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Predict the major product for the reaction: 2-methyl-2-pentene + HCl →
A) (CH3)2CHCHClCH2CH3
B) CH2=C(CH3)CHClCH2CH3
C) (CH3)2CClCCl=CHCH3
D) (CH3)2CClCH2CH2CH3
E) no reaction
A) (CH3)2CHCHClCH2CH3
B) CH2=C(CH3)CHClCH2CH3
C) (CH3)2CClCCl=CHCH3
D) (CH3)2CClCH2CH2CH3
E) no reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Write down the rate law for E1 reactions (S is a substrate and B is a base).
A) rate = k[S]
B) rate = k[S][B]
C) rate = k[B]
D) rate = k[S]2
E) rate = k[S]1/2
A) rate = k[S]
B) rate = k[S][B]
C) rate = k[B]
D) rate = k[S]2
E) rate = k[S]1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Predict the major product for the reaction: 2-methyl-2-butene + HBr →
A) (CH3)2CBrCH2CH3
B) (CH3)2CBrCH=CH2
C) (CH3)2CHCHBrCH3
D) CH2=C(CH3)CH2CH3
E) no reaction
A) (CH3)2CBrCH2CH3
B) (CH3)2CBrCH=CH2
C) (CH3)2CHCHBrCH3
D) CH2=C(CH3)CH2CH3
E) no reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



