Deck 25: Nuclear Chemistry 1-41
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Nuclear Chemistry 1-41
1
Which of the following are true for alpha particles? I) α particles are equivalent to 2 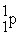 + 2
+ 2 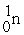 .
.
II) α decay decreases the atomic number by four.
III) α particles are deflected more strongly than e- by magnetic fields, but in the opposite direction.
IV) α particles are easily stopped as they strike matter.
A) I and II
B) I, II, III
C) I and III
D) I and IV
E) I, II, III, and IV
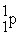 + 2
+ 2 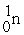 .
.II) α decay decreases the atomic number by four.
III) α particles are deflected more strongly than e- by magnetic fields, but in the opposite direction.
IV) α particles are easily stopped as they strike matter.
A) I and II
B) I, II, III
C) I and III
D) I and IV
E) I, II, III, and IV
I and IV
2
Artificially induced radioactivity is caused by bombarding a nucleus with another particle.
True
3
Which of the following statements concerning alpha decay is INCORRECT?
A) It involves nuclides with atomic number larger than 83 and mass number larger than 200.
B) It has great penetrating power, but little ionizing power.
C) It often leaves the nucleus in an excited state.
D) The atomic number decreases by two.
E) The alpha particle is made up of two protons and two neutrons.
A) It involves nuclides with atomic number larger than 83 and mass number larger than 200.
B) It has great penetrating power, but little ionizing power.
C) It often leaves the nucleus in an excited state.
D) The atomic number decreases by two.
E) The alpha particle is made up of two protons and two neutrons.
It has great penetrating power, but little ionizing power.
4
Cancerous cells are more easily killed by radiation than normal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Fission is the process of combining small nuclei into larger nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Fusion is the process of combining small nuclei into larger nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Ion production is the way radiation causes the most damage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Radioactive decay is:
A) temperature independent
B) a second-order process
C) a zero-order process
D) a process with a large activation energy
A) temperature independent
B) a second-order process
C) a zero-order process
D) a process with a large activation energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Radioactive nuclides that lie above the band of stability become more stable by positron emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The nuclear binding energy is the energy required to separate the neutrons and protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is FALSE?
A) A β- particle is essentially an e- originating from the nucleus.
B) A β- decay results in a decrease in atomic number.
C) A β- decay is accompanied by the emission of a neutrino.
D) A β+ decay converts a proton to a neutron in the nucleus of an atom.
E) An e- capture converts a proton to a neutron in the nucleus of an atom.
A) A β- particle is essentially an e- originating from the nucleus.
B) A β- decay results in a decrease in atomic number.
C) A β- decay is accompanied by the emission of a neutrino.
D) A β+ decay converts a proton to a neutron in the nucleus of an atom.
E) An e- capture converts a proton to a neutron in the nucleus of an atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Transuraniun elements are elements with atomic numbers greater than 92.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Identify a reaction that follows a different decay process than the rest.
A)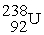 →
→
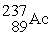
B)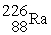 →
→
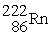
C)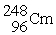 →
→
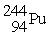
D)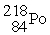 →
→
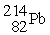
E)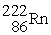 →
→
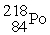
A)
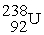 →
→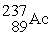
B)
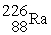 →
→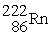
C)
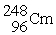 →
→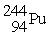
D)
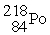 →
→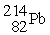
E)
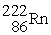 →
→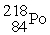

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The most highly charged particle is:
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
D) positron
E) neutron
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
D) positron
E) neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Radioactivity is a first order kinetics process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Radioactive decay series decay by alpha and positron emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When a nuclide undergoes positron emission, the change in the number of protons, neutrons, and mass number is, respectively,
A) -1, +1, no change
B) +1, -1, no change
C) -1, +1, -1
D) +1, +1, -1
A) -1, +1, no change
B) +1, -1, no change
C) -1, +1, -1
D) +1, +1, -1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) Radioactivity is the emission of ionizing radiation.
B) An alpha particle is the nucleus of a helium-4 atom.
C) A beta particle is a neutron.
D) A positron is like a beta particle but with a positive charge.
E) Gamma rays are emitted from a nucleus in an excited state.
A) Radioactivity is the emission of ionizing radiation.
B) An alpha particle is the nucleus of a helium-4 atom.
C) A beta particle is a neutron.
D) A positron is like a beta particle but with a positive charge.
E) Gamma rays are emitted from a nucleus in an excited state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The most massive particle is:
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
D) positron
E) neutron
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
D) positron
E) neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Odd proton, odd neutron isotopes are generally more stable than even proton, even neutron isotopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A nuclide has a decay constant of 4.28 × 10-4/h. If the activity of a sample is 3.14 × 105/s, how many atoms of the nuclide are present in the sample?
A) 7.34 × 108
B) 2.64 × 1012
C) 4.84 × 105
D) 1.34 × 102
E) 2.34 × 1011
A) 7.34 × 108
B) 2.64 × 1012
C) 4.84 × 105
D) 1.34 × 102
E) 2.34 × 1011

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
There have been two ways of making transuranium elements: neutron bombardment and:
A) beta bombardment
B) gamma bombardment
C) positron bombardment
D) photon bombardment
E) heavy-atom bombardment
A) beta bombardment
B) gamma bombardment
C) positron bombardment
D) photon bombardment
E) heavy-atom bombardment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following would have the greatest penetrating power through matter?
A) gamma rays
B) alpha particles
C) protons
D) beta particles
E) positron particles
A) gamma rays
B) alpha particles
C) protons
D) beta particles
E) positron particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The half-life of 238U, which decomposes to 206Pb, is 4.51 × 109 y. A rock contains equal masses of these two isotopes. How old is this rock?
A) 4.07 × 109 y
B) 4.06 × 109 y
C) 9.02 × 109 y
D) 4.51 × 109 y
E) 5.00 × 109 y
A) 4.07 × 109 y
B) 4.06 × 109 y
C) 9.02 × 109 y
D) 4.51 × 109 y
E) 5.00 × 109 y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the decay constant for 131I if the half-life is 8.04 d?
A) 9.98 x 10-7 s-1
B) 9.31 x 10-5 s-1
C) 3.48 x 10-6 s-1
D) 4.81 x 10-4 s-1
A) 9.98 x 10-7 s-1
B) 9.31 x 10-5 s-1
C) 3.48 x 10-6 s-1
D) 4.81 x 10-4 s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The following nuclear reaction is known to occur: 2 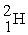 →
→ 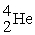 This reaction is used in a fusion bomb or H bomb. How many joules of energy are produced by this reaction if 33.0 g of 2H are used? You are given the following masses: electron 0.00055 amu; proton 1.00782 amu; neutron 1.00867 amu; 2H atom 2.010410 amu;
This reaction is used in a fusion bomb or H bomb. How many joules of energy are produced by this reaction if 33.0 g of 2H are used? You are given the following masses: electron 0.00055 amu; proton 1.00782 amu; neutron 1.00867 amu; 2H atom 2.010410 amu; 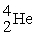 atom 4.00260 amu.
atom 4.00260 amu.
A) 3.82 × 10-12 J
B) 2.30 × 1012 J
C) 3.77 × 1013 J
D) 7.60 × 1013 J
E) 1.34 J
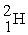 →
→ 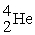 This reaction is used in a fusion bomb or H bomb. How many joules of energy are produced by this reaction if 33.0 g of 2H are used? You are given the following masses: electron 0.00055 amu; proton 1.00782 amu; neutron 1.00867 amu; 2H atom 2.010410 amu;
This reaction is used in a fusion bomb or H bomb. How many joules of energy are produced by this reaction if 33.0 g of 2H are used? You are given the following masses: electron 0.00055 amu; proton 1.00782 amu; neutron 1.00867 amu; 2H atom 2.010410 amu; 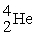 atom 4.00260 amu.
atom 4.00260 amu.A) 3.82 × 10-12 J
B) 2.30 × 1012 J
C) 3.77 × 1013 J
D) 7.60 × 1013 J
E) 1.34 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
There have been two ways of making transuranium elements: heavy-atom bombardment and:
A) beta bombardment
B) gamma bombardment
C) positron bombardment
D) photon bombardment
E) neutron bombardment
A) beta bombardment
B) gamma bombardment
C) positron bombardment
D) photon bombardment
E) neutron bombardment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the decay constant for 131I is 9.98 x 10-7 s-1, calculate the activity of a 1.00 mg sample.
A) 4.59 x 1012 atoms/s
B) 4.73 x 1012 atoms/s
C) 4.61 x 1024 atoms/s
D) 9.98 x 10-4 atoms/s
A) 4.59 x 1012 atoms/s
B) 4.73 x 1012 atoms/s
C) 4.61 x 1024 atoms/s
D) 9.98 x 10-4 atoms/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the case of radioactive element X, which decays by electron emission with a half-life of 4 days to a stable nuclide of element Z:
A) 2 g of element X is required to produce 1.5 g of element Z after 8 days
B) element Z will weigh considerably less than element X after decay is complete because of the loss of electrons
C) element Z will weigh more than element X when decay is complete since Z has the higher atomic number
D) after 8 days the sample will consist of one-fourth element Z and three-fourths element X
E) after 8 days element X will be all element Z
A) 2 g of element X is required to produce 1.5 g of element Z after 8 days
B) element Z will weigh considerably less than element X after decay is complete because of the loss of electrons
C) element Z will weigh more than element X when decay is complete since Z has the higher atomic number
D) after 8 days the sample will consist of one-fourth element Z and three-fourths element X
E) after 8 days element X will be all element Z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Half-life is: I) the time for a sample to decay completely.
II) constant for a given radioisotope.
III) the time required for half of a sample to decay.
IV) inversely proportional to the decay constant.
A) I and II
B) I, II, and III
C) I and III
D) I, III, and IV
E) II, III, and IV
II) constant for a given radioisotope.
III) the time required for half of a sample to decay.
IV) inversely proportional to the decay constant.
A) I and II
B) I, II, and III
C) I and III
D) I, III, and IV
E) II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) Bi-209 has the highest mass number and atomic number of any stable isotope.
B) The radioactive decay law is A = θN.
C) Radioactive decay is a first-order process.
D) The half-life is the length of time for all atoms of an isotope to decay.
E) Wood can be dated by radiocarbon dating.
A) Bi-209 has the highest mass number and atomic number of any stable isotope.
B) The radioactive decay law is A = θN.
C) Radioactive decay is a first-order process.
D) The half-life is the length of time for all atoms of an isotope to decay.
E) Wood can be dated by radiocarbon dating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following types of nuclear decay result in a decrease in nuclear charge? I) alpha emission
II) beta emission
III) position emission
IV) electron-capture
A) I and II
B) II and IV
C) I and III
D) III and IV
E) IV only
II) beta emission
III) position emission
IV) electron-capture
A) I and II
B) II and IV
C) I and III
D) III and IV
E) IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Transuranium elements can be produced by bombarding nuclei with:
A) neutrons
B) other nuclei
C) alpha particles
D) positrons
E) neutrons and/or other nuclei
A) neutrons
B) other nuclei
C) alpha particles
D) positrons
E) neutrons and/or other nuclei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the following nuclear reactions. 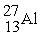 +
+ 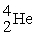 → 1 +
→ 1 + 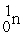 1 →
1 → 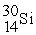 + 2 What are the nuclides 1 and 2, respectively?
+ 2 What are the nuclides 1 and 2, respectively?
A)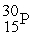 and
and
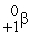
B)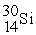 and
and
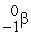
C)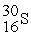 and
and
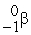
D)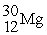 and 2
and 2
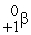
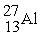 +
+ 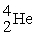 → 1 +
→ 1 + 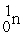 1 →
1 → 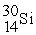 + 2 What are the nuclides 1 and 2, respectively?
+ 2 What are the nuclides 1 and 2, respectively?A)
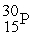 and
and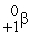
B)
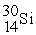 and
and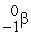
C)
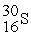 and
and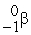
D)
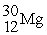 and 2
and 2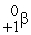

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The charcoal from ashes found in a cave gave 3.34 14C counts per gram per minute. Wood from the outer portion of a growing tree gives a comparable count of 16.0. The half-life of 14C is 5700 years. How old are the ashes?
A) 8.93 × 103 yr
B) 6.87 × 103 yr
C) 1.29 × 104 yr
D) 1.93 × 104 yr
E) 1.90 × 104 yr
A) 8.93 × 103 yr
B) 6.87 × 103 yr
C) 1.29 × 104 yr
D) 1.93 × 104 yr
E) 1.90 × 104 yr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The observation that a 30 g sample of C-14 has a decay rate faster than that of a 20 g sample of C-14 would be consistent with the:
A) Half-Life Principle
B) Disintegration Rule
C) Radioactive decay law
D) Mass-Rate Principle
E) Mass-decay ratio
A) Half-Life Principle
B) Disintegration Rule
C) Radioactive decay law
D) Mass-Rate Principle
E) Mass-decay ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The masses of 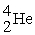 ,
, 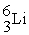 and
and 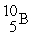 are 4.0015, 6.0135 and 10.0102 amu, respectively. Splitting a boron-10 nucleus to helium-4 and lithium-6 would:
are 4.0015, 6.0135 and 10.0102 amu, respectively. Splitting a boron-10 nucleus to helium-4 and lithium-6 would:
A) absorb energy
B) evolve energy
C) result in no energy change
D) cannot be determined
E) boron cannot be split
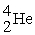 ,
, 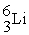 and
and 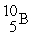 are 4.0015, 6.0135 and 10.0102 amu, respectively. Splitting a boron-10 nucleus to helium-4 and lithium-6 would:
are 4.0015, 6.0135 and 10.0102 amu, respectively. Splitting a boron-10 nucleus to helium-4 and lithium-6 would:A) absorb energy
B) evolve energy
C) result in no energy change
D) cannot be determined
E) boron cannot be split

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Choose the possible products for the nuclear reaction 40Ca + 4He(alpha).
A) 43Ar + n
B) 43Sc + p
C) 43Ca + n
D) 42Ca + 2H
E) 42Ti + n
A) 43Ar + n
B) 43Sc + p
C) 43Ca + n
D) 42Ca + 2H
E) 42Ti + n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Most periodic tables indicate the elements for which all isotopes are radioactive. Which pair of elements with atomic number less than 83 have only radioactive isotopes?
A) Pb and At
B) Tc and Cd
C) K and Pm
D) Tc and Pm
E) C and K
A) Pb and At
B) Tc and Cd
C) K and Pm
D) Tc and Pm
E) C and K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A wooden artifact is subjected to radiocarbon dating. The activity associated with its 14C content is 12 dis min-1 g-1. A sample of wood from a modern source gave 15 dis min-1 g-1. If the half-life of 14C is 5730 y, what is the age of the artifact?
A) 1.8 x 103 y
B) 800 y
C) 1.3 x 103 y
D) 7.2 x 103 y
A) 1.8 x 103 y
B) 800 y
C) 1.3 x 103 y
D) 7.2 x 103 y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The binding energy per nucleon is largest for ________.
A) 3He
B) 59Co
C) 235U
D) 98Tc
E) 1H
A) 3He
B) 59Co
C) 235U
D) 98Tc
E) 1H

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Nuclear binding energy is: I) the energy liberated when forming a nucleus
II) related to "lost" mass by the relationship 1 amu = 28.4 MeV
III) related to "lost" mass by the relationship 1 amu = 931.5 MeV
IV) the force which holds the 3 atomic particles together
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) I, II, and IV
D) I, III, and IV
E) III and IV
II) related to "lost" mass by the relationship 1 amu = 28.4 MeV
III) related to "lost" mass by the relationship 1 amu = 931.5 MeV
IV) the force which holds the 3 atomic particles together
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) I, II, and IV
D) I, III, and IV
E) III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) The nuclear binding energy is the mass changed to energy that holds the nucleus together.
B) Magic numbers are certain numbers of protons and/or neutrons which are especially stable.
C) Even numbers of protons and neutrons are more stable.
D) Particular ratios of neutrons to protons are more stable.
E) All isotopes below Bi are stable.
A) The nuclear binding energy is the mass changed to energy that holds the nucleus together.
B) Magic numbers are certain numbers of protons and/or neutrons which are especially stable.
C) Even numbers of protons and neutrons are more stable.
D) Particular ratios of neutrons to protons are more stable.
E) All isotopes below Bi are stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Choose the correct word to describe the nuclear stability of the following isotope. If it is radioactive, choose the most likely mode of decay. 197Au
A) radioactive, beta
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable
A) radioactive, beta
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Choose the correct word to describe the nuclear stability of the following isotope. If it is radioactive, choose the most likely mode of decay. 212Po
A) radioactive, beta
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable
A) radioactive, beta
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) An isotope that will fission when hit by a neutron is said to be fertile.
B) A moderator slows down neutrons.
C) Control rods absorb energy to control the fission reaction.
D) Electrons dislodged from an atom or molecule by alpha or beta particles are called primary electrons.
E) Radiation exposes photographic film the same as light.
A) An isotope that will fission when hit by a neutron is said to be fertile.
B) A moderator slows down neutrons.
C) Control rods absorb energy to control the fission reaction.
D) Electrons dislodged from an atom or molecule by alpha or beta particles are called primary electrons.
E) Radiation exposes photographic film the same as light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the reaction 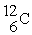 +
+ 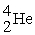 →
→ 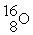 how much energy is produced per gram of carbon used? Masses, in unified atomic mass units are:
how much energy is produced per gram of carbon used? Masses, in unified atomic mass units are: 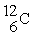 = 12.00000,
= 12.00000, 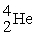 = 4.00260, = 15.99491. Express your answer in Joules/gram of carbon.
= 4.00260, = 15.99491. Express your answer in Joules/gram of carbon.
A) 2.10 × 1019 J/g
B) 5.76 × 1010 J/g
C) 7.77 × 104 J/g
D) 2.80 × 1011 J/g
E) 3.36 × 1015 J/g
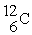 +
+ 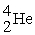 →
→ 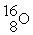 how much energy is produced per gram of carbon used? Masses, in unified atomic mass units are:
how much energy is produced per gram of carbon used? Masses, in unified atomic mass units are: 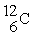 = 12.00000,
= 12.00000, 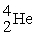 = 4.00260, = 15.99491. Express your answer in Joules/gram of carbon.
= 4.00260, = 15.99491. Express your answer in Joules/gram of carbon.A) 2.10 × 1019 J/g
B) 5.76 × 1010 J/g
C) 7.77 × 104 J/g
D) 2.80 × 1011 J/g
E) 3.36 × 1015 J/g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Choose the correct word to describe the nuclear stability of the following isotope. If it is radioactive, choose the most likely mode of decay. 238U
A) radioactive, beta
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable
A) radioactive, beta
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Choose the correct word to describe the nuclear stability of the following isotope. If it is radioactive, choose the most likely mode of decay. 50Mn
A) radioactive, beta plus (positron)
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable
A) radioactive, beta plus (positron)
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
On forming the nuclide from the protons, neutrons and electrons, the mass loss per nucleon for the 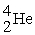 is 0.00759 amu, whereas that for
is 0.00759 amu, whereas that for 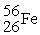 is 0.00944 amu. This means that:
is 0.00944 amu. This means that:
A)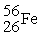 undergoes nuclear fission
undergoes nuclear fission
B)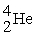 is more stable than
is more stable than
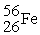
C) thirteen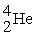 nuclei could react to form one
nuclei could react to form one
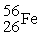 nucleus
nucleus
D)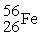 is more stable than
is more stable than
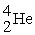
E)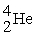 weighs more than
weighs more than
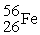
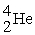 is 0.00759 amu, whereas that for
is 0.00759 amu, whereas that for 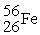 is 0.00944 amu. This means that:
is 0.00944 amu. This means that:A)
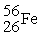 undergoes nuclear fission
undergoes nuclear fissionB)
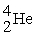 is more stable than
is more stable than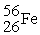
C) thirteen
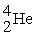 nuclei could react to form one
nuclei could react to form one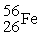 nucleus
nucleusD)
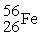 is more stable than
is more stable than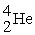
E)
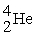 weighs more than
weighs more than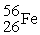

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What total energy is released when 0.75 grams of 235U undergo fission if each atom averages 3.2 × 10-11 J of energy released?
A) 1.45 × 1013 J
B) 6.01 × 1031 J
C) 6.15 × 1010 J
D) 6.15 × 107 J
E) 1.45 × 1010 J
A) 1.45 × 1013 J
B) 6.01 × 1031 J
C) 6.15 × 1010 J
D) 6.15 × 107 J
E) 1.45 × 1010 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following nuclear species would require the least amount of kinetic energy to penetrate the nucleus of a lead (Pb) atom?
A)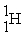
B)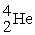
C)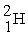
D)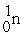
E)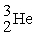
A)
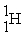
B)
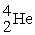
C)
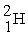
D)
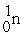
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) Fission is the combining of small nuclei into a larger nucleus.
B) Thermal neutrons induce more fission reactions than energetic neutrons.
C) Water is a good moderator, it slows down neutrons.
D) Control rods absorb neutrons.
E) Breeder reactors generate new fuel as well as electricity.
A) Fission is the combining of small nuclei into a larger nucleus.
B) Thermal neutrons induce more fission reactions than energetic neutrons.
C) Water is a good moderator, it slows down neutrons.
D) Control rods absorb neutrons.
E) Breeder reactors generate new fuel as well as electricity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is true concerning the nuclei of stable heavier elements?
A) #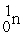 = #
= #
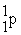
B) #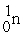 > #
> #
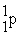
C) # < #
< #
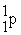
D) #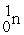 = #
= #
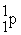 > #e-
> #e-
A) #
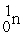 = #
= #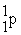
B) #
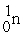 > #
> #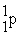
C) #
 < #
< #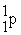
D) #
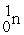 = #
= #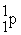 > #e-
> #e-
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An isotope which has too high a neutron-proton ratio can gain stability by:
A) beta emission
B) K-capture
C) proton emission
D) gamma emission
E) alpha emission
A) beta emission
B) K-capture
C) proton emission
D) gamma emission
E) alpha emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following nuclides is most likely to be stable?
A) 208Pb
B) 209Bi
C) 205Tl
D) 24Na
A) 208Pb
B) 209Bi
C) 205Tl
D) 24Na

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Choose the correct word to describe the nuclear stability of the following isotope. If it is radioactive, choose the most likely mode of decay. 19F
A) radioactive, beta
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable
A) radioactive, beta
B) radioactive, fission
C) radioactive, alpha
D) radioactive, neutron
E) stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Find the INCORRECT nuclear reaction.
A)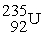 +
+
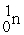 →
→
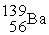 +
+
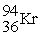 + 3
+ 3
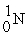
B)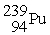 +
+
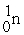 →
→
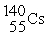 +
+
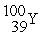
C)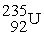 +
+
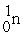 →
→
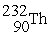 +
+
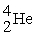
D)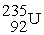 +
+
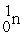 →
→
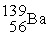 +
+
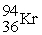 +
+
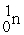
E)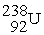 +
+
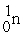 →
→
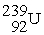
A)
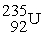 +
+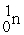 →
→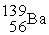 +
+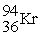 + 3
+ 3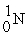
B)
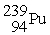 +
+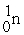 →
→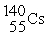 +
+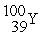
C)
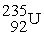 +
+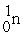 →
→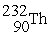 +
+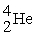
D)
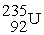 +
+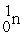 →
→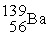 +
+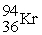 +
+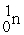
E)
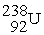 +
+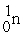 →
→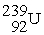

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Choose the correct statement.
A) Instability leading to decay by alpha particle emission is found mostly in nuclides of very large mass number.
B) Decay by beta emission is confined to nuclides of very low mass number.
C) Ejection of an electron by a nuclide results in a nuclide of next lower mass number.
D) All radiations emitted by radioactive nuclides consist of charged, high energy particles.
E) Many alpha and beta emissions are followed by gamma emissions.
A) Instability leading to decay by alpha particle emission is found mostly in nuclides of very large mass number.
B) Decay by beta emission is confined to nuclides of very low mass number.
C) Ejection of an electron by a nuclide results in a nuclide of next lower mass number.
D) All radiations emitted by radioactive nuclides consist of charged, high energy particles.
E) Many alpha and beta emissions are followed by gamma emissions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The nuclear binding energy for cobalt-59 is the energy released when:
A) 27 protons and 32 neutrons form cobalt-59
B) iron-56 and 2 protons form cobalt-59
C) 27 protons and 27 neutrons form cobalt-59
D) cobalt-58 and 1 neutron form cobalt -59
A) 27 protons and 32 neutrons form cobalt-59
B) iron-56 and 2 protons form cobalt-59
C) 27 protons and 27 neutrons form cobalt-59
D) cobalt-58 and 1 neutron form cobalt -59

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Radiation can be detected as it interacts with matter by the use of: I) photographic film
II) a bubble chamber
III) Geiger-Müller counter
A) I, II, III
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) III only
II) a bubble chamber
III) Geiger-Müller counter
A) I, II, III
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
E) III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The beta decay of 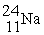 produces an isotope of ________.
produces an isotope of ________.
A) Al
B) Mg
C) Na
D) Ne
E) O
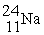 produces an isotope of ________.
produces an isotope of ________.A) Al
B) Mg
C) Na
D) Ne
E) O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The unit of radiation which is equivalent to 0.010 J/kg of matter is the:
A) curie
B) roentgen
C) rad
D) rem
E) MeV
A) curie
B) roentgen
C) rad
D) rem
E) MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) Radioactive 32P as a phosphate can be used to trace the uptake of phosphorus in plants.
B) The thyroid gland can be studied by the use of radioactive iodine.
C) There is no difference in physical properties between isotopes.
D) The mechanism of a chemical reaction can be followed by a radioactive tracer such as 35S.
E) Industrial catalysts can be followed by a tracer such as 192Ir.
A) Radioactive 32P as a phosphate can be used to trace the uptake of phosphorus in plants.
B) The thyroid gland can be studied by the use of radioactive iodine.
C) There is no difference in physical properties between isotopes.
D) The mechanism of a chemical reaction can be followed by a radioactive tracer such as 35S.
E) Industrial catalysts can be followed by a tracer such as 192Ir.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When a nitrogen nucleus containing six neutrons emits a positron, the product is ________.
A)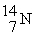
B)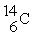
C)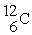
D)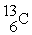
E)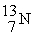
A)
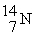
B)
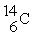
C)
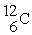
D)
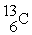
E)
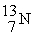

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The type of radioactive emission with the greatest penetrating power is ________.
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
D) positron
E) neutrino
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
D) positron
E) neutrino

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which statement below is correct?
A) In order for fusion to be sustained, the critical mass must be exceeded.
B) Fission reactions with light nuclei, such as helium are easily controlled but do not produce as much energy as with heavy nuclei.
C) Breeder reactors are able to convert fissile nuclides into fertile ones, thus "breeding" more fuel.
D) In a pressurized water reactor, cadmium metal usually acts as the moderator.
E)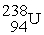 requires energetic neutrons in order to undergo fission and subsequently produces
requires energetic neutrons in order to undergo fission and subsequently produces
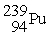 .
.
A) In order for fusion to be sustained, the critical mass must be exceeded.
B) Fission reactions with light nuclei, such as helium are easily controlled but do not produce as much energy as with heavy nuclei.
C) Breeder reactors are able to convert fissile nuclides into fertile ones, thus "breeding" more fuel.
D) In a pressurized water reactor, cadmium metal usually acts as the moderator.
E)
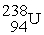 requires energetic neutrons in order to undergo fission and subsequently produces
requires energetic neutrons in order to undergo fission and subsequently produces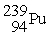 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
________ + β- → 37Cl
A) 37Ar
B) 38Ar
C) 38Cl
D) 37K
E) 36K
A) 37Ar
B) 38Ar
C) 38Cl
D) 37K
E) 36K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
An employee at a chemical laboratory studying radioisotopes would wear a badge to keep a check on the amount of radiation to which he is exposed. This radiation dosage would be measured in the unit:
A) curie
B) rad
C) rem
D) Joules
E) Joules per kilogram
A) curie
B) rad
C) rem
D) Joules
E) Joules per kilogram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
210Pb → 4He + ________
A) 214Pb
B) 206Hg
C) 214Hg
D) 206Pb
E) 206Br
A) 214Pb
B) 206Hg
C) 214Hg
D) 206Pb
E) 206Br

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following instruments would be least suitable for detecting particles given off in radioactive decay?
A) electron microscope
B) bubble or cloud chamber
C) film
D) Geiger counter
E) Geiger-Müller counter
A) electron microscope
B) bubble or cloud chamber
C) film
D) Geiger counter
E) Geiger-Müller counter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
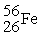 can be prepared by electron-capture from ________.
can be prepared by electron-capture from ________.A)
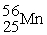
B)
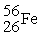
C)
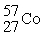
D)
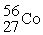
E)
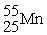

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
6He → β- + ________
A) 6H
B) 5He
C) 7He
D) 6Li
E) 7Be
A) 6H
B) 5He
C) 7He
D) 6Li
E) 7Be

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
205Pb + ________ → 205Tl
A)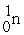
B)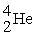
C)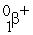
D) gamma
E)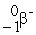
A)
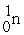
B)
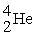
C)
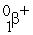
D) gamma
E)
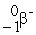

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The most ionizing radiation is of what type?
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
D) electron
E) neutron
A) alpha
B) beta
C) gamma
D) electron
E) neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
8Be → 4He + ________
A) 3Be
B) 8He
C) 4He
D) 4Li
E) 12C
A) 3Be
B) 8He
C) 4He
D) 4Li
E) 12C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Emission of which one of the following leaves both atomic number and mass number unchanged?
A) alpha particle
B) positron
C) neutron
D) gamma radiation
E) beta ray
A) alpha particle
B) positron
C) neutron
D) gamma radiation
E) beta ray

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) Geiger-Müller counters detect radiation by the ionization caused in the gas in the counter.
B) Bubble chambers detect radiation by the ionization trail left by the radiation.
C) Radiation causes no harm to the human body.
D) Radiation kills cancer cells more easily than normal cells.
E) Alpha particles are less penetrating than beta particles.
A) Geiger-Müller counters detect radiation by the ionization caused in the gas in the counter.
B) Bubble chambers detect radiation by the ionization trail left by the radiation.
C) Radiation causes no harm to the human body.
D) Radiation kills cancer cells more easily than normal cells.
E) Alpha particles are less penetrating than beta particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) Fusion is the basis of the hydrogen bomb.
B) Fusion is the splitting of a nucleus into two smaller nuclei.
C) Fusion is a reaction that occurs on the sun.
D) Fusion is not now used to produce electricity commercially.
E) Fusion can produce an almost unlimited amount of energy.
A) Fusion is the basis of the hydrogen bomb.
B) Fusion is the splitting of a nucleus into two smaller nuclei.
C) Fusion is a reaction that occurs on the sun.
D) Fusion is not now used to produce electricity commercially.
E) Fusion can produce an almost unlimited amount of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Choose the INCORRECT statement.
A) Cancer cannot be caused by ionizing radiation.
B) Cancer can be treated with gamma rays.
C) Radiation works against cancer because cancer cells are more easily damaged than normal cells.
D) Protons, x-rays, and neutrons can also be used against cancer cells.
E) Ionizing radiation tends to kill all cells.
A) Cancer cannot be caused by ionizing radiation.
B) Cancer can be treated with gamma rays.
C) Radiation works against cancer because cancer cells are more easily damaged than normal cells.
D) Protons, x-rays, and neutrons can also be used against cancer cells.
E) Ionizing radiation tends to kill all cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



