Deck 8: DNA- the Chemical Nature of the Gene
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/87
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: DNA- the Chemical Nature of the Gene
1
Which hypothesis contributed to the idea that protein is the genetic material because, with its 20 different amino acids, protein structure could be highly variable?
A)Tetranucleotide hypothesis
B)Central dogma hypothesis
C)RNA world hypothesis
D)One gene, one enzyme hypothesis
E)Adaptor hypothesis
A)Tetranucleotide hypothesis
B)Central dogma hypothesis
C)RNA world hypothesis
D)One gene, one enzyme hypothesis
E)Adaptor hypothesis
A
2
Hershey and Chase determined whether DNA or protein was the genetic material in bacteriophages.What isotope did they use to label the viral protein?
A)14C
B)15N
C)18O
D)32P
E)35S
A)14C
B)15N
C)18O
D)32P
E)35S
E
3
A molecule that consists of a nitrogenous base bonded to the 1' carbon of a ribose or deoxyribose is a(n):
A)nucleoside.
B)hairpin.
C)isotope.
D)polynucleotide.
E)nucleotide.
A)nucleoside.
B)hairpin.
C)isotope.
D)polynucleotide.
E)nucleotide.
nucleoside.
4
With respect to their 3' and 5' ends, the two polynucleotide chains of a double-stranded DNA molecule are:
A)antiparallel.
B)isotopes.
C)methylated.
D)complementary.
E)nitrogenous.
A)antiparallel.
B)isotopes.
C)methylated.
D)complementary.
E)nitrogenous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How did Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase contribute to our understanding of DNA?
A)Used X-ray diffraction to examine the structure of DNA
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria
A)Used X-ray diffraction to examine the structure of DNA
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How did Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty contribute to our understanding of DNA?
A)Used X-ray diffraction to examine the structure of DNA
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria
A)Used X-ray diffraction to examine the structure of DNA
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How did Fred Griffith contribute to our understanding of DNA?
A)Used X-ray diffraction to examine the structure of DNA
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria
A)Used X-ray diffraction to examine the structure of DNA
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleoside?
A)A nucleotide has a phosphate group, and a nucleoside does not.
B)A nucleoside has a phosphate group, and a nucleotide does not.
C)A nucleotide has a ribose sugar, and a nucleoside has a deoxyribose sugar.
D)A nucleotide has a deoxyribose sugar, and a nucleoside has a ribose sugar.
A)A nucleotide has a phosphate group, and a nucleoside does not.
B)A nucleoside has a phosphate group, and a nucleotide does not.
C)A nucleotide has a ribose sugar, and a nucleoside has a deoxyribose sugar.
D)A nucleotide has a deoxyribose sugar, and a nucleoside has a ribose sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT characteristic of A-form DNA compared to B- or Z-form DNA?
A)Has right-handed helixes
B)Exists when less water is present
C)Is long and narrow
D)Has 50% purines, 50% pyrimidines
E)Has a deeper major groove and a narrower minor groove
A)Has right-handed helixes
B)Exists when less water is present
C)Is long and narrow
D)Has 50% purines, 50% pyrimidines
E)Has a deeper major groove and a narrower minor groove

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Indicate which of the following statements is TRUE.
A)There are three phosphates between each sugar in a molecule of DNA.
B)A-, B-, and Z-form DNA are all right-handed helixes.
C)There are three hydrogen bonds between AT pairs.
D)Ribose sugars have a hydroxyl on the 2'carbon.
E)All organisms contain DNA that is roughly 25% A, 25% T, 25% G, and 25% C.
A)There are three phosphates between each sugar in a molecule of DNA.
B)A-, B-, and Z-form DNA are all right-handed helixes.
C)There are three hydrogen bonds between AT pairs.
D)Ribose sugars have a hydroxyl on the 2'carbon.
E)All organisms contain DNA that is roughly 25% A, 25% T, 25% G, and 25% C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Hershey and Chase determined whether DNA or protein was the genetic material in bacteriophages.What isotope did they use to label the viral DNA?
A)14C
B)15N
C)18O
D)32P
E)35S
A)14C
B)15N
C)18O
D)32P
E)35S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The bonds that connect nucleotides in a single strand are called _____ bonds.
A)phosphodiester
B)peptide
C)ionic
D)hydrogen
E)glycosidic
A)phosphodiester
B)peptide
C)ionic
D)hydrogen
E)glycosidic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Indicate which of the following statements is FALSE.
A)Covalent bonds connect nucleotides in a strand; noncovalent interactions hold strands into a double-stranded structure.
B)Uracil is similar to thymine except that uracil lacks a methyl group on the carbon at position 5 on the carbon-nitrogen ring.
C)Frederick Griffith demonstrated that a transforming chemical from dead bacteria could change the genetic information of living bacteria.
D)Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty showed that DNA is the genetic information of cells and that RNA is the genetic information of viruses.
E)The pyrimidine bases in nucleic acids are cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
A)Covalent bonds connect nucleotides in a strand; noncovalent interactions hold strands into a double-stranded structure.
B)Uracil is similar to thymine except that uracil lacks a methyl group on the carbon at position 5 on the carbon-nitrogen ring.
C)Frederick Griffith demonstrated that a transforming chemical from dead bacteria could change the genetic information of living bacteria.
D)Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty showed that DNA is the genetic information of cells and that RNA is the genetic information of viruses.
E)The pyrimidine bases in nucleic acids are cytosine, thymine, and uracil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the difference in hydrogen bonding between A/T pairs versus G/C pairs?
A)A/T pairs have one more hydrogen bond than G/C pairs.
B)G/C pairs have one more hydrogen bond than A/T pairs.
C)A/T pairs have two more hydrogen bonds than G/C pairs.
D)G/C pairs have two more hydrogen bonds than A/T pairs.
E)G/C pairs have three more hydrogen bonds than A/T pairs.
A)A/T pairs have one more hydrogen bond than G/C pairs.
B)G/C pairs have one more hydrogen bond than A/T pairs.
C)A/T pairs have two more hydrogen bonds than G/C pairs.
D)G/C pairs have two more hydrogen bonds than A/T pairs.
E)G/C pairs have three more hydrogen bonds than A/T pairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The concept that genetic information passes from DNA to RNA to protein is called the:
A)central dogma.
B)nitrogenous base.
C)transforming principle.
D)polynucleotide strand.
E)reverse transcription.
A)central dogma.
B)nitrogenous base.
C)transforming principle.
D)polynucleotide strand.
E)reverse transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How did Rosalind Franklin contribute to our understanding of DNA?
A)Used X-ray diffraction to show that the structure of DNA is helical
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria
A)Used X-ray diffraction to show that the structure of DNA is helical
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If a nucleic acid is found to contain 20% G and 27% T, the molecule is probably:
A)single-stranded DNA.
B)double-stranded DNA.
C)single-stranded RNA.
D)double-stranded RNA.
A)single-stranded DNA.
B)double-stranded DNA.
C)single-stranded RNA.
D)double-stranded RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How did Albert Kossel contribute to our understanding of DNA?
A)Used X-ray diffraction to examine the structure of DNA
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria
A)Used X-ray diffraction to examine the structure of DNA
B)Determined that DNA contains four different nitrogenous bases
C)Found that "the transforming principle" is destroyed by enzymes that hydrolyze DNA
D)Found that the phosphorus-containing components are the genetic material of phages
E)Discovered "the transforming principle" that could genetically alter bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is NOT a key characteristic that genetic material must possess?
A)Genetic material must contain complex information.
B)Genetic material must replicate faithfully.
C)Genetic material must encode the phenotype.
D)Genetic material must have the capacity to vary.
E)Genetic material must contain nitrogen but not sulfur.
A)Genetic material must contain complex information.
B)Genetic material must replicate faithfully.
C)Genetic material must encode the phenotype.
D)Genetic material must have the capacity to vary.
E)Genetic material must contain nitrogen but not sulfur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a nucleic acid is found to contain 20% A and 20% T, the molecule is probably:
A)single-stranded DNA.
B)double-stranded DNA.
C)single-stranded RNA.
D)double-stranded RNA.
A)single-stranded DNA.
B)double-stranded DNA.
C)single-stranded RNA.
D)double-stranded RNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is NOT a chemical or structural characteristic of RNA that is different from those of DNA?
A)The RNA sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose.
B)RNA is usually a single-stranded molecule instead of a hydrogen-bonded double strand like DNA.
C)The bases in RNA include uracil instead of thymine.
D)RNA molecules are generally shorter in length than those of DNA macromolecules.
E)The 2' carbon of ribose has an H, unlike the OH in that position of deoxyribose.
A)The RNA sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose.
B)RNA is usually a single-stranded molecule instead of a hydrogen-bonded double strand like DNA.
C)The bases in RNA include uracil instead of thymine.
D)RNA molecules are generally shorter in length than those of DNA macromolecules.
E)The 2' carbon of ribose has an H, unlike the OH in that position of deoxyribose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which CORRECTLY describes the molecule below? 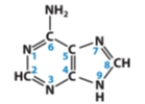
A)Thymine base
B)Purine base
C)Pyrimidine base
D)Nucleotide
E)Amino acid

A)Thymine base
B)Purine base
C)Pyrimidine base
D)Nucleotide
E)Amino acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which diagram shows a nucleotide that would be used to make RNA? 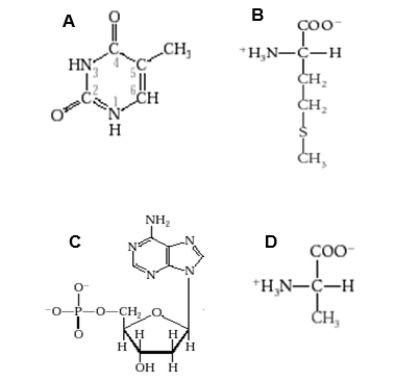
A)Diagram A
B)Diagram B
C)Diagram C
D)Diagram D
E)None of these choices

A)Diagram A
B)Diagram B
C)Diagram C
D)Diagram D
E)None of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How many hydrogen bonds will be involved in base pairing in a DNA molecule of 50 base pairs that contains 15 cytosine bases?
A)45
B)100
C)115
D)135
E)150
A)45
B)100
C)115
D)135
E)150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a DNA molecule is 30% cytosine (C), what is the percentage of guanine (G)?
A)30%
B)60%
C)35%
D)70%
E)15%
A)30%
B)60%
C)35%
D)70%
E)15%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following would NOT necessarily be true for a DNA molecule?
A)A = T
B)C = G
C)A + G = C + T
D)A + C = G + T
E)A + T = G + C
A)A = T
B)C = G
C)A + G = C + T
D)A + C = G + T
E)A + T = G + C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which circle shows a bond that would also be found in an RNA transcribed from one strand of this DNA? 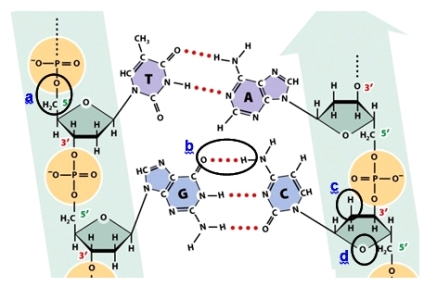
A)Circle a
B)Circle b
C)Circle c
D)Circle d

A)Circle a
B)Circle b
C)Circle c
D)Circle d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which diagram shows a nucleotide as it would appear in DNA? 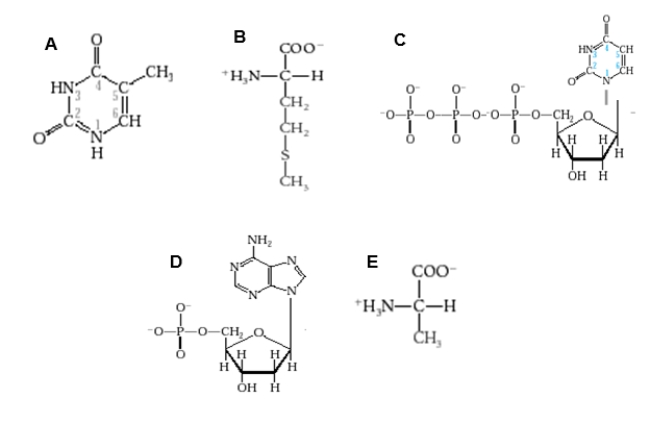
A)Diagram A
B)Diagram B
C)Diagram C
D)Diagram D
E)Diagram E

A)Diagram A
B)Diagram B
C)Diagram C
D)Diagram D
E)Diagram E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
DNA is said to be like a ladder where _____ connected by _____ bonds make up the sides of the ladder and the _____ connected by _____ bonds make up the rungs of the ladder.
A)nitrogenous bases; covalent; sugar-phosphates; hydrogen
B)sugar-phosphates; covalent; nitrogenous bases; hydrogen
C)nitrogenous bases; hydrogen; sugar-phosphates; covalent
D)sugar-phosphates; hydrogen; nitrogenous bases; covalent
A)nitrogenous bases; covalent; sugar-phosphates; hydrogen
B)sugar-phosphates; covalent; nitrogenous bases; hydrogen
C)nitrogenous bases; hydrogen; sugar-phosphates; covalent
D)sugar-phosphates; hydrogen; nitrogenous bases; covalent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which diagram shows a nucleotide with a purine base? 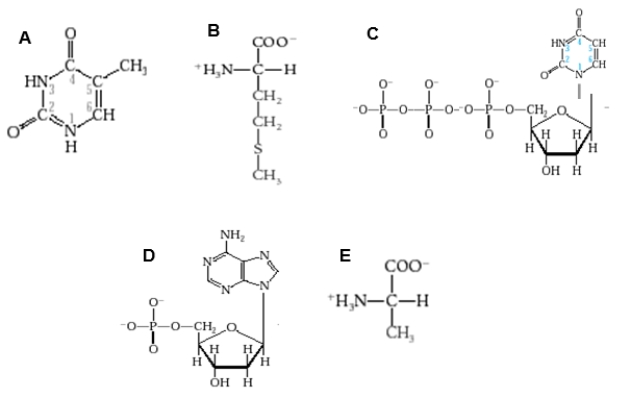
A)Diagram A
B)Diagram B
C)Diagram C
D)Diagram D
E)Diagram E

A)Diagram A
B)Diagram B
C)Diagram C
D)Diagram D
E)Diagram E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A double-stranded DNA molecule of 50 base pairs contains 15 cytosine bases (C), how many thymine bases will it have?
A)10
B)15
C)30
D)35
E)60
A)10
B)15
C)30
D)35
E)60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Considering what you know about the anti-parallel nature of DNA, which of the following structures is possible? 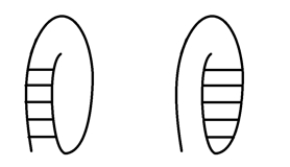
A)The left
B)The right
C)Both are possible.
D)Neither is possible.

A)The left
B)The right
C)Both are possible.
D)Neither is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is NOT an example of secondary structure in nucleic acids?
A)Hairpin
B)Stem
C)H-DNA
D)B-DNA
E)C-DNA
A)Hairpin
B)Stem
C)H-DNA
D)B-DNA
E)C-DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Imagine you forgot to cap your DNA sample and it became desiccated (dried out).What form would the DNA take?
A)A-DNA
B)B-DNA
C)C-DNA
D)H-DNA
E)Z-DNA
A)A-DNA
B)B-DNA
C)C-DNA
D)H-DNA
E)Z-DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Why does DNA have a purine across from a pyrimidine?
A)This allows the DNA to be able to stack correctly.
B)This allows DNA to be negatively charged.
C)This allows DNA to be the same width from top to bottom.
D)This allows DNA to be a double helix.
A)This allows the DNA to be able to stack correctly.
B)This allows DNA to be negatively charged.
C)This allows DNA to be the same width from top to bottom.
D)This allows DNA to be a double helix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What type of secondary structure is formed by the pairing of three strands of DNA?
A)A-DNA
B)B-DNA
C)C-DNA
D)H-DNA
E)Z-DNA
A)A-DNA
B)B-DNA
C)C-DNA
D)H-DNA
E)Z-DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which figure shows one of the amino acids that was key to distinguishing DNA from protein in the Hershey and Chase experiment? 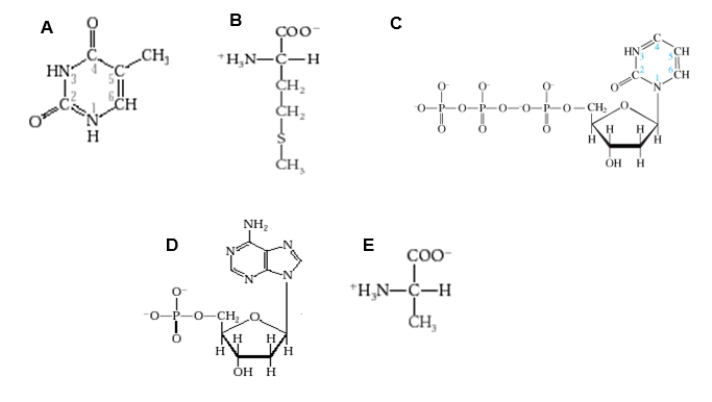
A)Diagram A
B)Diagram B
C)Diagram C
D)Diagram D
E)Diagram E

A)Diagram A
B)Diagram B
C)Diagram C
D)Diagram D
E)Diagram E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which circle shows a noncovalent bond? 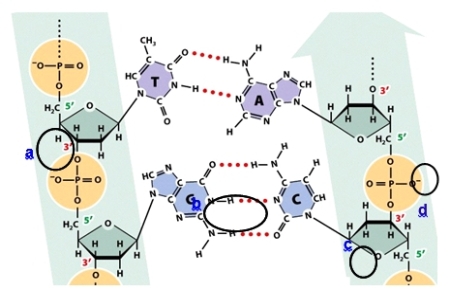
A)Circle a
B)Circle b
C)Circle c
D)Circle d

A)Circle a
B)Circle b
C)Circle c
D)Circle d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the sequence of one strand of DNA is 5'-GCTAGCGTCG-3', what is the sequence of the complementary strand?
A)3'-GCTAGCGTCG-5'
B)5'-GCTGCGATCG-3'
C)3'-CGATCGCAGC-5'
D)5'0-CGATCGCAGC-3'
E)5'-CGAUCGCAGC-3'
A)3'-GCTAGCGTCG-5'
B)5'-GCTGCGATCG-3'
C)3'-CGATCGCAGC-5'
D)5'0-CGATCGCAGC-3'
E)5'-CGAUCGCAGC-3'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which circle shows a phosphodiester bond? 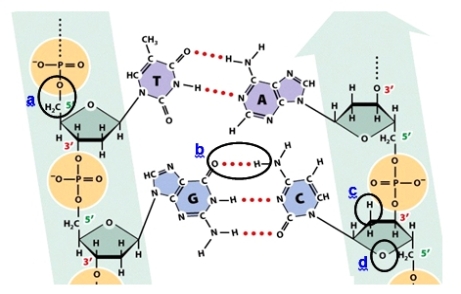
A)Circle a
B)Circle b
C)Circle c
D)Circle d

A)Circle a
B)Circle b
C)Circle c
D)Circle d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following amino acids has a positive charge that helps to hold the DNA in contact with the histones?
A)Alanine
B)Arginine
C)Leucine
D)Valine
E)Serine
A)Alanine
B)Arginine
C)Leucine
D)Valine
E)Serine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is NOT true of heterochromatin?
A)Remains in a highly condensed state throughout the cell cycle
B)Makes up most chromosomal material and is where most transcription occurs
C)Exists at the centromeres and telomeres
D)Occurs along one entire X chromosome in female mammals when this X becomes inactivated
E)Is characterized by the absence of crossing over and replication late in the S phase
A)Remains in a highly condensed state throughout the cell cycle
B)Makes up most chromosomal material and is where most transcription occurs
C)Exists at the centromeres and telomeres
D)Occurs along one entire X chromosome in female mammals when this X becomes inactivated
E)Is characterized by the absence of crossing over and replication late in the S phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How many base pairs per turn of the helix would MOST likely correspond to a positively supercoiled DNA molecule?
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
You are a research assistant in a lab that studies nucleic acids.Your advisor gave you four tubes for analysis.Each of these tubes differs in its contents by the source of its nucleic acids: mouse cytoplasm (single-stranded RNA), yeast nuclei (double-stranded DNA), rotavirus (double-stranded RNA), and parvovirus (single-stranded DNA).The approximate nucleotide base composition of each sample is given in the table below. 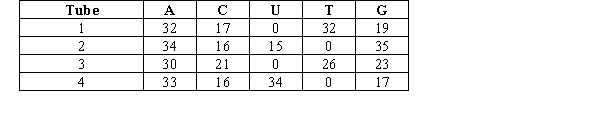 Which tube MOST likely contains rotavirus?
Which tube MOST likely contains rotavirus?
A)Tube 1
B)Tube 2
C)Tube 3
D)Tube 4
 Which tube MOST likely contains rotavirus?
Which tube MOST likely contains rotavirus?A)Tube 1
B)Tube 2
C)Tube 3
D)Tube 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How many complete rotations would most likely correspond to a positively supercoiled DNA molecule that is 100 bp in length?
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How many base pairs per turn of the helix would MOST likely correspond to a relaxed DNA molecule?
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
You are studying a small eukaryotic gene of about 2000 bp in length.Estimate how many copies of histone H4 you would find along this region of the chromosome.
A)10
B)20
C)40
D)80
E)100
A)10
B)20
C)40
D)80
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How many base pairs per turn of the helix would MOST likely correspond to a negatively supercoiled DNA molecule?
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The human Y chromosome is about 50 million base pairs long.About how many nucleosomes would you expect to find associated with this chromosome?
A)2, 500
B)50, 000
C)250, 000
D)1, 000, 000
E)50, 000, 000
A)2, 500
B)50, 000
C)250, 000
D)1, 000, 000
E)50, 000, 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
You are a research assistant in a lab that studies nucleic acids.Your advisor gave you four tubes for analysis.Each of these tubes differs in its contents by the source of its nucleic acids: mouse cytoplasm (single-stranded RNA), yeast nuclei (double-stranded DNA), rotavirus (double-stranded RNA), and parvovirus (single-stranded DNA).The approximate nucleotide base composition of each sample is given in the table below. 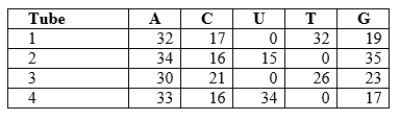 Which samples would be destroyed by a DNase?
Which samples would be destroyed by a DNase?
A)Tubes 1 and 3
B)Tubes 2 and 4
C)Tubes 1 and 2
D)Tubes 3 and 4
E)All tubes 1, 2, 3, 4
 Which samples would be destroyed by a DNase?
Which samples would be destroyed by a DNase?A)Tubes 1 and 3
B)Tubes 2 and 4
C)Tubes 1 and 2
D)Tubes 3 and 4
E)All tubes 1, 2, 3, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
You are a research assistant in a lab that studies nucleic acids.Your advisor gave you four tubes for analysis.Each of these tubes differs in its contents by the source of its nucleic acids: mouse cytoplasm (single-stranded RNA), yeast nuclei (double-stranded DNA), rotavirus (double-stranded RNA), and parvovirus (single-stranded DNA).The approximate nucleotide base composition of each sample is given in the table below. 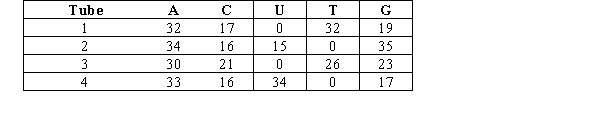 Which tube MOST likely contains yeast nuclei?
Which tube MOST likely contains yeast nuclei?
A)Tube 1
B)Tube 2
C)Tube 3
D)Tube 4
 Which tube MOST likely contains yeast nuclei?
Which tube MOST likely contains yeast nuclei?A)Tube 1
B)Tube 2
C)Tube 3
D)Tube 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
How does histone acetylation affect chromatin?
A)It loosens the chromatin and allows increased transcription.
B)It allows DNA to become resistant to damage.
C)It helps the histones have a greater affinity for DNA.
D)It inhibits DNA replication by making it more difficult to separate the DNA strands.
E)It causes the chromatin to become more condensed in preparation for metaphase.
A)It loosens the chromatin and allows increased transcription.
B)It allows DNA to become resistant to damage.
C)It helps the histones have a greater affinity for DNA.
D)It inhibits DNA replication by making it more difficult to separate the DNA strands.
E)It causes the chromatin to become more condensed in preparation for metaphase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How many complete rotations would MOST likely correspond to a negatively supercoiled DNA molecule that is 100 bp in length?
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How many complete rotations would MOST likely correspond to a relaxed DNA molecule that is 100 bp in length?
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100
A)0
B)5
C)10
D)15
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
You are a research assistant in a lab that studies nucleic acids.Your advisor gave you four tubes for analysis.Each of these tubes differs in its contents by the source of its nucleic acids: mouse cytoplasm (single-stranded RNA), yeast nuclei (double-stranded DNA), rotavirus (double-stranded RNA), and parvovirus (single-stranded DNA).The approximate nucleotide base composition of each sample is given in the table below. 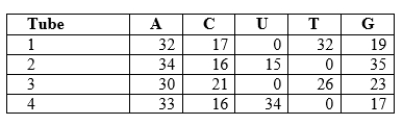 Which tube MOST likely contains parvovirus?
Which tube MOST likely contains parvovirus?
A)Tube 1
B)Tube 2
C)Tube 3
D)Tube 4
 Which tube MOST likely contains parvovirus?
Which tube MOST likely contains parvovirus?A)Tube 1
B)Tube 2
C)Tube 3
D)Tube 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is an example of an epigenetic change in eukaryotes?
A)A loss of an AT base pair from a gene
B)The addition of methyl groups to cytosines in the promoter region of a gene
C)The substitution of an AT base pair by a GC base pair in a gene as a result of a mistake during DNA replication
D)A deletion that simultaneously removes two genes from the genome
E)None of the above represents epigenetic changes.
A)A loss of an AT base pair from a gene
B)The addition of methyl groups to cytosines in the promoter region of a gene
C)The substitution of an AT base pair by a GC base pair in a gene as a result of a mistake during DNA replication
D)A deletion that simultaneously removes two genes from the genome
E)None of the above represents epigenetic changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is NOT true of negatively supercoiled DNA?
A)Eases the separation of nucleotide strands during replication and transcription
B)Allows DNA to be packed into small spaces
C)Has less than 10 bp per turn of its helix
D)Is more negatively charged due to additional phosphates per turn of the helix
E)Is found in most cells
A)Eases the separation of nucleotide strands during replication and transcription
B)Allows DNA to be packed into small spaces
C)Has less than 10 bp per turn of its helix
D)Is more negatively charged due to additional phosphates per turn of the helix
E)Is found in most cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
You are a research assistant in a lab that studies nucleic acids.Your advisor gave you four tubes for analysis.Each of these tubes differs in its contents by the source of its nucleic acids: mouse cytoplasm (single-stranded RNA), yeast nuclei (double-stranded DNA), rotavirus (double-stranded RNA), and parvovirus (single-stranded DNA).The approximate nucleotide base composition of each sample is given in the table below. 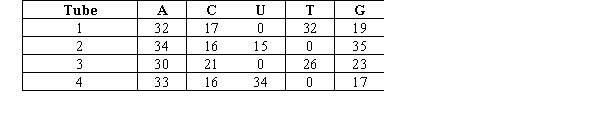 Which tube MOST likely contains mouse cytoplasm?
Which tube MOST likely contains mouse cytoplasm?
A)Tube 1
B)Tube 2
C)Tube 3
D)Tube 4
 Which tube MOST likely contains mouse cytoplasm?
Which tube MOST likely contains mouse cytoplasm?A)Tube 1
B)Tube 2
C)Tube 3
D)Tube 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
You are studying a small eukaryotic gene of about 2000 bp in length.Estimate how many copies of histone H1 you would find along this region of the chromosome.
A)10
B)20
C)40
D)80
E)100
A)10
B)20
C)40
D)80
E)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is NOT true of bacterial DNA?
A)Most bacterial genomes consist of a single circular DNA molecule.
B)Bacterial DNA is not attached to any proteins that help to compact it.
C)Bacterial DNA is confined to a region in the cell called the nucleoid.
D)Many bacteria contain additional DNA in the form of small circular molecules called plasmids.
E)About 3 to 4 million base pairs of DNA are found in a typical bacterial genome.
A)Most bacterial genomes consist of a single circular DNA molecule.
B)Bacterial DNA is not attached to any proteins that help to compact it.
C)Bacterial DNA is confined to a region in the cell called the nucleoid.
D)Many bacteria contain additional DNA in the form of small circular molecules called plasmids.
E)About 3 to 4 million base pairs of DNA are found in a typical bacterial genome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
List three characteristics required of genetic material.For each characteristic, indicate how the structure of DNA helps us to understand the characteristic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A ribosomal RNA gene is an example of which type of DNA sequence in eukaryotes?
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
While doing research on deep-sea vents, you discover a very simple new life form.After some initial analysis you find that this life form contains small fragments of DNA, small complementary RNA fragments, and proteins.Fortuitously, you collected two strains, one that is purple and one that is yellow.What experiments would you perform to determine which of these three cellular constituents serve as the genetic material in your new organism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A telomere is an example of which type of DNA sequence in eukaryotes?'
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Where would you expect to find the variant histone CenH3?
A)Telomere
B)Euchromatin
C)Centromere
D)Mitochondria
E)Chloroplast
A)Telomere
B)Euchromatin
C)Centromere
D)Mitochondria
E)Chloroplast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How did the work of Hershey and Chase contribute to the model of DNA as the genetic material? What technique helped them to distinguish between viral DNA and protein?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A tRNA gene is an example of which type of DNA sequence in eukaryotes?
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A normal chromosome in a higher eukaryotic species would be expected to contain all of the following EXCEPT:
A)one centromere.
B)one telomere.
C)two copies of histone 2A per nucleosome.
D)satellite DNA.
E)tandem repeat sequences.
A)one centromere.
B)one telomere.
C)two copies of histone 2A per nucleosome.
D)satellite DNA.
E)tandem repeat sequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Describe two characteristics of Z-DNA that distinguish it from B-DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A gene-encoding sequence is an example of which type of DNA sequence in eukaryotes?
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The agouti locus helps determine coat color in mice, and this phenotype can vary from light to dark between genetically identical individuals.You discovered a drug that reduces the variation in the agouti phenotype.What is a likely explanation for this drug's mechanism of action?
A)Inhibits DNA polymerases
B)Inhibits DNA methyl transferases
C)Activates shelterin proteins
D)Activates mitochondrial transcription
E)Causes DNA damage
A)Inhibits DNA polymerases
B)Inhibits DNA methyl transferases
C)Activates shelterin proteins
D)Activates mitochondrial transcription
E)Causes DNA damage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Copies of a gene that arose by gene duplication are part of a gene _____.
A)complex
B)family
C)tandemoplex
D)structure
E)chromosome
A)complex
B)family
C)tandemoplex
D)structure
E)chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An Alu sequence is an example of which type of DNA sequence in eukaryotes?
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Describe the many reasons why scientists felt that DNA could not be the genetic material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Telomeres exist to help with the _____ of the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes.
A)transcription
B)replication
C)metabolism
D)destabilization
E)translation
A)transcription
B)replication
C)metabolism
D)destabilization
E)translation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Describe the secondary structure that DNA might form in an ancient, dehydrated tissue sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
How did Chargaff's rules contribute to Watson and Crick's elucidation of the structure of DNA?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A centromere is an example of which type of DNA sequence in eukaryotes?
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA
A)Moderately repetitive DNA
B)Highly repetitive DNA
C)Short interspersed elements
D)Long interspersed elements
E)Unique-sequence DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following has repetitive DNA and heterochromatin?
A)Telomere
B)Centromere
C)Mitochondria
D)Chloroplast
E)Telomere and centromere
A)Telomere
B)Centromere
C)Mitochondria
D)Chloroplast
E)Telomere and centromere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
List and briefly describe the three different secondary structures of DNA and discuss the physiological significance of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



