Deck 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, and Protein Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, and Protein Metabolism
1
In the Cori cycle, compounds are cycled _____
A)from the muscles to the kidneys and back to the muscles.
B)from the muscles to the liver and back to the muscles.
C)from the kidneys to the liver and back to the kidneys.
D)from the liver to the brain and back to the liver.
A)from the muscles to the kidneys and back to the muscles.
B)from the muscles to the liver and back to the muscles.
C)from the kidneys to the liver and back to the kidneys.
D)from the liver to the brain and back to the liver.
B
2
How much ATP results from the transformation of two (2)molecules of acetyl CoA to four (4)molecules of CO2?
A)2 ATP molecules
B)5 ATP molecules
C)12 ATP molecules
D)20 ATP molecules
E)32 ATP molecules
A)2 ATP molecules
B)5 ATP molecules
C)12 ATP molecules
D)20 ATP molecules
E)32 ATP molecules
D
3
How many cycles of -oxidation are needed for complete catabolism of a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)18CO2H?
A)1
B)9
C)10
D)18
E)20
A)1
B)9
C)10
D)18
E)20
9
4
Which compound can rise to dangerously high levels in individuals with galactosemia?
A)galactase
B)glucose 1-phosphate
C)galactose
D)galactose 6-phosphate
A)galactase
B)glucose 1-phosphate
C)galactose
D)galactose 6-phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which is not a step in the Cori cycle?
A)The catabolism of glucose in muscle forms pyruvate, which is reduced to lactate when the oxygen supply is limited.
B)Lactate is transported to the liver.
C)Oxidation of lactate forms pyruvate, which is then converted to glucose by the 10-step process of gluconeogenesis.
D)Pyruvate and NAD+ are transported to the muscle.
A)The catabolism of glucose in muscle forms pyruvate, which is reduced to lactate when the oxygen supply is limited.
B)Lactate is transported to the liver.
C)Oxidation of lactate forms pyruvate, which is then converted to glucose by the 10-step process of gluconeogenesis.
D)Pyruvate and NAD+ are transported to the muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which food product does not rely on fermentation for its production?
A)cheese
B)beer
C)yogurt
D)yeast bread
E)All of the food products listed above rely on fermentation for their production.
A)cheese
B)beer
C)yogurt
D)yeast bread
E)All of the food products listed above rely on fermentation for their production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement best describes the energy requirement for the conversion of a fatty acid to a thioester with coenzyme A in the -oxidation of a fatty acid?
A)This process requires energy.
B)This process is energy neutral - energy is neither required nor released.
C)This process releases energy.
D)Whether energy is required or released depends on the identity of the fatty acid being oxidized.
A)This process requires energy.
B)This process is energy neutral - energy is neither required nor released.
C)This process releases energy.
D)Whether energy is required or released depends on the identity of the fatty acid being oxidized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
-Oxidation of a fatty acid requires how many steps to cleave a two carbon acetyl CoA unit from the starting acyl CoA?
A)2
B)4
C)8
D)10
E)The number of steps required is dependent on the identity of the starting acyl CoA.
A)2
B)4
C)8
D)10
E)The number of steps required is dependent on the identity of the starting acyl CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How many molecules of ATP are formed during the complete catabolism of a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)20CO2H?
A)32
B)98
C)140
D)148
E)150
A)32
B)98
C)140
D)148
E)150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which class(es)of compounds generates pyruvate as it is metabolized to acetyl CoA?
A)only fatty acids
B)only proteins
C)only carbohydrates
D)proteins and carbohydrates
E)fatty acids, proteins, and carbohydrates
A)only fatty acids
B)only proteins
C)only carbohydrates
D)proteins and carbohydrates
E)fatty acids, proteins, and carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How much ATP results from the transformation of one glucose molecule to two (2)molecules of acetyl CoA?
A)2 ATP molecules
B)5 ATP molecules
C)12 ATP molecules
D)20 ATP molecules
E)32 ATP molecules
A)2 ATP molecules
B)5 ATP molecules
C)12 ATP molecules
D)20 ATP molecules
E)32 ATP molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How is pyruvate converted to acetyl CoA?
A)under aerobic conditions
B)under anaerobic conditions
C)during fermentation
D)This conversion is favorable under all of the conditions above.
A)under aerobic conditions
B)under anaerobic conditions
C)during fermentation
D)This conversion is favorable under all of the conditions above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which enzyme is capable of catalyzing the reaction shown? 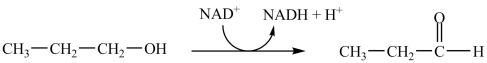
A)propanol kinase
B)propanol isomerase
C)propanol dehydrogenase
D)propanol carboxylase

A)propanol kinase
B)propanol isomerase
C)propanol dehydrogenase
D)propanol carboxylase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How many molecules of coenzyme A are needed for complete catabolism of a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)18CO2H?
A)1
B)9
C)10
D)18
E)20
A)1
B)9
C)10
D)18
E)20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Glycolysis converts _____
A)polysaccharides to glucose.
B)glucose to pyruvate, which is then metabolized to acetyl CoA.
C)fatty acids to thioesters, which are then metabolized to acetyl CoA.
D)amino acids to urea.
A)polysaccharides to glucose.
B)glucose to pyruvate, which is then metabolized to acetyl CoA.
C)fatty acids to thioesters, which are then metabolized to acetyl CoA.
D)amino acids to urea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which is not one of the three major products formed in glycolysis?
A)glucose
B)ATP
C)NADH
D)pyruvate
A)glucose
B)ATP
C)NADH
D)pyruvate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The -oxidation of a fatty acid may be described as which type of metabolic pathway?
A)an anabolic pathway
B)a cyclic pathway
C)a spiral pathway
D)a linear pathway
A)an anabolic pathway
B)a cyclic pathway
C)a spiral pathway
D)a linear pathway

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the starting material in step [1] in gluconeogenesis?
A)glucose
B)galactose
C)pyruvate
D)lactate
E)acetyl CoA
A)glucose
B)galactose
C)pyruvate
D)lactate
E)acetyl CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How many molecules of NADH are formed during the complete catabolism of a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)20CO2H?
A)1
B)10
C)11
D)20
E)22
A)1
B)10
C)11
D)20
E)22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How many moles of ATP per gram of fatty acid are formed during the complete catabolism of a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)24CO2H (molar mass 397 g/mol)?
A)0.0806 moles ATP / g fatty acid
B)0.297 moles ATP / g fatty acid
C)0.423 moles ATP / g fatty acid
D)0.443 moles ATP / g fatty acid
E)0.448 moles ATP / g fatty acid
A)0.0806 moles ATP / g fatty acid
B)0.297 moles ATP / g fatty acid
C)0.423 moles ATP / g fatty acid
D)0.443 moles ATP / g fatty acid
E)0.448 moles ATP / g fatty acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Glucogenic amino acids _____.
A)are converted to acetyl CoA.
B)are converted to glucose.
C)are catabolized to pyruvate or an intermediate in the citric acid cycle.
D)can be converted to ketone bodies.
A)are converted to acetyl CoA.
B)are converted to glucose.
C)are catabolized to pyruvate or an intermediate in the citric acid cycle.
D)can be converted to ketone bodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The reduction of acetaldehyde, shown below, is the last step in the fermentation process. What is the product of the reduction of acetaldehyde? 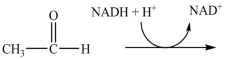
A)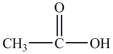
B)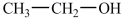
C)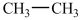
D)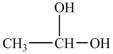
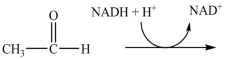
A)

B)
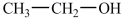
C)
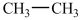
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which factors increase the rate of gluconeogenesis?
A)high glycogen reserves
B)low carbohydrate diet
C)high carbohydrate diet
D)low oxygen concentration
A)high glycogen reserves
B)low carbohydrate diet
C)high carbohydrate diet
D)low oxygen concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The first step in gluconeogenesis is the oxidation of lactic acid. What product is formed when lactic acid is oxidized? 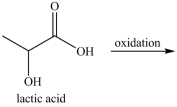
A)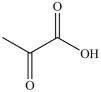
B)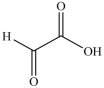
C)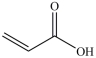
D)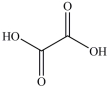

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What metabolic intermediate is formed from the carbon skeleton of the amino acid asparagine?
A) -ketoglutarate
B)oxaloacetate
C)citrate
D)succinyl CoA
E)fumarate
A) -ketoglutarate
B)oxaloacetate
C)citrate
D)succinyl CoA
E)fumarate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Where does gluconeogenesis take place?
A)in the brain
B)in the muscle tissue
C)in the liver
D)in the kidney
E)Gluconeogenesis takes place in all of the locations listed above.
A)in the brain
B)in the muscle tissue
C)in the liver
D)in the kidney
E)Gluconeogenesis takes place in all of the locations listed above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which compound is necessary for the oxidative deamination of the glutamate formed by transamination?
A)acetyl CoA
B)ATP
C)NADH
D)NAD+
E)FADH2
A)acetyl CoA
B)ATP
C)NADH
D)NAD+
E)FADH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which quantities need to be considered in determining the ATP yield from the complete catabolism of a fatty acid?
A)the ATP used up in the synthesis of the acyl CoA
B)the ATP generated from coenzymes produced during -oxidation
C)the ATP that results from the catabolism of each acetyl CoA
D)All of the quantities above need to be considered.
A)the ATP used up in the synthesis of the acyl CoA
B)the ATP generated from coenzymes produced during -oxidation
C)the ATP that results from the catabolism of each acetyl CoA
D)All of the quantities above need to be considered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What are the products formed in the transamination reaction shown? 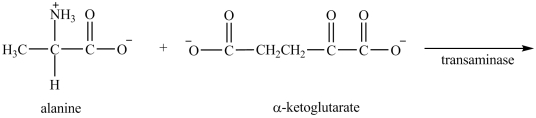
A)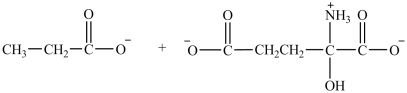
B)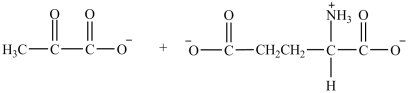
C)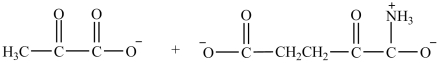
D)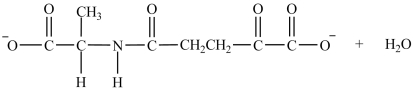

A)
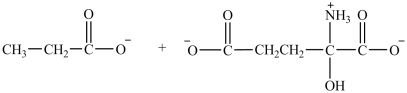
B)
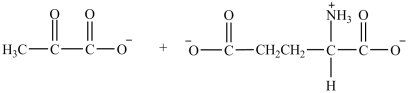
C)
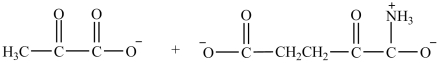
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What product(s)is formed in a transamination reaction?
A)an amino acid
B)urea
C)ammonia
D)an -keto acid
E)an amino acid and an -keto acid are both formed
A)an amino acid
B)urea
C)ammonia
D)an -keto acid
E)an amino acid and an -keto acid are both formed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is ketosis?
A)the accumulation of ketone bodies
B)the synthesis of ketones from acetyl CoA
C)the reduction of ketone bodies
D)a medical condition that results from the consumption of acetone and/or other toxic ketones
A)the accumulation of ketone bodies
B)the synthesis of ketones from acetyl CoA
C)the reduction of ketone bodies
D)a medical condition that results from the consumption of acetone and/or other toxic ketones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which condition does not lead to increased levels of ketone bodies?
A)uncontrolled diabetes
B)starvation
C)high carbohydrate diet
D)All of the conditions above result in increased levels of ketone bodies.
A)uncontrolled diabetes
B)starvation
C)high carbohydrate diet
D)All of the conditions above result in increased levels of ketone bodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which compound is not a ketone body?
A)acetoacetate
B)acetone
C) -hydroxybutyrate
D)acetyl CoA
A)acetoacetate
B)acetone
C) -hydroxybutyrate
D)acetyl CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The first step in gluconeogenesis is the oxidation of lactic acid. What product is formed when lactic acid is oxidized? 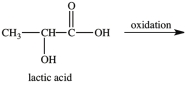
A)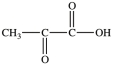
B)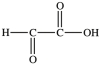
C)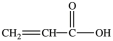
D)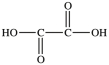

A)

B)

C)
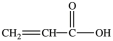
D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which amino acid is classified as glucogenic?
A)leucine
B)proline
C)lysine
D)None of the amino acids are classified as glucogenic.
A)leucine
B)proline
C)lysine
D)None of the amino acids are classified as glucogenic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How is the amino group of an amino acid lost as a result of transamination and oxidative deamination?
A)NH2-
B)NH3
C)NH4+
D)CH3NH2
A)NH2-
B)NH3
C)NH4+
D)CH3NH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What metabolic intermediate is formed from the carbon skeleton of the amino acid valine?
A) -ketoglutarate
B)oxaloacetate
C)citrate
D)succinyl CoA
E)fumarate
A) -ketoglutarate
B)oxaloacetate
C)citrate
D)succinyl CoA
E)fumarate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which process requires the coenzyme NADH?
A)glucose pyruvate
B)pyruvate acetaldehyde
C)pyruvate lactate
D)pyruvate acetyl CoA
E)More than one of the processes above requires the coenzyme NADH.
A)glucose pyruvate
B)pyruvate acetaldehyde
C)pyruvate lactate
D)pyruvate acetyl CoA
E)More than one of the processes above requires the coenzyme NADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How many molecules of ATP are formed per carbon atom in the fatty acid during the complete catabolism of a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)24CO2H?
A)1.23 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid
B)4.54 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid
C)6.46 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid
D)6.77 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid
E)6.85 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid
A)1.23 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid
B)4.54 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid
C)6.46 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid
D)6.77 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid
E)6.85 molecules ATP / carbon atom in the fatty acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which amino acid is classified as ketogenic?
A)histidine
B)valine
C)arginine
D)leucine
A)histidine
B)valine
C)arginine
D)leucine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Fermentation is the aerobic conversion of glucose to ethanol and CO2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Ketogenesis is the synthesis of ketone bodies from acetyl CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? ![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_d2b5_9547_2def152b19ba_TB5866_00.jpg)
A)![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_d2b6_9547_41430d240891_TB5866_00.jpg)
B)![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_d2b7_9547_d1d2017eb449_TB5866_00.jpg)
C)![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_d2b8_9547_f7b466352439_TB5866_00.jpg)
D)![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_f9c9_9547_67d235e91e10_TB5866_00.jpg)
![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_d2b5_9547_2def152b19ba_TB5866_00.jpg)
A)
![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_d2b6_9547_41430d240891_TB5866_00.jpg)
B)
![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_d2b7_9547_d1d2017eb449_TB5866_00.jpg)
C)
![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_d2b8_9547_f7b466352439_TB5866_00.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Step [9] in glycolysis, shown below, involves the dehydration of 2-phosphoglycerate. What is the structure of the dehydration product? </strong> A) B) C) D)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_f9c9_9547_67d235e91e10_TB5866_00.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Glucosamine, shown below, is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme hexokinase, which catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose in the first step of glycolysis (Eqn. 1 below). Which statement best describes the inhibition by glucosamine? 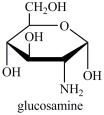
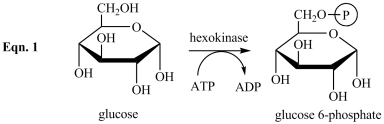
A)Glucosamine reacts with glucose, preventing glucose from binding to the active site of hexokinase.
B)Glucosamine binds to the active site of hexokinase, preventing glucose from binding.
C)Glucosamine stabilizes the active site of hexokinase, preventing glucose 6-phosphate from being released.
D)Glucosamine binds to the surface of hexokinase, causing a change in shape of the enzyme and the active site, preventing glucose from binding.


A)Glucosamine reacts with glucose, preventing glucose from binding to the active site of hexokinase.
B)Glucosamine binds to the active site of hexokinase, preventing glucose from binding.
C)Glucosamine stabilizes the active site of hexokinase, preventing glucose 6-phosphate from being released.
D)Glucosamine binds to the surface of hexokinase, causing a change in shape of the enzyme and the active site, preventing glucose from binding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When acetyl CoA levels exceed the capacity of the citric acid cycle, acetyl CoA is converted to ketone bodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Six of the steps of gluconeogenesis use the same enzymes as used in glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Many cancerous tumors depend largely on glycolysis to supply their energy needs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Ketone bodies are produced in the kidneys, and since they are small molecules that can hydrogen bond with water, they are readily soluble in blood and urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Individuals with galactosemia lack one of the enzymes necessary for converting galactose to glucose 6-phosphate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An abnormally high concentration of ketone bodies can lead to ketoacidosis-that is, an increase in the blood pH caused by the increased level of -hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The phosphorylation of mannose to form mannose 6-phosphate requires energy from ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The glycerol formed from triacylglycerol hydrolysis is converted in two steps to dihydroxyacetone phosphate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Oxygen is needed to oxidize NADH to NAD+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The breakdown of amino acids forms NH4+, which enters the urea cycle to form urea, and a carbon skeleton that is metabolized to either pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or an intermediate in the citric acid cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In glycolysis, two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate (CH3COCO2-)are formed from each glucose molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Step [7] of glycolysis is shown below. Which statement concerning this step is true? ![<strong>Step [7] of glycolysis is shown below. Which statement concerning this step is true? </strong> A)The hydrolysis of ATP provides the necessary energy for the removal of a phosphate group from 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate. B)The formation of 3-phosphoglycerate provides the necessary energy for the phosphorylation of ADP. C)The energy required in the hydrolysis of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate is stored in ADP. D)The hydrolysis of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate is an unfavorable reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_f9ca_9547_21ad9b846452_TB5866_00.jpg)
A)The hydrolysis of ATP provides the necessary energy for the removal of a phosphate group from 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate.
B)The formation of 3-phosphoglycerate provides the necessary energy for the phosphorylation of ADP.
C)The energy required in the hydrolysis of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate is stored in ADP.
D)The hydrolysis of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate is an unfavorable reaction.
![<strong>Step [7] of glycolysis is shown below. Which statement concerning this step is true? </strong> A)The hydrolysis of ATP provides the necessary energy for the removal of a phosphate group from 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate. B)The formation of 3-phosphoglycerate provides the necessary energy for the phosphorylation of ADP. C)The energy required in the hydrolysis of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate is stored in ADP. D)The hydrolysis of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate is an unfavorable reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5866/11eaaeeb_de4b_f9ca_9547_21ad9b846452_TB5866_00.jpg)
A)The hydrolysis of ATP provides the necessary energy for the removal of a phosphate group from 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate.
B)The formation of 3-phosphoglycerate provides the necessary energy for the phosphorylation of ADP.
C)The energy required in the hydrolysis of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate is stored in ADP.
D)The hydrolysis of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate is an unfavorable reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Conceptually, gluconeogenesis is the reverse of glycolysis; that is, two molecules of pyruvate are converted to glucose by a stepwise pathway that passes through all of the same intermediates encountered in glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Catabolism of a fatty acid produces more than twice the energy per gram as glucose (in terms of moles of ATP generated).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Gluconeogenesis is an anabolic process that synthesizes glucose from pyruvate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Gluconeogenesis is not a commonly used metabolic pathway when carbohydrate intake is high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Step [1] of the -oxidation of a fatty acid is considered an oxidation reaction even though the product has no additional C-O bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The urea cycle is a multistep pathway that converts ammonium ions to urea, (NH2)2C=O, in the kidneys.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A glucogenic amino acid may also be a ketogenic amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A carboxylase enzyme catalyzes the removal of carbon dioxide from a substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Low carbohydrate diets such as the Atkins diet induce the catabolism of stored fat for energy production to assist in weight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Glycolysis is a cyclic, 10-step pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Glycolysis occurs when the body has depleted its supplies of glucose and stored glycogen, and occurs during sustained physical exercise and fasting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Cortisol is an anti-inflammatory agent that also regulates carbohydrate metabolism. Cortisol contains a primary alcohol, a secondary alcohol, and a quaternary alcohol. 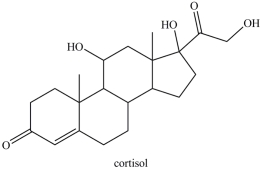


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The products that result when alanine is subjected to transamination followed by oxidative deamination are properly indicated below. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Gluconeogenesis is simply the reverse of glycolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The major products of glycolysis are glucose and ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Transamination removes the amino group from an amino acid, leaving a carbon skeleton that contains only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A kinase enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from one substrate to another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In oxidative deamination, glutamate is re-converted to -ketoglutarate, which can undergo transamination with another molecule of an amino acid and the cycle repeats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Glycolysis is an anaerobic pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The rate of glycolysis decreases when the body's ATP concentration is high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Cortisol is an anti-inflammatory agent that also regulates carbohydrate metabolism. Cortisol contains a primary alcohol, a secondary alcohol, and a quaternary alcohol. 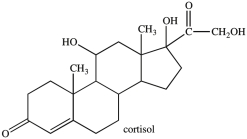


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In fermentation, the six carbon atoms of glucose are converted to three molecules of ethanol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The overall result of transamination and oxidative deamination is to remove an amino group from an amino acid and form an ammonium ion, NH4+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When oxygen is plentiful, pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA, which can enter the citric acid cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



