Deck 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/88
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
1
How many chirality centers are in leu-enkephalin (structure shown)? 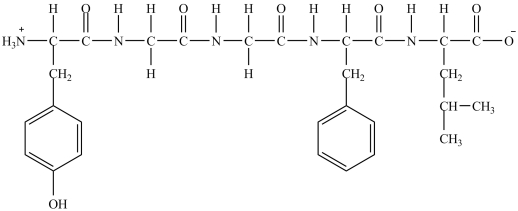
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)9

A)3
B)4
C)5
D)9
A
2
The term protein is usually reserved for polymers of more than _____ amino acids.
A)10
B)40
C)200
D)1000
A)10
B)40
C)200
D)1000
B
3
Which amino acid is a basic amino acid?
A)serine
B)arginine
C)cysteine
D)alanine
A)serine
B)arginine
C)cysteine
D)alanine
B
4
Which is the simplest amino acid?
A)serine
B)glutamine
C)cysteine
D)glycine
A)serine
B)glutamine
C)cysteine
D)glycine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the N-terminal amino acid in the tetrapeptide glycylalanyisoleucylmethionine?
A)alanine
B)glycine
C)methionine
D)isoleucine
A)alanine
B)glycine
C)methionine
D)isoleucine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many different tripeptides can be formed when one isoleucine, one alanine, and one glycine react?
A)3
B)6
C)18
D)27
A)3
B)6
C)18
D)27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the charge on an amino acid at a pH below its pI?
A)positive
B)neutral
C)negative
D)The charge or lack of charge varies depending on the amino acid.
A)positive
B)neutral
C)negative
D)The charge or lack of charge varies depending on the amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How many different dipeptides can be formed when one valine reacts with one glycine?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the particular sequence of amino acids of a protein that are joined together by peptide bonds called?
A)the primary structure of a protein
B)the secondary structure of a protein
C)the tertiary structure of a protein
D)the quaternary structure of a protein
A)the primary structure of a protein
B)the secondary structure of a protein
C)the tertiary structure of a protein
D)the quaternary structure of a protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which Fischer projections represent naturally-occurring amino acids? 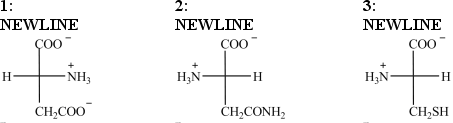
A)only structure 1
B)only structure 2
C)structures 1, 2, and 3
D)structures 2 and 3

A)only structure 1
B)only structure 2
C)structures 1, 2, and 3
D)structures 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement about oxytocin and vasopressin is not true?
A)Oxytocin and vasopressin each contain nine amino acids.
B)Oxytocin and vasopressin each contain cysteine on both sides of a disulfide bond.
C)Oxytocin and vasopressin each contain a single disulfide bond.
D)Oxytocin and vasopressin each contain cysteine as the C-terminal amino acid.
A)Oxytocin and vasopressin each contain nine amino acids.
B)Oxytocin and vasopressin each contain cysteine on both sides of a disulfide bond.
C)Oxytocin and vasopressin each contain a single disulfide bond.
D)Oxytocin and vasopressin each contain cysteine as the C-terminal amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which protein stores iron in the liver?
A)ferritin
B)keratin
C)myoglobin
D)collagen
A)ferritin
B)keratin
C)myoglobin
D)collagen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the one-letter abbreviation of arginine?
A)A
B)R
C)P
D)G
A)A
B)R
C)P
D)G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the three-letter abbreviation of asparagine?
A)Asp
B)Asg
C)Asn
D)Arg
A)Asp
B)Asg
C)Asn
D)Arg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
How is a dipeptide formed?
A)The -NH3+ group of one amino acid forms an amide bond with the -NH3+ group of another amino acid and the elements of H2 are removed.
B)The -NH3+ group of one amino acid forms an amide bond with the carboxylate (-COO-)of another amino acid, and the elements of H2O are removed.
C)The carboxylate (-COO-)group of one amino acid forms an amide bond with the carboxylate (-COO-)of another amino acid, and the elements of O2 are removed.
D)The carboxylate (-COO-)group of one amino acid forms an amide bond the -NH3+ group of another amino acid, and the elements of H2 are removed.
A)The -NH3+ group of one amino acid forms an amide bond with the -NH3+ group of another amino acid and the elements of H2 are removed.
B)The -NH3+ group of one amino acid forms an amide bond with the carboxylate (-COO-)of another amino acid, and the elements of H2O are removed.
C)The carboxylate (-COO-)group of one amino acid forms an amide bond with the carboxylate (-COO-)of another amino acid, and the elements of O2 are removed.
D)The carboxylate (-COO-)group of one amino acid forms an amide bond the -NH3+ group of another amino acid, and the elements of H2 are removed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the C-terminal amino acid in the tetrapeptide glycylalanyisoleucylmethionine?
A)alanine
B)glycine
C)methionine
D)isoleucine
A)alanine
B)glycine
C)methionine
D)isoleucine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the name of the amino acid shown below? 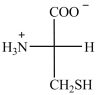
A)L-cysteine
B)D-cysteine
C)L-serine
D)D-serine

A)L-cysteine
B)D-cysteine
C)L-serine
D)D-serine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the charge on a zwitterion?
A)positive
B)neutral
C)negative
D)The charge or lack of charge varies depending on the amino acid.
A)positive
B)neutral
C)negative
D)The charge or lack of charge varies depending on the amino acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the function of myosin in the human body?
A)as connective tissue found in tendons, bone, cartilage, and blood vessels
B)control muscle contractions
C)stores iron in the liver
D)controls blood glucose levels
A)as connective tissue found in tendons, bone, cartilage, and blood vessels
B)control muscle contractions
C)stores iron in the liver
D)controls blood glucose levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which protein stores O2 in tissues?
A)keratin
B)ferritin
C)hemoglobin
D)myoglobin
A)keratin
B)ferritin
C)hemoglobin
D)myoglobin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
About one half of the 223 amino acid residues in the enzyme trypsin are hydrophobic. Where in the tertiary structure of this globular protein are these residues most likely to be found?
A)At the N-terminal end of the peptide chain.
B)At the C-terminal end of the peptide chain.
C)On the exterior surface of the folded protein.
D)In the interior of the folded protein.
A)At the N-terminal end of the peptide chain.
B)At the C-terminal end of the peptide chain.
C)On the exterior surface of the folded protein.
D)In the interior of the folded protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Trypsin is a digestive enzyme that hydrolyzes peptide bonds only when the carbonyl group in the amide bond comes from Lys or Arg. What fragments result when the peptide Gly-Lys-Arg-Ala-Ala-Arg is hydrolyzed by trypsin?
A)Gly, Lys, Arg, Ala-Ala, Arg
B)Gly-Lys, Arg-Ala-Ala, Arg
C)Gly-Lys, Arg, Ala-Ala, Arg
A)Gly, Lys, Arg, Ala-Ala, Arg
B)Gly-Lys, Arg-Ala-Ala, Arg
C)Gly-Lys, Arg, Ala-Ala, Arg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The side chain of which amino acid can form hydrogen bonds with asparagine?
A)glycine
B)valine
C)tyrosine
D)alanine
A)glycine
B)valine
C)tyrosine
D)alanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the strongest type of interaction between two cysteine amino acid side chains in a protein?
A)hydrogen bonding
B)London dispersion forces
C)disulfide bond
D)electrostatic interactions
A)hydrogen bonding
B)London dispersion forces
C)disulfide bond
D)electrostatic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the strongest type of interaction between the side chains of an isoleucine amino acid and a phenylalanine amino acid in a protein?
A)hydrogen bonding
B)London dispersion forces
C)disulfide bond
D)electrostatic interactions
A)hydrogen bonding
B)London dispersion forces
C)disulfide bond
D)electrostatic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider the following forms of the amino acid valine (Val). Which statement concerning these structures is false? 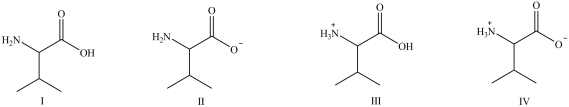
A)Structure I represents the form of Val present in blood at physiological pH.
B)Structure II represents the form of Val present in the basic environment of the intestines.
C)Structure III represents the form of Val present in the acidic environment of the stomach.
D)Structure IV represents the zwitterions of Val.
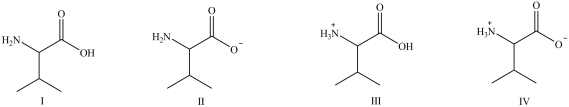
A)Structure I represents the form of Val present in blood at physiological pH.
B)Structure II represents the form of Val present in the basic environment of the intestines.
C)Structure III represents the form of Val present in the acidic environment of the stomach.
D)Structure IV represents the zwitterions of Val.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which conditions are commonly diagnosed by measuring the levels of specific enzymes in the blood?
A)heart attack
B)high blood pressure
C)pregnancy
D)migraines
A)heart attack
B)high blood pressure
C)pregnancy
D)migraines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider the following forms of the amino acid valine (Val). Which statement concerning these structures is false? 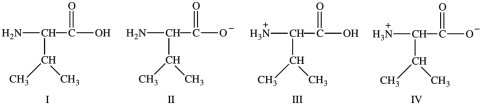
A)Structure I represents the form of Val present in blood at physiological pH.
B)Structure II represents the form of Val present in the basic environment of the intestines.
C)Structure III represents the form of Val present in the acidic environment of the stomach.
D)Structure IV represents the zwitterions of Val.

A)Structure I represents the form of Val present in blood at physiological pH.
B)Structure II represents the form of Val present in the basic environment of the intestines.
C)Structure III represents the form of Val present in the acidic environment of the stomach.
D)Structure IV represents the zwitterions of Val.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Tuftsin is a peptide that stimulate and promotes the destruction of tumor cells. Its primary structure is Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg. Which statement is NOT a valid interpretation of its primary structure?
A)It is a tetrapeptide.
B)Threonine is the N-terminal amino acid and arginine is the C-terminal amino acid.
C)The amino group of arginine is not joined to any other amino acid.
D)The carboxyl group of lysine is joined to the amino group of proline.
A)It is a tetrapeptide.
B)Threonine is the N-terminal amino acid and arginine is the C-terminal amino acid.
C)The amino group of arginine is not joined to any other amino acid.
D)The carboxyl group of lysine is joined to the amino group of proline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Based on its name, which compound is an enzyme?
A)glucose
B)triosephosphate isomerase
C)N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
D)dihydrofolate
A)glucose
B)triosephosphate isomerase
C)N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
D)dihydrofolate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What type of inhibitor binds to the enzyme but does not bind at the active site?
A)a noncompetitive inhibitor
B)a competitive inhibitor
C)a reversible inhibitor
D)an irreversible inhibitor
A)a noncompetitive inhibitor
B)a competitive inhibitor
C)a reversible inhibitor
D)an irreversible inhibitor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which is not a characteristic of an -helix?
A)The N-H and C=O bonds point along the axis of the helix in opposite directions.
B)The R groups of the amino acids extend inward toward the core of the helix.
C)There are 3.6 amino acids in each turn of the helix.
D)The C=O group of one amino acid is hydrogen bonded to an N-H group four amino acid residues farther along the chain.
A)The N-H and C=O bonds point along the axis of the helix in opposite directions.
B)The R groups of the amino acids extend inward toward the core of the helix.
C)There are 3.6 amino acids in each turn of the helix.
D)The C=O group of one amino acid is hydrogen bonded to an N-H group four amino acid residues farther along the chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the process of altering the shape of a protein without breaking the amide bonds that form the primary structure?
A)hydrolysis
B)competitive inhibition
C)denaturation
D)oxidation
A)hydrolysis
B)competitive inhibition
C)denaturation
D)oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement is not true?
A)A cofactor is always a metal ion needed for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction to occur.
B)The names of most enzymes end in the suffix -ase.
C)An enzyme-catalyzed reaction can be 106 to 1012 times faster than a similar uncatalyzed reaction.
D)Enzymes are proteins that serve as biological catalysts for reactions in all living organisms.
A)A cofactor is always a metal ion needed for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction to occur.
B)The names of most enzymes end in the suffix -ase.
C)An enzyme-catalyzed reaction can be 106 to 1012 times faster than a similar uncatalyzed reaction.
D)Enzymes are proteins that serve as biological catalysts for reactions in all living organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Denaturation of a protein results in the loss of its native conformation and its biological activity. Which statement best describes what happens to a protein when it is denatured?
A)Peptide bonds are broken.
B)New amino acids are joined to the peptide backbone.
C)Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels of structure are disrupted.
D)The N-terminal and C-terminal ends of the protein are hydrolyzed by enzymes.
A)Peptide bonds are broken.
B)New amino acids are joined to the peptide backbone.
C)Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels of structure are disrupted.
D)The N-terminal and C-terminal ends of the protein are hydrolyzed by enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which is an example of a globular protein?
A)collagen
B) -keratin
C)hemoglobin
D)amylopectin
A)collagen
B) -keratin
C)hemoglobin
D)amylopectin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which is an example of a cofactor?
A)lactose
B)lactose dehydrogenase
C)NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
D)tryptophan
A)lactose
B)lactose dehydrogenase
C)NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
D)tryptophan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is a zymogen?
A)an amino acid with a neutral charge
B)inactive precursor of an enzyme
C)a molecule that causes an enzyme to lose activity
D)a nonprotein organic molecule needed for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction to occur
A)an amino acid with a neutral charge
B)inactive precursor of an enzyme
C)a molecule that causes an enzyme to lose activity
D)a nonprotein organic molecule needed for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction to occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Amino acids are the building blocks of the body's proteins. Which statement concerning amino acids is false? 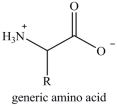
A)There are approximately 200 standard amino acids that occur naturally in the proteins of the human body.
B)Except for when R=H, amino acids are chiral molecules.
C)The amino acids found in human proteins are "alpha" amino acids.
D)The properties of amino acids and the proteins they compose are determined by the nature of the side chain groups that are present.

A)There are approximately 200 standard amino acids that occur naturally in the proteins of the human body.
B)Except for when R=H, amino acids are chiral molecules.
C)The amino acids found in human proteins are "alpha" amino acids.
D)The properties of amino acids and the proteins they compose are determined by the nature of the side chain groups that are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Amino acids are the building blocks of the body's proteins. Which statement concerning amino acids is false? 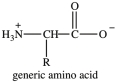
A)There are approximately 200 standard amino acids that occur naturally in the proteins of the human body.
B)Except for when R=H, amino acids are chiral molecules.
C)The amino acids found in human proteins are "alpha" amino acids.
D)The properties of amino acids and the proteins they compose are determined by the nature of the side chain groups that are present.

A)There are approximately 200 standard amino acids that occur naturally in the proteins of the human body.
B)Except for when R=H, amino acids are chiral molecules.
C)The amino acids found in human proteins are "alpha" amino acids.
D)The properties of amino acids and the proteins they compose are determined by the nature of the side chain groups that are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Insulin is a small protein consisting of two polypeptide chains held together by hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A diet of rice and tofu provides all essential amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Secretion of vasopressin by the pituitary gland causes the kidneys to retain fluid, resulting in decreased urine output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Both the myosin and the -keratin are proteins composed almost entirely of -pleated sheets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is called a cofactor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When the peptide below is hydrolyzed with water, the products are the amino acids proline, cysteine, and glutamine. 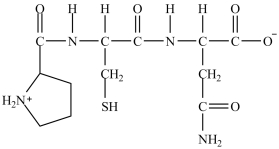


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
D-Amino acids have the -NH3+ group on the left side in the Fischer projection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A dipeptide contains two amino acids joined together by two amide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The -pleated sheet forms when two or more peptide chains, called strands, line up side-by-side with the C=O and N-H bonds in the plane of the sheets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The hydrolysis of the amide bonds in a protein forms the individual amino acids that comprise the primary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The -helix and the -pleated sheet are examples of the tertiary structure of a protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The Fischer projection below represents a basic amino acid. 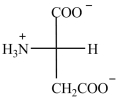


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Globular proteins are coiled into compact shapes with hydrophilic outer surfaces that make them water soluble.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The lock-and-key model is often used to explain why some enzymes catalyze a wide variety of substrate reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
By convention, the C-terminal amino acid is always written at the right end of the peptide chain and the N-terminal amino acid at the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The Fischer projection below represents a naturally occurring amino acid. 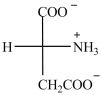


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Hemoglobin, collagen, and myoglobin are all examples of conjugated proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The antibiotics penicillin and sulfanilamide, and drugs used to treat high blood pressure and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)are classified as coenzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The amide bonds in peptides and proteins are called peptide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Acidic amino acids have lower pI values than basic amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The amino acids aspartic acid and glutamic acid have a +1 net charge at low pH, and a -2 net charge at high pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The peptide leucylphenylalanylvalylvaline is abbreviated as Leu-Phen-Ala-Val-Val.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
There are _____ amino acids that occur naturally in proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
-Keratin in hair is a fibrous protein composed almost exclusively of -helix units that wind together to form a superhelix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The "cartoon" shown is an example of noncompetitive inhibition. 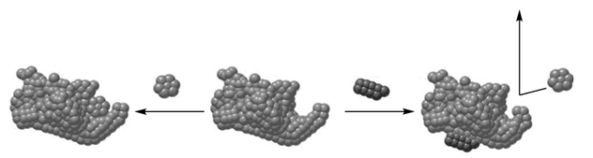


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
All amino acids have at least one chirality center.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Humans can synthesize only twenty of the amino acids needed for proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
No one plant source has sufficient amounts of all of the essential amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
HIV protease inhibitors are used to treat HIV by binding to an enzyme needed by the virus to replicate itself.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The -pleated sheet arrangement of a protein is favored by amino acids with small side chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The enzyme in the ribbon diagram shown is composed primarily of -pleated sheets. 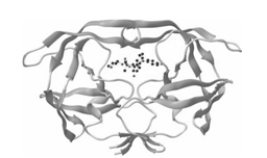


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Hydrogen bonding is possible between the side chains of the amino acids tyrosine and threonine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In hydrolysis of a peptide or protein, the addition of water breaks the hydrogen bonds that hold the amino acids together in the peptide chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Zwitterions have low melting points and are water soluble.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The "cartoon" shown is an example of competitive inhibition. 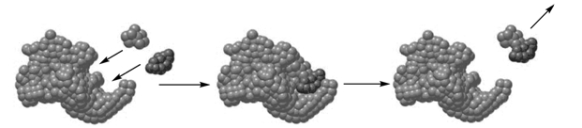


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Amino acids with an additional COOH group in the side chain are classified as acidic amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
It is possible for two different proteins to contain the same number and type of amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Amino acids typically exist in nature as neutral molecules with all uncharged atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Serine exists primarily in its neutral form at a pH ~ 6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Fibrin and thrombin, two proteins involved in blood clotting, are first synthesized as the zymogens fibrinogen and prothrombin, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



