Deck 11: Electrochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Electrochemistry
1
How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction?
SO32-(aq) + MnO4-(aq) → SO42-(aq) + Mn2+(aq)
A) 4
B) 10
C) 3
D) 2
E) 6
SO32-(aq) + MnO4-(aq) → SO42-(aq) + Mn2+(aq)
A) 4
B) 10
C) 3
D) 2
E) 6
10
2
The standard potential for the reaction Zn + 2Ag+ → Zn2+ + 2Ag is 1.56 V. Given that the standard reduction potential for Ag+ + e- → Ag is 0.80 V, determine the standard reduction potential for Zn2+ + 2e- → Zn.
A) 0.04 V
B) -0.38 V
C) -0.76 V
D) 0.76 V
E) none of these
A) 0.04 V
B) -0.38 V
C) -0.76 V
D) 0.76 V
E) none of these
-0.76 V
3
Determine the standard potential, E°, of a cell that employs the reaction
Co + Ag+ → Co2+ +Ag
A) 1.88 V
B) -1.08 V
C) 1.08 V
D) -0.52 V
E) none of these
Co + Ag+ → Co2+ +Ag
A) 1.88 V
B) -1.08 V
C) 1.08 V
D) -0.52 V
E) none of these
1.08 V
4
The following questions refer to a galvanic cell that utilizes the following reaction (unbalanced):(AuCl4)-(aq) + Cu(s) → Au(s) + Cl-(aq) + Cu2+(aq)
Determine the number of electrons transferred during the reaction (when balanced).
A) 2
B) 6
C) 4
D) 3
E) 9
Determine the number of electrons transferred during the reaction (when balanced).
A) 2
B) 6
C) 4
D) 3
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The following two half-reactions take place in a galvanic cell. At standard conditions, what species are produced at each electrode? 
A) Sn is produced at the cathode, and Cu2+ is produced at the anode.
B) Cu is produced at the anode, and Sn2+ is produced at the cathode.
C) Cu is produced at the cathode, and Sn2+ is produced at the anode.
D) Sn is produced at the anode, and Cu is produced at the cathode.
E) Sn is produced at the anode, and Cu2+ is produced at the cathode.

A) Sn is produced at the cathode, and Cu2+ is produced at the anode.
B) Cu is produced at the anode, and Sn2+ is produced at the cathode.
C) Cu is produced at the cathode, and Sn2+ is produced at the anode.
D) Sn is produced at the anode, and Cu is produced at the cathode.
E) Sn is produced at the anode, and Cu2+ is produced at the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When the equation for the following reaction in basic solution is balanced, what is the sum of the coefficients?
MnO4-(aq) + CN-(aq) → MnO2(s) + CNO-(aq)
A) 20
B) 10
C) 8
D) 13
E) 11
MnO4-(aq) + CN-(aq) → MnO2(s) + CNO-(aq)
A) 20
B) 10
C) 8
D) 13
E) 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the oxidation state of Mn in MnO4-?
A) 1
B) 9
C) 7
D) -1
E) 3
A) 1
B) 9
C) 7
D) -1
E) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is the best reducing agent? 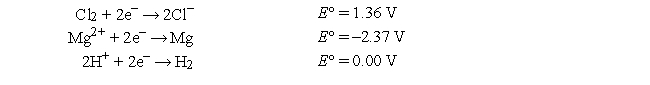
A) Cl-
B) Cl2
C) H2
D) Mg
E) Mg2+
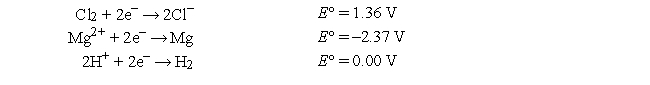
A) Cl-
B) Cl2
C) H2
D) Mg
E) Mg2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Silver will spontaneously reduce which of the following?
A) Fe2+
B) Na+
C) Al3+
D) Co2+
E) none of these
A) Fe2+
B) Na+
C) Al3+
D) Co2+
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How many electrons are transferred in the following reaction?
2Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 6Cl- → 2Cr3+ + 3Cl2 + 7H2O
A) 4
B) 2
C) 8
D) 6
E) none of these
2Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 6Cl- → 2Cr3+ + 3Cl2 + 7H2O
A) 4
B) 2
C) 8
D) 6
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which metal, Al or Ni, could reduce Zn2+ to Zn(s) if placed in a Zn2+(aq) solution? 
A) Ni
B) Al
C) Both Al and Ni would work.
D) Neither Al nor Ni would work.
E) This cannot be determined.

A) Ni
B) Al
C) Both Al and Ni would work.
D) Neither Al nor Ni would work.
E) This cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment). 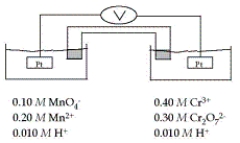 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 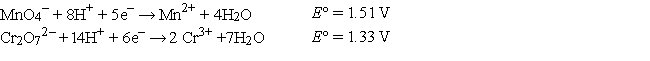
What is the oxidation state of Cr in Cr2O72-?
A) +6
B) -2
C) +12
D) -1
E) +7
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 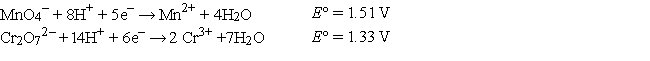
What is the oxidation state of Cr in Cr2O72-?
A) +6
B) -2
C) +12
D) -1
E) +7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The following questions refer to a galvanic cell that utilizes the following reaction (unbalanced):(AuCl4)-(aq) + Cu(s) → Au(s) + Cl-(aq) + Cu2+(aq)
Given the following information, determine the standard cell potential.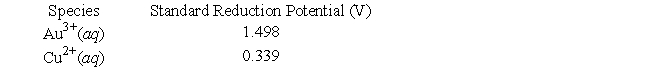
A) 1.159 V
B) 2.102 V
C) 1.979 V
D) 1.462 V
E) 1.837 V
Given the following information, determine the standard cell potential.
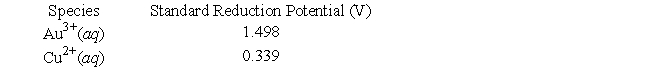
A) 1.159 V
B) 2.102 V
C) 1.979 V
D) 1.462 V
E) 1.837 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Ammonium metavanadate reacts with sulfur dioxide in acidic solution as follows (hydrogen ions and H2O omitted):
XVO3- + ySO2 → xVO2+ + ySO42-
The ratio x : y is
A) 1 : 3
B) 1 : 2
C) 2 : 1
D) 3 : 1
E) 1 : 1
XVO3- + ySO2 → xVO2+ + ySO42-
The ratio x : y is
A) 1 : 3
B) 1 : 2
C) 2 : 1
D) 3 : 1
E) 1 : 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is the strongest oxidizing agent? 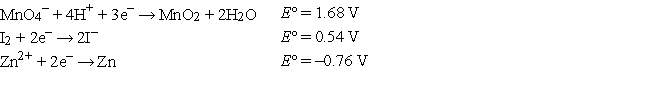
A) Zn2+
B) I2
C) MnO4-
D) Zn
E) MnO2
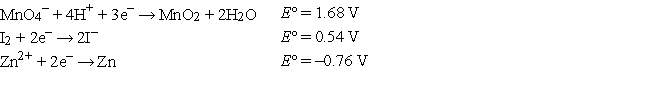
A) Zn2+
B) I2
C) MnO4-
D) Zn
E) MnO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The following reaction occurs in basic solution:
Ag+ + Cu → Ag + Cu2+
When the equation is balanced, what is the sum of the coefficients?
A) 7
B) 6
C) 5
D) 4
E) 8
Ag+ + Cu → Ag + Cu2+
When the equation is balanced, what is the sum of the coefficients?
A) 7
B) 6
C) 5
D) 4
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A strip of copper is placed in a 1 M solution of copper nitrate, and a strip of silver is placed in a 1 M solution of silver nitrate. The two metal strips are connected to a voltmeter by wires, and a salt bridge connects the solutions. The following standard reduction potentials apply:  When the voltmeter is removed and the two electrodes are connected by a wire, which of the following does not take place?
When the voltmeter is removed and the two electrodes are connected by a wire, which of the following does not take place?
A) Negative ions pass through the salt bridge from the silver half-cell to the copper half-cell.
B) The silver electrode increases in mass as the cell operates.
C) Electrons flow in the external circuit from the copper electrode to the silver electrode.
D) Some positive copper ions pass through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the silver half-cell.
E) There is a net general movement of silver ions through the salt bridge to the copper half-cell.
 When the voltmeter is removed and the two electrodes are connected by a wire, which of the following does not take place?
When the voltmeter is removed and the two electrodes are connected by a wire, which of the following does not take place?A) Negative ions pass through the salt bridge from the silver half-cell to the copper half-cell.
B) The silver electrode increases in mass as the cell operates.
C) Electrons flow in the external circuit from the copper electrode to the silver electrode.
D) Some positive copper ions pass through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the silver half-cell.
E) There is a net general movement of silver ions through the salt bridge to the copper half-cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The reaction below occurs in basic solution. In the balanced equation, what is the sum of the coefficients?
Zn + NO3- → Zn(OH)42- + NH3
A) 27
B) 19
C) 23
D) 12
E) 15
Zn + NO3- → Zn(OH)42- + NH3
A) 27
B) 19
C) 23
D) 12
E) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following would be the best reducing agent?
A) F-
B) F2
C) Na+
D) Cl2
E) Na
A) F-
B) F2
C) Na+
D) Cl2
E) Na

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the equation for the following reaction in basic solution is balanced, what is the sum of the coefficients?
MnO2 + HO2- → MnO4-
A) 11
B) 9
C) 18
D) 31
E) 14
MnO2 + HO2- → MnO4-
A) 11
B) 9
C) 18
D) 31
E) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The reaction Cr(s) + NO3-(aq) → Cr3+(aq) + NO(g) takes place in acidic solution.
How many electrons are transferred per mole of NO(g)?
A) 4
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
E) 1
How many electrons are transferred per mole of NO(g)?
A) 4
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider an electrochemical cell with a copper electrode immersed in 1.0 M Cu2+ and a silver electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ag+. 
Which of the electrodes is the anode?
A) the silver electrode
B) the copper electrode

Which of the electrodes is the anode?
A) the silver electrode
B) the copper electrode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a common car battery, six identical cells each carry out the following reaction:
Pb + PbO2 + 2HSO4- + 2H+ → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
For such a cell, E° is 2.04 V. Calculate ΔG° at 25°C.
A) -787 kJ
B) -197 kJ
C) -394 kJ
D) -98 kJ
E) -0.121 kJ
Pb + PbO2 + 2HSO4- + 2H+ → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
For such a cell, E° is 2.04 V. Calculate ΔG° at 25°C.
A) -787 kJ
B) -197 kJ
C) -394 kJ
D) -98 kJ
E) -0.121 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In which direction do electrons flow in the external circuit?
A) right to left
B) left to right
C) No current flows; the cell is at equilibrium.
A) right to left
B) left to right
C) No current flows; the cell is at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The reduction potentials for Au3+ and Ni2+ are as follows:
Au3+ + 3e- → Au E° = +1.50 V
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni E° = -0.23 V
Calculate ΔG° (at 25°C) for the reaction
2Au3+ + 3Ni → 3Ni2+ + 2Au
A) -1.00 × 103 kJ
B) -2140 kJ
C) +5.00 × 102 kJ
D) -5.00 × 102 kJ
E) +1.00 × 103 kJ
Au3+ + 3e- → Au E° = +1.50 V
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni E° = -0.23 V
Calculate ΔG° (at 25°C) for the reaction
2Au3+ + 3Ni → 3Ni2+ + 2Au
A) -1.00 × 103 kJ
B) -2140 kJ
C) +5.00 × 102 kJ
D) -5.00 × 102 kJ
E) +1.00 × 103 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How many electrons are transferred in the balanced reaction (that is, what will be the value of n in the Nernst equation)?
A) 22
B) 30
C) 2
D) 6
E) 5
A) 22
B) 30
C) 2
D) 6
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment). 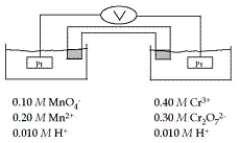 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 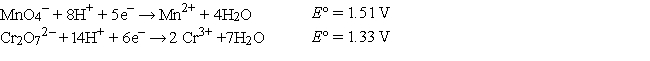
When current is allowed to flow, which species is reduced?
A) H+
B) MnO4-
C) Cr3+
D) Mn2+
E) Cr2O72-
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 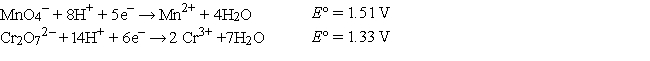
When current is allowed to flow, which species is reduced?
A) H+
B) MnO4-
C) Cr3+
D) Mn2+
E) Cr2O72-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Choose the correct statement(s) given the following information: 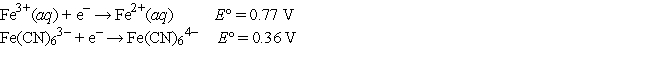
I.Fe2+(aq) is more likely to be oxidized than Fe2+ complexed to CN-.
II.Fe3+(aq) is more likely to be reduced than Fe3+ complexed to CN-.
III.Complexation of Fe ions with CN- has no effect on their tendencies to become
Oxidized or reduced.
A) I and II
B) II only
C) I only
D) III only
E) None of these is true.
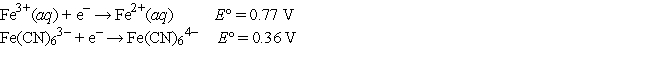
I.Fe2+(aq) is more likely to be oxidized than Fe2+ complexed to CN-.
II.Fe3+(aq) is more likely to be reduced than Fe3+ complexed to CN-.
III.Complexation of Fe ions with CN- has no effect on their tendencies to become
Oxidized or reduced.
A) I and II
B) II only
C) I only
D) III only
E) None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The reaction Cr(s) + NO3-(aq) → Cr3+(aq) + NO(g) takes place in acidic solution.
What is the coefficient of H2O(l) in the balanced equation?
A) 3
B) 5
C) 4
D) 2
E) 1
What is the coefficient of H2O(l) in the balanced equation?
A) 3
B) 5
C) 4
D) 2
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consider an electrochemical cell with a copper electrode immersed in 1.0 M Cu2+ and a silver electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ag+. 
Calculate E° for this cell.
A) 0.46 V
B) 1.14 V
C) 1.26 V
D) 1.48 V
E) none of these

Calculate E° for this cell.
A) 0.46 V
B) 1.14 V
C) 1.26 V
D) 1.48 V
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consider the galvanic cell shown below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment). 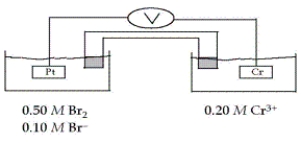 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 
Which of the following statements about this cell is false?
A) To complete the circuit, cations migrate into the left half-cell and anions migrate into the right half-cell from the salt bridge.
B) This is a galvanic cell.
C) Electrons flow from the Pt electrode to the Cr electrode.
D) The cell is not at standard conditions.
E) Reduction occurs at the Pt electrode.
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 
Which of the following statements about this cell is false?
A) To complete the circuit, cations migrate into the left half-cell and anions migrate into the right half-cell from the salt bridge.
B) This is a galvanic cell.
C) Electrons flow from the Pt electrode to the Cr electrode.
D) The cell is not at standard conditions.
E) Reduction occurs at the Pt electrode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The standard free energies of formation of several aqueous species are 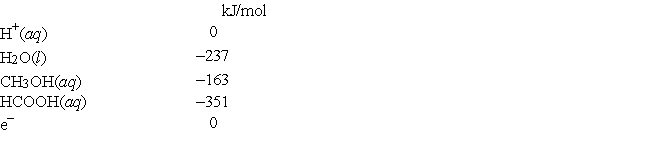 What is the standard reduction potential of methanoic acid in aqueous solution (that is, for HCOOH + 4H+ + 4e- → CH3OH + H2O)?
What is the standard reduction potential of methanoic acid in aqueous solution (that is, for HCOOH + 4H+ + 4e- → CH3OH + H2O)?
A) +0.13 V
B) +0.25 V
C) -0.25 V
D) -0.13 V
E) +0.17 V
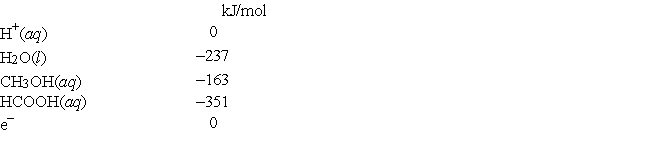 What is the standard reduction potential of methanoic acid in aqueous solution (that is, for HCOOH + 4H+ + 4e- → CH3OH + H2O)?
What is the standard reduction potential of methanoic acid in aqueous solution (that is, for HCOOH + 4H+ + 4e- → CH3OH + H2O)?A) +0.13 V
B) +0.25 V
C) -0.25 V
D) -0.13 V
E) +0.17 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell where
H2(g) + O2(g) H2O(l)
H2O(l)
ΔG° = -237.18 kJ/mol H2
Which of the following statements is(are) true?
I.At standard conditions, the maximum work the fuel cell could do on the surroundings
Is 237.18 kJ/mol.
II.In the real world, the actual amount of useful work the cell can do is less than 237.18 kJ.
III.More energy is dissipated as waste heat in the fuel cell than in the reversible pathway.
A) I
B) I, II, and III
C) II
D) III
E) None of the statements is true.
H2(g) + O2(g)
 H2O(l)
H2O(l) ΔG° = -237.18 kJ/mol H2
Which of the following statements is(are) true?
I.At standard conditions, the maximum work the fuel cell could do on the surroundings
Is 237.18 kJ/mol.
II.In the real world, the actual amount of useful work the cell can do is less than 237.18 kJ.
III.More energy is dissipated as waste heat in the fuel cell than in the reversible pathway.
A) I
B) I, II, and III
C) II
D) III
E) None of the statements is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the following reduction potentials:  For a galvanic cell employing the Cu, Cu2+ and Pb, Pb2+ couples, calculate the maximum amount of work that would accompany the reaction of 1 mol of lead under standard conditions.
For a galvanic cell employing the Cu, Cu2+ and Pb, Pb2+ couples, calculate the maximum amount of work that would accompany the reaction of 1 mol of lead under standard conditions.
A) -90.7 kJ
B) No work can be done. The system is at equilibrium.
C) -40.5 kJ
D) -45.3 kJ
E) none of these
 For a galvanic cell employing the Cu, Cu2+ and Pb, Pb2+ couples, calculate the maximum amount of work that would accompany the reaction of 1 mol of lead under standard conditions.
For a galvanic cell employing the Cu, Cu2+ and Pb, Pb2+ couples, calculate the maximum amount of work that would accompany the reaction of 1 mol of lead under standard conditions.A) -90.7 kJ
B) No work can be done. The system is at equilibrium.
C) -40.5 kJ
D) -45.3 kJ
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Consider the galvanic cell shown below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment).  The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 
What is E° for this cell?
A) 0.36 V
B) 4.40 V
C) 1.79 V
D) 1.82 V
E) 4.75 V
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 
What is E° for this cell?
A) 0.36 V
B) 4.40 V
C) 1.79 V
D) 1.82 V
E) 4.75 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment).  The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 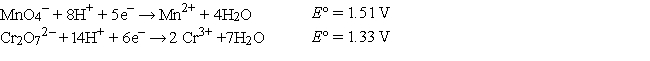
When current is allowed to flow, which species is oxidized?
A) Mn2+
B) Cr3+
C) MnO4-
D) Cr2O72-
E) H+
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 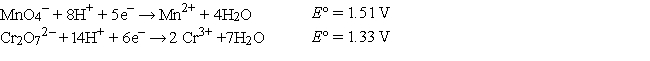
When current is allowed to flow, which species is oxidized?
A) Mn2+
B) Cr3+
C) MnO4-
D) Cr2O72-
E) H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment). 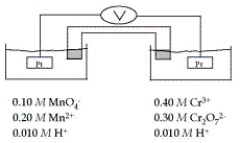 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 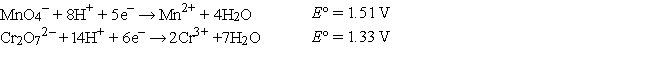
What is the value of E°cell?
A) 2.84 V
B) 0.18 V
C) -0.18 V
D) 1.79 V
E) 2.29 V
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 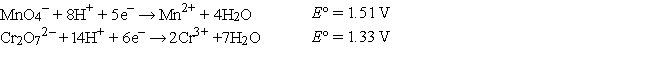
What is the value of E°cell?
A) 2.84 V
B) 0.18 V
C) -0.18 V
D) 1.79 V
E) 2.29 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In which of the following cases must E be equal to zero?
I.In any cell at equilibrium
II.In a concentration cell
III.E° can never be equal to zero.
A) II only
B) I and II
C) III
D) I only
I.In any cell at equilibrium
II.In a concentration cell
III.E° can never be equal to zero.
A) II only
B) I and II
C) III
D) I only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In which of the following cases can E° be equal to zero?
I.In any cell at equilibrium
II.In a concentration cell
III.E° can never be equal to zero.
A) I only
B) III
C) I and II
D) II only
I.In any cell at equilibrium
II.In a concentration cell
III.E° can never be equal to zero.
A) I only
B) III
C) I and II
D) II only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment).  The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 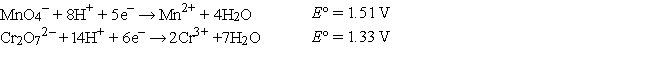
In the balanced cell reaction, what is the stoichiometric coefficient for H+?
A) 5
B) 30
C) 22
D) 2
E) 6
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 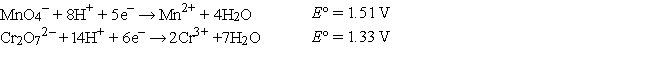
In the balanced cell reaction, what is the stoichiometric coefficient for H+?
A) 5
B) 30
C) 22
D) 2
E) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A concentration cell is constructed using two Ni electrodes with Ni2+ concentrations of 1.66 M and 1.60 × 10-4 M in the two half-cells. The reduction potential of Ni2+ is -0.23 V. Calculate the potential of the cell at 25°C.
A) -0.237 V
B) +0.119 V
C) +0.349 V
D) -0.273 V
E) 0.0073 V
A) -0.237 V
B) +0.119 V
C) +0.349 V
D) -0.273 V
E) 0.0073 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider an electrochemical cell that has a nickel electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ni2+ and a platinum electrode immersed in 0.010 M Co2+. 
Calculate E for this cell.
A) 0.51 V
B) 0.56 V
C) 0.05 V
D) 0.11 V
E) none of these

Calculate E for this cell.
A) 0.51 V
B) 0.56 V
C) 0.05 V
D) 0.11 V
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The standard potential for the reaction A(s) + B3+ (aq)  A3+ (aq) + B (s) is 0.49 V. What is the equilibrium constant K for this reaction at 25°C?
A3+ (aq) + B (s) is 0.49 V. What is the equilibrium constant K for this reaction at 25°C?
A) 0.015
B) 7.7×10-26
C) 17
D) 1.3×1025
E) -17
 A3+ (aq) + B (s) is 0.49 V. What is the equilibrium constant K for this reaction at 25°C?
A3+ (aq) + B (s) is 0.49 V. What is the equilibrium constant K for this reaction at 25°C?A) 0.015
B) 7.7×10-26
C) 17
D) 1.3×1025
E) -17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An excess of finely divided iron is stirred up with a solution that contains Cu2+ ion, and the system is allowed to come to equilibrium. The solid materials are then filtered off, and electrodes of solid copper and solid iron are inserted into the remaining solution. What is the value of the ratio [Fe2+]/[Cu2+] at 25°C?
A) 1
B) 2.5 × 1026
C) 0
D) 4.0 × 10-27
E) none of these
A) 1
B) 2.5 × 1026
C) 0
D) 4.0 × 10-27
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A fuel cell designed to react grain alcohol with oxygen has the following net reaction:
C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
The maximum work that 1 mol of alcohol can yield by this process is 1320 kJ. What is the theoretical maximum voltage this cell can achieve?
A) 1.14 V
B) 2.28 V
C) 13.7 V
D) 2.01 V
E) 0.760 V
C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
The maximum work that 1 mol of alcohol can yield by this process is 1320 kJ. What is the theoretical maximum voltage this cell can achieve?
A) 1.14 V
B) 2.28 V
C) 13.7 V
D) 2.01 V
E) 0.760 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment). 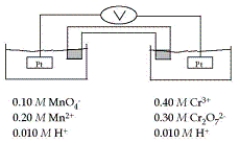 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 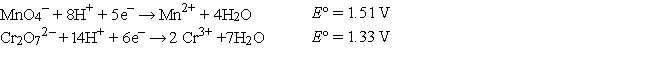
What is the cell potential at 25°C as read on the digital voltmeter?
A) 0.18 V
B) 2.58 V
C) 0.59 V
D) 0.10 V
E) 0.26 V
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 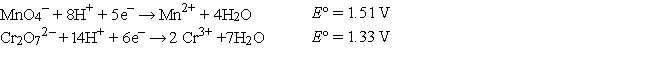
What is the cell potential at 25°C as read on the digital voltmeter?
A) 0.18 V
B) 2.58 V
C) 0.59 V
D) 0.10 V
E) 0.26 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For a reaction in a voltaic cell, both ΔH° and ΔS° are positive. Which of the following statements is true?
A) E°cell will increase with an increase in temperature.
B) E°cell will decrease with an increase in temperature.
C) E°cell will not change when the temperature increases.
D) ΔG° > 0 for all temperatures.
E) None of the above statements is true.
A) E°cell will increase with an increase in temperature.
B) E°cell will decrease with an increase in temperature.
C) E°cell will not change when the temperature increases.
D) ΔG° > 0 for all temperatures.
E) None of the above statements is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Consider an electrochemical cell that has a nickel electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ni2+ and a platinum electrode immersed in 0.010 M Co2+. 
Calculate the concentration of Ni2+ if the cell is allowed to run to equilibrium at 25°C.
A) 1.0 M
B) 1.1 M
C) 1.9 × 10-4 M
D) 0.020 M
E) none of these

Calculate the concentration of Ni2+ if the cell is allowed to run to equilibrium at 25°C.
A) 1.0 M
B) 1.1 M
C) 1.9 × 10-4 M
D) 0.020 M
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If a reducing agent M reacts with an oxidizing agent A+ to give M+ and A, and the equilibrium constant for the reaction is 1.0, then what is the E° value for the oxidation-reduction reaction at 25°C?
A) 0.059 V
B) 1.0 V
C) 0.0 V
D) 0.68 V
E) -1.0 V
A) 0.059 V
B) 1.0 V
C) 0.0 V
D) 0.68 V
E) -1.0 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the galvanic cell shown below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment). 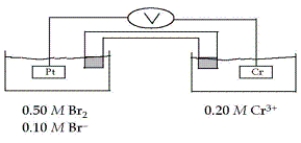 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 
What is the value of E for this cell at 25°C?
A) 1.88 V
B) 2.12 V
C) 1.76 V
D) 2.21 V
E) 0.59 V
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 
What is the value of E for this cell at 25°C?
A) 1.88 V
B) 2.12 V
C) 1.76 V
D) 2.21 V
E) 0.59 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An excess of finely divided iron is stirred up with a solution that contains Cu2+ ion, and the system is allowed to come to equilibrium. The solid materials are then filtered off, and electrodes of solid copper and solid iron are inserted into the remaining solution. What potential develops between these two electrodes at 25°C?
A) 0
B) 0.592 V
C) 0.296 V
D) -0.78 V
E) Not enough information is given.
A) 0
B) 0.592 V
C) 0.296 V
D) -0.78 V
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A cell is set up with copper and lead electrodes in contact with CuSO4(aq) and Pb(NO3)2(aq), respectively, at 25°C. The standard reduction potentials are
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb E° = -0.13 V
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu E° = +0.34 V
If sulfuric acid is added to the Pb(NO3)2 solution, forming a precipitate of PbSO4, the cell potential
A) It is impossible to tell what will happen.
B) decreases.
C) is unchanged.
D) increases.
Pb2+ + 2e- → Pb E° = -0.13 V
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu E° = +0.34 V
If sulfuric acid is added to the Pb(NO3)2 solution, forming a precipitate of PbSO4, the cell potential
A) It is impossible to tell what will happen.
B) decreases.
C) is unchanged.
D) increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consider an electrochemical cell with a copper electrode immersed in 1.0 M Cu2+ and a silver electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ag+. ![<strong>Consider an electrochemical cell with a copper electrode immersed in 1.0 M Cu<sup>2+</sup> and a silver electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ag<sup>+</sup>. If [Cu<sup>2+</sup>]<sub>0</sub> is 0.0038 M and [Ag<sup>+</sup>]<sub>0</sub> is 0.27 M, calculate E.</strong> A) 0.41 V B) 0.50 V C) 0.42 V D) 0.51 V E) 0.59 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6422/11eaaf91_9e0d_bb7a_892c_eb25b03f24ae_TB6422_00.jpg)
If [Cu2+]0 is 0.0038 M and [Ag+]0 is 0.27 M, calculate E.
A) 0.41 V
B) 0.50 V
C) 0.42 V
D) 0.51 V
E) 0.59 V
![<strong>Consider an electrochemical cell with a copper electrode immersed in 1.0 M Cu<sup>2+</sup> and a silver electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ag<sup>+</sup>. If [Cu<sup>2+</sup>]<sub>0</sub> is 0.0038 M and [Ag<sup>+</sup>]<sub>0</sub> is 0.27 M, calculate E.</strong> A) 0.41 V B) 0.50 V C) 0.42 V D) 0.51 V E) 0.59 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6422/11eaaf91_9e0d_bb7a_892c_eb25b03f24ae_TB6422_00.jpg)
If [Cu2+]0 is 0.0038 M and [Ag+]0 is 0.27 M, calculate E.
A) 0.41 V
B) 0.50 V
C) 0.42 V
D) 0.51 V
E) 0.59 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment).  The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 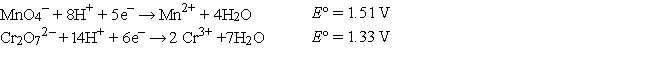
What is the value of Q, the reaction quotient, for this cell reaction?
A) 1.5 × 10-4
B) 6.7 × 103
C) 6.7 × 1040
D) 1.5 × 10-41
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 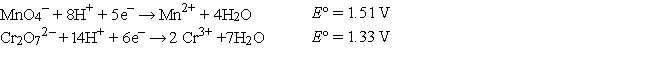
What is the value of Q, the reaction quotient, for this cell reaction?
A) 1.5 × 10-4
B) 6.7 × 103
C) 6.7 × 1040
D) 1.5 × 10-41

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
You make a cell with a copper electrode in a solution of copper nitrate and a silver electrode in a solution of silver nitrate. 
If you could increase the concentration of Cu2+, which of the following would be true about the cell potential?
A) It would remain constant.
B) This cannot be determined.
C) It would increase.
D) It would decrease.

If you could increase the concentration of Cu2+, which of the following would be true about the cell potential?
A) It would remain constant.
B) This cannot be determined.
C) It would increase.
D) It would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Determine the equilibrium constant at 25°C for the reaction
Zn + Ni2+ → Zn2+ + Ni
A) 4.1 × 103
B) 9.3 × 108
C) 8.6 × 1017
D) 6.4 × 10-6
E) none of these
Zn + Ni2+ → Zn2+ + Ni

A) 4.1 × 103
B) 9.3 × 108
C) 8.6 × 1017
D) 6.4 × 10-6
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A galvanic cell is constructed with copper electrodes and Cu2+ in each compartment. In one compartment, [Cu2+] = 2.4 × 10-3 M, and in the other compartment, [Cu2+] = 3.0 M. Calculate the potential for this cell at 25°C. The standard reduction potential for Cu2+ is +0.34 V.
A) 0.77 V
B) 0.092 V
C) -0.092 V
D) -0.43 V
E) 0.43 V
A) 0.77 V
B) 0.092 V
C) -0.092 V
D) -0.43 V
E) 0.43 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A concentration cell is constructed using two Co electrodes with Co2+ concentrations of 0.20 M and 3.6 × 10-5 M in the two half-cells. Determine the standard reduction potential of Co2+, given that the potential of the cell at 25°C is 0.111 V.
A) +0.221 V
B) +0.111 V
C) -0.111 V
D) This cannot be determined with the information given.
E) 0 V
A) +0.221 V
B) +0.111 V
C) -0.111 V
D) This cannot be determined with the information given.
E) 0 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment).  The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 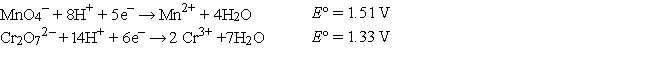
What is the value of the equilibrium constant at 25°C for the net spontaneous cell reaction?
A) 7.3 × 10-11
B) 4.3 × 10-92
C) 1.1 × 103
D) 91
E) 2.3 × 1091
 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 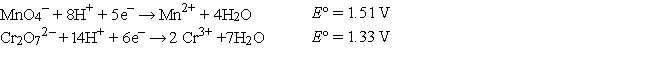
What is the value of the equilibrium constant at 25°C for the net spontaneous cell reaction?
A) 7.3 × 10-11
B) 4.3 × 10-92
C) 1.1 × 103
D) 91
E) 2.3 × 1091

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
You make a cell with a copper electrode in a solution of copper nitrate and a silver electrode in a solution of silver nitrate. 
If you could increase the concentration of Ag+, which of the following would be true about the cell potential?
A) This cannot be determined.
B) It would increase.
C) It would remain constant.
D) It would decrease.

If you could increase the concentration of Ag+, which of the following would be true about the cell potential?
A) This cannot be determined.
B) It would increase.
C) It would remain constant.
D) It would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In a common car battery, six identical cells each carry out the following reaction:
Pb + PbO2 + 2HSO4- + 2H+ → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
Suppose that to start a car on a cold morning, 138 amperes is drawn for 12.0 seconds from such a cell. How many grams of Pb are consumed? (The atomic mass of Pb is 207.19 g/mol.)
A) 0.562 g
B) 7.11 g
C) 1.78 g
D) 0.01235 g
E) 3.56 g
Pb + PbO2 + 2HSO4- + 2H+ → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O
Suppose that to start a car on a cold morning, 138 amperes is drawn for 12.0 seconds from such a cell. How many grams of Pb are consumed? (The atomic mass of Pb is 207.19 g/mol.)
A) 0.562 g
B) 7.11 g
C) 1.78 g
D) 0.01235 g
E) 3.56 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Calculate E at 25°C for this cell, given the following data: 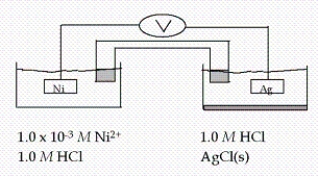 Ag+ + e- → Ag(s) E° = 0.80 V
Ag+ + e- → Ag(s) E° = 0.80 V
Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni(s) E° = -0.23 V
Ksp for AgCl = 1.6 × 10-10
A) 2.98 V
B) This cannot be determined from the data given
C) 0.83 V
D) 1.01 V
E) 0.54 V
 Ag+ + e- → Ag(s) E° = 0.80 V
Ag+ + e- → Ag(s) E° = 0.80 VNi2+ + 2e- → Ni(s) E° = -0.23 V
Ksp for AgCl = 1.6 × 10-10
A) 2.98 V
B) This cannot be determined from the data given
C) 0.83 V
D) 1.01 V
E) 0.54 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Fe2+ + 2e- → Fe(s) E° = -0.440 V
2H+ + 2e- → H2(g) E° = 0.000 V
In a galvanic cell, the iron compartment contains an iron electrode, and [Fe2+] = 1.00 × 10-3 M. The hydrogen compartment contains a platinum electrode (PH2 = 1.00 atm) and a weak acid HA at an initial concentration of 1.00 M. If the observed cell potential is 0.333 V at 25°C, calculate Ka for the weak acid HA at 25°C.
2H+ + 2e- → H2(g) E° = 0.000 V
In a galvanic cell, the iron compartment contains an iron electrode, and [Fe2+] = 1.00 × 10-3 M. The hydrogen compartment contains a platinum electrode (PH2 = 1.00 atm) and a weak acid HA at an initial concentration of 1.00 M. If the observed cell potential is 0.333 V at 25°C, calculate Ka for the weak acid HA at 25°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An antique automobile bumper is to be chrome plated. The bumper, which is dipped into an acidic Cr2O72- solution, serves as a cathode of an electrolytic cell. The atomic mass of Cr is 51.996; 1 faraday = 96,485 coulombs.
If oxidation of H2O occurs at the anode, how many moles of oxygen gas will evolve for every 3.30 × 102 g of Cr(s) deposited?
A) 8.46 mol
B) 9.52 mol
C) 4.23 mol
D) 6.35 mol
E) 3.17 mol
If oxidation of H2O occurs at the anode, how many moles of oxygen gas will evolve for every 3.30 × 102 g of Cr(s) deposited?
A) 8.46 mol
B) 9.52 mol
C) 4.23 mol
D) 6.35 mol
E) 3.17 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A solution of MnO42- is electrolytically reduced to Mn3+. A current of 8.46 amp is passed through the solution for 15.0 minutes. What is the number of moles of Mn3+ produced in this process? (1 faraday = 96,485 coulombs)
A) 0.000438 mol
B) 0.0197 mol
C) 0.0789 mol
D) 0.0395 mol
E) 0.0263 mol
A) 0.000438 mol
B) 0.0197 mol
C) 0.0789 mol
D) 0.0395 mol
E) 0.0263 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If an electrolysis plant operates its electrolytic cells at a total current of 1.0 × 106 amp, how long will it take to produce one metric ton (one million grams) of Mg(s) from seawater containing Mg2+? (1 faraday = 96,485 coulombs)
A) 55 min
B) 3.7 h
C) 2.2 h
D) 1 year
E) 2.4 days
A) 55 min
B) 3.7 h
C) 2.2 h
D) 1 year
E) 2.4 days

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How many seconds would it take to deposit 21.40 g of Ag (atomic mass = 107.87) from a solution of AgNO3 using a current of 10.00 amp?
A) 4825 s
B) 9649 s
C) 3828 s
D) 1914 s
E) none of these
A) 4825 s
B) 9649 s
C) 3828 s
D) 1914 s
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a constant current of 5.2 amperes is passed through a cell containing Cr3+ for 2.1 hour, how many grams of Cr will plate out onto the cathode? (The atomic mass of Cr is 51.996 g/mol.)
A) 0.12 g
B) 1.1 g
C) 64 g
D) 21 g
E) 7.1 g
A) 0.12 g
B) 1.1 g
C) 64 g
D) 21 g
E) 7.1 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What quantity of charge is required to reduce 32.6 g of CrCl3 to chromium metal? (1 faraday = 96,485 coulombs)
A) 3.97 × 104 C
B) 7.95 × 104 C
C) 5.96 × 104 C
D) 1.81 × 105 C
E) 1.99 × 104 C
A) 3.97 × 104 C
B) 7.95 × 104 C
C) 5.96 × 104 C
D) 1.81 × 105 C
E) 1.99 × 104 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following data to calculate the Ksp value at 25°C for PbSO4(s). 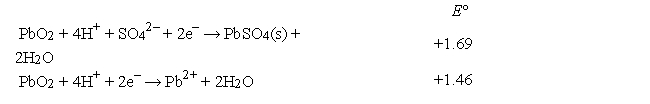
A) 3.89 × 10-105
B) 2.57 × 10105
C) 1.7 × 10-8
D) 5.9 × 107
E) None of these is within 5% of the correct answer.
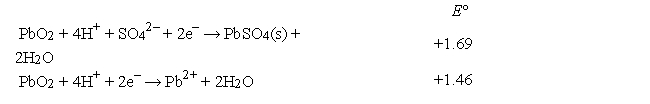
A) 3.89 × 10-105
B) 2.57 × 10105
C) 1.7 × 10-8
D) 5.9 × 107
E) None of these is within 5% of the correct answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An electrolytic cell process involves plating Zr(s) from a solution containing Zr4+. If 5.80 amp is run through this mixture for 1.86 h, what mass of Zr is plated?
A) 36.7 g
B) 9.18 g
C) 0.153 g
D) 0.101 g
E) none of these
A) 36.7 g
B) 9.18 g
C) 0.153 g
D) 0.101 g
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Electrolysis of a molten salt with the formula MCl, using a current of 3.86 amp for 16.2 min, deposits 1.52 g of metal. Identify the metal. (1 faraday = 96,485 coulombs)
A) Rb
B) Na
C) Li
D) Ca
E) K
A) Rb
B) Na
C) Li
D) Ca
E) K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Why is aluminum protected from corrosion? (Note: The standard reduction potential for Al3+ is -1.66 V.)
A) Oxygen and aluminum have no affinity for one another.
B) The oxidation of aluminum is not a favored process, as seen by the standard reduction potential for Al3+.
C) Aluminum forms a protective oxide coating.
D) At least two of these are correct.
E) Aluminum is not protected from corrosion.
A) Oxygen and aluminum have no affinity for one another.
B) The oxidation of aluminum is not a favored process, as seen by the standard reduction potential for Al3+.
C) Aluminum forms a protective oxide coating.
D) At least two of these are correct.
E) Aluminum is not protected from corrosion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Ag+ + e- ? Ag(s) E° = 0.80 V
Cu2+ + 2e- ? Cu(s) E° = 0.34 V
In a galvanic cell, the silver compartment contains a silver electrode and excess AgCl(s) (Ksp = 1.6 × 10-10). The copper compartment contains a copper electrode, and [Cu2+] = 2.0 M.
A. Calculate the potential for this cell at 25°C.
B. Assuming 1.0 L of 2.0 M Cu2+ in the copper compartment, calculate how many moles of NH3 would have to be added to establish the cell potential at 0.52 V at 25°C (assume no volume change on addition of NH3).
Cu2+ + 4NH3![Ag<sup>+</sup> + e<sup>-</sup> ? Ag(s) E° = 0.80 V Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 2e<sup>-</sup> ? Cu(s) E° = 0.34 V In a galvanic cell, the silver compartment contains a silver electrode and excess AgCl(s) (K<sub>sp</sub> = 1.6 × 10<sup>-10</sup>). The copper compartment contains a copper electrode, and [Cu<sup>2+</sup>] = 2.0 M. A. Calculate the potential for this cell at 25°C. B. Assuming 1.0 L of 2.0 M Cu<sup>2+</sup> in the copper compartment, calculate how many moles of NH<sub>3</sub> would have to be added to establish the cell potential at 0.52 V at 25°C (assume no volume change on addition of NH<sub>3</sub>). Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>S1U112+</sup> K<sub>f</sub> = 1.0 ×10<sup>13</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6422/11eaaf91_9e0f_b652_892c_194cf975a8b4_TB6422_11.jpg) Cu(NH3)4S1U112+ Kf = 1.0 ×1013
Cu(NH3)4S1U112+ Kf = 1.0 ×1013
Cu2+ + 2e- ? Cu(s) E° = 0.34 V
In a galvanic cell, the silver compartment contains a silver electrode and excess AgCl(s) (Ksp = 1.6 × 10-10). The copper compartment contains a copper electrode, and [Cu2+] = 2.0 M.
A. Calculate the potential for this cell at 25°C.
B. Assuming 1.0 L of 2.0 M Cu2+ in the copper compartment, calculate how many moles of NH3 would have to be added to establish the cell potential at 0.52 V at 25°C (assume no volume change on addition of NH3).
Cu2+ + 4NH3
![Ag<sup>+</sup> + e<sup>-</sup> ? Ag(s) E° = 0.80 V Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 2e<sup>-</sup> ? Cu(s) E° = 0.34 V In a galvanic cell, the silver compartment contains a silver electrode and excess AgCl(s) (K<sub>sp</sub> = 1.6 × 10<sup>-10</sup>). The copper compartment contains a copper electrode, and [Cu<sup>2+</sup>] = 2.0 M. A. Calculate the potential for this cell at 25°C. B. Assuming 1.0 L of 2.0 M Cu<sup>2+</sup> in the copper compartment, calculate how many moles of NH<sub>3</sub> would have to be added to establish the cell potential at 0.52 V at 25°C (assume no volume change on addition of NH<sub>3</sub>). Cu<sup>2+</sup> + 4NH<sub>3</sub> Cu(NH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>4</sub>S1U112+</sup> K<sub>f</sub> = 1.0 ×10<sup>13</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6422/11eaaf91_9e0f_b652_892c_194cf975a8b4_TB6422_11.jpg) Cu(NH3)4S1U112+ Kf = 1.0 ×1013
Cu(NH3)4S1U112+ Kf = 1.0 ×1013
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Copper is electroplated from an aqueous CuSO4 solution. A constant current of 4.70 amp is applied by an external power supply. How long will it take to deposit 3.76 × 102 g of Cu? The atomic mass of copper is 63.546 g/mol.
A) 33.7 h
B) 101.2 h
C) 2.08 h
D) 67.5 h
E) 135.0 h
A) 33.7 h
B) 101.2 h
C) 2.08 h
D) 67.5 h
E) 135.0 h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Calculate the solubility product of silver iodide at 25°C, given the following data: 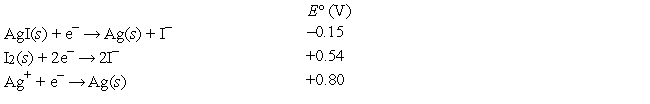
A) 1.9 × 10-4
B) 8.4 × 10-17
C) 3.5 × 10-20
D) 2.9 × 10-3
E) 2.1 × 10-12
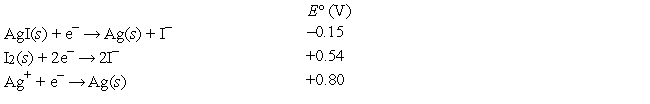
A) 1.9 × 10-4
B) 8.4 × 10-17
C) 3.5 × 10-20
D) 2.9 × 10-3
E) 2.1 × 10-12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An antique automobile bumper is to be chrome plated. The bumper, which is dipped into an acidic Cr2O72- solution, serves as a cathode of an electrolytic cell. The atomic mass of Cr is 51.996; 1 faraday = 96,485 coulombs.
If the current is 18.8 amperes, how long will it take to deposit 1.66 × 102 g of Cr(s) onto the bumper?
A) 27.3 h
B) 13.4 h
C) 45.5 min
D) 18.2 h
E) 54.6 h
If the current is 18.8 amperes, how long will it take to deposit 1.66 × 102 g of Cr(s) onto the bumper?
A) 27.3 h
B) 13.4 h
C) 45.5 min
D) 18.2 h
E) 54.6 h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Gold (atomic mass = 197 g/mol) is plated from a solution of chlorauric acid, HAuCl4; it deposits on the cathode. Calculate the time it takes to deposit 0.55 g of gold, passing a current of 0.12 amperes. (1 faraday = 96,485 coulombs)
A) 0.0018 days
B) 0.62 h
C) 1.9 h
D) 2.5 h
E) 1.2 h
A) 0.0018 days
B) 0.62 h
C) 1.9 h
D) 2.5 h
E) 1.2 h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Nickel is electroplated from a NiSO4 solution. A constant current of 5.72 amp is applied by an external power supply. How long will it take to deposit 2.08 × 102 g of Ni? (The atomic mass of Ni is 58.69 g/mol.)
A) 16.6 h
B) 33.2 h
C) 1.51 h
D) 19.9 min
E) 49.8 h
A) 16.6 h
B) 33.2 h
C) 1.51 h
D) 19.9 min
E) 49.8 h

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Gold is produced electrochemically from an aqueous solution of Au(CN)2- containing an excess of CN-. Gold metal and oxygen gas are produced at the electrodes. How many moles of O2 will be produced during the production of 1.00 mol of gold?
A) 4.00 mol
B) 3.56 mol
C) 0.50 mol
D) 1.00 mol
E) 0.25 mol
A) 4.00 mol
B) 3.56 mol
C) 0.50 mol
D) 1.00 mol
E) 0.25 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



