Deck 23: Metabolism and Energy Production
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/86
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Metabolism and Energy Production
1
The citric acid cycle is used in the oxidation of
A) glucose only.
B) glucose and fatty acids only.
C) fatty acids only.
D) glucose, fatty acids, and proteins.
E) proteins only.
A) glucose only.
B) glucose and fatty acids only.
C) fatty acids only.
D) glucose, fatty acids, and proteins.
E) proteins only.
glucose, fatty acids, and proteins.
2
Which of the following compounds in the citric acid cycle undergoes oxidative decarboxylation?
A) citrate
B) isocitrate
C) succinate
D) fumarate
E) succinyl CoA
A) citrate
B) isocitrate
C) succinate
D) fumarate
E) succinyl CoA
isocitrate
3
FAD is a coenzyme which usually participates in
A) oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes.
B) formation of carbon-carbon double bonds.
C) decarboxylation reactions.
D) phosphorylation reactions.
E) β-oxidation reactions.
A) oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes.
B) formation of carbon-carbon double bonds.
C) decarboxylation reactions.
D) phosphorylation reactions.
E) β-oxidation reactions.
formation of carbon-carbon double bonds.
4
Which coenzyme is the electron acceptor in the following reaction? 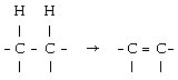
A) FAD
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) NADH
E) FADH₂
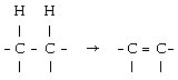
A) FAD
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) NADH
E) FADH₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The transformation of citrate to isocitrate in the citric acid cycle requires two __________ reactions.
A) oxidation
B) reduction
C) hydrolysis
D) decarboxylation
E) dehydration-hydration
A) oxidation
B) reduction
C) hydrolysis
D) decarboxylation
E) dehydration-hydration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Another name for the citric acid cycle is
A) the Krebs cycle.
B) gluconeogenesis.
C) glucose hydrolysis.
D) oxidative phosphorylation.
E) the chemiosmotic pump.
A) the Krebs cycle.
B) gluconeogenesis.
C) glucose hydrolysis.
D) oxidative phosphorylation.
E) the chemiosmotic pump.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Most of the energy released in the citric acid cycle is used to produce
A) glucose.
B) acetyl CoA.
C) NADH and FADH₂.
D) carbon dioxide and water.
E) citric acid.
A) glucose.
B) acetyl CoA.
C) NADH and FADH₂.
D) carbon dioxide and water.
E) citric acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the first reaction of the citric acid cycle
A) glucose becomes pyruvate.
B) ATP is produced.
C) NADH is produced.
D) acetyl CoA reacts with oxaloacetate to give citrate.
E) pyruvate becomes CO₂ and H₂O.
A) glucose becomes pyruvate.
B) ATP is produced.
C) NADH is produced.
D) acetyl CoA reacts with oxaloacetate to give citrate.
E) pyruvate becomes CO₂ and H₂O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
During the first reaction in the citric acid cycle,
A) free CoA is released.
B) acetyl CoA is made.
C) a decarboxylation occurs.
D) a decomposition occurs.
E) ATP is synthesized.
A) free CoA is released.
B) acetyl CoA is made.
C) a decarboxylation occurs.
D) a decomposition occurs.
E) ATP is synthesized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
NAD+ participates in reactions that produce
A) a CH₂ group.
B) a C=O bond.
C) phosphorylation.
D) ADP from ATP.
E) a C-C bond.
A) a CH₂ group.
B) a C=O bond.
C) phosphorylation.
D) ADP from ATP.
E) a C-C bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The citric acid cycle operates only under aerobic conditions because
A) oxygen is a reactant in the citric acid cycle.
B) oxygen is a product of the citric acid cycle.
C) CO₂ is a product of the citric acid cycle.
D) the NADH and FADH₂ produced by the citric acid cycle can only be reoxidized by the electron transport chain.
E) the NAD+ and FAD produced by the citric acid cycle can only be reduced by the electron transport chain.
A) oxygen is a reactant in the citric acid cycle.
B) oxygen is a product of the citric acid cycle.
C) CO₂ is a product of the citric acid cycle.
D) the NADH and FADH₂ produced by the citric acid cycle can only be reoxidized by the electron transport chain.
E) the NAD+ and FAD produced by the citric acid cycle can only be reduced by the electron transport chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is the net reaction for one turn of the citric acid cycle?
A) Acetyl-S-CoA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H₂O → 2 CO₂ + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH₂ + HS-CoA + GTP
B) Pyruvate + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H₂O → 3 CO₂ + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH₂ + GTP
C) Acetyl-S-CoA + NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi → 2 CO₂ + NADH + H+ + FADH₂ + HS-CoA + GTP
D) Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2GDP + 2 Pi + 2H₂O → 2Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + GTP
E) Glucose + 2GDP + 2Pi → 2Lactate + 2GTP
A) Acetyl-S-CoA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H₂O → 2 CO₂ + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH₂ + HS-CoA + GTP
B) Pyruvate + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H₂O → 3 CO₂ + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH₂ + GTP
C) Acetyl-S-CoA + NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi → 2 CO₂ + NADH + H+ + FADH₂ + HS-CoA + GTP
D) Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2GDP + 2 Pi + 2H₂O → 2Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + GTP
E) Glucose + 2GDP + 2Pi → 2Lactate + 2GTP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which coenzyme is the electron acceptor in the following reaction? 
A) FAD
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) NADH
E) FADH₂

A) FAD
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) NADH
E) FADH₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What electron acceptor(s) is(are) used in the citric acid cycle?
A) FAD only
B) NAD+ only
C) NADH + FADH₂ + CoASH
D) FMN
E) NAD+ + FAD
A) FAD only
B) NAD+ only
C) NADH + FADH₂ + CoASH
D) FMN
E) NAD+ + FAD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the three major stages of metabolism includes the citric acid cycle?
A) Stage one
B) Stage two
C) Stage three
A) Stage one
B) Stage two
C) Stage three

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Another name for the citric acid cycle is
A) electron transport.
B) glycolysis.
C) the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle.
D) glucolysis.
E) the transamination pathway.
A) electron transport.
B) glycolysis.
C) the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle.
D) glucolysis.
E) the transamination pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In order to enter the citric acid cycle, pyruvate is first converted to
A) ate.
B) acetaldehyde.
C) citrate.
D) acetyl CoA.
E) ethanol.
A) ate.
B) acetaldehyde.
C) citrate.
D) acetyl CoA.
E) ethanol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The citric acid cycle takes place in the
A) mitochondria.
B) cytosol.
C) cytoplasm.
D) Golgi apparatus.
E) endoplasmic reticulum.
A) mitochondria.
B) cytosol.
C) cytoplasm.
D) Golgi apparatus.
E) endoplasmic reticulum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When oxygen is in plentiful supply in the cell, pyruvate is converted to
A) CoA.
B) acetyl CoA.
C) glucose.
D) lactate.
E) fructose.
A) CoA.
B) acetyl CoA.
C) glucose.
D) lactate.
E) fructose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When combined with electron transport, one turn of the citric acid cycle produces __________ ATP.
A) 24
B) 12
C) 11
D) 14
E) 2
A) 24
B) 12
C) 11
D) 14
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The citric acid cycle step that removes the first CO₂ molecule is a(n)
A) oxidative decarboxylation.
B) reduction.
C) carbonylation.
D) hydrolysis.
E) combination.
A) oxidative decarboxylation.
B) reduction.
C) carbonylation.
D) hydrolysis.
E) combination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Under anaerobic conditions, there is a net production of __________ ATP during glycolysis.
A) zero
B) two
C) four
D) six
E) eight
A) zero
B) two
C) four
D) six
E) eight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the chemiosmotic model, protons circulate through a protein complex called
A) iron-sulfur clusters.
B) FMA.
C) CoA.
D) CoQ.
E) ATP synthase.
A) iron-sulfur clusters.
B) FMA.
C) CoA.
D) CoQ.
E) ATP synthase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In electron transport, the oxidized product from the reaction of FMN + NADH + H+ is
A) CoQ.
B) FMNH₂.
C) FADH.
D) FAD.
E) NAD+.
A) CoQ.
B) FMNH₂.
C) FADH.
D) FAD.
E) NAD+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Step 5 of the citric acid cycle is the hydrolysis of succinyl CoA. In this reaction
A) the energy released is used to make GTP.
B) the energy released is used to make ATP.
C) carbon dioxide is released.
D) α-ketoglutarate is released.
E) the enzyme aconitase is needed.
A) the energy released is used to make GTP.
B) the energy released is used to make ATP.
C) carbon dioxide is released.
D) α-ketoglutarate is released.
E) the enzyme aconitase is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the chemiosmotic model of oxidative phosphorylation, ATP is synthesized as
A) OH- flows through ATP synthase.
B) electrons flow through ATP synthase.
C) Ca2+ flows through ATP synthase.
D) H+ flows through ATP synthase.
E) Na+ flows through ATP synthase.
A) OH- flows through ATP synthase.
B) electrons flow through ATP synthase.
C) Ca2+ flows through ATP synthase.
D) H+ flows through ATP synthase.
E) Na+ flows through ATP synthase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The electron carrier __________ provides two ATP via electron transport.
A) FADH₂
B) NADH
C) NADPH
D) CoASH
E) FNMH₂
A) FADH₂
B) NADH
C) NADPH
D) CoASH
E) FNMH₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In electron transport, the three protein complexes (I, III, and IV)
A) act as proton pumps, which generate a proton gradient.
B) transfer electrons from NAD+ to O₂.
C) transfer electrons from FAD to O₂.
D) act as electron pumps, which generate an electron gradient.
E) act as Ca2+ pumps, which generate a Ca2+ gradient.
A) act as proton pumps, which generate a proton gradient.
B) transfer electrons from NAD+ to O₂.
C) transfer electrons from FAD to O₂.
D) act as electron pumps, which generate an electron gradient.
E) act as Ca2+ pumps, which generate a Ca2+ gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the dehydration of succinate to fumarate in the citric acid cycle, the coenzyme used is
A) CoA.
B) acetyl CoA.
C) NAD+.
D) NADH.
E) FAD.
A) CoA.
B) acetyl CoA.
C) NAD+.
D) NADH.
E) FAD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The GTP formed in step 5 of the citric acid cycle is used to make
A) carbon dioxide.
B) oxygen.
C) water.
D) CoA.
E) ATP.
A) carbon dioxide.
B) oxygen.
C) water.
D) CoA.
E) ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the hydrolysis of succinyl CoA in step 5 of the citric acid cycle, CoA is released as
A) CoA-SH.
B) CoA-OH.
C) CoA-O-.
D) CoA- S-
E) CoA- COO-.
A) CoA-SH.
B) CoA-OH.
C) CoA-O-.
D) CoA- S-
E) CoA- COO-.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The last step in the citric acid cycle converts malate to
A) citrate.
B) isocitrate.
C) succinate.
D) fumarate.
E) oxaloacetate.
A) citrate.
B) isocitrate.
C) succinate.
D) fumarate.
E) oxaloacetate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The process which requires oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water is called
A) fermentation.
B) reduction.
C) decomposition.
D) oxidation.
E) respiration.
A) fermentation.
B) reduction.
C) decomposition.
D) oxidation.
E) respiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Cyanide ion and carbon monoxide inhibit
A) cytochrome c oxidase.
B) ATP production.
C) antibiotic activity.
D) CoQ formation.
E) CoA formation.
A) cytochrome c oxidase.
B) ATP production.
C) antibiotic activity.
D) CoQ formation.
E) CoA formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The components of the electron transport chain do NOT include
A) oxygen (O₂).
B) cytochromes.
C) FMN.
D) CoQ.
E) acetyl CoA.
A) oxygen (O₂).
B) cytochromes.
C) FMN.
D) CoQ.
E) acetyl CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In electron transport, the synthesis of ATP from ADP + Pi is called
A) glycolysis.
B) fermentation.
C) oxidative phosphorylation.
D) isomerization.
E) hydrolysis.
A) glycolysis.
B) fermentation.
C) oxidative phosphorylation.
D) isomerization.
E) hydrolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
One method of regulation of the citric acid cycle is
A) allosteric control.
B) osmosis.
C) temperature control.
D) carbon dioxide production.
E) water concentration.
A) allosteric control.
B) osmosis.
C) temperature control.
D) carbon dioxide production.
E) water concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the third major step of the citric acid cycle, NAD+ is converted to
A) NAS-.
B) NAD2+.
C) NADH₂
D) NAD.
E) NADH.
A) NAS-.
B) NAD2+.
C) NADH₂
D) NAD.
E) NADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In step 7 of the citric acid cycle, fumarate is converted to malate by a __________ reaction.
A) hydrolysis
B) dehydrogenation
C) hydrogenation
D) hydration
E) dehydration
A) hydrolysis
B) dehydrogenation
C) hydrogenation
D) hydration
E) dehydration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following metabolic pathways can occur in the absence of oxygen?
A) electron transport
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) citric acid cycle
D) glycolysis
E) β-oxidation
A) electron transport
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) citric acid cycle
D) glycolysis
E) β-oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
substance 8

substance 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Overall, one turn of the citric acid cycle produces
A) three CO₂ molecules.
B) three NADH molecules.
C) two FADH₂ molecules.
D) 6 ATP.
E) 2 GTP.
A) three CO₂ molecules.
B) three NADH molecules.
C) two FADH₂ molecules.
D) 6 ATP.
E) 2 GTP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
substance 6

substance 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
substance 1

substance 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which is the best choice for the box labeled "Answer" in the illustration below? 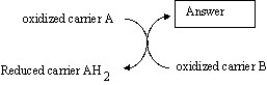
A) oxidized carrier B
B) carbon dioxide
C) OH-
D) reduced carrier BH₂
E) energy

A) oxidized carrier B
B) carbon dioxide
C) OH-
D) reduced carrier BH₂
E) energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
substance 7

substance 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
substance 2

substance 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the correct coefficient for ATP in the complete combustion of glucose? C6H12O6 + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + _____ ATP + 6H₂O
A) 6
B) 12
C) 18
D) 24
E) 36
A) 6
B) 12
C) 18
D) 24
E) 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The energy released during electron transport is used to produce
A) glucose.
B) citric acid.
C) carbon dioxide.
D) ATP.
E) NADH.
A) glucose.
B) citric acid.
C) carbon dioxide.
D) ATP.
E) NADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In glycolysis, glucose produces 2 pyruvate ions and a total of __________ ATP molecules.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 12
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
One example of an electron carrier in the respiratory chain is
A) ATP.
B) GTP.
C) coenzyme Q.
D) citrate.
E) water.
A) ATP.
B) GTP.
C) coenzyme Q.
D) citrate.
E) water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Electron transport is also called
A) the citric acid cycle.
B) β-oxidation.
C) transamination.
D) the respiratory chain.
E) fermentation.
A) the citric acid cycle.
B) β-oxidation.
C) transamination.
D) the respiratory chain.
E) fermentation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The complete oxidation of glucose produces __________ ATP molecules.
A) 2
B) 8
C) 12
D) 24
E) 36
A) 2
B) 8
C) 12
D) 24
E) 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In stage three of metabolism, the overall result is to release
A) glucose and water.
B) lactate and acetyl CoA.
C) lactate and glucose.
D) glycogen and water.
E) carbon dioxide and energy.
A) glucose and water.
B) lactate and acetyl CoA.
C) lactate and glucose.
D) glycogen and water.
E) carbon dioxide and energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
substance 5

substance 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
substance 4

substance 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
substance 3

substance 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is NOT a possible product of pyruvate under anaerobic conditions?
A) lactate
B) acetaldehyde
C) fumarate
D) ethanol
E) CO₂
A) lactate
B) acetaldehyde
C) fumarate
D) ethanol
E) CO₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In electron transport, NADH and FADH₂ are used to provide
A) oxygen.
B) electrons and hydrogen ions.
C) carbon atoms.
D) water and carbon dioxide.
E) thiol groups.
A) oxygen.
B) electrons and hydrogen ions.
C) carbon atoms.
D) water and carbon dioxide.
E) thiol groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The compounds in the respiratory chain that remove hydrogen ions and electrons from NADH are classified as
A) oxidative transporters.
B) osmotic carriers.
C) electron carriers.
D) phosphorylators.
E) citrates.
A) oxidative transporters.
B) osmotic carriers.
C) electron carriers.
D) phosphorylators.
E) citrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The conversion of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate produces 7.3 kcal/mole of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Indicate the amount of ATP produced when each of the following reactions occurs.
complete oxidation of glucose
A)6 ATP
B)2 ATP
C)36 ATP
D)12 ATP
E)3 ATP
complete oxidation of glucose
A)6 ATP
B)2 ATP
C)36 ATP
D)12 ATP
E)3 ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In this figure, depicting part 1 of the Citric Acid Cycle, taken from your text, identify the substances numbered. 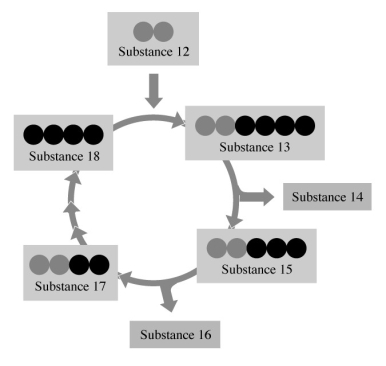
substance 13

substance 13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In this figure, depicting part 1 of the Citric Acid Cycle, taken from your text, identify the substances numbered. 
substance 15

substance 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
NAD+ acts as a hydrogen acceptor in metabolic reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In this figure, depicting part 1 of the Citric Acid Cycle, taken from your text, identify the substances numbered. 
substance 17

substance 17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In reaction 4 of the citric acid cycle, α-ketoglutarase , a five-carbon keto acid, is decarboxylated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
12 ATP are produced when glucose is oxidized to CO₂ and H₂O.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Indicate the amount of ATP produced when each of the following reactions occurs.
glucose → 2 pyruvate under aerobic conditions
A)6 ATP
B)2 ATP
C)36 ATP
D)12 ATP
E)3 ATP
glucose → 2 pyruvate under aerobic conditions
A)6 ATP
B)2 ATP
C)36 ATP
D)12 ATP
E)3 ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In this figure, depicting part 1 of the Citric Acid Cycle, taken from your text, identify the substances numbered. 
substance 18

substance 18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
process 10

process 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Indicate the amount of ATP produced when each of the following reactions occurs.
Acetyl CoA → 2CO₂
A)6 ATP
B)2 ATP
C)36 ATP
D)12 ATP
E)3 ATP
Acetyl CoA → 2CO₂
A)6 ATP
B)2 ATP
C)36 ATP
D)12 ATP
E)3 ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In this figure, depicting part 1 of the Citric Acid Cycle, taken from your text, identify the substances numbered. 
substance 14

substance 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
process 11

process 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In this figure depicting the Stages of Metabolism taken from your text, identify the metabolic substance numbered. 
process 9

process 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In this figure, depicting part 1 of the Citric Acid Cycle, taken from your text, identify the substances numbered. 
substance 16

substance 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In this figure, depicting part 1 of the Citric Acid Cycle, taken from your text, identify the substances numbered. 
substance 12

substance 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
FADH₂ is the oxidized form of FAD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Cyt c is a component of complex IV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The energy levels of complexes decrease as electron transport progresses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 86 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



