Deck 19: Amino Acids and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/103
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Amino Acids and Proteins
1
Wool is primarily made up of
A) protein.
B) carbohydrate.
C) globin.
D) triacylglycerols.
E) enkephalin.
A) protein.
B) carbohydrate.
C) globin.
D) triacylglycerols.
E) enkephalin.
protein.
2
The side chain for histidine is classified as a __________ R group.
A) basic
B) neutral
C) acidic
D) nonpolar
E) polar
A) basic
B) neutral
C) acidic
D) nonpolar
E) polar
basic
3
A basic amino acid has an R group that contains
A) an amine group.
B) a carboxyl group.
C) a methyl group.
D) an alcohol group.
E) a thiol group.
A) an amine group.
B) a carboxyl group.
C) a methyl group.
D) an alcohol group.
E) a thiol group.
an amine group.
4
Amino acids that are not synthesized in the body and must be obtained from the diet are called
A) essential.
B) polar.
C) nonpolar.
D) complete.
E) incomplete.
A) essential.
B) polar.
C) nonpolar.
D) complete.
E) incomplete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following would be most likely to be deficient in at least one essential amino acid?
A) eggs
B) milk
C) beans
D) steak
E) ham
A) eggs
B) milk
C) beans
D) steak
E) ham

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The following amino acid R group chain is 
A) polar.
B) hydrophobic.
C) hydrophilic.
D) acidic.
E) basic.

A) polar.
B) hydrophobic.
C) hydrophilic.
D) acidic.
E) basic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider a mixture of the amino acids lysine (pI = 9.7), tyrosine (pI = 5.7), and glutamic acid (pI = 3.2) at a pH 5.7 that is subjected to an electric current. __________ will remain stationary.
A) Lysine
B) Tyrosine
C) Glutamic acid
D) All of the amino acids
A) Lysine
B) Tyrosine
C) Glutamic acid
D) All of the amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
At a pH > 9, the zwitterion of glycine (pI=6.0) will have
A) a net positive charge.
B) a net negative charge.
C) an overall charge of zero.
D) low solubility in water.
E) a negative charge on the nitrogen.
A) a net positive charge.
B) a net negative charge.
C) an overall charge of zero.
D) low solubility in water.
E) a negative charge on the nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The R group for serine is -CH₂OH. As a zwitterion, serine has the structural formula
A)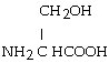
B)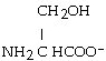
C)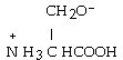
D)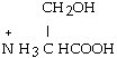
E)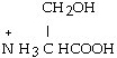
A)
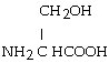
B)
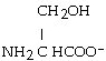
C)
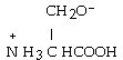
D)
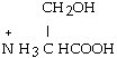
E)
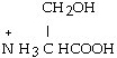

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider a mixture of the amino acids lysine (pI = 9.7), tyrosine (pI = 5.7), and glutamic acid (pI = 3.2) at a pH 5.7 that is subjected to an electric current. __________ will migrate towards the positive electrode(+).
A) Lysine
B) Tyrosine
C) Glutamic acid
D) All of the amino acids
A) Lysine
B) Tyrosine
C) Glutamic acid
D) All of the amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Sucrase, the protein that facilitates the hydrolysis of sucrose, would be classified as a __________ protein.
A) transport
B) hormonal
C) catalytic
D) structural
E) contractile
A) transport
B) hormonal
C) catalytic
D) structural
E) contractile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins?
A) provide structural components
B) stores the genetic information of a living organism
C) movement of muscles
D) catalyze reactions in the cells
E) transport substances through the bloodstream
A) provide structural components
B) stores the genetic information of a living organism
C) movement of muscles
D) catalyze reactions in the cells
E) transport substances through the bloodstream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Collagen, a protein found in tendons and cartilage, would be classified as a __________ protein.
A) catalytic
B) structural
C) transport
D) storage
E) hormone
A) catalytic
B) structural
C) transport
D) storage
E) hormone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The structural formulas of amino acids are the same EXCEPT for the
A) carboxyl group.
B) alpha carbon.
C) amino group.
D) side (R) group.
E) hydrogen bonding.
A) carboxyl group.
B) alpha carbon.
C) amino group.
D) side (R) group.
E) hydrogen bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a typical amino acid zwitterion, the carboxylate end is
A) positively charged.
B) negatively charged.
C) neutral.
D) soluble in a nonpolar solvent.
E) attached to an amine.
A) positively charged.
B) negatively charged.
C) neutral.
D) soluble in a nonpolar solvent.
E) attached to an amine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
At a pH < 5, the zwitterion for alanine (pI = 6) will have
A) a net positive charge.
B) a net negative charge.
C) an overall charge of zero.
D) low solubility in water.
E) a negative charge on the carboxyl group.
A) a net positive charge.
B) a net negative charge.
C) an overall charge of zero.
D) low solubility in water.
E) a negative charge on the carboxyl group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Methionine is an amino acid that contains
A) a sulfur atom.
B) a chlorine atom.
C) a sodium atom.
D) a phenyl ring.
E) a heterocyclic ring.
A) a sulfur atom.
B) a chlorine atom.
C) a sodium atom.
D) a phenyl ring.
E) a heterocyclic ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the structural formula of glutamic acid (pI = 3.2) at pH = 1?
A)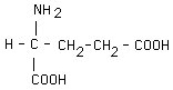
B)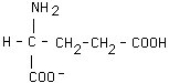
C)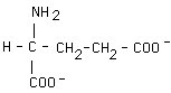
D)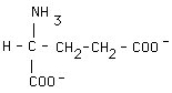
E)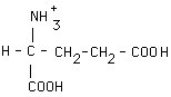
A)

B)
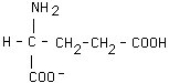
C)
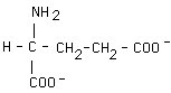
D)
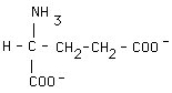
E)
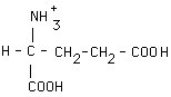

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Glycine is the only naturally occurring amino acid that is
A) negatively charged.
B) positively charged.
C) neutral.
D) in the L- form.
E) achiral.
A) negatively charged.
B) positively charged.
C) neutral.
D) in the L- form.
E) achiral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A completely vegetarian diet will contain all the essential amino acids if it includes
A) wheat and rice.
B) rice and beans.
C) almonds and walnuts.
D) corn and beans.
E) wheat and corn.
A) wheat and rice.
B) rice and beans.
C) almonds and walnuts.
D) corn and beans.
E) wheat and corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The peptide bonds that combine amino acids in a protein are
A) ester bonds.
B) ether bonds.
C) amide bonds.
D) glycosidic bonds.
E) sulfide bonds.
A) ester bonds.
B) ether bonds.
C) amide bonds.
D) glycosidic bonds.
E) sulfide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following functional groups of an amino acid would be in the ionized state at high pH?
A)
B) -CH?OH
C) -CH3
D)
E)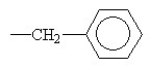
A)
B) -CH?OH
C) -CH3
D)
E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The interactions that are important in the secondary structure of a protein are
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) hydrophobic interactions.
C) disulfide bonds.
D) salt bridges.
E) peptide bonds.
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) hydrophobic interactions.
C) disulfide bonds.
D) salt bridges.
E) peptide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Enkephalins, naturally produced opiates in the body, are found in
A) muscles and bone tissue.
B) brain and kidney tissue.
C) thalamus and spinal cord tissue.
D) heart and lung tissue.
E) pancreas and liver tissue.
A) muscles and bone tissue.
B) brain and kidney tissue.
C) thalamus and spinal cord tissue.
D) heart and lung tissue.
E) pancreas and liver tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A chain made of more than 50 amino acids is usually referred to as a(n)
A) peptide.
B) protein.
C) enzyme.
D) globulin.
E) hormone.
A) peptide.
B) protein.
C) enzyme.
D) globulin.
E) hormone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is the correct structure for Ser-Ala-Asp? The appropriate side chains look like this. Ala: - CH3; Ser: - CH?OH; Asp:
A)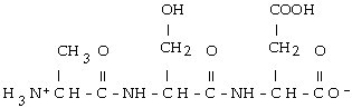
B)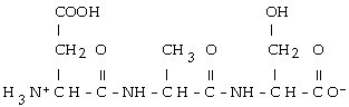
C)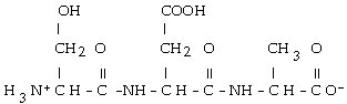
D)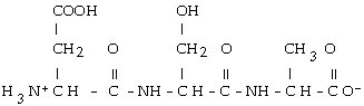
E)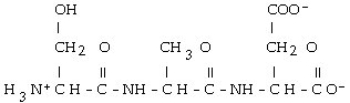
A)

B)

C)
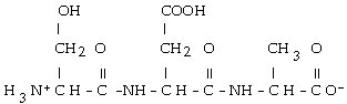
D)

E)
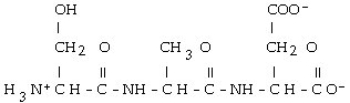

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is an example of a secondary protein structure?
A) dipeptide
B) triglyceride
C) a helix
D) amino acid
E) fatty acid
A) dipeptide
B) triglyceride
C) a helix
D) amino acid
E) fatty acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the peptide Ala-Try-Gly-Phe, the N-terminal amino acid is
A) alanine.
B) phenylalanine.
C) tryptophan.
D) aspartic acid.
E) glycine.
A) alanine.
B) phenylalanine.
C) tryptophan.
D) aspartic acid.
E) glycine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following shows all of the tripeptides that can be formed from one molecule each of glycine (Gly), valine (Val), and leucine (Leu)?
A) Gly-Val-Leu, Gly-Leu-Val, Val-Leu-Gly, Val-Gly-Leu, Leu-Gly-Val, Leu-Val-Gly
B) Gly-Val-Leu, Gly-Leu-Val, Leu-Gly-Val
C) Val-Gly-Leu, Gly-Val-Leu, Gly-Leu-Val, Leu-Gly-Val
D) Val-Gly-Leu, Gly-Leu-Val
E) Gly-Val-Leu
A) Gly-Val-Leu, Gly-Leu-Val, Val-Leu-Gly, Val-Gly-Leu, Leu-Gly-Val, Leu-Val-Gly
B) Gly-Val-Leu, Gly-Leu-Val, Leu-Gly-Val
C) Val-Gly-Leu, Gly-Val-Leu, Gly-Leu-Val, Leu-Gly-Val
D) Val-Gly-Leu, Gly-Leu-Val
E) Gly-Val-Leu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Enkephalins are polypeptides that have
A) a sweet taste.
B) a bitter taste.
C) extra caloric value.
D) pain-killing properties.
E) hormone activity.
A) a sweet taste.
B) a bitter taste.
C) extra caloric value.
D) pain-killing properties.
E) hormone activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A peptide bond contains which kind of functional group?
A) alcohol
B) amine
C) amide
D) carboxylic acid
E) ketone
A) alcohol
B) amine
C) amide
D) carboxylic acid
E) ketone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following shows all of the tripeptides that can be formed from one molecule each of lysine (Lys), threonine (Thr), and histidine (His)?
A) Lys-Thr-His
B) Lys-Thr-His, Lys-His-Thr, His-Thr-Lys, His-Lys-Thr, Thr-Lys-His, Thr-His-Lys
C) Lys-Thr-His, Lys-His-Thr, His-Lys-Thr, Thr-His-Lys
D) Lys-Thr-His, Lys-His-Thr, His-Lys-Thr
E) Lys-Thr-His, Lys-His-Thr
A) Lys-Thr-His
B) Lys-Thr-His, Lys-His-Thr, His-Thr-Lys, His-Lys-Thr, Thr-Lys-His, Thr-His-Lys
C) Lys-Thr-His, Lys-His-Thr, His-Lys-Thr, Thr-His-Lys
D) Lys-Thr-His, Lys-His-Thr, His-Lys-Thr
E) Lys-Thr-His, Lys-His-Thr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The α helix of the secondary structure of a protein is held together by __________ between two widely separated parts of a protein chain.
A) hydrogen bonds
B) disulfide bridges
C) salt bridges
D) hydrophilic interactions
E) hydrophobic interactions
A) hydrogen bonds
B) disulfide bridges
C) salt bridges
D) hydrophilic interactions
E) hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The heme in hemoglobin is a(n)
A) protein chain.
B) small molecule within a protein.
C) helix area in the hemoglobin molecule.
D) pleated sheet area in the hemoglobin molecule.
E) oxygen molecule within the hemoglobin molecule.
A) protein chain.
B) small molecule within a protein.
C) helix area in the hemoglobin molecule.
D) pleated sheet area in the hemoglobin molecule.
E) oxygen molecule within the hemoglobin molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In insulin, two peptide chains are held together in a single unit by
A) disulfide bridges.
B) hydrogen bonds.
C) salt bridges.
D) a prosthetic group.
E) a β-pleated sheet.
A) disulfide bridges.
B) hydrogen bonds.
C) salt bridges.
D) a prosthetic group.
E) a β-pleated sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the β-pleated sheet secondary structure of a protein, two or more amino acid sequences in separate parts of the protein are held together
A) in a coil, by hydrogen bonding.
B) in random order, due to hydrophobic interactions.
C) in a triple helix.
D) in a double helix.
E) in a zig-zag conformation, by hydrogen bonding.
A) in a coil, by hydrogen bonding.
B) in random order, due to hydrophobic interactions.
C) in a triple helix.
D) in a double helix.
E) in a zig-zag conformation, by hydrogen bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The secondary structure of collagen is distinguished by
A) single α helix strands.
B) double α helix strands.
C) many α helixes wound into fibrils.
D) a braided triple helix.
E) many glycoside links.
A) single α helix strands.
B) double α helix strands.
C) many α helixes wound into fibrils.
D) a braided triple helix.
E) many glycoside links.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is a secondary protein structure?
A) α helix
B) Ser-Met-Ala-Gly-Ile
C) disulfide bond
D) salt bridges
E) hydrophobic interactions
A) α helix
B) Ser-Met-Ala-Gly-Ile
C) disulfide bond
D) salt bridges
E) hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Hemoglobin is an example of a protein with
A) primary structure only.
B) two protein chains held together.
C) a globular structure.
D) primarily a β-pleated sheet structure.
E) primarily an α helix structure.
A) primary structure only.
B) two protein chains held together.
C) a globular structure.
D) primarily a β-pleated sheet structure.
E) primarily an α helix structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the peptide Ser-Cys-Ala-Gly, the C-terminal end is
A) serine.
B) serotonin.
C) glycine.
D) glycerine.
E) alanine.
A) serine.
B) serotonin.
C) glycine.
D) glycerine.
E) alanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In sickle-cell anemia, the hemoglobin molecules
A) come apart into separate chains.
B) enlarge to twice normal size.
C) clump together into insoluble fibers.
D) dissolve in the plasma.
E) undergo crenation.
A) come apart into separate chains.
B) enlarge to twice normal size.
C) clump together into insoluble fibers.
D) dissolve in the plasma.
E) undergo crenation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The peptide hormone that regulates uterine contractions during labor is __________.
A) oxytocin
B) vasopressin
C) myoglobin
D) an endorphin
E) an enkephalin
A) oxytocin
B) vasopressin
C) myoglobin
D) an endorphin
E) an enkephalin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Disulfide bonds in a protein chain connect
A) an amine and a carboxylic acid group.
B) an alcohol and a carboxylic acid group.
C) tryptophan and alanine residues.
D) two cysteine residues.
E) two asparagine residues.
A) an amine and a carboxylic acid group.
B) an alcohol and a carboxylic acid group.
C) tryptophan and alanine residues.
D) two cysteine residues.
E) two asparagine residues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Acids and bases denature a protein by disrupting
A) peptide bonds and ionic bonds.
B) amide bonds and alkene bonds
C) hydrophobic interactions and peptide bonds.
D) ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions.
E) ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds.
A) peptide bonds and ionic bonds.
B) amide bonds and alkene bonds
C) hydrophobic interactions and peptide bonds.
D) ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions.
E) ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What type of interaction would you expect between the following R groups in the tertiary structure of a protein? 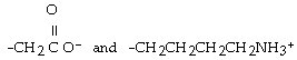
A) disulfide bonds
B) salt bridges
C) hydrogen bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
E) peptide bonds
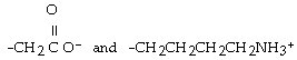
A) disulfide bonds
B) salt bridges
C) hydrogen bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
E) peptide bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The fibrous protein responsible for the structure of hair and wool is
A) keratin.
B) collagen.
C) endorphin.
D) myosin.
E) casein.
A) keratin.
B) collagen.
C) endorphin.
D) myosin.
E) casein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
One heavy metal that can cause denaturation of a protein is
A) silver.
B) sodium.
C) barium.
D) iron.
E) calcium.
A) silver.
B) sodium.
C) barium.
D) iron.
E) calcium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The function of myoglobin is to
A) carry vitamins in the blood.
B) carry oxygen in the blood.
C) support the skeletal muscles.
D) carry oxygen in the muscle.
E) provide strength in cartilage.
A) carry vitamins in the blood.
B) carry oxygen in the blood.
C) support the skeletal muscles.
D) carry oxygen in the muscle.
E) provide strength in cartilage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the R groups of the following amino acids: cysteine: -CH₂SH; alanine: - 3CH3; serine: -CH₂OH
The name for the dipeptide shown below is __________.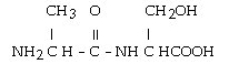
A) alanyl-cysteine
B) alanyl-serine
C) seryl-alanine
D) seryl-cysteine
E) serine-alanine
The name for the dipeptide shown below is __________.
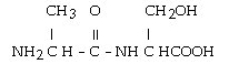
A) alanyl-cysteine
B) alanyl-serine
C) seryl-alanine
D) seryl-cysteine
E) serine-alanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Within hemoglobin, the heme functions as
A) a disulfide bridge.
B) an oxygen carrier.
C) a reducing agent.
D) an α subunit.
E) one of the four protein subunits.
A) a disulfide bridge.
B) an oxygen carrier.
C) a reducing agent.
D) an α subunit.
E) one of the four protein subunits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Denaturation of a protein
A) changes the primary structure of a protein.
B) disrupts the secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
C) is always irreversible.
D) hydrolyzes peptide bonds.
E) can only occur in a protein with quaternary structure.
A) changes the primary structure of a protein.
B) disrupts the secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
C) is always irreversible.
D) hydrolyzes peptide bonds.
E) can only occur in a protein with quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Hemoglobin has a total of __________ protein chains in its quaternary structure.
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What kinds of interactions are NOT part of tertiary protein structure?
A) peptide bonds
B) disulfide bonds
C) hydrophilic interactions
D) salt bridges
E) hydrophobic interactions
A) peptide bonds
B) disulfide bonds
C) hydrophilic interactions
D) salt bridges
E) hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which R group would most likely be found in a hydrophobic area of the tertiary structure of a globular protein?
A) -CH?OH
B) - CH?COO-
C)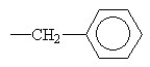
D) - CH?CH?CH?CH? H3
E)
A) -CH?OH
B) - CH?COO-
C)

D) - CH?CH?CH?CH? H3
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
At what pH would you expect valine, an amino acid with a neutral R group, to be in the zwitterionic form?
A) 1
B) 4
C) 7
D) 10
E) 14
A) 1
B) 4
C) 7
D) 10
E) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Heavy metals denature proteins by
A) releasing amino acids.
B) disrupting hydrophobic interactions.
C) changing the pH of the protein solution.
D) changing the temperature of the protein solution.
E) disrupting disulfide bonds.
A) releasing amino acids.
B) disrupting hydrophobic interactions.
C) changing the pH of the protein solution.
D) changing the temperature of the protein solution.
E) disrupting disulfide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An acid can denature a protein by
A) agitating the protein chains.
B) disrupting hydrogen bonds between R groups chains.
C) disrupting hydrophobic interactions within a protein chain.
D) removing helping molecules such as heme.
E) breaking disulfide bridges.
A) agitating the protein chains.
B) disrupting hydrogen bonds between R groups chains.
C) disrupting hydrophobic interactions within a protein chain.
D) removing helping molecules such as heme.
E) breaking disulfide bridges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What amino acids have polar R groups that are attracted to water?
A) hydrophilic
B) hydrophobic
C) nonpolar
D) aromatic
E) hydrocarbon
A) hydrophilic
B) hydrophobic
C) nonpolar
D) aromatic
E) hydrocarbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Heat denatures a protein by disrupting
A) ionic bonds and peptide bonds.
B) hydrophobic bonds and hydrogen bonds.
C) peptide bonds and hydrophobic bonds.
D) disulfide bonds and peptide bonds.
E) hydrogen bonds and disulfide bonds.
A) ionic bonds and peptide bonds.
B) hydrophobic bonds and hydrogen bonds.
C) peptide bonds and hydrophobic bonds.
D) disulfide bonds and peptide bonds.
E) hydrogen bonds and disulfide bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Immunoglobulin, a protein that stimulates immune responses, would be classified as a __________ protein.
A) transport
B) structural
C) storage
D) protection
E) catalytic
A) transport
B) structural
C) storage
D) protection
E) catalytic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The protein that transports oxygen in the blood is __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The isoelectric point for any amino acid is the pH at which the amino acid has a net charge of __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Insulin is a transport protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In an enzyme, the polypeptide chain folds into a compact shape known as the __________ structure.
A) pleated
B) primary
C) secondary
D) tertiary
E) quaternary
A) pleated
B) primary
C) secondary
D) tertiary
E) quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Hemoglobin is a transport protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The dipeptide abbreviated as Gly-Lys is the same as the dipeptide abbreviated as Lys-Gly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Electrophoresis is a laboratory technique for separating amino acids using their different __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In digestion, proteins are broken down into amino acids by a(n) __________ reaction.
A) saponification
B) reduction
C) hydrolysis
D) oxidation
E) denaturation
A) saponification
B) reduction
C) hydrolysis
D) oxidation
E) denaturation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When two protein chains combine to form an active protein, the structural level is __________.
A) pleated
B) primary
C) secondary
D) tertiary
E) quaternary
A) pleated
B) primary
C) secondary
D) tertiary
E) quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Amino acids that are not synthesized in the body but must be ingested with the diet are called __________ amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Proteins that stimulate immune response are known as __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What process occurs when heat, acids, bases, and heavy metal ions cause a loss of biological function of a protein?
A) denaturation
B) saponification
C) hydrogenation
D) amidation
E) esterification
A) denaturation
B) saponification
C) hydrogenation
D) amidation
E) esterification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Sickle-cell anemia is caused by a change in the primary structure of a subunit of the hemoglobin protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A zwitterion of any amino acid has a net charge of __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Hydrophobic interactions help to stabilize the __________ structure(s) of a protein.
A) primary
B) secondary
C) secondary and tertiary
D) tertiary and quaternary
E) secondary and quaternary
A) primary
B) secondary
C) secondary and tertiary
D) tertiary and quaternary
E) secondary and quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Zwitterions have an overall positive charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The peptide sequence Gly-Gly-Gly gives the primary structure of a tripeptide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Write the zwitterion of glycine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Circle the peptide bond in this structure. 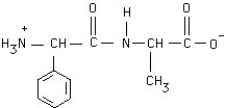


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Collagen can be classified as a __________ protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



