Deck 20: Open-Economy Macroeconomics: the Balance of Payments and Exchange Rates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Open-Economy Macroeconomics: the Balance of Payments and Exchange Rates
1
How can a trade deficit occur?
A trade deficit occurs when a country's exports of goods and services are less than its imports of goods and services in a given period.
2
Compare and contrast a country's balance sheet with its balance of payments.
A balance sheet for a firm or a country measures that entity's stock of assets and liabilities at a moment in time. The balance of payments, by contrast, measures flows, usually over a period of a month, a quarter, or a year. Despite its name, the balance of payments is not a balance sheet.
3
All other things equal what should happen to the value of Japanese yen if there is an increased appetite by Americans for Japanese-produced cars? Does this make Japanese cars more expensive or less expensive? Why?
The increased demand for Japanese-produced cars will increase the demand for the Japanese yen and cause it to appreciate. This effectively means that Japanese cars will become more expensive to American consumers.
4
In 1971, what did most countries do to the exchange rate system in place at the time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the early part of the twentieth century, what backed up nearly all currencies? What did this mean for the average citizen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How is any transaction that causes foreign exchange to leave a country handled on a country's balance of payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Explain how the market for currencies is not that much different from the market for goods or services. Use U.S. dollars and British pounds to illustrate your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What was the correct about the U.S. current account and capital account until about the 1970s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
From a macroeconomic point of view what is the main difference between an international transaction and a domestic transaction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What circumstance gave rise to the creation of the Betton Woods agreement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Assume that Italian citizens buy U.S. bonds. How is this handled on the balance of payments for the U.S.?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How are the exports of a country handled on a country's balance of payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Explain what would happen to the dollar-price of yen if there was an increase in the supply of dollars and an increase in the demand for Japanese yen?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Explain the basic terms of the Bretton Woods agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is a country's balance of trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Give a basic definition of the balance of payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How are the imports of a country handled on a country's balance of payments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Define the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The U.S. demand for foreign exchange arises because its citizens want to buy things whose prices are quoted in other currencies, such as Australian jewelry, vacations in Mexico, and bonds or stocks issued by Sony Corporation of Japan. Whenever U.S. citizens make these purchases, they first buy the foreign currencies and then make the purchases. If that is true then where does the supply of foreign exhange come from?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the current account is in surplus what must be true about the capital account? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Explain what the balance on current account means.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Many transactions get recorded in the capital account that do not pertain to the current account. Consider the purchase of a U.K. security by a U.S. citizen. Explain how this affects one account but not the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the balance on capital account a measure of in the United States?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
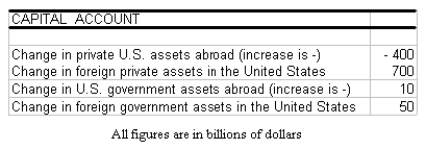
Using the table above calculate the balance on capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose that a Mexican company buys a building in New York City from an American company. Assume that this American company takes the proceeds from this sale and purchases and equal amount of stock in a Mexican based company. How will the effect of these two transactions impact the net wealth position of the U.S.?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider the purchase of a Japanese car by a U.S. citizen. Say that the yen/dollar exchange rate is 100 yen to a dollar and that the yen price of the car is 2.0 million yen, which is $20,000. The U.S. citizen (probably an automobile dealer) takes $20,000, buys 2.0 million yen, and then buys the car. Explain what happends to U.S. imports and the capital account after this transaction and the net wealth position of the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
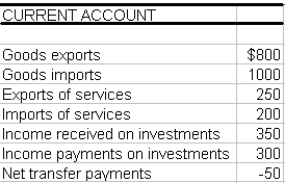
Using the table above calculate the balance on current account.
(1) Net exports of goods $ 800
- 1000
- 200
(2) Net export of services 250
- 200
50
(3) Net investment income 350
300
50
(4) Net transfer payments - 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Identify whether each of the following would lead to an appreciation or depreciation of the dollar. In each case, explain why the currency either appreciates or depreciates.
(a) U.S. citizens switch from buying stock in British companies to buying stock in U.S. companies.
(b) The inflation rate in the United States increases relative to the inflation rate in England.
(c) The money supply is increased in the United States.
(d) Income in the United States increases.
(a) U.S. citizens switch from buying stock in British companies to buying stock in U.S. companies.
(b) The inflation rate in the United States increases relative to the inflation rate in England.
(c) The money supply is increased in the United States.
(d) Income in the United States increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Define net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
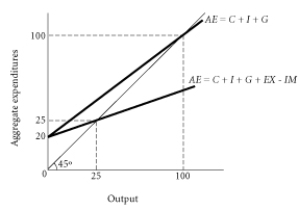
Using the above graph, compute the marginal propensity to consume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If there are no errors of measurement in the data collection, to what must the balance on capital account always be equal? Why is this true?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
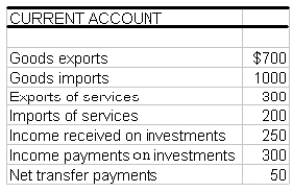
Using the table above calculate the balance on current account.
(1) Net exports of goods $ 700
- 1000
- 300
(2) Net export of services $ 300
- 200
100
(3) Net investment income $ 250
300
- 50
(4) Net transfer payments $ 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What are all of the components of planned aggregate expenditures in an open economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the marginal propensity to import is .1 and there is a $3500 increase in income what impact will this have on imports? Calculate the precise change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the economic meaning of having a positive balance in the capital account for a country?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
All other things equal, what would happen to the level of U.S. exports if its trading partners' economies were to slide into a recession?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Compare the current account position of the U.S. prior to the mid 1970s with what transpired after that and up to the present. Also discuss what happened to its net wealth position in these two time periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Assume planned aggregate expenditures are $240 billion, consumption is $140 billion, investment is $70 billion, government spending is $50 billion. Compute the trade balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Define a nation's balance of payments. Explain the major accounts of a country's balance of payments and explain their relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Assume planned aggregate expenditures are $400 billion, consumption is $120 billion, investment is $60 billion, and government spending is $70 billion. Compute the trade balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If in 2003 the MPM = .15 and there was a $5,000 increase in income, would import spending change? By how much?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Define marginal propensity to import.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If two countries don't trade, what should we expect will happen to the price level in one country when the other country's price level rises?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Define the price feedback effect. Graphically illustrate how the price feedback effect causes the domestic aggregate supply and demand curves to shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Answer the questions below using the following information about the economy of Tumania. Hint: Don't forget about taxes!
C = 100 + .8(Yd)
I = 100
G = 75
T = 60
EX = 50
IM = 40 + .15(Yd)
(a) Determine the equilibrium level of GDP.
(b) What is the government budget deficit?
(c) At this level of equilibrium is there a trade deficit or surplus? What is the amount of deficit or surplus?
(d) What is the open-economy multiplier in this economy?
(e) If government spending increases by 15, what happens to equilibrium GDP? Does the balance of trade situation change when government spending increases?
(f) The country of Tumania experiences a 5% appreciation of its currency. Assume that for every 1% increase in its currency's value, imports increase by 6 units and exports fall by 3 units. How does this currency appreciation affect GDP?
C = 100 + .8(Yd)
I = 100
G = 75
T = 60
EX = 50
IM = 40 + .15(Yd)
(a) Determine the equilibrium level of GDP.
(b) What is the government budget deficit?
(c) At this level of equilibrium is there a trade deficit or surplus? What is the amount of deficit or surplus?
(d) What is the open-economy multiplier in this economy?
(e) If government spending increases by 15, what happens to equilibrium GDP? Does the balance of trade situation change when government spending increases?
(f) The country of Tumania experiences a 5% appreciation of its currency. Assume that for every 1% increase in its currency's value, imports increase by 6 units and exports fall by 3 units. How does this currency appreciation affect GDP?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Why is it that a sustained increase in government spending (or investment) on income is smaller in an open economy than in a closed economy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Explain why there must be a surplus in a country's capital account if the country is running a deficit in its current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why is it in the best interest of the United States when its trading partners' levels of economic activity increase?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Why is it true that when the prices of a country's imports increase, the prices of domestic goods may increase in response? Provide two explanations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How is it possible for an increase in U.S. imports to eventually benefit U.S. exporters? What is this effect called?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Explain the trade feedback effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Calculate the open-economy multiplier where the MPC = .9 and the MPM = .1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53

Using the above graph, compute the marginal propensity to consume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What are a country's export prices generally a function of and how does this affect exportable and nonexportable goods for that country?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Write out the equation for the open-economy multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Compare and contrast the impact on the economy of an increase in government spending in a closed economy to that of an open economy. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Explain why the size of the government spending multiplier is smaller in an open economy than in a closed economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Explain the trade feedback effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Japan imports over 90% of its consumption of oil. If the price of oil increases, what can we expect would happen to Japan's aggregate supply curve and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
You are given the following information about an economy: C = 200 + .75Yd; I = 50; G = 100; EX = 25; IM = .15Yd; and T = 60.
(a) What is the equilibrium level of income?
(b) At the equilibrium level of income is the economy running a trade deficit or trade surplus? What is the amount of the trade deficit or surplus?
(c) What is the open-economy multiplier?
(d) If government spending increases by 100, what will be the change in income? What is the new equilibrium level of income?
(e) At the new equilibrium level of income, what is the level of imports and exports?
(a) What is the equilibrium level of income?
(b) At the equilibrium level of income is the economy running a trade deficit or trade surplus? What is the amount of the trade deficit or surplus?
(c) What is the open-economy multiplier?
(d) If government spending increases by 100, what will be the change in income? What is the new equilibrium level of income?
(e) At the new equilibrium level of income, what is the level of imports and exports?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Give five reasons why demand for a foreign currency may increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What determines a flexible exchange rate between two countries?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain how the size of the multiplier in an open economy is different from the size of the multiplier in a closed economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64

The table above represents a list of private buyers and sellers in international exchange markets in the United States and Mexico. Identify each as either "demanding pesos" or "supplying pesos."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
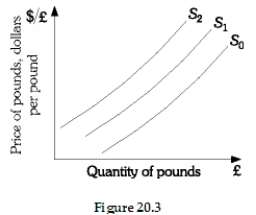
Using the graph above and assuming that we are initially operating on the S1 supply curve, what would be the impact of a decrease in British income?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What are floating exchange rates?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67

Using the graph above and assuming that we are initially operating on the S1 supply curve, what would be the impact if British citizens invested less in the United States?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the expression for planned aggregate expenditures for an open economy? Briefly explain why and how this is different from the expression of planned aggregate expenditures for a closed economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69

Using the graph above and assuming that we are initially operating on the S1 supply curve, what would be the impact if the British price level were to increase?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
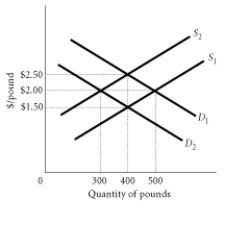
Using the above graph to answer the following question. Assume the demand and supply of pounds are D1 and S1. If the demand shifts to D2 and supply remains unchanged at S1 What will happen to the value of the dollar and the quantity of pounds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
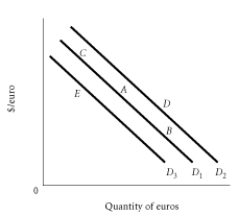
Using the graph above assume the dollar is currently at Point A. A decrease in the price level in the EU will cause a movement to which point?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Definition of equilibrium income Y = AE
(a) Calculate the equilibrium level of income for this economy.
(b) Based on your answer in Part (a), is the country experiencing a trade surplus or deficit? If so, what is the size of the deficit or surplus?
(c) Suppose government spending increases by 100. Calculate what happens to the size of the trade deficit or surplus. Briefly explain any changes in the size of any surplus or deficit.
(d) What is the government spending multiplier?
(e) What is the size of the deficit response index for this economy? Explain.
(a) Calculate the equilibrium level of income for this economy.
(b) Based on your answer in Part (a), is the country experiencing a trade surplus or deficit? If so, what is the size of the deficit or surplus?
(c) Suppose government spending increases by 100. Calculate what happens to the size of the trade deficit or surplus. Briefly explain any changes in the size of any surplus or deficit.
(d) What is the government spending multiplier?
(e) What is the size of the deficit response index for this economy? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Define currency depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74

Using the graph above assume the dollar is currently at Point A. A depreciation of the euro causes a movement to which point?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Define currency appreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76

Draw the supply of Mexican pesos in the foreign exchange market. Assume that the "price" of pesos is in dollars. Explain what happens as the price of the peso rises.
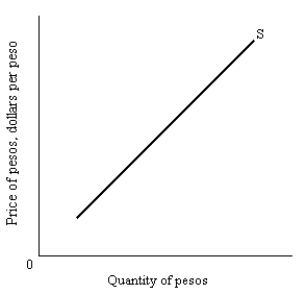

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77

Using the graph above assume the dollar is currently at Point A. An decrease in income in the U.S. will cause a movement to which point?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Explain what effect a fiscal expansion would have in an open economy under flexible exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

Draw a demand for pesos. Assume that the "price" of pesos is in dollars. Explain what happens as the price of the peso falls.
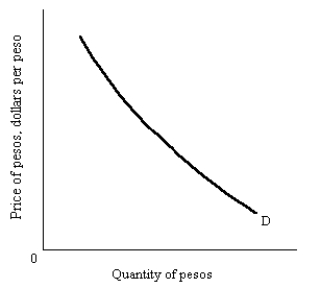

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80

Using the graph above, if the demand and supply of pounds are D1 and S1, identify the equilibrium exchange rate. Explain why a higher or lower exchange rate won't last very long.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



