Deck 44: Quarks, Leptons, and the Big Bang
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 44: Quarks, Leptons, and the Big Bang
1
A particle with spin angular momentum 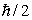 is called a:
is called a:
A) lepton
B) hadron
C) fermion
D) boson
E) electron
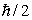 is called a:
is called a:A) lepton
B) hadron
C) fermion
D) boson
E) electron
fermion
2
Which of the following particles is stable?
A) Neutron
B) Proton
C) Pion
D) Muon
E) Kaon
A) Neutron
B) Proton
C) Pion
D) Muon
E) Kaon
Proton
3
Different types of neutrinos can be distinguished from each other by:
A) the directions of their spins
B) the leptons with which they interact
C) the baryons with which they interact
D) the number of photons that accompany them
E) their baryon numbers
A) the directions of their spins
B) the leptons with which they interact
C) the baryons with which they interact
D) the number of photons that accompany them
E) their baryon numbers
the leptons with which they interact
4
The stability of the proton is predicted by the laws of conservation of energy and conservation of:
A) momentum
B) angular momentum
C) baryon number
D) lepton number
E) strangeness
A) momentum
B) angular momentum
C) baryon number
D) lepton number
E) strangeness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A positron cannot decay into three neutrinos. Of the following conservation laws, which would be violated if it did?
A) Energy
B) Baryon number
C) Lepton number
D) Linear momentum
E) Angular momentum
A) Energy
B) Baryon number
C) Lepton number
D) Linear momentum
E) Angular momentum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A particle with spin angular momentum 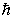 is called a:
is called a:
A) lepton
B) hadron
C) fermion
D) boson
E) electron
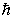 is called a:
is called a:A) lepton
B) hadron
C) fermion
D) boson
E) electron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When a kaon decays via the strong interaction the products must include a:
A) baryon
B) lepton
C) strange particle
D) electron
E) neutrino
A) baryon
B) lepton
C) strange particle
D) electron
E) neutrino

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following particles has a lepton number of zero?
A) e+
B) +
C) ve
D)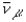
E) p
A) e+
B) +
C) ve
D)
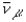
E) p

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following particles has a lepton number of +1?
A) e+
B) +
C) -
D)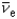
E) p
A) e+
B) +
C) -
D)
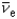
E) p

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
+ represents a pion (a meson), - represents a muon (a lepon), ve represents an electron neutrino (a lepton), and v and p represents a proton a muon neutrino (a lepton). Which of the following decays might occur?
A) + - + v
B) + + + ve
C)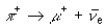
D)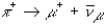
E) + + + v
A) + - + v
B) + + + ve
C)
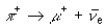
D)
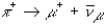
E) + + + v

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The interaction - + p - + + violates the principle of conservation of:
A) baryon number
B) lepton number
C) strangeness
D) angular momentum
E) none of these
A) baryon number
B) lepton number
C) strangeness
D) angular momentum
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An example of a fermion is a:
A) photon
B) pion
C) neutrino
D) kaon
E) none of these
A) photon
B) pion
C) neutrino
D) kaon
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The interaction - + p K- + + violates the principle of conservation of:
A) baryon number
B) lepton number
C) strangeness
D) angular momentum
E) none of these
A) baryon number
B) lepton number
C) strangeness
D) angular momentum
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A particle can decay to particles with greater rest mass:
A) only if antiparticles are produced
B) only if photons are also produced
C) only if neutrinos are also produced
D) only if the original particle has kinetic energy
E) never
A) only if antiparticles are produced
B) only if photons are also produced
C) only if neutrinos are also produced
D) only if the original particle has kinetic energy
E) never

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
All particles with spin angular momentum 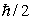 :
:
A) interact via the strong force
B) travel at the speed of light
C) obey the Pauli exclusion principle
D) have non-zero rest mass
E) are charged
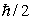 :
:A) interact via the strong force
B) travel at the speed of light
C) obey the Pauli exclusion principle
D) have non-zero rest mass
E) are charged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Strangeness is conserved in:
A) all particle decays
B) no particle decays
C) all weak particle decays
D) all strong particle decays
E) some strong particle decays
A) all particle decays
B) no particle decays
C) all weak particle decays
D) all strong particle decays
E) some strong particle decays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An electron participates in:
A) the strong force only
B) the strong and weak forces only
C) the electromagnetic and gravitational forces only
D) the electromagnetic, gravitational, and weak forces only
E) the electromagnetic, gravitational, and strong forces only
A) the strong force only
B) the strong and weak forces only
C) the electromagnetic and gravitational forces only
D) the electromagnetic, gravitational, and weak forces only
E) the electromagnetic, gravitational, and strong forces only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A neutral muon cannot decay into two neutrinos. Of the following conservation laws, which would be violated if it did?
A) Energy
B) Baryon number
C) Linear Momentum
D) Angular momentum
E) None of the above
A) Energy
B) Baryon number
C) Linear Momentum
D) Angular momentum
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An example of a boson is a:
A) photon
B) electron
C) neutrino
D) proton
E) neutron
A) photon
B) electron
C) neutrino
D) proton
E) neutron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
All leptons interact with each other via the:
A) strong force
B) weak force
C) electromagnetic force
D) strange force
E) none of these
A) strong force
B) weak force
C) electromagnetic force
D) strange force
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The quark content of a + meson is:
A) uu
B)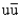
C) ud
D)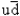
E)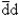
A) uu
B)
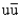
C) ud
D)
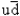
E)
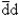

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Two baryons interact to produce pions only, the original baryons disappearing. One of the baryons must have been:
A) a proton
B) an omega minus
C) a sigma
D) an antiparticle
E) none of these
A) a proton
B) an omega minus
C) a sigma
D) an antiparticle
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Two particles interact to produce only photons, with the original particles disappearing. The particles must have been:
A) mesons
B) strange particles
C) strongly interacting
D) leptons
E) a particle, antiparticle pair
A) mesons
B) strange particles
C) strongly interacting
D) leptons
E) a particle, antiparticle pair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Messenger particles of the electromagnetic interaction are called:
A) gluons
B) photons
C) W and Z
D) gravitons
E) pions
A) gluons
B) photons
C) W and Z
D) gravitons
E) pions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Any meson is a combination of:
A) three quarks
B) two quarks and an antiquark
C) one quark and two antiquarks
D) one quark and one antiquark
E) two quarks
A) three quarks
B) two quarks and an antiquark
C) one quark and two antiquarks
D) one quark and one antiquark
E) two quarks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The two basic interactions that have finite ranges are:
A) electromagnetic and gravitational
B) electromagnetic and strong
C) electromagnetic and weak
D) gravitational and weak
E) weak and strong
A) electromagnetic and gravitational
B) electromagnetic and strong
C) electromagnetic and weak
D) gravitational and weak
E) weak and strong

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All known quarks have:
A) charges that are multiples of e and integer baryon numbers
B) charges that are multiples of e and baryon numbers that are either +1/3 or -1/3
C) charges that are multiples of e/3 and integer baryon numbers
D) charges that are multiples of e/3 and baryon numbers that are either +1/3 or -1/3
E) charges that are multiples of 2e/3 and baryon numbers that are either +1/3 or -1/3
A) charges that are multiples of e and integer baryon numbers
B) charges that are multiples of e and baryon numbers that are either +1/3 or -1/3
C) charges that are multiples of e/3 and integer baryon numbers
D) charges that are multiples of e/3 and baryon numbers that are either +1/3 or -1/3
E) charges that are multiples of 2e/3 and baryon numbers that are either +1/3 or -1/3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In order of increasing strength the four basic interactions are:
A) gravitational, weak, electromagnetic, and strong
B) gravitational, electromagnetic, weak, and strong
C) weak, gravitational, electromagnetic, and strong
D) weak, electromagnetic, gravitational, and strong
E) weak, electromagnetic, strong, and gravitational
A) gravitational, weak, electromagnetic, and strong
B) gravitational, electromagnetic, weak, and strong
C) weak, gravitational, electromagnetic, and strong
D) weak, electromagnetic, gravitational, and strong
E) weak, electromagnetic, strong, and gravitational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The up quark u has charge +2e/3 and strangeness 0; the down quark d has charge -e/3 and strangeness 0; the strange quark s has charge -e/3 and strangeness -1. This means there can be no baryon with:
A) charge 0 and strangeness 0
B) charge -e and strangeness -1
C) charge +e and strangeness -1
D) charge +e and strangeness -2
E) charge 0 and strangeness +2
A) charge 0 and strangeness 0
B) charge -e and strangeness -1
C) charge +e and strangeness -1
D) charge +e and strangeness -2
E) charge 0 and strangeness +2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In terms of quark content a beta decay can be written:
A) udd uud + e- +
B) udd udd + dd +
C) udd udd + dd + e-
D) udd uud + ud +
E) udd uud + ud + e- +
A) udd uud + e- +
B) udd udd + dd +
C) udd udd + dd + e-
D) udd uud + ud +
E) udd uud + ud + e- +

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Compared to the lifetimes of particles that decay via the weak interaction, the lifetimes of particles that decay via the strong interaction are:
A) 10-12 times as long
B) 10-23 times as long
C) 1024 times as long
D) 1012 times as long
E) about the same
A) 10-12 times as long
B) 10-23 times as long
C) 1024 times as long
D) 1012 times as long
E) about the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The baryon number of a quark is:
A) 0
B) 1/2
C) 1/3
D) 2/3
E) 1
A) 0
B) 1/2
C) 1/3
D) 2/3
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Any baryon is a combination of:
A) three quarks
B) two quarks and an antiquark
C) one quark and two antiquarks
D) one quark and one antiquark
E) two quarks
A) three quarks
B) two quarks and an antiquark
C) one quark and two antiquarks
D) one quark and one antiquark
E) two quarks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The quark content of a proton is:
A) uuu
B) uud
C) udd
D) ddd
E) uds
A) uuu
B) uud
C) udd
D) ddd
E) uds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A certain process produces baryons that decay with a lifetime of 4 * 10-24 s. The decay is a result of:
A) the gravitational interaction
B) the weak interaction
C) the electromagnetic interaction
D) the strong interaction
E) some combination of the above
A) the gravitational interaction
B) the weak interaction
C) the electromagnetic interaction
D) the strong interaction
E) some combination of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Quarks are the constituents of:
A) all particles
B) all leptons
C) all strongly interacting particles
D) only strange particles
E) only mesons
A) all particles
B) all leptons
C) all strongly interacting particles
D) only strange particles
E) only mesons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A baryon with strangeness 0 decays via the strong interaction into two particles, one of which is a baryon with strangeness +1. The other might be:
A) a baryon with strangeness 0
B) a baryon with strangeness +1
C) a baryon with strangeness -1
D) a meson with strangeness +1
E) a meson with strangeness -1
A) a baryon with strangeness 0
B) a baryon with strangeness +1
C) a baryon with strangeness -1
D) a meson with strangeness +1
E) a meson with strangeness -1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A baryon with strangeness -1 decays via the strong interaction into two particles, one of which is a baryon with strangeness 0. The other might be:
A) a baryon with strangeness 0
B) a baryon with strangeness +1
C) a meson with strangeness -1
D) a meson with strangeness +1
E) a meson with strangeness 0
A) a baryon with strangeness 0
B) a baryon with strangeness +1
C) a meson with strangeness -1
D) a meson with strangeness +1
E) a meson with strangeness 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The up quark u has charge +2/3 and strangeness 0; the down quark d has charge -1/3 and strangeness 0; the strange quark s has charge -1/3 and strangeness -1. This means there can be no meson with:
A) charge 0 and strangeness -1
B) charge -1 and strangeness -1
C) charge +1 and strangeness -1
D) charge -1 and strangeness +1
E) charge 0 and strangeness +1
A) charge 0 and strangeness -1
B) charge -1 and strangeness -1
C) charge +1 and strangeness -1
D) charge -1 and strangeness +1
E) charge 0 and strangeness +1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A certain process produces mesons that decay with a lifetime of 6 * 10-10 s. The decay is a result of:
A) the gravitational interaction
B) the weak interaction
C) the electromagnetic interaction
D) the strong interaction
E) some combination of the above
A) the gravitational interaction
B) the weak interaction
C) the electromagnetic interaction
D) the strong interaction
E) some combination of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The intensity of the microwave background radiation, a remnant of the big bang:
A) is greatest in directions toward the center of the galaxy
B) is leasr in directions toward the center of the galaxy
C) is proportional to the reciprocal of the distance from us
D) is proportional to the square of the distance from us
E) is mearly the same in all directions
A) is greatest in directions toward the center of the galaxy
B) is leasr in directions toward the center of the galaxy
C) is proportional to the reciprocal of the distance from us
D) is proportional to the square of the distance from us
E) is mearly the same in all directions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Messenger particles of the weak interaction are called:
A) gluons
B) photons
C) W and Z
D) gravitons
E) pions
A) gluons
B) photons
C) W and Z
D) gravitons
E) pions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A down quark can be changed into an up quark (plus other particles perhaps) by:
A) the gravitational interaction
B) the electromagnetic interaction
C) the weak interaction
D) the strong interaction
E) none of these
A) the gravitational interaction
B) the electromagnetic interaction
C) the weak interaction
D) the strong interaction
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If dark matter did not exist it is likely that:
A) the universe would expand forever
B) the universe would begin contracting soon
C) the night sky would be brighter
D) the night sky would be darker
E) we would be able to see the center of the universe
A) the universe would expand forever
B) the universe would begin contracting soon
C) the night sky would be brighter
D) the night sky would be darker
E) we would be able to see the center of the universe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The velocities of distant objects in the universe indicate that the time elapsed since the big bang is about:
A) 105 y
B) 1010 y
C) 1015 y
D) 1020 y
E) 1025 y
A) 105 y
B) 1010 y
C) 1015 y
D) 1020 y
E) 1025 y

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Color is carried by:
A) only quarks
B) only leptons
C) only quarks and leptons
D) only quarks and gluons
E) only photons and gluons
A) only quarks
B) only leptons
C) only quarks and leptons
D) only quarks and gluons
E) only photons and gluons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
As a result of the big bang there is, in addition to the microwave background radiation, a uniform distribution of background:
A) electrons
B) quarks
C) gluons
D) neutrinos
E) atoms
A) electrons
B) quarks
C) gluons
D) neutrinos
E) atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Objects in the universe are receding from us with a speed that is proportional to:
A) the reciprocal of their distance from us
B) the reciprocal of the square of their distance from us
C) their distance form us
D) the square of their distance from us
E) their distance from the center of the universe
A) the reciprocal of their distance from us
B) the reciprocal of the square of their distance from us
C) their distance form us
D) the square of their distance from us
E) their distance from the center of the universe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Hubble's law is evidence that:
A) the speed of light is increasing
B) the universe is expanding
C) the Earth is slowing down in its orbit
D) galaxies have rotational motion
E) none of the above
A) the speed of light is increasing
B) the universe is expanding
C) the Earth is slowing down in its orbit
D) galaxies have rotational motion
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The color theory explains why quarks:
A) form particles in pairs and triplets
B) have charge that is a multiple of e/3
C) have spin
D) have mass
E) none of the above
A) form particles in pairs and triplets
B) have charge that is a multiple of e/3
C) have spin
D) have mass
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Dark matter suspected to exist in the universe because:
A) the night sky is dark between stars
B) the orbital period of stars in the outer parts of a galaxy is greater than the orbital period of stars near the galactic center
C) the orbital period of stars in the outer parts of a galaxy is less than the orbital period of stars near the galactic center
D) the orbital period of stars in the outer parts of a galaxy is about the same as the orbital period of stars near the galactic center
E) all galaxies have about the same mass
A) the night sky is dark between stars
B) the orbital period of stars in the outer parts of a galaxy is greater than the orbital period of stars near the galactic center
C) the orbital period of stars in the outer parts of a galaxy is less than the orbital period of stars near the galactic center
D) the orbital period of stars in the outer parts of a galaxy is about the same as the orbital period of stars near the galactic center
E) all galaxies have about the same mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Messenger particles of the strong interaction are called:
A) gluons
B) photons
C) W and Z
D) gravitons
E) pions
A) gluons
B) photons
C) W and Z
D) gravitons
E) pions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



