Deck 20: Wind: a Global Geologic Process
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Wind: a Global Geologic Process
1
How do the dunes at Jockey's Ridge compare the dunes at Death Valley?
A) The dunes at Jockey's Ridge cover a much smaller area.
B) The dunes at Jockey's Ridge cover a much larger area.
C) The dunes at Jockey's Ridge cover about the same area.
A) The dunes at Jockey's Ridge cover a much smaller area.
B) The dunes at Jockey's Ridge cover a much larger area.
C) The dunes at Jockey's Ridge cover about the same area.
A
2
High pressure areas occur when
A) cold air sinks or hot air rises.
B) wind blows.
C) cold air sinks.
D) hot air rises.
A) cold air sinks or hot air rises.
B) wind blows.
C) cold air sinks.
D) hot air rises.
A
3
The world record for the longest period without rainfall occurred in a
A) polar desert.
B) sub-tropical desert.
C) rain-shadow desert.
D) coastal desert.
A) polar desert.
B) sub-tropical desert.
C) rain-shadow desert.
D) coastal desert.
D
4
Wind speed is most closely related to
A) humidity.
B) temperature.
C) landform shapes.
D) pressure.
A) humidity.
B) temperature.
C) landform shapes.
D) pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The largest typical size for grains of sand that can be commonly moved by wind is
A) 5 micrometers.
B) 0.5 millimeter.
C) 1.0 millimeter.
D) 1.0 centimeter.
A) 5 micrometers.
B) 0.5 millimeter.
C) 1.0 millimeter.
D) 1.0 centimeter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Hurricanes coincide with areas of
A) extremely high air pressure where warm, moisture-rich air rises rapidly upward
B) extremely low air pressure where cool, moisture-rich air rises rapidly upward
C) extremely low air pressure where warm, moisture-rich air rises rapidly upward
D) extremely high air pressure where cool, moisture-rich air rises rapidly upward
A) extremely high air pressure where warm, moisture-rich air rises rapidly upward
B) extremely low air pressure where cool, moisture-rich air rises rapidly upward
C) extremely low air pressure where warm, moisture-rich air rises rapidly upward
D) extremely high air pressure where cool, moisture-rich air rises rapidly upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Most deserts are located near
A) 15° latitude.
B) the equator.
C) 30° latitude.
D) 45° latitude.
A) 15° latitude.
B) the equator.
C) 30° latitude.
D) 45° latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which desert is not subtropical?
A) Arabian
B) Sahara
C) Kalahari
D) Namib
A) Arabian
B) Sahara
C) Kalahari
D) Namib

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Deserts coincide with
A) subtropical high-pressure belts.
B) subtropical low-pressure belts.
C) temperate high-pressure zones.
D) temperate low-pressure zones.
A) subtropical high-pressure belts.
B) subtropical low-pressure belts.
C) temperate high-pressure zones.
D) temperate low-pressure zones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Deserts are
A) regions that receive less than 25 centimeters of rain.
B) regions that receive more than 85% daily sunshine.
C) places that are both very hot and very dry due to little rain.
D) any ecosystem underlain by 2 meters or more of sand.
A) regions that receive less than 25 centimeters of rain.
B) regions that receive more than 85% daily sunshine.
C) places that are both very hot and very dry due to little rain.
D) any ecosystem underlain by 2 meters or more of sand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the main difference between rain-shadow deserts and tropical deserts?
A) cause of the lack of precipitation
B) the parent rock type
C) the amount of precipitation
D) the typical vegetation
A) cause of the lack of precipitation
B) the parent rock type
C) the amount of precipitation
D) the typical vegetation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The highest sand dune in Death Valley is about how many stories high?
A) 50
B) 35
C) 15
D) 5
A) 50
B) 35
C) 15
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is not a characteristic of Death Valley National Park?
A) a rare variety of desert lifeforms, including animals such a camels, cacti, jack rabbits, etc.
B) virtually no vegetation
C) widespread fans of stream-transported sand and gravel at the mountain bases
D) a gravitational anomaly due to low topography
A) a rare variety of desert lifeforms, including animals such a camels, cacti, jack rabbits, etc.
B) virtually no vegetation
C) widespread fans of stream-transported sand and gravel at the mountain bases
D) a gravitational anomaly due to low topography

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A sand dune is considered "active" when
A) it is being moved by wind.
B) it is being colonized by new plants.
C) it has been formed by volcanic activity.
D) it is being dissolved into the sea.
A) it is being moved by wind.
B) it is being colonized by new plants.
C) it has been formed by volcanic activity.
D) it is being dissolved into the sea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which condition is least important for wind to have a major effect on landscape?
A) parent rock type
B) frequent strong winds
C) sparse vegetation
D) abundant loose-surface particles
A) parent rock type
B) frequent strong winds
C) sparse vegetation
D) abundant loose-surface particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is not a common cause and effect related to dust?
A) Swirling dust reduces visibility and causes highway accidents.
B) Vegetated land is changed to barren desert by windstorms.
C) Topsoil loses its nutrients and agriculture becomes less productive in a given area.
D) Cities experience hazy skies, even thousands of kilometers from dust storms.
A) Swirling dust reduces visibility and causes highway accidents.
B) Vegetated land is changed to barren desert by windstorms.
C) Topsoil loses its nutrients and agriculture becomes less productive in a given area.
D) Cities experience hazy skies, even thousands of kilometers from dust storms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Plants do not grow on coastal dunes primarily due to
A) lack of moisture.
B) infertility of sand.
C) ocean winds.
D) presence of ocean water.
A) lack of moisture.
B) infertility of sand.
C) ocean winds.
D) presence of ocean water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which is not a common characteristic of places where large sand dunes form?
A) hot year-round climate
B) blowing wind
C) an abundance of loose sand
D) very little vegetation
A) hot year-round climate
B) blowing wind
C) an abundance of loose sand
D) very little vegetation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
"Globally, varying air pressures result from large-scale air circulation driven by heating and cooling." Evaluate this statement.
A) It is true; air pressure increases as hot air rises and pushes against cooler air masses.
B) It is partially true; however, Earth's rotation also plays an important part.
C) It is partially true; however, it is much more complicated due to ocean currents.
D) It is false; varying air pressure is caused solely by Earth's rotation and ocean currents.
A) It is true; air pressure increases as hot air rises and pushes against cooler air masses.
B) It is partially true; however, Earth's rotation also plays an important part.
C) It is partially true; however, it is much more complicated due to ocean currents.
D) It is false; varying air pressure is caused solely by Earth's rotation and ocean currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not part of dust?
A) mineral particles
B) water molecules
C) pollen and spores
D) microbes
A) mineral particles
B) water molecules
C) pollen and spores
D) microbes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Yardangs form from
A) sedimentary rock, which is strong enough to stay standing but soft enough to abrade.
B) metamorphic rock, which is strong enough to withstand extensive abrasion without being completely eroded and swept away.
C) igneous intrusions, which are left standing after sedimentary rock around it has been eroded.
D) volcanic rock, which is soft and easily abraded.
A) sedimentary rock, which is strong enough to stay standing but soft enough to abrade.
B) metamorphic rock, which is strong enough to withstand extensive abrasion without being completely eroded and swept away.
C) igneous intrusions, which are left standing after sedimentary rock around it has been eroded.
D) volcanic rock, which is soft and easily abraded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Crescent-shaped dunes formed where the amount of sand is outweighed by gravel and bedrock are
A) parabolic dunes.
B) barchan dunes.
C) transverse dunes.
D) star dunes.
A) parabolic dunes.
B) barchan dunes.
C) transverse dunes.
D) star dunes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
"Air masses that move over deserts are dry." Evaluate this statement.
A) This statement is true.
B) This statement is partially true; however, rain-shadow deserts carry moist coastal air across the desert without dropping the moisture from the air mass.
C) This statement is partially true; coastal deserts often have large wet-air masses move over them, but the air mass does not drop moisture.
D) This statement is false.
A) This statement is true.
B) This statement is partially true; however, rain-shadow deserts carry moist coastal air across the desert without dropping the moisture from the air mass.
C) This statement is partially true; coastal deserts often have large wet-air masses move over them, but the air mass does not drop moisture.
D) This statement is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which type of desert involves an air mass moving inward from the ocean?
A) subtropical desert
B) rain-shadow desert
C) coastal desert
D) polar desert
A) subtropical desert
B) rain-shadow desert
C) coastal desert
D) polar desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Geologists best estimate the shear stress applied to erosion by wind by measuring
A) the depth of the air mass.
B) the density of the air mass.
C) the average particle size carried by the wind.
D) the velocity of the wind.
A) the depth of the air mass.
B) the density of the air mass.
C) the average particle size carried by the wind.
D) the velocity of the wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How do sand dunes and ventifacts on Mars compare to sand dunes and ventifacts on Earth?
A) They are much larger.
B) They are shaped differently due to the composition of the Martian surface.
C) They are considerably smaller.
D) They are the same.
A) They are much larger.
B) They are shaped differently due to the composition of the Martian surface.
C) They are considerably smaller.
D) They are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How does loess typically change the shape of a landscape?
A) It piles up and sediments into mesas.
B) It blankets the landscape, then is easily eroded into deep canyons.
C) It piles up in a way that creates hills and valleys.
D) It does not change the shape of the landscape.
A) It piles up and sediments into mesas.
B) It blankets the landscape, then is easily eroded into deep canyons.
C) It piles up in a way that creates hills and valleys.
D) It does not change the shape of the landscape.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A pan is
A) an area in the desert where water has caused a depression.
B) a flat bench at the top of a sand dune caused by deflation.
C) an elliptical or circular depression caused by deflation.
D) a scoop shape in a dune caused by a stream of water.
A) an area in the desert where water has caused a depression.
B) a flat bench at the top of a sand dune caused by deflation.
C) an elliptical or circular depression caused by deflation.
D) a scoop shape in a dune caused by a stream of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Wind most commonly picks up particles by
A) shear force.
B) flow force.
C) abrasion.
D) plucking.
A) shear force.
B) flow force.
C) abrasion.
D) plucking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Wind velocity is typically highest at the sediment surface where
A) the surface has a steep slope.
B) the surface is near an ocean or large lake.
C) the surface is smooth with no plants.
D) there is smooth rock instead of sand.
A) the surface has a steep slope.
B) the surface is near an ocean or large lake.
C) the surface is smooth with no plants.
D) there is smooth rock instead of sand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which type of desert involves an air mass moving outward to the ocean?
A) subtropical desert
B) rain-shadow desert
C) coastal desert
D) polar desert
A) subtropical desert
B) rain-shadow desert
C) coastal desert
D) polar desert

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A playa, with its deposits of gypsum and halite, may form in a
A) yardang.
B) ventifact.
C) deflation.
D) pan.
A) yardang.
B) ventifact.
C) deflation.
D) pan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Deflation is derived from a Latin word meaning
A) to erode.
B) to blow away.
C) to lose volume.
D) to abrade or scrape.
A) to erode.
B) to blow away.
C) to lose volume.
D) to abrade or scrape.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
"Made by wind" is the meaning of the Latin root of the word
A) yardang.
B) ventifact.
C) deflation.
D) pan.
A) yardang.
B) ventifact.
C) deflation.
D) pan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Dunes that form in places where vegetation anchors some of the sand and therefore limits the sand supply are
A) parabolic dunes.
B) barchan dunes.
C) transverse dunes.
D) linear dunes.
A) parabolic dunes.
B) barchan dunes.
C) transverse dunes.
D) linear dunes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Tiny products of volcanic eruptions may remain aloft in the atmosphere for
A) up to six months.
B) up to three years.
C) about ten years.
D) about fifteen years.
A) up to six months.
B) up to three years.
C) about ten years.
D) about fifteen years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 20.9 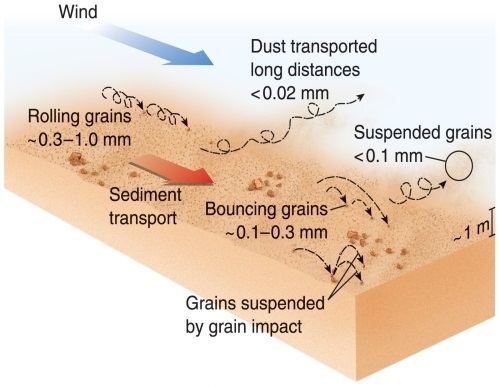
According to Figure 20.9 in your textbook, sediment grains that are about 0.1 to 0.3 millimeters will
A) roll.
B) bounce.
C) be suspended.
D) travel great distances.

According to Figure 20.9 in your textbook, sediment grains that are about 0.1 to 0.3 millimeters will
A) roll.
B) bounce.
C) be suspended.
D) travel great distances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Where are inactive sand dunes most common in the United States?
A) Pacific Northwest
B) Southeast
C) High Plains region
D) the windy Midwest
A) Pacific Northwest
B) Southeast
C) High Plains region
D) the windy Midwest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A grain size of 0.1 millimeter typically requires a wind speed of ________ in order to be picked up.
A) 1 kilometer per hour
B) 5 kilometers per hour
C) 8 kilometers per hour
D) 15 kilometers per hour
A) 1 kilometer per hour
B) 5 kilometers per hour
C) 8 kilometers per hour
D) 15 kilometers per hour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A sediment grain that bounces typically dislodges
A) one other sediment grain.
B) two or three more sediment grains.
C) ten more sediment grains.
D) twenty more sediment grains.
A) one other sediment grain.
B) two or three more sediment grains.
C) ten more sediment grains.
D) twenty more sediment grains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the summer, dust in the Southeast is red. This is due to
A) iron oxide minerals.
B) organic content.
C) clay minerals.
D) aluminum.
A) iron oxide minerals.
B) organic content.
C) clay minerals.
D) aluminum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Spring dust has its highest concentrations in the American
A) northwest.
B) southwest.
C) northeast.
D) southeast.
A) northwest.
B) southwest.
C) northeast.
D) southeast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Convective motion in the atmosphere is approximately ________ times faster than convective motion in the mantle.
A) 2,500,000,000
B) 100,000
C) 2,500,000
D) 2,500
A) 2,500,000,000
B) 100,000
C) 2,500,000
D) 2,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is not a natural process that could be involved in the creation of desert pavement?
A) dissolving and precipitation of sand minerals
B) wind blowing away sand, silt, and dust
C) rain washing fine dust downward
D) shrinking and swelling of silica minerals
A) dissolving and precipitation of sand minerals
B) wind blowing away sand, silt, and dust
C) rain washing fine dust downward
D) shrinking and swelling of silica minerals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Dust from Africa is most commonly found in the American
A) northwest.
B) southwest.
C) northeast.
D) southeast.
A) northwest.
B) southwest.
C) northeast.
D) southeast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Judge the following sentence according to the criteria given below: Deserts are arid regions with little precipitation because high temperatures lead to the evaporation of water.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Judge the following sentence according to the criteria given below: The temperature and moisture effects on air density commonly work together, because warm air can hold more moisture than cold air.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is true about loess and river valleys?
A) Loess deposits tend to be thinner and sandier close to river valleys.
B) Loess deposits tend to be thinner and less sandy close to river valleys.
C) Loess deposits tend to be thicker and sandier close to river valleys.
D) Loess deposits tend to be thicker and less sandy close to river valleys.
A) Loess deposits tend to be thinner and sandier close to river valleys.
B) Loess deposits tend to be thinner and less sandy close to river valleys.
C) Loess deposits tend to be thicker and sandier close to river valleys.
D) Loess deposits tend to be thicker and less sandy close to river valleys.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 20.23 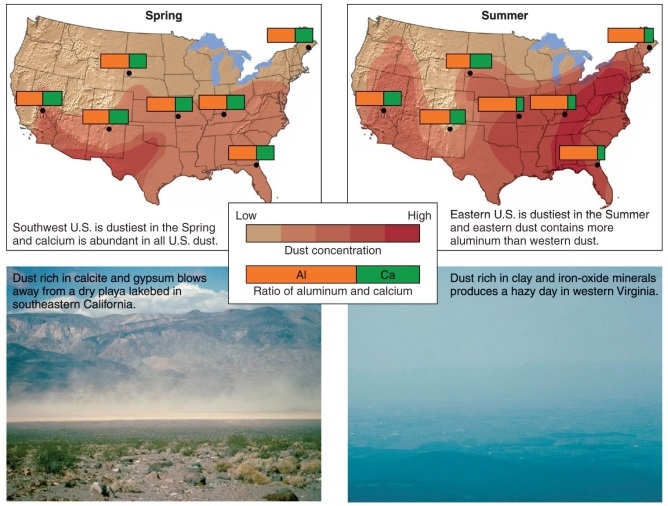
According to Figure 20.23 in your textbook, scientists trace dust origins by analyzing
A) mineral particles.
B) pollen grains.
C) microbe DNA.
D) element concentrations.

According to Figure 20.23 in your textbook, scientists trace dust origins by analyzing
A) mineral particles.
B) pollen grains.
C) microbe DNA.
D) element concentrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Dust that causes hazy days in the Southeastern United States comes from
A) northern South America.
B) the southeastern United States.
C) southern South America.
D) Africa.
A) northern South America.
B) the southeastern United States.
C) southern South America.
D) Africa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Plankton that cause poisonous red tide are nourished by
A) carbon.
B) calcium.
C) iron.
D) potassium.
A) carbon.
B) calcium.
C) iron.
D) potassium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not a source of dust in the United States?
A) Asian deserts
B) African deserts
C) South American deserts
D) other planets
A) Asian deserts
B) African deserts
C) South American deserts
D) other planets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The dunes that form where wind erosion attacks a barren area in a largely vegetated landscape are called
A) transverse dunes.
B) barchan dunes.
C) parabolic dunes.
D) star dunes.
A) transverse dunes.
B) barchan dunes.
C) parabolic dunes.
D) star dunes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In coastal areas you would expect ________ winds during the day and ________ during the night.
A) onshore, offshore
B) onshore, onshore
C) offshore, offshore
D) offshore, onshore
A) onshore, offshore
B) onshore, onshore
C) offshore, offshore
D) offshore, onshore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Long sand ridges oriented parallel to the prevailing wind direction are called
A) transverse dunes.
B) linear dunes.
C) parabolic dunes.
D) star dunes.
A) transverse dunes.
B) linear dunes.
C) parabolic dunes.
D) star dunes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Hurricanes coincide with areas of extremely ________.
A) low air temperature
B) high air temperature
C) low air pressure
D) high air pressure
A) low air temperature
B) high air temperature
C) low air pressure
D) high air pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Global wind patterns are a result of all of the following except
A) temperature driven convection.
B) evaporation and condensation of water vapor.
C) Earth's rotation.
D) Earth's magnetic field.
A) temperature driven convection.
B) evaporation and condensation of water vapor.
C) Earth's rotation.
D) Earth's magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What region of the United States has the highest summer dust concentrations?
A) northwest
B) southwest
C) northeast
D) southeast
A) northwest
B) southwest
C) northeast
D) southeast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Motion in the atmosphere is called
A) climate.
B) wind.
C) convection.
D) wave.
A) climate.
B) wind.
C) convection.
D) wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The greater the difference in air pressure, the ________.
A) more horizontal the wind direction
B) more vertical the wind direction
C) faster the wind speed
D) slower the wind speed
A) more horizontal the wind direction
B) more vertical the wind direction
C) faster the wind speed
D) slower the wind speed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How do polar deserts exist?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What are ventifacts?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The majority of Earth's deserts form as ________ deserts.
A) subtropical
B) rain-shadow
C) coastal
D) polar
A) subtropical
B) rain-shadow
C) coastal
D) polar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Warm moist air cools as it moves ________ in the atmosphere.
A) north
B) south
C) east
D) west
E) higher
A) north
B) south
C) east
D) west
E) higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why do wind directions not remain the same year round?
A) The Coriolis effect is a seasonal effect.
B) Lower air pressure over the continents in the summer.
C) Land and ocean surfaces heat evenly.
D) Atmospheric convection only occurs in the summer.
A) The Coriolis effect is a seasonal effect.
B) Lower air pressure over the continents in the summer.
C) Land and ocean surfaces heat evenly.
D) Atmospheric convection only occurs in the summer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Global wind patterns are the summed-up effects of all of the following except
A) rain, freezing rain and snowfall.
B) atmospheric convection.
C) Earth's rotation.
D) seasonal variation in solar heating.
E) uneven heating of land and sea.
A) rain, freezing rain and snowfall.
B) atmospheric convection.
C) Earth's rotation.
D) seasonal variation in solar heating.
E) uneven heating of land and sea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The cooling of rising air is due to a decrease in
A) pressure.
B) temperature.
C) motion.
D) volume.
A) pressure.
B) temperature.
C) motion.
D) volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Judge the following sentence according to the criteria given below. Evidence for the erosion and modification of the landscape by the wind is not seen everywhere in desert climates because some places in the desert lack vegetation and have strong winds.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
________ are a seasonal phenomena that occurs when moist air is drawn onto a continent from the adjacent ocean.
A) Hurricanes
B) Typhoons
C) Monsoons
D) Tsunami
A) Hurricanes
B) Typhoons
C) Monsoons
D) Tsunami

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Polar deserts form above ________ degrees north or south latitude.
A) 0
B) 15
C) 30
D) 45
E) 60
A) 0
B) 15
C) 30
D) 45
E) 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The Coriolis effect shifts moving objects to the ________ of their initial path in the northern hemisphere and to the ________ in the southern hemisphere.
A) right, right
B) right, left
C) left, left
D) left, right
A) right, right
B) right, left
C) left, left
D) left, right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which parcel of air has the lowest pressure?
A) warm moist air
B) warm dry air
C) cold moist air
D) cold dry air
A) warm moist air
B) warm dry air
C) cold moist air
D) cold dry air

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
How is it possible that coastal deserts exist in such a close proximity to ocean moisture?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Subtropical deserts form close to ________ degrees north or south latitude.
A) 0
B) 15
C) 30
D) 45
E) 60
A) 0
B) 15
C) 30
D) 45
E) 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which parcel of air has the highest pressure?
A) warm moist air
B) warm dry air
C) cold moist air
D) cold dry air
A) warm moist air
B) warm dry air
C) cold moist air
D) cold dry air

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Judge the following sentence according to the criteria given below. Motion in the atmosphere is fundamentally different from motion in the mantle because the atmosphere moves by convective motion and the mantle moves by conductive motion.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
It is unusual for the wind to move grains larger than ________ in diameter.
A) 0.05 mm
B) 0.5 mm
C) 5 mm
D) 0.5 cm
A) 0.05 mm
B) 0.5 mm
C) 5 mm
D) 0.5 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is deflation? Why can deflation not continue beneath the water table?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What does the Coriolis effect do?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Judge the following sentence according to the criteria given below. Grains are easier to move in water than air because the grains effectively weigh less in water than in air.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



