Deck 16: Streams: Flowing Water Shapes the Landscape
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Streams: Flowing Water Shapes the Landscape
1
In terms of the hydrologic cycle, where is precipitation generally greatest?
A) over wide, flat areas
B) near mountainous regions
C) over canyons
D) over lakes
A) over wide, flat areas
B) near mountainous regions
C) over canyons
D) over lakes
B
2
What causes the formation of distributary channels?
A) The stream clogs as the coarsest bedload is deposited.
B) The stream loses power as it widens.
C) The stream joins an ocean, sea, reservoir, or lake.
D) The stream meets an area where the underlying rock is much harder than the rock before it.
A) The stream clogs as the coarsest bedload is deposited.
B) The stream loses power as it widens.
C) The stream joins an ocean, sea, reservoir, or lake.
D) The stream meets an area where the underlying rock is much harder than the rock before it.
A
3
A landform produced by a sudden deposition of sediment where a stream enters a lake, reservoir, or sea is called
A) an alluvial fan.
B) a delta.
C) a distributary channel.
D) a bar.
A) an alluvial fan.
B) a delta.
C) a distributary channel.
D) a bar.
B
4
Which of the following is not a difference between the Mississippi River Basin and the Great Basin?
A) One empties into the ocean and the other does not.
B) One has more streams than the other.
C) One is much larger than the other.
D) One experiences evaporation and the other does not.
A) One empties into the ocean and the other does not.
B) One has more streams than the other.
C) One is much larger than the other.
D) One experiences evaporation and the other does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A piece of gravel in a stream is least likely to experience which motion?
A) sliding along the floor
B) bouncing along the floor
C) whirling in an eddy
D) rolling along the floor
A) sliding along the floor
B) bouncing along the floor
C) whirling in an eddy
D) rolling along the floor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A decrease in stream power can cause all of the following except
A) channel deepening.
B) a delta.
C) an alluvial fan.
D) migrating shorelines.
A) channel deepening.
B) a delta.
C) an alluvial fan.
D) migrating shorelines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 16.7 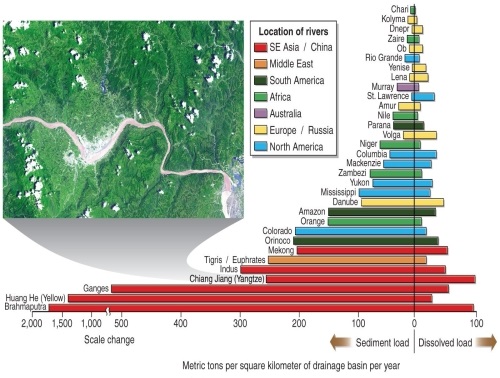
According to Figure 16.7 in your textbook, which river carries the greatest sediment load in North America?
A) the Columbia
B) the Mackenzie
C) the Mississippi
D) the Colorado

According to Figure 16.7 in your textbook, which river carries the greatest sediment load in North America?
A) the Columbia
B) the Mackenzie
C) the Mississippi
D) the Colorado

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
________ has the most rivers with high sediment loads.
A) North America
B) South America
C) Southeast Asia/China
D) Europe/Russia
A) North America
B) South America
C) Southeast Asia/China
D) Europe/Russia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Choose the option that sequences the loads in order from smallest particles to largest.
A) dissolved, bed, suspended
B) dissolved, suspended, bed
C) suspended, dissolved, bed
D) suspended, bed, dissolved
A) dissolved, bed, suspended
B) dissolved, suspended, bed
C) suspended, dissolved, bed
D) suspended, bed, dissolved

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Study Figure 16.10 in your textbook. Choose the option that puts the particles in order from greatest shear stress required to first move them from a stream bed, to least shear stress first required to move them from a stream bed.
A) 0.1 mm sand grain, 0.01 mm silt grain, 10 mm gravel grain, 0.001 mm clay grain
B) 0.001 mm clay grain, 10 mm gravel grain, 0.1 mm sand grain, 0.01 mm silt grain
C) 0.001 mm clay grain, 10 mm gravel grain, 0.01 mm silt grain, 0.1 mm sand grain
D) 10 mm gravel grain, 0.001 mm clay grain, 0.01 mm silt grain, 0.1 mm sand grain
A) 0.1 mm sand grain, 0.01 mm silt grain, 10 mm gravel grain, 0.001 mm clay grain
B) 0.001 mm clay grain, 10 mm gravel grain, 0.1 mm sand grain, 0.01 mm silt grain
C) 0.001 mm clay grain, 10 mm gravel grain, 0.01 mm silt grain, 0.1 mm sand grain
D) 10 mm gravel grain, 0.001 mm clay grain, 0.01 mm silt grain, 0.1 mm sand grain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For most streams, bank full discharge occurs
A) daily.
B) about once per month.
C) about once every 2 years.
D) about once every 75 years.
A) daily.
B) about once per month.
C) about once every 2 years.
D) about once every 75 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How does a river "pluck" particles?
A) hammer-like action of particles against the particles that are lodged in the side of river canyons
B) force of water rushing against particles in solid rock
C) scouring action of particles around the rock which encloses the rock that is plucked
D) shear stress of water against joints and cracks
A) hammer-like action of particles against the particles that are lodged in the side of river canyons
B) force of water rushing against particles in solid rock
C) scouring action of particles around the rock which encloses the rock that is plucked
D) shear stress of water against joints and cracks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Drainage basins are separated from one another by
A) divides.
B) tributaries.
C) headwaters.
D) playa.
A) divides.
B) tributaries.
C) headwaters.
D) playa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
All of these factors must decrease in order for a stream to deposit sediment except
A) shear stress.
B) velocity.
C) power.
D) volume.
A) shear stress.
B) velocity.
C) power.
D) volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Why might one river have a much greater dissolved load than another river?
A) faster flow rate
B) nature of the sediment-forming rock
C) fewer meanders and a broader basin
D) a narrow channel just before the sea
A) faster flow rate
B) nature of the sediment-forming rock
C) fewer meanders and a broader basin
D) a narrow channel just before the sea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why is a stream able to pick up a grain of sand, but not a smaller grain of silt?
A) Gravity forces the silt to remain on the ground.
B) Certain patterns of water flow work better for larger particles.
C) Adhesion keeps the silt particles attached to the rock below.
D) Cohesion keeps the silt particles attached to each other.
A) Gravity forces the silt to remain on the ground.
B) Certain patterns of water flow work better for larger particles.
C) Adhesion keeps the silt particles attached to the rock below.
D) Cohesion keeps the silt particles attached to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which factor must increase in order for a river to pick up larger particles?
A) velocity
B) viscosity
C) shear stress
D) water depth
A) velocity
B) viscosity
C) shear stress
D) water depth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Sediment is deposited in a stream when
A) stream power is less than required to move the sediment carried in from upstream.
B) stream power is equal to bedload.
C) bedload is greater than stream power.
D) stream power is greater than required to move the sediment carried in from upstream.
A) stream power is less than required to move the sediment carried in from upstream.
B) stream power is equal to bedload.
C) bedload is greater than stream power.
D) stream power is greater than required to move the sediment carried in from upstream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An example of land use planning is a floodway. What is a floodway?
A) The areas near a river that are developed with buildings, but far enough away from the river to avoid damage during a flood.
B) Areas along a stream or river that are developed, and the buildings sustain flood damage during bad floods.
C) Areas of little or no development alongside a stream that are wide enough and low enough to carry the predicted discharge of the 100-year flood.
D) Both B and C.
A) The areas near a river that are developed with buildings, but far enough away from the river to avoid damage during a flood.
B) Areas along a stream or river that are developed, and the buildings sustain flood damage during bad floods.
C) Areas of little or no development alongside a stream that are wide enough and low enough to carry the predicted discharge of the 100-year flood.
D) Both B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How is stream power calculated?
A) multiply average flow velocity and volume of flow
B) multiply shear stress and average flow velocity
C) divide shear stress by average flow velocity
D) divide average flow velocity by volume of flow
A) multiply average flow velocity and volume of flow
B) multiply shear stress and average flow velocity
C) divide shear stress by average flow velocity
D) divide average flow velocity by volume of flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 16.20 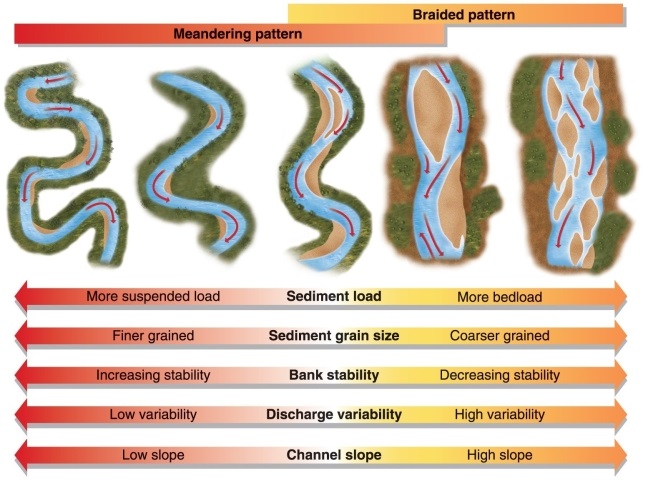
Using Figure 16.20 in your textbook, which statement comparing stream patterns is true?
A) A braided pattern is less stable and more variable than a meandering pattern.
B) A braided pattern is more stable and has coarser sediment grains than a meandering pattern.
C) A braided pattern is less stable and has finer sediment grains than a meandering pattern.
D) A braided pattern is less stable and has a lower slope than a meandering pattern.

Using Figure 16.20 in your textbook, which statement comparing stream patterns is true?
A) A braided pattern is less stable and more variable than a meandering pattern.
B) A braided pattern is more stable and has coarser sediment grains than a meandering pattern.
C) A braided pattern is less stable and has finer sediment grains than a meandering pattern.
D) A braided pattern is less stable and has a lower slope than a meandering pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
During a flood, which factor does not decrease further away from the channel during a flood?
A) height of the levee formed
B) grain size of sediment deposited
C) amount of bedload deposited
D) amount of suspended load deposited
A) height of the levee formed
B) grain size of sediment deposited
C) amount of bedload deposited
D) amount of suspended load deposited

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the recurrence interval that is considered acceptable by insurers for development on flood plains?
A) 10 years
B) 50 years
C) 100 years
D) 500 years
A) 10 years
B) 50 years
C) 100 years
D) 500 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the base level of a stream?
A) the elevation along a smooth concave-up profile
B) the elevation at its lowest point
C) the elevation at the headwaters
D) the elevation where it touches the bedrock
A) the elevation along a smooth concave-up profile
B) the elevation at its lowest point
C) the elevation at the headwaters
D) the elevation where it touches the bedrock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A smooth concave-up profile suggests that a river
A) is flowing quickly.
B) is flowing slowly.
C) has many meanders due to changes in bedrock type.
D) is well adjusted to its sediment load and discharge.
A) is flowing quickly.
B) is flowing slowly.
C) has many meanders due to changes in bedrock type.
D) is well adjusted to its sediment load and discharge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A(n) ________ is formed on a floodplain when ground water seeps into a cutoff channel of a meandering river.
A) cutoff lake
B) cutbank
C) oxbow lake
D) natural levee
A) cutoff lake
B) cutbank
C) oxbow lake
D) natural levee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
To make the data fall into a line that can be analyzed for a 100-year flood, scientists use
A) stream elevation data.
B) nonlinear axes.
C) polar graph paper.
D) rounded-off estimates of time intervals.
A) stream elevation data.
B) nonlinear axes.
C) polar graph paper.
D) rounded-off estimates of time intervals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is not a reason that grain size of sediment tends to decrease downstream?
A) gravity
B) abrasion
C) decreasing shear force
D) rounding
A) gravity
B) abrasion
C) decreasing shear force
D) rounding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The area where the flow is faster and deeper around the outside of a channel bend is called
A) a cutbank.
B) a meander.
C) a point bar.
D) a braid.
A) a cutbank.
B) a meander.
C) a point bar.
D) a braid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How are natural levees formed?
A) Bedload rises up over river banks during high floods.
B) Suspended load is deposited when the river covers the floodplain.
C) Minerals precipitate at the sides of rivers when the water is at bankfull level.
D) Cementing action occurs at the sides of streams as a result of the high velocity of the water.
A) Bedload rises up over river banks during high floods.
B) Suspended load is deposited when the river covers the floodplain.
C) Minerals precipitate at the sides of rivers when the water is at bankfull level.
D) Cementing action occurs at the sides of streams as a result of the high velocity of the water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
You are walking along a stream and you find small, smooth grains and sediment, that is very well-sorted. What can you deduce from this observation?
A) The sediment has traveled a short way, and the water that deposited it stopped moving very quickly.
B) The sediment has traveled a long way, and the water that deposited it stopped moving very slowly.
C) The sediment has traveled a short way, and the water that deposited it stopped moving very slowly.
D) The sediment has traveled a long way, and the water that deposited it stopped moving very quickly.
A) The sediment has traveled a short way, and the water that deposited it stopped moving very quickly.
B) The sediment has traveled a long way, and the water that deposited it stopped moving very slowly.
C) The sediment has traveled a short way, and the water that deposited it stopped moving very slowly.
D) The sediment has traveled a long way, and the water that deposited it stopped moving very quickly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which appears to be the best method of living near floodplains?
A) Using sandbags to block incoming water when floods occur.
B) Effective land use planning.
C) Build houses that will effectively block floodwaters.
D) It is best not to live near floodplains at all.
A) Using sandbags to block incoming water when floods occur.
B) Effective land use planning.
C) Build houses that will effectively block floodwaters.
D) It is best not to live near floodplains at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Where does a point bar accumulate?
A) on the outside of a meander
B) between distributary channels
C) at the outer ends of a delta
D) on the inside of a meander
A) on the outside of a meander
B) between distributary channels
C) at the outer ends of a delta
D) on the inside of a meander

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In terms of the 100-year flood area, estimates of water depth calculations generated by computer models are uncertain. Evaluate the impact of this fact on insurers of landowners residing near that area.
A) Insurers can rely on the calculations of the depth of the 100-year flood and need not investigate further.
B) Though the difference in depth is likely only a small amount, it may cover a large area of land because the land has a very low slope.
C) Computer calculations are not considered as reliable as observations, therefore insurers do not accept these estimates.
D) Landowners should only build outside the 500-year flood area, as the 100-year flood could happen at any time and insurers will not insure properties within that area.
A) Insurers can rely on the calculations of the depth of the 100-year flood and need not investigate further.
B) Though the difference in depth is likely only a small amount, it may cover a large area of land because the land has a very low slope.
C) Computer calculations are not considered as reliable as observations, therefore insurers do not accept these estimates.
D) Landowners should only build outside the 500-year flood area, as the 100-year flood could happen at any time and insurers will not insure properties within that area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In a channel, where is flow velocity the fastest?
A) near the inside of a meander
B) next to the outside bank of a meander
C) in the middle of a curve
D) near the outside bank of a meander
A) near the inside of a meander
B) next to the outside bank of a meander
C) in the middle of a curve
D) near the outside bank of a meander

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
________ would not increase the intensity of a flash flood.
A) Steep slopes
B) Paved ground
C) A narrow bedrock canyon
D) A broad alluvial fan
A) Steep slopes
B) Paved ground
C) A narrow bedrock canyon
D) A broad alluvial fan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A student in the field is taking observational notes about a stream and postulates, "This stream must be shallower and slower downstream." Evaluate this statement.
A) The statement could be true if the stream was also narrower.
B) The statement is false because streams always deepen as they proceed downstream.
C) The statement is probably false because discharge always increases as streams proceed downstream.
D) The statement is probably true, especially if the stream has a sandy bottom.
A) The statement could be true if the stream was also narrower.
B) The statement is false because streams always deepen as they proceed downstream.
C) The statement is probably false because discharge always increases as streams proceed downstream.
D) The statement is probably true, especially if the stream has a sandy bottom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What increases the severity of a prolonged flood?
A) decreased size of drainage basin
B) increased porous subsurface material
C) increased saturation of the ground
D) fewer tributary streams with large drainage basins of their own
A) decreased size of drainage basin
B) increased porous subsurface material
C) increased saturation of the ground
D) fewer tributary streams with large drainage basins of their own

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 16.28 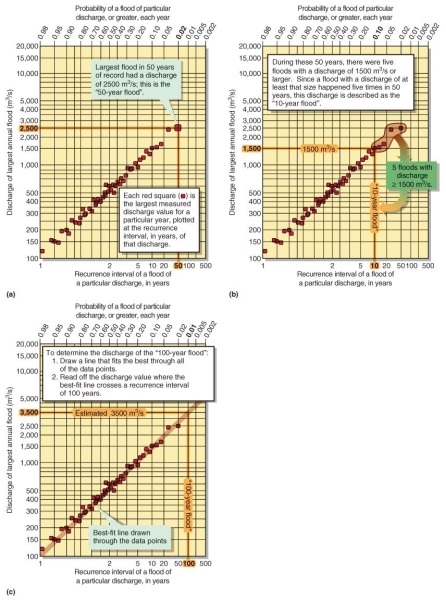
Using Figure 16.28 in your textbook, a flood level that occurred five times in 50 years is known as
A) a 5-year flood.
B) a 10-year flood.
C) a 25-year flood.
D) a 50-year flood.

Using Figure 16.28 in your textbook, a flood level that occurred five times in 50 years is known as
A) a 5-year flood.
B) a 10-year flood.
C) a 25-year flood.
D) a 50-year flood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which is not an effect resulting from dam construction on a river?
A) sediment deposition above the dam
B) erosion of the channel bed below the dam
C) increased sediment build-up below the dam
D) bank stabilization below the dam
A) sediment deposition above the dam
B) erosion of the channel bed below the dam
C) increased sediment build-up below the dam
D) bank stabilization below the dam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The effect of climate on sediment load is a result on the interaction of all of the following factors except
A) the vegetative cover.
B) the steepness of slopes.
C) the amount of precipitation.
D) the amount of sediment produced by weathering.
A) the vegetative cover.
B) the steepness of slopes.
C) the amount of precipitation.
D) the amount of sediment produced by weathering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Streamload that floats in the water column is called
A) float load.
B) suspended load.
C) column load.
D) roll load.
A) float load.
B) suspended load.
C) column load.
D) roll load.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When sea levels rise,
A) fresh water on Earth also increases and streams are generally more full.
B) fresh water on Earth has flowed into the oceans, so streams are generally less full.
C) base levels of river profiles where they reach the sea fall.
D) base levels of river profiles where they reach the sea rise.
A) fresh water on Earth also increases and streams are generally more full.
B) fresh water on Earth has flowed into the oceans, so streams are generally less full.
C) base levels of river profiles where they reach the sea fall.
D) base levels of river profiles where they reach the sea rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Deep Springs Lake in California does not have an outlet because
A) of surrounding topography.
B) of the rock type that forms the base of the lake.
C) evaporation keeps the lake from filling up.
D) rain does not fall on the lake, so it does not fill up.
A) of surrounding topography.
B) of the rock type that forms the base of the lake.
C) evaporation keeps the lake from filling up.
D) rain does not fall on the lake, so it does not fill up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
With regards to particle transport by streams, the resisting forces include all of the following except
A) water depth.
B) particle weight.
C) friction with its neighbors.
D) cohesion with its neighbors.
A) water depth.
B) particle weight.
C) friction with its neighbors.
D) cohesion with its neighbors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Why does water released from a dam erode the streambed so much more than it would have before the dam existed?
A) It has a greatly increased velocity.
B) It has more stream power than it would have had before the dam.
C) The dry stream bed below the dam weakens while it is left dry.
D) The stream power now exceeds the sediment load by a great amount.
A) It has a greatly increased velocity.
B) It has more stream power than it would have had before the dam.
C) The dry stream bed below the dam weakens while it is left dry.
D) The stream power now exceeds the sediment load by a great amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A stream increases its channel slope as it moves downstream. If the water depth remains the same or decreases slightly, this stream will
A) deposit some of its sediment load due to a decrease in shear stress.
B) erode additional sediment load due to an increase in shear stress.
C) continue to carry the same sediment load as there is no change in shear stress.
D) deposit some of its sediment load due to a increase in shear stress.
E) erode additional sediment load due to an decrease in shear stress.
A) deposit some of its sediment load due to a decrease in shear stress.
B) erode additional sediment load due to an increase in shear stress.
C) continue to carry the same sediment load as there is no change in shear stress.
D) deposit some of its sediment load due to a increase in shear stress.
E) erode additional sediment load due to an decrease in shear stress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Judge the following sentence according to the criteria given below. Sediment loads are largest in areas of steep relief because river slopes are steeper and steep valley walls are more prone to mass movement.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.
A) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
B) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
C) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Sediment deposits that form when stream flow abruptly changes from a confined channel to being unconfined are called
A) abrupt deposits.
B) unconfined fans.
C) gravel deposits.
D) alluvial fans.
A) abrupt deposits.
B) unconfined fans.
C) gravel deposits.
D) alluvial fans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Streams that flow through channels cut in solid rock are called ________ streams.
A) local
B) alluvial
C) channel
D) bedrock
A) local
B) alluvial
C) channel
D) bedrock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which option correctly describes an effect of human activity on a river channel?
A) If logging and clearing have increased the sediment load, the channel may fill and the banks may become higher.
B) If logging and clearing have increased the amount of runoff, the channel may fill and the banks may become higher.
C) If agriculture and building have decreased the amount of runoff, the channel may erode further and the banks will become lower.
D) If agriculture and building have increased the sediment load, the channel may erode further and the banks will become lower.
A) If logging and clearing have increased the sediment load, the channel may fill and the banks may become higher.
B) If logging and clearing have increased the amount of runoff, the channel may fill and the banks may become higher.
C) If agriculture and building have decreased the amount of runoff, the channel may erode further and the banks will become lower.
D) If agriculture and building have increased the sediment load, the channel may erode further and the banks will become lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A student makes the conclusion, "When a lot of precipitation falls, streams get deeper as a result." Evaluate this statement.
A) The statement is completely true.
B) The statement is usually true, unless there is a landslide in the stream.
C) The statement is true only when the precipitation does not bring a lot of new sediment into the stream.
D) The statement is false.
A) The statement is completely true.
B) The statement is usually true, unless there is a landslide in the stream.
C) The statement is true only when the precipitation does not bring a lot of new sediment into the stream.
D) The statement is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Streams transport ions in solution as
A) dissolved load.
B) sediment load.
C) bed load.
D) drainage.
A) dissolved load.
B) sediment load.
C) bed load.
D) drainage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is not an evaporite mineral left by dried-up lakes?
A) borax
B) halite
C) chlorite
D) gypsum
A) borax
B) halite
C) chlorite
D) gypsum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The town of Thistle in Utah was submerged by a lake formed by
A) excessive rainfall.
B) a dam formed by a lava flow from a volcano.
C) a dam formed by a landslide.
D) a human-made dam.
A) excessive rainfall.
B) a dam formed by a lava flow from a volcano.
C) a dam formed by a landslide.
D) a human-made dam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The world's rivers with the largest dissolved load occur in
A) Africa.
B) South America.
C) Asia.
D) North America.
E) Europe.
A) Africa.
B) South America.
C) Asia.
D) North America.
E) Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a great amount of precipitation falls on the drainage basin of a river that is surrounded by well-established trees, what is likely to happen?
A) The base level of the profile will rise.
B) The slope of the base level of the stream profile will increase.
C) The slope of the base level of the stream profile will decrease.
D) The base level of the profile will be lowered.
A) The base level of the profile will rise.
B) The slope of the base level of the stream profile will increase.
C) The slope of the base level of the stream profile will decrease.
D) The base level of the profile will be lowered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Where is the most mature soil found on a stream terrace formation?
A) on the highest-elevation terrace
B) on the lowest-elevation terrace
C) soil age is mixed throughout the terraces
D) under the densest layer of vegetation
A) on the highest-elevation terrace
B) on the lowest-elevation terrace
C) soil age is mixed throughout the terraces
D) under the densest layer of vegetation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is a playa?
A) a lake caused by a human dam
B) a lake caused by a natural dam
C) a lake above 8,000 feet in elevation
D) a salty, shallow lake
A) a lake caused by a human dam
B) a lake caused by a natural dam
C) a lake above 8,000 feet in elevation
D) a salty, shallow lake

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A stream's load consists of all of the following except
A) dissolved load.
B) suspended load.
C) float load.
D) bedload.
A) dissolved load.
B) suspended load.
C) float load.
D) bedload.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Why does it take less energy for a stream to pick up larger silt grains than smaller silt and clay sized particles?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How do you figure out the work done by a stream? What is stream power?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
How does flow velocity relate to discharge? How does area relate to discharge?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What type of stream pattern would you expect to develop in a stream that had a low bedload to suspended load ratio, a higher percentage of finer grained sediment, stable banks, constant discharge and a low channel slope?
A) highly meandering pattern
B) moderately meandering pattern
C) mixed meandering and braided pattern
D) moderately braided pattern
E) highly braided pattern
A) highly meandering pattern
B) moderately meandering pattern
C) mixed meandering and braided pattern
D) moderately braided pattern
E) highly braided pattern

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why would we want to know the height of water in a river bed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Using the hydrologic equation, what would you do to a river if you wanted to prevent flooding?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Streams preferentially erode ________ and ________ valleys where rock is most easily eroded.
A) deep, wide
B) deep, narrow
C) shallow, wide
D) shallow, narrow
A) deep, wide
B) deep, narrow
C) shallow, wide
D) shallow, narrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The landform produced when a stream enters into a lake, reservoir or sea is called a
A) alluvial fan.
B) sand bar.
C) delta.
D) gravel deposit.
A) alluvial fan.
B) sand bar.
C) delta.
D) gravel deposit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is obvious when standing on a stream bank?
A) channel depth
B) channel slope
C) flow velocity
D) channel outline
A) channel depth
B) channel slope
C) flow velocity
D) channel outline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Base level of a stream is a balance of
A) stream power and sediment load.
B) velocity and discharge.
C) precipitation and infiltration.
D) runoff and evaporation.
A) stream power and sediment load.
B) velocity and discharge.
C) precipitation and infiltration.
D) runoff and evaporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Deep incised river canyons most likely form through some combination of tectonic ________ and climate change that resulted in ________ precipitation.
A) uplift, more
B) uplift, less
C) subsidence, more
D) subsidence, less
A) uplift, more
B) uplift, less
C) subsidence, more
D) subsidence, less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
All of the following human activities will increase the sediment load in a river except
A) logging of forests on steep slopes.
B) converting cropland to natural vegetation.
C) surface mining for coal.
D) large-scale construction projects.
A) logging of forests on steep slopes.
B) converting cropland to natural vegetation.
C) surface mining for coal.
D) large-scale construction projects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If two streams undergo the same downstream drop in elevation of 300 meters, which stream would have the lowest channel slope?
A) highly sinuous stream
B) moderately sinuous stream
C) straight channel
D) not enough information provided
A) highly sinuous stream
B) moderately sinuous stream
C) straight channel
D) not enough information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
All of the following minerals form when lake water evaporates faster than water enters the lake, except
A) halite.
B) borax.
C) feldspar.
D) gypsum.
A) halite.
B) borax.
C) feldspar.
D) gypsum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A ________ of sea-level causes a lowering of base-level and ________ in the lower part of a stream valley that terminates in the ocean.
A) rising, incision
B) rising, sedimentation
C) lowering, sedimentation
D) lowering, incision
A) rising, incision
B) rising, sedimentation
C) lowering, sedimentation
D) lowering, incision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following stream properties tends to increase downstream?
A) stream power per area of stream bed
B) shear stress
C) sediment load
D) grain size of bedload
A) stream power per area of stream bed
B) shear stress
C) sediment load
D) grain size of bedload

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Based on observations, geologists have determined that this factor does not help to determine whether a stream will have a meandering or braided pattern.
A) bank stability
B) stream power per stream bed area
C) discharge variability
D) channel slope
A) bank stability
B) stream power per stream bed area
C) discharge variability
D) channel slope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements do not apply to flash floods?
A) form from high-intensity rainfall in small, steep, drainage basins.
B) are hard to predict because they happen so unexpectedly.
C) are deepest in narrow bedrock canyons.
D) progressively inundate larger and larger areas of the floodplain.
A) form from high-intensity rainfall in small, steep, drainage basins.
B) are hard to predict because they happen so unexpectedly.
C) are deepest in narrow bedrock canyons.
D) progressively inundate larger and larger areas of the floodplain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following stream properties tends to decrease downstream?
A) stream power per area of stream bed
B) sediment load
C) channel width
D) slope of channel bed
A) stream power per area of stream bed
B) sediment load
C) channel width
D) slope of channel bed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When a stream's discharge decreases from bankfull discharge, it has appropriate power to
A) transport all of the sediment on its bed and cause further erosion.
B) transport all of the sediment on its bed without causing any further erosion.
C) not transport all of its sediment load and deposits part of it.
D) not transport any of its sediment load and deposits all of it.
A) transport all of the sediment on its bed and cause further erosion.
B) transport all of the sediment on its bed without causing any further erosion.
C) not transport all of its sediment load and deposits part of it.
D) not transport any of its sediment load and deposits all of it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



