Deck 15: Mass Movements: Landscapes in Motion
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/85
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Mass Movements: Landscapes in Motion
1
Which mass movement is very slow detected only by dislocation or bending of features at the surface?
A) slide
B) creep
C) slump
D) fall
A) slide
B) creep
C) slump
D) fall
B
2
The Old Man in the Mountain, a granite cliff resembling a man's face located in the White Mountains of New Hampshire, collapsed in spring of 2003. What type of mass movement does this occurrence represent?
A) a slide
B) a slump
C) a fall
D) a flow
A) a slide
B) a slump
C) a fall
D) a flow
C
3
How do a slide and a slump differ?
A) type of rock
B) presence of water
C) shape of the surface
D) speed of the flow
A) type of rock
B) presence of water
C) shape of the surface
D) speed of the flow
C
4
Figure 15.2 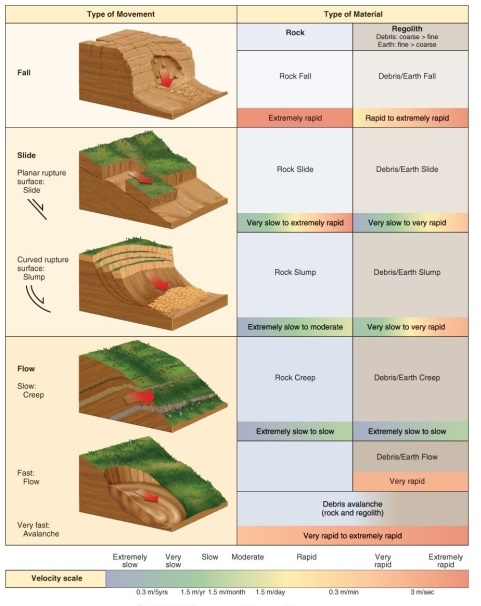
According to Figure 15.2 in your textbook, which mass movement is classified as having the fastest velocity?
A) slide
B) slump
C) creep
D) fall

According to Figure 15.2 in your textbook, which mass movement is classified as having the fastest velocity?
A) slide
B) slump
C) creep
D) fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why would people build their houses in areas where catastrophic mass movements occur?
A) Advanced technologies are able to take accurate measurements to predict when catastrophes might occur, so people can flee in time.
B) Catastrophes are rare, and people forget or do not suspect that they will occur.
C) Modern cities build retaining walls and other structures to prevent catastrophic damage.
D) Modern homes and buildings can withstand the destructive forces of mass movements.
A) Advanced technologies are able to take accurate measurements to predict when catastrophes might occur, so people can flee in time.
B) Catastrophes are rare, and people forget or do not suspect that they will occur.
C) Modern cities build retaining walls and other structures to prevent catastrophic damage.
D) Modern homes and buildings can withstand the destructive forces of mass movements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why does adding water to sand increase the angle of repose for the material?
A) Water increases friction.
B) Water increases cohesion.
C) Water increases the oversteep angle.
D) Water decreases friction.
A) Water increases friction.
B) Water increases cohesion.
C) Water increases the oversteep angle.
D) Water decreases friction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 15.2 
According to Figure 15.2 in your textbook, which mass movement is classified as having the slowest velocity?
A) slide
B) slump
C) creep
D) fall

According to Figure 15.2 in your textbook, which mass movement is classified as having the slowest velocity?
A) slide
B) slump
C) creep
D) fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which factor contributing to rock movement is not demonstrated by the brick-and-wood experiment?
A) smoothness of rock
B) density of rock
C) presence of water
D) angle of slope
A) smoothness of rock
B) density of rock
C) presence of water
D) angle of slope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following items describe the conditions relating to a slump except item ________. 1. curving, scallop-shaped rupture scarp 2. broken pavement and tilted trees 3. vertical sedimentary rock layers bent downslope 4. occurring in regolith or weak rock
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is a talus?
A) a pile of rock with no vegetation covering it
B) an arm of debris and regolith
C) a pile of rock at the bottom of a steep slope
D) a scooped-out area caused by a fall or slip of debris
A) a pile of rock with no vegetation covering it
B) an arm of debris and regolith
C) a pile of rock at the bottom of a steep slope
D) a scooped-out area caused by a fall or slip of debris

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which is not a factor that contributes to the modern increase in catastrophes in urban areas?
A) increased sports and leisure activities on slopes
B) increased urbanization in areas prone to slope failure
C) changes in local precipitation patterns
D) deforestation in urban areas
A) increased sports and leisure activities on slopes
B) increased urbanization in areas prone to slope failure
C) changes in local precipitation patterns
D) deforestation in urban areas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not a factor used to describe mass-movement processes?
A) water participation
B) nature of the solid mixture
C) type of motion
D) velocity of motion
A) water participation
B) nature of the solid mixture
C) type of motion
D) velocity of motion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements is not true of cohesion?
A) It is greater when particles are smaller.
B) It is the attraction of particles to each other at the atomic level.
C) It works with resistance to create the resisting strength of a rock formation.
D) It is possible along contact points only.
A) It is greater when particles are smaller.
B) It is the attraction of particles to each other at the atomic level.
C) It works with resistance to create the resisting strength of a rock formation.
D) It is possible along contact points only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure 15.13 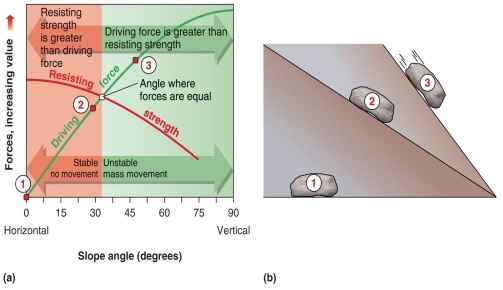
At which minimum angle will the driving force become greater than the resisting force in a mass movement, according to Figure 15.13 in your textbook?
A) 0
B) 32
C) 45
D) 60

At which minimum angle will the driving force become greater than the resisting force in a mass movement, according to Figure 15.13 in your textbook?
A) 0
B) 32
C) 45
D) 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is the best evidence that rock creep is occurring?
A) bent tree trunks
B) a cracked and displaced section of highway
C) a flowing-concrete appearance to a rock formation
D) talus slopes
A) bent tree trunks
B) a cracked and displaced section of highway
C) a flowing-concrete appearance to a rock formation
D) talus slopes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following terms is not a classification based on particle size?
A) rock
B) regolith
C) debris
D) earth
A) rock
B) regolith
C) debris
D) earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following landslides was partly caused by fire and rain?
A) Madison Canyon, Montana, 1959
B) Yosemite National Park, California, 1996
C) San Bernardino Mountains, California, 2003
D) near Lake City, Colorado, 2004
A) Madison Canyon, Montana, 1959
B) Yosemite National Park, California, 1996
C) San Bernardino Mountains, California, 2003
D) near Lake City, Colorado, 2004

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which is not a factor that contributes directly to the angle of repose of a sand castle?
A) friction
B) cohesion
C) size of particles
D) shape of particles
A) friction
B) cohesion
C) size of particles
D) shape of particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 15.11 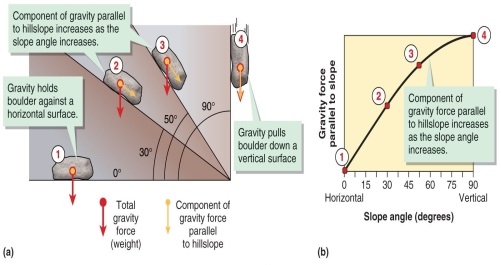
Study Figure 15.11 in your textbook. At which minimum angle will the component of gravity that pulls a boulder downward be greater than the component of gravity that holds a boulder against a surface?
A) 0
B) 30
C) 60
D) 90

Study Figure 15.11 in your textbook. At which minimum angle will the component of gravity that pulls a boulder downward be greater than the component of gravity that holds a boulder against a surface?
A) 0
B) 30
C) 60
D) 90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which two main factors determine the resisting strength that occurs in a mass movement?
A) rock roughness and density
B) friction and rock roughness
C) rock density and cohesion
D) rock friction and cohesion
A) rock roughness and density
B) friction and rock roughness
C) rock density and cohesion
D) rock friction and cohesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which option best describes the direction of the eruption of Mount St. Helens and the cause of this action, according to Figure 15.24 in your textbook?
A) Magma pressure built up and caused a vertical eruption of magma and ash.
B) A rock slide released pressure on the magma, causing a horizontal eruption.
C) An earthquake sheared off part of the mountain, causing a horizontal eruption.
D) An earthquake opened a vent in the top of the mountain, releasing pressure on the magma and causing a vertical eruption.
A) Magma pressure built up and caused a vertical eruption of magma and ash.
B) A rock slide released pressure on the magma, causing a horizontal eruption.
C) An earthquake sheared off part of the mountain, causing a horizontal eruption.
D) An earthquake opened a vent in the top of the mountain, releasing pressure on the magma and causing a vertical eruption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Volcanic eruptions can trigger lahars that may occur long after the volcanic activity has ceased. The simplest definition of a lahar is?
A) magma movement
B) a snow avalanche
C) a debris flow
D) a flood
A) magma movement
B) a snow avalanche
C) a debris flow
D) a flood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Where would you expect the thickest regolith?
A) the Appalachian foothills
B) the Gobi desert
C) a Hawaiian volcano peak
D) a rocky hillside in Utah
A) the Appalachian foothills
B) the Gobi desert
C) a Hawaiian volcano peak
D) a rocky hillside in Utah

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Resisting strength is greater when
A) bedding planes are parallel to a hillside.
B) water percolates into rock along joints.
C) bedding is not parallel to a hillside.
D) shale weathers to clay minerals.
A) bedding planes are parallel to a hillside.
B) water percolates into rock along joints.
C) bedding is not parallel to a hillside.
D) shale weathers to clay minerals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Where do the largest debris flows and rock slides occur?
A) in wide, broad canyons
B) in steep, narrow canyons
C) on steep mountains or hillsides
D) on volcanoes
A) in wide, broad canyons
B) in steep, narrow canyons
C) on steep mountains or hillsides
D) on volcanoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What was the motivation for production of slide-susceptibility maps by the U.S. Geological Survey?
A) development of new measurement technology
B) new urban development on tectonically active plains
C) new urban development in areas with slopes
D) new farming technology that increased agricultural use of slopes
A) development of new measurement technology
B) new urban development on tectonically active plains
C) new urban development in areas with slopes
D) new farming technology that increased agricultural use of slopes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not true about snow/heavy rain and mass movements?
A) Melting snow adds lubricating moisture to the soil.
B) Snow and rain both add weight to the soil.
C) A lot of rain completely saturates the ground and decreases cohesion between particles.
D) A lot of rain completely saturates the ground and increases cohesion between particles.
A) Melting snow adds lubricating moisture to the soil.
B) Snow and rain both add weight to the soil.
C) A lot of rain completely saturates the ground and decreases cohesion between particles.
D) A lot of rain completely saturates the ground and increases cohesion between particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which type of movement is least likely in the Great Smoky Mountains, where the regolith is thick?
A) creep
B) slump
C) flow
D) fall
A) creep
B) slump
C) flow
D) fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 15.24 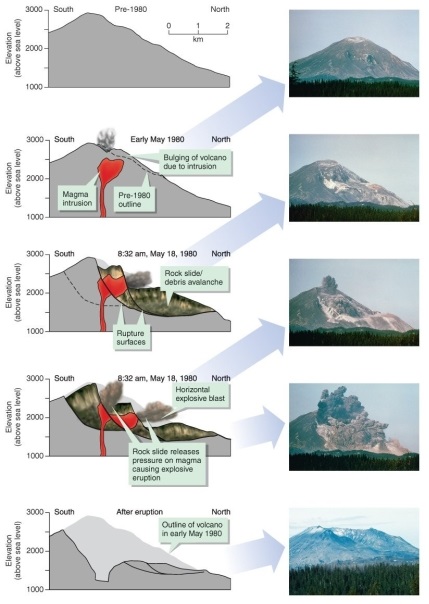
Using Figure 15.24 in your textbook, what was the overall elevation change of Mount St. Helens' peak as a result of the 1980 eruption?
A) a decrease of 400 m
B) a decrease of 900 m
C) it stayed the same
D) an increase of 100 m

Using Figure 15.24 in your textbook, what was the overall elevation change of Mount St. Helens' peak as a result of the 1980 eruption?
A) a decrease of 400 m
B) a decrease of 900 m
C) it stayed the same
D) an increase of 100 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which factor increases slope stability?
A) increased slope angle
B) increased frictional resistance
C) decreased contact cohesion
D) decreased compaction
A) increased slope angle
B) increased frictional resistance
C) decreased contact cohesion
D) decreased compaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A student who had once lived in Alaska describes the following personal experience: "The shaking of the ground beneath my house caused compaction of the particles, which caused a later mass movement resulting in my house breaking apart." Evaluate this statement.
A) It is probably true, except that it is unlikely that the mass movement would be strong enough to break a house apart.
B) It is probably false. Most breaking action occurs during an earthquake, not after the earthquake.
C) The entire statement is true.
D) It is more likely that liquefaction, caused by shaking regolith that contains water, caused the mass movement than it is likely that it was caused by compaction.
A) It is probably true, except that it is unlikely that the mass movement would be strong enough to break a house apart.
B) It is probably false. Most breaking action occurs during an earthquake, not after the earthquake.
C) The entire statement is true.
D) It is more likely that liquefaction, caused by shaking regolith that contains water, caused the mass movement than it is likely that it was caused by compaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What caused the debris avalanche from Mount St. Helens in 1980?
A) rainfall
B) earthquake
C) volcanic eruption
D) magma intrusion
A) rainfall
B) earthquake
C) volcanic eruption
D) magma intrusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What factor allows for the formation of thick regolith?
A) river erosion
B) landslides
C) flooding
D) dense vegetation
A) river erosion
B) landslides
C) flooding
D) dense vegetation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which is not a likely effect of snowfall on a mountain?
A) increased weight
B) decreased friction as snowmelts
C) increased cohesive binding by ice crystals
D) mass movement
A) increased weight
B) decreased friction as snowmelts
C) increased cohesive binding by ice crystals
D) mass movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Put the following events in order from those that occur with the greatest driving force to those that occur with the least driving force and/or have the least effect on hillside stability. 1. erosion 2. magma intrusion 3. volcanic eruption 4. liquefaction 5. earthquake
A) 1, 2, 3, 5, 4
B) 2, 1, 4, 5, 3
C) 3, 4, 5, 2, 1
D) 4, 5, 2, 3, 1
A) 1, 2, 3, 5, 4
B) 2, 1, 4, 5, 3
C) 3, 4, 5, 2, 1
D) 4, 5, 2, 3, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What triggered the debris avalanche that caused the destruction of Yungay, Peru?
A) rainfall
B) an earthquake
C) volcanic activity
D) snowmelt
A) rainfall
B) an earthquake
C) volcanic activity
D) snowmelt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following factors is not related to a lahar?
A) snowmelt
B) explosions deposit loose ash and lapilli
C) destruction of vegetation
D) tectonic fault movement
A) snowmelt
B) explosions deposit loose ash and lapilli
C) destruction of vegetation
D) tectonic fault movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Choose the option that lists the factors that are not influences of slope stability studied during hazard assessment?
A) slope angle, orientation of foliation planes, extent of weathering, extent of breakage by faults
B) type of rock, orientation of faults, amount of quartz content, orientation of bedding
C) type of regolith, extent of breakage by joints, orientation of foliation planes, type of rock
D) orientation of bedding, extent of breakage by faults, slope angle, type of regolith
A) slope angle, orientation of foliation planes, extent of weathering, extent of breakage by faults
B) type of rock, orientation of faults, amount of quartz content, orientation of bedding
C) type of regolith, extent of breakage by joints, orientation of foliation planes, type of rock
D) orientation of bedding, extent of breakage by faults, slope angle, type of regolith

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Shaking regolith will have the effect of
A) compaction, both wet and dry.
B) liquefaction, both wet and dry.
C) compaction when wet, and liquefaction when dry.
D) compaction when dry, and liquefaction when wet.
A) compaction, both wet and dry.
B) liquefaction, both wet and dry.
C) compaction when wet, and liquefaction when dry.
D) compaction when dry, and liquefaction when wet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is not a trigger for a mass movement?
A) rain and heavy snowfall
B) volcanic eruptions
C) strong winds
D) earthquakes
A) rain and heavy snowfall
B) volcanic eruptions
C) strong winds
D) earthquakes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The type of gravity-driven, downslope movement that results in a deposit of chaotically mixed fragments of different sizes with a very irregular, bumpy upper surface is called
A) fall.
B) slide.
C) slump.
D) creep.
E) flow.
A) fall.
B) slide.
C) slump.
D) creep.
E) flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Piles of rock, debris and earth that pile up at the base of steep slopes are called
A) rockpile.
B) debris jumble.
C) earth mound.
D) talus.
A) rockpile.
B) debris jumble.
C) earth mound.
D) talus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
It is possible for geologists to make maps of areas that are prone to future mass movements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Mass movement occurs when the resisting forces exceed the driving forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What happens when river slopes are uplifted beyond their maximum stable slope?
A) They are usually returned to the maximum stable slope by landslides.
B) They are usually returned to the maximum stable angle by erosion.
C) They usually remain at the uplifted angle but are more unstable when earthquakes occur.
D) The river water fills the deeper crevice and maintains that depth.
A) They are usually returned to the maximum stable slope by landslides.
B) They are usually returned to the maximum stable angle by erosion.
C) They usually remain at the uplifted angle but are more unstable when earthquakes occur.
D) The river water fills the deeper crevice and maintains that depth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If uplift increases elevation, which process most effectively lowers elevation?
A) erosion
B) mass movement
C) earthquakes
D) shear forces
A) erosion
B) mass movement
C) earthquakes
D) shear forces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which mineral gets weathered to weaken uplifted metamorphic rock?
A) silica
B) argentine
C) clay
D) serpentine
A) silica
B) argentine
C) clay
D) serpentine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What type would not be used as starting information when developing a hazard map?
A) slope map
B) topographic elevations map
C) geologic map
D) aerial photographs
A) slope map
B) topographic elevations map
C) geologic map
D) aerial photographs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Coarse-grained regolith where 20 to 80 percent of the fragments are greater than 2 millimeters in size is called
A) soil.
B) rock.
C) earth.
D) debris.
A) soil.
B) rock.
C) earth.
D) debris.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The type of gravity-driven, downslope movement where the material rotates as it moves downslope in contact with a curved surface of rupture is called
A) fall.
B) slide.
C) slump.
D) creep.
E) flow.
A) fall.
B) slide.
C) slump.
D) creep.
E) flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
How is an inventory of past slide movement usually obtained for input into GIS?
A) A geologist walks the entire area and makes detailed surface observations.
B) A geologist looks at aerial photographs of the area.
C) A team of geologists makes surface observations and takes core samples to analyze in the lab for evidence of past movement.
D) Past recorded seismographs are analyzed by computer technology.
A) A geologist walks the entire area and makes detailed surface observations.
B) A geologist looks at aerial photographs of the area.
C) A team of geologists makes surface observations and takes core samples to analyze in the lab for evidence of past movement.
D) Past recorded seismographs are analyzed by computer technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which set of data relating to the 1991 collapse of New Zealand's Mount Cook is correct?
A) The mountain was shortened by 10 m, the debris traveled for 7.5 km, and the avalanche traveled at speeds up to 200 km/h.
B) The mountain was shortened by 2 m, the debris traveled for 0.85 km, and the avalanche traveled at speeds up to 20 km/h.
C) The mountain was shortened by 100 m, the debris traveled for 75 km, and the avalanche traveled at speeds up to 800 km/h.
D) The mountain was shortened by 60 m, the debris traveled for 50 km, and the avalanche traveled at speeds up to 100 km/h.
A) The mountain was shortened by 10 m, the debris traveled for 7.5 km, and the avalanche traveled at speeds up to 200 km/h.
B) The mountain was shortened by 2 m, the debris traveled for 0.85 km, and the avalanche traveled at speeds up to 20 km/h.
C) The mountain was shortened by 100 m, the debris traveled for 75 km, and the avalanche traveled at speeds up to 800 km/h.
D) The mountain was shortened by 60 m, the debris traveled for 50 km, and the avalanche traveled at speeds up to 100 km/h.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The type of gravity-driven, downslope movement where the material moves very, very quickly as a high-viscosity fluid is called
A) fall.
B) slide.
C) slump.
D) creep.
E) avalanche.
A) fall.
B) slide.
C) slump.
D) creep.
E) avalanche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When describing the nature of materials involved in gravity-driven, downslope movement in order to classify the event it is crucial to describe the material after it has moved downslope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What accounts for most rock and regolith movement in mountains?
A) rivers and streams
B) weathering and erosion
C) mass movements
D) earthquakes
A) rivers and streams
B) weathering and erosion
C) mass movements
D) earthquakes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The type of gravity-driven, downslope movement where the material moves very, very slowly as a high-viscosity fluid is called
A) fall.
B) slide.
C) slump.
D) creep.
E) flow.
A) fall.
B) slide.
C) slump.
D) creep.
E) flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is a difference between rounded mountains and pointed ones?
A) the amount of uplift
B) pointed mountains are older
C) rocky type
D) rounded mountains have experienced more mass movement
A) the amount of uplift
B) pointed mountains are older
C) rocky type
D) rounded mountains have experienced more mass movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following types of flow moves the fastest?
A) slide
B) slump
C) creep
D) avalanche
A) slide
B) slump
C) creep
D) avalanche

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which is not a characteristic of clay minerals that increases the likelihood of a slide?
A) resistance to weathering
B) shrinking and swelling due to water and temperature
C) low cohesive strength when wet
D) low friction when wet
A) resistance to weathering
B) shrinking and swelling due to water and temperature
C) low cohesive strength when wet
D) low friction when wet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is not a typical data map used to input into GIS to generate a rock and debris-slide susceptibility map?
A) slope map
B) rock-type map
C) water course map
D) mass-movement inventory map
A) slope map
B) rock-type map
C) water course map
D) mass-movement inventory map

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Planar slides typically occur along bedding planes, foliation, or joint planes oriented ________ to the slope.
A) perpendicular
B) parallel
C) normal
D) adjacent
A) perpendicular
B) parallel
C) normal
D) adjacent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which three types of rocks are most commonly associated with more slides? Give an example of a location where this has been shown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The maximum angle of a stable slope is called the angle of
A) repose.
B) friction.
C) cohesion.
D) particle shapes.
A) repose.
B) friction.
C) cohesion.
D) particle shapes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which must be true for motion to begin to happen? What factor is important in determining if motion occurs?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Slumps are characterized as
A) free falling through the air.
B) material moving as a coherent block along a planar surface.
C) rotational slides on curved surfaces.
D) flowing as a high-viscosity liquid.
A) free falling through the air.
B) material moving as a coherent block along a planar surface.
C) rotational slides on curved surfaces.
D) flowing as a high-viscosity liquid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Bent tree trunks on a slope are indicative of
A) a fall.
B) a slump.
C) an avalanche.
D) creep.
A) a fall.
B) a slump.
C) an avalanche.
D) creep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Cohesion is a particularly important component of resisting strength in ________ minerals.
A) clay
B) iron-rich
C) water-bearing
D) hard
A) clay
B) iron-rich
C) water-bearing
D) hard

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Describe GIS. What does it stand for, what does it do, etc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A sudden stimulus that causes a mass movement is called
A) a trigger.
B) an earthquake.
C) a rainstorm.
D) an avalanche.
A) a trigger.
B) an earthquake.
C) a rainstorm.
D) an avalanche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Why do high elevations make actively rising hilltops unstable?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The attraction of particles to each other is called
A) cohesion.
B) friction.
C) sliding.
D) creep.
A) cohesion.
B) friction.
C) sliding.
D) creep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Read carefully through the following sentence, and decide which of the options is correct. Factors determining slope stability are the steepness of the slope, the composition and texture of material, the abundance of water, the presence and orientation of volcanic features in the rock, vegetation, and the amount of weathering.
A) The word "water" should be replaced by "clay."
B) The word "slope" should be replaced by "deviation."
C) The word "vegetation" should be replaced by "logging."
D) The word "volcanic" should be replaced by " planar."
A) The word "water" should be replaced by "clay."
B) The word "slope" should be replaced by "deviation."
C) The word "vegetation" should be replaced by "logging."
D) The word "volcanic" should be replaced by " planar."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following types of flow moves the slowest?
A) fall
B) avalanche
C) slide
D) creep
A) fall
B) avalanche
C) slide
D) creep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following scenarios would be least susceptible to mass movements?
A) steep slope, underlain by siltstone and mudstone
B) steep slope, underlain by sandstone and conglomerate
C) shallow slope, underlain by siltstone and mudstone
D) shallow slope, underlain by sandstone and conglomerate
A) steep slope, underlain by siltstone and mudstone
B) steep slope, underlain by sandstone and conglomerate
C) shallow slope, underlain by siltstone and mudstone
D) shallow slope, underlain by sandstone and conglomerate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The presence of a thin film of water on the surface of sand grains results in ________ angle of repose.
A) a higher
B) a lower
C) no change in the
A) a higher
B) a lower
C) no change in the

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The most common stimuli that abruptly imbalance driving and resisting forces governing the occurrence of mass movements include what?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following factors does not favor motion and slope instability?
A) increasing slope
B) smoother surfaces
C) the presence of water
D) the presence of vegetation
A) increasing slope
B) smoother surfaces
C) the presence of water
D) the presence of vegetation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
________ increases as the roughness between two objects in contact with one another increases.
A) Friction
B) Flow
C) Creep
D) Cohesion
A) Friction
B) Flow
C) Creep
D) Cohesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following scenarios would be most susceptible to mass movements?
A) steep slope, underlain by siltstone and mudstone
B) steep slope, underlain by sandstone and conglomerate
C) shallow slope, underlain by siltstone and mudstone
D) shallow slope, underlain by sandstone and conglomerate
A) steep slope, underlain by siltstone and mudstone
B) steep slope, underlain by sandstone and conglomerate
C) shallow slope, underlain by siltstone and mudstone
D) shallow slope, underlain by sandstone and conglomerate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The force opposing motion between two objects in contact with one another is called
A) friction.
B) cohesion.
C) repose.
D) slope.
A) friction.
B) cohesion.
C) repose.
D) slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 85 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



