Deck 11: Deformation of Rocks
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/88
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Deformation of Rocks
1
Which option describes a possible oil and gas trap?
A) an anticline made entirely of sandstone with an organic earth covering
B) a reverse fault with a sandstone layer and a shale layer underneath
C) an anticline with a sandstone layer and a shale layer on top
D) a syncline with a coal layer at the bottom, a sandstone middle, and a shale layer on top
A) an anticline made entirely of sandstone with an organic earth covering
B) a reverse fault with a sandstone layer and a shale layer underneath
C) an anticline with a sandstone layer and a shale layer on top
D) a syncline with a coal layer at the bottom, a sandstone middle, and a shale layer on top
C
2
The oldest rocks are exposed along the axis of
A) a syncline.
B) an anticline.
C) a dip.
D) a plunging fold.
A) a syncline.
B) an anticline.
C) a dip.
D) a plunging fold.
B
3
Figure 11.13 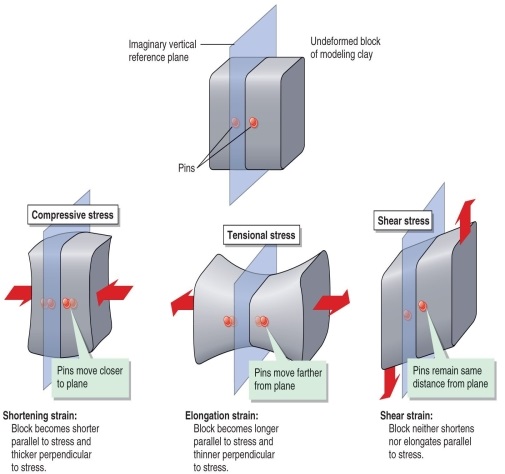
According to Figure 11.13, which option correctly describes the movement of two pins on either side of a plane in a block of clay submitted to tensional stress?
A) They remain in the same position.
B) They move farther from the plane.
C) They move closer to the plane.
D) They slide along at the same distance from the plane in opposite directions.

According to Figure 11.13, which option correctly describes the movement of two pins on either side of a plane in a block of clay submitted to tensional stress?
A) They remain in the same position.
B) They move farther from the plane.
C) They move closer to the plane.
D) They slide along at the same distance from the plane in opposite directions.
B
4
Choose the option that correctly orders the fluids from the one that sits at the bottom of a sandstone reservoir to the one that is closest to the low-porosity shale at the top of the reservoir.
A) oil, gas, water
B) gas, water, oil
C) water, gas, oil
D) gas, oil, water
A) oil, gas, water
B) gas, water, oil
C) water, gas, oil
D) gas, oil, water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The distinction between a joint and a fault is
A) the separation distance.
B) the distance that rock moves on each side of the line.
C) joints do not involve breaking rock and faults do.
D) joints are filled in with precipitated mineral crystals and faults are not.
A) the separation distance.
B) the distance that rock moves on each side of the line.
C) joints do not involve breaking rock and faults do.
D) joints are filled in with precipitated mineral crystals and faults are not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
At greater depths, rocks are
A) stronger and more brittle.
B) weaker and more plastic.
C) weaker and more brittle.
D) stronger and more plastic.
A) stronger and more brittle.
B) weaker and more plastic.
C) weaker and more brittle.
D) stronger and more plastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Figure 11.16 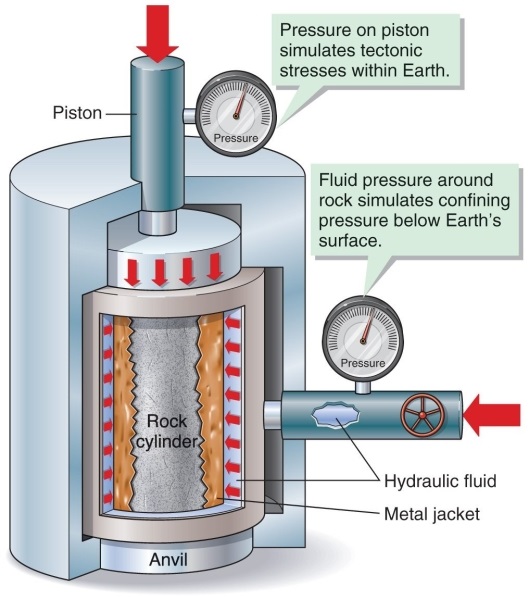
Which is not a reason for the hydraulic fluid around the cylinder in the experimental apparatus for measuring rock strength (as in Figure 11.16)?
A) to imitate tectonic stresses within Earth
B) to imitate surrounding rock pressures
C) to imitate pressures of depth
D) to imitate deep, confining pressures within Earth

Which is not a reason for the hydraulic fluid around the cylinder in the experimental apparatus for measuring rock strength (as in Figure 11.16)?
A) to imitate tectonic stresses within Earth
B) to imitate surrounding rock pressures
C) to imitate pressures of depth
D) to imitate deep, confining pressures within Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Why are some faults named "reverse" faults?
A) The rock moves in one direction, then reverses and moves in another direction.
B) The rock moves in opposite directions on each side of the fault.
C) The rock on the hanging wall moves opposite to the direction it does in a normal fault.
D) The rock on the hanging wall moves perpendicular to the direction of a thrust fault.
A) The rock moves in one direction, then reverses and moves in another direction.
B) The rock moves in opposite directions on each side of the fault.
C) The rock on the hanging wall moves opposite to the direction it does in a normal fault.
D) The rock on the hanging wall moves perpendicular to the direction of a thrust fault.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Figure 11.13 
According to Figure 11.13, which option correctly describes the movement of two pins on either side of a plane in a block of clay submitted to shear stress?
A) They remain in the same position.
B) They move farther from the plane.
C) They move closer to the plane.
D) They slide along at the same distance from the plane in opposite directions.

According to Figure 11.13, which option correctly describes the movement of two pins on either side of a plane in a block of clay submitted to shear stress?
A) They remain in the same position.
B) They move farther from the plane.
C) They move closer to the plane.
D) They slide along at the same distance from the plane in opposite directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A brittle deformation
A) is a shattering motion that occurs at a fault.
B) is a break that occurs at a relatively small strain.
C) is a plastic deformation that occurs under high pressure.
D) is a deformation that may reverse to its original form.
A) is a shattering motion that occurs at a fault.
B) is a break that occurs at a relatively small strain.
C) is a plastic deformation that occurs under high pressure.
D) is a deformation that may reverse to its original form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following occurs as a result of compression?
A) elongation
B) strain
C) shortening
D) strength
A) elongation
B) strain
C) shortening
D) strength

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a geologist creates a geologic map of an area and then draws a cross-section of that area, what type of scientific process is shown?
A) interpretation
B) observation
C) conclusion
D) experimentation
A) interpretation
B) observation
C) conclusion
D) experimentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Faults that show a combination of dip-slip and strike-slip movement are
A) reverse faults.
B) strike-dip faults.
C) oblique-slip faults.
D) diagonal-strike faults.
A) reverse faults.
B) strike-dip faults.
C) oblique-slip faults.
D) diagonal-strike faults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Deformation under low stress, below yield strength, is often
A) elastic.
B) plastic.
C) irreversible.
D) compressive.
A) elastic.
B) plastic.
C) irreversible.
D) compressive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Choose the option that places the rock types in order from most brittle at surface temperature to most plastic.
A) rock salt, schist, basalt
B) granite, limestone, marble
C) quartzite, mudstone, sandstone
D) shale, basalt, sandstone
A) rock salt, schist, basalt
B) granite, limestone, marble
C) quartzite, mudstone, sandstone
D) shale, basalt, sandstone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A(n) ________ forms where rocks both fold and tilt.
A) syncline
B) anticline
C) dip
D) plunging fold
A) syncline
B) anticline
C) dip
D) plunging fold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which term is defined as a measure of the amount of stress that a material can endure before it fails by breaking or flowing?
A) elongation
B) strain
C) shortening
D) strength
A) elongation
B) strain
C) shortening
D) strength

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Figure 11.20 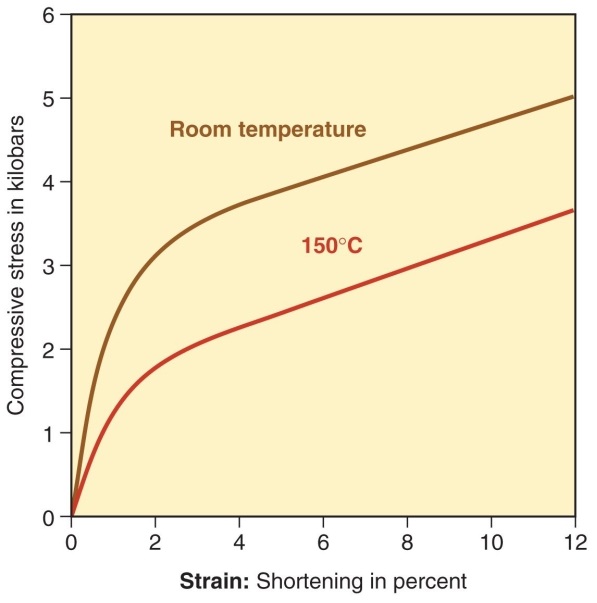
Which option would incorrectly complete the following statement? According to Figure 11.20, to shorten marble by five percent
A) requires one fewer kilobar if the material is wet than when it is dry.
B) requires about two fewer kilobars if the material is wet and hot than when it is dry at room temperature.
C) requires about two fewer kilobars if it is hot and dry than when it is cold and dry.
D) requires about one fewer kilobar if it is hot and dry than when it is cold and dry.

Which option would incorrectly complete the following statement? According to Figure 11.20, to shorten marble by five percent
A) requires one fewer kilobar if the material is wet than when it is dry.
B) requires about two fewer kilobars if the material is wet and hot than when it is dry at room temperature.
C) requires about two fewer kilobars if it is hot and dry than when it is cold and dry.
D) requires about one fewer kilobar if it is hot and dry than when it is cold and dry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 11.14 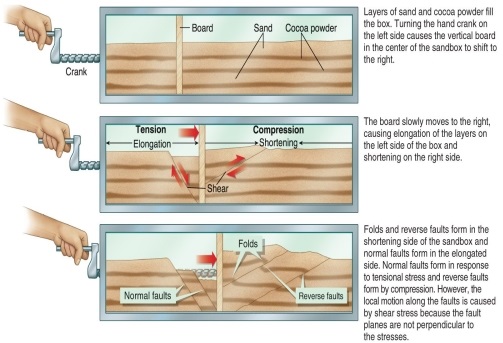
In a sandbox with a crankable division, which of the following may be illustrated?
A) Normal faults fold in the area under compression and reverse faults form where the sand is pressed together.
B) Normal faults fold in the area under tension and reverse faults form where the sand is given more space.
C) Normal faults fold in the area under compression and reverse faults form where the sand is given more space.
D) Normal faults fold in the area under tension and reverse faults form where the sand is pressed together.

In a sandbox with a crankable division, which of the following may be illustrated?
A) Normal faults fold in the area under compression and reverse faults form where the sand is pressed together.
B) Normal faults fold in the area under tension and reverse faults form where the sand is given more space.
C) Normal faults fold in the area under compression and reverse faults form where the sand is given more space.
D) Normal faults fold in the area under tension and reverse faults form where the sand is pressed together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which piece of measured evidence would not help geologists produce geologic cross sections in order to interpret subsurface geology?
A) subsurface layers
B) orientation of rock layers
C) orientation of folds
D) faults
A) subsurface layers
B) orientation of rock layers
C) orientation of folds
D) faults

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
According to the elastic rebound theory, what may occur before a major earthquake?
A) minor shocks
B) deformation of rock in shear directions and bending rock
C) deformation and bending of rock into anticlines
D) deformation and bending of rock into synclines
A) minor shocks
B) deformation of rock in shear directions and bending rock
C) deformation and bending of rock into anticlines
D) deformation and bending of rock into synclines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An M7 earthquake has ________ times more energy than an M5 earthquake.
A) 2
B) 100
C) 32
D) 1024
A) 2
B) 100
C) 32
D) 1024

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
You are asleep and are awakened to hear dishes rattling, and you feel a sensation that resembles a heavy truck striking your building. On the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale, what intensity is the earthquake you've experienced?
A) IV
B) VII
C) IX
D) XI
A) IV
B) VII
C) IX
D) XI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
"Tsunami" refers to
A) huge waves at sea that diminish somewhat and reach land.
B) a sudden buildup of wave amplitude in shallow water.
C) high-amplitude, high-frequency waves that reach shore.
D) a series of waves that reach the shore in fast succession, causing extreme damage.
A) huge waves at sea that diminish somewhat and reach land.
B) a sudden buildup of wave amplitude in shallow water.
C) high-amplitude, high-frequency waves that reach shore.
D) a series of waves that reach the shore in fast succession, causing extreme damage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Liquefaction occurs when
A) rock heats enough that it behaves like a liquid.
B) rivers and water bodies overrun and dissolve earth materials during a quake.
C) grains of earth materials settle downward during shaking and wet ground becomes fluid.
D) grains rise up to the surface in groundwater during an earthquake and cause mass movement.
A) rock heats enough that it behaves like a liquid.
B) rivers and water bodies overrun and dissolve earth materials during a quake.
C) grains of earth materials settle downward during shaking and wet ground becomes fluid.
D) grains rise up to the surface in groundwater during an earthquake and cause mass movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is not a factor that is considered when comparing the strength of the oceanic and continental lithosphere?
A) laboratory rock-strength data
B) varying thickness of the continental and oceanic crust
C) chemical composition and water content
D) varying pressure under the ocean and the continents
A) laboratory rock-strength data
B) varying thickness of the continental and oceanic crust
C) chemical composition and water content
D) varying pressure under the ocean and the continents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Evaluate this statement: "Earthquake damage depends primarily on the magnitude of the quake."
A) This statement is true.
B) This statement is true, but earthquake damage also depends on the proximity to the epicenter and the characteristics of materials through which the earthquake passes.
C) This statement is false; the most important factor in earthquake damage is the quality of building materials used.
D) This statement is false; the most important factor in earthquake damage is the location's proximity to the epicenter.
A) This statement is true.
B) This statement is true, but earthquake damage also depends on the proximity to the epicenter and the characteristics of materials through which the earthquake passes.
C) This statement is false; the most important factor in earthquake damage is the quality of building materials used.
D) This statement is false; the most important factor in earthquake damage is the location's proximity to the epicenter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The word "graben" originates from
A) the German word for "ditch."
B) the English word for "grab."
C) the German word for "tumble."
D) the Japanese word for "nest."
A) the German word for "ditch."
B) the English word for "grab."
C) the German word for "tumble."
D) the Japanese word for "nest."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
On the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale, destroyed bridges, bent rails, and most buildings destroyed are indicative of ________ intensity?
A) IV
B) VII
C) IX
D) XI
A) IV
B) VII
C) IX
D) XI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Earthquake damage occurs when
A) stress exceeds strain of materials.
B) stress exceeds strength of materials.
C) strain exceeds strength of materials.
D) strength exceeds strain of materials.
A) stress exceeds strain of materials.
B) stress exceeds strength of materials.
C) strain exceeds strength of materials.
D) strength exceeds strain of materials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Tension results in strike-slip faults when
A) the fractures are parallel to the stress direction.
B) the fractures are perpendicular to the stress direction.
C) suitable reverse faults are acted upon.
D) suitable normal faults are acted upon.
A) the fractures are parallel to the stress direction.
B) the fractures are perpendicular to the stress direction.
C) suitable reverse faults are acted upon.
D) suitable normal faults are acted upon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which action would geologists take in order to determine the Richter magnitude of an earthquake?
A) analyze seismic instrument readouts
B) take core samples at several spots and from different distances from the epicenter
C) assess financial costs of rebuilding roads, buildings, and public areas in the quake zone
D) interview people who experienced the quake
A) analyze seismic instrument readouts
B) take core samples at several spots and from different distances from the epicenter
C) assess financial costs of rebuilding roads, buildings, and public areas in the quake zone
D) interview people who experienced the quake

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What type of data to date is most useful for earthquake prediction?
A) study of rock types
B) study of earthquake patterns in other locations
C) monitoring known precursor events
D) monitoring world-wide seismic data and extrapolating patterns
A) study of rock types
B) study of earthquake patterns in other locations
C) monitoring known precursor events
D) monitoring world-wide seismic data and extrapolating patterns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Arched folds where limbs dip away from the hinge line are called
A) inclines.
B) anticlines.
C) synclines.
D) reclines.
A) inclines.
B) anticlines.
C) synclines.
D) reclines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What action would geologists take when creating a Modified Mercalli Intensity map of an earthquake?
A) analyze seismic instrument readouts
B) take core samples at several spots and from different distances from the epicenter
C) assess financial costs of rebuilding roads, buildings, and public areas in the quake zone
D) interview people who experienced the quake
A) analyze seismic instrument readouts
B) take core samples at several spots and from different distances from the epicenter
C) assess financial costs of rebuilding roads, buildings, and public areas in the quake zone
D) interview people who experienced the quake

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Put the steps in the correct order. 1. Stress exceeds rock yield strength. 2. Potential energy is released as motion energy. 3. Strong rocks absorb large stresses during elastic strain. 4. Rock breaks.
A) 3, 2, 1, 4
B) 3, 1, 2, 4
C) 3, 1, 4, 2
D) 3, 2, 4, 1
A) 3, 2, 1, 4
B) 3, 1, 2, 4
C) 3, 1, 4, 2
D) 3, 2, 4, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What does earthquake intensity measure?
A) amplitude of seismic waves
B) reach of the quake from the epicenter in km
C) cost of reconstruction
D) damage and secondary effects of the quake
A) amplitude of seismic waves
B) reach of the quake from the epicenter in km
C) cost of reconstruction
D) damage and secondary effects of the quake

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
"Horst," meaning "nest," is a suitable word for the rock formation it describes because
A) these rock formations are also in ditches or valleys, like nests.
B) these rock formations are typically in protected valleys.
C) these rock formations are pushed up to a high place, and horsts are nests in high places.
D) these rock formations are circular and cupped like nests.
A) these rock formations are also in ditches or valleys, like nests.
B) these rock formations are typically in protected valleys.
C) these rock formations are pushed up to a high place, and horsts are nests in high places.
D) these rock formations are circular and cupped like nests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Arched folds where limbs dip toward the hinge line are called
A) synclines.
B) reclines.
C) anticlines.
D) inclines.
A) synclines.
B) reclines.
C) anticlines.
D) inclines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Strength
A) decreases with depth.
B) increases with depth because of pressure, then decreases at further depths because of temperature.
C) increases with depth.
D) decreases with depth because of pressure, then increases at further depths because of temperature.
A) decreases with depth.
B) increases with depth because of pressure, then decreases at further depths because of temperature.
C) increases with depth.
D) decreases with depth because of pressure, then increases at further depths because of temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Faults are:
A) cracks where displacement has occurred.
B) fracture planes along which rocks used to move but don't any longer.
C) fractures in the bedrock.
D) fracture planes along which rocks move.
A) cracks where displacement has occurred.
B) fracture planes along which rocks used to move but don't any longer.
C) fractures in the bedrock.
D) fracture planes along which rocks move.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Richter magnitude is based on
A) the amount of damage caused.
B) the maximum amplitude recorded.
C) the difference in arrival times of S and P waves.
D) the distance from the epicenter.
A) the amount of damage caused.
B) the maximum amplitude recorded.
C) the difference in arrival times of S and P waves.
D) the distance from the epicenter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Dip-slip faults include normal, reverse and thrust faults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Judge the following sentence according to the criteria given below. There is a link between mining and faults because minerals precipitate from water percolating along faults.
A) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
B) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
C) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
D) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.
A) The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
B) The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
C) The assertion and the reason are both correct, and the reason is valid.
D) The assertion and the reason are both correct, but the reason is invalid.
E) Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The rocks above the fault are called the hanging wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A seismic station records an earthquake that has a maximum surface wave amplitude of 50 mm and the S-wave arrives 2 seconds after the P-wave. The Richter magnitude of this earthquake is
A) 3.
B) 4.
C) 5.
D) 6.
A) 3.
B) 4.
C) 5.
D) 6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The rocks below a fault are called the footwall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The block of rock above an inclined fault plane is called the ________.
A) footwall
B) hanging-wall
C) strike-wall
D) dipwall
A) footwall
B) hanging-wall
C) strike-wall
D) dipwall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Oppositely dipping sides of the fold of a rock are called its limbs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A normal fault forms when:
A) the hanging wall rock moves downward compared to the footwall.
B) the hanging wall rock moves up along a dip-slip fault compared to the footwall.
C) the fault dips at an angle steeper than 45 degrees.
D) the fault dips at an angle less than 45 degrees.
A) the hanging wall rock moves downward compared to the footwall.
B) the hanging wall rock moves up along a dip-slip fault compared to the footwall.
C) the fault dips at an angle steeper than 45 degrees.
D) the fault dips at an angle less than 45 degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A measure of earthquake size that corresponds to the energy released during the earthquake is called the
A) focus.
B) epicenter.
C) intensity.
D) magnitude.
A) focus.
B) epicenter.
C) intensity.
D) magnitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A seismic station records an earthquake that has a maximum surface wave amplitude of 1 mm and the S-wave arrives 2 seconds after the P-wave. The Richter magnitude of this earthquake is
A) 1.
B) 1.5.
C) 2.
D) 2.5.
A) 1.
B) 1.5.
C) 2.
D) 2.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Joints are:
A) cracks where some displacement of the rock occurred.
B) cracks where no displacement of the rock occurred.
C) fractures where some displacement has occurred.
D) fractures where no displacement has occurred.
A) cracks where some displacement of the rock occurred.
B) cracks where no displacement of the rock occurred.
C) fractures where some displacement has occurred.
D) fractures where no displacement has occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The San Andreas fault has shifted rocks hundreds of kilometers. For example, plutonic rocks on the Pacific Ocean (western)side of the fault have been displaced from southern California to northern California, relative to rocks on the North American (eastern) side. The San Andreas fault is classified as a
A) normal dip-slip fault.
B) reverse dip-slip fault.
C) right-lateral strike-slip fault.
D) left-lateral strike-slip fault.
A) normal dip-slip fault.
B) reverse dip-slip fault.
C) right-lateral strike-slip fault.
D) left-lateral strike-slip fault.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Strike-slip faults include right-lateral, left-lateral and thrust faults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Cracks where displacement of rock has occurred are called
A) faults.
B) sills.
C) joints.
D) dikes.
A) faults.
B) sills.
C) joints.
D) dikes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A seismic station records an earthquake that has a maximum surface wave amplitude of 20 mm and the S-wave arrives 40 seconds after the P-wave. The Richter magnitude of this earthquake is
A) 4.5.
B) 5.
C) 5.5.
D) 6.
A) 4.5.
B) 5.
C) 5.5.
D) 6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Cracks where very little or no displacement of rock has occurred are called
A) faults.
B) sills.
C) joints.
D) dikes.
A) faults.
B) sills.
C) joints.
D) dikes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
All of the seismic hazards in the United States are located west of the Rocky Mountains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a normal fault, the footwall moves ________ relative to the hanging-wall.
A) down
B) up
C) right
D) left
A) down
B) up
C) right
D) left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How can earthquakes cripple emergency services, transportation networks, water and gas utilities, and communication?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Does the "Ring of Fire" include any part of the United States? Where?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Grabens are:
A) blocks of crust jostled upward along normal faults.
B) blocks of crust jostled downward along normal faults.
C) blocks of crust jostled left along normal faults.
D) blocks of crust jostled right along normal faults.
A) blocks of crust jostled upward along normal faults.
B) blocks of crust jostled downward along normal faults.
C) blocks of crust jostled left along normal faults.
D) blocks of crust jostled right along normal faults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Thrust faults are formed by horizontal movement along the strike direction of the fault plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In an earthquake, what causes the most damage and deaths?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What caused the giant tsunami in the Indian Ocean in 2004?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Movement along a dip-slip fault causes an abrupt vertical displacement of the ground surface called a fault scarp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Most of the energy released in an earthquake is released:
A) during the foreshock.
B) during the aftershock.
C) during the foreshock and the aftershock.
D) during a single mainshock.
A) during the foreshock.
B) during the aftershock.
C) during the foreshock and the aftershock.
D) during a single mainshock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the amplitude in an earthquake?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the downside of using moment magnitude as an earthquake measurement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The elastic rebound theory explains earthquakes as sudden brittle failure following the buildup of elastic strain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Currently, what is the best method for predicting earthquakes within the crucial 2 hour time period?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Oil and gas, like groundwater, move through pore spaces in rock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale is a quantitative measure of an earthquake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Intensity measures the violence of ground shaking during an earthquake in terms of the extent to which people felt the earthquake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Why is it good to measure the magnitude, rather than intensity, of an earthquake?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A reverse fault forms when:
A) the hanging wall rock moves downward compared to the footwall.
B) the hanging wall rock moves up along a dip-slip fault compared to the footwall.
C) the fault dips at an angle steeper than 45 degrees.
D) the fault dips at an angle less than 45 degrees.
A) the hanging wall rock moves downward compared to the footwall.
B) the hanging wall rock moves up along a dip-slip fault compared to the footwall.
C) the fault dips at an angle steeper than 45 degrees.
D) the fault dips at an angle less than 45 degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Magnitude is:
A) a measure of earthquake size that is related to the energy released during the earthquake.
B) a directly measured physical quantity.
C) a value that is calculated from measurements taken during an earthquake.
D) determined using the amplitude of P and S waves.
A) a measure of earthquake size that is related to the energy released during the earthquake.
B) a directly measured physical quantity.
C) a value that is calculated from measurements taken during an earthquake.
D) determined using the amplitude of P and S waves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Horsts are:
A) blocks of crust jostled upward along normal faults.
B) blocks of crust jostled downward along normal faults.
C) blocks of crust jostled left along normal faults.
D) blocks of crust jostled right along normal faults.
A) blocks of crust jostled upward along normal faults.
B) blocks of crust jostled downward along normal faults.
C) blocks of crust jostled left along normal faults.
D) blocks of crust jostled right along normal faults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What is the best construction method for a building situated in an earthquake prone area?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



