Deck 12: Serial Correlation and Heteroskedasticity in Time Series Regressions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Serial Correlation and Heteroskedasticity in Time Series Regressions
1
Which of the following is an example of FGLS estimation?
A)Dickey-Fuller estimation
B)Vector error correction estimation
C) Prais-Winsten estimation
D) OLS estimation.
A)Dickey-Fuller estimation
B)Vector error correction estimation
C) Prais-Winsten estimation
D) OLS estimation.
C
Explanation: Prais-Winsten estimation is a type of FGLS estimation.
Explanation: Prais-Winsten estimation is a type of FGLS estimation.
2
Which of the following identifies an advantage of first differencing a time-series?
A)First differencing eliminates most of the serial correlation.
B)First differencing eliminates most of the heteroskedastcicty.
C) First differencing eliminates most of the multicollinearity.
D) First differencing eliminates the possibility of spurious regression.
A)First differencing eliminates most of the serial correlation.
B)First differencing eliminates most of the heteroskedastcicty.
C) First differencing eliminates most of the multicollinearity.
D) First differencing eliminates the possibility of spurious regression.
A
Explanation: First differencing of a time-series helps eliminate most of the serial correlation.
Explanation: First differencing of a time-series helps eliminate most of the serial correlation.
3
Which of the following is a test for serial correlation in the error terms?
A)Johansen test
B)Dickey Fuller test
C) Durbin Watson test
D) White test
A)Johansen test
B)Dickey Fuller test
C) Durbin Watson test
D) White test
C
Explanation: The Durbin Watson test can be used to test for serial correlation in error terms.
Explanation: The Durbin Watson test can be used to test for serial correlation in error terms.
4
A smaller standard error means:
A)a larger t statistic.
B)a smaller t statistic.
C) a larger F statistic.
D) a smaller F statistic.
A)a larger t statistic.
B)a smaller t statistic.
C) a larger F statistic.
D) a smaller F statistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is the reason why standard errors measured by OLS differ from standard errors measured through Prais-Winsten transformation?
A)OLS standard errors account for serial correlation, whereas Prais-Winsten estimations do not.
B)Prais-Winsten standard errors account for serial correlation, whereas OLS estimations do not.
C) Prais-Winsten standard errors account for heteroskedasticity, whereas OLS estimations do not.
D) OLS standard errors account for heteroskedasticity, whereas Prais-Winsten estimations do not.
A)OLS standard errors account for serial correlation, whereas Prais-Winsten estimations do not.
B)Prais-Winsten standard errors account for serial correlation, whereas OLS estimations do not.
C) Prais-Winsten standard errors account for heteroskedasticity, whereas OLS estimations do not.
D) OLS standard errors account for heteroskedasticity, whereas Prais-Winsten estimations do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Durbin's alternative test is valid even if the explanatory variables are strictly exogenous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
For a given significance level, if the calculated value of the Durbin Watson statistic lies between the lower critical value and the upper critical value, _____.
A)the hypothesis of no serial correlation is accepted
B)the hypothesis of no serial correlation is rejected
C) the test is inconclusive
D) the hypothesis of heteroskedasticity is accepted
A)the hypothesis of no serial correlation is accepted
B)the hypothesis of no serial correlation is rejected
C) the test is inconclusive
D) the hypothesis of heteroskedasticity is accepted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When a series is stationary, weakly dependent, and has serial correlation:
A)the adjusted R2 is inconsistent, while R2 is a consistent estimator of the population parameter.
B)the adjusted R2 is consistent, while R2 is an inconsistent estimator of the population parameter.
C) both the adjusted R2 and R2 are inconsistent estimators of the population parameter.
D) both the adjusted R2 and R2 are consistent estimators of the population parameter.
A)the adjusted R2 is inconsistent, while R2 is a consistent estimator of the population parameter.
B)the adjusted R2 is consistent, while R2 is an inconsistent estimator of the population parameter.
C) both the adjusted R2 and R2 are inconsistent estimators of the population parameter.
D) both the adjusted R2 and R2 are consistent estimators of the population parameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the time series literature, the serial correlation-robust standard errors are sometimes called:
A)homoskedasticity and autocorrelation inconsistent standard errors.
B)homoskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent standard errors.
C) heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation inconsistent standard errors.
D) heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent standard errors.
A)homoskedasticity and autocorrelation inconsistent standard errors.
B)homoskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent standard errors.
C) heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation inconsistent standard errors.
D) heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent standard errors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The equation u2t =  0 +
0 +  1u2t - 1 + vt is an autoregressive model in _____.
1u2t - 1 + vt is an autoregressive model in _____.
A)ut
B)u2t
C) vt
D) ut - 1
 0 +
0 +  1u2t - 1 + vt is an autoregressive model in _____.
1u2t - 1 + vt is an autoregressive model in _____.A)ut
B)u2t
C) vt
D) ut - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the presence of heteroskedasticity, the usual OLS estimates of:
A)standard errors are valid, whereas the t statistics and F statistics are invalid.
B)t statistics are valid, but the standard errors and F statistics are invalid.
C) F statistics are valid, but the standard errors and t statistics are invalid.
D) standard errors, t statistics, and F statistics are invalid.
A)standard errors are valid, whereas the t statistics and F statistics are invalid.
B)t statistics are valid, but the standard errors and F statistics are invalid.
C) F statistics are valid, but the standard errors and t statistics are invalid.
D) standard errors, t statistics, and F statistics are invalid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consistency of FGLS requires:
A)ut to be uncorrelated with xt-1, xt, and xt+1.
B)ut to be uncorrelated with xt and xt+1.
C) ut to be correlated with xt and xt+1.
D) ut to be correlated with xt-1, xt, and xt+1.
A)ut to be uncorrelated with xt-1, xt, and xt+1.
B)ut to be uncorrelated with xt and xt+1.
C) ut to be correlated with xt and xt+1.
D) ut to be correlated with xt-1, xt, and xt+1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following tests can be used to test for heteroskedasticity in a time series?
A)Johansen test
B)Dickey-Fuller test
C) Breusch-Pagan test
D) Durbin's alternative test
A)Johansen test
B)Dickey-Fuller test
C) Breusch-Pagan test
D) Durbin's alternative test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In presence of serial correlation, the OLS variance formula accurately estimates the true variance of the OLS estimator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Prais-Winsten and Cochrane-Orcutt transformations are consistent when explanatory variables are not strictly exogenous.
B)The SC-robust standard errors cannot be estimated in models with lagged dependent variables.
C) The SC-robust standard errors work better after quasi-differencing a time series that is expected to be serially correlated.
D) Estimation of SC-robust standard errors is independent of the sample size.
A)Prais-Winsten and Cochrane-Orcutt transformations are consistent when explanatory variables are not strictly exogenous.
B)The SC-robust standard errors cannot be estimated in models with lagged dependent variables.
C) The SC-robust standard errors work better after quasi-differencing a time series that is expected to be serially correlated.
D) Estimation of SC-robust standard errors is independent of the sample size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is true?
A)When explanatory variables are not strictly exogenous, the t test for serial correlation is valid.
B)When explanatory variables are not strictly exogenous, the Durbin Watson test for serial correlation is valid.
C) Breusch-Godfrey test can be used to check for second order serial correlation.
D) White test can be used to check for second order serial correlation.
A)When explanatory variables are not strictly exogenous, the t test for serial correlation is valid.
B)When explanatory variables are not strictly exogenous, the Durbin Watson test for serial correlation is valid.
C) Breusch-Godfrey test can be used to check for second order serial correlation.
D) White test can be used to check for second order serial correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the presence of serial correlation:
A)estimated standard errors remain valid.
B)estimated test statistics remain valid.
C) estimated OLS values are not BLUE.
D) estimated variance does not differ from the case of no serial correlation.
A)estimated standard errors remain valid.
B)estimated test statistics remain valid.
C) estimated OLS values are not BLUE.
D) estimated variance does not differ from the case of no serial correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Breusch-Godfrey test statistic follows a:
A)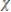 2distribution.
2distribution.
B)t distribution.
C) normal distribution.
D) F distribution.
A)
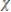 2distribution.
2distribution.B)t distribution.
C) normal distribution.
D) F distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In a model based on a weakly dependent time series with serial correlation and strictly exogenous explanatory variables, _____.
A)the feasible generalized least square estimates are unbiased
B)the feasible generalized least square estimates are BLUE
C) the feasible generalized least square estimates are asymptotically more efficient than OLS estimates
D) the feasible generalized least square estimates are asymptotically less efficient than OLS estimates
A)the feasible generalized least square estimates are unbiased
B)the feasible generalized least square estimates are BLUE
C) the feasible generalized least square estimates are asymptotically more efficient than OLS estimates
D) the feasible generalized least square estimates are asymptotically less efficient than OLS estimates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a limitation of serial correlation-robust standard errors?
A)The serial correlation-robust standard errors are smaller than OLS standard errors when there is serial correlation.
B)The serial correlation-robust standard errors can be poorly behaved when there is substantial serial correlation and the sample size is small.
C) The serial correlation-robust standard errors cannot be calculated for autoregressive processes of an order greater than one.
D) The serial correlation-robust standard errors cannot be calculated after relaxing the assumption of homoskedasticity.
A)The serial correlation-robust standard errors are smaller than OLS standard errors when there is serial correlation.
B)The serial correlation-robust standard errors can be poorly behaved when there is substantial serial correlation and the sample size is small.
C) The serial correlation-robust standard errors cannot be calculated for autoregressive processes of an order greater than one.
D) The serial correlation-robust standard errors cannot be calculated after relaxing the assumption of homoskedasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Cochrane-Orcutt and Prais-Winsten methods are iterative methods of feasible generalized least square (FGLS) estimation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
FGLS estimates are efficient when explanatory variables are not strictly exogenous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consistency of feasible generalized least square estimators requires the error term to be correlated with lags of the explanatory variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The serial correlation-robust standard errors are typically larger than the usual OLS standard errors when there is serial correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In time series regressions, it is advisable to check for serial correlation first, before checking for heteroskedasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



