Deck 18: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Chemical Equilibrium
1
Which of the following is the best description of the activation energy for the forward reaction for the reaction A2 + B2  2 AB?
2 AB?
A)The difference between the energy of the activated complex and the reactant energies
B)The difference between the product energies and the energy of the activated complex
C)The difference between the product energies and the reactant energies
D)The sum of the energy of the activated complex and the reactant energies
E)The sum of the energy of the activated complex and the product energies
 2 AB?
2 AB?A)The difference between the energy of the activated complex and the reactant energies
B)The difference between the product energies and the energy of the activated complex
C)The difference between the product energies and the reactant energies
D)The sum of the energy of the activated complex and the reactant energies
E)The sum of the energy of the activated complex and the product energies
The difference between the energy of the activated complex and the reactant energies
2
Which of the following statements does not correctly describe the character of a chemical equilibrium?
A)As a system comes to equilibrium,the chemical reactions come to a stop
B)In a liquid-gas equilibrium,the number of moles of the gas does not necessarily equal the number of moles of the liquid
C)In a solution equilibrium,the number of moles of the solvent does not necessarily equal the number of moles of the liquid
D)All of the statements above correctly describe a chemical equilibrium
E)None of the statements above correctly describes a chemical equilibrium
A)As a system comes to equilibrium,the chemical reactions come to a stop
B)In a liquid-gas equilibrium,the number of moles of the gas does not necessarily equal the number of moles of the liquid
C)In a solution equilibrium,the number of moles of the solvent does not necessarily equal the number of moles of the liquid
D)All of the statements above correctly describe a chemical equilibrium
E)None of the statements above correctly describes a chemical equilibrium
As a system comes to equilibrium,the chemical reactions come to a stop
3
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
(i)Undissolved sugar in contact with a saturated sugar solution in an open beaker cannot reach equilibrium
(ii)A liquid and its vapor enclosed in two one-liter containers connected by an open glass tube cannot reach equilibrium
(iii)A solution of a weak acid,hydronium ion,and the conjugate base of the weak acid cannot reach equilibrium
A)i only
B)ii only
C)i and ii
D)ii and iii
E)i,ii,and iii
(i)Undissolved sugar in contact with a saturated sugar solution in an open beaker cannot reach equilibrium
(ii)A liquid and its vapor enclosed in two one-liter containers connected by an open glass tube cannot reach equilibrium
(iii)A solution of a weak acid,hydronium ion,and the conjugate base of the weak acid cannot reach equilibrium
A)i only
B)ii only
C)i and ii
D)ii and iii
E)i,ii,and iii
i,ii,and iii
4
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(i)The collision theory of chemical reactions states that what we see as a chemical reaction is the overall effect of a high number of individual collisions between reacting particles
(ii)A violent,bond-breaking collision is most apt to occur if the colliding molecules are moving at high speed
(iii)Most collisions do not result in a reaction
A)iii only
B)i and iii
C)ii and iii
D)All statements are correct
E)All statements are incorrect
(i)The collision theory of chemical reactions states that what we see as a chemical reaction is the overall effect of a high number of individual collisions between reacting particles
(ii)A violent,bond-breaking collision is most apt to occur if the colliding molecules are moving at high speed
(iii)Most collisions do not result in a reaction
A)iii only
B)i and iii
C)ii and iii
D)All statements are correct
E)All statements are incorrect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a reaction is carried out in an aqueous solution,which of the following changes would not affect the rate of the reaction?
A)Increasing the temperature
B)Changing the concentration of reactants
C)Increasing the size of the reaction vessel
D)Adding a catalyst
E)More than one would not affect the rate of the reaction
A)Increasing the temperature
B)Changing the concentration of reactants
C)Increasing the size of the reaction vessel
D)Adding a catalyst
E)More than one would not affect the rate of the reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How does a catalyst alter the rate of a reaction?
A)Catalysts replace part of the reactants
B)Catalysts provide the activation energy needed
C)A catalyst interferes with the attainment of chemical equilibrium
D)Catalysts provide more heat to the reaction,and the increased temperature leads to an increased reaction rate
E)Catalysts provide a reaction pathway with a lower energy of activation
A)Catalysts replace part of the reactants
B)Catalysts provide the activation energy needed
C)A catalyst interferes with the attainment of chemical equilibrium
D)Catalysts provide more heat to the reaction,and the increased temperature leads to an increased reaction rate
E)Catalysts provide a reaction pathway with a lower energy of activation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How will the rate of reaction change if the concentration of reactants is decreased?
A)The rate will increase
B)The rate will decrease
C)Products will form more rapidly,so there will be no change in the rate
D)The rate of product formation will increase
E)A change in concentration leads to an unpredictable effect on the rate of reaction
A)The rate will increase
B)The rate will decrease
C)Products will form more rapidly,so there will be no change in the rate
D)The rate of product formation will increase
E)A change in concentration leads to an unpredictable effect on the rate of reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How does increasing the temperature increase the rate of a chemical reaction?
A)The fraction of sample with the minimum kinetic energy required to react is increased
B)The activation energy for the reaction is decreased
C)The bond energy of the reactants is decreased
D)The likelihood that molecules and ions will have the required geometry is increased
E)The electrons become more reactive because they spin on their own axes at a higher rate
A)The fraction of sample with the minimum kinetic energy required to react is increased
B)The activation energy for the reaction is decreased
C)The bond energy of the reactants is decreased
D)The likelihood that molecules and ions will have the required geometry is increased
E)The electrons become more reactive because they spin on their own axes at a higher rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following conditions is not found in a system that is at equilibrium?
A)Reactants and products are being converted into one another continually
B)The forward rate of reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
C)The concentration of reactants is equal to the concentration of the products
D)The system is closed and isolated from its surroundings
E)The reaction can be represented by an equation with a double arrow
A)Reactants and products are being converted into one another continually
B)The forward rate of reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
C)The concentration of reactants is equal to the concentration of the products
D)The system is closed and isolated from its surroundings
E)The reaction can be represented by an equation with a double arrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider the following reaction coordinate diagram. 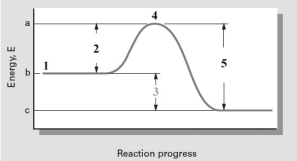 Based on this diagram,which of the following is correct?
Based on this diagram,which of the following is correct?
A)2 represents E and the reaction is exothermic.
B)2 represents E and the reaction is endothermic
C)3 represents E and the reaction is endothermic
D)3 represents E and the reaction is exothermic
E)5 represents E and the reaction is exothermic
 Based on this diagram,which of the following is correct?
Based on this diagram,which of the following is correct?A)2 represents E and the reaction is exothermic.
B)2 represents E and the reaction is endothermic
C)3 represents E and the reaction is endothermic
D)3 represents E and the reaction is exothermic
E)5 represents E and the reaction is exothermic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A molecular collision is sufficiently energetic to cause a reaction,yet no reaction occurs.Which of the following is the least likely explanation?
A)The proton-proton interaction is too large
B)The molecules have poor orientation
C)One of the molecules is not moving too slowly.
D)One or both the molecules does not have enough energy.
E)All of the above could be an explanation.
A)The proton-proton interaction is too large
B)The molecules have poor orientation
C)One of the molecules is not moving too slowly.
D)One or both the molecules does not have enough energy.
E)All of the above could be an explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider the diagram given below. 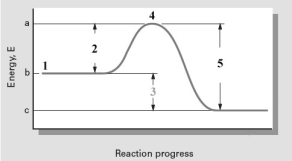 Which number point on the diagram indicates the Ea for the forward reaction?
Which number point on the diagram indicates the Ea for the forward reaction?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
 Which number point on the diagram indicates the Ea for the forward reaction?
Which number point on the diagram indicates the Ea for the forward reaction?A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the hypothetical reaction A + 2 B  AB2 at equilibrium.Which is true?
AB2 at equilibrium.Which is true?
A)The reverse reaction rate is at a maximum
B)The concentration of A must equal the concentration of B
C)The concentration of A must equal one-half the concentration of B
D)The forward reaction rate is equal to the reverse reaction rate
E)The forward reaction rate is equal to the equilibrium reaction rate
 AB2 at equilibrium.Which is true?
AB2 at equilibrium.Which is true?A)The reverse reaction rate is at a maximum
B)The concentration of A must equal the concentration of B
C)The concentration of A must equal one-half the concentration of B
D)The forward reaction rate is equal to the reverse reaction rate
E)The forward reaction rate is equal to the equilibrium reaction rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Consider the following reaction coordinate diagram. 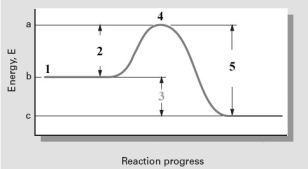 Which numbered point represents the transition state of the reaction?
Which numbered point represents the transition state of the reaction?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
 Which numbered point represents the transition state of the reaction?
Which numbered point represents the transition state of the reaction?A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i)An object hanging motionless on a spring is in a static equilibrium
(ii)In a dynamic equilibrium,the reversible changes occur continuously,even though there is no appearance of change
(iii)The amounts of substances present in a system at equilibrium are equal
A)i only
B)ii only
C)iii only
D)i and ii
E)ii and iii
(i)An object hanging motionless on a spring is in a static equilibrium
(ii)In a dynamic equilibrium,the reversible changes occur continuously,even though there is no appearance of change
(iii)The amounts of substances present in a system at equilibrium are equal
A)i only
B)ii only
C)iii only
D)i and ii
E)ii and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is the primary reason for a higher reaction rate at higher temperatures?
A)Molecules move faster at higher temperatures,producing more violent collisions
B)Electrons occupy higher principal energy levels and are therefore more reactive
C)There is a larger fraction of molecules with sufficient energy to react
D)Molecules increase in size with increasing temperature,providing more surface area for potential collisions
E)The higher temperature creates a lower activation energy,so more molecules can pass over the potential energy barrier
A)Molecules move faster at higher temperatures,producing more violent collisions
B)Electrons occupy higher principal energy levels and are therefore more reactive
C)There is a larger fraction of molecules with sufficient energy to react
D)Molecules increase in size with increasing temperature,providing more surface area for potential collisions
E)The higher temperature creates a lower activation energy,so more molecules can pass over the potential energy barrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements are incorrect?
(i)When opposing reversible reactions occur at different rates,the faster reaction gradually becomes slower.
(ii)Equilibrium is established when forward and reverse reaction rates become equal
(iii)In the development of a chemical equilibrium,the reverse reaction rate decreases over time until equilibrium is established
A)iii only
B)i and ii
C)i and iii
D)ii and iii
E)i,ii,and iii
(i)When opposing reversible reactions occur at different rates,the faster reaction gradually becomes slower.
(ii)Equilibrium is established when forward and reverse reaction rates become equal
(iii)In the development of a chemical equilibrium,the reverse reaction rate decreases over time until equilibrium is established
A)iii only
B)i and ii
C)i and iii
D)ii and iii
E)i,ii,and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the particulate level representation of a reaction of the form: 
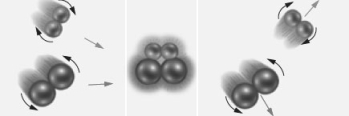
Based on just this diagram,which of the following does not correctly describes this reaction?
A)The collision was ineffective.
B)Product did not form.
C)The orientation of the reactants to with respect to each other was wrong.
D)The molecules had too much potential energy.
E)All of the above do describe this reaction.


Based on just this diagram,which of the following does not correctly describes this reaction?
A)The collision was ineffective.
B)Product did not form.
C)The orientation of the reactants to with respect to each other was wrong.
D)The molecules had too much potential energy.
E)All of the above do describe this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What kind of molecular collisions will not lead to the formation of product in a reaction?
A)Only those without sufficient kinetic energy
B)Only those with the wrong orientation,regardless of the kinetic energy
C)Collisions between molecules that have more energy than the minimum required
D)Those without sufficient kinetic energy and with the wrong orientation
E)Those with effective collisions
A)Only those without sufficient kinetic energy
B)Only those with the wrong orientation,regardless of the kinetic energy
C)Collisions between molecules that have more energy than the minimum required
D)Those without sufficient kinetic energy and with the wrong orientation
E)Those with effective collisions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the following reaction coordinate diagram. 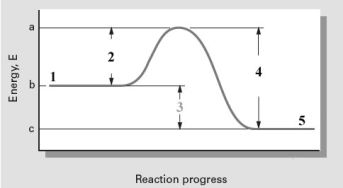 The energy value corresponding to which point(s)will change if a catalyst is added to this reaction?
The energy value corresponding to which point(s)will change if a catalyst is added to this reaction?
A)1 and 5
B)1,3,and 5
C)2,3,and 4
D)2 and 4
E)All will change their energy value.
 The energy value corresponding to which point(s)will change if a catalyst is added to this reaction?
The energy value corresponding to which point(s)will change if a catalyst is added to this reaction?A)1 and 5
B)1,3,and 5
C)2,3,and 4
D)2 and 4
E)All will change their energy value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i)The forward reaction in an equilibrium reaction is exactly the reverse of the reverse reaction
(ii)A dynamic equilibrium is established when two molecules collide
(iii)As reactant concentrations in a chemical equilibrium reaction decrease,the forward reaction rate declines
A)ii only
B)i and ii
C)i and iii
D)ii and iii
E)i,ii,and iii
(i)The forward reaction in an equilibrium reaction is exactly the reverse of the reverse reaction
(ii)A dynamic equilibrium is established when two molecules collide
(iii)As reactant concentrations in a chemical equilibrium reaction decrease,the forward reaction rate declines
A)ii only
B)i and ii
C)i and iii
D)ii and iii
E)i,ii,and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If a copper(II)nitrate solution is added to a sodium sulfide solution the following equilibrium will be attained: Cu2+(aq)+ S2-(aq)  CuS(s).For this equilibrium,K = 6.3*1047.Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression and the correct direction favored at equilibrium.
CuS(s).For this equilibrium,K = 6.3*1047.Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression and the correct direction favored at equilibrium.
A)K =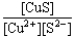 forward
forward
B)K =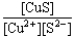 reverse
reverse
C)K =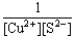 forward
forward
D)K =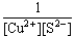 reverse
reverse
E)K =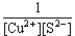 appreciable quantities of all species are present at equilibrium
appreciable quantities of all species are present at equilibrium
 CuS(s).For this equilibrium,K = 6.3*1047.Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression and the correct direction favored at equilibrium.
CuS(s).For this equilibrium,K = 6.3*1047.Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression and the correct direction favored at equilibrium.A)K =
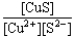 forward
forwardB)K =
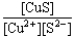 reverse
reverseC)K =
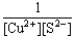 forward
forwardD)K =
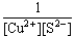 reverse
reverseE)K =
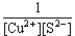 appreciable quantities of all species are present at equilibrium
appreciable quantities of all species are present at equilibrium
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What will happen if the temperature is decreased after equilibrium has been established in the reaction below? 2 C2H6(g)+ 7 O2(g)  4 CO2(g)+ 6 H2O(g)+ 2855 kJ
4 CO2(g)+ 6 H2O(g)+ 2855 kJ
A)There will be no change in the system
B)The concentration of ethane will increase
C)The partial pressure of oxygen will increase
D)The number of water molecules will decrease
E)More carbon dioxide will form
 4 CO2(g)+ 6 H2O(g)+ 2855 kJ
4 CO2(g)+ 6 H2O(g)+ 2855 kJA)There will be no change in the system
B)The concentration of ethane will increase
C)The partial pressure of oxygen will increase
D)The number of water molecules will decrease
E)More carbon dioxide will form

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What will happen if the temperature is increased after equilibrium has been established in the reaction shown? 2 Cl2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)+ 113 kJ  4 HCl(g)+ O2(g)
4 HCl(g)+ O2(g)
A)The position of equilibrium shifts to the left
B)More HCl will form
C)More Cl2 will form
D)The partial pressure of oxygen will decrease
E)The concentration of H2O will increase
 4 HCl(g)+ O2(g)
4 HCl(g)+ O2(g)A)The position of equilibrium shifts to the left
B)More HCl will form
C)More Cl2 will form
D)The partial pressure of oxygen will decrease
E)The concentration of H2O will increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
K = 1.3 * 10-10 for the reaction HC6H5O(aq)  H+(aq)+ C6H5O-(aq).In which direction is the equilibrium favored?
H+(aq)+ C6H5O-(aq).In which direction is the equilibrium favored?
A)Forward
B)Reverse
C)Appreciable quantities of all species are present at equilibrium
D)No direction is favored
E)There is not enough information to determine the direction
 H+(aq)+ C6H5O-(aq).In which direction is the equilibrium favored?
H+(aq)+ C6H5O-(aq).In which direction is the equilibrium favored?A)Forward
B)Reverse
C)Appreciable quantities of all species are present at equilibrium
D)No direction is favored
E)There is not enough information to determine the direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(i)If an equilibrium constant is very large,the reverse reaction is favored
(ii)If an equilibrium constant is very small,the forward reaction is favored
(iii)If an equilibrium constant is neither large nor small,appreciable quantities of all species are present at equilibrium
A)iii only
B)i and ii
C)ii and iii
D)All statements are incorrect
E)All statements are correct
(i)If an equilibrium constant is very large,the reverse reaction is favored
(ii)If an equilibrium constant is very small,the forward reaction is favored
(iii)If an equilibrium constant is neither large nor small,appreciable quantities of all species are present at equilibrium
A)iii only
B)i and ii
C)ii and iii
D)All statements are incorrect
E)All statements are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If one is trying to change the amount of reactants and products in a gaseous equilibrium system,which of the following will probably not have the desired effect?
A)addition of a catalyst
B)addition of a reactant
C)removal of a product
D)altering the temperature
E)changing the volume of the container
A)addition of a catalyst
B)addition of a reactant
C)removal of a product
D)altering the temperature
E)changing the volume of the container

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In writing the expression for the equilibrium constant for a reaction,which of the following should not be done?
A)The concentration of products is placed in the numerator.
B)The concentration of reactants is placed in the demoninator.
C)There are terms for liquids,gases and solutions are included but not solids.
D)The coefficients from the chemical reaction are the exponents for the concentration term.
E)All of these are correct and should be observed.
A)The concentration of products is placed in the numerator.
B)The concentration of reactants is placed in the demoninator.
C)There are terms for liquids,gases and solutions are included but not solids.
D)The coefficients from the chemical reaction are the exponents for the concentration term.
E)All of these are correct and should be observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression for the equilibrium H2(g)+ I2(g)  2 HI(g)
2 HI(g)
A)K =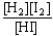
B)K =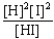
C)K =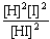
D)K =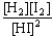
E)K =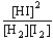
 2 HI(g)
2 HI(g)A)K =
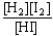
B)K =
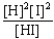
C)K =
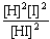
D)K =
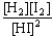
E)K =
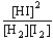

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression for the equilibrium CO(g)+ Cl2(g)  COCl2(g).
COCl2(g).
A)K =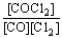
B)K =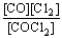
C)K =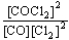
D)K =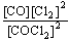
E)K =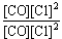
 COCl2(g).
COCl2(g).A)K =
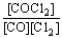
B)K =
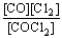
C)K =
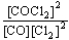
D)K =
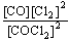
E)K =
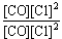

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Calculate the molar solubility of aluminum phosphate in water given that Ksp = 1.3 *10-20.
A)1.1 * 10-10 M
B)1.5 *10-7 M
C)1.7 *10-40 M
D)5.9 * 1039 M
E)7.7 * 1019 M
A)1.1 * 10-10 M
B)1.5 *10-7 M
C)1.7 *10-40 M
D)5.9 * 1039 M
E)7.7 * 1019 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If an aluminum nitrate solution is added to a sodium fluoride solution the following equilibrium will be reached: Al3+(aq)+ 6 F-(aq)  AlF63-(aq).For this equilibrium,K = 5.0 *1023.Choose the correct equilibrium constant and the correct direction favored at equilibrium.
AlF63-(aq).For this equilibrium,K = 5.0 *1023.Choose the correct equilibrium constant and the correct direction favored at equilibrium.
A)K =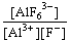 reverse
reverse
B)K =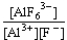 forward
forward
C)K =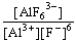 reverse
reverse
D)K =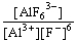 forward
forward
E)K =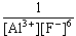 forward
forward
 AlF63-(aq).For this equilibrium,K = 5.0 *1023.Choose the correct equilibrium constant and the correct direction favored at equilibrium.
AlF63-(aq).For this equilibrium,K = 5.0 *1023.Choose the correct equilibrium constant and the correct direction favored at equilibrium.A)K =
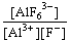 reverse
reverseB)K =
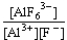 forward
forwardC)K =
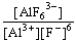 reverse
reverseD)K =
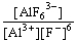 forward
forwardE)K =
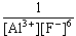 forward
forward
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression for the hypothetical equilibrium 2 A(g)+ 3 B(g)  4 C(g)+ 5 D(g).
4 C(g)+ 5 D(g).
A)K =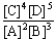
B)K =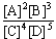
C)K =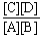
D)K =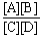
E)K =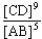
 4 C(g)+ 5 D(g).
4 C(g)+ 5 D(g).A)K =
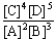
B)K =
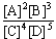
C)K =
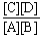
D)K =
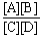
E)K =
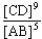

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the position of equilibrium shifts to the left,what will happen?
A)The concentration of products will increase
B)The concentration of reactants will increase
C)The temperature will rise
D)The temperature will decrease
E)The concentrations of both products and reactants will increase
A)The concentration of products will increase
B)The concentration of reactants will increase
C)The temperature will rise
D)The temperature will decrease
E)The concentrations of both products and reactants will increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Calculate the molar solubility of magnesium fluoride (Ksp = 6.9 *10-9)in a solution that also 0.010 M NaF.
A)6.9 * 10-5 M
B)6.9 *10-7 M
C)6.9 * 10-11 M
D)1.7 *10-5 M
E)3.5 * 10-7 M
A)6.9 * 10-5 M
B)6.9 *10-7 M
C)6.9 * 10-11 M
D)1.7 *10-5 M
E)3.5 * 10-7 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Consider the hypothetical reaction A2 + B2  2 AB When will the forward reaction rate be at a maximum,and when will the reverse reaction rate be at a maximum?
2 AB When will the forward reaction rate be at a maximum,and when will the reverse reaction rate be at a maximum?
A)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established
B)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum at time zero
C)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum at time zero,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established
D)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum between time zero and when equilibrium is established,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established
E)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum between time zero and when equilibrium is established
 2 AB When will the forward reaction rate be at a maximum,and when will the reverse reaction rate be at a maximum?
2 AB When will the forward reaction rate be at a maximum,and when will the reverse reaction rate be at a maximum?A)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established
B)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum at time zero
C)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum at time zero,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established
D)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum between time zero and when equilibrium is established,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established
E)The forward reaction rate will be at a maximum when equilibrium is established,and the reverse reaction rate will be at a maximum between time zero and when equilibrium is established

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression for the equilibrium 2 H2(g)+ O2(g)  2 H2O(
2 H2O(  ).
).
A)K =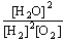
B)K =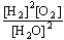
C)K =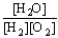
D)K =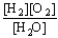
E)K =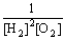
 2 H2O(
2 H2O( 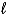 ).
).A)K =
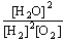
B)K =
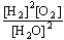
C)K =
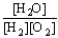
D)K =
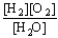
E)K =
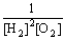

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Predict what will happen if the partial pressure of nitrogen is increased after the reaction N2(g)+ 3 H2(g)  2 NH3(g)has reached equilibrium.
2 NH3(g)has reached equilibrium.
A)The position of equilibrium will shift to the left
B)The molar concentration of H2 will increase
C)The partial pressure of H2 will increase
D)The concentration of NH3 will decrease
E)More ammonia will form
 2 NH3(g)has reached equilibrium.
2 NH3(g)has reached equilibrium.A)The position of equilibrium will shift to the left
B)The molar concentration of H2 will increase
C)The partial pressure of H2 will increase
D)The concentration of NH3 will decrease
E)More ammonia will form

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What will happen to the position of equilibrium if the volume of the system is decreased in the reaction shown? N2(g)+ 3 H2  2 NH3(g)
2 NH3(g)
A)It will shift to the left
B)There will be no shift in the position of equilibrium
C)The position will shift left and then return to its original place
D)It will shift to the right
E)It will shift so that the system volume is increased again
 2 NH3(g)
2 NH3(g)A)It will shift to the left
B)There will be no shift in the position of equilibrium
C)The position will shift left and then return to its original place
D)It will shift to the right
E)It will shift so that the system volume is increased again

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Choose the correct equilibrium constant expression for the equilibrium 4 NO(g)+ 6 H2O(g)  4 NH3(g)+ 5 O2(g)
4 NH3(g)+ 5 O2(g)
A)K =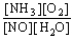
B)K =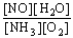
C)K =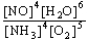
D)K =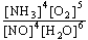
E)K =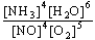
 4 NH3(g)+ 5 O2(g)
4 NH3(g)+ 5 O2(g)A)K =
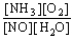
B)K =
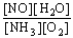
C)K =
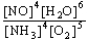
D)K =
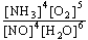
E)K =
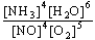

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Find the pH of a 0.10 M solution of benzoic acid,C6H5COOH,if the solution is also 0.15 M in C6H5COO-.Ka = 6.3 *10-5.
A)9.62
B)5.20
C)4.02
D)4.20
E)4.38
A)9.62
B)5.20
C)4.02
D)4.20
E)4.38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the pH of a 0.20 M solution of nitrous acid? Ka = 4.5 *10-4
A)9.02
B)4.66
C)4.05
D)2.02
E)0.70
A)9.02
B)4.66
C)4.05
D)2.02
E)0.70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Ka = 1.8 *10-5 for the ionization of HC2H3O2(aq).Determine the [HC2H3O2]/[C2H3O2-] ratio that will produce a buffer at pH = 5.00.
A)3.6 * 10-6
B)9.0 *10-5
C)0.18
D)0.56
E)1.8
A)3.6 * 10-6
B)9.0 *10-5
C)0.18
D)0.56
E)1.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following correctly expresses Ka for the weak acid HF(aq)?
A)Ka = [HF]
B)Ka =![<strong>Which of the following correctly expresses K<sub>a</sub> for the weak acid HF(aq)?</strong> A)K<sub>a</sub> = [HF] B)K<sub>a</sub> = C)K<sub>a</sub> = D)K<sub>a</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] E)K<sub>a</sub> =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6511/11eab070_b116_5d69_a51f_110b2e11f6f7_TB6511_11.jpg)
C)Ka =![<strong>Which of the following correctly expresses K<sub>a</sub> for the weak acid HF(aq)?</strong> A)K<sub>a</sub> = [HF] B)K<sub>a</sub> = C)K<sub>a</sub> = D)K<sub>a</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] E)K<sub>a</sub> =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6511/11eab070_b116_847a_a51f_ed283d31b4a2_TB6511_11.jpg)
D)Ka = [H+][F-]
E)Ka =![<strong>Which of the following correctly expresses K<sub>a</sub> for the weak acid HF(aq)?</strong> A)K<sub>a</sub> = [HF] B)K<sub>a</sub> = C)K<sub>a</sub> = D)K<sub>a</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] E)K<sub>a</sub> =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6511/11eab070_b116_847b_a51f_e1c404aa760b_TB6511_11.jpg)
A)Ka = [HF]
B)Ka =
![<strong>Which of the following correctly expresses K<sub>a</sub> for the weak acid HF(aq)?</strong> A)K<sub>a</sub> = [HF] B)K<sub>a</sub> = C)K<sub>a</sub> = D)K<sub>a</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] E)K<sub>a</sub> =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6511/11eab070_b116_5d69_a51f_110b2e11f6f7_TB6511_11.jpg)
C)Ka =
![<strong>Which of the following correctly expresses K<sub>a</sub> for the weak acid HF(aq)?</strong> A)K<sub>a</sub> = [HF] B)K<sub>a</sub> = C)K<sub>a</sub> = D)K<sub>a</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] E)K<sub>a</sub> =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6511/11eab070_b116_847a_a51f_ed283d31b4a2_TB6511_11.jpg)
D)Ka = [H+][F-]
E)Ka =
![<strong>Which of the following correctly expresses K<sub>a</sub> for the weak acid HF(aq)?</strong> A)K<sub>a</sub> = [HF] B)K<sub>a</sub> = C)K<sub>a</sub> = D)K<sub>a</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][F<sup>-</sup>] E)K<sub>a</sub> =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6511/11eab070_b116_847b_a51f_e1c404aa760b_TB6511_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



