Deck 19: Oxidation-Reduction Redoxreactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Oxidation-Reduction Redoxreactions
1
Examine the two beakers shown below. 

If the metals were connected by a wire containing a meter and the two solutions by a salt bridge,the meter shows are reading of 0.95 V.Which of the following is correct?
A)A spontaneous reaction occurs.
B)A voltaic cell has been constructed.
C)Electrons flow from the anode to the cathode.
D)Reduction occurs at the cathode.
E)All of the above are correct in this situation.


If the metals were connected by a wire containing a meter and the two solutions by a salt bridge,the meter shows are reading of 0.95 V.Which of the following is correct?
A)A spontaneous reaction occurs.
B)A voltaic cell has been constructed.
C)Electrons flow from the anode to the cathode.
D)Reduction occurs at the cathode.
E)All of the above are correct in this situation.
All of the above are correct in this situation.
2
Consider the following images.The reactions occurring in each are shown in the choices. 



A B C D
Which of the following is an example of an electron transfer reaction?
A)Pb(NO3)2(aq)+ Na2SO4(aq)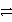 2 NaNO3(aq)+ PbSO4(s)
2 NaNO3(aq)+ PbSO4(s)
B)H2CO3(aq)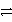 H2O(l)+ CO2(g)
H2O(l)+ CO2(g)
C)Ca(s)+ 2HCl(aq)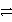 CaCl2(aq)+ H2(g)
CaCl2(aq)+ H2(g)
D)Zn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)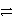 Zn2+(aq)+ Cu(s)
Zn2+(aq)+ Cu(s)
E)Both c and d are electron transfer reactions.




A B C D
Which of the following is an example of an electron transfer reaction?
A)Pb(NO3)2(aq)+ Na2SO4(aq)
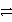 2 NaNO3(aq)+ PbSO4(s)
2 NaNO3(aq)+ PbSO4(s)B)H2CO3(aq)
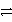 H2O(l)+ CO2(g)
H2O(l)+ CO2(g)C)Ca(s)+ 2HCl(aq)
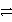 CaCl2(aq)+ H2(g)
CaCl2(aq)+ H2(g)D)Zn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
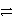 Zn2+(aq)+ Cu(s)
Zn2+(aq)+ Cu(s)E)Both c and d are electron transfer reactions.
Both c and d are electron transfer reactions.
3
Which of the following processes is a reduction reaction?
A)2 Br- becoming Br2
B)Ni2+ becoming Ni3+
C)Hg22+ becoming 2 Hg
D)Tin(II)becoming tin(IV)
E)Iron(II)becoming iron(III)
A)2 Br- becoming Br2
B)Ni2+ becoming Ni3+
C)Hg22+ becoming 2 Hg
D)Tin(II)becoming tin(IV)
E)Iron(II)becoming iron(III)
Hg22+ becoming 2 Hg
4
What is the balanced redox equation that results from the combination of the following half-reactions?
Cr3+ + 3e-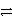
Cr and 2 Cl-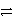
Cl2 + 2 e-
A)CrCl2+ + e-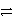 Cr + Cl2
Cr + Cl2
B)Cr3+ + 2 Cl- + e-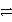 Cr + Cl2
Cr + Cl2
C)Cr3+ + 3 Cl-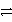 CrCl3
CrCl3
D)2 Cr3+ + 6 Cl- + 3 e-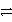 3 Cl2 + 2 Cr + 2 e-
3 Cl2 + 2 Cr + 2 e-
E)2 Cr3+ + 6 Cl-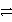 3 Cl2 + 2 Cr
3 Cl2 + 2 Cr
Cr3+ + 3e-
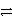
Cr and 2 Cl-
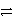
Cl2 + 2 e-
A)CrCl2+ + e-
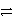 Cr + Cl2
Cr + Cl2B)Cr3+ + 2 Cl- + e-
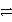 Cr + Cl2
Cr + Cl2C)Cr3+ + 3 Cl-
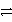 CrCl3
CrCl3D)2 Cr3+ + 6 Cl- + 3 e-
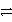 3 Cl2 + 2 Cr + 2 e-
3 Cl2 + 2 Cr + 2 e-E)2 Cr3+ + 6 Cl-
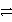 3 Cl2 + 2 Cr
3 Cl2 + 2 Cr
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the oxidation number of Cl in Cl2?
A)-1
B)-2
C)+2
D)0
E)One atom is +1 and the other is -1.
A)-1
B)-2
C)+2
D)0
E)One atom is +1 and the other is -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify the reduction half-reaction in the redox equation:
4 Ag + O2(g)+ 2 H2O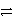
4 Ag+ + 4 OH-
A)Ag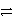 Ag + e-
Ag + e-
B)4 Ag + 4 e-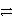 4 Ag+
4 Ag+
C)2 H2O + 2e-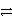 4 OH-
4 OH-
D)O2(g)+ 2 H2O + 4 e-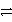 4 OH-
4 OH-
E)2 H2O + 2 e-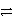 H2 + 2 OH-
H2 + 2 OH-
4 Ag + O2(g)+ 2 H2O
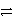
4 Ag+ + 4 OH-
A)Ag
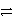 Ag + e-
Ag + e-B)4 Ag + 4 e-
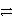 4 Ag+
4 Ag+C)2 H2O + 2e-
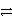 4 OH-
4 OH-D)O2(g)+ 2 H2O + 4 e-
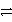 4 OH-
4 OH-E)2 H2O + 2 e-
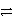 H2 + 2 OH-
H2 + 2 OH-
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the half-reaction for the oxidation of sulfide ions in aqueous solution?
A)S2-(aq)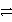 S(s)+ 2 e-
S(s)+ 2 e-
B)S-(aq)+ e-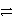 S2-(aq)
S2-(aq)
C)S(s)+ 2 e-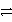 S2-(aq)
S2-(aq)
D)SO32-(aq)+ 6 H+(aq)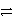 S(s)+ 3 H2O(
S(s)+ 3 H2O(  )+ 4 e-
)+ 4 e-
E)SO42-(aq)+ 8 H+(aq)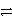 S(s)+ 4 H2O(
S(s)+ 4 H2O( 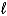 )+ 6 e-
)+ 6 e-
A)S2-(aq)
 S(s)+ 2 e-
S(s)+ 2 e-B)S-(aq)+ e-
 S2-(aq)
S2-(aq)C)S(s)+ 2 e-
 S2-(aq)
S2-(aq)D)SO32-(aq)+ 6 H+(aq)
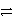 S(s)+ 3 H2O(
S(s)+ 3 H2O( 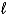 )+ 4 e-
)+ 4 e-E)SO42-(aq)+ 8 H+(aq)
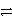 S(s)+ 4 H2O(
S(s)+ 4 H2O( 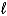 )+ 6 e-
)+ 6 e-
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Oxidation-reduction reactions are also known as...
A)electron-transfer reactions
B)proton-transfer reactions
C)neutron bombardment reactions
D)neutralization reactions
E)double displacement reactions
A)electron-transfer reactions
B)proton-transfer reactions
C)neutron bombardment reactions
D)neutralization reactions
E)double displacement reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify the oxidation half-reaction in the redox equation:
Cu(s)+ Cl2(g)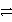
Cu2+ + 2 Cl-
A)Cl2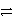 2 Cl- + 2 e-
2 Cl- + 2 e-
B)Cl2 + 2 e-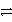 2 Cl-
2 Cl-
C)Cu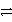 Cu2+ + 2 e-
Cu2+ + 2 e-
D)Cu + 2 e-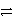 Cu2+
Cu2+
E)Cu + Cl2 + 2 e-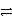 Cu2+ + 2 Cl- + 2 e-
Cu2+ + 2 Cl- + 2 e-
Cu(s)+ Cl2(g)
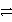
Cu2+ + 2 Cl-
A)Cl2
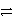 2 Cl- + 2 e-
2 Cl- + 2 e-B)Cl2 + 2 e-
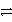 2 Cl-
2 Cl-C)Cu
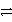 Cu2+ + 2 e-
Cu2+ + 2 e-D)Cu + 2 e-
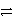 Cu2+
Cu2+E)Cu + Cl2 + 2 e-
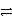 Cu2+ + 2 Cl- + 2 e-
Cu2+ + 2 Cl- + 2 e-
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the oxidation number of titanium in TiO2?
A)+4
B)+2
C)+6
D)-4
E)zero
A)+4
B)+2
C)+6
D)-4
E)zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which among the following are the parts that comprose an electrolytic cell?
(i)Two electrodes
(ii)A molecular liquid
(iii)A salt bridge
(iv)An ionic solution
A)i and ii
B)i and iv
C)ii,iii,and iv
D)i,ii,and iii
E)i,iii,and iv
(i)Two electrodes
(ii)A molecular liquid
(iii)A salt bridge
(iv)An ionic solution
A)i and ii
B)i and iv
C)ii,iii,and iv
D)i,ii,and iii
E)i,iii,and iv

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What happens in a galvanic cell?
A)Cations are changed into ions
B)Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy
C)Anions combine with cations to produce electricity
D)Less reactive metals are turned into more reactive metals by the action of an electric current
E)Matter is changed into energy
A)Cations are changed into ions
B)Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy
C)Anions combine with cations to produce electricity
D)Less reactive metals are turned into more reactive metals by the action of an electric current
E)Matter is changed into energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Reduction can be defined as...
A)a increase in oxidation number
B)the gain of protons
C)the loss of protons
D)a gain of electrons
E)a loss of electrons
A)a increase in oxidation number
B)the gain of protons
C)the loss of protons
D)a gain of electrons
E)a loss of electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in sulfite ion,SO32-?
A)+6
B)+4
C)-2
D)+2
E)-4
A)+6
B)+4
C)-2
D)+2
E)-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the following beakers.In the beaker on the left copper metal is placed in a solution of silver nitrate.The reaction is allowed to run for 60 minutes producing the products shown on the right. 

The equation for the oxidation half-reaction would be:
A)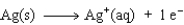
B)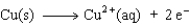
C)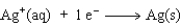
D)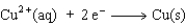


The equation for the oxidation half-reaction would be:
A)
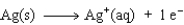
B)
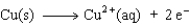
C)
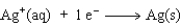
D)
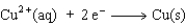

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify the oxidation half-reaction in the following group.
A)Ag(NH3)2 + e-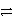 Ag + 2 NH3
Ag + 2 NH3
B)Ag + Cl-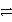 AgCl + e-
AgCl + e-
C)PbSO4(s)+ 2 e-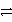 Pb(s)+ SO42-
Pb(s)+ SO42-
D)Ag(CN)2 + e-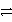 Ag + 2 CN-
Ag + 2 CN-
E)Cr2O72- + H2O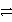 2 CrO42- + 2 H+
2 CrO42- + 2 H+
A)Ag(NH3)2 + e-
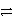 Ag + 2 NH3
Ag + 2 NH3B)Ag + Cl-
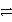 AgCl + e-
AgCl + e-C)PbSO4(s)+ 2 e-
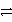 Pb(s)+ SO42-
Pb(s)+ SO42-D)Ag(CN)2 + e-
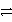 Ag + 2 CN-
Ag + 2 CN-E)Cr2O72- + H2O
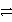 2 CrO42- + 2 H+
2 CrO42- + 2 H+
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is the half-reaction for reduction of chlorine to chloride ions in water?
A)Cl2(aq)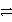 Cl-(aq)+ Cl+(aq)
Cl-(aq)+ Cl+(aq)
B)Cl-(aq)+ H+(aq)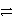 HCl(aq)
HCl(aq)
C)2 Cl-(aq)+ 2 e-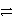 Cl2(aq)
Cl2(aq)
D)Cl2(aq)+ 2 e-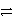 2 Cl-(aq)
2 Cl-(aq)
E)2 Cl-(aq)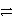 Cl2(aq)+ 2 e-
Cl2(aq)+ 2 e-
A)Cl2(aq)
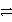 Cl-(aq)+ Cl+(aq)
Cl-(aq)+ Cl+(aq)B)Cl-(aq)+ H+(aq)
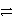 HCl(aq)
HCl(aq)C)2 Cl-(aq)+ 2 e-
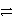 Cl2(aq)
Cl2(aq)D)Cl2(aq)+ 2 e-
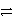 2 Cl-(aq)
2 Cl-(aq)E)2 Cl-(aq)
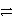 Cl2(aq)+ 2 e-
Cl2(aq)+ 2 e-
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is correct for an electrolytic cell?
A)Electrons flow through the external circuit from the anode to the cathode
B)The electrode at which oxidation occurs is the cathode
C)The reaction occurring in the cell can be used to generate an electric current.
D)Charge is carried through the solution by electrons in one direction and by protons in the other direction
E)None of the statements above is correct
A)Electrons flow through the external circuit from the anode to the cathode
B)The electrode at which oxidation occurs is the cathode
C)The reaction occurring in the cell can be used to generate an electric current.
D)Charge is carried through the solution by electrons in one direction and by protons in the other direction
E)None of the statements above is correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How many electrons are transferred in the balanced redox equation that results from combining these two half-reactions on a molar scale?
Al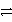
Al3+ + 3e- and Cu2+ + 2 e-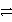
Cu
A)6
B)5
C)3
D)2
E)1
Al
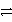
Al3+ + 3e- and Cu2+ + 2 e-
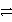
Cu
A)6
B)5
C)3
D)2
E)1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a reduction reaction?
A)Conversion of 2 Cl- to Cl2
B)Conversion of copper(I)ions into copper(II)ions
C)Conversion of Ag+ into Ag
D)Conversion of Al3+ to Al
E)Conversion of plutonium into uranium
A)Conversion of 2 Cl- to Cl2
B)Conversion of copper(I)ions into copper(II)ions
C)Conversion of Ag+ into Ag
D)Conversion of Al3+ to Al
E)Conversion of plutonium into uranium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In comparing acid-base neutralization reactions and redox reactions,which of the following is correct?
A)A strong acid readily gains protons while a strong oxidizing agent readily gains electrons.
B)A strong acid readily provides protons while a strong reducing agent readily gains electrons.
C)A strong base readily gains protons while a strong oxidizing agent readily gains electrons.
D)A strong base readily provides protons while a strong reducing agent readily loses electrons.
A)A strong acid readily gains protons while a strong oxidizing agent readily gains electrons.
B)A strong acid readily provides protons while a strong reducing agent readily gains electrons.
C)A strong base readily gains protons while a strong oxidizing agent readily gains electrons.
D)A strong base readily provides protons while a strong reducing agent readily loses electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What role does the reducing agent play in a redox reaction?
A)It catalyzes the reaction
B)It picks up electrons
C)It picks up protons from the oxidizing agent
D)It donates protons to the oxidizing agent
E)It donates some of its electrons
A)It catalyzes the reaction
B)It picks up electrons
C)It picks up protons from the oxidizing agent
D)It donates protons to the oxidizing agent
E)It donates some of its electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the reducing agent in the reaction of hydrazine as a rocket fuel: N2H4( 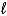 )+ O2(g)
)+ O2(g) 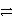 N2(g)+ 2 H2O(
N2(g)+ 2 H2O( 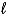 )?
)?
A)N2H4
B)O2
C)N2
D)H2O
E)There is no reducing agent in this reaction
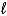 )+ O2(g)
)+ O2(g) 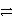 N2(g)+ 2 H2O(
N2(g)+ 2 H2O( 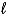 )?
)?A)N2H4
B)O2
C)N2
D)H2O
E)There is no reducing agent in this reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the reaction of carbon with oxygen,which substance is oxidized? The equation for the reaction is
C(s)+ O2(g)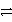
CO2(g).
A)O2(g)
B)CO2(g)
C)No substance is oxidized in this reaction
D)C(s)
E)Both C(s)and O2(g)
C(s)+ O2(g)
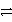
CO2(g).
A)O2(g)
B)CO2(g)
C)No substance is oxidized in this reaction
D)C(s)
E)Both C(s)and O2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider the following table of relative strengths of oxidizing and reducing agents:
Oxidizing Agent
Reducing Agent
Stronger
A+ + e-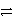
A
Weaker
B2+ + 2 e-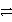
B
Weaker
C3+ + 3 e-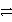
C
Stronger
Which of the following is the correct net ionic equation for the redox reaction between A+ and C and the correct direction that is favored?
A)A+ + C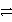 A + C3+ forward
A + C3+ forward
B)A+ + C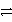 A + C3+ reverse
A + C3+ reverse
C)3 A+ + C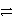 3 A + C3+ forward
3 A + C3+ forward
D)3 A+ + C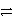 3 A + C3+ reverse
3 A + C3+ reverse
E)A+ + C + e-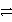 A + C3+ + 3 e- forward
A + C3+ + 3 e- forward
Oxidizing Agent
Reducing Agent
Stronger
A+ + e-
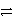
A
Weaker
B2+ + 2 e-
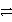
B
Weaker
C3+ + 3 e-
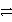
C
Stronger
Which of the following is the correct net ionic equation for the redox reaction between A+ and C and the correct direction that is favored?
A)A+ + C
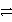 A + C3+ forward
A + C3+ forwardB)A+ + C
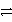 A + C3+ reverse
A + C3+ reverseC)3 A+ + C
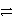 3 A + C3+ forward
3 A + C3+ forwardD)3 A+ + C
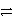 3 A + C3+ reverse
3 A + C3+ reverseE)A+ + C + e-
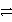 A + C3+ + 3 e- forward
A + C3+ + 3 e- forward
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When zinc is plated to iron,the zinc corrodes rather than the iron.Which statement is true?
A)Zinc is less reactive than iron
B)Zinc is more active metal than iron
C)Zinc is a better oxidizing agent than iron
D)Iron is a better reducing agent than zinc
E)Both metals are Lewis metals
A)Zinc is less reactive than iron
B)Zinc is more active metal than iron
C)Zinc is a better oxidizing agent than iron
D)Iron is a better reducing agent than zinc
E)Both metals are Lewis metals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following substances is most likely to be a reducing agent?
A)NH4+
B)S2-
C)Mg2+
D)KMnO4
E)Cl2
A)NH4+
B)S2-
C)Mg2+
D)KMnO4
E)Cl2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is the correct net ionic equation for the redox reaction between nickel ion and metallic silver and the correct direction that is favored? The half reactions are:
Ag+ + e-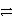
Ag(s)Ni2+ + 2e-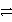
Ni(s)Ag+ is a stronger oxidizing agent than Ni2+.
A)Ni2+(aq)+ Ag(s)+ e-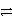 Ni(s)+ Ag+ (aq)forward
Ni(s)+ Ag+ (aq)forward
B)Ni2+(aq)+ Ag(s)+ e-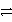 Ni(s)+ Ag+(aq)reverse
Ni(s)+ Ag+(aq)reverse
C)Ni2+(aq)+ Ag(s)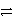 Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)reverse
Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)reverse
D)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)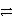 Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)forward
Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)forward
E)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)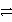 Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)reverse
Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)reverse
Ag+ + e-
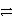
Ag(s)Ni2+ + 2e-
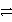
Ni(s)Ag+ is a stronger oxidizing agent than Ni2+.
A)Ni2+(aq)+ Ag(s)+ e-
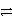 Ni(s)+ Ag+ (aq)forward
Ni(s)+ Ag+ (aq)forwardB)Ni2+(aq)+ Ag(s)+ e-
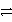 Ni(s)+ Ag+(aq)reverse
Ni(s)+ Ag+(aq)reverseC)Ni2+(aq)+ Ag(s)
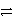 Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)reverse
Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)reverseD)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
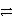 Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)forward
Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)forwardE)Ni2+(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
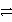 Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)reverse
Ni(s)+ 2 Ag+(aq)reverse
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A)Acid-base reactions involve a transfer of protons; redox reactions,a transfer of electrons
B)In both redox and acid-base reactions,the reactants are given special names to indicate their roles in the transfer process
C)Just as certain species can either donate or accept protons and thereby behave as an acid in one reaction and a base in another,certain species can either accept or donate electrons,acting as an oxidizing agent in one reaction and a reducing agent in another
D)Just as acids and bases may be classified as "strong" or "weak" depending on how readily they donate or accept protons,the strengths of oxidizing and reducing agents may be compared according to their tendencies to attract or release electrons
E)Unlike most acid-base reactions in aqueous solution,which reach a state of equilibrium,most aqueous redox reactions do not reach a state of equilibrium and proceed entirely in either the forward or reverse direction
A)Acid-base reactions involve a transfer of protons; redox reactions,a transfer of electrons
B)In both redox and acid-base reactions,the reactants are given special names to indicate their roles in the transfer process
C)Just as certain species can either donate or accept protons and thereby behave as an acid in one reaction and a base in another,certain species can either accept or donate electrons,acting as an oxidizing agent in one reaction and a reducing agent in another
D)Just as acids and bases may be classified as "strong" or "weak" depending on how readily they donate or accept protons,the strengths of oxidizing and reducing agents may be compared according to their tendencies to attract or release electrons
E)Unlike most acid-base reactions in aqueous solution,which reach a state of equilibrium,most aqueous redox reactions do not reach a state of equilibrium and proceed entirely in either the forward or reverse direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is the correct net ionic equation for the redox reaction between zinc and the copper(II)ion and the correct direction that is favored? The half-reactions are:
Cu2+ + 2 e-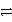
Cu(s)Zn2+ + 2 e-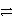
Zn(s)Cu2+ is a stronger oxidizing agent than Zn2+.
A)Cu2+(aq)+ Zn(s)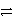 Cu(s)+ Zn2+(aq)reverse
Cu(s)+ Zn2+(aq)reverse
B)Cu2+(aq)+ Zn(s)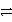 Cu(s)+ Zn2+(aq)forward
Cu(s)+ Zn2+(aq)forward
C)Cu2+(aq)+ Zn2+(s)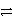 Cu(s)+ Zn(s) reverse
Cu(s)+ Zn(s) reverse
D)Cu2+(aq)+ Zn2+(s)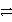 Cu(s)+ Zn(s) forward
Cu(s)+ Zn(s) forward
E)Zn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)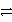 Zn+(aq)+ Cu+(aq)forward
Zn+(aq)+ Cu+(aq)forward
Cu2+ + 2 e-
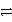
Cu(s)Zn2+ + 2 e-
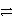
Zn(s)Cu2+ is a stronger oxidizing agent than Zn2+.
A)Cu2+(aq)+ Zn(s)
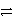 Cu(s)+ Zn2+(aq)reverse
Cu(s)+ Zn2+(aq)reverseB)Cu2+(aq)+ Zn(s)
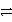 Cu(s)+ Zn2+(aq)forward
Cu(s)+ Zn2+(aq)forwardC)Cu2+(aq)+ Zn2+(s)
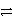 Cu(s)+ Zn(s) reverse
Cu(s)+ Zn(s) reverseD)Cu2+(aq)+ Zn2+(s)
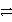 Cu(s)+ Zn(s) forward
Cu(s)+ Zn(s) forwardE)Zn(s)+ Cu2+(aq)
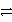 Zn+(aq)+ Cu+(aq)forward
Zn+(aq)+ Cu+(aq)forward
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following cannot be a reducing agent?
A)H+(aq)
B)H2(g)
C)H2O2(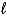 )
)
D)CH4(g)
E)All of the above can be a reducing agent
A)H+(aq)
B)H2(g)
C)H2O2(
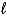 )
)D)CH4(g)
E)All of the above can be a reducing agent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the oxidizing agent in this redox reaction?
2 MnO2(s)+ 2 NH4Cl(s)+ Zn(s)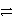
Zn(NH3)2Cl2(s)+ Mn2O3(s)+ H2O(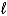 )
)
A)NH4Cl
B)MnO2
C)Zn
D)Zn(NH3)2Cl2
E)Mn2O3
2 MnO2(s)+ 2 NH4Cl(s)+ Zn(s)
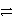
Zn(NH3)2Cl2(s)+ Mn2O3(s)+ H2O(
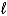 )
)A)NH4Cl
B)MnO2
C)Zn
D)Zn(NH3)2Cl2
E)Mn2O3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Match each term with its correct classification:
Proton Donor Proton Acceptor Electron Donor Electron Acceptor
A)Reducing Agent Oxidizing Agent Acid Base
B)Base Acid Reducing Agent Oxidizing Agent
C)Base Acid Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent
D)Acid Base Reducing Agent Oxidizing Agent
E)Acid Base Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent
Proton Donor Proton Acceptor Electron Donor Electron Acceptor
A)Reducing Agent Oxidizing Agent Acid Base
B)Base Acid Reducing Agent Oxidizing Agent
C)Base Acid Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent
D)Acid Base Reducing Agent Oxidizing Agent
E)Acid Base Oxidizing Agent Reducing Agent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What happens to an elemental oxidizing agent in a redox reaction?
A)It speeds the rate of the reaction although it doesn't actually participate in the reaction
B)It gives up some of its electrons
C)It increases the oxidation number
D)It gets oxidized
E)It gets reduced
A)It speeds the rate of the reaction although it doesn't actually participate in the reaction
B)It gives up some of its electrons
C)It increases the oxidation number
D)It gets oxidized
E)It gets reduced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the oxidation number of chromium in Cr2O72-?
A)+12
B)+3
C)+6
D)-2
E)-1
A)+12
B)+3
C)+6
D)-2
E)-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Silver metal will not react with hydrochloric acid.What does this suggest about silver and hydrochloric acid?
A)HCl is a weak acid
B)HCl is a strong acid
C)Ag is a weaker reducing agent than H+ in HCl(aq)
D)Ag is a stronger oxidizing agent than HCl
E)No conclusion can be made based on this information
A)HCl is a weak acid
B)HCl is a strong acid
C)Ag is a weaker reducing agent than H+ in HCl(aq)
D)Ag is a stronger oxidizing agent than HCl
E)No conclusion can be made based on this information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What evidence suggests that Na+ ions are very weak oxidizing agents?
A)NaCl is a strong electrolyte
B)Na metal does not occur in the Earth's crust
C)NaOH is a strong base
D)Na metal is soft and can be cut with a knife
E)Na+ ions are a component of table salt
A)NaCl is a strong electrolyte
B)Na metal does not occur in the Earth's crust
C)NaOH is a strong base
D)Na metal is soft and can be cut with a knife
E)Na+ ions are a component of table salt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which substance gets reduced in this redox reaction?
Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 2 H2SO4(aq)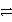
2 PbSO4(s)+ 2 H2O(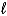 )
)
A)H2SO4(s)
B)Pb(s)
C)PbO2(s)
D)PbSO4(s)
E)No substance is reduced in this reaction
Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 2 H2SO4(aq)
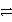
2 PbSO4(s)+ 2 H2O(
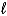 )
)A)H2SO4(s)
B)Pb(s)
C)PbO2(s)
D)PbSO4(s)
E)No substance is reduced in this reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Balance the following redox reaction in acidic solution and determine how many water molecules are in the equation.
MnO4- + ClO-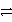
ClO3- + Mn2+ + H2O
A)8
B)2
C)6
D)5
E)4
MnO4- + ClO-
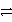
ClO3- + Mn2+ + H2O
A)8
B)2
C)6
D)5
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the following table of relative strengths of oxidizing and reducing agents:
Oxidizing Agent
Reducing Agent
Stronger
A+ + e-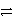
A
Weaker
B2+ + 2 e-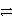
B
Weaker
C3+ + 3 e-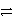
C
Stronger
Which correctly lists the oxidizing agents in order of increasing strength?
A)A < B < C
B)C < B < A
C)A+ < B2+ < C3+
D)B2+ < A+ < C3+
E)C3+ < B2+ < A+
Oxidizing Agent
Reducing Agent
Stronger
A+ + e-
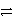
A
Weaker
B2+ + 2 e-
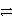
B
Weaker
C3+ + 3 e-
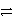
C
Stronger
Which correctly lists the oxidizing agents in order of increasing strength?
A)A < B < C
B)C < B < A
C)A+ < B2+ < C3+
D)B2+ < A+ < C3+
E)C3+ < B2+ < A+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Balance the half-reaction in acidic solution and determine the coefficient for hydrogen ion:
___ Cr3+ + ___ H2O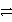
___ Cr2O72- + ___ H+
A)2
B)5
C)8
D)11
E)14
___ Cr3+ + ___ H2O
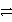
___ Cr2O72- + ___ H+
A)2
B)5
C)8
D)11
E)14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In balancing the half-reaction
SO42-(aq)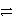
S(s)how many H+ ions are added to which side?
A)4 H+ to the left side
B)8 H+ to the right side
C)4 H+ to the right side
D)8 H+ to the left side
E)6 H+ to the left side
SO42-(aq)
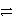
S(s)how many H+ ions are added to which side?
A)4 H+ to the left side
B)8 H+ to the right side
C)4 H+ to the right side
D)8 H+ to the left side
E)6 H+ to the left side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Balance the following redox equation in acidic solution and determine the coefficient placed in front of H2O: ___ Cu + ___ NO3- + ___ H+ 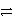 ___ Cu2+ + ___ NO + ___ H2O
___ Cu2+ + ___ NO + ___ H2O
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6
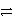 ___ Cu2+ + ___ NO + ___ H2O
___ Cu2+ + ___ NO + ___ H2OA)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In balancing the half-reaction
NO(g)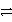
NO3-(aq)in acidic solution,how many electrons are added,and to which side?
A)1 electron to the right side
B)3 electrons to the left side
C)5 electrons to the left side
D)5 electrons to the right side
E)3 electrons to the right side
NO(g)
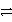
NO3-(aq)in acidic solution,how many electrons are added,and to which side?
A)1 electron to the right side
B)3 electrons to the left side
C)5 electrons to the left side
D)5 electrons to the right side
E)3 electrons to the right side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 44 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



