Deck 17: Acid-Base Proton-Transferreactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Acid-Base Proton-Transferreactions
1
What is a Brønsted-Lowry base?
A)An electron pair source
B)A hydroxide ion source
C)A metal ion
D)A proton source
E)A proton remover
A)An electron pair source
B)A hydroxide ion source
C)A metal ion
D)A proton source
E)A proton remover
A proton remover
2
Which of the following is a characteristic property traditionally associated with an Arrhenius acid?
A)Turns litmus indicator blue
B)Feels slippery
C)Tastes bitter
D)Sour taste
E)Contain OH- ions
A)Turns litmus indicator blue
B)Feels slippery
C)Tastes bitter
D)Sour taste
E)Contain OH- ions
Sour taste
3
Which of these statements is true?
A)All Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases are also Arrhenius acids and bases
B)All Lewis acids are Brønsted-Lowry acids
C)All Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases are stronger than Arrhenius acids and bases
D)All Arrhenius acids and bases are also Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases
E)There is no relationship between Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases and Lewis acids and bases
A)All Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases are also Arrhenius acids and bases
B)All Lewis acids are Brønsted-Lowry acids
C)All Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases are stronger than Arrhenius acids and bases
D)All Arrhenius acids and bases are also Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases
E)There is no relationship between Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases and Lewis acids and bases
All Arrhenius acids and bases are also Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases
4
Identify the conjugate acid base pairs in the reaction H2SO4 + HNO3 H2NO3+ + HSO4-.
A)H2SO4/HSO4- and H2NO3+/HNO3
B)H2SO4/HNO3 and H2NO3+/HSO4-
C)HNO3/HSO4- and H2SO4/H2NO3+
D)HNO3/NO3- and HSO4-/SO42-
E)HNO3/H2SO4 and H2NO3+/HSO4-
A)H2SO4/HSO4- and H2NO3+/HNO3
B)H2SO4/HNO3 and H2NO3+/HSO4-
C)HNO3/HSO4- and H2SO4/H2NO3+
D)HNO3/NO3- and HSO4-/SO42-
E)HNO3/H2SO4 and H2NO3+/HSO4-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following properties is traditionally associated with Arrhenius bases?
A)They cause blue litmus indicator to turn red
B)They form precipitates with solutions of most metals
C)They react with carbonates to release CO2
D)They release hydrogen when zinc is added
E)They contain hydronium ions
A)They cause blue litmus indicator to turn red
B)They form precipitates with solutions of most metals
C)They react with carbonates to release CO2
D)They release hydrogen when zinc is added
E)They contain hydronium ions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following cannot act as a Brønsted-Lowry acid?
A)HCO3-(aq)
B)HOH(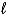 )
)
C)NH3(g)
D)CO32-(aq)
E)CH3OH(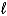 )
)
A)HCO3-(aq)
B)HOH(
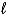 )
)C)NH3(g)
D)CO32-(aq)
E)CH3OH(
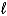 )
)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to Arrhenius theory,what is an acid?
A)A substance that contains a high concentration of hydrogen ions in solutions with water
B)A substance that will lower the hydrogen ion concentration when placed in water
C)A substance that has an H in its formula
D)An electron pair donor
E)An electron pair acceptor
A)A substance that contains a high concentration of hydrogen ions in solutions with water
B)A substance that will lower the hydrogen ion concentration when placed in water
C)A substance that has an H in its formula
D)An electron pair donor
E)An electron pair acceptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a Brønsted-Lowry base but not an Arrhenius base?
A)HSO3-(aq)
B)NaOH(s)
C)NH4+(aq)
D)Al(OH)3(s)
E)NH4OH(aq)
A)HSO3-(aq)
B)NaOH(s)
C)NH4+(aq)
D)Al(OH)3(s)
E)NH4OH(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the conjugate base of water?
A)HCl(aq)
B)H3O+(aq)
C)OH-(aq)
D)H+ ion
E)H2O(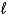 )
)
A)HCl(aq)
B)H3O+(aq)
C)OH-(aq)
D)H+ ion
E)H2O(
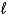 )
)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a Lewis acid but not a Brønsted-Lowry acid?
A)OH-
B)HPO42-
C)HCl
D)NH4+
E)Fe3+
A)OH-
B)HPO42-
C)HCl
D)NH4+
E)Fe3+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A Brønsted-Lowry acid is defined as a(n)...
A)proton remover
B)electron source
C)proton source
D)electron pair remover
E)electron pair source
A)proton remover
B)electron source
C)proton source
D)electron pair remover
E)electron pair source

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not capable of acting like a Brønsted-Lowry base?
A)H2O(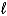 )
)
B)NH4+ ion
C)Cl- ion
D)HNO3(aq)
E)H2PO4-(aq)
A)H2O(
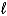 )
)B)NH4+ ion
C)Cl- ion
D)HNO3(aq)
E)H2PO4-(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the following generalized reaction.  For this reaction,which of the following is correct?
For this reaction,which of the following is correct?
A)A is proton source.
B)B is a proton remover.
C)A is an electron pair donor.
D)B is an electron pair acceptor.
E)This a Lewis acid-base reaction.
 For this reaction,which of the following is correct?
For this reaction,which of the following is correct?A)A is proton source.
B)B is a proton remover.
C)A is an electron pair donor.
D)B is an electron pair acceptor.
E)This a Lewis acid-base reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which pair below cannot have a Brønsted-Lowry acid base reaction between them?
A)OH- and NH
B)PO43- and ClO-
C)HCO3- and SO32-
D)HClO4 and HNO2
E)HSO4- and HCl
A)OH- and NH
B)PO43- and ClO-
C)HCO3- and SO32-
D)HClO4 and HNO2
E)HSO4- and HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following substances is amphoteric?
A)H2O(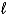 )
)
B)CO32- ion
C)NH4+ ion
D)H3PO4
E)NaOH(aq)
A)H2O(
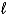 )
)B)CO32- ion
C)NH4+ ion
D)H3PO4
E)NaOH(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A substance that can act as both a proton source and a proton remover is called ...
A)a Brønsted-Lowry acid
B)a Lewis acid
C)amphibious
D)amphoteric
E)neither an acid nor a base
A)a Brønsted-Lowry acid
B)a Lewis acid
C)amphibious
D)amphoteric
E)neither an acid nor a base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Consider the following image which depicts the reactants in an acid-base reaction.Atoms other than H are labeled with the element symbol. 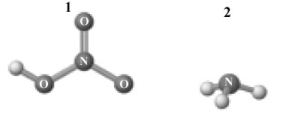 The products of this reaction are shown below.
The products of this reaction are shown below. 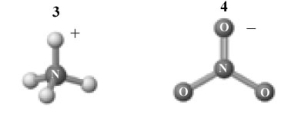
Which of the following is a correct interpretation of this reaction?
A)1 is a Brønsted-Lowry acid.
B)2 is a Brønsted-Lowry base.
C)The reaction is an acid-base neutralization.
D)1 is also an Arrhenius acid.
E)All of the above are correct interpretations of this reaction.
 The products of this reaction are shown below.
The products of this reaction are shown below. 
Which of the following is a correct interpretation of this reaction?
A)1 is a Brønsted-Lowry acid.
B)2 is a Brønsted-Lowry base.
C)The reaction is an acid-base neutralization.
D)1 is also an Arrhenius acid.
E)All of the above are correct interpretations of this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the conjugate acid of HPO42-(aq)?
A)H3PO4(aq)
B)HPO42-(aq)
C)H2PO4-(aq)
D)PO43-(aq)
E)H3O+(aq)
A)H3PO4(aq)
B)HPO42-(aq)
C)H2PO4-(aq)
D)PO43-(aq)
E)H3O+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following conforms to the Arrhenius definition of an acid?
A)H2O(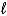 )
)
B)HBrO3(aq)
C)HCO3-(aq)
D)Al3+(aq)
E)Mg(OH)2(s)
A)H2O(
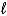 )
)B)HBrO3(aq)
C)HCO3-(aq)
D)Al3+(aq)
E)Mg(OH)2(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consider the following image which depicts the reactants in an acid-base reaction.Atoms other than H are labeled with the element symbol. 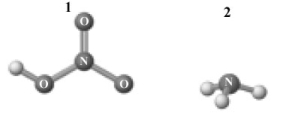 The products of this reaction are shown below.
The products of this reaction are shown below. 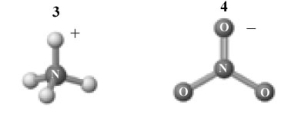
Which of the following is a correct interpretation of this reaction?
A)1 and 2 are a conjugate acid-base pair.
B)3 and 4are a conjugate acid-base pair.
C)1 and 4 are a conjugate acid-base pair.
D)2 and 4 are a conjugate acid-base pair.
E)1 and 3 are a conjugate acid-base pair.
 The products of this reaction are shown below.
The products of this reaction are shown below. 
Which of the following is a correct interpretation of this reaction?
A)1 and 2 are a conjugate acid-base pair.
B)3 and 4are a conjugate acid-base pair.
C)1 and 4 are a conjugate acid-base pair.
D)2 and 4 are a conjugate acid-base pair.
E)1 and 3 are a conjugate acid-base pair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What are the [H+] and [OH-] of a solution made by dissolving 0.0001 mole of HI in sufficient water to make 1.00 liter of solution?
A)[H+] = 4 M [OH-] = 10 M
B)[H+] = 1 *10-14 M [OH-] = 1 *10-4 M
C)[H+] = 1*10-10 M [OH-] = 1 * 10-4 M
D)[H+] = 1 *10-4 M [OH-] = 1 *10-14 M
E)[H+] = 1 *10-4 M [OH-] = 1 *10-10 M
A)[H+] = 4 M [OH-] = 10 M
B)[H+] = 1 *10-14 M [OH-] = 1 *10-4 M
C)[H+] = 1*10-10 M [OH-] = 1 * 10-4 M
D)[H+] = 1 *10-4 M [OH-] = 1 *10-14 M
E)[H+] = 1 *10-4 M [OH-] = 1 *10-10 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements is incorrect ?
(i)Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.0 * 10-14 at 25°C.
(ii)Water or water solutions in which [H+] = [OH-] = 10-7 M are neutral solutions,neither acidic nor basic.
(iii)A solution in which [H+] > [OH-] is basic
Iv)A solution in which [OH- ] > [H+] is acidic
A)i and ii
B)iii and iv
C)ii,iii,and iv
D)All statements are correct
E)All statements are incorrect
(i)Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.0 * 10-14 at 25°C.
(ii)Water or water solutions in which [H+] = [OH-] = 10-7 M are neutral solutions,neither acidic nor basic.
(iii)A solution in which [H+] > [OH-] is basic
Iv)A solution in which [OH- ] > [H+] is acidic
A)i and ii
B)iii and iv
C)ii,iii,and iv
D)All statements are correct
E)All statements are incorrect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A water solution is considered acidic when what is true?
A)[H+] = [OH-]
B)[H+] < [OH-]
C)[OH- ] > [H+]
D)[H+] > [OH-]
E)[H+] = Kw
A)[H+] = [OH-]
B)[H+] < [OH-]
C)[OH- ] > [H+]
D)[H+] > [OH-]
E)[H+] = Kw

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the conjugate base of ammonia?
A)NH3(g)
B)NH4+(aq)
C)NH4OH(aq)
D)NH2-(aq)
E)OH-(aq)
A)NH3(g)
B)NH4+(aq)
C)NH4OH(aq)
D)NH2-(aq)
E)OH-(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The hydroxide ion concentration of a solution is 0.00001 moles per liter.What is the hydrogen ion concentration,and is the solution acidic or basic?
A)10-10,acidic
B)10-9,acidic
C)10-5,acidic
D)10-5,basic
E)10-9,basic
A)10-10,acidic
B)10-9,acidic
C)10-5,acidic
D)10-5,basic
E)10-9,basic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A solution has a hydroxide ion concentration of 1 * 10-11 M.What is the pH of the solution,and is it acidic or basic?
A)pH = 11,basic
B)pH = 3,basic
C)pH = 3,acidic
D)pH = -11 acidic
E)pH = -11,basic
A)pH = 11,basic
B)pH = 3,basic
C)pH = 3,acidic
D)pH = -11 acidic
E)pH = -11,basic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reactions,which of the following species are favored at equilibrium?
A)The weaker acid and the weaker base
B)The weaker acid and the stronger base
C)The stronger acid and the weaker base
D)The stronger acid and the stronger base
E)At equilibrium,neither side is favored
A)The weaker acid and the weaker base
B)The weaker acid and the stronger base
C)The stronger acid and the weaker base
D)The stronger acid and the stronger base
E)At equilibrium,neither side is favored

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A pH meter is used to test the pH of a solution.See the figure below.  How is the solution classified?
How is the solution classified?
A)neutral
B)acidic
C)basic
 How is the solution classified?
How is the solution classified?A)neutral
B)acidic
C)basic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Consider a general comparison between acid-base and redox reactions.Which of the following is correct?
A)The acid-base analog of a reducing agent is an acid.
B)The acid-base analog of a oxidizing agent is a base.
C)The acid-base analog of electrons are protons..
D)All of the above represent correct comparisons.
A)The acid-base analog of a reducing agent is an acid.
B)The acid-base analog of a oxidizing agent is a base.
C)The acid-base analog of electrons are protons..
D)All of the above represent correct comparisons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following solutions is most acidic?
A)[H+] = 1 *10-4
B)[H+] = 1 *10-14
C)[OH-] = 1 *10-3
D)pH = 10
E)pOH = 12
A)[H+] = 1 *10-4
B)[H+] = 1 *10-14
C)[OH-] = 1 *10-3
D)pH = 10
E)pOH = 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A)Acid-base reactions involve a transfer of protons; redox reactions,a transfer of electrons
B)In both redox and acid-base reactions,the reactants are given special names to indicate their roles in the transfer process
C)Just as certain species can either donate or accept protons and thereby behave as an acid in one reaction and a base in another,certain species can either accept or donate electrons,acting as an oxidizing agent in one reaction and a reducing agent in another
D)Just as acids and bases may be classified as "strong" or "weak" depending on how readily they donate or accept protons,the strengths of oxidizing and reducing agents may be compared according to their tendencies to attract or release electrons
E)Unlike most acid-base reactions in solution,which reach a state of equilibrium,most aqueous redox reactions do not reach a state of equilibrium and proceed entirely either in the forward or reverse direction
A)Acid-base reactions involve a transfer of protons; redox reactions,a transfer of electrons
B)In both redox and acid-base reactions,the reactants are given special names to indicate their roles in the transfer process
C)Just as certain species can either donate or accept protons and thereby behave as an acid in one reaction and a base in another,certain species can either accept or donate electrons,acting as an oxidizing agent in one reaction and a reducing agent in another
D)Just as acids and bases may be classified as "strong" or "weak" depending on how readily they donate or accept protons,the strengths of oxidizing and reducing agents may be compared according to their tendencies to attract or release electrons
E)Unlike most acid-base reactions in solution,which reach a state of equilibrium,most aqueous redox reactions do not reach a state of equilibrium and proceed entirely either in the forward or reverse direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A solution is made by dissolving 0.0010 mole KOH in enough water to make 1.00 liter of solution.What are the pH and the pOH of the solution?
A)pH = 3,pOH = 11
B)pH = 3,pOH = 3
C)pH = -11,pOH = -3
D)pH = 11,pOH = 3
E)pH = 10-11,pOH = 10-3
A)pH = 3,pOH = 11
B)pH = 3,pOH = 3
C)pH = -11,pOH = -3
D)pH = 11,pOH = 3
E)pH = 10-11,pOH = 10-3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which is the correct net ionic equation for the reaction between HC2O4- and HPO42-? (Note: H2C2O4 is a stronger acid than H2PO4-.)
A)HC2O4- + HPO42-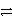 H+ + H2O42- + HPO42-
H+ + H2O42- + HPO42-
B)HC2O4- + HPO42-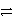 H+ + HC2O4- + PO43-
H+ + HC2O4- + PO43-
C)HC2O4- + HPO42-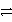 C2O42- + H2PO4-
C2O42- + H2PO4-
D)HC2O4- + HPO42-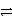 H2C2O4 + PO43-
H2C2O4 + PO43-
E)HC2O4- + HPO42-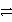 H2 + C2O42- + PO43-
H2 + C2O42- + PO43-
A)HC2O4- + HPO42-
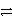 H+ + H2O42- + HPO42-
H+ + H2O42- + HPO42-B)HC2O4- + HPO42-
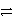 H+ + HC2O4- + PO43-
H+ + HC2O4- + PO43-C)HC2O4- + HPO42-
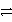 C2O42- + H2PO4-
C2O42- + H2PO4-D)HC2O4- + HPO42-
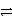 H2C2O4 + PO43-
H2C2O4 + PO43-E)HC2O4- + HPO42-
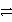 H2 + C2O42- + PO43-
H2 + C2O42- + PO43-
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the conjugate base of H3C6H5O7?
A)C6H5O73-
B)H2C6H5O7-
C)H3C6H5O7-
D)H4C6H5O7+
E)H3C6H5O7(OH)-
A)C6H5O73-
B)H2C6H5O7-
C)H3C6H5O7-
D)H4C6H5O7+
E)H3C6H5O7(OH)-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Given the following acid strengths: HF > H2S > HCN,which of the following reactions is predicted to occur from left to right as written?
A)HCN(aq)+ H2S(aq) H3S(aq)+ CN-(aq)
B)HCN(aq)+ F-(aq) HF(aq)+ CN-(aq)
C)HF(aq)+ CN-(aq) HCN(aq)+ F-(aq)
D)H2S(aq)+ F-(aq) HF(aq)+ HS-(aq)
E)H2S(aq)+ HF(aq) H2F+(aq)+ HS-(aq)
A)HCN(aq)+ H2S(aq) H3S(aq)+ CN-(aq)
B)HCN(aq)+ F-(aq) HF(aq)+ CN-(aq)
C)HF(aq)+ CN-(aq) HCN(aq)+ F-(aq)
D)H2S(aq)+ F-(aq) HF(aq)+ HS-(aq)
E)H2S(aq)+ HF(aq) H2F+(aq)+ HS-(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Given the following relative acid strengths,starting with the weakest: HCO3- < HNO3 < HBr,what is the relative strength of each conjugate base,starting with the weakest?
A)CO32- < NO3- < Br-
B)Br- < CO32- < NO3-
C)NO3- < Br- < CO32-
D)Br- < NO3-< CO32-
E)CO32- < Br- < NO3-
A)CO32- < NO3- < Br-
B)Br- < CO32- < NO3-
C)NO3- < Br- < CO32-
D)Br- < NO3-< CO32-
E)CO32- < Br- < NO3-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is the correct net ionic equation for the reaction between nitrous acid and hydrogen sulfide ion?
A)HNO2 + HS-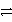 H2NO2+ + S2-
H2NO2+ + S2-
B)HNO2 + HS-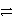 NO2- + H2S
NO2- + H2S
C)HNO2 + HSO4-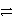 H2NO2+ + SO42-
H2NO2+ + SO42-
D)HNO2 + HSO4-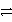 NO2- + H2SO4
NO2- + H2SO4
E)HNO3 + HSO4-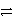 NO3- + H2SO4
NO3- + H2SO4
A)HNO2 + HS-
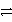 H2NO2+ + S2-
H2NO2+ + S2-B)HNO2 + HS-
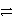 NO2- + H2S
NO2- + H2SC)HNO2 + HSO4-
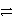 H2NO2+ + SO42-
H2NO2+ + SO42-D)HNO2 + HSO4-
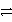 NO2- + H2SO4
NO2- + H2SO4E)HNO3 + HSO4-
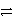 NO3- + H2SO4
NO3- + H2SO4
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the hydroxide ion concentration in a solution with pH = 3?
A)10-3 M
B)11 M
C)10-11 M
D)3 M
E)1011 M
A)10-3 M
B)11 M
C)10-11 M
D)3 M
E)1011 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is 1 * 10-4 M.What is the pH of the solution,and is it acidic or basic?
A)pH = 10,acidic
B)pH = 10,basic
C)pH =13,basic
D)pH = -4,basic
E)pH = 4,acidic
A)pH = 10,acidic
B)pH = 10,basic
C)pH =13,basic
D)pH = -4,basic
E)pH = 4,acidic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Given the following relative base strengths,starting with the weakest: HSO3- < F- < C2H3O2-,what is the relative strength of each conjugate acid,starting with the weakest?
A)HC2H3O2 < HF < H2SO3
B)HC2H3O2 < H2SO3 < HF
C)H2SO3 < HF < HC2H3O2
D)H2SO3 < HC2H3O2 < HF
E)HF < H2SO3 < HC2H3O2
A)HC2H3O2 < HF < H2SO3
B)HC2H3O2 < H2SO3 < HF
C)H2SO3 < HF < HC2H3O2
D)H2SO3 < HC2H3O2 < HF
E)HF < H2SO3 < HC2H3O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The pH of a solution is 5.330.Find [OH-].
A)[OH-] = 2.14*10-9 molar
B)[OH-] = 4.70 *10-11 molar
C)[OH-] = 5.33 *10-7 molar
D)[OH-] = 4.70 * 10-6 molar
E)[OH-] = 5.33 molar
A)[OH-] = 2.14*10-9 molar
B)[OH-] = 4.70 *10-11 molar
C)[OH-] = 5.33 *10-7 molar
D)[OH-] = 4.70 * 10-6 molar
E)[OH-] = 5.33 molar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the following image.  Based on the reading,what is the hydrogen ion concentration in this solution?
Based on the reading,what is the hydrogen ion concentration in this solution?
A)0.100 M
B)0.00010 M
C)1.0 * 10-10 M
D)zero
E)10.00 M
 Based on the reading,what is the hydrogen ion concentration in this solution?
Based on the reading,what is the hydrogen ion concentration in this solution?A)0.100 M
B)0.00010 M
C)1.0 * 10-10 M
D)zero
E)10.00 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A solution is made by dissolving 12.50 g of NaOH,a strong base,in water to produce 2.0 liters of solution.What is the pH of this solution?
A)13.50
B)13.19
C)11.74
D)0.81
E)0.31
A)13.50
B)13.19
C)11.74
D)0.81
E)0.31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the pH of a solution if [H+] = 3.1 *10-4 molar?
A)pH = 4.31
B)pH = 10.49
C)pH = -9.69
D)pH = -3.51
E)pH = 3.51
A)pH = 4.31
B)pH = 10.49
C)pH = -9.69
D)pH = -3.51
E)pH = 3.51

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution with pH = 11.27? Is the solution acidic or basic?
A)5.4 * 10-12 M basic
B)1.86 *0-3 M basic
C)5.37 * 10-12 M acidic
D)1.86 *10-3 M acidic
E)2.73 M acidic
A)5.4 * 10-12 M basic
B)1.86 *0-3 M basic
C)5.37 * 10-12 M acidic
D)1.86 *10-3 M acidic
E)2.73 M acidic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



