Deck 4: The Supply of Labor
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: The Supply of Labor
1
As Susan's wage increases,she decides to work fewer hours.This implies leisure is a(n)
A) normal good.
B) inferior good.
C) luxury good
D) Giffen good.
E) A and C
A) normal good.
B) inferior good.
C) luxury good
D) Giffen good.
E) A and C
A
2
What is Sarah's total utility if she works 8 hours and spends all her earned income but not her initial wealth (assume her time endowment,T,is a day,so T = 24 hours)?
A) 11 utils
B) 72 utils
C) 100 utils
D) 101 utils
E) 150 utils
A) 11 utils
B) 72 utils
C) 100 utils
D) 101 utils
E) 150 utils
B
3
The solution to a utility maximization problem:
A) is located outside the budget constraint.
B) is an interior solution located on the budget line,where the individual chooses to work.
C) is a corner solution where the individual does not work and lives off her unearned income,A0.
D) must meet the tangency requirement.
E) answers B or C
A) is located outside the budget constraint.
B) is an interior solution located on the budget line,where the individual chooses to work.
C) is a corner solution where the individual does not work and lives off her unearned income,A0.
D) must meet the tangency requirement.
E) answers B or C
E
4
What is Mark's marginal rate of substitution,MRS,between consumption and leisure?
A) 0.7 dollars per hour
B) 1.5 dollars per hour
C) 3.5 dollars per hour
D) 4 dollars per hour
E) 5.5 dollars per hour
A) 0.7 dollars per hour
B) 1.5 dollars per hour
C) 3.5 dollars per hour
D) 4 dollars per hour
E) 5.5 dollars per hour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a budget constraint is kinked,budget sets lead to a clustering of equilibrium points,while budget sets lead to divergence.
A) convex,convex
B) concave,concave
C) convex,concave
D) concave,convex
E) linear,convex
A) convex,convex
B) concave,concave
C) convex,concave
D) concave,convex
E) linear,convex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is true about point R on the indifference curve 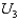 ?
?
A) It corresponds to the utility maximizing solution.
B) It represents a corner solution where the worker chooses to remain out of the labor force.
C) It is not feasible given the constraints.
D) It satisfies the tangency condition.
E) It represents a feasible outcome that does not maximize the worker's utility.
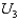 ?
?A) It corresponds to the utility maximizing solution.
B) It represents a corner solution where the worker chooses to remain out of the labor force.
C) It is not feasible given the constraints.
D) It satisfies the tangency condition.
E) It represents a feasible outcome that does not maximize the worker's utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is true about point P on the indifference curve 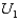 ?
?
A) It corresponds to the utility maximizing solution.
B) It represents a corner solution where the worker chooses to remain out of the labor force.
C) It is not feasible given the constraints.
D) It satisfies the tangency condition.
E) It represents a feasible outcome that does not maximize the worker's utility.
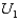 ?
?A) It corresponds to the utility maximizing solution.
B) It represents a corner solution where the worker chooses to remain out of the labor force.
C) It is not feasible given the constraints.
D) It satisfies the tangency condition.
E) It represents a feasible outcome that does not maximize the worker's utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is Mark's marginal utility of consumption, 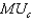 ?
?
A) 0.8 utils per dollar
B) 1.1 utils per dollar
C) 1.7 utils per dollar
D) 2.5 utils per dollar
E) 5.0 utils per dollar
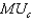 ?
?A) 0.8 utils per dollar
B) 1.1 utils per dollar
C) 1.7 utils per dollar
D) 2.5 utils per dollar
E) 5.0 utils per dollar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A decrease in an individual's wage causes the budget set to experience
A) a parallel shift outward.
B) a parallel shift inward.
C) no change.
D) a pivot upward.
E) a pivot downward.
A) a parallel shift outward.
B) a parallel shift inward.
C) no change.
D) a pivot upward.
E) a pivot downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A decrease in an individual's wealth causes the budget set to experience
A) a parallel shift outward.
B) a parallel shift inward.
C) a no change.
D) a pivot upward.
E) a pivot downward.
A) a parallel shift outward.
B) a parallel shift inward.
C) a no change.
D) a pivot upward.
E) a pivot downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If Sarah works 8 hours a day,what is the amount she can spend on consumption in one day (assume she also can spend her initial wealth)?
A) $300
B) $320
C) $620
D) $800
E) $1020
A) $300
B) $320
C) $620
D) $800
E) $1020

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not a necessary characteristic of an indifference curve?
A) Indifference curves slope downward.
B) Indifference curves are differentiable.
C) Indifference curves are convex.
D) Indifference curves of the same person cannot cross.
E) The negative of the slope of an indifference curve is the marginal rate of substitution.
A) Indifference curves slope downward.
B) Indifference curves are differentiable.
C) Indifference curves are convex.
D) Indifference curves of the same person cannot cross.
E) The negative of the slope of an indifference curve is the marginal rate of substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As wealth increases,demand for a good decreases.This type of good is a
A) normal good.
B) inferior good.
C) luxury good.
D) Giffen good.
E) B and D
A) normal good.
B) inferior good.
C) luxury good.
D) Giffen good.
E) B and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is Mark's baseline utility?
A) 42 utils
B) 100 utils
C) 119 utils
D) 168 utils
E) 200 utils
A) 42 utils
B) 100 utils
C) 119 utils
D) 168 utils
E) 200 utils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following does not limit a worker's choices?
A) Each individual has to contribute 30% of their income toward an income tax.
B) A new state law states each person can only work 40 hours a week.
C) An individual is given $200 a week for disability payments.
D) A worker prefers to not work 40 hours a week.
E) There are 24 hours in a day.
A) Each individual has to contribute 30% of their income toward an income tax.
B) A new state law states each person can only work 40 hours a week.
C) An individual is given $200 a week for disability payments.
D) A worker prefers to not work 40 hours a week.
E) There are 24 hours in a day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If an individual's wage increases,it is theoretically ambiguous if the individual will work more or less.Why?
A) The wealth effect will decrease the number of hours worked,but no one knows the direction of the substitution effect.
B) The wealth effect has an ambiguous effect on the number of hours worked,but the substitution effect will increase the number of hours worked.
C) Both the wealth effect and substitution effect have an ambiguous effect on earnings.
D) The wealth effect will increase the number of hours worked,but the
Substitution effect will decrease the number of hours worked.
E) The wealth effect will decrease the number of hours worked,but the
Substitution effect will increase the number of hours worked.
A) The wealth effect will decrease the number of hours worked,but no one knows the direction of the substitution effect.
B) The wealth effect has an ambiguous effect on the number of hours worked,but the substitution effect will increase the number of hours worked.
C) Both the wealth effect and substitution effect have an ambiguous effect on earnings.
D) The wealth effect will increase the number of hours worked,but the
Substitution effect will decrease the number of hours worked.
E) The wealth effect will decrease the number of hours worked,but the
Substitution effect will increase the number of hours worked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is Mark's marginal utility of leisure, 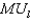 ?
?
A) 0.8 utils per hour
B) 1.1 utils per hour
C) 1.7 utils per hour
D) 2.5 utils per hour
E) 5.0 utils per hour
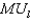 ?
?A) 0.8 utils per hour
B) 1.1 utils per hour
C) 1.7 utils per hour
D) 2.5 utils per hour
E) 5.0 utils per hour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose the government imposes an income tax of 30%.How much can Sarah spend on consumption now (assume she can spend her initial wealth)?
A) $390
B) $416
C) $620
D) $716
E) $806
A) $390
B) $416
C) $620
D) $716
E) $806

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is true about point Q on the indifference curve 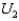 ?
?
A) It corresponds to the utility maximizing solution.
B) It represents a corner solution where the worker chooses to remain out of the labor force.
C) It is not feasible given the constraints.
D) It satisfies the tangency condition.
E) A and D
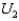 ?
?A) It corresponds to the utility maximizing solution.
B) It represents a corner solution where the worker chooses to remain out of the labor force.
C) It is not feasible given the constraints.
D) It satisfies the tangency condition.
E) A and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The marginal rate of substitution
A) represents the amount of money an individual has to be paid to work another hour.
B) is constant along an individual's entire indifference curve.
C) is the reason why indifference curves are convex.
D) is always negative.
E) helps determine how to increase a person's utility.
A) represents the amount of money an individual has to be paid to work another hour.
B) is constant along an individual's entire indifference curve.
C) is the reason why indifference curves are convex.
D) is always negative.
E) helps determine how to increase a person's utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If leisure is a normal good,then a decrease in non-labor income will cause the desired number of hours worked to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) increase for skilled workers only.
E) increase for unskilled workers only.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain the same.
D) increase for skilled workers only.
E) increase for unskilled workers only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Graphically,when considering the effect of an increase in wealth,the wealth effect is a and the substitution effect is a .
A) movement along a new indifference curve,movement along the initial indifference curve
B) movement along a new indifference curve,change in the budget constraint.
C) change in the budget constraint,movement along a new indifference curve
D) movement along the initial indifference curve,change in the budget constraint
E) change in the budget constraint,movement along the initial indifference curve
A) movement along a new indifference curve,movement along the initial indifference curve
B) movement along a new indifference curve,change in the budget constraint.
C) change in the budget constraint,movement along a new indifference curve
D) movement along the initial indifference curve,change in the budget constraint
E) change in the budget constraint,movement along the initial indifference curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose Janet's initial wealth is $480 and there are 24 hours in a day.What is Janet's reservation wage?
A) $10
B) $20
C) $24
D) $240
E) $480
A) $10
B) $20
C) $24
D) $240
E) $480

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An example of a worker adjusting along the extensive margin is when
A) a worker's wage is increased,so he decides to work more.
B) a worker's wage is increased,so he decides to work less.
C) a worker's wage is decreased,so he switches to another job but works the same number of hours.
D) a worker's wage is decreased,so he leaves the labor force.
E) a worker's wage is decreased,so he works more hours.
A) a worker's wage is increased,so he decides to work more.
B) a worker's wage is increased,so he decides to work less.
C) a worker's wage is decreased,so he switches to another job but works the same number of hours.
D) a worker's wage is decreased,so he leaves the labor force.
E) a worker's wage is decreased,so he works more hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider the situation depicted in Figure 4.2,where the worker experiences a decrease in her wage.Her initial budget constraint is B0D,and following the decrease her new budget constraint is B1D.The move from to is the substitution effect,and the move from to is the income effect.
A) R,P,Q,R
B) R,Q,Q,P
C) Q,R,P,Q
D) P,Q,Q,R
E) R,P,P,Q
A) R,P,Q,R
B) R,Q,Q,P
C) Q,R,P,Q
D) P,Q,Q,R
E) R,P,P,Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The own wage elasticity
A) is the percentage response in labor supply induced by a 1% impulse in the wage.
B) is the effect of a 1% increase in wage on the decision to participate in the labor force.
C) is always negative.
D) is always positive.
E) is always one.
A) is the percentage response in labor supply induced by a 1% impulse in the wage.
B) is the effect of a 1% increase in wage on the decision to participate in the labor force.
C) is always negative.
D) is always positive.
E) is always one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For a nonparticipant,the substitution effect is and the income effect is.
A) zero,zero
B) zero,negative
C) zero,positive
D) negative,zero
E) positive,zero
A) zero,zero
B) zero,negative
C) zero,positive
D) negative,zero
E) positive,zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An example of a worker adjusting along the intensive margin is when
A) a worker decides to join the labor force.
B) a worker,who is currently not working,chooses to reject a job offer.
C) a worker decides to leave the labor force.
D) a worker's wage is cut,so he switches jobs but works the same number of hours.
E) a worker's wage is cut,so he works fewer hours.
A) a worker decides to join the labor force.
B) a worker,who is currently not working,chooses to reject a job offer.
C) a worker decides to leave the labor force.
D) a worker's wage is cut,so he switches jobs but works the same number of hours.
E) a worker's wage is cut,so he works fewer hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Sample selection occurs because
A) workers choose not to participate in the labor force.
B) the individuals who choose not to participate in the labor force are not random.
C) economists do not know with certainty what wage a worker needs to be offered to work
D) economists can estimate the income elasticity of the working population.
E) economists can estimate the substitution effect of the working population.
A) workers choose not to participate in the labor force.
B) the individuals who choose not to participate in the labor force are not random.
C) economists do not know with certainty what wage a worker needs to be offered to work
D) economists can estimate the income elasticity of the working population.
E) economists can estimate the substitution effect of the working population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A worker's reservation wage is
A) the minimum wage a worker must receive to join the labor force.
B) the maximum wage a worker must receive to stay in the labor force.
C) the minimum wage a worker must receive to decide to receive public assistance.
D) the maximum wage a worker must receive to decide to receive public assistance.
E) the wage at which a worker will switch from part time to full time employment.
A) the minimum wage a worker must receive to join the labor force.
B) the maximum wage a worker must receive to stay in the labor force.
C) the minimum wage a worker must receive to decide to receive public assistance.
D) the maximum wage a worker must receive to decide to receive public assistance.
E) the wage at which a worker will switch from part time to full time employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



