Deck 15: Tasks,technologies,and Organizational Design
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/14
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Tasks,technologies,and Organizational Design
1
The distribution of earnings in the United States is skewed to the ______ but the distribution of intelligence is more or less symmetric.One explanation for this earnings skew is that in most developed countries production is organized within firms in a ______.
A) right;hierarchical top-to-toe manner
B) right;inverted pyramidal shape
C) right;system with equal numbers of workers at each level
D) left;hierarchical top-to-toe manner
E) left;inverted pyramidal shape
A) right;hierarchical top-to-toe manner
B) right;inverted pyramidal shape
C) right;system with equal numbers of workers at each level
D) left;hierarchical top-to-toe manner
E) left;inverted pyramidal shape
A
2
Which of the following is NOT a principal characteristic of high-performance work practices?
A) homogeneous pay
B) training
C) problem-solving teams
D) screening
E) information sharing
A) homogeneous pay
B) training
C) problem-solving teams
D) screening
E) information sharing
A
3
Which of the following is NOT a true statement about isoquants?
A) Each curve represents the particular combinations of tasks that generate the same quantity of output.
B) Isoquants are finite in number.
C) The absolute value of the slope is the marginal rate of technical substitution between task 2 and task 1.
D) Isoquants differ in the quantity of output they represent.
E) The slopes of the isoquants represent how easy it is for the firm to substitute task 1 for task 2.
A) Each curve represents the particular combinations of tasks that generate the same quantity of output.
B) Isoquants are finite in number.
C) The absolute value of the slope is the marginal rate of technical substitution between task 2 and task 1.
D) Isoquants differ in the quantity of output they represent.
E) The slopes of the isoquants represent how easy it is for the firm to substitute task 1 for task 2.
B
4

A) A;A
B) A;B
C) B;A
D) B;B
E) neither;A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of hierarchical organizational structure?
A) workers on each rank monitor those below them to limit shirking.
B) the scale of operations effect
C) high-performance work practices
D) ease of dealing with processing and communicating information to the final decision makers
E) higher ability workers make more of an impact than lower ability workers
A) workers on each rank monitor those below them to limit shirking.
B) the scale of operations effect
C) high-performance work practices
D) ease of dealing with processing and communicating information to the final decision makers
E) higher ability workers make more of an impact than lower ability workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
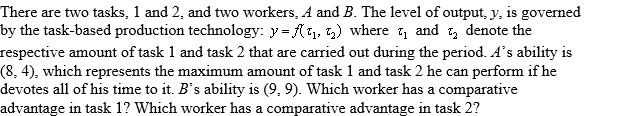
A) A;A
B) A;B
C) B;A
D) B;B
E) neither;A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is NOT one of the five steps to the practice of insider conometrics?
A) Visit a number of sites that use the particular production process.
B) Create a dataset with aggregate industry variables and estimate a macroeconomic model.
C) Collect panel data on the universe of firms that use the particular process and use econometric methods to estimate the parameters of an economic model.
D) Conduct field research to thoroughly understand the production process.
E) Form a conclusion from the econometric estimates.
A) Visit a number of sites that use the particular production process.
B) Create a dataset with aggregate industry variables and estimate a macroeconomic model.
C) Collect panel data on the universe of firms that use the particular process and use econometric methods to estimate the parameters of an economic model.
D) Conduct field research to thoroughly understand the production process.
E) Form a conclusion from the econometric estimates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is NOT a principal characteristic of high-performance work practices?
A) information sharing
B) training
C) a discernable chain of command
D) screening
E) problem-solving teams
A) information sharing
B) training
C) a discernable chain of command
D) screening
E) problem-solving teams

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT an implication of the scale of operations effect?
A) The optimal hierarchical structure is pyramidal in shape.
B) The closer a worker is to the top of the hierarchy the greater the impact of his performance.
C) The distribution of earnings is skewed to the left.
D) Higher-ability workers are optimally placed at the top of the hierarchy.
E) There is an unequal number of workers at each level.
A) The optimal hierarchical structure is pyramidal in shape.
B) The closer a worker is to the top of the hierarchy the greater the impact of his performance.
C) The distribution of earnings is skewed to the left.
D) Higher-ability workers are optimally placed at the top of the hierarchy.
E) There is an unequal number of workers at each level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

A) 4
B) 2
C) 1
D) 1/2
E) 1/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is NOT an explanation for the slow adoption-rate puzzle?
A) Reorganization is a costly experiment.
B) Some firms may not benefit from the introduction of new techniques.
C) There are opportunity costs to being an early adopter.
D) Firms are unsure about the viability of new ideas when they are untested.
E) Ideas that are worth implementing are created at a slow rate.
A) Reorganization is a costly experiment.
B) Some firms may not benefit from the introduction of new techniques.
C) There are opportunity costs to being an early adopter.
D) Firms are unsure about the viability of new ideas when they are untested.
E) Ideas that are worth implementing are created at a slow rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is an advantage of just-in-time production?
A) Productive tools are flexible or lean.
B) Homogeneous hiring allows firms to pay workers a homogeneous wage.
C) Fewer productive inputs are tied up in inventories.
D) This type of production calls for dramatic organizational restructuring.
E) Workers are induced to operate at comparatively higher levels of effort.
A) Productive tools are flexible or lean.
B) Homogeneous hiring allows firms to pay workers a homogeneous wage.
C) Fewer productive inputs are tied up in inventories.
D) This type of production calls for dramatic organizational restructuring.
E) Workers are induced to operate at comparatively higher levels of effort.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is an advantage of just-in-time production?
A) Productive tools are flexible or lean.
B) Product quality is enhanced because manufacturing defects can be quickly identified and rectified.
C) This type of production calls for dramatic organizational restructuring.
D) Workers are more efficient because they start work immediately upon entering the workplace because training takes place on the job.
E) Workers are induced to operate at comparatively higher levels of effort.
A) Productive tools are flexible or lean.
B) Product quality is enhanced because manufacturing defects can be quickly identified and rectified.
C) This type of production calls for dramatic organizational restructuring.
D) Workers are more efficient because they start work immediately upon entering the workplace because training takes place on the job.
E) Workers are induced to operate at comparatively higher levels of effort.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is a reason workers may NOT be assigned tasks based on their comparative advantages?
A) significant indivisibilities
B) one worker may have an absolute advantage
C) a productivity gap between workers
D) assortative matching
E) a tournament scheme has been instituted
A) significant indivisibilities
B) one worker may have an absolute advantage
C) a productivity gap between workers
D) assortative matching
E) a tournament scheme has been instituted

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 14 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



