Deck 9: DNA-Based Information Technologies
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: DNA-Based Information Technologies
1
Which statement does NOT apply to the construction or use of a DNA library?
A) Determining the location of a particular DNA sequence in a DNA library requires a suitable hybridization probe.
B) Genomic libraries are better for expressing gene products than cDNA libraries.
C) Many segments of DNA from a cellular genome are cloned.
D) Specialized DNA libraries can be made by cloning DNA copies of mRNAs.
E) The DNA copies of mRNA found in a cDNA library are made by reverse transcriptase.
A) Determining the location of a particular DNA sequence in a DNA library requires a suitable hybridization probe.
B) Genomic libraries are better for expressing gene products than cDNA libraries.
C) Many segments of DNA from a cellular genome are cloned.
D) Specialized DNA libraries can be made by cloning DNA copies of mRNAs.
E) The DNA copies of mRNA found in a cDNA library are made by reverse transcriptase.
B
2
Which compound is NOT needed to build a cDNA library?
A) genomic DNA
B) mRNA
C) reverse transcriptase
D) dNTPs
E) DNA polymerase
A) genomic DNA
B) mRNA
C) reverse transcriptase
D) dNTPs
E) DNA polymerase
A
3
Restriction enzymes:
A) act at the membrane to restrict the passage of certain molecules into the cell.
B) are highly specialized ribonucleases that degrade mRNA soon after its synthesis.
C) are sequence-specific DNA endonucleases.
D) are very specific proteases that cleave peptides at only certain sequences.
E) catalyze the addition of a certain amino acid to a specific tRNA.
A) act at the membrane to restrict the passage of certain molecules into the cell.
B) are highly specialized ribonucleases that degrade mRNA soon after its synthesis.
C) are sequence-specific DNA endonucleases.
D) are very specific proteases that cleave peptides at only certain sequences.
E) catalyze the addition of a certain amino acid to a specific tRNA.
C
4
Which compound is NOT needed in 454 pyrosequencing of DNA?
A) dNTPs
B) sulfurylase
C) luciferase
D) ddNTPs
E) apyrase
A) dNTPs
B) sulfurylase
C) luciferase
D) ddNTPs
E) apyrase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The biological role of restriction enzymes is to:
A) aid recombinant DNA research.
B) degrade foreign DNA that enters a bacterium.
C) make bacteria resistant to antibiotics.
D) restrict the damage to DNA by ultraviolet light.
E) restrict the size of DNA in certain bacteria.
A) aid recombinant DNA research.
B) degrade foreign DNA that enters a bacterium.
C) make bacteria resistant to antibiotics.
D) restrict the damage to DNA by ultraviolet light.
E) restrict the size of DNA in certain bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
_____ is NOT a commonly used tag for affinity purification of cloned proteins.
A) Glutathione-S-transferase
B) Maltose binding protein
C) Nickel
D) Protein A
E) Chitin-binding domain
A) Glutathione-S-transferase
B) Maltose binding protein
C) Nickel
D) Protein A
E) Chitin-binding domain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the laboratory, recombinant plasmids are commonly introduced into bacterial cells by:
A) electrophoresis-a gentle low-voltage gradient draws the DNA into the cell.
B) infection with a bacteriophage that carries the plasmid.
C) microinjection.
D) mixing plasmids with an extract of broken cells.
E) transformation-heat shock of the cells incubated with plasmid DNA in the presence of CaCl2.
A) electrophoresis-a gentle low-voltage gradient draws the DNA into the cell.
B) infection with a bacteriophage that carries the plasmid.
C) microinjection.
D) mixing plasmids with an extract of broken cells.
E) transformation-heat shock of the cells incubated with plasmid DNA in the presence of CaCl2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Certain restriction enzymes produce cohesive (sticky) ends. This means that they:
A) cut both DNA strands at the same base pair.
B) cut in regions of high GC content, leaving ends that can form more hydrogen bonds than ends of high AT content.
C) make a staggered double-strand cut, leaving ends with a few nucleotides of single-stranded DNA protruding.
D) make ends that can anneal to cohesive ends generated by any other restriction enzyme.
E) stick tightly to the ends of the DNA they have cut.
A) cut both DNA strands at the same base pair.
B) cut in regions of high GC content, leaving ends that can form more hydrogen bonds than ends of high AT content.
C) make a staggered double-strand cut, leaving ends with a few nucleotides of single-stranded DNA protruding.
D) make ends that can anneal to cohesive ends generated by any other restriction enzyme.
E) stick tightly to the ends of the DNA they have cut.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The PCR reaction mixture does NOT include:
A) all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates.
B) DNA containing the sequence to be amplified.
C) DNA ligase.
D) heat-stable DNA polymerase.
E) oligonucleotide primer(s).
A) all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates.
B) DNA containing the sequence to be amplified.
C) DNA ligase.
D) heat-stable DNA polymerase.
E) oligonucleotide primer(s).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The E. coli recombinant plasmid pBR322 has been widely utilized in genetic engineering experiments. Which feature does pBR322 NOT have?
A) a number of conveniently located recognition sites for restriction enzymes
B) a number of palindromic sequences near the EcoRI site, which permit the plasmid to assume a conformation that protects newly inserted DNA from nuclease degradation
C) a replication origin, which permits it to replicate autonomously
D) resistance to two different antibiotics, which permits rapid screening for recombinant plasmids containing foreign DNA
E) small overall size, which facilitates entry of the plasmid into host cells
A) a number of conveniently located recognition sites for restriction enzymes
B) a number of palindromic sequences near the EcoRI site, which permit the plasmid to assume a conformation that protects newly inserted DNA from nuclease degradation
C) a replication origin, which permits it to replicate autonomously
D) resistance to two different antibiotics, which permits rapid screening for recombinant plasmids containing foreign DNA
E) small overall size, which facilitates entry of the plasmid into host cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement about the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is FALSE?
A) DNA amplified by PCR can be cloned.
B) DNA amplification is linear in magnitude.
C) Newly synthesized DNA must be heat-denatured before the next round of DNA synthesis begins.
D) The boundaries of the amplified DNA segment are determined by the synthetic oligonucleotides used to prime DNA synthesis.
E) The technique is sufficiently sensitive that DNA sequences can be amplified from a single animal or human hair.
A) DNA amplified by PCR can be cloned.
B) DNA amplification is linear in magnitude.
C) Newly synthesized DNA must be heat-denatured before the next round of DNA synthesis begins.
D) The boundaries of the amplified DNA segment are determined by the synthetic oligonucleotides used to prime DNA synthesis.
E) The technique is sufficiently sensitive that DNA sequences can be amplified from a single animal or human hair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Common features found in a cloning plasmid used for protein do NOT include:
A) a polylinker.
B) an origin of replication.
C) an antibiotic resistance marker(s).
D) a ribosome binding site.
E) telomeric ends.
A) a polylinker.
B) an origin of replication.
C) an antibiotic resistance marker(s).
D) a ribosome binding site.
E) telomeric ends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which statement about Type II restriction enzymes is FALSE?
A) Many make staggered (off-center) cuts within their recognition sequences.
B) Some cut DNA to generate blunt ends.
C) They are part of a bacterial defense system in which foreign DNA is cleaved.
D) They cleave and ligate DNA.
E) They cleave DNA only at recognition sequences specific to a given restriction enzyme.
A) Many make staggered (off-center) cuts within their recognition sequences.
B) Some cut DNA to generate blunt ends.
C) They are part of a bacterial defense system in which foreign DNA is cleaved.
D) They cleave and ligate DNA.
E) They cleave DNA only at recognition sequences specific to a given restriction enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The technique known as two hybrid analysis for detecting interacting gene products depend on:
A) activation of DNA polymerase by the nearby binding of hybridizing protein complexes.
B) direct binding of a Gal4p activation domain to a DNA sequence in the promoter region.
C) having a promoter that responds directly to one of the two proteins whose interactions is being measured.
D) hybridization of DNA segments corresponding to the two genes being examined.
E) stimulation of transcription by interaction of two Gal4p domains via fused protein sequences.
A) activation of DNA polymerase by the nearby binding of hybridizing protein complexes.
B) direct binding of a Gal4p activation domain to a DNA sequence in the promoter region.
C) having a promoter that responds directly to one of the two proteins whose interactions is being measured.
D) hybridization of DNA segments corresponding to the two genes being examined.
E) stimulation of transcription by interaction of two Gal4p domains via fused protein sequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which analytical technique does NOT help illuminate a gene's cellular function?
A) DNA microarray analysis
B) protein chip analysis
C) Southern blotting
D) two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
E) two-hybrid analysis
A) DNA microarray analysis
B) protein chip analysis
C) Southern blotting
D) two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
E) two-hybrid analysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A(n) _____ would NOT used as a heterologous host for the expression of recombinant proteins/
A) retrovirus
B) bacterium such as E. coli
C) eukaryote such as S. cerevisiae
D) insect cell
E) mammalian cell
A) retrovirus
B) bacterium such as E. coli
C) eukaryote such as S. cerevisiae
D) insect cell
E) mammalian cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A convenient cloning vector with which to introduce foreign DNA into E. coli is a(n):
A) E. coli chromosome.
B) messenger RNA.
C) plasmid.
D) yeast "ARS" sequence.
E) yeast transposable element.
A) E. coli chromosome.
B) messenger RNA.
C) plasmid.
D) yeast "ARS" sequence.
E) yeast transposable element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The size of the DNA region specifically recognized by Type II restriction enzymes is typically:
A) 4 to 6 base pairs.
B) 10 to 15 base pairs.
C) 50 to 60 base pairs.
D) 200 to 300 base pairs.
E) about the size of an average gene.
A) 4 to 6 base pairs.
B) 10 to 15 base pairs.
C) 50 to 60 base pairs.
D) 200 to 300 base pairs.
E) about the size of an average gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which statement regarding plasmid-cloning vectors is CORRECT?
A) Circular plasmids do not require an origin of replication to be propagated in E. coli.
B) Foreign DNA fragments up to 45,000 base pairs can be cloned in a typical plasmid.
C) Plasmids do not need to contain genes that confer resistance to antibiotics.
D) Plasmid vectors must carry promoters for inserted gene fragments.
E) The copy number of plasmids may vary from a few to several hundred.
A) Circular plasmids do not require an origin of replication to be propagated in E. coli.
B) Foreign DNA fragments up to 45,000 base pairs can be cloned in a typical plasmid.
C) Plasmids do not need to contain genes that confer resistance to antibiotics.
D) Plasmid vectors must carry promoters for inserted gene fragments.
E) The copy number of plasmids may vary from a few to several hundred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which tag is NOT used to study protein function?
A) green fluorescent protein (GFP)
B) synteny tag
C) tandem affinity purification (TAP)
D) Gal4p DNA binding domain
E) Gal4p activation domain
A) green fluorescent protein (GFP)
B) synteny tag
C) tandem affinity purification (TAP)
D) Gal4p DNA binding domain
E) Gal4p activation domain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which technique can be used to estimate the relative copy numbers of particular DNA sequences in a sample?
A) reverse transcriptase PCR
B) quantitative PCR
C) some gel based analysis such as with the Bioanalyzer and Fragment Analyzer gel band density are used in calculating concentration in a lot of labs.
D) normal PCR
E) in vitro transcription
A) reverse transcriptase PCR
B) quantitative PCR
C) some gel based analysis such as with the Bioanalyzer and Fragment Analyzer gel band density are used in calculating concentration in a lot of labs.
D) normal PCR
E) in vitro transcription

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is a polylinker?
A) a type of cloning vector
B) a DNA fragment with multiple recognition sequences for restriction endonucleases
C) a type of expression vector
D) an enzyme that joins DNA molecules together
E) a method of getting DNA into a cell
A) a type of cloning vector
B) a DNA fragment with multiple recognition sequences for restriction endonucleases
C) a type of expression vector
D) an enzyme that joins DNA molecules together
E) a method of getting DNA into a cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Current estimates indicate that _____% of the human genome is translated into protein.
A) less than 0.5
B) roughly 1.5
C) roughly 10
D) roughly 25
E) more than 50
A) less than 0.5
B) roughly 1.5
C) roughly 10
D) roughly 25
E) more than 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Common problems with expression of eukaryotic proteins in bacteria may include proteins:
A) aggregating into inclusion bodies.
B) not folding correctly due to absence of chaperones.
C) not undergoing posttranslational modification.
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) aggregating into inclusion bodies.
B) not folding correctly due to absence of chaperones.
C) not undergoing posttranslational modification.
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which statement regarding Type I and Type II restriction endonucleases is NOT accurate?
A) Type I endonucleases cleave DNA at random sites.
B) Type II endonucleases recognize small (4-6 bp) palindromic sequences.
C) Type II endonucleases always make staggered cuts in DNA strands.
D) Type I endonucleases require ATP.
E) Type I endonucleases are generally large, multisubunit complexes.
A) Type I endonucleases cleave DNA at random sites.
B) Type II endonucleases recognize small (4-6 bp) palindromic sequences.
C) Type II endonucleases always make staggered cuts in DNA strands.
D) Type I endonucleases require ATP.
E) Type I endonucleases are generally large, multisubunit complexes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which DNA sequence is a palindrome?
A) AATGCC
B) GGATCC
C) GATATG
D) CCCGCG
E) AGTAGT
A) AATGCC
B) GGATCC
C) GATATG
D) CCCGCG
E) AGTAGT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A good expression vector for protein expression in E. coli should have which feature(s)?
A) an origin of replication
B) a selectable marker
C) a promoter, operator, and ribosome-binding site
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) an origin of replication
B) a selectable marker
C) a promoter, operator, and ribosome-binding site
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which amino acid when repeated six to ten times at the N- or C-terminal ends of a protein allows that protein to bind to Ni2+ ions?
A) Glu
B) His
C) Ala
D) Tyr
E) Asp
A) Glu
B) His
C) Ala
D) Tyr
E) Asp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which method is NOT used in linkage analysis?
A) comparing densely spaced polymorphisms
B) collecting DNA from a family affected by the disease of interest
C) sequencing selected parts of the genome
D) introducing retroviruses at the mutated locus
E) looking for SNP variants
A) comparing densely spaced polymorphisms
B) collecting DNA from a family affected by the disease of interest
C) sequencing selected parts of the genome
D) introducing retroviruses at the mutated locus
E) looking for SNP variants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which restriction endonuclease cuts DNA in a way that leaves blunt ends?
A) EcoRI
B) HindIII
C) BamHI
D) EcoRV
E) PstI
A) EcoRI
B) HindIII
C) BamHI
D) EcoRV
E) PstI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If you wanted to create specific DNA sequence changes to a plasmid in the coding sequence for a protein you are researching, but there are no suitably located restriction sites nearby, which technique would you use?
A) error-prone PCR
B) site-directed mutagenesis
C) oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis
D) exposing the plasmid DNA to UV light
E) exposing the cells containing the plasmid DNA to chemical mutagens
A) error-prone PCR
B) site-directed mutagenesis
C) oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis
D) exposing the plasmid DNA to UV light
E) exposing the cells containing the plasmid DNA to chemical mutagens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If you wanted to clone a large fragment of DNA into a unicellular eukaryotic host, what would you use?
A) a bacmid
B) a plasmid
C) a bacterial artificial chromosome
D) a yeast artificial chromosome
E) a virus
A) a bacmid
B) a plasmid
C) a bacterial artificial chromosome
D) a yeast artificial chromosome
E) a virus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which list ranks the organisms in order from smallest genome (number of base pairs of DNA) to largest genome?
A) Human, fruit fly, E. coli bacterium
B) E. coli bacterium, human, fruit fly
C) E. coli bacterium, fruit fly, human
D) fruit fly, E. coli bacterium, human
E) fruit fly, human, E. coli bacterium
A) Human, fruit fly, E. coli bacterium
B) E. coli bacterium, human, fruit fly
C) E. coli bacterium, fruit fly, human
D) fruit fly, E. coli bacterium, human
E) fruit fly, human, E. coli bacterium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A good cloning vector should NOT have:
A) an origin of replication.
B) an antibiotic resistance gene.
C) several unique restriction sites.
D) a small size.
E) genes allowing its insertion into the host chromosome.
A) an origin of replication.
B) an antibiotic resistance gene.
C) several unique restriction sites.
D) a small size.
E) genes allowing its insertion into the host chromosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If you want to clone a gene by using E. coli and then transfer that cloned gene into yeast to express the protein the gene encodes, what type of self-replicating DNA should you use for your cloning process?
A) a bacmid
B) a plasmid
C) a yeast artificial chromosome
D) a shuttle vector
E) a bacterial artificial chromosome
A) a bacmid
B) a plasmid
C) a yeast artificial chromosome
D) a shuttle vector
E) a bacterial artificial chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A restriction endonuclease that has a recognition sequence of 8 bp in length would be expected to cut dsDNA on average once in how many base pairs?
A) 256
B) 1024
C) 4096
D) 65536
E) 1048576
A) 256
B) 1024
C) 4096
D) 65536
E) 1048576

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When cloning a gene into a plasmid, which enzyme would you use to covalently attach the gene to the plasmid DNA?
A) DNA polymerase
B) exonuclease III
C) DNA Ligase
D) alkaline phosphatase
E) a restriction endonuclease
A) DNA polymerase
B) exonuclease III
C) DNA Ligase
D) alkaline phosphatase
E) a restriction endonuclease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which type of DNA sequence is NOT found in the human genome?
A) long repetitive repeats
B) introns
C) retro-palindromes
D) simple sequence repeats
E) transposons
A) long repetitive repeats
B) introns
C) retro-palindromes
D) simple sequence repeats
E) transposons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Current estimates indicate that humans have about _____ genes.
A) 3,000
B) 10,000
C) 30,000
D) 100,000
E) 300,000
A) 3,000
B) 10,000
C) 30,000
D) 100,000
E) 300,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which way is NOT a means of inserting DNA into a cell?
A) transformation
B) transfection
C) transduction
D) electroporation
E) ligation
A) transformation
B) transfection
C) transduction
D) electroporation
E) ligation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Genes that have sequence and functional relationships to each other within a single species are called:
A) orthologs.
B) paralogs.
C) analogs.
D) homologs.
E) lincolnlogs.
A) orthologs.
B) paralogs.
C) analogs.
D) homologs.
E) lincolnlogs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The gene for green fluorescent protein was originally isolated from which species?
A) a panda
B) a firefly
C) a mushroom
D) a jellyfish
E) a glowworm
A) a panda
B) a firefly
C) a mushroom
D) a jellyfish
E) a glowworm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If you wanted to study the effects of inactivating a specific gene on development of a mouse, which technique or system would you use to inactivate that gene?
A) transfection
B) CRISPR/Cas9
C) tandem affinity purification
D) yeast two-hybrid
E) oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis
A) transfection
B) CRISPR/Cas9
C) tandem affinity purification
D) yeast two-hybrid
E) oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A method of determining if proteins are interacting in vivo that makes use of a transcription factor involved in regulating galactose metabolism genes is:
A) a DNA microarray.
B) yeast two-hybrid analysis.
C) tandem affinity purification.
D) immunofluorescence.
E) quantitiative PCR.
A) a DNA microarray.
B) yeast two-hybrid analysis.
C) tandem affinity purification.
D) immunofluorescence.
E) quantitiative PCR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The fluorophore in GFP is derived from covalent modifications of which structures located at the interior of the protein?
A) coenzymes
B) amino acids
C) prosthetic groups
D) metal ions
E) nucleotides
A) coenzymes
B) amino acids
C) prosthetic groups
D) metal ions
E) nucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If you want to determine which proteins might be interacting in a cell, which technique would you use to examine the interaction in a living cell?
A) yeast two-hybrid analysis
B) immunoprecipitation
C) a DNA microarray
D) immunofluorescence
E) comparative genomics
A) yeast two-hybrid analysis
B) immunoprecipitation
C) a DNA microarray
D) immunofluorescence
E) comparative genomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is a significant problem with regard to making cDNA libraries to analyze overall gene function in an eukaryotic organism?
A) A cDNA library will only contain genes that are actively transcribed in the organism.
B) Reverse transcriptase cannot be used to make cDNA libraries.
C) cDNA cannot be amplified by PCR.
D) cDNA libraries do not contain intron sequences.
E) cDNA libraries may contain several alternatively spliced forms of the same gene.
A) A cDNA library will only contain genes that are actively transcribed in the organism.
B) Reverse transcriptase cannot be used to make cDNA libraries.
C) cDNA cannot be amplified by PCR.
D) cDNA libraries do not contain intron sequences.
E) cDNA libraries may contain several alternatively spliced forms of the same gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The biochemical activity of a protein, such as its enzymatic activity, is called its _____ function.
A) phenotypic
B) genotypic
C) cellular
D) molecular
E) organismal
A) phenotypic
B) genotypic
C) cellular
D) molecular
E) organismal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which method of visualizing a protein's location should you use if you want to determine its location in a living cell?
A) a GFP fusion tag
B) immunofluorescence
C) qPCR
D) Gram stain
E) affinity purification
A) a GFP fusion tag
B) immunofluorescence
C) qPCR
D) Gram stain
E) affinity purification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Conserved gene order observed in the chromosomes of two distantly related organisms provides evidence of a(n) _____ relationship between genes.
A) orthologous
B) homologous
C) paralogous
D) analogous
E) genologous
A) orthologous
B) homologous
C) paralogous
D) analogous
E) genologous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which protein forms a complex with a guide RNA to target DNA for cleavage and destruction?
A) RecA
B) Cas9
C) EcoRI
D) Gal4p
E) GST
A) RecA
B) Cas9
C) EcoRI
D) Gal4p
E) GST

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which type of organism do you NOT expect to express functionally fluorescent GFP?
A) an obligate aerobe
B) a multicellular eukarotic organism
C) a facultative anaerobe
D) an obligate anaerobe
E) a unicellular eukaryotic organism
A) an obligate aerobe
B) a multicellular eukarotic organism
C) a facultative anaerobe
D) an obligate anaerobe
E) a unicellular eukaryotic organism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A method of comparing the relative gene expression of all the genes in an organism at two different stages of its development is:
A) a DNA microarray.
B) yeast two-hybrid analysis.
C) tandem affinity purification.
D) immunofluorescence.
E) quantitiative PCR.
A) a DNA microarray.
B) yeast two-hybrid analysis.
C) tandem affinity purification.
D) immunofluorescence.
E) quantitiative PCR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If you want to determine what other proteins might be interacting with the protein you have been studying, what type of fusion tag would you add to your protein to aid in purification of both the protein you have been studying and the proteins interacting with it?
A) a green fluorescent protein fusion tag
B) a tandem affinity purification tag
C) a maltose-binding protein tag
D) an epitope tag
E) a -galactosidase tag
A) a green fluorescent protein fusion tag
B) a tandem affinity purification tag
C) a maltose-binding protein tag
D) an epitope tag
E) a -galactosidase tag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If you are comparing the total gene expression of a black panther during its early development and later adult life and have labeled the cDNA you obtained from its early development stages with a green fluorophore and the cDNA you obtained from its adult life stages with a red fluorophore, what color would you expect to see on your DNA microarray for genes that are equally expressed in both the early development and adult life stages?
A) green
B) red
C) yellow
D) brown
E) magenta
A) green
B) red
C) yellow
D) brown
E) magenta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which factor is required to accurately determine the relative amount of gene expression of two or more genes in an organism using qPCR?
A) a "no template" control
B) an oligonucleotide probe labeled with a fluorophore and a quenching molecule at its ends
C) use of reverse transcriptase to copy the RNA products into DNA
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) a "no template" control
B) an oligonucleotide probe labeled with a fluorophore and a quenching molecule at its ends
C) use of reverse transcriptase to copy the RNA products into DNA
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What common protein tertiary structure does green fluorescent protein contain?
A) an helix
B) a barrel
C) a coiled coil
D) a Greek key
E) a four-helix bundle
A) an helix
B) a barrel
C) a coiled coil
D) a Greek key
E) a four-helix bundle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which technique is NOT used to make a cDNA library?
A) extraction of DNA from the organism you are studying
B) extraction of mRNA from the organism you are studying
C) use of reverse transcriptase to copy RNA into DNA
D) ligation of DNA into a cloning vector
E) insertion of a cloning vector into cells
A) extraction of DNA from the organism you are studying
B) extraction of mRNA from the organism you are studying
C) use of reverse transcriptase to copy RNA into DNA
D) ligation of DNA into a cloning vector
E) insertion of a cloning vector into cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
To make an DNA copy of a RNA sequence, you need the reverse transcriptase enzyme and an oligonucleotide primer made of which nucleotide?
A) deoxyadenosine
B) deoxythymine
C) deoxycytosine
D) deoxyuridine
E) deoxyguanosine
A) deoxyadenosine
B) deoxythymine
C) deoxycytosine
D) deoxyuridine
E) deoxyguanosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If you want to express two different genes on different plasmids in a bacterial host, which procedure will NOT be successful?
A) using plasmids that have the same promoter sequence
B) using EcoRI and BamHI restriction endonucleases to clone the genes into their respective plasmids
C) placing different fusion tags on each of the genes when cloning them
D) using plasmids with the same origin of replication
E) using plasmids that have different selectable markers
A) using plasmids that have the same promoter sequence
B) using EcoRI and BamHI restriction endonucleases to clone the genes into their respective plasmids
C) placing different fusion tags on each of the genes when cloning them
D) using plasmids with the same origin of replication
E) using plasmids that have different selectable markers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
For what reason is the mitochondrial genome and the Y chromosome the easiest portions of human DNA to use to trace human evolutionary lineages?
A) All human cells have mitochondria and Y chromosomes.
B) Mitochondrial DNA and the Y chromosome do not undergo significant meiotic recombination.
C) The size of the mitochondrial genome and the Y chromosome is small.
D) Mitochondrial DNA and the Y chromosome exhibit very unstable haplotypes.
E) Mitochondrial DNA is inherited along both the male and female human evolutionary. lineages
A) All human cells have mitochondria and Y chromosomes.
B) Mitochondrial DNA and the Y chromosome do not undergo significant meiotic recombination.
C) The size of the mitochondrial genome and the Y chromosome is small.
D) Mitochondrial DNA and the Y chromosome exhibit very unstable haplotypes.
E) Mitochondrial DNA is inherited along both the male and female human evolutionary. lineages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Approximately how much of the human genome encodes the exons of protein-coding sequences?
A) 1.5%
B) 5%
C) 30%
D) 100%
E) 80%
A) 1.5%
B) 5%
C) 30%
D) 100%
E) 80%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Chimpanzees and humans differ by approximately how much due to transposons, base-pair changes, and chromosome segment duplications and rearrangements across their entire genomic sequences?
A) 1.5%
B) 4%
C) 95%
D) 10%
E) 0.1%
A) 1.5%
B) 4%
C) 95%
D) 10%
E) 0.1%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A plasmid that encodes resistance to ampicillin and tetracycline is digested with the restriction enzyme PstI, which cuts the plasmid at a single site in the ampicillin-resistance gene. The DNA is then annealed with a PstI digest of human DNA, ligated, and used to transform E. coli cells. (a) What antibiotic would you put in an agar plate to ensure that the cells of a bacterial colony contain the plasmid? (b) What antibiotic-resistance phenotypes will be found on the plate? (c) Which phenotype will indicate the presence of plasmids that contain human DNA fragments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match each feature of the plasmid pBR322 (at left) with one appropriate description presented (at right) (see illustration of pBR322 below). Descriptions may be used more than once. 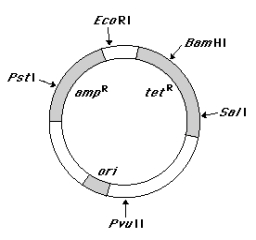 ____ ampR sequence
____ ampR sequence
(a) Permits selection of bacteria containing the plasmid.
____ ori sequence
(b) A sequence required for packaging recombinant plasmids
____ tetR
into bacteriophage.
____ BamHI sequence
(c) Origin of replication.
____ PstI sequence
(d) Cleavage of the plasmid here does not affect antibiotic
sequence resistance genes.
(e) Insertion of foreign DNA here permits identification of
bacteria containing recombinant plasmids .
 ____ ampR sequence
____ ampR sequence(a) Permits selection of bacteria containing the plasmid.
____ ori sequence
(b) A sequence required for packaging recombinant plasmids
____ tetR
into bacteriophage.
____ BamHI sequence
(c) Origin of replication.
____ PstI sequence
(d) Cleavage of the plasmid here does not affect antibiotic
sequence resistance genes.
(e) Insertion of foreign DNA here permits identification of
bacteria containing recombinant plasmids .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which statement is NOT correct?
A) Humans and chimpanzees share a common ancestor.
B) Orangutans are an outgroup when compared with humans and chimpanzees.
C) Humans and chimpanzees differ over approximately 4% of their genomes.
D) Humans evolved from chimpanzees.
E) Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, while chimpanzees have 24 pairs of chromosomes.
A) Humans and chimpanzees share a common ancestor.
B) Orangutans are an outgroup when compared with humans and chimpanzees.
C) Humans and chimpanzees differ over approximately 4% of their genomes.
D) Humans evolved from chimpanzees.
E) Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, while chimpanzees have 24 pairs of chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Due primarily to single nucleotide polymorphisms, each human differs from every other human, on average, by what percentage of the human genome?
A) 6%
B) 15%
C) 0.1%
D) 98%
E) 1.5%
A) 6%
B) 15%
C) 0.1%
D) 98%
E) 1.5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which statement about transposons is NOT correct?
A) They are a form of molecular parasite.
B) They have played a major role in human evolution.
C) All transposons are active and move around the human genome.
D) Some transposons move to another genomic location via an RNA intermediate.
E) They often contain genes that encode proteins that catalyze transposon movement.
A) They are a form of molecular parasite.
B) They have played a major role in human evolution.
C) All transposons are active and move around the human genome.
D) Some transposons move to another genomic location via an RNA intermediate.
E) They often contain genes that encode proteins that catalyze transposon movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Explain briefly the properties of the plasmid pBR322 that make it so convenient as a vector for cloning fragments of foreign DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Compensatory mutations in genes for noncoding RNAs indicate that:
A) these genes are not important for the function of the organism.
B) the secondary structure of the noncoding RNA is important for its function.
C) the noncoding RNA is not undergoing accelerated evolution.
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) these genes are not important for the function of the organism.
B) the secondary structure of the noncoding RNA is important for its function.
C) the noncoding RNA is not undergoing accelerated evolution.
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If you wanted to compare the sequence of a gene you isolated in the laboratory with a database of other genetic sequences, which tool would you use?
A) linkage analysis
B) BLAST
C) forensic DNA analysis
D) haplotype identification
E) quantitative PCR
A) linkage analysis
B) BLAST
C) forensic DNA analysis
D) haplotype identification
E) quantitative PCR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Mutations in which genetic sequences are NOT likely to have a phenotypic effect?
A) noncoding RNAs
B) exons
C) interspersed nuclear elements
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) noncoding RNAs
B) exons
C) interspersed nuclear elements
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which repeating sequences in the human genome are the targets of technologies used in forensic DNA analysis?
A) simple-sequence repeats
B) single nucleotide polymorphisms
C) introns
D) short tandem repeats
E) long repetitive sequences
A) simple-sequence repeats
B) single nucleotide polymorphisms
C) introns
D) short tandem repeats
E) long repetitive sequences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
You are comparing the DNA sequences of several species with a shared evolutionary ancestry. Species 1 has a sequence of ATGCCA, species 2 has a sequence of ATACCA, species 3 has a sequence of ATACTA, species 4 has a sequence of ACACTG, and species 5 has a sequence of ATGCCA. Which species is an outgroup compared with all the others?
A) species 1
B) species 2
C) species 3
D) species 4
E) species 5
A) species 1
B) species 2
C) species 3
D) species 4
E) species 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Explain how each of the following is used in cloning in a plasmid: (a) antibiotic-resistance genes; (b) origin of replication; (c) polylinker region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
During their multiple migrations from Africa to the rest of the world, gene flow likely occurred between which populations of early humanoids?
A) between Neanderthals and modern humans
B) between Denisovans and modern humans
C) between Neanderthals and Denisovans
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) between Neanderthals and modern humans
B) between Denisovans and modern humans
C) between Neanderthals and Denisovans
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Yeast two-hybrid analysis functions due to which reason?
A) The DNA-binding domain and transcriptional activation domain of a separated transcription factor are only brought into close proximity when the two proteins of interest interact with each other.
B) The DNA-binding domain and the transcriptional activation domain of a separated transcription factor may remain stable independent of each other.
C) Yeast can be grown as either a haploid or a diploid cell.
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) The DNA-binding domain and transcriptional activation domain of a separated transcription factor are only brought into close proximity when the two proteins of interest interact with each other.
B) The DNA-binding domain and the transcriptional activation domain of a separated transcription factor may remain stable independent of each other.
C) Yeast can be grown as either a haploid or a diploid cell.
D) All of the answers are correct.
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Especially stable haplotypes exist in which portions of the human genome due to their relative lack of meiotic recombination?
A) the Y chromosome
B) the X chromosome
C) the mitochondrial genome
D) both the Y chromosome and the mitochondrial genome
E) both the X chromosome and the mitochondrial genome
A) the Y chromosome
B) the X chromosome
C) the mitochondrial genome
D) both the Y chromosome and the mitochondrial genome
E) both the X chromosome and the mitochondrial genome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Groups of single nucleotide polymorphisms that are usually inherited together from one parent are called:
A) genotypes.
B) haplotypes.
C) phenotypes.
D) karyotypes.
E) cytotypes.
A) genotypes.
B) haplotypes.
C) phenotypes.
D) karyotypes.
E) cytotypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The process of linkage analysis does NOT rely on which technique to determine the genetic causes of diseases?
A) analysis of family pedigrees
B) identification of SNPs that are most often inherited with the disease-causing gene
C) the sequence of the entire chromosome where the disease-causing gene is located to directly identify it
D) comparing the DNA of people who have the disease with the DNA of people who don't have the disease
E) obtaining many sequences of a region of the chromosome that is associated with the disease
A) analysis of family pedigrees
B) identification of SNPs that are most often inherited with the disease-causing gene
C) the sequence of the entire chromosome where the disease-causing gene is located to directly identify it
D) comparing the DNA of people who have the disease with the DNA of people who don't have the disease
E) obtaining many sequences of a region of the chromosome that is associated with the disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



