Deck 1: The Foundations of Biochemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: The Foundations of Biochemistry
1
In a bacterial cell, the DNA is in the:
A) cell envelope.
B) cell membrane.
C) nucleoid.
D) nucleus.
E) ribosomes.
A) cell envelope.
B) cell membrane.
C) nucleoid.
D) nucleus.
E) ribosomes.
C
2
Which is a list of organelles?
A) mitochondria, chromatin, endoplasmic reticulum
B) peroxisomes, lysosomes, plasma membrane
C) proteasomes, peroxisomes, lysosomes
D) mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisomes
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) mitochondria, chromatin, endoplasmic reticulum
B) peroxisomes, lysosomes, plasma membrane
C) proteasomes, peroxisomes, lysosomes
D) mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, peroxisomes
E) All of the answers are correct.
D
3
Which list has the cellular components arranged in order of INCREASING size?
A) amino acid < protein < mitochondrion < ribosome
B) amino acid < protein < ribosome < mitochondrion
C) amino acid < ribosome < protein < mitochondrion
D) protein < amino acid < mitochondrion < ribosome
E) protein < ribosome < mitochondrion < amino acid
A) amino acid < protein < mitochondrion < ribosome
B) amino acid < protein < ribosome < mitochondrion
C) amino acid < ribosome < protein < mitochondrion
D) protein < amino acid < mitochondrion < ribosome
E) protein < ribosome < mitochondrion < amino acid
B
4
Humans maintain a nearly constant level of hemoglobin by continually synthesizing and degrading it. This is an example of a(n):
A) dynamic steady state.
B) equilibrium state.
C) exergonic change.
D) free-energy change.
E) waste of energy.
A) dynamic steady state.
B) equilibrium state.
C) exergonic change.
D) free-energy change.
E) waste of energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which group of single-celled microorganisms has many members found growing in extreme environments?
A) bacteria
B) archaea
C) eukaryotes
D) heterotrophs
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) bacteria
B) archaea
C) eukaryotes
D) heterotrophs
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which element is NOT among the four most abundant in living organisms?
A) carbon
B) hydrogen
C) nitrogen
D) oxygen
E) phosphorus
A) carbon
B) hydrogen
C) nitrogen
D) oxygen
E) phosphorus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A major change occurring in the evolution of eukaryotes from prokaryotes was the development of:
A) DNA.
B) photosynthetic capability.
C) plasma membranes.
D) ribosomes.
E) the nucleus.
A) DNA.
B) photosynthetic capability.
C) plasma membranes.
D) ribosomes.
E) the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other are known as:
A) anomers.
B) cis-trans isomers.
C) diastereoisomers.
D) enantiomers.
E) geometric isomers.
A) anomers.
B) cis-trans isomers.
C) diastereoisomers.
D) enantiomers.
E) geometric isomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In eukaryotes, the nucleus is enclosed by a double membrane called the:
A) cell membrane.
B) nuclear envelope.
C) nucleolus.
D) nucleoplasm.
E) nucleosome.
A) cell membrane.
B) nuclear envelope.
C) nucleolus.
D) nucleoplasm.
E) nucleosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The catalog of all proteins functioning in a cell is the:
A) metabolome.
B) proteasome.
C) lysosome.
D) proteome.
E) genome.
A) metabolome.
B) proteasome.
C) lysosome.
D) proteome.
E) genome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If heat energy is absorbed by the system during a chemical reaction, the reaction is said to be:
A) at equilibrium.
B) endergonic.
C) endothermic.
D) exergonic.
E) exothermic.
A) at equilibrium.
B) endergonic.
C) endothermic.
D) exergonic.
E) exothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The dimensions of living cells are limited, on the lower end by the minimum number of biomolecules necessary for function, and on the upper end by the rate of diffusion of solutes such as oxygen. Except for highly elongated cells, they usually have lengths and diameters in the range of:
A) 0.1 m to 10 m.
B) 0.3 m to 30 m.
C) 0.3 m to 100 m.
D) 1 m to 100 m.
E) 1 m to 300 m.
A) 0.1 m to 10 m.
B) 0.3 m to 30 m.
C) 0.3 m to 100 m.
D) 1 m to 100 m.
E) 1 m to 300 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The three-dimensional structure of macromolecules is formed and maintained primarily through noncovalent interactions. Which one of the following is NOT considered a noncovalent interaction?
A) carbon-carbon bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) ionic interactions
E) van der Waals interactions
A) carbon-carbon bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C) hydrophobic interactions
D) ionic interactions
E) van der Waals interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Use the terms a) chemoautotrophs, b) chemoheterotrophs, c) photoautotrophs, and d) photoheterotrophs and identify the answer that CORRECTLY finishes the statement: Carnivores are _____ and herbivores are _____.
A) b; c
B) b; d
C) b; b
D) a; b
E) a; a
A) b; c
B) b; d
C) b; b
D) a; b
E) a; a

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The enzyme fumarase catalyzes the reversible hydration of fumaric acid to l-malate, but it will not catalyze the hydration of maleic acid, the cis isomer of fumaric acid. This is an example of:
A) biological activity.
B) chiral activity.
C) racemization.
D) stereoisomerization.
E) stereospecificity.
A) biological activity.
B) chiral activity.
C) racemization.
D) stereoisomerization.
E) stereospecificity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the free energy change G for a reaction is -46.11 kJ/mol, the reaction is:
A) at equilibrium.
B) endergonic.
C) endothermic.
D) exergonic.
E) exothermic.
A) at equilibrium.
B) endergonic.
C) endothermic.
D) exergonic.
E) exothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What functional groups are present on this molecule? 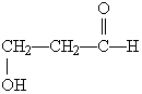
A) ether and aldehyde
B) hydroxyl and aldehyde
C) hydroxyl and carboxylic acid
D) hydroxyl and ester
E) hydroxyl and ketone

A) ether and aldehyde
B) hydroxyl and aldehyde
C) hydroxyl and carboxylic acid
D) hydroxyl and ester
E) hydroxyl and ketone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The macromolecules that serve in the storage and transmission of genetic information are:
A) carbohydrates.
B) lipids.
C) membranes.
D) nucleic acids.
E) proteins.
A) carbohydrates.
B) lipids.
C) membranes.
D) nucleic acids.
E) proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The four covalent bonds in methane (CH4) are arranged around carbon to give which geometry?
A) linear
B) tetrahedral
C) trigonal bipyramidal
D) trigonal planar
E) trigonal pyramidal
A) linear
B) tetrahedral
C) trigonal bipyramidal
D) trigonal planar
E) trigonal pyramidal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The bacterium E. coli requires simple organic molecules for growth and energy-it is therefore a:
A) chemoautotroph.
B) chemoheterotroph.
C) lithotroph.
D) photoautotroph.
E) photoheterotroph.
A) chemoautotroph.
B) chemoheterotroph.
C) lithotroph.
D) photoautotroph.
E) photoheterotroph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement is NOT a distinguishing feature of living organisms?
A) There exists a high degree of organizational complexity.
B) The structure of components influences their function.
C) Organisms can reproduce themselves.
D) Organisms do not need to interact with their environment.
E) Organisms change over time.
A) There exists a high degree of organizational complexity.
B) The structure of components influences their function.
C) Organisms can reproduce themselves.
D) Organisms do not need to interact with their environment.
E) Organisms change over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which organelle does NOT consist of a double membrane?
A) mitochondrion
B) ribosome
C) chloroplast
D) endoplasmic reticulum
E) Golgi body
A) mitochondrion
B) ribosome
C) chloroplast
D) endoplasmic reticulum
E) Golgi body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What did Jacques Monod mean when he wrote, "What is true of E. coli is true of the elephant?"
A) Bacterial cells are identical to animal cells.
B) Bacterial cells can synthesize ivory under certain conditions.
C) Bacterial cells contain a chromosome similar to animal cells.
D) Bacterial cells contain enzymes similar to those found in animal cells.
E) Bacterial cells contain molecules with complexity similar to molecules found in in the "mineral world."
A) Bacterial cells are identical to animal cells.
B) Bacterial cells can synthesize ivory under certain conditions.
C) Bacterial cells contain a chromosome similar to animal cells.
D) Bacterial cells contain enzymes similar to those found in animal cells.
E) Bacterial cells contain molecules with complexity similar to molecules found in in the "mineral world."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which statement is TRUE regarding energy sources used by organisms?
A) Phototrophs can use carbon dioxide as a carbon source.
B) Phototrophs can use carbon dioxide as an energy source.
C) All phototrophs are autotrophs.
D) All chemotrophs are heterotrophs.
E) All phototrophs are autotrophs that can use carbon dioxide as a carbon source.
A) Phototrophs can use carbon dioxide as a carbon source.
B) Phototrophs can use carbon dioxide as an energy source.
C) All phototrophs are autotrophs.
D) All chemotrophs are heterotrophs.
E) All phototrophs are autotrophs that can use carbon dioxide as a carbon source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Energy requiring metabolic pathways that yield complex molecules from simpler precursors are:
A) amphibolic.
B) anabolic.
C) autotrophic.
D) catabolic.
E) heterotrophic.
A) amphibolic.
B) anabolic.
C) autotrophic.
D) catabolic.
E) heterotrophic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which reason is MOST probable for why carbon is used in living organisms but not silicon?
A) Carbon can make four bonds, whereas silicon can only make three.
B) Carbon can make double bonds, but silicon cannot.
C) Carbon can form more preferred geometries when bonding.
D) Carbon is lighter, and therefore its bonds are stronger.
E) Silicon is heavier, and therefore its bonds are stronger.
A) Carbon can make four bonds, whereas silicon can only make three.
B) Carbon can make double bonds, but silicon cannot.
C) Carbon can form more preferred geometries when bonding.
D) Carbon is lighter, and therefore its bonds are stronger.
E) Silicon is heavier, and therefore its bonds are stronger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If an organism is a facultative anaerobe, which statement is TRUE?
A) The organism requires sulfur to live.
B) The organism will die if exposed to oxygen.
C) The organism requires oxygen to live.
D) The organism does not require oxygen to live but will not die if exposed to oxygen.
E) The organism requires methane to live.
A) The organism requires sulfur to live.
B) The organism will die if exposed to oxygen.
C) The organism requires oxygen to live.
D) The organism does not require oxygen to live but will not die if exposed to oxygen.
E) The organism requires methane to live.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which organic molecules can be considered "alive"?
A) proteins
B) carbohydrates
C) nucleic acids
D) saccharides
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) proteins
B) carbohydrates
C) nucleic acids
D) saccharides
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which method is MOST useful when fractionating cellular organelles?
A) centrifugation
B) precipitation
C) chromatography
D) restriction digest
E) peroxidation
A) centrifugation
B) precipitation
C) chromatography
D) restriction digest
E) peroxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which organelle is NOT found in plant cells?
A) ribosome
B) lysosome
C) chloroplast
D) vacuole
E) mitochondrion
A) ribosome
B) lysosome
C) chloroplast
D) vacuole
E) mitochondrion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which statement is NOT true regarding the plasma membrane?
A) It is a physical barrier separating the inside of the cell from its surroundings.
B) It is a flexible, hydrophobic structure.
C) The individual lipids and proteins of the plasma membrane are covalently linked.
D) The plasma membrane incorporates newly made lipid and protein components as a cell grows.
E) Cell division occurs without loss of the membrane integrity.
A) It is a physical barrier separating the inside of the cell from its surroundings.
B) It is a flexible, hydrophobic structure.
C) The individual lipids and proteins of the plasma membrane are covalently linked.
D) The plasma membrane incorporates newly made lipid and protein components as a cell grows.
E) Cell division occurs without loss of the membrane integrity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The major difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that:
A) prokaryotes have a nucleus, while eukaryotes do not.
B) eukaryotes have a nucleus, while prokaryotes do not.
C) eukaryotes have double-stranded DNA, while prokaryotes have single-stranded DNA.
D) prokaryotes have double-stranded DNA, while eukaryotes have single-stranded DNA.
E) prokaryotes do not have ribosomes.
A) prokaryotes have a nucleus, while eukaryotes do not.
B) eukaryotes have a nucleus, while prokaryotes do not.
C) eukaryotes have double-stranded DNA, while prokaryotes have single-stranded DNA.
D) prokaryotes have double-stranded DNA, while eukaryotes have single-stranded DNA.
E) prokaryotes do not have ribosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The three-dimensional structure of a protein is determined primarily by:
A) electrostatic guidance from nucleic acid structure.
B) how many amino acids are in the protein.
C) hydrophobic interaction with lipids that provide a folding framework.
D) modification during interactions with ribosomes.
E) the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
A) electrostatic guidance from nucleic acid structure.
B) how many amino acids are in the protein.
C) hydrophobic interaction with lipids that provide a folding framework.
D) modification during interactions with ribosomes.
E) the sequence of amino acids in the protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which statement is FALSE regarding bacterial and archaeal cells?
A) Archaeal and bacterial plasma membranes consist of a thin bilayer of lipid molecules penetrated by proteins.
B) Bacteria and archaea have group specific specializations in their cell envelope.
C) Archaea can have a single- or double-layered membrane.
D) Bacteria can have a single- or double-layered membrane.
E) Both bacteria and archaea have a layer of peptidoglycan in their cell envelope.
A) Archaeal and bacterial plasma membranes consist of a thin bilayer of lipid molecules penetrated by proteins.
B) Bacteria and archaea have group specific specializations in their cell envelope.
C) Archaea can have a single- or double-layered membrane.
D) Bacteria can have a single- or double-layered membrane.
E) Both bacteria and archaea have a layer of peptidoglycan in their cell envelope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When a region of DNA must be repaired by removing and replacing some of the nucleotides, what ensures that the new nucleotides are in the correct sequence?
A) DNA cannot be repaired and this explains why mutations occur.
B) Specific enzymes bind the correct nucleotides.
C) The new nucleotides base pair accurately with those on the complementary strand.
D) The repair enzyme recognizes the removed nucleotide and brings in an identical one to replace it.
E) The three-dimensional structure determines the order of nucleotides.
A) DNA cannot be repaired and this explains why mutations occur.
B) Specific enzymes bind the correct nucleotides.
C) The new nucleotides base pair accurately with those on the complementary strand.
D) The repair enzyme recognizes the removed nucleotide and brings in an identical one to replace it.
E) The three-dimensional structure determines the order of nucleotides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Hereditary information (with the exception of some viruses) is preserved in:
A) deoxyribonucleic acid.
B) membrane structures.
C) nuclei.
D) polysaccharides.
E) ribonucleic acid.
A) deoxyribonucleic acid.
B) membrane structures.
C) nuclei.
D) polysaccharides.
E) ribonucleic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Enzymes are biological catalysts that enhance the rate of a reaction by:
A) decreasing the activation energy.
B) decreasing the amount of free energy released.
C) increasing the activation energy.
D) increasing the amount of free energy released.
E) increasing the energy of the transition state.
A) decreasing the activation energy.
B) decreasing the amount of free energy released.
C) increasing the activation energy.
D) increasing the amount of free energy released.
E) increasing the energy of the transition state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to Oparin's theory for the origin of life, the prebiotic atmosphere:
A) already contained some primitive RNA molecules.
B) basically was very similar to the atmosphere of today.
C) contained many amino acids.
D) had an abundance of methane, ammonia, and water.
E) was rich in oxygen.
A) already contained some primitive RNA molecules.
B) basically was very similar to the atmosphere of today.
C) contained many amino acids.
D) had an abundance of methane, ammonia, and water.
E) was rich in oxygen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The major carrier of chemical energy in all cells is:
A) acetyl triphosphate.
B) adenosine monophosphate.
C) adenosine triphosphate.
D) cytosine tetraphosphate.
E) uridine diphosphate.
A) acetyl triphosphate.
B) adenosine monophosphate.
C) adenosine triphosphate.
D) cytosine tetraphosphate.
E) uridine diphosphate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which group includes the four most abundant elements in living organisms?
A) carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, iron
B) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
C) carbon, hydrogen, phosphorous, oxygen
D) carbon, nitrogen, phosphorous, oxygen
E) carbon, hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen
A) carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, iron
B) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
C) carbon, hydrogen, phosphorous, oxygen
D) carbon, nitrogen, phosphorous, oxygen
E) carbon, hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When energy is used by a system, can it be "used up"?
A) Yes, it is used up when the energy source is depleted.
B) Yes, it is used up when all energy is converted into chemical energy.
C) No, all energy is converted into potential energy.
D) No, all energy is converted into kinetic energy.
E) No, energy can be converted into kinetic and potential energy.
A) Yes, it is used up when the energy source is depleted.
B) Yes, it is used up when all energy is converted into chemical energy.
C) No, all energy is converted into potential energy.
D) No, all energy is converted into kinetic energy.
E) No, energy can be converted into kinetic and potential energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which ranking CORRECTLY describes the rigidity of the red bond (the central bond) shown in the figure? 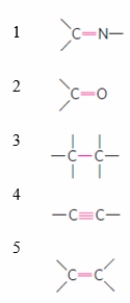
A) 2 = most rigid, 3 = least rigid
B) 1 = most rigid, 5 = least rigid
C) 4 = most rigid, 3 = least rigid
D) 2 = most rigid, 1 = least rigid
E) 4 = most rigid, 1 = least rigid
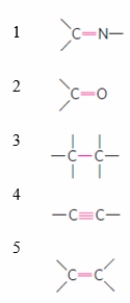
A) 2 = most rigid, 3 = least rigid
B) 1 = most rigid, 5 = least rigid
C) 4 = most rigid, 3 = least rigid
D) 2 = most rigid, 1 = least rigid
E) 4 = most rigid, 1 = least rigid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The joining of two amino acids via a peptide bond (the process of protein synthesis) has a positive G value. What does this imply?
A) Forming a peptide bond is endergonic and must be coupled to another reaction.
B) Forming a peptide bond is exergonic and must be coupled to another reaction.
C) Forming a peptide bond is spontaneous and does not need to be coupled to another reaction.
D) Forming a peptide bond is spontaneous and can sometimes be coupled to another reaction.
E) Forming a peptide bond increases the entropy of a system.
A) Forming a peptide bond is endergonic and must be coupled to another reaction.
B) Forming a peptide bond is exergonic and must be coupled to another reaction.
C) Forming a peptide bond is spontaneous and does not need to be coupled to another reaction.
D) Forming a peptide bond is spontaneous and can sometimes be coupled to another reaction.
E) Forming a peptide bond increases the entropy of a system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If a scientist wanted to know whether a particular hydrocarbon was in use in a cell's plasma membrane, they could search the organism's:
A) metabolome.
B) lipidome.
C) glycome.
D) proteome.
E) genome.
A) metabolome.
B) lipidome.
C) glycome.
D) proteome.
E) genome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the CORRECT name for the configuration of the molecule shown in the figure? 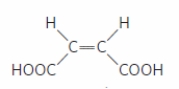
A) orthogonal
B) trans
C) cis
D) zis
E) chiros

A) orthogonal
B) trans
C) cis
D) zis
E) chiros

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In an oxidation-reduction reaction, the oxidized reagent _____, and the reduced reagent _____.
A) is energized; is deenergized
B) is deenergized; is energized
C) loses electrons; gains electrons
D) gains electrons; loses electrons
E) maintains the same number of electrons; loses electrons
A) is energized; is deenergized
B) is deenergized; is energized
C) loses electrons; gains electrons
D) gains electrons; loses electrons
E) maintains the same number of electrons; loses electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which answer choice represents the LARGEST percentage, by weight, of an E. coli cell?
A) RNA
B) DNA
C) protein
D) lipids
E) water
A) RNA
B) DNA
C) protein
D) lipids
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Reaction 1 has a G° of -12.3 kJ/mol, and Reaction 2 has a G° of 23.4 kJ/mol. Which statement is TRUE of these two reactions?
A) Reaction 1 occurs faster.
B) Reaction 2 occurs faster.
C) Both reactions occur at the same rate.
D) Reaction 2 will not occur.
E) It is impossible to know which reaction occurs faster with this information.
A) Reaction 1 occurs faster.
B) Reaction 2 occurs faster.
C) Both reactions occur at the same rate.
D) Reaction 2 will not occur.
E) It is impossible to know which reaction occurs faster with this information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Fructose-1-phosphate can be hydrolyzed into fructose + inorganic phosphate (Pi) with a G° of -16.0 kJ/mol. If ATP can be hydrolyzed into ADP + Pi with a G° of -30.5 kJ/mol, what is the free energy change for the reaction of fructose + ATP fructose 1-phospate + ADP?
A) -46.5 kJ/mol
B) -14.5 kJ/mol
C) 46.5 kJ/mol
D) 14.5 kJ/mol
E) -1.4 Genetic Foundations5 kJ/mol
A) -46.5 kJ/mol
B) -14.5 kJ/mol
C) 46.5 kJ/mol
D) 14.5 kJ/mol
E) -1.4 Genetic Foundations5 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which types of molecules can serve as informational macromolecules in cells?
A) proteins
B) nucleic acids
C) oligosaccharides
D) both proteins and nucleic acids
E) proteins, nucleic acids, and oligosaccharides
A) proteins
B) nucleic acids
C) oligosaccharides
D) both proteins and nucleic acids
E) proteins, nucleic acids, and oligosaccharides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An increase in the entropy of a system can be described as an increase in the total amount of _____ of a system.
A) kinetic energy
B) potential energy
C) oxidative energy
D) disorder
E) order
A) kinetic energy
B) potential energy
C) oxidative energy
D) disorder
E) order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which choice CORRECTLY lists the molecular masses from smallest to largest?
A) 18 kDa < 15,000 Da < 15,100 amu < 1.8 MDa < 1.8 mDa
B) 1.8 mDa < 15,000 Da < 15,100 amu <18 kDa < 1.8 MDa
C) 1.8 MDa < 15,000 Da < 15,100 amu <18 kDa < 1.8 mDa
D) 1.8 mDa < 15,100 amu < 15,000 Da <18 kDa < 1.8 MDa
E) 1.8 MDa < 18 kDa < 15,100 amu < 1.8 mDa <15,000 Da
A) 18 kDa < 15,000 Da < 15,100 amu < 1.8 MDa < 1.8 mDa
B) 1.8 mDa < 15,000 Da < 15,100 amu <18 kDa < 1.8 MDa
C) 1.8 MDa < 15,000 Da < 15,100 amu <18 kDa < 1.8 mDa
D) 1.8 mDa < 15,100 amu < 15,000 Da <18 kDa < 1.8 MDa
E) 1.8 MDa < 18 kDa < 15,100 amu < 1.8 mDa <15,000 Da

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which statement about living systems is NOT true?
A) Living organisms can be described as an open system.
B) Living systems maintain a more-or-less constant composition.
C) Living systems are in equilibrium with their surroundings.
D) Living systems exist in a dynamic steady-state.
E) Living systems have efficient mechanisms to convert chemical energy from one form into another.
A) Living organisms can be described as an open system.
B) Living systems maintain a more-or-less constant composition.
C) Living systems are in equilibrium with their surroundings.
D) Living systems exist in a dynamic steady-state.
E) Living systems have efficient mechanisms to convert chemical energy from one form into another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which discipline uses an approach that tries to integrate information to give a molecular picture of all the activities of a cell under certain conditions?
A) metabolomics
B) genomics
C) systems biology
D) proteomics
E) lipidomics
A) metabolomics
B) genomics
C) systems biology
D) proteomics
E) lipidomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
It is possible to separate a racemic mixture by:
A) combustion.
B) crystallization.
C) centrifugation.
D) distillation.
E) magnetism.
A) combustion.
B) crystallization.
C) centrifugation.
D) distillation.
E) magnetism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which statement CORRECTLY describes the molecules shown in the figure? 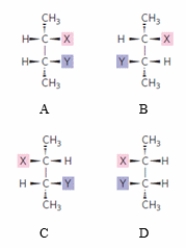
A) A and D are enantiomers, and B and C are diastereomers.
B) A and D are diastereomers, and B and C are enantiomers.
C) A and C are enantiomers, and B and D are diastereomers.
D) A and C are diastereomers, and B and D are enantiomers.
E) All are diastereomers to each other.

A) A and D are enantiomers, and B and C are diastereomers.
B) A and D are diastereomers, and B and C are enantiomers.
C) A and C are enantiomers, and B and D are diastereomers.
D) A and C are diastereomers, and B and D are enantiomers.
E) All are diastereomers to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which factor can be changed WITHOUT breaking covalent bonds?
A) conformation
B) configuration
C) chirality
D) stereochemistry
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) conformation
B) configuration
C) chirality
D) stereochemistry
E) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which substance is NOT a secondary metabolite?
A) adenine
B) morphine
C) quinine
D) nicotine
E) salicylic acid
A) adenine
B) morphine
C) quinine
D) nicotine
E) salicylic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which list of descriptive terms for biological molecules is placed in CORRECT order from smallest to largest?
A) monomer, oligomer, polymer
B) monomer, multimer, macromer
C) oligomer, monomer, polymer
D) polymer, oligomer, monomer
E) metamer, oligomer, polymer
A) monomer, oligomer, polymer
B) monomer, multimer, macromer
C) oligomer, monomer, polymer
D) polymer, oligomer, monomer
E) metamer, oligomer, polymer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Living cells produce only one chiral form of a biomolecule because:
A) biomolecules, by definition, can exist as only one chiral form.
B) living cells can only create L isomers.
C) living cells choose to express only the correct isomer.
D) living cells have enzymes that are also chiral.
E) living cells can produce the opposite chiral form only under certain metabolic conditions.
A) biomolecules, by definition, can exist as only one chiral form.
B) living cells can only create L isomers.
C) living cells choose to express only the correct isomer.
D) living cells have enzymes that are also chiral.
E) living cells can produce the opposite chiral form only under certain metabolic conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane composed of lipid and protein molecules. What is the function of the plasma membrane?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Accurate folding of a protein does NOT depend on:
A) proper pH.
B) correct ionic strength.
C) correct temperature.
D) correct metal ion concentration.
E) All of the conditions listed are important for correct folding of a protein.
A) proper pH.
B) correct ionic strength.
C) correct temperature.
D) correct metal ion concentration.
E) All of the conditions listed are important for correct folding of a protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which present-day observable piece of evidence supports the "RNA world" hypothesis?
A) RNA molecules participate in biologically significant reactions.
B) RNA can serve as an information-carrying molecule.
C) RNA nucleotides catalyze peptide bond formation.
D) RNA molecules participate in biologically significant reactions, and RNA nucleotides catalyze peptide bond formation.
E) RNA molecules participate in biologically significant reactions, RNA can serve as an information-carrying molecule, and RNA nucleotides catalyze peptide bond formation.
A) RNA molecules participate in biologically significant reactions.
B) RNA can serve as an information-carrying molecule.
C) RNA nucleotides catalyze peptide bond formation.
D) RNA molecules participate in biologically significant reactions, and RNA nucleotides catalyze peptide bond formation.
E) RNA molecules participate in biologically significant reactions, RNA can serve as an information-carrying molecule, and RNA nucleotides catalyze peptide bond formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
List the types of noncovalent interactions that are important in providing stability to the three-dimensional structures of macromolecules. (b) Why is it important that these interactions be noncovalent, rather than covalent, bonds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which statement is NOT true about the formation of early organisms?
A) The first organisms were anaerobic because the atmosphere was devoid of oxygen.
B) The original electron donor for photosynthetic processes was probably H2S.
C) Oxygen, a powerful oxidant, was probably welcomed by anaerobic organisms as a preferable choice for metabolic reactions.
D) The transfer of electrons to O2 releases more energy than transferring electrons to SO42-
E) Cyanobacteria are modern descendants of early photosynthetic oxygen-producers.
A) The first organisms were anaerobic because the atmosphere was devoid of oxygen.
B) The original electron donor for photosynthetic processes was probably H2S.
C) Oxygen, a powerful oxidant, was probably welcomed by anaerobic organisms as a preferable choice for metabolic reactions.
D) The transfer of electrons to O2 releases more energy than transferring electrons to SO42-
E) Cyanobacteria are modern descendants of early photosynthetic oxygen-producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
E. coli is known as a gram-negative bacterial species. (a) How is this determined? (b) How do gram-negative bacteria differ structurally from gram-positive bacteria?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which statement is NOT true about genetic mutations?
A) Mutations arise from an unrepaired mistake in DNA replication.
B) Mutations arise from incorrectly repaired damage to one of the DNA strands.
C) Mutations in reproductive cells can be passed on to offspring.
D) Mutations may better equip an organism or cell to survive in its environment.
E) All of the statements are true.
A) Mutations arise from an unrepaired mistake in DNA replication.
B) Mutations arise from incorrectly repaired damage to one of the DNA strands.
C) Mutations in reproductive cells can be passed on to offspring.
D) Mutations may better equip an organism or cell to survive in its environment.
E) All of the statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
_____ pathways _____ large molecules, _____ energy.
A) Catabolic; break down; releasing
B) Anabolic; break down; releasing
C) Catabolic; break down; storing
D) Anabolic; break down; storing
E) Anabolic; build up; releasing
A) Catabolic; break down; releasing
B) Anabolic; break down; releasing
C) Catabolic; break down; storing
D) Anabolic; break down; storing
E) Anabolic; build up; releasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Most cells of higher plants have a cell wall outside the plasma membrane. What is the function of the cell wall?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The _____ of homologous proteins can be used to estimate the degree of evolutionary divergence.
A) three-dimensional structure
B) expression profiles
C) sequence similarity
D) endosymbiotic nature
E) chromosomes
A) three-dimensional structure
B) expression profiles
C) sequence similarity
D) endosymbiotic nature
E) chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The diagram below is a generic example of what process? 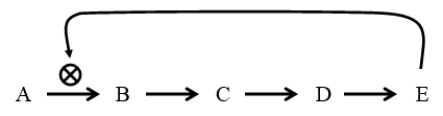
A) systems biology
B) feedback inhibition
C) positive feedback
D) equilibrium
E) catabolism

A) systems biology
B) feedback inhibition
C) positive feedback
D) equilibrium
E) catabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What six characteristics distinguish living organisms from inanimate objects?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In double-stranded DNA, the two strands are held together by _____ bonds.
A) covalent
B) ionic
C) polypeptide
D) hydrogen
E) phosphodiester
A) covalent
B) ionic
C) polypeptide
D) hydrogen
E) phosphodiester

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In general, increasing the temperature of a reaction will have what effect, based on the relationship between standard free energy change and the equilibrium constant?
A) The reaction will be inhibited.
B) The reaction will go faster.
C) The reaction will become more spontaneous.
D) The reaction will become less spontaneous.
E) There will be no effect on the reaction.
A) The reaction will be inhibited.
B) The reaction will go faster.
C) The reaction will become more spontaneous.
D) The reaction will become less spontaneous.
E) There will be no effect on the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
_____ are typically expressed under all conditions and are not subject to regulation.
A) Housekeeping genes
B) Homologous genes
C) Bacterial genomes
D) Eukaryotic genomes
E) Endosymbiotic genes
A) Housekeeping genes
B) Homologous genes
C) Bacterial genomes
D) Eukaryotic genomes
E) Endosymbiotic genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which statement is NOT true regarding orthologous genes?
A) They share similar sequences.
B) They usually have the same function.
C) They usually have a similar three-dimensional structure.
D) They presumably arose from a gene duplication event.
E) All of the statements are true.
A) They share similar sequences.
B) They usually have the same function.
C) They usually have a similar three-dimensional structure.
D) They presumably arose from a gene duplication event.
E) All of the statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The similarities of gene sequences and metabolic pathways across the three domains of life are evidence for:
A) evolution.
B) a common ancestor.
C) cross-species genetic transfer.
D) both evolution and a common ancestor.
E) both a common ancestor and cross-species genetic transfer.
A) evolution.
B) a common ancestor.
C) cross-species genetic transfer.
D) both evolution and a common ancestor.
E) both a common ancestor and cross-species genetic transfer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The precise three-dimensional structure, or _____ conformation, is critical to a protein's function.
A) native
B) molecular
C) chaperone
D) macromolecular
E) high-affinity
A) native
B) molecular
C) chaperone
D) macromolecular
E) high-affinity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which organelle probably originated as an endosymbiotic engulfing of an aerobic bacterium by a eukaryotic cell?
A) ribosome
B) mitochondrion
C) Golgi body
D) nucleus
E) endoplasmic reticulum
A) ribosome
B) mitochondrion
C) Golgi body
D) nucleus
E) endoplasmic reticulum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When Stanley Miller, in Harold Urey's laboratory, subjected a gaseous mixture mimicking the prebiotic atmosphere on Earth to electrical sparks, he found that _____ were formed.
A) amino acids
B) aldehydes
C) ribonucleotides
D) both amino acids and aldehydes
E) amino acids, aldehydes, and ribonucleotides
A) amino acids
B) aldehydes
C) ribonucleotides
D) both amino acids and aldehydes
E) amino acids, aldehydes, and ribonucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



