Deck 14: Routine and Point-Of-Care Testing in Hematology: Manual and Semiautomated Methods
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/37
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Routine and Point-Of-Care Testing in Hematology: Manual and Semiautomated Methods
1
For which patient is a hemoglobin of 10.5 g/dL normal?
A) A newborn
B) A 2-year-old child
C) A female adult
D) A male adult
A) A newborn
B) A 2-year-old child
C) A female adult
D) A male adult
A 2-year-old child
2
Interpret the following results (all tests performed manually) on an adult female named Mary Jones.
RBC: 3.22*1012/L
Hemoglobin: 16.0 g/dL
Hematocrit: 30.0%
A) All are normal.
B) All are decreased.
C) Hemoglobin is elevated and other two are normal.
D) Values do not agree with the "rule of three."
RBC: 3.22*1012/L
Hemoglobin: 16.0 g/dL
Hematocrit: 30.0%
A) All are normal.
B) All are decreased.
C) Hemoglobin is elevated and other two are normal.
D) Values do not agree with the "rule of three."
Values do not agree with the "rule of three."
3
In the center square on one side of a hemocytometer, 100 platelets were found; 200 were found in the center square on the other side. Select the best course of action.
A) Report the count as 150 *109/L.
B) Verify the count by estimating the platelet number on the blood film.
C) Recount the hemocytometer on a phase microscope.
D) Repeat the procedure-the two counts are not close enough.
A) Report the count as 150 *109/L.
B) Verify the count by estimating the platelet number on the blood film.
C) Recount the hemocytometer on a phase microscope.
D) Repeat the procedure-the two counts are not close enough.
Repeat the procedure-the two counts are not close enough.
4
Twenty cells are counted in one of the nine large squares of a hemocytometer. The sample is diluted 1:10. How many cells are present per L?
A) 200
B) 1000
C) 2000
D) 20,000
A) 200
B) 1000
C) 2000
D) 20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Any of the following could be an explanation for the invalid hemoglobin for Mary Jones (Questions 13 through 16) except:
A) The blood sample is hemolyzed.
B) Lipemia is present in the plasma.
C) The patient has hemoglobin S (Hb S).
D) The patient's white count is 150.0 *109/L.
A) The blood sample is hemolyzed.
B) Lipemia is present in the plasma.
C) The patient has hemoglobin S (Hb S).
D) The patient's white count is 150.0 *109/L.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the total volume of one side of a hemocytometer if the ruled area is 3 * 3 mm and the depth is 0.1 mm?
A) 0.3 mm3
B) 0.9 mm3
C) 1.0 mm3
D) 9 mm3
A) 0.3 mm3
B) 0.9 mm3
C) 1.0 mm3
D) 9 mm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The platelet count from the automated cell counter is 80 * 109/L. Platelet satellites around neutrophils are observed on the blood film estimate. A sodium citrate tube is drawn, and the count reads 300 *109/L from the cell counter. What platelet count * 109/L should be reported?
A) 80
B) 300
C) 330
D) The estimated count from the blood film
A) 80
B) 300
C) 330
D) The estimated count from the blood film

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The MCV on a patient is calculated to be 115 fL and the MCHC is 35 g/dL. What, in general terms, must be true of the MCH if it is consistent with the previous two indices?
A) It is impossible to know.
B) It should be in the reference range.
C) It should be below reference range.
D) It should be above reference range.
A) It is impossible to know.
B) It should be in the reference range.
C) It should be below reference range.
D) It should be above reference range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What red cell morphology would support the red cell indices calculated for Mary Jones in Question 14?
A) Microcytic hyperchromic red cells
B) Normocytic hyperchromic red cells
C) Macrocytic hyperchromic red cells
D) No red cell morphology supports these indices.
A) Microcytic hyperchromic red cells
B) Normocytic hyperchromic red cells
C) Macrocytic hyperchromic red cells
D) No red cell morphology supports these indices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The calculated indices on Mary Jones from Question 13 are:



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A hemoglobin of 19 g/dL is normal for which of the following patients?
A) A newborn
B) A 2-year-old child
C) A female adult
D) A male adult
A) A newborn
B) A 2-year-old child
C) A female adult
D) A male adult

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What error was probably made if red cells are seen when attempting to manually count white blood cell (WBCs) on a hemocytometer?
A) The Unopette was not mixed before charging the hemocytometer.
B) Diluent was squeezed out and lost when filling the Unopette.
C) The wrong dilution was made.
D) The Unopette was not allowed to sit for 10 minutes for complete red blood cell (RBC) lysis.
A) The Unopette was not mixed before charging the hemocytometer.
B) Diluent was squeezed out and lost when filling the Unopette.
C) The wrong dilution was made.
D) The Unopette was not allowed to sit for 10 minutes for complete red blood cell (RBC) lysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following could account for the red cell indices on Mary Jones reviewing Questions 13 through 15?
A) Determining a likely cause is not possible.
B) An error in the hemoglobin probably has been made.
C) An error in the red cell count probably has been made.
D) An error in the microhematocrit probably has been made.
A) Determining a likely cause is not possible.
B) An error in the hemoglobin probably has been made.
C) An error in the red cell count probably has been made.
D) An error in the microhematocrit probably has been made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Why is it important to have a scrupulously clean hemocytometer when manually counting platelets?
A) So few platelets exist that they can be missed if dirt is present.
B) They are so refractile, they can be confused with dirt.
C) Their small size makes them easily confused with dirt.
D) They are easily confused with the red cells that are present.
A) So few platelets exist that they can be missed if dirt is present.
B) They are so refractile, they can be confused with dirt.
C) Their small size makes them easily confused with dirt.
D) They are easily confused with the red cells that are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Ten nucleated red blood cells (NRBCs) are found in a blood film when differentiating 100 white cells. What is the corrected white blood count if the automated cell counter printed a count of 10.0* 109/L?
A) 0.91* 109/L
B) 9.1* 109/L
C) 91 * 109/L
D) Ten NRBCs not enough to require a correction
A) 0.91* 109/L
B) 9.1* 109/L
C) 91 * 109/L
D) Ten NRBCs not enough to require a correction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following would cause a manual cell count to be falsely high?
A) Unopette not mixed before charging the hemocytometer
B) Not wiping excess blood from outside of pipette when filling
C) Using a smaller volume pipette than that specified by the Unopette system
D) Pulling blood out of the pipette when wiping away excess on the outside
A) Unopette not mixed before charging the hemocytometer
B) Not wiping excess blood from outside of pipette when filling
C) Using a smaller volume pipette than that specified by the Unopette system
D) Pulling blood out of the pipette when wiping away excess on the outside

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Manual cell counting methods in automated hematology laboratories are used for all of the following except:
A) Routine testing
B) Very low counts
C) Malfunctioning automated instruments
D) Counting spinal fluids
A) Routine testing
B) Very low counts
C) Malfunctioning automated instruments
D) Counting spinal fluids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following could cause the microhematocrit to be falsely decreased?
A) Specimen contaminated with intravenous fluid
B) Trapped plasma from abnormally shaped red cells
C) Dehydration
D) Insufficient centrifugation
A) Specimen contaminated with intravenous fluid
B) Trapped plasma from abnormally shaped red cells
C) Dehydration
D) Insufficient centrifugation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the four large corner squares of a hemocytometer, 95, 102, 105, and 98 white cells were counted from a 1:20 dilution. Select the correct interpretation for the white blood count calculated from these values.
A) Normal for infant and elevated for an adult
B) Normal for any patient
C) Elevated for any patient
D) Normal for an infant and decreased for an adult
A) Normal for infant and elevated for an adult
B) Normal for any patient
C) Elevated for any patient
D) Normal for an infant and decreased for an adult

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
On a standard reticulocyte preparation with new methylene blue, 100 cells are counted that contain blue-stained granulofilamentous material. The red blood count is 3.22 *1012/L, and the hematocrit is 30%. Calculate the reticulocyte count as a percentage.
A) 0.1%
B) 1.0%
C) 10.0%
D) 100.0%
A) 0.1%
B) 1.0%
C) 10.0%
D) 100.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Diagnostic testing at or near the site of patient care is known as:
A) Preanalytic testing
B) Point-of-care testing (POCT)
C) Neutral-site testing
D) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) testing
A) Preanalytic testing
B) Point-of-care testing (POCT)
C) Neutral-site testing
D) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) testing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A manual hemoglobin is determined on a patient, and the dilution still appears turbid after letting it sit for 15 minutes. The stained blood film is examined, and sickle cells are observed on the blood film. Equal volumes of the diluted hemoglobin sample and water are mixed together, and the absorbance of this read on a spectrophotometer. How should the hemoglobin result be determined from the standard calibrated graph?
A) Add the results from the turbid and second dilution together and divide by 2.
B) Multiply the result obtained from the graph on the diluted specimen by 2.
C) Divide the result obtained from the graph on the diluted specimen by 2.
D) There was no reason to perform this second dilution.
A) Add the results from the turbid and second dilution together and divide by 2.
B) Multiply the result obtained from the graph on the diluted specimen by 2.
C) Divide the result obtained from the graph on the diluted specimen by 2.
D) There was no reason to perform this second dilution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following red cell indices support microcytic hypochromic red cell morphology?
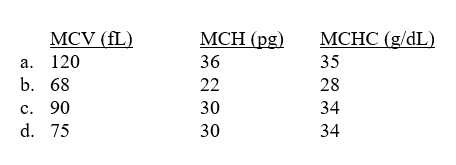


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A 1:20 dilution of blood is made for a white count, and the following number of cells counted in the four large corner mm2 of the hemocytometer: 12, 28, 18, and 15. What should be done next?
A) Report the white count as 3.7 *109/L.
B) Clean the hemocytometer and recharge with a well-mixed dilution.
C) Increase the number of mm2 counted.
D) Compare this cell count to the one on the other side.
A) Report the white count as 3.7 *109/L.
B) Clean the hemocytometer and recharge with a well-mixed dilution.
C) Increase the number of mm2 counted.
D) Compare this cell count to the one on the other side.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
On a standard reticulocyte preparation with new methylene blue, 100 cells are counted containing blue-stained granulofilamentous material. The red blood count is 3.22 * 1012/L, and the hematocrit is 30%. Calculate the reticulocyte production index (RPI).
A) 1.5
B) 2.7
C) 3.4
D) 13.4
A) 1.5
B) 2.7
C) 3.4
D) 13.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following red cell indices support macrocytic normochromic red cell morphology?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A manual WBC count is performed using a system that makes a 1:20 dilution of blood. When the cells in the four large corner mm2 of the hemocytometer are counted, the following numbers of cells are obtained: 8, 12, 9, and 11. What would be the next step?
A) Count the cells in all 9 mm2 of the hemocytometer.
B) Redo the dilution of blood using a new 1:20 dilution.
C) Redo the dilution of blood using a 1:100 dilution.
D) Calculate the count using the values from the 4 mm2 and report the result.
A) Count the cells in all 9 mm2 of the hemocytometer.
B) Redo the dilution of blood using a new 1:20 dilution.
C) Redo the dilution of blood using a 1:100 dilution.
D) Calculate the count using the values from the 4 mm2 and report the result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is a good use of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)?
A) Monitor patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
B) Diagnose acute appendicitis.
C) Diagnose multiple myeloma.
D) Monitor patients with osteoarthritis.
A) Monitor patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
B) Diagnose acute appendicitis.
C) Diagnose multiple myeloma.
D) Monitor patients with osteoarthritis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following red cell indices support normocytic normochromic red cell morphology?
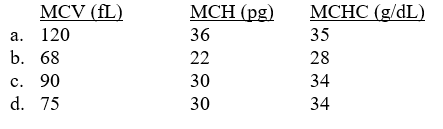


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
On a standard reticulocyte preparation with new methylene blue, 100 cells are counted containing blue-stained granulofilamentous material. The red blood count is 3.22 *1012/L, and the hematocrit is 30%. Calculate the corrected reticulocyte count.
A) 1.5%
B) 3.0%
C) 6.7%
D) 15.0%
A) 1.5%
B) 3.0%
C) 6.7%
D) 15.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
On a standard reticulocyte preparation with new methylene blue, 100 cells are counted containing blue-stained granulofilamentous material. The red blood count is 3.22 * 1012/L, and the hematocrit is 30%. Calculate the absolute reticulocyte count.
A) 0.32* 1012/L
B) 3.2 *1012/L
C) 32.2*1012/L
D) 0.99 * 1012/L
A) 0.32* 1012/L
B) 3.2 *1012/L
C) 32.2*1012/L
D) 0.99 * 1012/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
On a standard reticulocyte preparation with new methylene blue, 100 cells are counted containing blue-stained granulofilamentous material. The red blood count is 3.22 * 1012/L, and the hematocrit is 30%. Using information determined from Questions 23 through 27, what is the correct interpretation for this patient's condition?
A) Microcytic anemia with inadequate bone marrow response
B) Macrocytic anemia with adequate bone marrow response
C) Normocytic anemia with inadequate bone marrow response
D) Normocytic anemia with adequate bone marrow response
A) Microcytic anemia with inadequate bone marrow response
B) Macrocytic anemia with adequate bone marrow response
C) Normocytic anemia with inadequate bone marrow response
D) Normocytic anemia with adequate bone marrow response

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What make RBCs settle faster through the plasma when inflammation or infection exist?
A) Bacteria cause red cells to agglutinate and fall faster.
B) Increased number of neutrophils cause red cells to form rouleaux.
C) Inflammation makes the plasma less viscous.
D) Acute phase reactant proteins disrupt the electrical charge that normally separates cells.
A) Bacteria cause red cells to agglutinate and fall faster.
B) Increased number of neutrophils cause red cells to form rouleaux.
C) Inflammation makes the plasma less viscous.
D) Acute phase reactant proteins disrupt the electrical charge that normally separates cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following can cause a falsely increased ESR?
A) Concentration of anticoagulant increased
B) Tube not totally vertical
C) Tuberculosis
D) Increased plasma viscosity
A) Concentration of anticoagulant increased
B) Tube not totally vertical
C) Tuberculosis
D) Increased plasma viscosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
On a standard reticulocyte preparation with new methylene blue, 100 cells are counted containing blue-stained granulofilamentous material. The red blood count is 3.22 * 1012/L, and the hematocrit is 30%. Calculate the MCV.
A) 80 fL
B) 93 fL
C) 98 fL
D) 108 fL
A) 80 fL
B) 93 fL
C) 98 fL
D) 108 fL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The following RBC indices are obtained on a patient when calculated using results from manual methods:
MCV: 73 fL
MCH: 24 pg
MCHC: 33.4 g/dL
When the stained blood film is evaluated, the RBCs are normocytic normochromic. What conclusion can be made from this information?
A) The hematocrit is too low.
B) The hemoglobin is too low.
C) The red count is too high.
D) It is impossible to come to any conclusion.
MCV: 73 fL
MCH: 24 pg
MCHC: 33.4 g/dL
When the stained blood film is evaluated, the RBCs are normocytic normochromic. What conclusion can be made from this information?
A) The hematocrit is too low.
B) The hemoglobin is too low.
C) The red count is too high.
D) It is impossible to come to any conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How do sickle cells or spherocytes interfere with the ESR?
A) Prevent rouleaux formation, so falsely decrease
B) Encourage rouleaux formation, so falsely increase
C) Agglutinate and increase red cell mass, so falsely increase
D) Decrease plasma viscosity, so falsely decrease
A) Prevent rouleaux formation, so falsely decrease
B) Encourage rouleaux formation, so falsely increase
C) Agglutinate and increase red cell mass, so falsely increase
D) Decrease plasma viscosity, so falsely decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



