Deck 5: Quality Assurance in Hematology and Hemostasis Testing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Quality Assurance in Hematology and Hemostasis Testing
1
One of two controls that have been evaluated over the last 28 days gives a result on day 29 between 2 and 3 SDs of the mean; the other control is within 2 SDs of its mean. What is the correct procedure to follow?
A) Ignore the result unless it happens again the next day.
B) Rerun the control and if acceptable continue with patients.
C) Recalibrate the instrument.
D) Open new vials of controls and repeat both controls.
A) Ignore the result unless it happens again the next day.
B) Rerun the control and if acceptable continue with patients.
C) Recalibrate the instrument.
D) Open new vials of controls and repeat both controls.
Rerun the control and if acceptable continue with patients.
2
Which of the following groups of patients should not be included in establishing moving averages using red cell indices?
A) Chemotherapy patients
B) Female patients
C) Obstetric patients
D) Surgical patients
A) Chemotherapy patients
B) Female patients
C) Obstetric patients
D) Surgical patients
Female patients
3
A laboratory gets numerous complaints regarding the length of time it takes hematology results to get to the emergency department. What would be an appropriate response?
A) Make this a quality assurance project.
B) Ignore the complaints.
C) Explain why it takes so long.
D) Tell the employees to work faster.
A) Make this a quality assurance project.
B) Ignore the complaints.
C) Explain why it takes so long.
D) Tell the employees to work faster.
Make this a quality assurance project.
4
The following hemoglobin results, reported in g/dL, are obtained on a hospitalized patient on 3 consecutive days:
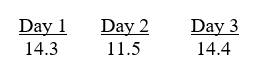
The SD for this hemoglobin method was calculated in Question 18. A delta check was obtained on day 2. Controls were run as appropriate each day and were all within limits for this procedure.
What is the most probable reason for the day 2 result when compared with those for days 1 and 3?
A) It is within the 95.5% confidence levels for this test.
B) It may represent an error in patient identification.
C) The patient had a major blood loss between days 1 and 2.
D) It is within the 99% confidence levels for this test.
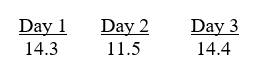
The SD for this hemoglobin method was calculated in Question 18. A delta check was obtained on day 2. Controls were run as appropriate each day and were all within limits for this procedure.
What is the most probable reason for the day 2 result when compared with those for days 1 and 3?
A) It is within the 95.5% confidence levels for this test.
B) It may represent an error in patient identification.
C) The patient had a major blood loss between days 1 and 2.
D) It is within the 99% confidence levels for this test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A patient's white blood cells (WBCs) are counted on an automated cell counter 10 times. The mean white count is 8000/mL, and the standard deviation (SD) is 300. What is the coefficient of variation (CV)?
A) 0.04%
B) 2.6%
C) 3.8%
D) 26%
A) 0.04%
B) 2.6%
C) 3.8%
D) 26%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The best way to prevent errors in the laboratory is to ensure:
A) Purchasing quality instruments from reputable vendors
B) Hiring only well-trained, conscientious workers
C) Having quality management
D) Performing external quality control procedures
A) Purchasing quality instruments from reputable vendors
B) Hiring only well-trained, conscientious workers
C) Having quality management
D) Performing external quality control procedures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is true regarding reference ranges?
A) Should be derived from reference books
B) Need to be determined only for adults
C) Can be established by running the test procedure on 10 healthy people
D) Are ranges of values for an analyte in normal healthy people
A) Should be derived from reference books
B) Need to be determined only for adults
C) Can be established by running the test procedure on 10 healthy people
D) Are ranges of values for an analyte in normal healthy people

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A patient specimen is analyzed on an instrument known to be in control from previous assays performed on a calibrated instrument and gives a hemoglobin result of 13.2 g/dL. Two hours later it is evaluated on another instrument that is being evaluated for purchase by the laboratory. The result is 11.8 g/dL. This result, when compared with the first, is:
A) Acceptable agreement
B) Reportable
C) Precise agreement
D) Inaccurate
A) Acceptable agreement
B) Reportable
C) Precise agreement
D) Inaccurate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What does the CV calculated in Question 2 describe about the white cell counts?
A) Accuracy
B) Reliability
C) Proper calibration
D) Precision
A) Accuracy
B) Reliability
C) Proper calibration
D) Precision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Proper specimen collection and patient satisfaction are components of:
A) Quality control
B) Quality assurance
C) Reliability
D) Precision
A) Quality control
B) Quality assurance
C) Reliability
D) Precision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The control values for both controls for the prothrombin test were ranging between the mean and 1 SD for the first 19 days of use. Starting on day 20, the values for both were consistently between +1 and +2 SDs. This is an example of a:
A) Shift
B) Trend
C) Random error
D) Predictable error
A) Shift
B) Trend
C) Random error
D) Predictable error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A purchased hemoglobin standard is used to adjust a hemoglobinometer. This standard is being used as a:
A) Control
B) Precision check
C) Delta check
D) Calibrator
A) Control
B) Precision check
C) Delta check
D) Calibrator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The antinuclear antibody (ANA) test is positive in almost all people who have systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). It is also positive in some patients who do not have SLE. The anti-deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) test is positive only in people with SLE but not in all who do. Which of the following is true?
A) The ANA test is a good screening test, and anti-DNA test is a good confirmatory test.
B) The anti-DNA test is a good screening test, and the ANA test is a good confirmatory test.
C) Both are good screening tests for SLE.
D) Neither of these tests is valid.
A) The ANA test is a good screening test, and anti-DNA test is a good confirmatory test.
B) The anti-DNA test is a good screening test, and the ANA test is a good confirmatory test.
C) Both are good screening tests for SLE.
D) Neither of these tests is valid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A test that is positive in all patients who have the disease but also in some who do not have the disease is:
A) Sensitive
B) Specific
C) Precise
D) Reliable
A) Sensitive
B) Specific
C) Precise
D) Reliable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The tubing that brings the lyse reagent to the hemoglobin cuvette on an automated cell counter is pinched and not delivering any reagent. All hemoglobin values are greater than 20 g/dL. This represents what type of error?
A) Random
B) Imprecision
C) Constant systematic
D) Proportional systematic
A) Random
B) Imprecision
C) Constant systematic
D) Proportional systematic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The precision limits of a method are defined by:
A) The mean
B) The SD
C) Sensitivity
D) Specificity
A) The mean
B) The SD
C) Sensitivity
D) Specificity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A laboratory comparing its results to those of other laboratories on the same specimen is an example of:
A) Precision monitoring
B) Internal quality control
C) External quality control
D) Delta checks
A) Precision monitoring
B) Internal quality control
C) External quality control
D) Delta checks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following would most likely be associated with the situation described in Question 11?
A) Operator error
B) Fading light source
C) Instrument miscalibrated
D) Starting a new lot number of thromboplastin reagent
A) Operator error
B) Fading light source
C) Instrument miscalibrated
D) Starting a new lot number of thromboplastin reagent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A clinical laboratory scientist performs 30 replicate hemoglobin determinations on a single blood sample. When statistics are used to determine the precision of the method, the mean is 13.8 g/dL and 1 SD is 0.1 g/dL. This means that 95.5% of the results on this specimen lie:
A) Between 13.4 and 14.2 g/dL
B) Between 13.6 and 14.0 g/dL
C) Between 13.5 and 14.1 g/dL
D) Between 13.7 and 13.9 g/dL
A) Between 13.4 and 14.2 g/dL
B) Between 13.6 and 14.0 g/dL
C) Between 13.5 and 14.1 g/dL
D) Between 13.7 and 13.9 g/dL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



