Deck 16: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/135
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Chemical Equilibrium
1
What equilibrium constant applies to an aqueous solution of a weak acid or a weak base?
A)general equilibrium constant,Keq
B)ionization equilibrium constant,Ki
C)ionization equilibrium constant,Kw
D)solubility product equilibrium constant,Ksp
E)none of the above
A)general equilibrium constant,Keq
B)ionization equilibrium constant,Ki
C)ionization equilibrium constant,Kw
D)solubility product equilibrium constant,Ksp
E)none of the above
ionization equilibrium constant,Ki
2
What is the term for a type of equilibrium in which F all of the participating species are in the same physical state?
A)concentration equilibrium
B)heterogeneous equilibrium
C)homogeneous equilibrium
D)physical equilibrium
E)none of the above
A)concentration equilibrium
B)heterogeneous equilibrium
C)homogeneous equilibrium
D)physical equilibrium
E)none of the above
homogeneous equilibrium
3
What is the term for the energy necessary for reactants to achieve the transition state and form products?
A)activation energy
B)collision energy
C)heat of reaction
D)energy barrier
E)rate barrier
A)activation energy
B)collision energy
C)heat of reaction
D)energy barrier
E)rate barrier
activation energy
4
What is the term for the change in concentration of reactants per unit time?
A)rate of change
B)rate of reaction
C)reactant profile
D)reaction profile
E)none of the above
A)rate of change
B)rate of reaction
C)reactant profile
D)reaction profile
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What law states that the following relationship for a reversible reaction at equilibrium is equal to a constant: [C]c [D]d / [A]a [B]b?
A)law of chemical equilibrium
B)law of heterogeneous equilibrium
C)law of homogeneous equilibrium
D)law of molecular equilibrium
E)none of the above
A)law of chemical equilibrium
B)law of heterogeneous equilibrium
C)law of homogeneous equilibrium
D)law of molecular equilibrium
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What equilibrium constant applies to an aqueous solution of a slightly dissociated ionic compound?
A)general equilibrium constant,Keq
B)ionization equilibrium constant,Ki
C)ionization equilibrium constant,Kw
D)solubility product equilibrium constant,Ksp
E)none of the above
A)general equilibrium constant,Keq
B)ionization equilibrium constant,Ki
C)ionization equilibrium constant,Kw
D)solubility product equilibrium constant,Ksp
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following influences the rate of a chemical reaction?
A)collision frequency
B)collision energy
C)collision orientation
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)collision frequency
B)collision energy
C)collision orientation
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the term for a substance that allows a reaction to proceed faster by lowering the energy of activation?
A)activation energy
B)collision energy
C)energy barrier
D)catalyst
E)rate barrier
A)activation energy
B)collision energy
C)energy barrier
D)catalyst
E)rate barrier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which principle states that a reversible reaction at equilibrium will shift to relieve the stress by a change in concentration,temperature,or pressure?
A)equilibrium principle
B)Le Chatelier's principle
C)Guldberg's principle
D)Waage's principle
E)none of the above
A)equilibrium principle
B)Le Chatelier's principle
C)Guldberg's principle
D)Waage's principle
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What equilibrium constant applies to a reversible reaction involving a gaseous mixture at equilibrium?
A)general equilibrium constant,Keq
B)ionization equilibrium constant,Ki
C)ionization equilibrium constant,Kw
D)solubility product equilibrium constant,Ksp
E)none of the above
A)general equilibrium constant,Keq
B)ionization equilibrium constant,Ki
C)ionization equilibrium constant,Kw
D)solubility product equilibrium constant,Ksp
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following increases the collision frequency of molecules?
A)increasing the concentration
B)decreasing the temperature
C)adding a catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)increasing the concentration
B)decreasing the temperature
C)adding a catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the term for a dynamic state of a reversible reaction in which the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal?
A)chemical equilibrium
B)concentration equilibrium
C)dynamic equilibrium
D)rate equilibrium
E)reversible equilibrium
A)chemical equilibrium
B)concentration equilibrium
C)dynamic equilibrium
D)rate equilibrium
E)reversible equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the term for a type of equilibrium in which F all of the participating species are not in the same physical state?
A)concentration equilibrium
B)heterogeneous equilibrium
C)homogeneous equilibrium
D)physical equilibrium
E)none of the above
A)concentration equilibrium
B)heterogeneous equilibrium
C)homogeneous equilibrium
D)physical equilibrium
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the term for a reaction that proceeds simultaneously in the forward direction toward products,as well as in the opposite direction toward reactants?
A)acid-base reaction
B)amphiprotic reaction
C)converse reaction
D)reversible reaction
E)none of the above
A)acid-base reaction
B)amphiprotic reaction
C)converse reaction
D)reversible reaction
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the term for a reaction that proceeds by releasing heat energy?
A)endothermic reaction
B)exothermic reaction
C)isothermal reaction
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)endothermic reaction
B)exothermic reaction
C)isothermal reaction
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the term for the highest point on the reaction profile at which reactants and products have the greatest energy?
A)equilibrium state
B)product state
C)reactant state
D)transition state
E)none of the above
A)equilibrium state
B)product state
C)reactant state
D)transition state
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the term for the graph of the energy of reactants and products as the reaction progresses?
A)endothermic profile
B)exothermic profile
C)reactant profile
D)reaction profile
E)none of the above
A)endothermic profile
B)exothermic profile
C)reactant profile
D)reaction profile
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the term for the difference in heat energy between the reactants and the products for a given chemical reaction?
A)activation energy
B)endothermic
C)exothermic
D)heat of reaction
E)none of the above
A)activation energy
B)endothermic
C)exothermic
D)heat of reaction
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the term for a reaction that proceeds by absorbing heat energy?
A)endothermic reaction
B)exothermic reaction
C)isothermal reaction
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)endothermic reaction
B)exothermic reaction
C)isothermal reaction
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the term for the principle that the rate of reaction is regulated by the frequency,energy,and orientation of molecules striking each other?
A)collision theory
B)energy theory
C)frequency theory
D)orientation theory
E)rate theory
A)collision theory
B)energy theory
C)frequency theory
D)orientation theory
E)rate theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Refer to the following graphs to answer the question(s)below. 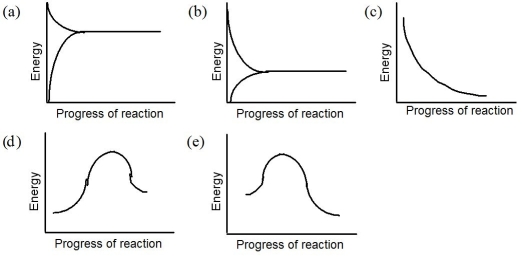
What is the reaction profile for: 3 O₂(g)+ heat 2 O₃(g)?
2 O₃(g)?
A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

What is the reaction profile for: 3 O₂(g)+ heat
 2 O₃(g)?
2 O₃(g)?A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following factors increases the rate of a chemical reaction?
A)decreasing the concentration
B)decreasing the temperature
C)adding a catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)decreasing the concentration
B)decreasing the temperature
C)adding a catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following increases the amount of product from a reaction?
A)adding a metal catalyst
B)adding an acid catalyst
C)using a UV light catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)adding a metal catalyst
B)adding an acid catalyst
C)using a UV light catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Refer to the following graphs to answer the question(s)below. 
What is the reaction profile for: N₂O₄(g)+ heat 2 NO₂(g)?
2 NO₂(g)?
A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

What is the reaction profile for: N₂O₄(g)+ heat
 2 NO₂(g)?
2 NO₂(g)?A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the temperature of a reaction increases,which of the following is true?
A)the amount of product decreases
B)the heat of reaction increases
C)the rate of reaction increases
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)the amount of product decreases
B)the heat of reaction increases
C)the rate of reaction increases
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the following graphs to answer the question(s)below. 
What is the reaction profile for the following exothermic chemical reaction: H₂(g)+ F2(g) 2 HF(g)?
2 HF(g)?
A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

What is the reaction profile for the following exothermic chemical reaction: H₂(g)+ F2(g)
 2 HF(g)?
2 HF(g)?A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the following graphs to answer the question(s)below. 
What is the reaction profile for: PCl3(g)+ Cl₂(g) PCl5(g)+ heat?
PCl5(g)+ heat?
A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

What is the reaction profile for: PCl3(g)+ Cl₂(g)
 PCl5(g)+ heat?
PCl5(g)+ heat?A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is true before a reaction reaches chemical equilibrium?
A)The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are increasing.
B)The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are decreasing.
C)The rate of the forward reaction is increasing,and the rate of the reverse reaction is decreasing.
D)The rate of the forward reaction is decreasing,and the rate of the reverse reaction is increasing.
E)none of the above
A)The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are increasing.
B)The rates of the forward and reverse reactions are decreasing.
C)The rate of the forward reaction is increasing,and the rate of the reverse reaction is decreasing.
D)The rate of the forward reaction is decreasing,and the rate of the reverse reaction is increasing.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following factors influences the rate of a chemical reaction?
A)concentration
B)temperature
C)catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)concentration
B)temperature
C)catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the temperature of a reaction decreases,which of the following is true?
A)the amount of product increases
B)the heat of reaction decreases
C)the rate of reaction decreases
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)the amount of product increases
B)the heat of reaction decreases
C)the rate of reaction decreases
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following increases the collision frequency of molecules?
A)decreasing the concentration
B)increasing the temperature
C)adding a catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)decreasing the concentration
B)increasing the temperature
C)adding a catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the heat of reaction is endothermic,which of the following is always true?
A)the reaction rate is fast
B)the reaction rate is slow
C)the energy of the reactants is greater than the products
D)the energy of the reactants is less than the products
E)none of the above
A)the reaction rate is fast
B)the reaction rate is slow
C)the energy of the reactants is greater than the products
D)the energy of the reactants is less than the products
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Refer to the following graphs to answer the question(s)below. 
What is the reaction profile for the following exothermic chemical reaction: 4 HCl(g)+ O₂(g) 2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)?
2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)?
A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

What is the reaction profile for the following exothermic chemical reaction: 4 HCl(g)+ O₂(g)
 2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)?
2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)?A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the heat of reaction is exothermic,which of the following is always true?
A)the reaction rate is fast
B)the reaction rate is slow
C)the energy of the reactants is greater than the products
D)the energy of the reactants is less than the products
E)none of the above
A)the reaction rate is fast
B)the reaction rate is slow
C)the energy of the reactants is greater than the products
D)the energy of the reactants is less than the products
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the following graphs to answer the question(s)below. 
What is the reaction profile for the following endothermic chemical reaction: H₂(g)+ I₂(g) 2 HI(g)?
2 HI(g)?
A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

What is the reaction profile for the following endothermic chemical reaction: H₂(g)+ I₂(g)
 2 HI(g)?
2 HI(g)?A)Graph (a)
B)Graph (b)
C)Graph (c)
D)Graph (d)
E)Graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the concentration of reactants decreases,which of the following is true?
A)the amount of product increases
B)the heat of reaction decreases
C)the rate of reaction decreases
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)the amount of product increases
B)the heat of reaction decreases
C)the rate of reaction decreases
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the Eact is lowered,which of the following is always true?
A)the reaction proceeds faster
B)the reaction proceeds slower
C)the reaction is exothermic
D)the reaction is endothermic
E)none of the above
A)the reaction proceeds faster
B)the reaction proceeds slower
C)the reaction is exothermic
D)the reaction is endothermic
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the concentration of reactants increases,which of the following is true?
A)the amount of product decreases
B)the heat of reaction increases
C)the rate of reaction increases
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)the amount of product decreases
B)the heat of reaction increases
C)the rate of reaction increases
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is true before a reaction reaches chemical equilibrium?
A)The amount of reactants is increasing.
B)The amount of products is increasing.
C)The amount of reactants and products are constant.
D)The amount of reactants and products are equal.
E)none of the above
A)The amount of reactants is increasing.
B)The amount of products is increasing.
C)The amount of reactants and products are constant.
D)The amount of reactants and products are equal.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following increases the collision energy of gaseous molecules?
A)increasing the concentration
B)increasing the temperature
C)adding a catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above
A)increasing the concentration
B)increasing the temperature
C)adding a catalyst
D)all of the above
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2 N₂O5(g) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2 N₂O5(g) 4 NO₂(g)+ O₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [N₂O5]2 / [NO₂]4 [O₂] B)Keq = [N₂O5]2 / [NO₂]4 [O₂]2 C)Keq = [NO₂]4 [O₂] / [N₂O5]2 D)Keq = [NO₂]4 [O₂]2 / [N₂O5]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_069f_896a_1913046653b8_TB3370_11.jpg) 4 NO₂(g)+ O₂(g)
4 NO₂(g)+ O₂(g)
A)Keq = [N₂O5]2 / [NO₂]4 [O₂]
B)Keq = [N₂O5]2 / [NO₂]4 [O₂]2
C)Keq = [NO₂]4 [O₂] / [N₂O5]2
D)Keq = [NO₂]4 [O₂]2 / [N₂O5]2
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2 N₂O5(g) 4 NO₂(g)+ O₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [N₂O5]2 / [NO₂]4 [O₂] B)Keq = [N₂O5]2 / [NO₂]4 [O₂]2 C)Keq = [NO₂]4 [O₂] / [N₂O5]2 D)Keq = [NO₂]4 [O₂]2 / [N₂O5]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_069f_896a_1913046653b8_TB3370_11.jpg) 4 NO₂(g)+ O₂(g)
4 NO₂(g)+ O₂(g)A)Keq = [N₂O5]2 / [NO₂]4 [O₂]
B)Keq = [N₂O5]2 / [NO₂]4 [O₂]2
C)Keq = [NO₂]4 [O₂] / [N₂O5]2
D)Keq = [NO₂]4 [O₂]2 / [N₂O5]2
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 4 HCl(g)+ O₂(g) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 4 HCl(g)+ O₂(g) 2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)</strong> A)Keq = [HCl] [O₂] / [Cl₂] [H₂O] B)Keq = [HCl]4 [O₂] / [Cl₂]2 [H₂O]2 C)Keq = [Cl₂] [H₂O] / [HCl] [O₂] D)Keq = [Cl₂]2 [H₂O]2 / [HCl]4 [O₂] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_2db2_896a_cf509cc88449_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)
2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)
A)Keq = [HCl] [O₂] / [Cl₂] [H₂O]
B)Keq = [HCl]4 [O₂] / [Cl₂]2 [H₂O]2
C)Keq = [Cl₂] [H₂O] / [HCl] [O₂]
D)Keq = [Cl₂]2 [H₂O]2 / [HCl]4 [O₂]
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 4 HCl(g)+ O₂(g) 2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)</strong> A)Keq = [HCl] [O₂] / [Cl₂] [H₂O] B)Keq = [HCl]4 [O₂] / [Cl₂]2 [H₂O]2 C)Keq = [Cl₂] [H₂O] / [HCl] [O₂] D)Keq = [Cl₂]2 [H₂O]2 / [HCl]4 [O₂] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_2db2_896a_cf509cc88449_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)
2 Cl₂(g)+ 2 H₂O(g)A)Keq = [HCl] [O₂] / [Cl₂] [H₂O]
B)Keq = [HCl]4 [O₂] / [Cl₂]2 [H₂O]2
C)Keq = [Cl₂] [H₂O] / [HCl] [O₂]
D)Keq = [Cl₂]2 [H₂O]2 / [HCl]4 [O₂]
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? CaCO₃(s) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? CaCO₃(s) CaO(s)+ CO₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [CaO] [CO₂] / [CaCO₃] B)Keq = [CaO] [CO₂] C)Keq = [CO₂] D)Keq = 1 / [CO₂] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_7bd5_896a_7f8a5880b5ec_TB3370_11.jpg) CaO(s)+ CO₂(g)
CaO(s)+ CO₂(g)
A)Keq = [CaO] [CO₂] / [CaCO₃]
B)Keq = [CaO] [CO₂]
C)Keq = [CO₂]
D)Keq = 1 / [CO₂]
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? CaCO₃(s) CaO(s)+ CO₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [CaO] [CO₂] / [CaCO₃] B)Keq = [CaO] [CO₂] C)Keq = [CO₂] D)Keq = 1 / [CO₂] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_7bd5_896a_7f8a5880b5ec_TB3370_11.jpg) CaO(s)+ CO₂(g)
CaO(s)+ CO₂(g)A)Keq = [CaO] [CO₂] / [CaCO₃]
B)Keq = [CaO] [CO₂]
C)Keq = [CO₂]
D)Keq = 1 / [CO₂]
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2 CH₄(g)+ O₂(g) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2 CH₄(g)+ O₂(g) 2 CO(g)+ 4 H₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [CH₄] [O₂] / [CO] [H₂] B)Keq = [CH₄]2 [O₂] / [CO]2 [H₂]4 C)Keq = [CO] [H₂] / [CH₄] [O₂] D)Keq = [CO]2 [H₂]4 / [CH₄]2 [O₂] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_2db1_896a_1d35f9eacfd4_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 CO(g)+ 4 H₂(g)
2 CO(g)+ 4 H₂(g)
A)Keq = [CH₄] [O₂] / [CO] [H₂]
B)Keq = [CH₄]2 [O₂] / [CO]2 [H₂]4
C)Keq = [CO] [H₂] / [CH₄] [O₂]
D)Keq = [CO]2 [H₂]4 / [CH₄]2 [O₂]
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2 CH₄(g)+ O₂(g) 2 CO(g)+ 4 H₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [CH₄] [O₂] / [CO] [H₂] B)Keq = [CH₄]2 [O₂] / [CO]2 [H₂]4 C)Keq = [CO] [H₂] / [CH₄] [O₂] D)Keq = [CO]2 [H₂]4 / [CH₄]2 [O₂] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_2db1_896a_1d35f9eacfd4_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 CO(g)+ 4 H₂(g)
2 CO(g)+ 4 H₂(g)A)Keq = [CH₄] [O₂] / [CO] [H₂]
B)Keq = [CH₄]2 [O₂] / [CO]2 [H₂]4
C)Keq = [CO] [H₂] / [CH₄] [O₂]
D)Keq = [CO]2 [H₂]4 / [CH₄]2 [O₂]
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: 2 A ![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: 2 A B + 3 C?</strong> A)Keq = [A] / [B] [C] B)Keq = [A]2 / [B] [C]3 C)Keq = [B] [C] / [A] D)Keq = [B] [C]3 / [A]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_b87a_896a_9d95fb932b63_TB3370_11.jpg) B + 3 C?
B + 3 C?
A)Keq = [A] / [B] [C]
B)Keq = [A]2 / [B] [C]3
C)Keq = [B] [C] / [A]
D)Keq = [B] [C]3 / [A]2
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: 2 A B + 3 C?</strong> A)Keq = [A] / [B] [C] B)Keq = [A]2 / [B] [C]3 C)Keq = [B] [C] / [A] D)Keq = [B] [C]3 / [A]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_b87a_896a_9d95fb932b63_TB3370_11.jpg) B + 3 C?
B + 3 C?A)Keq = [A] / [B] [C]
B)Keq = [A]2 / [B] [C]3
C)Keq = [B] [C] / [A]
D)Keq = [B] [C]3 / [A]2
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 4 NH₃(g)+ 5 O₂(g) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 4 NH₃(g)+ 5 O₂(g) 4 NO(g)+ 6 H₂O(g)</strong> A)Keq = [NO] [H₂O] / [NH₃] [O₂] B)Keq = [NO]4 [H₂O]6 / [NH₃]4 [O₂]5 C)Keq = [NH₃] [O₂] / [NO] [H₂O] D)Keq = [NH₃]4 [O₂]5 / [NO]4 [H₂O]6 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_54c3_896a_a5c4f06dc2fa_TB3370_11.jpg) 4 NO(g)+ 6 H₂O(g)
4 NO(g)+ 6 H₂O(g)
A)Keq = [NO] [H₂O] / [NH₃] [O₂]
B)Keq = [NO]4 [H₂O]6 / [NH₃]4 [O₂]5
C)Keq = [NH₃] [O₂] / [NO] [H₂O]
D)Keq = [NH₃]4 [O₂]5 / [NO]4 [H₂O]6
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 4 NH₃(g)+ 5 O₂(g) 4 NO(g)+ 6 H₂O(g)</strong> A)Keq = [NO] [H₂O] / [NH₃] [O₂] B)Keq = [NO]4 [H₂O]6 / [NH₃]4 [O₂]5 C)Keq = [NH₃] [O₂] / [NO] [H₂O] D)Keq = [NH₃]4 [O₂]5 / [NO]4 [H₂O]6 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_54c3_896a_a5c4f06dc2fa_TB3370_11.jpg) 4 NO(g)+ 6 H₂O(g)
4 NO(g)+ 6 H₂O(g)A)Keq = [NO] [H₂O] / [NH₃] [O₂]
B)Keq = [NO]4 [H₂O]6 / [NH₃]4 [O₂]5
C)Keq = [NH₃] [O₂] / [NO] [H₂O]
D)Keq = [NH₃]4 [O₂]5 / [NO]4 [H₂O]6
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Nitrogen dioxide is produced from the reaction of nitric oxide and oxygen gases.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction given the equilibrium concentrations at 25 °C: [NO] = 1.08 x 10-7,[O₂] = 0.500,and [NO₂] = 0.100. 2 NO(g)+ O₂(g) ![<strong>Nitrogen dioxide is produced from the reaction of nitric oxide and oxygen gases.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction given the equilibrium concentrations at 25 °C: [NO] = 1.08 x 10-7,[O₂] = 0.500,and [NO₂] = 0.100. 2 NO(g)+ O₂(g) 2 NO₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = 5.83 x 10-13 B)Keq = 1.85 x 1055 C)Keq = 1.85 x 106 D)Keq = 1.71 x 1012 E)Keq = 1.71 x 1013](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_a2e9_896a_517d0a2ed491_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 NO₂(g)
2 NO₂(g)
A)Keq = 5.83 x 10-13
B)Keq = 1.85 x 1055
C)Keq = 1.85 x 106
D)Keq = 1.71 x 1012
E)Keq = 1.71 x 1013
![<strong>Nitrogen dioxide is produced from the reaction of nitric oxide and oxygen gases.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction given the equilibrium concentrations at 25 °C: [NO] = 1.08 x 10-7,[O₂] = 0.500,and [NO₂] = 0.100. 2 NO(g)+ O₂(g) 2 NO₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = 5.83 x 10-13 B)Keq = 1.85 x 1055 C)Keq = 1.85 x 106 D)Keq = 1.71 x 1012 E)Keq = 1.71 x 1013](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_a2e9_896a_517d0a2ed491_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 NO₂(g)
2 NO₂(g)A)Keq = 5.83 x 10-13
B)Keq = 1.85 x 1055
C)Keq = 1.85 x 106
D)Keq = 1.71 x 1012
E)Keq = 1.71 x 1013

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: 2 A + 3 B ![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: 2 A + 3 B C?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] B)Keq = [A]2 [B]3 / [C] C)Keq = [C] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C] / [A]2 [B]3 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_b879_896a_47018cc61256_TB3370_11.jpg) C?
C?
A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C]
B)Keq = [A]2 [B]3 / [C]
C)Keq = [C] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C] / [A]2 [B]3
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: 2 A + 3 B C?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] B)Keq = [A]2 [B]3 / [C] C)Keq = [C] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C] / [A]2 [B]3 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_b879_896a_47018cc61256_TB3370_11.jpg) C?
C?A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C]
B)Keq = [A]2 [B]3 / [C]
C)Keq = [C] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C] / [A]2 [B]3
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: A + 3 B ![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: A + 3 B 2 C?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] B)Keq = [A] [B]3 / [C]2 C)Keq = [C] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C]2 / [A] [B]3 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_b878_896a_b5cb5937e4e6_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 C?
2 C?
A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C]
B)Keq = [A] [B]3 / [C]2
C)Keq = [C] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C]2 / [A] [B]3
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: A + 3 B 2 C?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] B)Keq = [A] [B]3 / [C]2 C)Keq = [C] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C]2 / [A] [B]3 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_b878_896a_b5cb5937e4e6_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 C?
2 C?A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C]
B)Keq = [A] [B]3 / [C]2
C)Keq = [C] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C]2 / [A] [B]3
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? CO(g)+ 2 H₂(g) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? CO(g)+ 2 H₂(g) CH₃OH(l)</strong> A)Keq = [CH₃OH] / [CO] [H₂] B)Keq = [CH₃OH] / [CO] [H₂]2 C)Keq = [CO] [H₂]2 D)Keq = 1 / [CO] [H₂]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_7bd6_896a_b3e0e9d00f3c_TB3370_11.jpg) CH₃OH(l)
CH₃OH(l)
A)Keq = [CH₃OH] / [CO] [H₂]
B)Keq = [CH₃OH] / [CO] [H₂]2
C)Keq = [CO] [H₂]2
D)Keq = 1 / [CO] [H₂]2
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? CO(g)+ 2 H₂(g) CH₃OH(l)</strong> A)Keq = [CH₃OH] / [CO] [H₂] B)Keq = [CH₃OH] / [CO] [H₂]2 C)Keq = [CO] [H₂]2 D)Keq = 1 / [CO] [H₂]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_7bd6_896a_b3e0e9d00f3c_TB3370_11.jpg) CH₃OH(l)
CH₃OH(l)A)Keq = [CH₃OH] / [CO] [H₂]
B)Keq = [CH₃OH] / [CO] [H₂]2
C)Keq = [CO] [H₂]2
D)Keq = 1 / [CO] [H₂]2
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: A + 3 B ![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: A + 3 B 2 C + D?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D] B)Keq = [A] [B]3 / [C]2 [D] C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C]2 [D] / [A] [B]3 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_df8c_896a_191966d784a3_TB3370_00.jpg) 2 C + D?
2 C + D?
A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D]
B)Keq = [A] [B]3 / [C]2 [D]
C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C]2 [D] / [A] [B]3
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: A + 3 B 2 C + D?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D] B)Keq = [A] [B]3 / [C]2 [D] C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C]2 [D] / [A] [B]3 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_df8c_896a_191966d784a3_TB3370_00.jpg) 2 C + D?
2 C + D?A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D]
B)Keq = [A] [B]3 / [C]2 [D]
C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C]2 [D] / [A] [B]3
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? SO₂(g)+ O₃(g) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? SO₂(g)+ O₃(g) SO₃(g)+ O₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [SO₃] [O₂] / [SO₂] [O₃] B)Keq = [SO₃]3 [O₂]2 / [SO₂]2 [O₃]3 C)Keq = [SO₂] [O₃] / [SO₃] [O₂] D)Keq = [SO₂]2 [O₃]3 / [SO₃]3 [O₂]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_2db0_896a_69ceeb98a6ed_TB3370_11.jpg) SO₃(g)+ O₂(g)
SO₃(g)+ O₂(g)
A)Keq = [SO₃] [O₂] / [SO₂] [O₃]
B)Keq = [SO₃]3 [O₂]2 / [SO₂]2 [O₃]3
C)Keq = [SO₂] [O₃] / [SO₃] [O₂]
D)Keq = [SO₂]2 [O₃]3 / [SO₃]3 [O₂]2
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? SO₂(g)+ O₃(g) SO₃(g)+ O₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [SO₃] [O₂] / [SO₂] [O₃] B)Keq = [SO₃]3 [O₂]2 / [SO₂]2 [O₃]3 C)Keq = [SO₂] [O₃] / [SO₃] [O₂] D)Keq = [SO₂]2 [O₃]3 / [SO₃]3 [O₂]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_2db0_896a_69ceeb98a6ed_TB3370_11.jpg) SO₃(g)+ O₂(g)
SO₃(g)+ O₂(g)A)Keq = [SO₃] [O₂] / [SO₂] [O₃]
B)Keq = [SO₃]3 [O₂]2 / [SO₂]2 [O₃]3
C)Keq = [SO₂] [O₃] / [SO₃] [O₂]
D)Keq = [SO₂]2 [O₃]3 / [SO₃]3 [O₂]2
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? C(s)+ CO₂(g) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? C(s)+ CO₂(g) 2 CO(g)</strong> A)Keq = [CO] / [CO₂] B)Keq = [CO] / [C] [CO₂] C)Keq = [CO]2 / [CO₂] D)Keq = [CO]2 / [C] [CO₂] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_54c4_896a_4df762d33bf8_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 CO(g)
2 CO(g)
A)Keq = [CO] / [CO₂]
B)Keq = [CO] / [C] [CO₂]
C)Keq = [CO]2 / [CO₂]
D)Keq = [CO]2 / [C] [CO₂]
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? C(s)+ CO₂(g) 2 CO(g)</strong> A)Keq = [CO] / [CO₂] B)Keq = [CO] / [C] [CO₂] C)Keq = [CO]2 / [CO₂] D)Keq = [CO]2 / [C] [CO₂] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_54c4_896a_4df762d33bf8_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 CO(g)
2 CO(g)A)Keq = [CO] / [CO₂]
B)Keq = [CO] / [C] [CO₂]
C)Keq = [CO]2 / [CO₂]
D)Keq = [CO]2 / [C] [CO₂]
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A 0.500 M sample of phosgene gas,COCl₂,decomposes to give carbon monoxide and chlorine gases.If the equilibrium concentration of Cl₂ is 0.045 M,what is the equilibrium constant for the reaction? COCl₂(g)  CO(g)+ Cl₂(g)
CO(g)+ Cl₂(g)
A)Keq = 0.0041
B)Keq = 0.0045
C)Keq = 0.099
D)Keq = 220
E)Keq = 250
 CO(g)+ Cl₂(g)
CO(g)+ Cl₂(g)A)Keq = 0.0041
B)Keq = 0.0045
C)Keq = 0.099
D)Keq = 220
E)Keq = 250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: A + 2 B ![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: A + 2 B C + D?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D] B)Keq = [A] [B]2 / [C] [D] C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_df8b_896a_d70aedac2bc2_TB3370_11.jpg) C + D?
C + D?
A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D]
B)Keq = [A] [B]2 / [C] [D]
C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]2
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: A + 2 B C + D?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D] B)Keq = [A] [B]2 / [C] [D] C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_df8b_896a_d70aedac2bc2_TB3370_11.jpg) C + D?
C + D?A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D]
B)Keq = [A] [B]2 / [C] [D]
C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]2
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is true after a reaction reaches chemical equilibrium?
A)The amount of reactants is increasing.
B)The amount of products is increasing.
C)The amount of reactants and products are constant.
D)The amount of reactants and products are equal.
E)none of the above
A)The amount of reactants is increasing.
B)The amount of products is increasing.
C)The amount of reactants and products are constant.
D)The amount of reactants and products are equal.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Ultraviolet light converts oxygen to ozone in the upper atmosphere.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction given the equilibrium concentrations at 20 °C: [O₂] = 9.38 x 10-3 and [O₃] = 3.40 x 10-15. 3 O₂(g) ![<strong>Ultraviolet light converts oxygen to ozone in the upper atmosphere.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction given the equilibrium concentrations at 20 °C: [O₂] = 9.38 x 10-3 and [O₃] = 3.40 x 10-15. 3 O₂(g) 2 O₃(g)</strong> A)Keq = 4.11 x 10-28 B)Keq = 1.40 x 10-23 C)Keq = 3.62 x 10-13 D)Keq = 2.43 x 108 E)Keq = 7.14 x 1022](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_a2e8_896a_8d9c506f30e9_TB3370_00.jpg) 2 O₃(g)
2 O₃(g)
A)Keq = 4.11 x 10-28
B)Keq = 1.40 x 10-23
C)Keq = 3.62 x 10-13
D)Keq = 2.43 x 108
E)Keq = 7.14 x 1022
![<strong>Ultraviolet light converts oxygen to ozone in the upper atmosphere.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction given the equilibrium concentrations at 20 °C: [O₂] = 9.38 x 10-3 and [O₃] = 3.40 x 10-15. 3 O₂(g) 2 O₃(g)</strong> A)Keq = 4.11 x 10-28 B)Keq = 1.40 x 10-23 C)Keq = 3.62 x 10-13 D)Keq = 2.43 x 108 E)Keq = 7.14 x 1022](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_a2e8_896a_8d9c506f30e9_TB3370_00.jpg) 2 O₃(g)
2 O₃(g)A)Keq = 4.11 x 10-28
B)Keq = 1.40 x 10-23
C)Keq = 3.62 x 10-13
D)Keq = 2.43 x 108
E)Keq = 7.14 x 1022

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Dinitrogen tetraoxide decomposes to produce nitrogen dioxide.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction given the equilibrium concentrations at 100 °C: [N₂O₄] = 0.800 and [NO₂] = 0.400. N₂O₄(g) ![<strong>Dinitrogen tetraoxide decomposes to produce nitrogen dioxide.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction given the equilibrium concentrations at 100 °C: [N₂O₄] = 0.800 and [NO₂] = 0.400. N₂O₄(g) 2 NO₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = 0.200 B)Keq = 0.500 C)Keq = 0.625 D)Keq = 2.00 E)Keq = 5.00](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_7bd7_896a_9318d46a3d7a_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 NO₂(g)
2 NO₂(g)
A)Keq = 0.200
B)Keq = 0.500
C)Keq = 0.625
D)Keq = 2.00
E)Keq = 5.00
![<strong>Dinitrogen tetraoxide decomposes to produce nitrogen dioxide.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction given the equilibrium concentrations at 100 °C: [N₂O₄] = 0.800 and [NO₂] = 0.400. N₂O₄(g) 2 NO₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = 0.200 B)Keq = 0.500 C)Keq = 0.625 D)Keq = 2.00 E)Keq = 5.00](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_7bd7_896a_9318d46a3d7a_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 NO₂(g)
2 NO₂(g)A)Keq = 0.200
B)Keq = 0.500
C)Keq = 0.625
D)Keq = 2.00
E)Keq = 5.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2 CO(g)+ O₂(g) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2 CO(g)+ O₂(g) 2 CO₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [CO₂]2 / [CO]2 [O₂] B)Keq = [CO₂]2 / [CO]2 [O₂]2 C)Keq = [CO]2 [O₂] / [CO₂]2 D)Keq = [CO]2 [O₂]2 / [CO₂]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_069e_896a_8f5ab2525a95_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 CO₂(g)
2 CO₂(g)
A)Keq = [CO₂]2 / [CO]2 [O₂]
B)Keq = [CO₂]2 / [CO]2 [O₂]2
C)Keq = [CO]2 [O₂] / [CO₂]2
D)Keq = [CO]2 [O₂]2 / [CO₂]2
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following reaction? 2 CO(g)+ O₂(g) 2 CO₂(g)</strong> A)Keq = [CO₂]2 / [CO]2 [O₂] B)Keq = [CO₂]2 / [CO]2 [O₂]2 C)Keq = [CO]2 [O₂] / [CO₂]2 D)Keq = [CO]2 [O₂]2 / [CO₂]2 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_069e_896a_8f5ab2525a95_TB3370_11.jpg) 2 CO₂(g)
2 CO₂(g)A)Keq = [CO₂]2 / [CO]2 [O₂]
B)Keq = [CO₂]2 / [CO]2 [O₂]2
C)Keq = [CO]2 [O₂] / [CO₂]2
D)Keq = [CO]2 [O₂]2 / [CO₂]2
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: 2 A + 3 B ![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: 2 A + 3 B 4 C + D?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D] B)Keq = [A]2 [B]3 / [C]4 [D] C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C]4 [D] / [A]2 [B]3 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_df8d_896a_83ac18d6aec4_TB3370_11.jpg) 4 C + D?
4 C + D?
A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D]
B)Keq = [A]2 [B]3 / [C]4 [D]
C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C]4 [D] / [A]2 [B]3
E)none of the above
![<strong>What is the general equilibrium constant expression,Keq,for the following reversible reaction: 2 A + 3 B 4 C + D?</strong> A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D] B)Keq = [A]2 [B]3 / [C]4 [D] C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B] D)Keq = [C]4 [D] / [A]2 [B]3 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bb_df8d_896a_83ac18d6aec4_TB3370_11.jpg) 4 C + D?
4 C + D?A)Keq = [A] [B] / [C] [D]
B)Keq = [A]2 [B]3 / [C]4 [D]
C)Keq = [C] [D] / [A] [B]
D)Keq = [C]4 [D] / [A]2 [B]3
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? 2 NO(g)+ 2 CO(g) ![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? 2 NO(g)+ 2 CO(g) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)increase [CO] B)decrease [CO₂] C)increase temperature D)decrease volume E)add krypton gas](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_6647_896a_abe45b0685fc_TB3370_11.jpg) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat
N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat
A)increase [CO]
B)decrease [CO₂]
C)increase temperature
D)decrease volume
E)add krypton gas
![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? 2 NO(g)+ 2 CO(g) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)increase [CO] B)decrease [CO₂] C)increase temperature D)decrease volume E)add krypton gas](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_6647_896a_abe45b0685fc_TB3370_11.jpg) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat
N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heatA)increase [CO]
B)decrease [CO₂]
C)increase temperature
D)decrease volume
E)add krypton gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? SO₃(g)+ NO(g)+ heat ![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? SO₃(g)+ NO(g)+ heat SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)</strong> A)increase [SO₃] B)increase [SO₂] C)decrease temperature D)increase volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_f10d_896a_a1fded8be6b0_TB3370_11.jpg) SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)
SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)
A)increase [SO₃]
B)increase [SO₂]
C)decrease temperature
D)increase volume
E)add a catalyst
![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? SO₃(g)+ NO(g)+ heat SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)</strong> A)increase [SO₃] B)increase [SO₂] C)decrease temperature D)increase volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_f10d_896a_a1fded8be6b0_TB3370_11.jpg) SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)
SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)A)increase [SO₃]
B)increase [SO₂]
C)decrease temperature
D)increase volume
E)add a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the changes listed has no effect on the equilibrium for the following reversible reaction? 2 NO(g)+ 2 CO(g) ![<strong>Which of the changes listed has no effect on the equilibrium for the following reversible reaction? 2 NO(g)+ 2 CO(g) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)increase [NO] B)increase [CO₂] C)increase temperature D)increase volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_6648_896a_935911883047_TB3370_11.jpg) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat
N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat
A)increase [NO]
B)increase [CO₂]
C)increase temperature
D)increase volume
E)add a catalyst
![<strong>Which of the changes listed has no effect on the equilibrium for the following reversible reaction? 2 NO(g)+ 2 CO(g) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)increase [NO] B)increase [CO₂] C)increase temperature D)increase volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_6648_896a_935911883047_TB3370_11.jpg) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat
N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heatA)increase [NO]
B)increase [CO₂]
C)increase temperature
D)increase volume
E)add a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? SO₃(g)+ NO(g)+ heat ![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? SO₃(g)+ NO(g)+ heat SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)</strong> A)increase [NO] B)decrease [SO₂] C)decrease temperature D)decrease volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_f10e_896a_1158d619393c_TB3370_11.jpg) SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)
SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)
A)increase [NO]
B)decrease [SO₂]
C)decrease temperature
D)decrease volume
E)add a catalyst
![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? SO₃(g)+ NO(g)+ heat SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)</strong> A)increase [NO] B)decrease [SO₂] C)decrease temperature D)decrease volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bc_f10e_896a_1158d619393c_TB3370_11.jpg) SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)
SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)A)increase [NO]
B)decrease [SO₂]
C)decrease temperature
D)decrease volume
E)add a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A 4.750 M sample of hydrogen iodide decomposes to give hydrogen and iodine gases.If the equilibrium concentration of H₂ is 0.500 M,what is the equilibrium constant for the reaction? 2 HI(g)  H₂(g)+ I₂(g)
H₂(g)+ I₂(g)
A)Keq = 0.0111
B)Keq = 0.0138
C)Keq = 0.0178
D)Keq = 0.0588
E)Keq = 0.0667
 H₂(g)+ I₂(g)
H₂(g)+ I₂(g)A)Keq = 0.0111
B)Keq = 0.0138
C)Keq = 0.0178
D)Keq = 0.0588
E)Keq = 0.0667

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? 2 NO(g)+ 2 CO(g) ![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? 2 NO(g)+ 2 CO(g) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)decrease [NO] B)increase [N₂] C)increase temperature D)decrease volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_6646_896a_39dfcd5c67e3_TB3370_11.jpg) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat
N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat
A)decrease [NO]
B)increase [N₂]
C)increase temperature
D)decrease volume
E)add a catalyst
![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? 2 NO(g)+ 2 CO(g) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)decrease [NO] B)increase [N₂] C)increase temperature D)decrease volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_6646_896a_39dfcd5c67e3_TB3370_11.jpg) N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heat
N₂(g)+ 2 CO₂(g)+ heatA)decrease [NO]
B)increase [N₂]
C)increase temperature
D)decrease volume
E)add a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the changes listed has no effect on the equilibrium for the following reversible reaction? CO(g)+ H₂O(g)  CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat
CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat
A)increase volume
B)decrease volume
C)add a catalyst
D)add neon gas
E)all of the above
 CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat
CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heatA)increase volume
B)decrease volume
C)add a catalyst
D)add neon gas
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₂CO₃(aq) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₂CO₃(aq) H+(aq)+ HCO₃-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [H+] [HCO₃-] / [H₂CO₃] B)Ki = [H+]2 [HCO₃-] / [H₂CO₃] C)Ki = [H+]2 [CO₃2-] / [H₂CO₃] D)Ki = [H₂CO₃] / [H+] [HCO₃-] E)Ki = [H₂CO₃] / [H+]2 [CO₃2-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_b46b_896a_730fcd13e20f_TB3370_11.jpg) H+(aq)+ HCO₃-(aq)
H+(aq)+ HCO₃-(aq)
A)Ki = [H+] [HCO₃-] / [H₂CO₃]
B)Ki = [H+]2 [HCO₃-] / [H₂CO₃]
C)Ki = [H+]2 [CO₃2-] / [H₂CO₃]
D)Ki = [H₂CO₃] / [H+] [HCO₃-]
E)Ki = [H₂CO₃] / [H+]2 [CO₃2-]
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₂CO₃(aq) H+(aq)+ HCO₃-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [H+] [HCO₃-] / [H₂CO₃] B)Ki = [H+]2 [HCO₃-] / [H₂CO₃] C)Ki = [H+]2 [CO₃2-] / [H₂CO₃] D)Ki = [H₂CO₃] / [H+] [HCO₃-] E)Ki = [H₂CO₃] / [H+]2 [CO₃2-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_b46b_896a_730fcd13e20f_TB3370_11.jpg) H+(aq)+ HCO₃-(aq)
H+(aq)+ HCO₃-(aq)A)Ki = [H+] [HCO₃-] / [H₂CO₃]
B)Ki = [H+]2 [HCO₃-] / [H₂CO₃]
C)Ki = [H+]2 [CO₃2-] / [H₂CO₃]
D)Ki = [H₂CO₃] / [H+] [HCO₃-]
E)Ki = [H₂CO₃] / [H+]2 [CO₃2-]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₃PO₄(aq) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₃PO₄(aq) H+(aq)+ H₂PO₄-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [H+] [H₂PO₄-] / [H₃PO₄] B)Ki = [H+]3 [H₂PO₄-] / [H₃PO₄] C)Ki = [H+]3 [PO₄3-] / [H₃PO₄] D)Ki = [H₃PO₄] / [H+] [H₂PO₄-] E)Ki = [H₃PO₄] / [H+]3 [PO₄3-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_b46c_896a_c91f308e2ced_TB3370_11.jpg) H+(aq)+ H₂PO₄-(aq)
H+(aq)+ H₂PO₄-(aq)
A)Ki = [H+] [H₂PO₄-] / [H₃PO₄]
B)Ki = [H+]3 [H₂PO₄-] / [H₃PO₄]
C)Ki = [H+]3 [PO₄3-] / [H₃PO₄]
D)Ki = [H₃PO₄] / [H+] [H₂PO₄-]
E)Ki = [H₃PO₄] / [H+]3 [PO₄3-]
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₃PO₄(aq) H+(aq)+ H₂PO₄-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [H+] [H₂PO₄-] / [H₃PO₄] B)Ki = [H+]3 [H₂PO₄-] / [H₃PO₄] C)Ki = [H+]3 [PO₄3-] / [H₃PO₄] D)Ki = [H₃PO₄] / [H+] [H₂PO₄-] E)Ki = [H₃PO₄] / [H+]3 [PO₄3-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_b46c_896a_c91f308e2ced_TB3370_11.jpg) H+(aq)+ H₂PO₄-(aq)
H+(aq)+ H₂PO₄-(aq)A)Ki = [H+] [H₂PO₄-] / [H₃PO₄]
B)Ki = [H+]3 [H₂PO₄-] / [H₃PO₄]
C)Ki = [H+]3 [PO₄3-] / [H₃PO₄]
D)Ki = [H₃PO₄] / [H+] [H₂PO₄-]
E)Ki = [H₃PO₄] / [H+]3 [PO₄3-]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak base? NH₂OH(aq)+ H₂O(l) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak base? NH₂OH(aq)+ H₂O(l) NH₃OH+(aq)+ OH-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] / [NH₂OH] B)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] / [NH₂OH] [H₂O] C)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] D)Ki = [NH₂OH] / [NH₃OH+] [OH-] E)Ki = [NH₂OH] [H₂O] / [NH₃OH+] [OH-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_db7e_896a_65833ce2f992_TB3370_11.jpg) NH₃OH+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
NH₃OH+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
A)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] / [NH₂OH]
B)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] / [NH₂OH] [H₂O]
C)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-]
D)Ki = [NH₂OH] / [NH₃OH+] [OH-]
E)Ki = [NH₂OH] [H₂O] / [NH₃OH+] [OH-]
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak base? NH₂OH(aq)+ H₂O(l) NH₃OH+(aq)+ OH-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] / [NH₂OH] B)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] / [NH₂OH] [H₂O] C)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] D)Ki = [NH₂OH] / [NH₃OH+] [OH-] E)Ki = [NH₂OH] [H₂O] / [NH₃OH+] [OH-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_db7e_896a_65833ce2f992_TB3370_11.jpg) NH₃OH+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
NH₃OH+(aq)+ OH-(aq)A)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] / [NH₂OH]
B)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-] / [NH₂OH] [H₂O]
C)Ki = [NH₃OH+] [OH-]
D)Ki = [NH₂OH] / [NH₃OH+] [OH-]
E)Ki = [NH₂OH] [H₂O] / [NH₃OH+] [OH-]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A 0.750 M sample of phosphorus pentachloride decomposes to give phosphorus trichloride and chlorine gases.If the equilibrium concentration of PCl5 is 0.650M,what is the equilibrium constant for the reaction? PCl5(g)  PCl3(g)+ Cl₂(g)
PCl3(g)+ Cl₂(g)
A)Keq = 0.0133
B)Keq = 0.0154
C)Keq = 0.133
D)Keq = 0.154
E)Keq = 65.0
 PCl3(g)+ Cl₂(g)
PCl3(g)+ Cl₂(g)A)Keq = 0.0133
B)Keq = 0.0154
C)Keq = 0.133
D)Keq = 0.154
E)Keq = 65.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? CO(g)+ H₂O(g) ![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? CO(g)+ H₂O(g) CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)increase [CO] B)increase [CO₂] C)increase temperature D)increase volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_1820_896a_73a4c9791174_TB3370_11.jpg) CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat
CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat
A)increase [CO]
B)increase [CO₂]
C)increase temperature
D)increase volume
E)add a catalyst
![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? CO(g)+ H₂O(g) CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)increase [CO] B)increase [CO₂] C)increase temperature D)increase volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_1820_896a_73a4c9791174_TB3370_11.jpg) CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat
CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heatA)increase [CO]
B)increase [CO₂]
C)increase temperature
D)increase volume
E)add a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? CH₄(g)+ H₂O(g)+ heat ![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? CH₄(g)+ H₂O(g)+ heat CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)</strong> A)increase [H₂O] B)decrease [H₂] C)decrease temperature D)increase volume E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_3f34_896a_0d9e10c3b4e3_TB3370_11.jpg) CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)
CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)
A)increase [H₂O]
B)decrease [H₂]
C)decrease temperature
D)increase volume
E)none of the above
![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? CH₄(g)+ H₂O(g)+ heat CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)</strong> A)increase [H₂O] B)decrease [H₂] C)decrease temperature D)increase volume E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_3f34_896a_0d9e10c3b4e3_TB3370_11.jpg) CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)
CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)A)increase [H₂O]
B)decrease [H₂]
C)decrease temperature
D)increase volume
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the changes listed has no effect on the equilibrium for the following reversible reaction? SO₃(g)+ NO(g)+ heat  SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)
SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)
A)increase volume
B)decrease volume
C)add a catalyst
D)add helium gas
E)all of the above
 SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)
SO₂(g)+ NO₂(g)A)increase volume
B)decrease volume
C)add a catalyst
D)add helium gas
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₂SO₃(aq) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₂SO₃(aq) H+(aq)+ HSO₃-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [H+] [HSO₃-] / [H₂SO₃] B)Ki = [H+]2 [HSO₃-] / [H₂SO₃] C)Ki = [H+]2 [SO₃2-] / [H₂SO₃] D)Ki = [H₂SO₃] / [H+] [HSO₃-] E)Ki = [H₂SO₃] / [H+]2 [SO₃2-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_8d5a_896a_eded4c8d3bd5_TB3370_11.jpg) H+(aq)+ HSO₃-(aq)
H+(aq)+ HSO₃-(aq)
A)Ki = [H+] [HSO₃-] / [H₂SO₃]
B)Ki = [H+]2 [HSO₃-] / [H₂SO₃]
C)Ki = [H+]2 [SO₃2-] / [H₂SO₃]
D)Ki = [H₂SO₃] / [H+] [HSO₃-]
E)Ki = [H₂SO₃] / [H+]2 [SO₃2-]
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₂SO₃(aq) H+(aq)+ HSO₃-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [H+] [HSO₃-] / [H₂SO₃] B)Ki = [H+]2 [HSO₃-] / [H₂SO₃] C)Ki = [H+]2 [SO₃2-] / [H₂SO₃] D)Ki = [H₂SO₃] / [H+] [HSO₃-] E)Ki = [H₂SO₃] / [H+]2 [SO₃2-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_8d5a_896a_eded4c8d3bd5_TB3370_11.jpg) H+(aq)+ HSO₃-(aq)
H+(aq)+ HSO₃-(aq)A)Ki = [H+] [HSO₃-] / [H₂SO₃]
B)Ki = [H+]2 [HSO₃-] / [H₂SO₃]
C)Ki = [H+]2 [SO₃2-] / [H₂SO₃]
D)Ki = [H₂SO₃] / [H+] [HSO₃-]
E)Ki = [H₂SO₃] / [H+]2 [SO₃2-]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? CH₄(g)+ H₂O(g)+ heat ![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? CH₄(g)+ H₂O(g)+ heat CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)</strong> A)increase [CH₄] B)decrease [CO] C)increase temperature D)increase volume E)all of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_3f33_896a_b39744b64346_TB3370_11.jpg) CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)
CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)
A)increase [CH₄]
B)decrease [CO]
C)increase temperature
D)increase volume
E)all of the above
![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the right for the following reversible reaction? CH₄(g)+ H₂O(g)+ heat CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)</strong> A)increase [CH₄] B)decrease [CO] C)increase temperature D)increase volume E)all of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_3f33_896a_b39744b64346_TB3370_11.jpg) CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)
CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)A)increase [CH₄]
B)decrease [CO]
C)increase temperature
D)increase volume
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? CO(g)+ H₂O(g) ![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? CO(g)+ H₂O(g) CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)increase [H₂O] B)decrease [CO₂] C)increase temperature D)decrease volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_1821_896a_6b75dc9023a8_TB3370_11.jpg) CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat
CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat
A)increase [H₂O]
B)decrease [CO₂]
C)increase temperature
D)decrease volume
E)add a catalyst
![<strong>Which of the changes listed will shift the equilibrium to the left for the following reversible reaction? CO(g)+ H₂O(g) CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat</strong> A)increase [H₂O] B)decrease [CO₂] C)increase temperature D)decrease volume E)add a catalyst](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_1821_896a_6b75dc9023a8_TB3370_11.jpg) CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heat
CO₂(g)+ H₂(g)+ heatA)increase [H₂O]
B)decrease [CO₂]
C)increase temperature
D)decrease volume
E)add a catalyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₂S(aq) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₂S(aq) H+(aq)+ HS-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [H+] [HS-] / [H₂S] B)Ki = [H+]2 [HS-] / [H₂S] C)Ki = [H+]2 [S₂-] / [H₂S] D)Ki = [H₂S] / [H+] [HS-] E)Ki = [H₂S] / [H+]2 [HS-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_8d59_896a_a5b82af8bd4a_TB3370_11.jpg) H+(aq)+ HS-(aq)
H+(aq)+ HS-(aq)
A)Ki = [H+] [HS-] / [H₂S]
B)Ki = [H+]2 [HS-] / [H₂S]
C)Ki = [H+]2 [S₂-] / [H₂S]
D)Ki = [H₂S] / [H+] [HS-]
E)Ki = [H₂S] / [H+]2 [HS-]
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak acid? H₂S(aq) H+(aq)+ HS-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [H+] [HS-] / [H₂S] B)Ki = [H+]2 [HS-] / [H₂S] C)Ki = [H+]2 [S₂-] / [H₂S] D)Ki = [H₂S] / [H+] [HS-] E)Ki = [H₂S] / [H+]2 [HS-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_8d59_896a_a5b82af8bd4a_TB3370_11.jpg) H+(aq)+ HS-(aq)
H+(aq)+ HS-(aq)A)Ki = [H+] [HS-] / [H₂S]
B)Ki = [H+]2 [HS-] / [H₂S]
C)Ki = [H+]2 [S₂-] / [H₂S]
D)Ki = [H₂S] / [H+] [HS-]
E)Ki = [H₂S] / [H+]2 [HS-]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak base? NH₄OH(aq) ![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak base? NH₄OH(aq) NH₄+(aq)+ OH-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [NH₄+] [OH-] / [NH₄OH] B)Ki = [NH₄+]4 [OH-] / [NH₄OH] C)Ki = [NH₄+]4 [OH-] D)Ki = [NH₄OH] / [NH₄+] [OH-] E)Ki = [NH₄OH] / [NH₄+]4 [OH-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_b46d_896a_157afb95cf09_TB3370_11.jpg) NH₄+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
NH₄+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
A)Ki = [NH₄+] [OH-] / [NH₄OH]
B)Ki = [NH₄+]4 [OH-] / [NH₄OH]
C)Ki = [NH₄+]4 [OH-]
D)Ki = [NH₄OH] / [NH₄+] [OH-]
E)Ki = [NH₄OH] / [NH₄+]4 [OH-]
![<strong>What is the equilibrium constant expression,Ki,for the following weak base? NH₄OH(aq) NH₄+(aq)+ OH-(aq)</strong> A)Ki = [NH₄+] [OH-] / [NH₄OH] B)Ki = [NH₄+]4 [OH-] / [NH₄OH] C)Ki = [NH₄+]4 [OH-] D)Ki = [NH₄OH] / [NH₄+] [OH-] E)Ki = [NH₄OH] / [NH₄+]4 [OH-]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_b46d_896a_157afb95cf09_TB3370_11.jpg) NH₄+(aq)+ OH-(aq)
NH₄+(aq)+ OH-(aq)A)Ki = [NH₄+] [OH-] / [NH₄OH]
B)Ki = [NH₄+]4 [OH-] / [NH₄OH]
C)Ki = [NH₄+]4 [OH-]
D)Ki = [NH₄OH] / [NH₄+] [OH-]
E)Ki = [NH₄OH] / [NH₄+]4 [OH-]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the changes listed has no effect on the equilibrium for the following reversible reaction? CH₄(g)+ H₂O(g)+ heat ![<strong>Which of the changes listed has no effect on the equilibrium for the following reversible reaction? CH₄(g)+ H₂O(g)+ heat CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)</strong> A)increase [H₂O] B)decrease [H₂] C)decrease temperature D)increase volume E)add argon gas](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_3f35_896a_03b3be3726a8_TB3370_11.jpg) CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)
CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)
A)increase [H₂O]
B)decrease [H₂]
C)decrease temperature
D)increase volume
E)add argon gas
![<strong>Which of the changes listed has no effect on the equilibrium for the following reversible reaction? CH₄(g)+ H₂O(g)+ heat CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)</strong> A)increase [H₂O] B)decrease [H₂] C)decrease temperature D)increase volume E)add argon gas](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3370/11eab151_65bd_3f35_896a_03b3be3726a8_TB3370_11.jpg) CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)
CO(g)+ 3 H₂(g)A)increase [H₂O]
B)decrease [H₂]
C)decrease temperature
D)increase volume
E)add argon gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



