Deck 18: The Government and the Macroeconomy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: The Government and the Macroeconomy
1
The federal government usually finances its budget deficit by:
A) raising taxes.
B) selling its real assets.
C) selling government bonds.
D) borrowing from commercial banks.
E) borrowing from foreign governments.
A) raising taxes.
B) selling its real assets.
C) selling government bonds.
D) borrowing from commercial banks.
E) borrowing from foreign governments.
selling government bonds.
2
The ratio of all levels of government spending to GDP in the United States is about ________ percent.
A) 10
B) 50
C) 20
D) 70
E) 40
A) 10
B) 50
C) 20
D) 70
E) 40
40
3
Refer to the following figure when answering the following questions.
Figure 18.2: Government Outlays and Receipts as a Percentage
of GDP, 1947-2012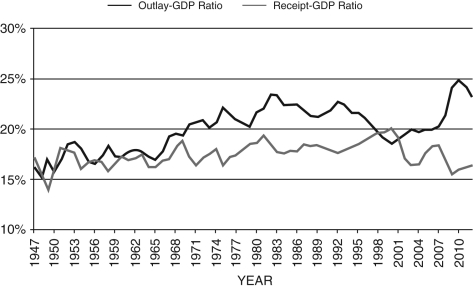
Consider Figure 18.2. The only period(s) in which the federal government ran a budget surplus since 1970 was/were:
A) 1998-2002
B) 1970
C) 1973-2001
D) None of these answers is correct.
E) All of these answers are correct.
Figure 18.2: Government Outlays and Receipts as a Percentage
of GDP, 1947-2012

Consider Figure 18.2. The only period(s) in which the federal government ran a budget surplus since 1970 was/were:
A) 1998-2002
B) 1970
C) 1973-2001
D) None of these answers is correct.
E) All of these answers are correct.
1998-2002
4
Refer to the following figure when answering the following questions.
Figure 18.2: Government Outlays and Receipts as a Percentage
of GDP, 1947-2012
Consider Figure 18.2. During which of the following periods did the federal government run a budget surplus?
A) 1947-1949
B) 1998-2002
C) 1955-1958
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.
Figure 18.2: Government Outlays and Receipts as a Percentage
of GDP, 1947-2012

Consider Figure 18.2. During which of the following periods did the federal government run a budget surplus?
A) 1947-1949
B) 1998-2002
C) 1955-1958
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Government expenditures include ________ government spending.
A) state
B) federal
C) local
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) state
B) federal
C) local
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The budget balance is the:
A) level of firm investment.
B) difference between exports and imports.
C) difference between household spending and income.
D) difference between tax revenue and government spending.
E) difference between movements of assets across countries.
A) level of firm investment.
B) difference between exports and imports.
C) difference between household spending and income.
D) difference between tax revenue and government spending.
E) difference between movements of assets across countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In 2012, the ratio of government spending to GDP in Denmark, France, and Sweden was ________ percent.
A) -40
B) over 50
C) 40
D) less than 10
E) over 100
A) -40
B) over 50
C) 40
D) less than 10
E) over 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In 2015, the largest single source of U.S. federal government revenue was:
A) individual income taxes.
B) health insurance (Medicare and Medicaid).
C) retirement (Social Security).
D) interest on assets.
E) corporate taxes.
A) individual income taxes.
B) health insurance (Medicare and Medicaid).
C) retirement (Social Security).
D) interest on assets.
E) corporate taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In 2014, the debt-to-GDP ratio in the United States was about ________ percent.
A) 24
B) 120
C) 75
D) 53
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) 24
B) 120
C) 75
D) 53
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In 2015, the U.S. federal government spent, on average, ________ per person.
A) $23,500
B) $4,250
C) $10,110
D) -$1,360
E) $11,470
A) $23,500
B) $4,250
C) $10,110
D) -$1,360
E) $11,470

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The federal government's largest expenditure in 2011 was:
A) net interest payments.
B) the environment.
C) Social Security.
D) defense.
E) health.
A) net interest payments.
B) the environment.
C) Social Security.
D) defense.
E) health.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The government debt is:
A) the total accumulation of deficits in the current period.
B) the outstanding stock of bonds that have been issued in the past.
C) the annual difference between government spending and tax revenues.
D) equal to total tax receipts.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) the total accumulation of deficits in the current period.
B) the outstanding stock of bonds that have been issued in the past.
C) the annual difference between government spending and tax revenues.
D) equal to total tax receipts.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In 2012, the ratio of all levels of government spending to GDP in the United States was about ________ percent.
A) 61
B) 43
C) 40
D) 10
E) 35
A) 61
B) 43
C) 40
D) 10
E) 35

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Refer to the following figure when answering the following questions.
Figure 18.2: Government Outlays and Receipts as a Percentage
of GDP, 1947-2012
Consider Figure 18.2. What was the cause of the huge budget deficit beginning in 1981?
A) the oil crisis
B) the Great Recession
C) President Reagan's defense expenditures and tax cuts
D) the first Gulf War
E) the Volcker recession
Figure 18.2: Government Outlays and Receipts as a Percentage
of GDP, 1947-2012

Consider Figure 18.2. What was the cause of the huge budget deficit beginning in 1981?
A) the oil crisis
B) the Great Recession
C) President Reagan's defense expenditures and tax cuts
D) the first Gulf War
E) the Volcker recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Refer to the following figure when answering the following questions.
Figure 18.1: Federal Government Receipts and Outlays, 1990-2012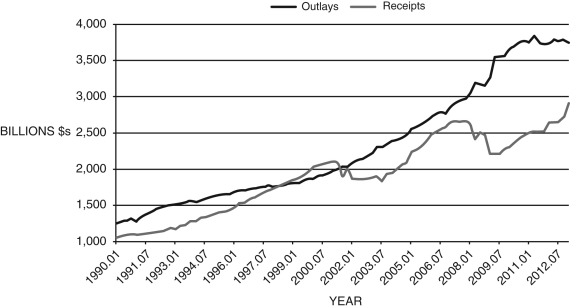 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
Consider Figure 18.1. The federal government ran a deficit at all points during the period:
A) 1990-1997.
B) 1990-1999.
C) 2000-2006.
D) 1998-2002.
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 18.1: Federal Government Receipts and Outlays, 1990-2012
 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)Consider Figure 18.1. The federal government ran a deficit at all points during the period:
A) 1990-1997.
B) 1990-1999.
C) 2000-2006.
D) 1998-2002.
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Refer to the following figure when answering the following questions.
Figure 18.1: Federal Government Receipts and Outlays, 1990-2012 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
Consider Figure 18.1. The federal government ran a surplus during the period:
A) 1990-1993.
B) 1993-1997.
C) 1998-2002.
D) 2002-2006.
E) Not enough information is given.
Figure 18.1: Federal Government Receipts and Outlays, 1990-2012
 (Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)
(Source: Federal Reserve Economic Data, St. Louis Federal Reserve)Consider Figure 18.1. The federal government ran a surplus during the period:
A) 1990-1993.
B) 1993-1997.
C) 1998-2002.
D) 2002-2006.
E) Not enough information is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In 2011, the federal government's budget deficit was about:
A) 8.6 percent of GDP.
B) 100 percent of GDP.
C) 21 percent of household consumption.
D) 150 percent of nonresidential private investment.
E) zero.
A) 8.6 percent of GDP.
B) 100 percent of GDP.
C) 21 percent of household consumption.
D) 150 percent of nonresidential private investment.
E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The federal government's largest source of revenue in 2011 was:
A) Medicare taxes.
B) Social Security taxes.
C) personal income taxes.
D) corporate income taxes.
E) natural resource extraction royalties.
A) Medicare taxes.
B) Social Security taxes.
C) personal income taxes.
D) corporate income taxes.
E) natural resource extraction royalties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In 2015, the largest single U.S. federal government expenditure was:
A) income security.
B) health.
C) national defense.
D) interest on existing debt.
E) education.
A) income security.
B) health.
C) national defense.
D) interest on existing debt.
E) education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Refer to the following figure when answering the following questions.
Figure 18.2: Government Outlays and Receipts as a Percentage
of GDP, 1947-2012
Consider Figure 18.2. What was the cause of the huge budget deficit beginning in 2007?
A) the oil crisis
B) the Great Recession
C) President Reagan's defense expenditures
D) the second Gulf War
E) the Volcker recession
Figure 18.2: Government Outlays and Receipts as a Percentage
of GDP, 1947-2012

Consider Figure 18.2. What was the cause of the huge budget deficit beginning in 2007?
A) the oil crisis
B) the Great Recession
C) President Reagan's defense expenditures
D) the second Gulf War
E) the Volcker recession

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In 2014, the ________ held about ________ of U.S. federal government debt.
A) Federal Reserve; $11 trillion
B) Peoples Bank of China; $3 trillion
C) Social Security trust fund; $2.7 trillion
D) largest investment banks; $100 billion
E) European Central Bank; $250 billion
A) Federal Reserve; $11 trillion
B) Peoples Bank of China; $3 trillion
C) Social Security trust fund; $2.7 trillion
D) largest investment banks; $100 billion
E) European Central Bank; $250 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following represents the government's budget constraint?
A)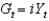
B)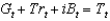
C)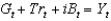
D)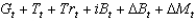
E)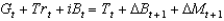
A)
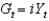
B)
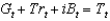
C)
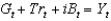
D)
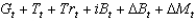
E)
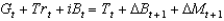

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following countries has the largest government spending-to-GDP ratio?
A) Austria
B) the United States
C) France
D) the United Kingdom
E) Germany
A) Austria
B) the United States
C) France
D) the United Kingdom
E) Germany

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Of the following countries, the one with the smallest annual government spending-to-GDP ratio in 2014 was:
A) France.
B) the United States.
C) the United Kingdom.
D) South Korea.
E) Japan.
A) France.
B) the United States.
C) the United Kingdom.
D) South Korea.
E) Japan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The difference between the gross federal debt and the debt by the public is debt held by:
A) other government entities.
B) the Social Security administration.
C) foreign central banks.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) other government entities.
B) the Social Security administration.
C) foreign central banks.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the post-World War II U.S. economy, the rapid expansion of federal government debt began during the:
A) oil embargo.
B) Kennedy administration.
C) Reagan administration.
D) collapse of the Bretton Woods system.
E) Clinton administration.
A) oil embargo.
B) Kennedy administration.
C) Reagan administration.
D) collapse of the Bretton Woods system.
E) Clinton administration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Since 1940, the largest gross federal debt-to-GDP ratio occurred during ________, when it reached about ________ percent.
A) 9/11; 90
B) the oil crisis; 110
C) the Volcker recession; 50
D) World War II; 108
E) the Vietnam War; 65
A) 9/11; 90
B) the oil crisis; 110
C) the Volcker recession; 50
D) World War II; 108
E) the Vietnam War; 65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Of the following countries, the one with the largest annual government spending-to-GDP ratio in 2014 was:
A) Japan.
B) South Korea.
C) the United States.
D) the United Kingdom.
E) France.
A) Japan.
B) South Korea.
C) the United States.
D) the United Kingdom.
E) France.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The source(s) of funds for the government is/are:
A) tax revenues.
B) new borrowing.
C) printing money.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) tax revenues.
B) new borrowing.
C) printing money.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The source(s) of funds for the government is/are:
A) sales of real assets.
B) loans from commercial banks.
C) gold.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) sales of real assets.
B) loans from commercial banks.
C) gold.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following countries has negative government debt?
A) Mexico
B) the United States
C) Norway
D) Russia
E) Germany
A) Mexico
B) the United States
C) Norway
D) Russia
E) Germany

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Since 1970, the federal government budget has been in surplus only during the:
A) oil embargo.
B) Kennedy administration.
C) Reagan administration.
D) collapse of the Bretton Woods system.
E) Clinton administration.
A) oil embargo.
B) Kennedy administration.
C) Reagan administration.
D) collapse of the Bretton Woods system.
E) Clinton administration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The difference between the primary and total deficits is that the primary deficit:
A) is always balanced.
B) includes spending on interest.
C) excludes spending on interest.
D) is never balanced.
E) equals zero.
A) is always balanced.
B) includes spending on interest.
C) excludes spending on interest.
D) is never balanced.
E) equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the United States, the average government spending-to-GDP ratio in 2014 was about ________ percent.
A) 65
B) 38
C) 42
D) 100
E) 57
A) 65
B) 38
C) 42
D) 100
E) 57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the euro area, the average government spending-to-GDP ratio in 2014 was about ________ percent.
A) 65
B) 5
C) 20
D) 100
E) 50
A) 65
B) 5
C) 20
D) 100
E) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If we assume that 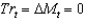 , which of the following represents the government's budget constraint?
, which of the following represents the government's budget constraint?
A)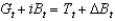
B)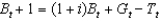
C)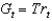
D)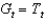
E)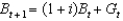
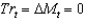 , which of the following represents the government's budget constraint?
, which of the following represents the government's budget constraint?A)
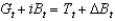
B)
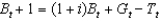
C)
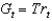
D)
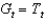
E)
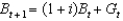

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The government uses funds to:
A) make transfer payments.
B) buy goods and services.
C) pay interest on outstanding debt.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) make transfer payments.
B) buy goods and services.
C) pay interest on outstanding debt.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
U.S. government debt that is not held by the public often is not counted in economic analyses because it is:
A) paid out to U.S. citizens.
B) debt to a very large institution.
C) an asset transfer from one branch of government to another.
D) part of the Social Security system.
E) rolled over into new debt.
A) paid out to U.S. citizens.
B) debt to a very large institution.
C) an asset transfer from one branch of government to another.
D) part of the Social Security system.
E) rolled over into new debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In 2005, the debt-to-GDP ratio in the United States was about ________ percent, but by 2014 it was about ________ percent.
A) 37; 75
B) 120; 67
C) 24; 53
D) 5; 43
E) 0; 12
A) 37; 75
B) 120; 67
C) 24; 53
D) 5; 43
E) 0; 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The amount of U.S. debt held by the public in 2015 was about:
A) $160 billion.
B) $13.2 trillion.
C) $18.3 trillion.
D) $41 trillion.
E) $0.
A) $160 billion.
B) $13.2 trillion.
C) $18.3 trillion.
D) $41 trillion.
E) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is an indicator of whether a country can borrow?
A) the size of the tax base
B) the size of the economy
C) the reputation of the head of government
D) the size of the military
E) All of these answers are correct.
A) the size of the tax base
B) the size of the economy
C) the reputation of the head of government
D) the size of the military
E) All of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is NOT an issue of large deficits and a large debt-to-GDP ratio for the economy?
A) intergenerational equity
B) the importance of economic growth
C) the possibility of high inflation or default
D) the impacts on the overall money supply
E) the extent to which deficits crowd out private investment
A) intergenerational equity
B) the importance of economic growth
C) the possibility of high inflation or default
D) the impacts on the overall money supply
E) the extent to which deficits crowd out private investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following might worry prospective lenders to a government?
A) high debt relative to income
B) a high debt-to-GDP ratio
C) a violent coup in the government
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) high debt relative to income
B) a high debt-to-GDP ratio
C) a violent coup in the government
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If investors begin to doubt the ability to finance spending with ________, markets will demand ________.
A) borrowing; more bonds
B) only taxes; higher interest rates
C) taxes and borrowing; higher interest rates
D) borrowing; less government spending
E) taxes and borrowing; lower interest rates
A) borrowing; more bonds
B) only taxes; higher interest rates
C) taxes and borrowing; higher interest rates
D) borrowing; less government spending
E) taxes and borrowing; lower interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following countries has defaulted on its debt?
A) France
B) Argentina
C) the United Kingdom
D) Belgium
E) China
A) France
B) Argentina
C) the United Kingdom
D) Belgium
E) China

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the past decade, which country has restructured its debt?
A) Greece
B) Brazil
C) the United Kingdom
D) Spain
E) India
A) Greece
B) Brazil
C) the United Kingdom
D) Spain
E) India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What was Japan's debt-to-GDP in 2015?
A) 76 percent
B) 65 percent
C) 100 percent
D) 35 percent
E) 120 percent
A) 76 percent
B) 65 percent
C) 100 percent
D) 35 percent
E) 120 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Under which condition can the government continue to accumulate debt?
A) if it issues more bonds
B) if it promises to pay the debt back
C) if the economy grows faster than the debt
D) if it appropriates funds from another economy
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) if it issues more bonds
B) if it promises to pay the debt back
C) if the economy grows faster than the debt
D) if it appropriates funds from another economy
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the intertemporal budget constraint, the term 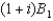 is called the:
is called the:
A) total debt.
B) initial debt.
C) government deficit.
D) government surplus.
E) None of these answers is correct.
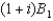 is called the:
is called the:A) total debt.
B) initial debt.
C) government deficit.
D) government surplus.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the government's intertemporal budget constraint: 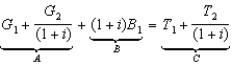 .
.
Term A is the ________, and term B is the ________.
A) present discounted value of government spending; initial debt
B) total annual spending; deficit
C) initial period's spending; initial debt
D) present value of government spending and taxes; present value of government spending
E) None of these answers is correct.
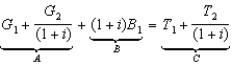 .
.Term A is the ________, and term B is the ________.
A) present discounted value of government spending; initial debt
B) total annual spending; deficit
C) initial period's spending; initial debt
D) present value of government spending and taxes; present value of government spending
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If a government has a difficult time raising funds by borrowing, it ________, which generates ________.
A) must print money; inflation
B) must print money; high real interest rates
C) raises taxes; inflation
D) raises taxes; unemployment
E) All of these answers are correct.
A) must print money; inflation
B) must print money; high real interest rates
C) raises taxes; inflation
D) raises taxes; unemployment
E) All of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The basic point of generational accounting is that high and rising debt-GDP ratios imply:
A) higher interest rates in the future.
B) lower tax rates on future generations.
C) higher tax rates on future generations.
D) reduced government expenditures in the future.
E) rising government expenditures in the future.
A) higher interest rates in the future.
B) lower tax rates on future generations.
C) higher tax rates on future generations.
D) reduced government expenditures in the future.
E) rising government expenditures in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The economic meaning of the intertemporal budget constraint is that:
A) the government's budget never has to balance.
B) the government's budget must balance period by period.
C) the present discounted value of the government's budget must balance.
D) the government can always push its debt on future generations.
E) every generation faces the same tax schedule.
A) the government's budget never has to balance.
B) the government's budget must balance period by period.
C) the present discounted value of the government's budget must balance.
D) the government can always push its debt on future generations.
E) every generation faces the same tax schedule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Given what you know about the sizes of economies, which of the following countries probably would find it impossible to borrow more than $1 trillion?
A) Egypt
B) Vietnam
C) Russia
D) Croatia
E) All of these answers are correct.
A) Egypt
B) Vietnam
C) Russia
D) Croatia
E) All of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The government's intertemporal budget constraint assumes that the budget is:
A) never balanced.
B) balanced in the first period.
C) balanced in the last period.
D) always balanced.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) never balanced.
B) balanced in the first period.
C) balanced in the last period.
D) always balanced.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The government's intertemporal budget constraint in the simple two-period case is:
A)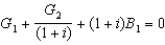 .
.
B)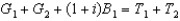
C)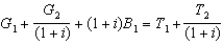 .
.
D)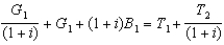 .
.
E)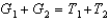 .
.
A)
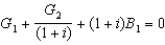 .
.B)
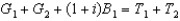
C)
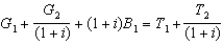 .
.D)
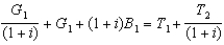 .
.E)
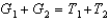 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The idea that present generations benefit from borrowing what future generations must pay is called:
A) the budget deficit.
B) intertemporal substitution.
C) the intertemporal budget constraint.
D) generational accounting.
E) discretionary spending.
A) the budget deficit.
B) intertemporal substitution.
C) the intertemporal budget constraint.
D) generational accounting.
E) discretionary spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following should economic policymakers consider to be associated with large deficits and a large debt-to-GDP ratio?
A) the importance of economic growth
B) the possibility of high inflation or default
C) intergenerational equity
D) the extent to which deficits crowd out private investment
E) All of these answers are correct.
A) the importance of economic growth
B) the possibility of high inflation or default
C) intergenerational equity
D) the extent to which deficits crowd out private investment
E) All of these answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An implication of the intertemporal budget constraint is that:
A) the government can borrow only as much as it can credibly pay back.
B) the government can borrow as much as it wants.
C) the government must always have a balanced budget.
D) the government must balance its budget over the business cycle.
E) all generations pay the same amount of taxes.
A) the government can borrow only as much as it can credibly pay back.
B) the government can borrow as much as it wants.
C) the government must always have a balanced budget.
D) the government must balance its budget over the business cycle.
E) all generations pay the same amount of taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Given what you know about the sizes of economies, which of the following countries probably would find it impossible to borrow more than $500 billion?
A) France
B) Mongolia
C) Germany
D) the United States
E) Japan
A) France
B) Mongolia
C) Germany
D) the United States
E) Japan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If domestic saving is less than domestic investment, then investment can be financed by:
A) the budget deficit.
B) foreign saving.
C) higher interest rates.
D) new savings instruments.
E) higher rates of inflation.
A) the budget deficit.
B) foreign saving.
C) higher interest rates.
D) new savings instruments.
E) higher rates of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
________ imply/implies that, holding the present value of government spending constant, budget deficits will not crowd out investment.
A) Crowding in
B) Generational accounting
C) Ricardian equivalence
D) Lower interest rates
E) Lower taxes
A) Crowding in
B) Generational accounting
C) Ricardian equivalence
D) Lower interest rates
E) Lower taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the language of generational accounting, by issuing bonds to finance a war in the present:
A) pay no burden to enjoy peace.
B) future generations are paying for the peace they enjoy.
C) past and present generations pay for the peace.
D) only past generations pay for peace.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) pay no burden to enjoy peace.
B) future generations are paying for the peace they enjoy.
C) past and present generations pay for the peace.
D) only past generations pay for peace.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the Congressional Budget Office report "A 125-Year Picture of the Federal Government's Share of the Economy, 1950 to 2075," Medicare, Medicaid, and Social Security will be about ________ percent of GDP in 2030.
A) 8
B) 15
C) 6
D) 0
E) 100
A) 8
B) 15
C) 6
D) 0
E) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
According to the Congressional Budget Office report "A 125-Year Picture of the Federal Government's Share of the Economy, 1950 to 2075," the main culprit(s) for the increase in federal government spending to about 40 percent of GDP in 2075 is/are:
A) Medicare
B) Medicaid
C) Social Security
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) Medicare
B) Medicaid
C) Social Security
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The difference between imports and exports is:
A) domestic saving.
B) the trade balance.
C) foreign saving.
D) the budget deficit.
E) the real interest rate.
A) domestic saving.
B) the trade balance.
C) foreign saving.
D) the budget deficit.
E) the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Income minus taxes is often called:
A) investment.
B) consumption.
C) disposable income.
D) gross income.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) investment.
B) consumption.
C) disposable income.
D) gross income.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If current generations are depleting nonrenewable resources, they must compensate future generations by investing in:
A) capital.
B) education.
C) research.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) capital.
B) education.
C) research.
D) All of these answers are correct.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If domestic saving is less than domestic investment, then investment is financed by:
A) an inflation tax.
B) nothing-it cannot be done.
C) higher interest rates.
D) foreign saving.
E) printing more money.
A) an inflation tax.
B) nothing-it cannot be done.
C) higher interest rates.
D) foreign saving.
E) printing more money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An explanation of why governments are willing to burden future generations with debt to finance a war today is that:
A) only present generations enjoy peace.
B) future generations will enjoy peace and must pay nothing.
C) future generations will enjoy peace and must pay something.
D) future generations will never enjoy peace but must pay for current generations to enjoy it.
E) current generations are more important to the government than future generations.
A) only present generations enjoy peace.
B) future generations will enjoy peace and must pay nothing.
C) future generations will enjoy peace and must pay something.
D) future generations will never enjoy peace but must pay for current generations to enjoy it.
E) current generations are more important to the government than future generations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If current generations are depleting nonrenewable resources, they must compensate future generations by:
A) saving gold.
B) printing more money.
C) investing in capital.
D) buying more military equipment.
E) increasing the stock of renewable resources.
A) saving gold.
B) printing more money.
C) investing in capital.
D) buying more military equipment.
E) increasing the stock of renewable resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When ________ hold(s), if the present value of government is held constant, budget deficits will not crowd out investment.
A) adaptive expectations
B) generational accounting
C) crowding in
D) lower interest rates
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) adaptive expectations
B) generational accounting
C) crowding in
D) lower interest rates
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Income minus taxes is often called:
A) government expenditures.
B) consumption.
C) investment.
D) gross income.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) government expenditures.
B) consumption.
C) investment.
D) gross income.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
According to the Congressional Budget Office report "A 125-Year Picture of the Federal Government's Share of the Economy, 1950 to 2075," the share of federal government spending in GDP will climb to 40 percent by 2075, assuming:
A) household consumption falls.
B) government spending rises sharply.
C) government spending falls slightly.
D) current policies stay in place.
E) the entire "baby boomer" generation retires in the same year.
A) household consumption falls.
B) government spending rises sharply.
C) government spending falls slightly.
D) current policies stay in place.
E) the entire "baby boomer" generation retires in the same year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
According to the Congressional Budget Office report "A 125-Year Picture of the Federal Government's Share of the Economy, 1950 to 2075," the share of government spending in GDP will ________, assuming current federal government spending patterns.
A) climb to 40 percent by 2075
B) climb to 40 percent by 2015
C) climb to 100 percent in 2075
D) fall to 0 percent in 2075
E) not change between now and 2075
A) climb to 40 percent by 2075
B) climb to 40 percent by 2015
C) climb to 100 percent in 2075
D) fall to 0 percent in 2075
E) not change between now and 2075

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The national income identity can be rearranged to show that ________ equals ________.
A) Private saving + Government saving +Foreign saving; Investment
B) Private saving - Government saving +Investment; the budget deficit
C) Private saving - Government saving -Foreign saving; Investment
D) private saving; investment
E) Private saving +Government saving +Foreign saving; tax revenues
A) Private saving + Government saving +Foreign saving; Investment
B) Private saving - Government saving +Investment; the budget deficit
C) Private saving - Government saving -Foreign saving; Investment
D) private saving; investment
E) Private saving +Government saving +Foreign saving; tax revenues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
________ is/are what may happen when the central government needs to borrow to finance its deficit to the detriment of private firms.
A) Lower interest rates
B) Crowding out
C) Higher rates of inflation
D) A lower marginal product of capital
E) More unemployment
A) Lower interest rates
B) Crowding out
C) Higher rates of inflation
D) A lower marginal product of capital
E) More unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
According to the Congressional Budget Office report "A 125-Year Picture of the Federal Government's Share of the Economy, 1950 to 2075," by the year 2075, spending on entitlement programs will be about:
A) 19 percent of GDP.
B) 21 percent of household expenditures.
C) 100 percent of tax revenues.
D) 21 percent of GDP.
E) zero.
A) 19 percent of GDP.
B) 21 percent of household expenditures.
C) 100 percent of tax revenues.
D) 21 percent of GDP.
E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If the government increases its budget deficit, ________ is/are ameliorated if the economy has access to ________.
A) crowding out; foreign savings
B) crowding out; a money printing press
C) inflation; household savings
D) unemployment; the tax structure
E) lower interest rates; foreign savings
A) crowding out; foreign savings
B) crowding out; a money printing press
C) inflation; household savings
D) unemployment; the tax structure
E) lower interest rates; foreign savings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
According to the Congressional Budget Office report "A 125-Year Picture of the Federal Government's Share of the Economy, 1950 to 2075," government revenues are projected to ________ by the year ________, assuming current federal government spending patterns.
A) stabilize; 2075
B) stabilize; 2020
C) begin growing faster; 2020
D) begin growing slower; 2010
E) be zero; 2075
A) stabilize; 2075
B) stabilize; 2020
C) begin growing faster; 2020
D) begin growing slower; 2010
E) be zero; 2075

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 122 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



