Deck 7: Offshoring of Goods and Services
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Offshoring of Goods and Services
1
The most important reason why firms consider offshoring is to decrease their:
A) labor costs.
B) transportation costs.
C) construction costs.
D) "trade costs."
A) labor costs.
B) transportation costs.
C) construction costs.
D) "trade costs."
A
2
Which of the following is an example of offshoring?
A) Intel undertakes direct foreign investment in China to produce computer chips for the Chinese market.
B) Ford establishes a factory in Germany to produce automobiles for the European market.
C) General Motors moves assembly operations for Chevrolets from Detroit to its plant in Mexico.
D) Nike closes its Indonesian factory and moves production to the United States to produce tennis shoes for the U.S. market.
A) Intel undertakes direct foreign investment in China to produce computer chips for the Chinese market.
B) Ford establishes a factory in Germany to produce automobiles for the European market.
C) General Motors moves assembly operations for Chevrolets from Detroit to its plant in Mexico.
D) Nike closes its Indonesian factory and moves production to the United States to produce tennis shoes for the U.S. market.
C
3
Intel produces microchips in China and Costa Rica using subsidiaries that it owns. Mattel, in contrast, contracts with firms in several different countries to produce the Barbie doll, which it then imports to the United States. Which of the following statements about the two companies is correct?
A) Intel is involved in foreign offshoring and Mattel is involved in foreign outsourcing.
B) Intel and Mattel are both involved in foreign outsourcing.
C) Intel and Mattel are both involved in foreign offshoring.
D) Intel is involved in foreign outsourcing, and Mattel is involved in foreign offshoring.
A) Intel is involved in foreign offshoring and Mattel is involved in foreign outsourcing.
B) Intel and Mattel are both involved in foreign outsourcing.
C) Intel and Mattel are both involved in foreign offshoring.
D) Intel is involved in foreign outsourcing, and Mattel is involved in foreign offshoring.
A
4
To analyze offshoring by firms, economists line up activities that a firm must undertake to produce a product in the order of the ratio of:
A) low-cost to high-cost activities.
B) high-skilled labor to low-skilled labor required for the activity.
C) variable cost to fixed cost.
D) manufacturing versus service activities.
A) low-cost to high-cost activities.
B) high-skilled labor to low-skilled labor required for the activity.
C) variable cost to fixed cost.
D) manufacturing versus service activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is the correct ranking (first to last) of the value chain by order of production?
A) component production, assembly, marketing and sales, R&D
B) component production, marketing and sales, assembly, R&D
C) R&D, component production, assembly, marketing and sales
D) R&D, marketing and sales, component production, assembly
A) component production, assembly, marketing and sales, R&D
B) component production, marketing and sales, assembly, R&D
C) R&D, component production, assembly, marketing and sales
D) R&D, marketing and sales, component production, assembly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An example of offshoring is when:
A) Boeing contracts with companies across the world to manufacture components for its 787 Dreamliner aircraft.
B) Boeing assembles its 787 Dreamliner in Everett, Washington.
C) Boeing contracts with another American company to construct sections of the 787 Dreamliner's fuselage in Charleston, South Carolina.
D) Boeing sends workers to Japan to learn the technology to assemble its 787 Dreamliner.
A) Boeing contracts with companies across the world to manufacture components for its 787 Dreamliner aircraft.
B) Boeing assembles its 787 Dreamliner in Everett, Washington.
C) Boeing contracts with another American company to construct sections of the 787 Dreamliner's fuselage in Charleston, South Carolina.
D) Boeing sends workers to Japan to learn the technology to assemble its 787 Dreamliner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
To predict which activities a U.S. firm will find profitable to offshore, we must assume that it can use relatively lower-cost labor in a foreign nation. This is usually _____ labor.
A) skilled
B) unskilled
C) economical
D) unnecessary
A) skilled
B) unskilled
C) economical
D) unnecessary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The term offshoring means:
A) purchasing component parts or services from domestic suppliers.
B) operating offshore oil rigs that are in international waters.
C) banking activities in money laundering countries.
D) operating a facility in another nation that produces component parts or services.
A) purchasing component parts or services from domestic suppliers.
B) operating offshore oil rigs that are in international waters.
C) banking activities in money laundering countries.
D) operating a facility in another nation that produces component parts or services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is the correct ranking of the value chain by level of skill of the labor force (from lowest to highest skill levels)?
A) component production, assembly, marketing and sales, R&D
B) assembly, component production, marketing and sales, R&D
C) assembly, marketing and sales, component production, R&D
D) component production, marketing and sales, assembly, R&D
A) component production, assembly, marketing and sales, R&D
B) assembly, component production, marketing and sales, R&D
C) assembly, marketing and sales, component production, R&D
D) component production, marketing and sales, assembly, R&D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How does the offshoring model differ from the type of trade analyzed with the Ricardian and Heckscher-Ohlin trade models?
A) There is no difference since the offshoring, Ricardian, and Heckscher-Ohlin trade models can be used to analyze offshoring.
B) The Ricardian and Heckscher-Ohlin trade models can only analyze trade in finished products.
C) The Ricardian model can be used to analyze offshoring while the Heckscher-Ohlin model only analyzes trade in finished products.
D) The Heckscher-Ohlin model can be used to analyze offshoring while the Ricardian model only analyzes trade in finished products
A) There is no difference since the offshoring, Ricardian, and Heckscher-Ohlin trade models can be used to analyze offshoring.
B) The Ricardian and Heckscher-Ohlin trade models can only analyze trade in finished products.
C) The Ricardian model can be used to analyze offshoring while the Heckscher-Ohlin model only analyzes trade in finished products.
D) The Heckscher-Ohlin model can be used to analyze offshoring while the Ricardian model only analyzes trade in finished products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The lineup of value-added activities from lowest to highest for a firm is often called:
A) the value-added formula.
B) the effective operational accounting equation.
C) the value-added tax.
D) the value chain for the product.
A) the value-added formula.
B) the effective operational accounting equation.
C) the value-added tax.
D) the value chain for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Some U.S. companies are choosing to move some operations back to the United States because lower costs of communication within the U.S. allow them to make quick changes to design and production. This phenomenon is called:
A) insourcing.
B) offshoring.
C) onshoring.
D) retrenching.
A) insourcing.
B) offshoring.
C) onshoring.
D) retrenching.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The provision of a service or input component part that is assembled into a final good at another location is known as:
A) barter.
B) component trade.
C) intermediate trade.
D) offshoring.
A) barter.
B) component trade.
C) intermediate trade.
D) offshoring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The offshoring model is mainly useful to:
A) study only changes in returns to capital in capital-abundant and labor-abundant countries.
B) study changes in returns to both capital and labor in capital-abundant and labor-abundant countries.
C) study changes in wage payments to low-skilled workers in capital-abundant and labor-abundant countries.
D) study changes in wage payments to both high-skilled and low-skilled workers in capital-abundant and labor-abundant countries.
A) study only changes in returns to capital in capital-abundant and labor-abundant countries.
B) study changes in returns to both capital and labor in capital-abundant and labor-abundant countries.
C) study changes in wage payments to low-skilled workers in capital-abundant and labor-abundant countries.
D) study changes in wage payments to both high-skilled and low-skilled workers in capital-abundant and labor-abundant countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following activities in the value chain is most likely to be offshored?
A) R&D
B) sales
C) component production
D) assembly
A) R&D
B) sales
C) component production
D) assembly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Though offshoring and outsourcing are technically different, Feenstra and Taylor use the term offshoring to include:
A) both offshoring and outsourcing activities.
B) only offshoring activities.
C) only outsourcing activities.
D) neither offshoring nor outsourcing activities.
A) both offshoring and outsourcing activities.
B) only offshoring activities.
C) only outsourcing activities.
D) neither offshoring nor outsourcing activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Among the activities in the value chain, assembly requires_____ labor and R&D requires _____ labor.
A) skilled; unskilled
B) unskilled; skilled
C) skilled; skilled
D) unskilled; unskilled
A) skilled; unskilled
B) unskilled; skilled
C) skilled; skilled
D) unskilled; unskilled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following activities in the value chain is LEAST likely to be offshored?
A) assembly
B) component production
C) R&D
D) sales
A) assembly
B) component production
C) R&D
D) sales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
"Offshoring" is technically different from "outsourcing" because:
A) the former is FDI that establishes a subsidiary in a foreign country.
B) the latter is FDI that establishes a subsidiary in a foreign country.
C) the former involves hiring firms to produce a product without investing in the foreign country.
D) the latter is sanctioned by the government.
A) the former is FDI that establishes a subsidiary in a foreign country.
B) the latter is FDI that establishes a subsidiary in a foreign country.
C) the former involves hiring firms to produce a product without investing in the foreign country.
D) the latter is sanctioned by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the difference between final goods and intermediate goods?
A) Final goods require further processing before consumption.
B) Intermediate goods are sold directly to the consumer.
C) Intermediate goods are inputs for other goods.
D) Final goods require further processing before consumption, while intermediate goods are inputs for other goods.
A) Final goods require further processing before consumption.
B) Intermediate goods are sold directly to the consumer.
C) Intermediate goods are inputs for other goods.
D) Final goods require further processing before consumption, while intermediate goods are inputs for other goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An increase in offshoring will raise the relative wage of skilled labor in both the home and offshored nations because:
A) the home nation will shift resources from lower-skilled to higher-skilled domestic workers, and the offshored nation will see a shift in in demand from lower-skilled to higher-skilled workers.
B) the home nation will shift resources from higher-skilled to lower-skilled domestic workers, and the offshored nation will see a shift in demand from higher-skilled to lower-skilled workers.
C) activities that used higher-priced, higher-skilled workers in the home nation now use lower-priced, lower-skilled workers in the offshored nation.
D) the home nation will shift resources from lower-skilled to higher-skilled domestic workers, while activities that used higher-priced, higher-skilled workers in the offshored nation will now use lower-priced, lower-skilled workers.
A) the home nation will shift resources from lower-skilled to higher-skilled domestic workers, and the offshored nation will see a shift in in demand from lower-skilled to higher-skilled workers.
B) the home nation will shift resources from higher-skilled to lower-skilled domestic workers, and the offshored nation will see a shift in demand from higher-skilled to lower-skilled workers.
C) activities that used higher-priced, higher-skilled workers in the home nation now use lower-priced, lower-skilled workers in the offshored nation.
D) the home nation will shift resources from lower-skilled to higher-skilled domestic workers, while activities that used higher-priced, higher-skilled workers in the offshored nation will now use lower-priced, lower-skilled workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When does it become more desirable to shift more activities in the value chain abroad?
A) when the wage of unskilled workers increases abroad
B) when trade costs decline
C) when the wage of skilled workers decreases at home
D) when the price of the final output rises
A) when the wage of unskilled workers increases abroad
B) when trade costs decline
C) when the wage of skilled workers decreases at home
D) when the price of the final output rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
(Table: Labor Requirements) The table gives U.S. and Indian labor requirements (hours per unit of output) needed in each of four activities to produce the final product. Suppose that wages of unskilled and skilled workers are $10 and $20 in the United States and $1 and $5 in India. Further suppose that trade costs equal 25% of wage costs in India. Now where is the value chain sliced? Which operations will the United States offshore to India? 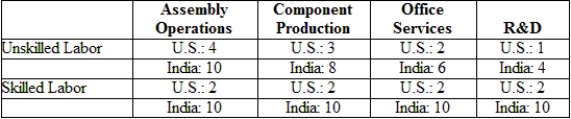
A) assembly operations only
B) assembly operations and component production
C) assembly operations, component production, and office services
D) assembly operations, component production, office services, and R&D

A) assembly operations only
B) assembly operations and component production
C) assembly operations, component production, and office services
D) assembly operations, component production, office services, and R&D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the most important labor market situation at home and abroad that affects a firm's decision to offshore?
A) the relative equilibrium wages of skilled versus unskilled workers at home and abroad
B) the relative educational attainment of workers at home and abroad
C) the absolute wages of workers at home and abroad
D) the ability of workers abroad to speak English
A) the relative equilibrium wages of skilled versus unskilled workers at home and abroad
B) the relative educational attainment of workers at home and abroad
C) the absolute wages of workers at home and abroad
D) the ability of workers abroad to speak English

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is NOT a consideration that firms should include in deciding whether to offshore part of its value chain of activities?
A) higher foreign costs of construction, electricity, and fuel.
B) higher foreign taxes.
C) higher transportation costs to ship the offshored product to the home country.
D) relatively higher costs of foreign skilled labor.
A) higher foreign costs of construction, electricity, and fuel.
B) higher foreign taxes.
C) higher transportation costs to ship the offshored product to the home country.
D) relatively higher costs of foreign skilled labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
"Slicing the value chain" refers to:
A) the practice of offshoring all activities with labor union representation at home.
B) the transfer of activities that are more profitable when carried out in foreign nations.
C) substituting capital for labor wherever possible.
D) the transfer of activities that are less profitable when carried out in foreign nations.
A) the practice of offshoring all activities with labor union representation at home.
B) the transfer of activities that are more profitable when carried out in foreign nations.
C) substituting capital for labor wherever possible.
D) the transfer of activities that are less profitable when carried out in foreign nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
(Table: Labor Requirements) The table gives U.S. and Indian labor requirements (hours per unit of output) needed in each of four activities to produce the final product. Suppose that wages of unskilled and skilled workers are $10 and $20 in the United States and $1 and $5 in India. If trade costs are zero, where is the value chain sliced? Which operations will the United States offshore to India? 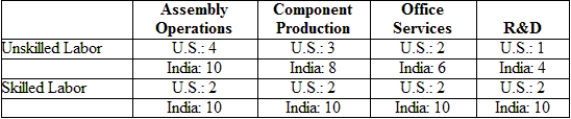
A) assembly operations only
B) assembly operations and component production
C) assembly operations, component production, and office services
D) assembly operations, component production, office services, and R&D

A) assembly operations only
B) assembly operations and component production
C) assembly operations, component production, and office services
D) assembly operations, component production, office services, and R&D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
"Slicing up the value chain" refers to dividing:
A) production between foreign operations using unskilled labor and domestic operations using skilled labor.
B) production between component production and assembly operations.
C) labor between domestic unskilled and skilled labor.
D) the marketing and sales and R&D functions.
A) production between foreign operations using unskilled labor and domestic operations using skilled labor.
B) production between component production and assembly operations.
C) labor between domestic unskilled and skilled labor.
D) the marketing and sales and R&D functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What will happen to wages of skilled workers domestically when offshoring occurs?
A) They will rise.
B) They will fall.
C) They will not change.
D) They will fall in the export sector.
A) They will rise.
B) They will fall.
C) They will not change.
D) They will fall in the export sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The offshoring decision revolves around:
A) the level of domestic opposition to the idea of offshoring.
B) the level of technology at home and abroad.
C) a comparison of the values added, the marginal costs, and the trade costs of a firm's activities at home versus abroad.
D) labor costs abroad versus in the home market.
A) the level of domestic opposition to the idea of offshoring.
B) the level of technology at home and abroad.
C) a comparison of the values added, the marginal costs, and the trade costs of a firm's activities at home versus abroad.
D) labor costs abroad versus in the home market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How will an increase in offshoring affect the demand for skilled labor and the wages of skilled labor in the home country?
A) The demand for skilled labor will increase, but the wages of skilled labor will decrease.
B) The demand for skilled labor and the wages of skilled labor will both decrease.
C) The demand for skilled labor will decrease, but the wages of skilled labor will increase.
D) The demand for skilled labor and the wages of skilled labor will both increase.
A) The demand for skilled labor will increase, but the wages of skilled labor will decrease.
B) The demand for skilled labor and the wages of skilled labor will both decrease.
C) The demand for skilled labor will decrease, but the wages of skilled labor will increase.
D) The demand for skilled labor and the wages of skilled labor will both increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
(Table: Labor Requirements) The table gives U.S. and Indian labor requirements (hours per unit of output) needed in each of four activities to produce the final product. Suppose that wages of unskilled and skilled workers are $10 and $20 in the United States and $1 and $5 in India. What is the cost of conducting assembly operations in the United States and India? 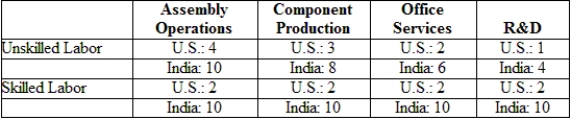
A) $6 in the United States and $20 in India
B) $60 in the United States and $20 in India
C) $80 in the United States and $100 in India
D) $80 in the United States and $60 in India

A) $6 in the United States and $20 in India
B) $60 in the United States and $20 in India
C) $80 in the United States and $100 in India
D) $80 in the United States and $60 in India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
(Table: Labor Requirements) The table gives U.S. and Indian labor requirements (hours per unit of output) needed in each of four activities to produce the final product. Suppose that wages of unskilled and skilled workers are $10 and $20 in the United States and $1 and $5 in India. Now suppose that the United States and India engage in offshoring. What will happen to the relative wage for skilled labor in each country? 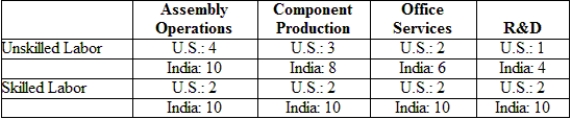
A) The Indian relative wage for skilled labor will increase, and the U.S. relative wage of skilled labor will decrease.
B) The Indian relative wage for skilled labor will decrease, and the U.S. relative wage of skilled labor will increase.
C) Both the Indian and U.S. relative wages for skilled labor will increase.
D) Both the Indian and U.S. relative wages for skilled labor will decrease.

A) The Indian relative wage for skilled labor will increase, and the U.S. relative wage of skilled labor will decrease.
B) The Indian relative wage for skilled labor will decrease, and the U.S. relative wage of skilled labor will increase.
C) Both the Indian and U.S. relative wages for skilled labor will increase.
D) Both the Indian and U.S. relative wages for skilled labor will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
(Table: Labor Requirements) The table gives U.S. and Indian labor requirements (hours per unit of output) needed in each of four activities to produce the final product. Suppose that wages of unskilled and skilled workers are $10 and $20 in the United States and $1 and $5 in India. What is the relative wage of skilled labor in the United States? 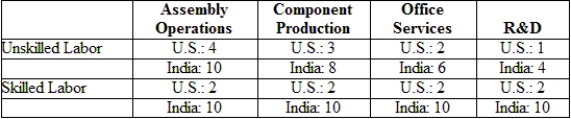
A) $2/$1
B) $1/$2
C) $4/$1
D) $5/$1

A) $2/$1
B) $1/$2
C) $4/$1
D) $5/$1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Reductions in trade costs will tend to:
A) discourage offshoring.
B) discourage foreign production.
C) encourage offshoring.
D) have no immediate effect on offshoring decisions.
A) discourage offshoring.
B) discourage foreign production.
C) encourage offshoring.
D) have no immediate effect on offshoring decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
(Table: Labor Requirements) The table gives U.S. and Indian labor requirements (hours per unit of output) needed in each of four activities to produce the final product. Suppose that wages of unskilled and skilled workers are $10 and $20 in the United States and $1 and $5 in India. Which country has a higher relative wage for skilled labor? 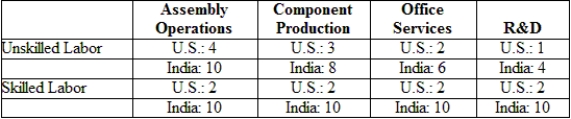
A) India
B) the United States
C) Both India and the United States have the same relative wages for skilled labor.
D) The United States and India have the same relative wage for unskilled labor.

A) India
B) the United States
C) Both India and the United States have the same relative wages for skilled labor.
D) The United States and India have the same relative wage for unskilled labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following groups of Ford Motor Company employees will be most adversely affected by Ford's offshoring of part of its operations to Mexico?
A) Ford engineers and scientists
B) Ford accountants
C) Ford managers
D) Ford assembly line workers
A) Ford engineers and scientists
B) Ford accountants
C) Ford managers
D) Ford assembly line workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
As offshoring activities increase, the relative demand for skilled workers in the home nation:
A) will increase.
B) will decrease.
C) will neither increase nor decrease.
D) will raise wages to the point that offshoring no longer becomes a possibility.
A) will increase.
B) will decrease.
C) will neither increase nor decrease.
D) will raise wages to the point that offshoring no longer becomes a possibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is a "trade cost" that firms need to consider when making offshoring decisions?
A) higher prices of utilities (electricity, fuel) in other countries
B) higher costs of construction of a plant in other countries
C) higher costs associated with poor communication and transportation
D) lower wages paid to low-skilled workers
A) higher prices of utilities (electricity, fuel) in other countries
B) higher costs of construction of a plant in other countries
C) higher costs associated with poor communication and transportation
D) lower wages paid to low-skilled workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When there is an increase in firms' offshoring to foreign nations, we can expect the demand for higher-skilled labor in the home market will _____ and its relative wage will _____.
A) decrease; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; increase
D) increase; decrease
A) decrease; decrease
B) increase; increase
C) decrease; increase
D) increase; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the 1980s, relative employment of U. S. occupations with the lowest wages:
A) rose.
B) fell.
C) were unchanged.
D) first rose, then fell.
A) rose.
B) fell.
C) were unchanged.
D) first rose, then fell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The offshoring of unskilled work from the home country to a foreign country will cause:
A) an increase in the wages for unskilled workers in the home country.
B) a decrease in the wages for skilled workers in the home country.
C) an increase in the wages for skilled workers in the home country.
D) a decrease in the wages for skilled workers in the foreign country.
A) an increase in the wages for unskilled workers in the home country.
B) a decrease in the wages for skilled workers in the home country.
C) an increase in the wages for skilled workers in the home country.
D) a decrease in the wages for skilled workers in the foreign country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
During the 1990s, the relative wage of U. S. nonproduction workers _____ and the relative employment of U. S. nonproduction workers _____.
A) rose; rose
B) fell; fell
C) rose; fell
D) fell; rose
A) rose; rose
B) fell; fell
C) rose; fell
D) fell; rose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following best describes the pattern of the real relative wage of U.S. nonproduction workers over the past 60 years?
A) The relative wage declined continuously over the past 60 years.
B) The relative wage remained constant over the past 60 years.
C) The relative wage rose continuously over the past 60 years.
D) The relative wage declined, then rose, then declined, then rose.
A) The relative wage declined continuously over the past 60 years.
B) The relative wage remained constant over the past 60 years.
C) The relative wage rose continuously over the past 60 years.
D) The relative wage declined, then rose, then declined, then rose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Together, offshoring and skill-biased technological change account for about what percentage of the increase in the relative demand for U.S. nonproduction workers during the 1980s?
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What accounts for increases in both the relative wage and the relative employment of U.S. nonproduction workers during the 1980s?
A) The relative demand for nonproduction workers fell.
B) The relative supply of nonproduction workers rose.
C) The relative demand for nonproduction workers rose.
D) The relative supply of nonproduction workers fell.
A) The relative demand for nonproduction workers fell.
B) The relative supply of nonproduction workers rose.
C) The relative demand for nonproduction workers rose.
D) The relative supply of nonproduction workers fell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Before NAFTA went into effect, movements in the wages of Mexican skilled versus nonskilled workers:
A) were widely different from the U.S. pattern from 1964 to 1996.
B) were exactly the same as the U.S. pattern from 1964 to 1996.
C) only matched the U.S. pattern from 1984 to 1996.
D) only matched the U.S. pattern from 1964 to 1984.
A) were widely different from the U.S. pattern from 1964 to 1996.
B) were exactly the same as the U.S. pattern from 1964 to 1996.
C) only matched the U.S. pattern from 1984 to 1996.
D) only matched the U.S. pattern from 1964 to 1984.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Most offshoring involves moving abroad those activities that have:
A) greater skill intensity.
B) lower skill intensity.
C) both greater and lower skill intensities.
D) high R&D components in their value chain.
A) greater skill intensity.
B) lower skill intensity.
C) both greater and lower skill intensities.
D) high R&D components in their value chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What has happened to the wages of high-skilled labor relative to that of low-skilled labor since 1980?
A) Wages of high-skilled labor relative to that of low-skilled labor have fallen.
B) Wages of high-skilled labor have increased faster than wages of low-skilled labor.
C) Wages of high-skilled workers have stagnated while wages of low-skilled workers have risen.
D) Wages of high-skilled and low-skilled labor have increased at the same rate, thus leaving the relative wage unchanged.
A) Wages of high-skilled labor relative to that of low-skilled labor have fallen.
B) Wages of high-skilled labor have increased faster than wages of low-skilled labor.
C) Wages of high-skilled workers have stagnated while wages of low-skilled workers have risen.
D) Wages of high-skilled and low-skilled labor have increased at the same rate, thus leaving the relative wage unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When work done by skilled workers is offshored, what will happen to wages of skilled workers abroad?
A) They will rise.
B) They will fall.
C) They will not change.
D) They will fall in the export sector.
A) They will rise.
B) They will fall.
C) They will not change.
D) They will fall in the export sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the 1980s, relative employment of U. S. occupations with the highest wages:
A) rose.
B) fell.
C) were unchanged.
D) first rose, then fell.
A) rose.
B) fell.
C) were unchanged.
D) first rose, then fell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
How would offshoring affect the demand for high-skilled workers in the home country?
A) The relative demand and the absolute demand for high-skilled workers would increase.
B) The relative demand would increase and the absolute demand would decrease.
C) The relative demand would decrease and the absolute demand would increase.
D) The relative demand and the absolute demand would decrease.
A) The relative demand and the absolute demand for high-skilled workers would increase.
B) The relative demand would increase and the absolute demand would decrease.
C) The relative demand would decrease and the absolute demand would increase.
D) The relative demand and the absolute demand would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
After NAFTA went into effect and increased U.S. offshoring, what was expected to happen to wages of unskilled labor relative to wages of skilled labor in Mexico and in the United States?
A) Both would rise.
B) Both would fall.
C) Wages of unskilled Mexican labor would rise, and wages of unskilled U.S. labor would fall.
D) Wages of unskilled Mexican labor would fall, and wages of unskilled U.S. labor would rise.
A) Both would rise.
B) Both would fall.
C) Wages of unskilled Mexican labor would rise, and wages of unskilled U.S. labor would fall.
D) Wages of unskilled Mexican labor would fall, and wages of unskilled U.S. labor would rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
After 2004, the relative wages of skilled (nonproduction) workers in the United States:
A) decreased compared with wages of less-skilled (production) workers.
B) rose compared with wages of less-skilled (production) workers.
C) did not change.
D) moved erratically.
A) decreased compared with wages of less-skilled (production) workers.
B) rose compared with wages of less-skilled (production) workers.
C) did not change.
D) moved erratically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Wage changes among skilled and unskilled workers in Mexico due to offshoring are different, depending on whether it is the _____ or _____.
A) maquiladora sector; nonmaquiladora sector
B) younger workers; older workers
C) male workers; female workers
D) nonunion workforces; unionized workforces
A) maquiladora sector; nonmaquiladora sector
B) younger workers; older workers
C) male workers; female workers
D) nonunion workforces; unionized workforces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What happened to wages of U.S. nonproduction workers relative to U.S. production workers from 2004 to 2014?
A) They rose.
B) They fell.
C) They did not change.
D) They fell in the export sector.
A) They rose.
B) They fell.
C) They did not change.
D) They fell in the export sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is a partial explanation for the increase in the relative demand for U.S. nonproduction workers during the 1980s?
A) declines in the rate of U.S. technological change
B) skilled-biased technological change
C) increased production of import-competing goods
D) declines in the rate of U.S. technological change and skilled-biased technological change
A) declines in the rate of U.S. technological change
B) skilled-biased technological change
C) increased production of import-competing goods
D) declines in the rate of U.S. technological change and skilled-biased technological change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
From 1982 to 2000, the relative wage of nonproduction to production workers in U.S. manufacturing and their share of total employment in U.S. manufacturing increased. One logical explanation would be:
A) that their wages fell in real terms.
B) that there was a decrease in demand for skilled workers.
C) that due to increased productivity or demand for products, there was a relative increase in demand for skilled workers.
D) that minimum wage increases shifted the demand for workers toward skilled workers.
A) that their wages fell in real terms.
B) that there was a decrease in demand for skilled workers.
C) that due to increased productivity or demand for products, there was a relative increase in demand for skilled workers.
D) that minimum wage increases shifted the demand for workers toward skilled workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Job polarization refers to situations in which:
A) the employment shares of jobs with lower and higher wages both fall.
B) the employment shares of jobs with lower and higher wages both rise.
C) the employment share of jobs with lower wages rises and the employment share of jobs with higher wages falls.
D) the employment share of jobs with lower wages falls and the employment share of jobs with higher wages rises.
A) the employment shares of jobs with lower and higher wages both fall.
B) the employment shares of jobs with lower and higher wages both rise.
C) the employment share of jobs with lower wages rises and the employment share of jobs with higher wages falls.
D) the employment share of jobs with lower wages falls and the employment share of jobs with higher wages rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
From 2000 to 2014, relative wages of U. S. nonproduction workers _____ and relative employment of U. S. nonproduction workers _____.
A) increased; decreased
B) increased; increased
C) decreased; increased.
D) were erratic; were erratic-neither had a clear pattern of movement
A) increased; decreased
B) increased; increased
C) decreased; increased.
D) were erratic; were erratic-neither had a clear pattern of movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
During the 1980s, there was a relative _____ in the demand for higher-skilled workers.
A) decrease
B) increase
C) increase, then a decrease
D) decrease, then an increase
A) decrease
B) increase
C) increase, then a decrease
D) decrease, then an increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring I) In the graph, which line shows the initial level of production for this firm? 
A) Y1
B) Y0
C) the bowed-out curved line
D) the vertical axis

A) Y1
B) Y0
C) the bowed-out curved line
D) the vertical axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring II) If the world price of components falls, it is likely that: 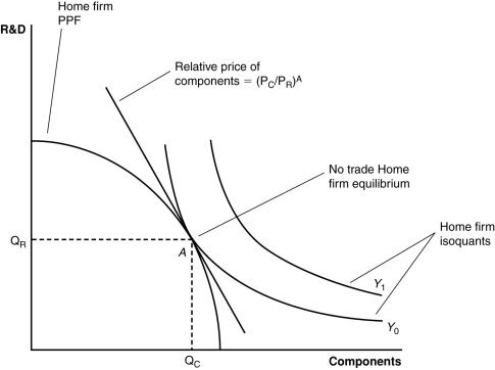
A) the home country will import more R&D from the foreign country.
B) the foreign country will get more R&D for its components.
C) the home country will produce more R&D and trade it for components.
D) there will be no impact on the home country.

A) the home country will import more R&D from the foreign country.
B) the foreign country will get more R&D for its components.
C) the home country will produce more R&D and trade it for components.
D) there will be no impact on the home country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring I) In a "no-offshoring" equilibrium, how many units of R&D production will there be? 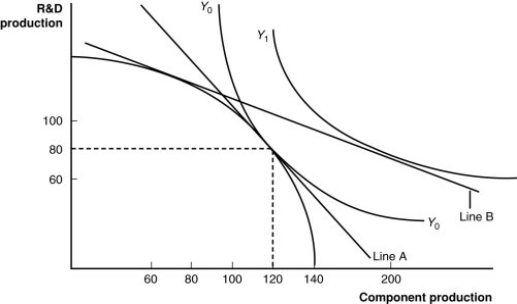
A) 60
B) 80
C) 100
D) 120

A) 60
B) 80
C) 100
D) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring II) If the price of R&D decreases, then it is likely that the home country: 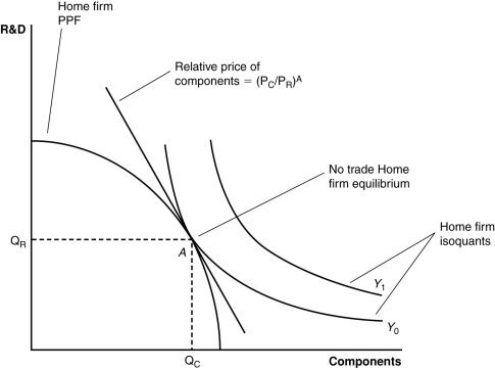
A) could see a decline in the amount of output produced.
B) will see a loss in comparative advantage in R&D.
C) could see a decline in the amount of output produced and a loss in comparative advantage in R&D.
D) could see an increase in the amount of output produced.

A) could see a decline in the amount of output produced.
B) will see a loss in comparative advantage in R&D.
C) could see a decline in the amount of output produced and a loss in comparative advantage in R&D.
D) could see an increase in the amount of output produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When countries open up for offshoring, which country will tend to specialize in research and development?
A) the skilled-labor-abundant country
B) the unskilled-labor-abundant country
C) neither country
D) both countries
A) the skilled-labor-abundant country
B) the unskilled-labor-abundant country
C) neither country
D) both countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring I) In "no-offshoring" equilibrium, how many units of component production will there be? 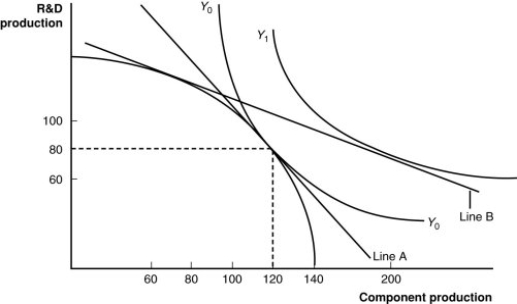
A) 60
B) 80
C) 100
D) 120

A) 60
B) 80
C) 100
D) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring II) If the relative price of components is cheaper in a foreign country than the home country, then: 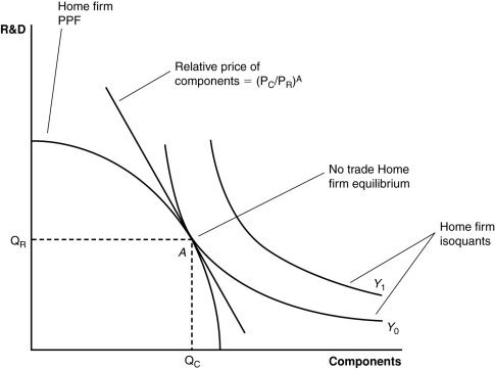
A) it is likely that the home country will offshore the R&D to the foreign country.
B) it is likely that the foreign country will offshore the components to the home country.
C) it is likely that the home country will offshore components to the foreign country.
D) no meaningful exchange is possible between the home and foreign country.

A) it is likely that the home country will offshore the R&D to the foreign country.
B) it is likely that the foreign country will offshore the components to the home country.
C) it is likely that the home country will offshore components to the foreign country.
D) no meaningful exchange is possible between the home and foreign country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What happened to growth rates of routine manual and routine cognitive jobs in the United States after 2007?
A) Both routine manual and routine cognitive jobs experienced high growth rates.
B) Both routine manual and routine cognitive jobs experienced negative growth rates.
C) Routine manual jobs experienced high growth rates while routine cognitive jobs experienced negative growth rates.
D) Routine manual jobs experienced negative growth rates while routine cognitive jobs experienced high growth rates.
A) Both routine manual and routine cognitive jobs experienced high growth rates.
B) Both routine manual and routine cognitive jobs experienced negative growth rates.
C) Routine manual jobs experienced high growth rates while routine cognitive jobs experienced negative growth rates.
D) Routine manual jobs experienced negative growth rates while routine cognitive jobs experienced high growth rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When two countries open up for offshoring, in which country does skilled labor tend to gain relative to unskilled labor?
A) the skilled-labor-abundant country
B) the unskilled-labor-abundant country
C) neither country
D) both countries
A) the skilled-labor-abundant country
B) the unskilled-labor-abundant country
C) neither country
D) both countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring II) If the home country offshores components to a foreign country and then exports R&D to the foreign country and imports components from the foreign country, then: 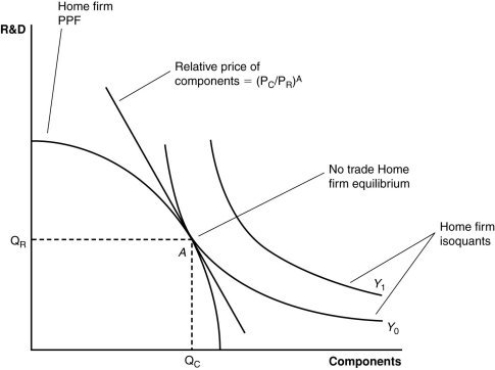
A) the exchange is not a beneficial one for the home country.
B) the exchange results in an increase in output at lower prices.
C) consumers benefit due to this offshoring.
D) the exchange results in an increase in output at lower prices and the consumers benefit due to this offshoring.

A) the exchange is not a beneficial one for the home country.
B) the exchange results in an increase in output at lower prices.
C) consumers benefit due to this offshoring.
D) the exchange results in an increase in output at lower prices and the consumers benefit due to this offshoring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring II) According to the combination of output shown by the isoquant, Y1: 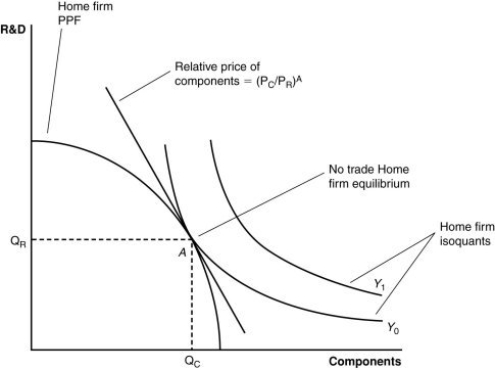
A) can be achieved using the present components and R&D in the country.
B) is beyond the nation's capabilities to produce.
C) could be achieved by trading with another country.
D) is beyond the firm's capabilities to produce domestically but could be achieved by trading with another country.

A) can be achieved using the present components and R&D in the country.
B) is beyond the nation's capabilities to produce.
C) could be achieved by trading with another country.
D) is beyond the firm's capabilities to produce domestically but could be achieved by trading with another country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring I) If this firm offshores its component production and exports R&D, how many units of each will it have available in equilibrium? 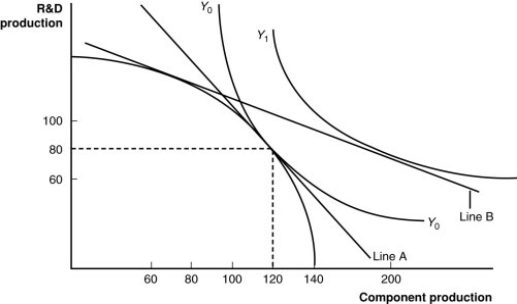
A) 60 R&D; 120 components
B) 80 R&D; 80 components
C) 100 R&D; 100 components
D) 80 R&D; 200 components

A) 60 R&D; 120 components
B) 80 R&D; 80 components
C) 100 R&D; 100 components
D) 80 R&D; 200 components

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
According to the text, what two factors account for the low (and sometimes negative) growth rates of routine manual and routine cognitive jobs in the United States since 1983?
A) offshoring and low economic growth
B) low economic growth and skill-biased technological change
C) offshoring and skill-biased technological change
D) immigration and offshoring
A) offshoring and low economic growth
B) low economic growth and skill-biased technological change
C) offshoring and skill-biased technological change
D) immigration and offshoring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What does the text predict for future growth rates for routine and nonroutine jobs in the United States?
A) Both types of jobs will grow at approximately the same rate.
B) Both types of jobs will experience negative growth rates.
C) The growth rate of routine jobs will be greater than that of nonroutine jobs.
D) The growth rate of nonroutine jobs will be greater than that of routine jobs.
A) Both types of jobs will grow at approximately the same rate.
B) Both types of jobs will experience negative growth rates.
C) The growth rate of routine jobs will be greater than that of nonroutine jobs.
D) The growth rate of nonroutine jobs will be greater than that of routine jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which groups in a high-skilled-labor-abundant country will gain from offshoring?
A) high-skilled and low-skilled labor
B) high-skilled labor and consumers
C) low-skilled labor and consumers
D) high-skilled labor, low-skilled labor, and consumers
A) high-skilled and low-skilled labor
B) high-skilled labor and consumers
C) low-skilled labor and consumers
D) high-skilled labor, low-skilled labor, and consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring I) If component parts become relatively cheaper abroad, this firm will have an incentive: 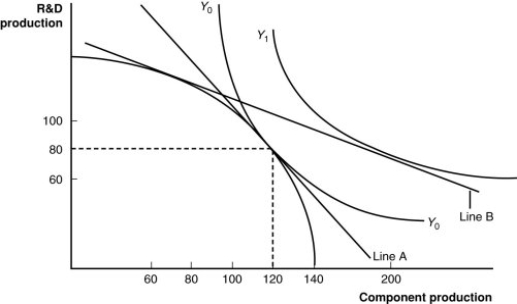
A) to offshore (import) components and export R&D.
B) to import R&D products along with skilled workers.
C) to export both R&D and component parts.
D) to make few changes in the trading regime because of the delicate international balance.

A) to offshore (import) components and export R&D.
B) to import R&D products along with skilled workers.
C) to export both R&D and component parts.
D) to make few changes in the trading regime because of the delicate international balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which types of jobs in the United States have experienced the highest growth rates?
A) routine manual and routine cognitive jobs
B) nonroutine manual and nonroutine cognitive jobs
C) routine manual and nonroutine cognitive jobs
D) nonroutine manual and routine cognitive jobs
A) routine manual and routine cognitive jobs
B) nonroutine manual and nonroutine cognitive jobs
C) routine manual and nonroutine cognitive jobs
D) nonroutine manual and routine cognitive jobs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring I) Which line shows the relative prices of skilled versus unskilled workers? 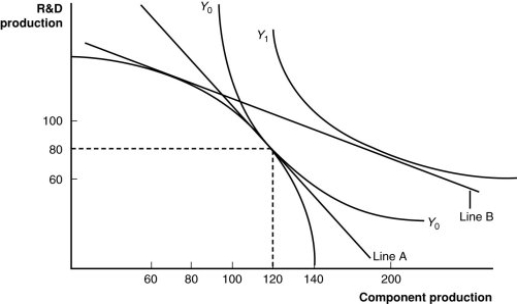
A) Line A
B) Y0 (the curved-in line)
C) the bowed-out curved line
D) the vertical axis

A) Line A
B) Y0 (the curved-in line)
C) the bowed-out curved line
D) the vertical axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
(Figure: A Firm's Production With and Without Offshoring I) Assuming skilled workers are needed for R&D and unskilled workers are needed for components, if there is an increase in the price for research and development products, this firm will _____ those products, the demand for _____ will increase, the wages of these workers will rise, and the price line in the graph will _____. 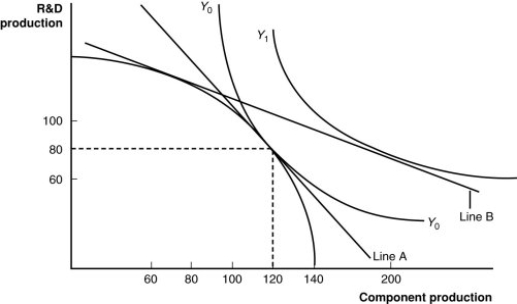
A) import; unskilled workers; become steeper
B) export; skilled workers; become flatter
C) neither import nor export; both workers in the same proportion; not change
D) import; unskilled workers; become flatter

A) import; unskilled workers; become steeper
B) export; skilled workers; become flatter
C) neither import nor export; both workers in the same proportion; not change
D) import; unskilled workers; become flatter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



