Deck 16: National and International Accounts: Income, Wealth, and the Balance of Payments
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/156
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: National and International Accounts: Income, Wealth, and the Balance of Payments
1
The current account of the balance of payments is calculated as:
A) the sum of imports, exports, and transfers.
B) the sum of national income and national expenditure.
C) the sum of the trade balance, net factor income from abroad, and net unilateral transfers.
D) the difference between GDP and GNE.
A) the sum of imports, exports, and transfers.
B) the sum of national income and national expenditure.
C) the sum of the trade balance, net factor income from abroad, and net unilateral transfers.
D) the difference between GDP and GNE.
C
2
In national accounts data, which is the largest share of GNEs?
A) consumption
B) investment
C) government consumption
D) All are roughly equal in size.
A) consumption
B) investment
C) government consumption
D) All are roughly equal in size.
A
3
The term net unilateral transfers refers to:
A) income earned abroad by a nation's own workers minus income paid to foreign non-resident workers.
B) gifts, charitable contributions, and foreign aid.
C) gifts, charitable contributions, and aid to foreign residents minus the same types of transfers to residents of the home nation.
D) government subsidies to home corporations minus the same government subsidies to international corporations.
A) income earned abroad by a nation's own workers minus income paid to foreign non-resident workers.
B) gifts, charitable contributions, and foreign aid.
C) gifts, charitable contributions, and aid to foreign residents minus the same types of transfers to residents of the home nation.
D) government subsidies to home corporations minus the same government subsidies to international corporations.
C
4
Asset exports occur when domestic entities:
A) save internationally by purchasing foreign assets.
B) borrow internationally by selling assets to foreigners.
C) increase savings and decrease spending both domestically and internationally.
D) decrease savings and increase spending on foreign goods.
A) save internationally by purchasing foreign assets.
B) borrow internationally by selling assets to foreigners.
C) increase savings and decrease spending both domestically and internationally.
D) decrease savings and increase spending on foreign goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Gross national expenditure in a closed economy is defined as:
A) government spending net of taxes.
B) personal consumption spending, government spending, and investment spending.
C) personal consumption spending, government spending, investment spending, and spending on exports.
D) production of consumer goods, government services, and capital goods.
A) government spending net of taxes.
B) personal consumption spending, government spending, and investment spending.
C) personal consumption spending, government spending, investment spending, and spending on exports.
D) production of consumer goods, government services, and capital goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Income paid to factors is called:
A) national income.
B) value added.
C) net exports.
D) the current account.
A) national income.
B) value added.
C) net exports.
D) the current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Net factor income from abroad is defined as:
A) the difference between foreign GDP and U.S. GDP.
B) the difference between what foreign firms pay U.S. factors of production hired to produce foreign GDP and what U.S. firms pay foreign factors of production hired to produce U.S. GDP.
C) taxes paid on income earned outside the country.
D) the difference between foreign national income and U.S. national income.
A) the difference between foreign GDP and U.S. GDP.
B) the difference between what foreign firms pay U.S. factors of production hired to produce foreign GDP and what U.S. firms pay foreign factors of production hired to produce U.S. GDP.
C) taxes paid on income earned outside the country.
D) the difference between foreign national income and U.S. national income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When calculating GDP in an open economy, we adjust GNE by:
A) subtracting exports and adding imports.
B) subtracting investment from foreigners and adding foreign investment by residents.
C) subtracting imports and adding exports.
D) subtracting depreciation from GDP.
A) subtracting exports and adding imports.
B) subtracting investment from foreigners and adding foreign investment by residents.
C) subtracting imports and adding exports.
D) subtracting depreciation from GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a closed economy, income generated from production is equal to:
A) GNE.
B) GDP.
C) GNI.
D) GNE, GDP, and GNI.
A) GNE.
B) GDP.
C) GNI.
D) GNE, GDP, and GNI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In a closed economy in which no international economic activity occurs, which of the following is NOT true?
A) Production in the nation must equal total demand (spending on final goods and services).
B) Total spending is equal to the sum of consumer spending, business investment, and government purchases.
C) Value added in the economy is equal to income paid to factors of production.
D) Value added in the economy is equal to the sum of consumer spending, business investment, and government purchases.
A) Production in the nation must equal total demand (spending on final goods and services).
B) Total spending is equal to the sum of consumer spending, business investment, and government purchases.
C) Value added in the economy is equal to income paid to factors of production.
D) Value added in the economy is equal to the sum of consumer spending, business investment, and government purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In an open economy, GNI is equal to:
A) exports of goods and services plus imports of goods and services.
B) GDP.
C) GDP, minus factor services imports, plus factor services exports.
D) GDP plus international transfers and gifts to foreigners.
A) exports of goods and services plus imports of goods and services.
B) GDP.
C) GDP, minus factor services imports, plus factor services exports.
D) GDP plus international transfers and gifts to foreigners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Summaries of international flows of goods and assets are recorded in a nation's:
A) national income and product accounts.
B) balances with the IMF.
C) balance of payments accounts.
D) balance on international indebtedness.
A) national income and product accounts.
B) balances with the IMF.
C) balance of payments accounts.
D) balance on international indebtedness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following factors is NOT part of the current account of a country?
A) exports
B) imports
C) unilateral transfers
D) Social Security contributions
A) exports
B) imports
C) unilateral transfers
D) Social Security contributions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Government consumption expenditure includes the following, EXCEPT government spending on:
A) national defense.
B) public works.
C) Social Security.
D) civil services.
A) national defense.
B) public works.
C) Social Security.
D) civil services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the flow diagram representing an open economy, which of the following is true?
A) GNE plus the trade balance (TB) are equal to GDP (total domestic production).
B) GNE are always less than GDP.
C) GDP rises as GNI rises.
D) GNE plus imports are equal to GDP.
A) GNE plus the trade balance (TB) are equal to GDP (total domestic production).
B) GNE are always less than GDP.
C) GDP rises as GNI rises.
D) GNE plus imports are equal to GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Tracking and measuring international flows of goods and assets are based on principles of:
A) economics.
B) statistics.
C) historical precedents.
D) accounting.
A) economics.
B) statistics.
C) historical precedents.
D) accounting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The personal consumption expenditure includes all of the following, EXCEPT spending by private households on:
A) final goods and services.
B) nondurable goods.
C) durable goods.
D) capital stock.
A) final goods and services.
B) nondurable goods.
C) durable goods.
D) capital stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The circular flow concept of a closed economy helps to explain why:
A) firms are able to earn profits.
B) GDP, GNI, and GNE are equal.
C) unemployment is not a problem in a closed economy-only in an open economy.
D) nominal GDP is always higher than real GDP.
A) firms are able to earn profits.
B) GDP, GNI, and GNE are equal.
C) unemployment is not a problem in a closed economy-only in an open economy.
D) nominal GDP is always higher than real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When calculating gross national disposable income in an open economy, we adjust gross national expenditure by:
A) subtracting exports and adding back imports.
B) adding in net income earned from foreign sources, plus the trade balance, plus net unilateral transfers from abroad.
C) subtracting depreciation, payroll taxes, and indirect business taxes, while adding in subsidies.
D) taking out net factor income from abroad and subtracting net unilateral transfers.
A) subtracting exports and adding back imports.
B) adding in net income earned from foreign sources, plus the trade balance, plus net unilateral transfers from abroad.
C) subtracting depreciation, payroll taxes, and indirect business taxes, while adding in subsidies.
D) taking out net factor income from abroad and subtracting net unilateral transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The disposable income of a nation is known as gross national disposable income, which can be defined as:
A) income earned from production plus net factor income from abroad plus net unilateral transfers.
B) income not saved and not spent.
C) government transfers to residents plus foreign transfers to residents.
D) income that is more than necessary to sustain life.
A) income earned from production plus net factor income from abroad plus net unilateral transfers.
B) income not saved and not spent.
C) government transfers to residents plus foreign transfers to residents.
D) income that is more than necessary to sustain life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
NFIA is the same thing as:
A) world real GDP.
B) sales of factor services to foreigners minus purchases of factor services from foreign nations.
C) income paid to domestic workers.
D) exactly 20% of domestic GDP.
A) world real GDP.
B) sales of factor services to foreigners minus purchases of factor services from foreign nations.
C) income paid to domestic workers.
D) exactly 20% of domestic GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
(Table: Hypothetical Irish National Income and Product Accounts Data) The GDP for Ireland is: 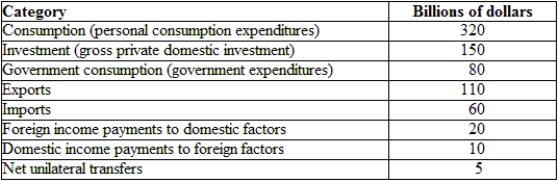
A) $150 billion.
B) $600 billion.
C) $780 billion.
D) $1,500 billion.

A) $150 billion.
B) $600 billion.
C) $780 billion.
D) $1,500 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
(Table: Hypothetical Canadian National Income and Product Accounts Data) Canada is running a: 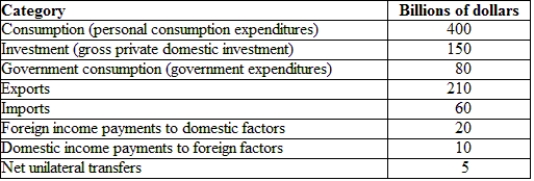
A) trade surplus.
B) balance of payments surplus.
C) trade deficit.
D) balance of payments deficit.

A) trade surplus.
B) balance of payments surplus.
C) trade deficit.
D) balance of payments deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An advantage to calculating national income from value added is that it avoids:
A) the net present value.
B) price changes.
C) double counting.
D) measurement error.
A) the net present value.
B) price changes.
C) double counting.
D) measurement error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
(Table: Hypothetical Canadian National Income and Product Accounts Data) Using the table, the trade balance for the economy provided is: 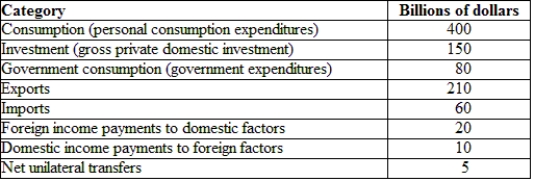
A) -$60 billion.
B) -$150 billion.
C) $150 billion.
D) $270 billion.

A) -$60 billion.
B) -$150 billion.
C) $150 billion.
D) $270 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
(Table: Hypothetical Canadian National Income and Product Accounts Data) Using the table, the GNE is: 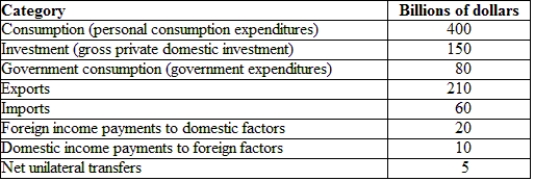
A) $630 billion.
B) $550 billion.
C) $230 billion.
D) $120 billion.

A) $630 billion.
B) $550 billion.
C) $230 billion.
D) $120 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Because of vertically specialized production processes, the volume of intermediate goods trade has risen. In 2010, it was approximately ____ of total world trade.
A) 15%
B) 25%
C) 40%
D) 60%
A) 15%
B) 25%
C) 40%
D) 60%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The total economic activity in a nation is an important measure. There are three approaches that economists use to measure key indicators. Which is a method that economists do NOT use to measure economic activity?
A) the accounting approach, using the idea that total private sales have to equal total private production
B) the income approach measuring income received by factors of production
C) the expenditure approach, using the idea that the total economic activity is equal to the combined purchases of the various sectors
D) the product approach, which measures GDP from a production standpoint
A) the accounting approach, using the idea that total private sales have to equal total private production
B) the income approach measuring income received by factors of production
C) the expenditure approach, using the idea that the total economic activity is equal to the combined purchases of the various sectors
D) the product approach, which measures GDP from a production standpoint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
(Table: Hypothetical U.S. National Income and Product Accounts Data) Using the table, the trade balance for the economy provided is: 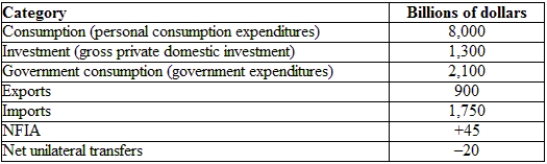
A) $1,750 billion.
B) -$900 billion.
C) $2,650 billion.
D) -$850 billion.

A) $1,750 billion.
B) -$900 billion.
C) $2,650 billion.
D) -$850 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The difference (balance) between asset exports and asset imports is called:
A) the current account.
B) the balance of debt.
C) capital remainder flows.
D) the balance on the financial account.
A) the current account.
B) the balance of debt.
C) capital remainder flows.
D) the balance on the financial account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
(Table: Hypothetical U.S. National Income and Product Accounts Data) Using the table, the GNE is: 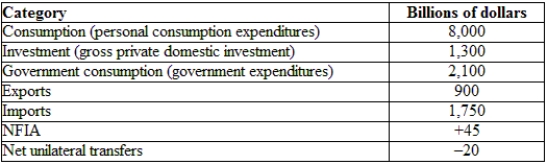
A) $9,300 billion.
B) $3,400 billion.
C) $10,550 billion.
D) $11,400 billion.

A) $9,300 billion.
B) $3,400 billion.
C) $10,550 billion.
D) $11,400 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements about the relationships between the domestic and international economy is true?
A) Domestic sales of goods and services to a foreign nation are always equal to domestic purchases of goods and services from the same nation.
B) Total goods and services produced and sold domestically by domestic firms plus imports are equal to the total domestic production plus exports.
C) GDP = GNE + (exports - imports).
D) Intermediate goods and services purchased by domestic firms from foreign firms are equal to international sales of intermediate goods to foreign firms.
A) Domestic sales of goods and services to a foreign nation are always equal to domestic purchases of goods and services from the same nation.
B) Total goods and services produced and sold domestically by domestic firms plus imports are equal to the total domestic production plus exports.
C) GDP = GNE + (exports - imports).
D) Intermediate goods and services purchased by domestic firms from foreign firms are equal to international sales of intermediate goods to foreign firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
(Table: Hypothetical Irish National Income and Product Accounts Data) The trade balance for Ireland is: 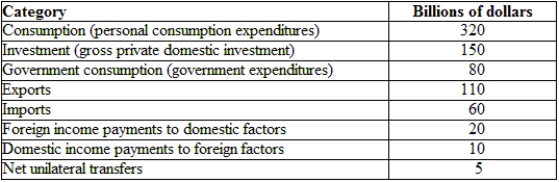
A) -$100 billion.
B) $0 billion.
C) $50 billion.
D) $150 billion.

A) -$100 billion.
B) $0 billion.
C) $50 billion.
D) $150 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How do we handle intermediate goods and services when converting from GNE to GDP?
A) Intermediate goods are already counted in GNE, so they do not have to be added in to GDP.
B) Imported intermediate goods are counted in GNE, so they must be subtracted from GDP to avoid double counting.
C) Exported intermediate goods are counted in GNE, so they must be subtracted from GDP to avoid double counting.
D) We add (to GNE) the value of imported goods and services and subtract the value of exported goods and services to get GDP.
A) Intermediate goods are already counted in GNE, so they do not have to be added in to GDP.
B) Imported intermediate goods are counted in GNE, so they must be subtracted from GDP to avoid double counting.
C) Exported intermediate goods are counted in GNE, so they must be subtracted from GDP to avoid double counting.
D) We add (to GNE) the value of imported goods and services and subtract the value of exported goods and services to get GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
(Table: Hypothetical Irish National Income and Product Accounts Data) Using the table, the GNE is: 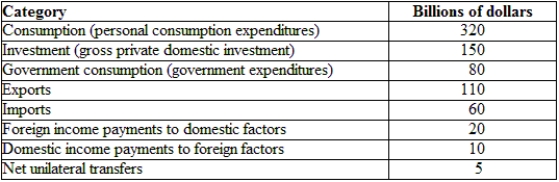
A) $900 billion.
B) $550 billion.
C) $630 billion.
D) $1,800 billion.

A) $900 billion.
B) $550 billion.
C) $630 billion.
D) $1,800 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
(Table: Hypothetical Canadian National Income and Product Accounts Data) The GDP for the economy provided is: 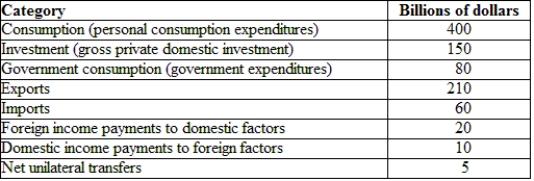
A) $630 billion.
B) $780 billion.
C) $840 billion.
D) $1,025 billion.

A) $630 billion.
B) $780 billion.
C) $840 billion.
D) $1,025 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
(Table: Hypothetical Irish National Income and Product Accounts Data) Ireland is running a: 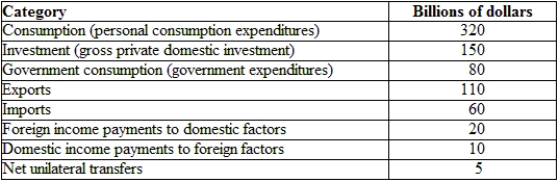
A) trade deficit.
B) balance of payments surplus.
C) trade surplus.
D) balance of payments deficit.

A) trade deficit.
B) balance of payments surplus.
C) trade surplus.
D) balance of payments deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
(Table: Hypothetical Canadian National Income and Product Accounts Data) The GNI for the economy provided is: 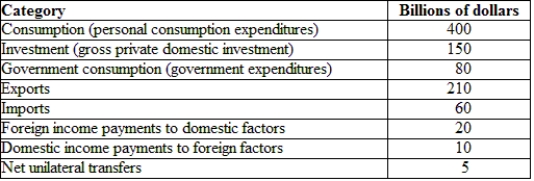
A) $10 billion.
B) $20 billion.
C) $780 billion.
D) $790 billion.

A) $10 billion.
B) $20 billion.
C) $780 billion.
D) $790 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
(Table: Hypothetical Irish National Income and Product Accounts Data) The GNDI for Ireland is: 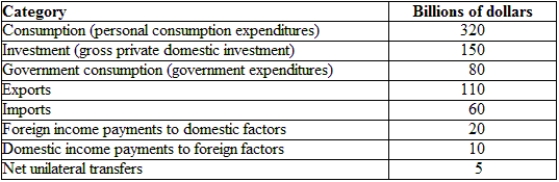
A) $680 billion.
B) $685 billion.
C) $690 billion.
D) $615 billion.

A) $680 billion.
B) $685 billion.
C) $690 billion.
D) $615 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
(Table: Hypothetical U.S. National Income and Product Accounts Data) The GDP for the economy provided is: 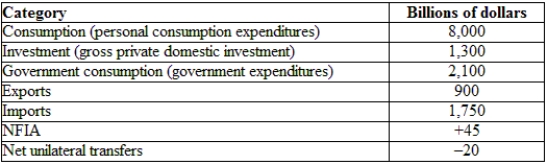
A) $11,400 billion.
B) $10,575 billion.
C) $10,550 billion.
D) $10,595 billion.

A) $11,400 billion.
B) $10,575 billion.
C) $10,550 billion.
D) $10,595 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Net transfers of income from foreign sources play a ____ role in the donor countries, but often play a _____ role in the economies of the recipient nations.
A) major; minor
B) neutral; significant
C) minor; major
D) significant; neutral
A) major; minor
B) neutral; significant
C) minor; major
D) significant; neutral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
(Table: Hypothetical U.S. National Income and Product Accounts Data) The GNI for the economy provided is: 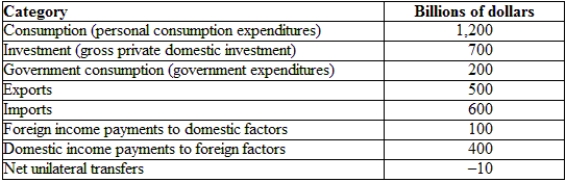
A) $1,900 billion.
B) $1,700 billion.
C) $2,300 billion.
D) $3,300 billion.

A) $1,900 billion.
B) $1,700 billion.
C) $2,300 billion.
D) $3,300 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The example in the text about Ireland demonstrates that:
A) every nation has the power to export and grow its economy through receipt of foreign investment.
B) GNI should not be used to measure the income of domestic factors of production.
C) a nation's GDP is not a good measure of income paid to domestic factors when payments to foreign factors are large.
D) countries should rely heavily on foreign investment to generate economic growth and increase their GDP.
A) every nation has the power to export and grow its economy through receipt of foreign investment.
B) GNI should not be used to measure the income of domestic factors of production.
C) a nation's GDP is not a good measure of income paid to domestic factors when payments to foreign factors are large.
D) countries should rely heavily on foreign investment to generate economic growth and increase their GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The assistance the United States provides to developing countries is through:
A) cash transfers only.
B) debt forgiveness only.
C) defense spending only.
D) cash transfers, debt forgiveness, and defense spending.
A) cash transfers only.
B) debt forgiveness only.
C) defense spending only.
D) cash transfers, debt forgiveness, and defense spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When a closed economy is compared with an open economy, what situation exists?
A) Economic activity is directed entirely by the state in an open economy.
B) Exports and imports are monitored and controlled, so there is never a trade imbalance in a closed economy.
C) In a closed economy, because there are no exports or imports, no international transfers, and no service payments, GDP, GNE, GNI, and GNDI are all equal.
D) GDP is always higher than GNE in an open economy because some goods remain unsold into the next accounting period.
A) Economic activity is directed entirely by the state in an open economy.
B) Exports and imports are monitored and controlled, so there is never a trade imbalance in a closed economy.
C) In a closed economy, because there are no exports or imports, no international transfers, and no service payments, GDP, GNE, GNI, and GNDI are all equal.
D) GDP is always higher than GNE in an open economy because some goods remain unsold into the next accounting period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A firm in one nation may purchase factor services from another nation. Payments for these services to the factors of production are called:
A) service income payments.
B) net income.
C) gross income.
D) wage and salary income.
A) service income payments.
B) net income.
C) gross income.
D) wage and salary income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
GDP is measured by:
A) examining how much is spent on demand for final goods and services.
B) tracking the amount of income received by different domestic entities.
C) the net value of all goods and services produced by the private sector.
D) the net value of all goods and services produced by home firms, excluding the value of intermediate goods.
A) examining how much is spent on demand for final goods and services.
B) tracking the amount of income received by different domestic entities.
C) the net value of all goods and services produced by the private sector.
D) the net value of all goods and services produced by home firms, excluding the value of intermediate goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
(Table: Hypothetical Canadian National Income and Product Accounts Data) According to the NUTs, economists would say that: 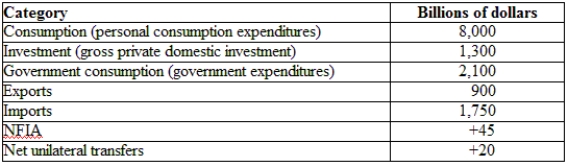
A) Canada has given away more foreign aid than it receives.
B) Canadians abroad have sent a lot of income home.
C) Mexicans in Canada have sent a lot of income home.
D) Canada has a balance of payments deficit.

A) Canada has given away more foreign aid than it receives.
B) Canadians abroad have sent a lot of income home.
C) Mexicans in Canada have sent a lot of income home.
D) Canada has a balance of payments deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The difference between Irish GDP per capita and Irish GNI per capita was:
A) the result of poor accounting.
B) the result of a large trade deficit.
C) an outcome from FDI inflows.
D) essentially zero.
A) the result of poor accounting.
B) the result of a large trade deficit.
C) an outcome from FDI inflows.
D) essentially zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
According to the article on the generosity of wealthy nations in helping low-income nations, the United States:
A) gave the least in absolute terms, although it had pledged to give the most.
B) was the largest single-nation donor, although in percentage of aid based on economic size, it was below most other developed nations.
C) was the only nation that could be counted on to help tsunami victims or provide free drugs for AIDS patients in Africa.
D) has dramatically raised the level of foreign aid during the past 20 years.
A) gave the least in absolute terms, although it had pledged to give the most.
B) was the largest single-nation donor, although in percentage of aid based on economic size, it was below most other developed nations.
C) was the only nation that could be counted on to help tsunami victims or provide free drugs for AIDS patients in Africa.
D) has dramatically raised the level of foreign aid during the past 20 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the United States, during the period 1990 to 2009, the current account deficit greatly ____ because of a(n) ____ in the trade deficit, thus, GDP was lower than GNE.
A) increased; increase
B) decreased; decrease
C) increased; decrease
D) decreased; increase
A) increased; increase
B) decreased; decrease
C) increased; decrease
D) decreased; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
GNDI is a superior measure of a nation's welfare because it considers net foreign factor earnings and other sources of income available to the population. The GNDI identity equation is as follows:
A) Y = GNDI = consumer production + capital goods (business investment) + government + net exports.
B) Y = GNDI = GNI + NUT.
C) Y = GNDI = wages + profits + interest + rental income + net foreign factor income.
D) Y = GNDI = foreign aid + income from outsourcing + returns on foreign investment.
A) Y = GNDI = consumer production + capital goods (business investment) + government + net exports.
B) Y = GNDI = GNI + NUT.
C) Y = GNDI = wages + profits + interest + rental income + net foreign factor income.
D) Y = GNDI = foreign aid + income from outsourcing + returns on foreign investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
(Table: Hypothetical Canadian National Income and Product Accounts Data) What is the current account for Canada? 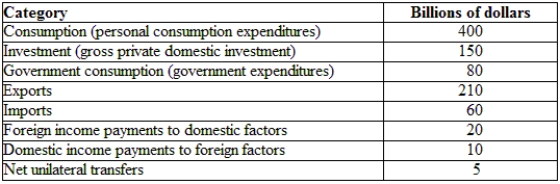
A) $165 billion
B) $150 billion
C) $15 billion
D) $5 billion

A) $165 billion
B) $150 billion
C) $15 billion
D) $5 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When measuring GNI in an open economy, one must recognize not only net transfer payments to factors of production but also:
A) net profit paid to corporations.
B) the increase in asset prices as a result of foreign investment.
C) income earned in the underground economy.
D) net unilateral transfers, which include official aid and private charitable gifts.
A) net profit paid to corporations.
B) the increase in asset prices as a result of foreign investment.
C) income earned in the underground economy.
D) net unilateral transfers, which include official aid and private charitable gifts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When analyzing economic situations in an open economy instead of a closed economy, one must take into account:
A) only the production of final goods and services rather than intermediate goods or services.
B) the relationship between domestic investment and the nominal rate of interest.
C) the influence of international political relationships, which do not exist in a closed economy.
D) the fact that international transactions can create an imbalance in the current account, so that GDP is not necessarily equal to GNI or GNE.
A) only the production of final goods and services rather than intermediate goods or services.
B) the relationship between domestic investment and the nominal rate of interest.
C) the influence of international political relationships, which do not exist in a closed economy.
D) the fact that international transactions can create an imbalance in the current account, so that GDP is not necessarily equal to GNI or GNE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The relationship between GNI and GDP is:
A) GNI - GDP = factor income receipts from foreign sources - payments of income to foreign factors (by domestic firms).
B) GDP is equal to GNI within the nation.
C) GDP is always less than GNI because of domestic transfer payments.
D) GNI includes transfers and gifts from the rest of the world; GDP does not.
A) GNI - GDP = factor income receipts from foreign sources - payments of income to foreign factors (by domestic firms).
B) GDP is equal to GNI within the nation.
C) GDP is always less than GNI because of domestic transfer payments.
D) GNI includes transfers and gifts from the rest of the world; GDP does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The difference between gross national income and gross domestic product is:
A) total indirect employee costs such as health or retirement insurance.
B) income earned in addition to salaries, commissions, and bonuses.
C) income earned abroad by residents minus income paid to foreign factors of production.
D) income not subject to taxation such as capital gains, illegal earnings, or casual earnings.
A) total indirect employee costs such as health or retirement insurance.
B) income earned in addition to salaries, commissions, and bonuses.
C) income earned abroad by residents minus income paid to foreign factors of production.
D) income not subject to taxation such as capital gains, illegal earnings, or casual earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
(Table: Hypothetical Irish National Income and Product Accounts Data) What is the current account for Ireland? 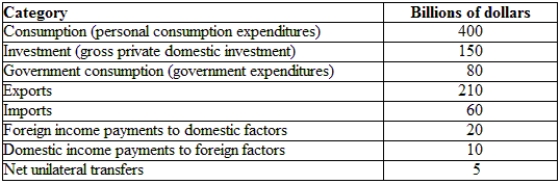
A) $310
B) $290
C) -$290
D) -$410

A) $310
B) $290
C) -$290
D) -$410

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
(Table: Hypothetical Canadian National Income and Product Accounts Data) The GNDI for the economy provided is: 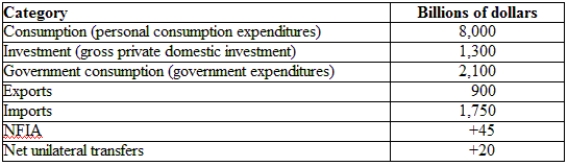
A) $11,825 billion.
B) $10,615 billion.
C) $8,625 billion.
D) $8,600 billion.

A) $11,825 billion.
B) $10,615 billion.
C) $8,625 billion.
D) $8,600 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Irish example indicates that GDP per capita and GNI per capita:
A) are always equal.
B) are usually close to each other.
C) can be quite different.
D) are unrelated.
A) are always equal.
B) are usually close to each other.
C) can be quite different.
D) are unrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Private savings deficits plus government budget deficits contribute to higher current account deficits. Some economists refer to the ______ during the 1990s to assert that government deficits are not the major cause of current account deficits.
A) savings boom
B) investment boom
C) baby boom
D) housing boom
A) savings boom
B) investment boom
C) baby boom
D) housing boom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If investment exceeds private savings, then the current account:
A) must be negative.
B) must be zero.
C) must be positive.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.
A) must be negative.
B) must be zero.
C) must be positive.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The capital account is now used mainly for:
A) errors and omissions.
B) recording of deeds and trusts.
C) investment flows that result in the purchase of new capital.
D) debt forgiveness, confiscation of assets, and nonfinancial assets such as copyrights and franchises.
A) errors and omissions.
B) recording of deeds and trusts.
C) investment flows that result in the purchase of new capital.
D) debt forgiveness, confiscation of assets, and nonfinancial assets such as copyrights and franchises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In addition to summarizing international flows of goods and services, factor inputs, and transfers, ____ includes financial flows such as deposits, purchases of stocks, bonds investment in plant and equipment, and real estate.
A) the financial account
B) balance of payments accounting
C) the current account
D) the capital account
A) the financial account
B) balance of payments accounting
C) the current account
D) the capital account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The financial account records international transactions involving:
A) high-value items, such as luxury autos, fine art, and jewelry.
B) financial assets and "real" assets, including property and structures.
C) corporate assets such as equipment, machinery, and other forms of capital.
D) goods and services sold on credit.
A) high-value items, such as luxury autos, fine art, and jewelry.
B) financial assets and "real" assets, including property and structures.
C) corporate assets such as equipment, machinery, and other forms of capital.
D) goods and services sold on credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Whenever there is a deficit in the current account GNDI is:
A) equal to GNE.
B) greater than GNE.
C) less than GNE.
D) equal to GNE only if there is no domestic investment spending.
A) equal to GNE.
B) greater than GNE.
C) less than GNE.
D) equal to GNE only if there is no domestic investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The term private saving is defined as:
A) government saving minus taxes.
B) after-tax disposable income minus consumption spending.
C) the difference between tax revenue and government purchases.
D) the inflow of investment funds from abroad.
A) government saving minus taxes.
B) after-tax disposable income minus consumption spending.
C) the difference between tax revenue and government purchases.
D) the inflow of investment funds from abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Private savings deficits plus government budget deficits contribute to higher current account deficits. Some economists refer to the Ricardian equivalence theory to assert that:
A) the public will offset its future tax liability to some degree by increasing saving.
B) the public abhors private and public debt and will demand an end to deficits.
C) savings will increase as the population ages, since older people save more.
D) the current account deficit is caused by trade and is not influenced by deficit spending.
A) the public will offset its future tax liability to some degree by increasing saving.
B) the public abhors private and public debt and will demand an end to deficits.
C) savings will increase as the population ages, since older people save more.
D) the current account deficit is caused by trade and is not influenced by deficit spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Whenever the balance on the current account is negative, it indicates that:
A) the trade deficit is shrinking.
B) total spending (GNE) in the economy is greater than income and is financed by borrowing from abroad.
C) domestic investment cannot be carried out because of a shortage of savings.
D) domestic investment is decreasing.
A) the trade deficit is shrinking.
B) total spending (GNE) in the economy is greater than income and is financed by borrowing from abroad.
C) domestic investment cannot be carried out because of a shortage of savings.
D) domestic investment is decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Net national saving is related to the balance on the current account in the following way:
A) domestic investment = net national saving = the balance on the current account - gross domestic product - gross national expenditure.
B) net national saving = domestic investment + the balance on the current account.
C) net national saving = domestic investment - the balance on the current account.
D) net national saving + the balance on the current account + domestic investment = gross domestic product.
A) domestic investment = net national saving = the balance on the current account - gross domestic product - gross national expenditure.
B) net national saving = domestic investment + the balance on the current account.
C) net national saving = domestic investment - the balance on the current account.
D) net national saving + the balance on the current account + domestic investment = gross domestic product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The current account represents the difference between gross national disposable income and:
A) GDP.
B) GNP.
C) domestic investment spending.
D) GNE.
A) GDP.
B) GNP.
C) domestic investment spending.
D) GNE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If we add the current account balances for every nation, the overall balance will equal:
A) the size of world GDP.
B) spending minus savings.
C) zero.
D) the value added in the manufacturing sectors of each nation.
A) the size of world GDP.
B) spending minus savings.
C) zero.
D) the value added in the manufacturing sectors of each nation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For most countries, the savings trend over the past 30 years has been:
A) upward.
B) steady.
C) downward.
D) downward, but less than the decline in investments.
A) upward.
B) steady.
C) downward.
D) downward, but less than the decline in investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If investment exceeds national savings, then the current account:
A) must be negative.
B) must be zero.
C) must be positive.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.
A) must be negative.
B) must be zero.
C) must be positive.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The balance on the financial account summarizes transactions in:
A) real estate, stocks, bonds, investment, and any financial asset.
B) goods, services, and bartered items.
C) accounting services provided by the big-eight accounting firms.
D) government transfers of currency.
A) real estate, stocks, bonds, investment, and any financial asset.
B) goods, services, and bartered items.
C) accounting services provided by the big-eight accounting firms.
D) government transfers of currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
(Table: Hypothetical Irish National Income and Product Accounts Data) Are Ireland's savings greater or smaller than its investment? 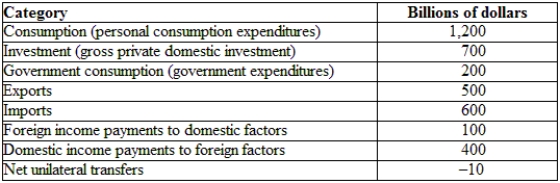
A) greater
B) smaller
C) the same size
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.

A) greater
B) smaller
C) the same size
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The term government saving is defined as:
A) government saving minus taxes.
B) after-tax disposable income minus consumption spending.
C) the difference between tax revenue and government purchases.
D) the inflow of investment funds from abroad.
A) government saving minus taxes.
B) after-tax disposable income minus consumption spending.
C) the difference between tax revenue and government purchases.
D) the inflow of investment funds from abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Government budget deficits and trade deficits tend to move:
A) independently from one another.
B) together.
C) in the opposite directions.
D) independently from one another, except in recessions.
A) independently from one another.
B) together.
C) in the opposite directions.
D) independently from one another, except in recessions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A deficit in the financial account means the nation has:
A) imported more assets than it exported.
B) exported more assets than it imported.
C) saved more than it invested.
D) produced more than it consumed.
A) imported more assets than it exported.
B) exported more assets than it imported.
C) saved more than it invested.
D) produced more than it consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The trend of increasingly older populations in industrialized nations probably has contributed to:
A) the "demographic burden" whereby there is decreased total saving.
B) a spike in spending on leisure activities.
C) an increase in technology and GDP.
D) an increase in tax collections.
A) the "demographic burden" whereby there is decreased total saving.
B) a spike in spending on leisure activities.
C) an increase in technology and GDP.
D) an increase in tax collections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 156 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



