Deck 14: Exchange Rates I: the Monetary Approach in the Long Run
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/162
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Exchange Rates I: the Monetary Approach in the Long Run
1
The idea that with frictionless trade all goods traded internationally will have the same equilibrium price no matter which currency they are priced in is known as:
A) covered interest parity.
B) arbitrage.
C) the law of one price.
D) relativity.
A) covered interest parity.
B) arbitrage.
C) the law of one price.
D) relativity.
C
2
If a pair of Nike shoes cost $45 in New York and $65 in Berlin, then we would expect the price to:
A) drop in New York and increase in Berlin.
B) remain the same in both places.
C) increase in New York and decrease in Berlin.
D) increase in Berlin and stay constant in New York.
A) drop in New York and increase in Berlin.
B) remain the same in both places.
C) increase in New York and decrease in Berlin.
D) increase in Berlin and stay constant in New York.
C
3
Purchasing power parity exists when: I. there are no arbitrage opportunities.
II) prices are the same when expressed in a common currency.
III) the goods in question are identical.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
II) prices are the same when expressed in a common currency.
III) the goods in question are identical.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
D
4
The real exchange rate between two currencies tells us:
A) changes in the exchange rate over time.
B) how many units of one currency can be purchased with one unit of the home currency.
C) how much in terms of goods and services the home currency will buy in the foreign nation compared with the home nation.
D) how much depreciation or appreciation has occurred in the home exchange rate.
A) changes in the exchange rate over time.
B) how many units of one currency can be purchased with one unit of the home currency.
C) how much in terms of goods and services the home currency will buy in the foreign nation compared with the home nation.
D) how much depreciation or appreciation has occurred in the home exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a real exchange rate depreciation occurs, which of the following results?
A) It takes more home goods to purchase the same quantity of foreign goods.
B) It takes fewer home goods to purchase the same quantity of foreign goods.
C) The nominal exchange rate has risen as well.
D) The nominal exchange rate has fallen.
A) It takes more home goods to purchase the same quantity of foreign goods.
B) It takes fewer home goods to purchase the same quantity of foreign goods.
C) The nominal exchange rate has risen as well.
D) The nominal exchange rate has fallen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In equilibrium, all traded goods sell at the same price internationally because of:
A) government direction.
B) arbitrage.
C) markets in which buyers and sellers do not interact.
D) the fact that the underlying value is the same everywhere.
A) government direction.
B) arbitrage.
C) markets in which buyers and sellers do not interact.
D) the fact that the underlying value is the same everywhere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In equilibrium, all traded goods sell at the same price internationally. If the same goods are expressed in their home prices, then the ratio of the prices is equal to:
A) one.
B) zero.
C) the rate of interest.
D) the nominal exchange rate between the two currencies.
A) one.
B) zero.
C) the rate of interest.
D) the nominal exchange rate between the two currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If an automobile costs $32,000 in New York and $1 = 0.8 euros, then under the condition of the law of one price, the cost of the automobile in Rome should be:
A) 32,000 euros.
B) 40,000 euros.
C) 35,000 euros.
D) 25,600 euros.
A) 32,000 euros.
B) 40,000 euros.
C) 35,000 euros.
D) 25,600 euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The relative purchasing power of a currency is:
A) the exchange rate expressed in ounces of gold.
B) the value of one currency in terms of the goods and services a unit will purchase compared with an equivalent amount of another currency.
C) the official value of one nation's currency compared with the official value of another currency.
D) the value of the currency during an economic expansion compared with its value during a recession.
A) the exchange rate expressed in ounces of gold.
B) the value of one currency in terms of the goods and services a unit will purchase compared with an equivalent amount of another currency.
C) the official value of one nation's currency compared with the official value of another currency.
D) the value of the currency during an economic expansion compared with its value during a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The monetary approach to exchange rates describes:
A) long-run relationships between money, prices, and exchange rates.
B) a short-run relationship between exchange rates and interest rates.
C) a short-run measure of fluctuations in exchange rates.
D) a theory based on the idea that exchange rates are constant in the long run.
A) long-run relationships between money, prices, and exchange rates.
B) a short-run relationship between exchange rates and interest rates.
C) a short-run measure of fluctuations in exchange rates.
D) a theory based on the idea that exchange rates are constant in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The law of one price requires:
A) trade frictions.
B) perfect competition.
C) trade frictions and perfect competition.
D) neither trade frictions nor perfect competition.
A) trade frictions.
B) perfect competition.
C) trade frictions and perfect competition.
D) neither trade frictions nor perfect competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If a pound of coffee beans costs 85 pesos in Mexico City and 10 pesos = 35 rupees, then the same pound of coffee should cost _________ rupees in New Delhi, under the condition of the law of one price.
A) 300
B) 297.50
C) 29,750
D) 3,500
A) 300
B) 297.50
C) 29,750
D) 3,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the international goods market, prices of goods in different countries expressed in a common currency must be equalized. This concept is called:
A) exchange rate theory.
B) the law of one price.
C) appreciation.
D) purchasing power parity (PPP).
A) exchange rate theory.
B) the law of one price.
C) appreciation.
D) purchasing power parity (PPP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When the price of a good in the United States is $2, while in Spain it is €2, and the nominal exchange rate is E$/€ = 1.5, what is the relative price of the good in Spain versus the United States?
A) 1
B) 1.5
C) 2/3
D) 1/2
A) 1
B) 1.5
C) 2/3
D) 1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The law of one price works under some assumptions. Which of the following is NOT an assumption for the law of one price?
A) There is free competition.
B) There is no transportation cost.
C) There are no tariffs.
D) The skill level of workers is identical in both countries.
A) There is free competition.
B) There is no transportation cost.
C) There are no tariffs.
D) The skill level of workers is identical in both countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If a basket of goods in the United States costs $1,000, and the same basket of goods in Japan costs ¥125,000, then for PPP to exist, $1 should trade for ____ Japanese yen.
A) 4
B) 50
C) 125
D) 125,000
A) 4
B) 50
C) 125
D) 125,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
While the law of one price relates prices on individual goods to the exchange rate, the theory of PPP relates:
A) the relative price level of a basket of goods to the exchange rate.
B) prices of individual goods to consumer demand.
C) exchange rates to interest rates.
D) goods markets to the market for services.
A) the relative price level of a basket of goods to the exchange rate.
B) prices of individual goods to consumer demand.
C) exchange rates to interest rates.
D) goods markets to the market for services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The nominal exchange rate between two currencies tells us:
A) changes in the exchange rate over time.
B) how many units of one currency can be purchased with one unit of the home currency.
C) how much in terms of goods and services the home currency will buy in the foreign nation compared with the home nation.
D) how much depreciation or appreciation has occurred in the home exchange rate.
A) changes in the exchange rate over time.
B) how many units of one currency can be purchased with one unit of the home currency.
C) how much in terms of goods and services the home currency will buy in the foreign nation compared with the home nation.
D) how much depreciation or appreciation has occurred in the home exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Absolute purchasing power parity implies that:
A) the price of a basket of goods is cheaper in one country than in another.
B) the price of a basket of goods is more expensive in one country than in another.
C) the price of a basket of goods is the same in the two countries.
D) the exchange rate is artificially held constant.
A) the price of a basket of goods is cheaper in one country than in another.
B) the price of a basket of goods is more expensive in one country than in another.
C) the price of a basket of goods is the same in the two countries.
D) the exchange rate is artificially held constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the relative price of a good in Germany versus the United States is 3, if the nominal exchange rate is E$/€ = 1.5 and the U.S. price is $10, what is the German price?
A) €4
B) €15
C) €20
D) €45
A) €4
B) €15
C) €20
D) €45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In equilibrium, with purchasing power parity, the nominal exchange rate will be equal to:
A) the two nations' real exchange rate.
B) the ratio of the two nations' GDPs.
C) the ratio of the two nations' price levels.
D) one.
A) the two nations' real exchange rate.
B) the ratio of the two nations' GDPs.
C) the ratio of the two nations' price levels.
D) one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
With relative PPP, a rise in a nation's inflation rate is always offset by an increase in the rate of __________ of its currency.
A) appreciation
B) revaluation
C) depreciation
D) devaluation
A) appreciation
B) revaluation
C) depreciation
D) devaluation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the situation when a home currency purchases fewer goods and services at home than abroad when converted to a foreign currency?
A) The domestic currency is undervalued.
B) The domestic currency is overvalued.
C) The domestic currency is unstable.
D) The domestic currency is appreciating.
A) The domestic currency is undervalued.
B) The domestic currency is overvalued.
C) The domestic currency is unstable.
D) The domestic currency is appreciating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Absolute PPP and relative PPP differ in what way?
A) Absolute PPP always holds but relative PPP may not.
B) Relative PPP may hold even when absolute PPP does not.
C) Relative and absolute PPP always hold.
D) Absolute PPP relates to changes in inflation and exchange rates, whereas relative PPP relates to their levels.
A) Absolute PPP always holds but relative PPP may not.
B) Relative PPP may hold even when absolute PPP does not.
C) Relative and absolute PPP always hold.
D) Absolute PPP relates to changes in inflation and exchange rates, whereas relative PPP relates to their levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Whenever two nations experience inflation, and the nominal exchange rates move by the same percentage to offset, we say there is:
A) absolute PPP.
B) indeterminate PPP.
C) inverted PPP.
D) relative PPP.
A) absolute PPP.
B) indeterminate PPP.
C) inverted PPP.
D) relative PPP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following situations would exhibit relative PPP?
A) Europe's yearly inflation rate rises from 5% to 7%, ceteris paribus, and the euro-yen rate depreciates by 7%.
B) Europe's yearly inflation rate rises from 5% to 7%, ceteris paribus, and the euro-yen rate depreciates by 2%.
C) Europe's yearly inflation rate rises from 5% to 7%, ceteris paribus, and the euro-yen rate appreciates by 2%.
D) Europe's yearly inflation rate rises from 5% to 7%, ceteris paribus, and the euro-yen rate appreciates by 5%.
A) Europe's yearly inflation rate rises from 5% to 7%, ceteris paribus, and the euro-yen rate depreciates by 7%.
B) Europe's yearly inflation rate rises from 5% to 7%, ceteris paribus, and the euro-yen rate depreciates by 2%.
C) Europe's yearly inflation rate rises from 5% to 7%, ceteris paribus, and the euro-yen rate appreciates by 2%.
D) Europe's yearly inflation rate rises from 5% to 7%, ceteris paribus, and the euro-yen rate appreciates by 5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
D) 1/PPP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When the Japanese inflation rate is less than the Australian inflation rate, Japanese prices are:
A) rising faster than Australian prices.
B) rising more slowly than Australian prices.
C) rising at the same rate as Australian prices.
D) not rising.
A) rising faster than Australian prices.
B) rising more slowly than Australian prices.
C) rising at the same rate as Australian prices.
D) not rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the situation when a home currency purchases more goods and services at home than abroad when converted to a foreign currency?
A) The domestic currency is undervalued.
B) The domestic currency is overvalued.
C) The domestic currency is unstable.
D) The domestic currency is depreciating.
A) The domestic currency is undervalued.
B) The domestic currency is overvalued.
C) The domestic currency is unstable.
D) The domestic currency is depreciating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Whenever the absolute purchasing power of two currencies is the same, the real exchange rate between them is equal to:
A) zero.
B) one.
C)
A) zero.
B) one.
C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a nation experiences 10% inflation and its trading partner does not, and if PPP holds, what happens to its nominal exchange rate?
A) It depreciates by 10%.
B) It appreciates by 10%.
C) It does not change.
D) It becomes negative.
A) It depreciates by 10%.
B) It appreciates by 10%.
C) It does not change.
D) It becomes negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the prices of goods in Europe increase, while the nominal exchange rate between the euro and the U.S. dollar remains the same, we say that the U.S. dollar has experienced a:
A) nominal appreciation.
B) nominal depreciation.
C) real appreciation.
D) real depreciation.
A) nominal appreciation.
B) nominal depreciation.
C) real appreciation.
D) real depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If a nation experiences 10% inflation and its trading partner does not, and if PPP holds, what happens to its real exchange rate?
A) It depreciates by 10%.
B) It appreciates by 10%.
C) It does not change.
D) It becomes negative.
A) It depreciates by 10%.
B) It appreciates by 10%.
C) It does not change.
D) It becomes negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If more home goods are required to buy the same amount of foreign goods, then we say that foreign currency has experienced a:
A) nominal appreciation.
B) nominal depreciation.
C) real appreciation.
D) real depreciation.
A) nominal appreciation.
B) nominal depreciation.
C) real appreciation.
D) real depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When the inflation rate in any nation changes, ceteris paribus:
A) only absolute PPP is disturbed.
B) only relative PPP is disturbed.
C) both absolute and relative PPP are disturbed.
D) the inflation rates in other nations will have to change as well.
A) only absolute PPP is disturbed.
B) only relative PPP is disturbed.
C) both absolute and relative PPP are disturbed.
D) the inflation rates in other nations will have to change as well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Evidence on the existence of relative PPP shows that:
A) the evidence for relative PPP is scanty and the theory is largely discredited.
B) the evidence for relative PPP is hit or miss, and so one should exercise caution in using relative PPP to predict changes in a nation's exchange rates.
C) relative PPP is an approximate guide to predicting the relationship between changes in inflation and exchange rates over long periods, such as decades.
D) both absolute and relative PPP hold nearly perfectly in the short and long run, and are used with great accuracy to make predictions.
A) the evidence for relative PPP is scanty and the theory is largely discredited.
B) the evidence for relative PPP is hit or miss, and so one should exercise caution in using relative PPP to predict changes in a nation's exchange rates.
C) relative PPP is an approximate guide to predicting the relationship between changes in inflation and exchange rates over long periods, such as decades.
D) both absolute and relative PPP hold nearly perfectly in the short and long run, and are used with great accuracy to make predictions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Under what circumstances would there be a "no-arbitrage" situation in goods markets between two nations?
A) when one of the currencies is undervalued
B) when one of the currencies is overvalued
C) when both of the currencies are overvalued
D) when the relative price of the currencies is equal to one
A) when one of the currencies is undervalued
B) when one of the currencies is overvalued
C) when both of the currencies are overvalued
D) when the relative price of the currencies is equal to one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If fewer home goods are required to buy the same amount of foreign goods, then we say that foreign currency has experienced a:
A) nominal appreciation.
B) nominal depreciation.
C) real appreciation.
D) real depreciation.
A) nominal appreciation.
B) nominal depreciation.
C) real appreciation.
D) real depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a real exchange rate appreciation occurs, which of the following results?
A) It takes more home goods to purchase the same quantity of foreign goods.
B) It takes fewer home goods to purchase the same quantity of foreign goods.
C) The nominal exchange rate has risen as well.
D) The nominal exchange rate has fallen.
A) It takes more home goods to purchase the same quantity of foreign goods.
B) It takes fewer home goods to purchase the same quantity of foreign goods.
C) The nominal exchange rate has risen as well.
D) The nominal exchange rate has fallen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When the Chinese yuan is appreciating against the U.S. dollar, if relative PPP holds, then this suggests that the U.S. inflation rate:
A) exceeds the Chinese inflation rate.
B) equals the Chinese inflation rate.
C) exceeds the Chinese interest rate.
D) equals the Chinese interest rate.
A) exceeds the Chinese inflation rate.
B) equals the Chinese inflation rate.
C) exceeds the Chinese interest rate.
D) equals the Chinese interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When the law of one price holds for all goods and services, the real exchange rate is always equal to:
A) one.
B) the nominal exchange rate.
C) relative prices across countries.
D) 1/nominal exchange rate.
A) one.
B) the nominal exchange rate.
C) relative prices across countries.
D) 1/nominal exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the Big Mac Index?
A) It is a price index for the top 20 stocks traded internationally.
B) It reflects inflation trends through trade in laptop computers and international price competition.
C) It is an index of the price of McDonald's hamburgers quoted in one currency designed to measure whether absolute PPP holds for Big Macs.
D) It is a measure of unemployment in the service industries of poor nations where Western retailers such as McDonalds have infiltrated.
A) It is a price index for the top 20 stocks traded internationally.
B) It reflects inflation trends through trade in laptop computers and international price competition.
C) It is an index of the price of McDonald's hamburgers quoted in one currency designed to measure whether absolute PPP holds for Big Macs.
D) It is a measure of unemployment in the service industries of poor nations where Western retailers such as McDonalds have infiltrated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Globalization trends may ____ the tendency for prices to converge.
A) retard
B) speed up
C) eliminate
D) render irrelevant
A) retard
B) speed up
C) eliminate
D) render irrelevant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How could conditions of imperfect competition explain deviations from PPP?
A) Imperfect competition means that prices are higher than costs and may not converge.
B) Governments often restrict trade in those goods.
C) Goods sold under conditions of imperfect competition are often inferior.
D) Arbitrageurs do not recognize profit opportunities in these markets.
A) Imperfect competition means that prices are higher than costs and may not converge.
B) Governments often restrict trade in those goods.
C) Goods sold under conditions of imperfect competition are often inferior.
D) Arbitrageurs do not recognize profit opportunities in these markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The data on exchange rate and price-level fluctuations in the United States and the United Kingdom from 1975 to 2010 suggest that:
A) absolute and relative PPP hold in the long run.
B) absolute and relative PPP hold in the short run.
C) absolute and relative PPP do not hold in the long run.
D) It is impossible to determine the relationship between inflation and exchange rates between the two nations.
A) absolute and relative PPP hold in the long run.
B) absolute and relative PPP hold in the short run.
C) absolute and relative PPP do not hold in the long run.
D) It is impossible to determine the relationship between inflation and exchange rates between the two nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
(Table: Exchange Rates and Prices) Suppose a computer costs $500 in the United States. If PPP were to hold at the given nominal exchange rate, then the price of a computer in South Africa would be _____ rands. 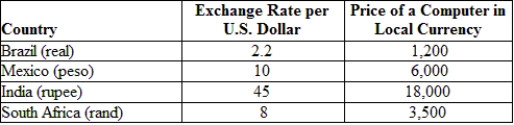
A) 4,000
B) 40
C) 800
D) 8,000

A) 4,000
B) 40
C) 800
D) 8,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
(Table: Exchange Rates and Prices) Suppose a computer costs $500 in the United States. With the price of the computer given in local currency, the Indian rupee is: 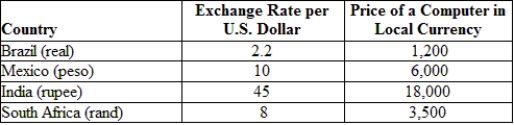
A) overvalued by 9.1%.
B) overvalued by 20%.
C) undervalued by 12.5%.
D) undervalued by 20%.

A) overvalued by 9.1%.
B) overvalued by 20%.
C) undervalued by 12.5%.
D) undervalued by 20%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Evidence suggests that convergence to PPP occurs:
A) instantly, as arbitrageurs take advantage of profit opportunities.
B) rapidly, as arbitrageurs learn of profit opportunities.
C) slowly, as arbitrageurs operate, and production, prices, and exchange rates adjust.
D) never.
A) instantly, as arbitrageurs take advantage of profit opportunities.
B) rapidly, as arbitrageurs learn of profit opportunities.
C) slowly, as arbitrageurs operate, and production, prices, and exchange rates adjust.
D) never.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Short-run PPP may not hold for a variety of reasons. Which of the following is NOT cited in your textbook as one of those reasons?
A) weather and other environmental conditions that affect trade
B) transactions costs
C) nontraded goods
D) imperfect competition and price stickiness
A) weather and other environmental conditions that affect trade
B) transactions costs
C) nontraded goods
D) imperfect competition and price stickiness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
As economies adjust to inflation, there is an adjustment of exchange rates to reflect the changed price level. This adjustment is called:
A) real exchange rates.
B) convergence.
C) adjustment costs.
D) revaluation.
A) real exchange rates.
B) convergence.
C) adjustment costs.
D) revaluation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
(Table: Exchange Rates and Prices) Suppose a computer costs $500 in the United States. According to the information provided, under conditions of PPP, the price of a computer should be ____ reals in Brazil. 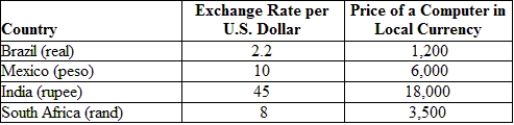
A) 2,200
B) 1,200
C) 1,100
D) 550

A) 2,200
B) 1,200
C) 1,100
D) 550

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following statements is NOT a reason for explaining the deviations from PPP?
A) Some goods are not tradeable.
B) Markets are imperfect and there could be legal obstacles.
C) Prices can be sticky in different countries.
D) There are no transportation costs.
A) Some goods are not tradeable.
B) Markets are imperfect and there could be legal obstacles.
C) Prices can be sticky in different countries.
D) There are no transportation costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Economists have developed models to predict changes in exchange rates based on inflation trends. To guide forecasts of exchange rates, economists calculate the average:
A) speed of convergence.
B) PPP.
C) interest parity.
D) price deviation.
A) speed of convergence.
B) PPP.
C) interest parity.
D) price deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
(Table: Exchange Rates and Prices) Suppose a computer costs $500 in the United States. With the price of the computer given in the local currency, the South African rand is _______. 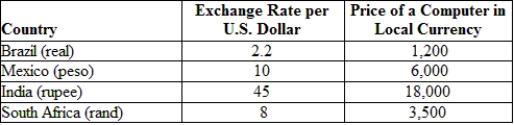
A) undervalued by 12.0%
B) overvalued by 3.0%
C) undervalued by 12.5%
D) undervalued by 1.25%

A) undervalued by 12.0%
B) overvalued by 3.0%
C) undervalued by 12.5%
D) undervalued by 1.25%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The half-life of a PPP divergence indicates how long it takes:
A) to disappear.
B) for half of it to disappear.
C) to appear.
D) to reach half its greatest value.
A) to disappear.
B) for half of it to disappear.
C) to appear.
D) to reach half its greatest value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
(Table: Exchange Rates and Prices) Suppose a computer costs $500 in the United States. With the price of the computer given in the local currency, the Brazilian real is _______. 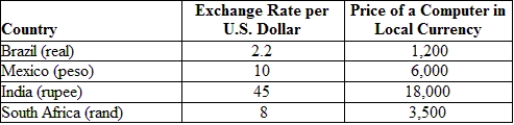
A) undervalued by 22%.
B) undervalued by 12%.
C) overvalued by 9.1%.
D) overvalued by 20%.

A) undervalued by 22%.
B) undervalued by 12%.
C) overvalued by 9.1%.
D) overvalued by 20%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An example of a nontraded product would be:
A) corn.
B) haircuts.
C) shoes.
D) aircraft.
A) corn.
B) haircuts.
C) shoes.
D) aircraft.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
(Table: Exchange Rates and Prices) Suppose a computer costs $500 in the United States. If PPP were to hold at the given nominal exchange rate, then the price of a computer in Mexico would be _____ pesos. 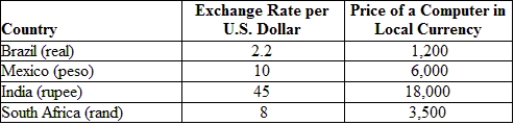
A) 500
B) 50
C) 5,000
D) 0.02

A) 500
B) 50
C) 5,000
D) 0.02

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The half-life of PPP deviations is about:
A) four months.
B) four quarters.
C) four years.
D) four decades.
A) four months.
B) four quarters.
C) four years.
D) four decades.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Price stickiness refers to:
A) slow movements in prices.
B) the sticker price for big-ticket items.
C) the price of oil.
D) the price of a Big Mac across countries.
A) slow movements in prices.
B) the sticker price for big-ticket items.
C) the price of oil.
D) the price of a Big Mac across countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Better communication technology has made it easier to conduct ____ in international markets, thus ____ exchange rate adjustments to economic conditions and inflation.
A) open market operations; eliminating
B) arbitrage; speeding up
C) sales and purchases of currency; slowing down
D) portfolio investment; fundamentally changing
A) open market operations; eliminating
B) arbitrage; speeding up
C) sales and purchases of currency; slowing down
D) portfolio investment; fundamentally changing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Assume nominal GDP = PY, and 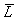 = the proportion of nominal income that the nation holds (demands) as money to cover its transactions. Because nominal money supply equals nominal money demand, then:
= the proportion of nominal income that the nation holds (demands) as money to cover its transactions. Because nominal money supply equals nominal money demand, then:
A) increases in nominal income cause an increase in the money supply.
B) decreases in nominal income cause an increase in the money supply.
C) price increases cause an increase in the money supply.
D) an increase in the money supply causes a proportional increase in nominal income.
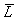 = the proportion of nominal income that the nation holds (demands) as money to cover its transactions. Because nominal money supply equals nominal money demand, then:
= the proportion of nominal income that the nation holds (demands) as money to cover its transactions. Because nominal money supply equals nominal money demand, then:A) increases in nominal income cause an increase in the money supply.
B) decreases in nominal income cause an increase in the money supply.
C) price increases cause an increase in the money supply.
D) an increase in the money supply causes a proportional increase in nominal income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The entity in any nation that accurately controls directly or indirectly the supply of money is referred to as the:
A) executive branch.
B) central bank.
C) treasury.
D) legislative branch.
A) executive branch.
B) central bank.
C) treasury.
D) legislative branch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The MOST restrictive measurement of money is:
A) M0.
B) M1.
C) M2.
D) M3.
A) M0.
B) M1.
C) M2.
D) M3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the quantity theory of money, the demand for money is equal to:
A) nominal income divided by real income.
B) a constant proportion of nominal income.
C) the demand for money held as an asset.
D) real income divided by velocity.
A) nominal income divided by real income.
B) a constant proportion of nominal income.
C) the demand for money held as an asset.
D) real income divided by velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If money growth is bigger than income growth, then we can expect:
A) unemployment to increase.
B) inflation to decrease.
C) inflation to increase.
D) inflation and unemployment to decrease.
A) unemployment to increase.
B) inflation to decrease.
C) inflation to increase.
D) inflation and unemployment to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Currency is a part of which measure of money?
A) M0 only
B) M1 only
C) M2 only
D) M0, M1, and M2
A) M0 only
B) M1 only
C) M2 only
D) M0, M1, and M2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If prices are held constant and income increases by 12%, the demand for money will:
A) decrease by 21%.
B) increase by 12%.
C) decrease by 12%.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.
A) decrease by 21%.
B) increase by 12%.
C) decrease by 12%.
D) Not enough information is provided to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Money's function as a medium of exchange is important because:
A) if there were no money, there would be no common unit of account.
B) if there were no money, society's wealth would be zero.
C) it eliminates the need for inefficient barter.
D) if there were no money, exchanges would be impossible.
A) if there were no money, there would be no common unit of account.
B) if there were no money, society's wealth would be zero.
C) it eliminates the need for inefficient barter.
D) if there were no money, exchanges would be impossible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A nation with greater income, ceteris paribus, will have:
A) lower prices.
B) higher prices.
C) lower money supply.
D) higher prices and higher money supply.
A) lower prices.
B) higher prices.
C) lower money supply.
D) higher prices and higher money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If nominal income in a nation decreases, economists would predict the:
A) supply of money will rise.
B) demand for money will rise.
C) supply of money will decrease.
D) demand for money will decrease.
A) supply of money will rise.
B) demand for money will rise.
C) supply of money will decrease.
D) demand for money will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The price level in the country is determined by ______ and _______.
A) nominal money supply; demand for real money
B) demand for real money; average tax rate
C) demand for real money; growth of GDP
D) supply of real money; demand for real money
A) nominal money supply; demand for real money
B) demand for real money; average tax rate
C) demand for real money; growth of GDP
D) supply of real money; demand for real money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The demand for real money balances is:
A) proportional to nominal income.
B) proportional to real income.
C) disproportional to real GDP.
D) determined by the real rate of interest.
A) proportional to nominal income.
B) proportional to real income.
C) disproportional to real GDP.
D) determined by the real rate of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Money can be defined:
A) only as a unit of account.
B) only as a store of value.
C) only as a medium of exchange.
D) as a unit of account, a store of value, and a medium of exchange.
A) only as a unit of account.
B) only as a store of value.
C) only as a medium of exchange.
D) as a unit of account, a store of value, and a medium of exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The broad measure of money is referred to as:
A) M0.
B) M1.
C) M2.
D) M3.
A) M0.
B) M1.
C) M2.
D) M3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
According to the long-run monetary model, we can rearrange terms in the money demand/supply in our long-run relationship to show that when the nominal supply of money is increased, ceteris paribus:
A) the demand for money is decreased.
B) the price level is increased.
C) real income is increased.
D) the price level is decreased.
A) the demand for money is decreased.
B) the price level is increased.
C) real income is increased.
D) the price level is decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The M1 measure of money includes demand deposits but excludes:
A) currency in circulation.
B) Federal Reserve notes.
C) travelers' checks.
D) bank reserves.
A) currency in circulation.
B) Federal Reserve notes.
C) travelers' checks.
D) bank reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If we adjust the supply of money for changes in the price level, we get real balances. The demand for real balances is proportional to:
A) real GDP.
B) the unemployment rate.
C) the population.
D) the exchange rate.
A) real GDP.
B) the unemployment rate.
C) the population.
D) the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The criterion for including an asset in any measure of money is whether it is:
A) used for transactions and highly liquid.
B) used as a store of value.
C) used as collateral for loans.
D) stable and durable.
A) used for transactions and highly liquid.
B) used as a store of value.
C) used as collateral for loans.
D) stable and durable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In general, monetary economic theory states that the demand for money is proportional to:
A) nominal income.
B) the unemployment rate.
C) the population.
D) the exchange rate.
A) nominal income.
B) the unemployment rate.
C) the population.
D) the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



