Deck 11: International Agreements: Trade, Labor, and the Environment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/173
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: International Agreements: Trade, Labor, and the Environment
1
The WTO is considered a _____, whereas NAFTA and the European Union are _____.
A) free-trade area; cartels
B) cartel; multilateral agreements
C) free-trade area; multilateral agreements
D) multilateral agreement; regional trade agreements
A) free-trade area; cartels
B) cartel; multilateral agreements
C) free-trade area; multilateral agreements
D) multilateral agreement; regional trade agreements
D
2
In the large-country case, when a tariff is imposed, the country:
A) sees a terms-of-trade gain.
B) is able to increase the world price of the imported good.
C) is going to experience an increase in consumer surplus.
D) is going to experience a decrease in producer surplus.
A) sees a terms-of-trade gain.
B) is able to increase the world price of the imported good.
C) is going to experience an increase in consumer surplus.
D) is going to experience a decrease in producer surplus.
A
3
(Figure: The Home and World Markets) If a tariff of $10 is imposed by the home country, it causes a loss in the world market (exclusive of any effects on the home market) of: 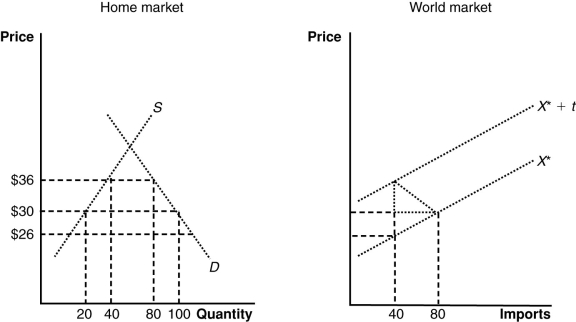
A) $240.
B) $160.
C) $200.
D) $80.

A) $240.
B) $160.
C) $200.
D) $80.
A
4
(Figure: The Home and World Markets) The graphs show the case for a tariff imposed by a large country. According to these graphs, if the world price of the product is given as $30, then home market firms will produce _____ and the total demand for the good will be _____. 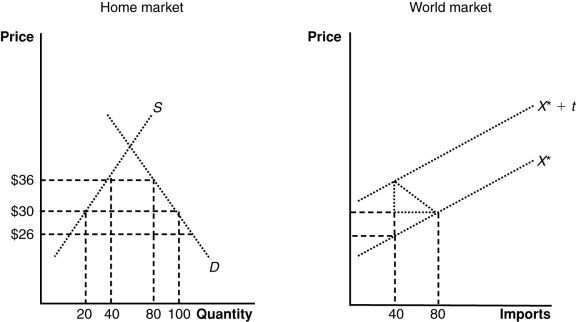
A) 40; 100
B) 20; 80
C) 20; 100
D) 40; 80

A) 40; 100
B) 20; 80
C) 20; 100
D) 40; 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Most proposed free-trade areas currently under consideration are a response to:
A) the failure of the Doha Round.
B) the success of the Kyoto agreement.
C) the failure of COP21.
D) the success of NAFTA.
A) the failure of the Doha Round.
B) the success of the Kyoto agreement.
C) the failure of COP21.
D) the success of NAFTA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Many regional trade agreements include other provisions that are not part of the treaty, but they are add-ons that might be important to trade issues. These are called:
A) addenda.
B) side agreements.
C) environmental pacts.
D) worker rights documents.
A) addenda.
B) side agreements.
C) environmental pacts.
D) worker rights documents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
(Figure: The Home and World Markets) The loss of consumer surplus in the home country is: 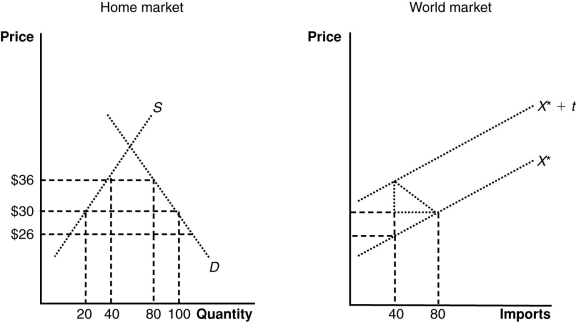
A) $480.
B) $540.
C) $160.
D) $600.

A) $480.
B) $540.
C) $160.
D) $600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a large-country case, an optimal tariff is one for which the terms-of-trade gain exceeds the:
A) producer surplus.
B) increased price of the product imported.
C) deadweight loss.
D) consumer surplus.
A) producer surplus.
B) increased price of the product imported.
C) deadweight loss.
D) consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When a large nation imposes a tariff, which of the following is NOT a cost incurred?
A) deadweight efficiency loss
B) reduced consumer surplus
C) deterioration of terms of trade for the trading partners
D) falling government revenues for the nation imposing the tariff
A) deadweight efficiency loss
B) reduced consumer surplus
C) deterioration of terms of trade for the trading partners
D) falling government revenues for the nation imposing the tariff

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The WTO is a _____, involving many countries, with an agreement to lower tariffs between all members.
A) bilateral trade organization
B) trilateral trade organization
C) multilateral trade organization
D) quasipolitical organization
A) bilateral trade organization
B) trilateral trade organization
C) multilateral trade organization
D) quasipolitical organization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is COP21?
A) an agreement negotiated in Copenhagen that resulted in developed countries immediately eliminating agricultural export subsidies
B) an agreement negotiated in Paris in which countries committed to develop plans to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases
C) an agreement negotiated in Kyoto, Japan, in which countries agreed to further reduce their trade barriers
D) an agreement negotiated in Doha, Qatar, in which countries agreed to reduce their agricultural export subsidies
A) an agreement negotiated in Copenhagen that resulted in developed countries immediately eliminating agricultural export subsidies
B) an agreement negotiated in Paris in which countries committed to develop plans to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases
C) an agreement negotiated in Kyoto, Japan, in which countries agreed to further reduce their trade barriers
D) an agreement negotiated in Doha, Qatar, in which countries agreed to reduce their agricultural export subsidies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
(Figure: The Home and World Markets) The terms-of-trade gain is _____, and the deadweight loss is _____. 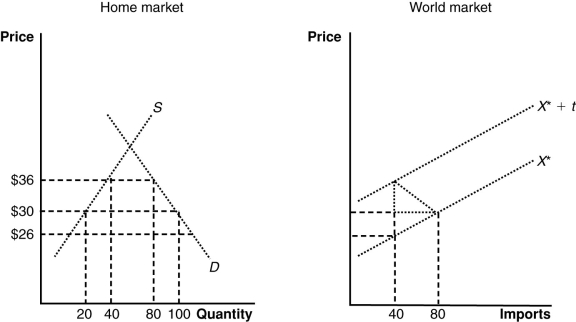
A) $120; $160
B) $160; $160
C) $160; $120
D) $120; $120

A) $120; $160
B) $160; $160
C) $160; $120
D) $120; $120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose that a large country imposes optimal tariffs on imports from another large country. The second country then responds with optimal tariffs on imports from the first country. For these two countries, the Nash equilibrium results in _____ for the first country and _____ for the second country.
A) losses; losses
B) gains; gains
C) losses; gains
D) gains; losses
A) losses; losses
B) gains; gains
C) losses; gains
D) gains; losses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is an effect of an international trade agreement that provides an incentive for nations NOT to impose tariffs?
A) an increase in world welfare and standard of living
B) an opportunity for small countries to improve their terms of trade
C) an opportunity for large countries to improve their terms of trade
D) an opportunity for low-income nations to receive foreign aid
A) an increase in world welfare and standard of living
B) an opportunity for small countries to improve their terms of trade
C) an opportunity for large countries to improve their terms of trade
D) an opportunity for low-income nations to receive foreign aid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A regional trade agreement involves:
A) most, if not all, of the nations in the world.
B) several nations, usually trading partners, with a common agenda or geographically linked.
C) nations that agree to trade only with nations in their region.
D) a region of the world with not only trade issues but also political cohesiveness.
A) most, if not all, of the nations in the world.
B) several nations, usually trading partners, with a common agenda or geographically linked.
C) nations that agree to trade only with nations in their region.
D) a region of the world with not only trade issues but also political cohesiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In a large-country case, an optimal tariff would be one:
A) that increases the producer surplus.
B) that raises the price of the product imported.
C) in which the terms-of-trade gain exceeds the deadweight loss.
D) that easily passes the legislative process.
A) that increases the producer surplus.
B) that raises the price of the product imported.
C) in which the terms-of-trade gain exceeds the deadweight loss.
D) that easily passes the legislative process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a regional trade agreement currently (2016) under consideration?
A) Mercosur-a trade agreement among Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay
B) the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership
C) the North American Free Trade Area
D) the United States-Japan Free Trade Area
A) Mercosur-a trade agreement among Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay
B) the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership
C) the North American Free Trade Area
D) the United States-Japan Free Trade Area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What happens when two countries apply tariffs against each other in an attempt to capture their terms-of-trade gain?
A) Both countries lose because the terms-of-trade gain for one country is canceled by the tariff in the other country.
B) Both countries gain because the terms-of-trade gain for one country is canceled by the tariff in the other country.
C) Neither country gains nor loses because the terms-of-trade gain for one country is canceled by the tariff in the other country.
D) The country initially applying the tariff gains because it captures the terms-of-trade gain; the other country neither gains nor loses.
A) Both countries lose because the terms-of-trade gain for one country is canceled by the tariff in the other country.
B) Both countries gain because the terms-of-trade gain for one country is canceled by the tariff in the other country.
C) Neither country gains nor loses because the terms-of-trade gain for one country is canceled by the tariff in the other country.
D) The country initially applying the tariff gains because it captures the terms-of-trade gain; the other country neither gains nor loses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The "most favored nation principle" means that member countries:
A) can enter into exclusive favorable agreements with some countries.
B) are barred from forming agreements outside their geographic vicinity.
C) must apply the same low tariffs to all WTO member countries.
D) must apply differential tariffs on imports from non-WTO countries.
A) can enter into exclusive favorable agreements with some countries.
B) are barred from forming agreements outside their geographic vicinity.
C) must apply the same low tariffs to all WTO member countries.
D) must apply differential tariffs on imports from non-WTO countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the "most favored nation" principle of the WTO?
A) Trading partners may choose a favorite nation to trade with.
B) Any nation can refuse to trade with another that is not its most favored nation.
C) The WTO has the right to choose the nation that has performed best within the WTO guidelines as its most favored nation.
D) Every nation must grant the same rights and treatment to other nations in the WTO as its "most favored nation."
A) Trading partners may choose a favorite nation to trade with.
B) Any nation can refuse to trade with another that is not its most favored nation.
C) The WTO has the right to choose the nation that has performed best within the WTO guidelines as its most favored nation.
D) Every nation must grant the same rights and treatment to other nations in the WTO as its "most favored nation."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which is a better outcome for income and standard of living levels for large nations?
A) no tariffs
B) low tariffs
C) high tariffs
D) equal tariffs for all nations
A) no tariffs
B) low tariffs
C) high tariffs
D) equal tariffs for all nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A customs union is a trade agreement in which:
A) member countries are free to set their separate tariffs on other countries.
B) members agree to set the same tariffs on nonmembers.
C) resources are free to move between member countries.
D) member countries have common currency.
A) member countries are free to set their separate tariffs on other countries.
B) members agree to set the same tariffs on nonmembers.
C) resources are free to move between member countries.
D) member countries have common currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Following the demise of the Doha Round, the WTO changed its agenda to focus on:
A) trade in services.
B) patent protection for pharmaceutical drugs.
C) achievable smaller packages of reforms.
D) fostering discussions of trade liberalization between free-trade areas.
A) trade in services.
B) patent protection for pharmaceutical drugs.
C) achievable smaller packages of reforms.
D) fostering discussions of trade liberalization between free-trade areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following agreements signed in 1989 is the precursor to NAFTA?
A) the United States-Mexico Free Trade Agreement
B) the Canada-Mexico Free Trade Agreement
C) the Canada-United States Free Trade Agreement
D) the Canada-Mexico-United States Free Trade Agreement
A) the United States-Mexico Free Trade Agreement
B) the Canada-Mexico Free Trade Agreement
C) the Canada-United States Free Trade Agreement
D) the Canada-Mexico-United States Free Trade Agreement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is often used to describe regional trade agreements that discriminate, giving better tariff treatment to other nations in the agreement over outside nations?
A) super-regionals
B) preferential trade agreements
C) exclusive trade arrangements
D) equity trade agreements
A) super-regionals
B) preferential trade agreements
C) exclusive trade arrangements
D) equity trade agreements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An example of the WTO's changed agenda is:
A) NAFTA.
B) the Nairobi agreement on agricultural export subsidies.
C) COP21.
D) allowing greater use of safeguard provisions of the GATT.
A) NAFTA.
B) the Nairobi agreement on agricultural export subsidies.
C) COP21.
D) allowing greater use of safeguard provisions of the GATT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is part of the NAFTA?
A) tariff elimination on trade among Canada, Mexico, and the United States
B) establishment of common tariffs applied to nonmember countries
C) partnering with the European Union to reduce tariffs
D) elimination of restrictions on labor mobility among the three countries
A) tariff elimination on trade among Canada, Mexico, and the United States
B) establishment of common tariffs applied to nonmember countries
C) partnering with the European Union to reduce tariffs
D) elimination of restrictions on labor mobility among the three countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which principle of the GATT/WTO do regional trade agreements violate?
A) the principle of first mover
B) the targeting principle
C) the most favored nation principle
D) the principle of comparative advantage
A) the principle of first mover
B) the targeting principle
C) the most favored nation principle
D) the principle of comparative advantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A free-trade area is:
A) a group of countries that agrees there will be "no rules" about trade-anything goes.
B) a group of countries that agrees to eliminate customs fees and containerized shipping charges on goods traded among them.
C) a group of countries that agrees to eliminate barriers to trade between themselves while keeping their separate tariffs in place against the rest of the world.
D) a group of countries that eliminates trade barriers among themselves and establishes common tariffs against all other nations.
A) a group of countries that agrees there will be "no rules" about trade-anything goes.
B) a group of countries that agrees to eliminate customs fees and containerized shipping charges on goods traded among them.
C) a group of countries that agrees to eliminate barriers to trade between themselves while keeping their separate tariffs in place against the rest of the world.
D) a group of countries that eliminates trade barriers among themselves and establishes common tariffs against all other nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A customs union is:
A) a group of countries that agrees there will be "no rules" about trade-anything goes.
B) a group of countries that agrees to eliminate customs fees and containerized shipping charges on goods traded among them.
C) a group of countries agreeing to eliminate barriers to trade among themselves but keeping tariffs in place against the rest of the world.
D) a group of countries that eliminates trade barriers among themselves and erects a common tariff against all other nations.
A) a group of countries that agrees there will be "no rules" about trade-anything goes.
B) a group of countries that agrees to eliminate customs fees and containerized shipping charges on goods traded among them.
C) a group of countries agreeing to eliminate barriers to trade among themselves but keeping tariffs in place against the rest of the world.
D) a group of countries that eliminates trade barriers among themselves and erects a common tariff against all other nations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
It can be shown that the Nash equilibrium would indicate that without any agreements, the best outcome for each large nation would be to:
A) not impose a tariff.
B) impose a tariff.
C) find other ways to reward their domestic firms.
D) impose a consumption tax.
A) not impose a tariff.
B) impose a tariff.
C) find other ways to reward their domestic firms.
D) impose a consumption tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The WTO (under the GATT agreement) provides that nations may enter into regional trade agreements as long as they:
A) limit such agreements to one.
B) extend the provisions to all other nations in the WTO.
C) do not jointly increase tariffs against outside countries.
D) make sure they include smaller nations in their regions.
A) limit such agreements to one.
B) extend the provisions to all other nations in the WTO.
C) do not jointly increase tariffs against outside countries.
D) make sure they include smaller nations in their regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Using game theory as an analytical tool, if one large nation imposes tariffs, the total cost is small; however, when several trading partners do the same:
A) the costs are even smaller.
B) the costs balance out and there is no harm.
C) the costs are the same but the potential gains are much smaller.
D) then all nations gain.
A) the costs are even smaller.
B) the costs balance out and there is no harm.
C) the costs are the same but the potential gains are much smaller.
D) then all nations gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements characterizes NAFTA's economic arrangements among its member countries (Canada, Mexico, and the United States)?
A) There are no restrictions on the movement of labor from one country to another.
B) There are no restrictions on the movement of capital from one country to another.
C) All three countries have adopted the same identical tariff system.
D) There is free trade among the three member countries.
A) There are no restrictions on the movement of labor from one country to another.
B) There are no restrictions on the movement of capital from one country to another.
C) All three countries have adopted the same identical tariff system.
D) There is free trade among the three member countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A "prisoner's dilemma" can arise when:
A) two large countries simultaneously and independently apply tariffs on imports from each other.
B) two large countries simultaneously and independently eliminate tariffs on imports from each other.
C) one large country eliminates tariffs on imports from another large country.
D) one small country eliminates tariffs on imports from a large country.
A) two large countries simultaneously and independently apply tariffs on imports from each other.
B) two large countries simultaneously and independently eliminate tariffs on imports from each other.
C) one large country eliminates tariffs on imports from another large country.
D) one small country eliminates tariffs on imports from a large country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the main difference between a customs union and a free-trade area?
A) There are no restrictions on the movement of labor and capital among customs union member countries, whereas labor and capital cannot move freely among free-trade member countries.
B) Customs union member countries adopt common tariffs against nonmembers, whereas free-trade area member countries maintain their separate tariff structures against nonmembers.
C) There is free trade among customs union member countries but not among free-trade area member countries.
D) Customs union member countries have adopted a common currency, whereas free-trade member countries use their separate national currencies.
A) There are no restrictions on the movement of labor and capital among customs union member countries, whereas labor and capital cannot move freely among free-trade member countries.
B) Customs union member countries adopt common tariffs against nonmembers, whereas free-trade area member countries maintain their separate tariff structures against nonmembers.
C) There is free trade among customs union member countries but not among free-trade area member countries.
D) Customs union member countries have adopted a common currency, whereas free-trade member countries use their separate national currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following statements about the European Union (EU) is correct?
A) EU member countries maintain separate tariff schedules.
B) There is free trade among EU member countries.
C) All EU member countries use a common currency (the euro).
D) All EU member countries have eliminated tariffs on imports from non-EU member countries.
A) EU member countries maintain separate tariff schedules.
B) There is free trade among EU member countries.
C) All EU member countries use a common currency (the euro).
D) All EU member countries have eliminated tariffs on imports from non-EU member countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In a prisoner's dilemma:
A) all competing parties gain.
B) one competitor gains at the expense of another.
C) all competing parties lose.
D) one competitor loses.
A) all competing parties gain.
B) one competitor gains at the expense of another.
C) all competing parties lose.
D) one competitor loses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In which type of trade agreement does the WTO allow exclusions to the most favored nation principle?
A) multilateral trade agreements
B) free-trade areas and customs unions
C) multilateral trade agreements and free-trade areas
D) customs unions and multilateral trade agreements
A) multilateral trade agreements
B) free-trade areas and customs unions
C) multilateral trade agreements and free-trade areas
D) customs unions and multilateral trade agreements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Of the following, which is NOT a regional trade agreement?
A) the World Trade Organization
B) the European Union
C) the North American Free Trade Agreement
D) the Central American Free Trade Agreement
A) the World Trade Organization
B) the European Union
C) the North American Free Trade Agreement
D) the Central American Free Trade Agreement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
It has been estimated that NAFTA increased U.S. GDP by _____ percentage point(s) relative to what it would have been had NAFTA not existed.
A) 1
B) 10
C) 25
D) 50
A) 1
B) 10
C) 25
D) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Implementing a regional free-trade agreement may have an effect in which, due to reduced tariffs, a nation in the agreement begins to import a product it had previously produced itself. This effect is called:
A) trade creation.
B) trade diversion.
C) reciprocal trade agreements.
D) the employment effect of FTAs.
A) trade creation.
B) trade diversion.
C) reciprocal trade agreements.
D) the employment effect of FTAs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What complex set of free-trade area regulations prohibits nonmember country imports to a high-tariff member country via a low-tariff member country?
A) environmental certification
B) rules of origin
C) health and safety standards
D) a codified trade agreement
A) environmental certification
B) rules of origin
C) health and safety standards
D) a codified trade agreement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Why is NAFTA a free-trade area requiring rules of origin rather than a customs union?
A) A free-trade agreement allows politically sensitive tariffs of each nation to remain unchanged.
B) A customs union also requires rules of origin.
C) The overall level of U.S. tariffs was much higher than the overall level of tariffs in Mexico and Canada.
D) The overall levels of tariffs in Canada, Mexico, and the United States are similar, making rules of origin irrelevant.
A) A free-trade agreement allows politically sensitive tariffs of each nation to remain unchanged.
B) A customs union also requires rules of origin.
C) The overall level of U.S. tariffs was much higher than the overall level of tariffs in Mexico and Canada.
D) The overall levels of tariffs in Canada, Mexico, and the United States are similar, making rules of origin irrelevant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is NOT part of the TPP agreement on environmental protection?
A) reduction of subsidies to prevent overfishing
B) prohibition of trade in endangered species
C) allowing any member country to arrest smugglers of endangered species
D) establishment of limitations on greenhouse gas emissions
A) reduction of subsidies to prevent overfishing
B) prohibition of trade in endangered species
C) allowing any member country to arrest smugglers of endangered species
D) establishment of limitations on greenhouse gas emissions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Patent protection, especially on pharmaceuticals, was a controversial issue in the Trans-Pacific Partnership negotiations. The TPP agreement:
A) establishes patent protection for fewer than the 12 years that pharmaceutical companies wanted.
B) establishes patent protection for more than the 12 years that pharmaceutical companies wanted.
C) eliminates patent protection for pharmaceuticals.
D) establishes patent protection for the market lifetime of the pharmaceutical.
A) establishes patent protection for fewer than the 12 years that pharmaceutical companies wanted.
B) establishes patent protection for more than the 12 years that pharmaceutical companies wanted.
C) eliminates patent protection for pharmaceuticals.
D) establishes patent protection for the market lifetime of the pharmaceutical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A customs union will increase the welfare of its members and the rest of the world if:
A) trade creation is greater than trade diversion.
B) trade creation is less than trade diversion.
C) trade creation is positive.
D) trade diversion is positive.
A) trade creation is greater than trade diversion.
B) trade creation is less than trade diversion.
C) trade creation is positive.
D) trade diversion is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following regional trade agreements is a free-trade area?
A) NAFTA
B) the European Union
C) Mercosur
D) NATO
A) NAFTA
B) the European Union
C) Mercosur
D) NATO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Automobiles imported from Canada or Mexico must have 60% North American content to be eligible for tariff elimination under NAFTA rules. This is an example of a(n):
A) rules of origin requirement.
B) environmental standard.
C) health and safety requirement.
D) preferential trade agreement.
A) rules of origin requirement.
B) environmental standard.
C) health and safety requirement.
D) preferential trade agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When products from a high-cost country within a customs union replace imports from a low-cost country that is not a member of the union, this is called:
A) trade creation.
B) trade diversion.
C) trade deflection.
D) trade development.
A) trade creation.
B) trade diversion.
C) trade deflection.
D) trade development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose country X currently produces widgets. Then it establishes a regional trade agreement with country Y. Following the formation of the regional trade agreement, country X no longer produces widgets and now imports widgets from country Y. What has occurred?
A) There is trade diversion and a welfare gain for both country X and country Y.
B) There is trade diversion, a welfare gain for country Y, and a welfare loss for country X.
C) There is trade creation and a welfare gain for both country X and country Y.
D) There is trade creation, a welfare gain for country Y, and a welfare loss for country X.
A) There is trade diversion and a welfare gain for both country X and country Y.
B) There is trade diversion, a welfare gain for country Y, and a welfare loss for country X.
C) There is trade creation and a welfare gain for both country X and country Y.
D) There is trade creation, a welfare gain for country Y, and a welfare loss for country X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
It has been estimated that the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) could increase U.S. national income by as much as:
A) $130,000.
B) $130,000,000.
C) $130,000,000,000.
D) $130,000,000,000,000.
A) $130,000.
B) $130,000,000.
C) $130,000,000,000.
D) $130,000,000,000,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following was NOT a controversial issue in the Trans-Pacific Partnership?
A) intellectual property protection
B) labor rights
C) dispute settlement
D) a common tariff structure against nonmember countries
A) intellectual property protection
B) labor rights
C) dispute settlement
D) a common tariff structure against nonmember countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Implementing a regional free-trade agreement may have an effect in which, due to reduced tariffs, a nation begins to import a product from another member country that it had previously imported from outside the new trade region. This effect is called:
A) trade creation.
B) trade diversion.
C) reciprocal trade agreements.
D) the employment effect of FTAs.
A) trade creation.
B) trade diversion.
C) reciprocal trade agreements.
D) the employment effect of FTAs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
As of May 2016, Republican and Democratic Presidential candidates:
A) oppose the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
B) are in favor of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
C) have not commented on the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
D) are indifferent about the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
A) oppose the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
B) are in favor of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
C) have not commented on the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
D) are indifferent about the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In which form of regional trading agreements are rules of origin required?
A) a free-trade area
B) a customs union
C) a common market
D) an economic union
A) a free-trade area
B) a customs union
C) a common market
D) an economic union

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose country X currently does not produce widgets. Instead, it imports widgets from country Z. Then country X establishes a regional trade agreement with country Y. Following the formation of the regional trade agreement, it imports widgets from country Y. What has occurred?
A) There is trade diversion and a welfare loss for country X.
B) There is trade creation and a welfare loss for country Y.
C) There is trade diversion and a welfare gain for country X.
D) There is trade creation and a welfare gain for country Y.
A) There is trade diversion and a welfare loss for country X.
B) There is trade creation and a welfare loss for country Y.
C) There is trade diversion and a welfare gain for country X.
D) There is trade creation and a welfare gain for country Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which country is expected to be the major loser if the Trans-Pacific Partnership is NOT approved by member countries?
A) China
B) India
C) the United States
D) Vietnam
A) China
B) India
C) the United States
D) Vietnam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The TPP:
A) has no provisions regarding labor rights.
B) has stronger labor rights provisions than those of NAFTA.
C) has weaker labor rights provisions than those of NAFTA.
D) will consider labor rights in its next round of negotiations.
A) has no provisions regarding labor rights.
B) has stronger labor rights provisions than those of NAFTA.
C) has weaker labor rights provisions than those of NAFTA.
D) will consider labor rights in its next round of negotiations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
To be able to enforce the rules of a free-trade area, goods from outside the region imported into the lowest-tariff nation cannot be shipped _____ into another nation in the area.
A) with no transportation costs
B) without a labor certificate
C) with no customs inspection
D) duty free
A) with no transportation costs
B) without a labor certificate
C) with no customs inspection
D) duty free

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
(Figure: U.S. Imports from Mexico and Asia) The graph illustrates a customs union between the United States and Mexico. The United States does not produce the product shown in the graph. Imports satisfy its domestic demand (designated by MUS). The curves Smex and Sasia describe Mexican and Asian supplies. With a free trade price of $150 per unit, how many units will the United States import? 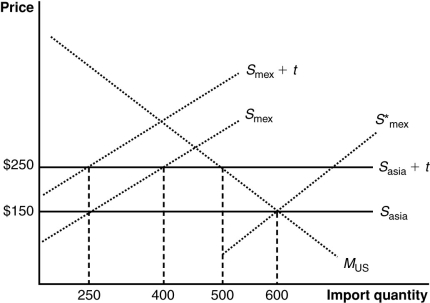
A) 250
B) 400
C) 500
D) 600

A) 250
B) 400
C) 500
D) 600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
(Scenario: Electric Fan Trade) U.S. firms can produce and sell electric fans for $25. The United States can also import electric fans from China at $19 each and from Canada at $20 each. Electric fans made in the United States, China, and Canada are identical. Currently, the United States imposes a 30% tariff on imported electric fans. Without a regional trade agreement, from which country(ies) will the United States import fans?
A) China
B) Canada
C) It will import fans from neither China nor Canada.
D) It will import fans from both China and Canada.
A) China
B) Canada
C) It will import fans from neither China nor Canada.
D) It will import fans from both China and Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
(Table: U.S. Demand for and Supply of Widgets) The United States can import widgets from China at $4 each and from Mexico at $5 each. The United States imposes a tariff of $2 on each of its widget imports. Is the United States better off or worse off in its trade in widgets following the free-trade agreement with Mexico? 
A) It is better off because trade creation gains exceed trade diversion losses.
B) It is worse off because trade diversion losses exceed trade creation gains.
C) It is worse off because trade creation losses exceed trade diversion gains.
D) It is better off because trade diversion gains exceed trade creation losses.

A) It is better off because trade creation gains exceed trade diversion losses.
B) It is worse off because trade diversion losses exceed trade creation gains.
C) It is worse off because trade creation losses exceed trade diversion gains.
D) It is better off because trade diversion gains exceed trade creation losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
(Figure: U.S. Imports from Mexico and Asia) The graph illustrates a customs union between the United States and Mexico. The United States does not produce the product shown in the graph. Imports satisfy its domestic demand (designated by MUS). The curves Smex and Sasia describe Mexican and Asian supplies. With a free trade price of $150, how many units EACH will the United States import from Mexico and from Asia? 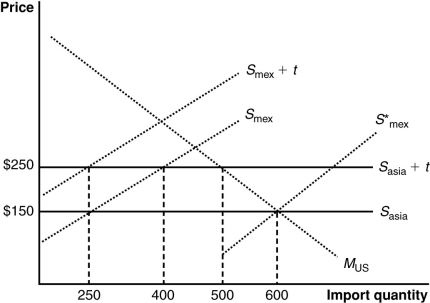
A) 250 from Mexico and 600 from Asia
B) 250 from Mexico and 350 from Asia
C) 350 from Mexico and 250 from Asia
D) 300 from each country

A) 250 from Mexico and 600 from Asia
B) 250 from Mexico and 350 from Asia
C) 350 from Mexico and 250 from Asia
D) 300 from each country

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
(Scenario: Electric Fan Trade) U.S. firms can produce and sell electric fans for $25. The United States can also import electric fans from China at $19 each and from Canada at $20 each. Electric fans made in the United States, China, and Canada are identical. Currently, the United States imposes a 30% tariff on imported electric fans. Suppose that the United States levied a 10% tariff on imported electric fans (rather than the 30% tariff described in the scenario). For the United States, would there be trade diversion losses, trade creation gains, or both as a result of the formation of NAFTA?
A) There would be only trade diversions losses.
B) There would be only trade creation gains.
C) There would be neither trade creation gains nor trade diversion losses.
D) There would be both trade creation gains and trade diversion losses.
A) There would be only trade diversions losses.
B) There would be only trade creation gains.
C) There would be neither trade creation gains nor trade diversion losses.
D) There would be both trade creation gains and trade diversion losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An example of how trade diversion results in a suboptimal situation is auto parts trade between Mexico and the United States. After NAFTA:
A) Mexico decreased its sales of auto parts to the United States.
B) the United States purchased more auto parts from Mexico because of the elimination of tariffs and reduced purchases from East Asia, which was the lowest-cost producer.
C) the United States brought a complaint against Mexico for low-quality auto parts.
D) the United States purchased fewer auto parts from Mexico because of the elimination of tariffs and increased purchases from East Asia, which was the lowest-cost producer.
A) Mexico decreased its sales of auto parts to the United States.
B) the United States purchased more auto parts from Mexico because of the elimination of tariffs and reduced purchases from East Asia, which was the lowest-cost producer.
C) the United States brought a complaint against Mexico for low-quality auto parts.
D) the United States purchased fewer auto parts from Mexico because of the elimination of tariffs and increased purchases from East Asia, which was the lowest-cost producer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The customs union could lead to losses for the home country if:
A) another country in the customs union is the most efficient producer.
B) another country in the customs unions is not the most efficient producer.
C) there are other countries outside the customs union that are inefficient.
D) all countries are efficient producers.
A) another country in the customs union is the most efficient producer.
B) another country in the customs unions is not the most efficient producer.
C) there are other countries outside the customs union that are inefficient.
D) all countries are efficient producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a customs union includes the lowest-cost world producer of a product, then member countries:
A) will always be better off in trade with that product.
B) will always be worse off in trade with that product.
C) can be better off or worse off depending on the strengths of the trade diversion and trade creation effects for that product.
D) will no longer export or import that product.
A) will always be better off in trade with that product.
B) will always be worse off in trade with that product.
C) can be better off or worse off depending on the strengths of the trade diversion and trade creation effects for that product.
D) will no longer export or import that product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
(Scenario: Electric Fan Trade) U.S. firms can produce and sell electric fans for $25. The United States can also import electric fans from China at $19 each and from Canada at $20 each. Electric fans made in the United States, China, and Canada are identical. Currently, the United States imposes a 30% tariff on imported electric fans. Suppose that the United States forms a free-trade area (NAFTA) with Canada and Mexico. From which country will the United States import fans?
A) China
B) Canada
C) It will import fans from neither China nor Canada.
D) It will import fans from both China and Canada.
A) China
B) Canada
C) It will import fans from neither China nor Canada.
D) It will import fans from both China and Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
(Figure: U.S. Imports from Mexico and Asia) The graph illustrates a customs union between the United States and Mexico. The United States does not produce the product shown in the graph. Imports satisfy its domestic demand (designated by MUS). The curves Smex and Sasia describe Mexican and Asian supplies. A $100 tariff by the United States results in a tariff revenue of: 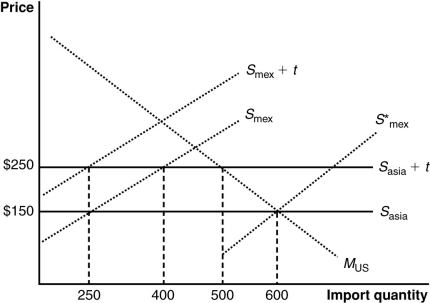
A) $25,000.
B) $5,000.
C) $50,000.
D) $2,500.

A) $25,000.
B) $5,000.
C) $50,000.
D) $2,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
(Scenario: Electric Fan Trade) U.S. firms can produce and sell electric fans for $25. The United States can also import electric fans from China at $19 each and from Canada at $20 each. Electric fans made in the United States, China, and Canada are identical. Currently, the United States imposes a 30% tariff on imported electric fans. For the United States, are there trade diversion losses, trade creation gains, or both as a result of the formation of NAFTA?
A) There are only trade diversions losses
B) There are only trade creation gains.
C) There are neither trade creation gains nor trade diversion losses.
D) There are both trade creation gains and trade diversion losses.
A) There are only trade diversions losses
B) There are only trade creation gains.
C) There are neither trade creation gains nor trade diversion losses.
D) There are both trade creation gains and trade diversion losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
(Figure: U.S. Imports from Mexico and Asia) The graph illustrates a customs union between the United States and Mexico. The United States does not produce the product shown in the graph. Imports satisfy its domestic demand (designated by MUS). The curves Smex and Sasia describe Mexican and Asian supplies. With a $100 tariff, the United States will import _____ units from Mexico and _____ units from China. 
A) 400; 100
B) 250; 250
C) 250; 500
D) 400; 200

A) 400; 100
B) 250; 250
C) 250; 500
D) 400; 200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If a regional trading agreement causes products from member countries to replace imports from nonmember countries, then the regional trading agreement will experience:
A) economic gains.
B) trade creation gains.
C) trade diversion losses.
D) trade perversion.
A) economic gains.
B) trade creation gains.
C) trade diversion losses.
D) trade perversion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In terms of efficiency, trade diversion is a _____ desirable outcome of a regional free-trade agreement, because trade is diverted from the _____ producer to the _____ producer.
A) more; high-cost; low-cost
B) more; less deserving; more deserving
C) less; low-cost; high-cost
D) less; foreign; domestic
A) more; high-cost; low-cost
B) more; less deserving; more deserving
C) less; low-cost; high-cost
D) less; foreign; domestic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
(Table: U.S. Demand for and Supply of Widgets) The United States can import widgets from China at $4 each and from Mexico at $5 each. The United States imposes a tariff of $2 on each of its widget imports. Suppose that the United States and Mexico form a free-trade area. How much trade in widgets is diverted in the U.S.-Mexican free-trade area? 
A) 0 widgets
B) 2 widgets
C) 4 widgets
D) 6 widgets

A) 0 widgets
B) 2 widgets
C) 4 widgets
D) 6 widgets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
(Table: U.S. Demand for and Supply of Widgets) The United States can import widgets from China at $4 each and from Mexico at $5 each. The United States imposes a tariff of $2 on each of its widget imports. How many pairs of widgets will the United States produce? 
A) 8
B) 9
C) 10
D) 11

A) 8
B) 9
C) 10
D) 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
(Figure: U.S. Imports from Mexico and Asia) The graph illustrates a customs union between the United States and Mexico. The United States does not produce the product shown in the graph. Imports satisfy its domestic demand (designated by MUS). The curves Smex and Sasia describe Mexican and Asian supplies. The combined welfare of the United States and Mexico is _____ by _____. 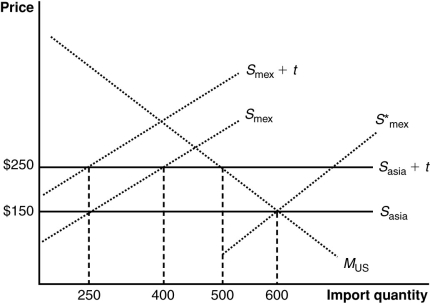
A) lower; $7,500
B) higher; $10,000
C) lower; $25,000
D) higher; $25,000

A) lower; $7,500
B) higher; $10,000
C) lower; $25,000
D) higher; $25,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
(Figure: U.S. Imports from Mexico and Asia) The graph illustrates a customs union between the United States and Mexico. The United States does not produce the product shown in the graph. Imports satisfy its domestic demand (designated by MUS). The curves Smex and Sasia describe Mexican and Asian supplies. If the United States forms a customs union with Mexico, it will result in a(n) _____ in producer surplus of _____ for Mexico. 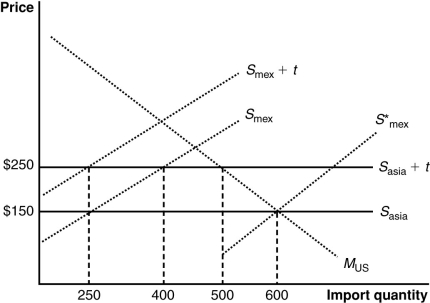
A) increase; $25,000
B) increase; $50,000
C) increase; $32,500
D) decrease; $50,000

A) increase; $25,000
B) increase; $50,000
C) increase; $32,500
D) decrease; $50,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
(Table: U.S. Demand for and Supply of Widgets) The United States can import widgets from China at $4 each and from Mexico at $5 each. The United States imposes a tariff of $2 on each of its widget imports. Suppose instead that the United States negotiated a free-trade agreement with China. Will the United States be better off or worse off as a result of its trade in widgets in the free-trade area with China? 
A) It is better off because there are no trade diversion losses.
B) It is worse off because there are no trade creation gains.
C) It is worse off because trade creation gains exceed trade diversion losses.
D) It is better off because trade diversion gains exceed trade creation losses.

A) It is better off because there are no trade diversion losses.
B) It is worse off because there are no trade creation gains.
C) It is worse off because trade creation gains exceed trade diversion losses.
D) It is better off because trade diversion gains exceed trade creation losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
(Table: U.S. Demand for and Supply of Widgets) The United States can import widgets from China at $4 each and from Mexico at $5 each. The United States imposes a tariff of $2 on each of its widget imports. Suppose that the United States and Mexico form a free-trade area. How much trade in widgets is created? 
A) 0 widgets
B) 2 widgets
C) 4 widgets
D) 6 widgets

A) 0 widgets
B) 2 widgets
C) 4 widgets
D) 6 widgets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



