Deck 20: Carbohydrates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/103
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Carbohydrates
1
Which of the following is the Fischer projection of D-glyceraldehyde?
A)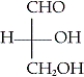
B)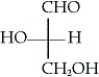
C)
D)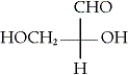
A)
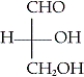
B)

C)

D)

A
2
Including pairs of enantiomers, how many different aldohexoses are there?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
D
3
Carbohydrates account for approximately what percentage of the body weight of animals?
A) 1%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 15%
A) 1%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 15%
A
4
How many different D-2-ketopentoses are there?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is true of the hydrolysis of carbohydrates?
A) Carbohydrates cannot be hydrolyzed.
B) Hydrolysis of carbohydrates can only yield polyhydroxyaldehydes.
C) Hydrolysis of carbohydrates can only yield polyhydroxyketones.
D) Hydrolysis of carbohydrates can yield polyhydroxyaldehydes and/or polyhydroxyketones.
A) Carbohydrates cannot be hydrolyzed.
B) Hydrolysis of carbohydrates can only yield polyhydroxyaldehydes.
C) Hydrolysis of carbohydrates can only yield polyhydroxyketones.
D) Hydrolysis of carbohydrates can yield polyhydroxyaldehydes and/or polyhydroxyketones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many different D-aldopentoses are there?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Including pairs of enantiomers, how many different trioses are there?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Including pairs of enantiomers, how many different aldopentoses are there?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How many different D-2-ketohexoses are there?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The configuration at which carbon of a tetrose determines if the tetrose has the D or L configuration?
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-3
D) C-4
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-3
D) C-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How many chiral carbons are present in the open-chain form of an aldohexose?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Including pairs of enantiomers, how many different 2-ketopentoses are there?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following carbohydrates is associated with crustacean shells?
A) cellulose
B) chitin
C) glucose
D) glycogen
A) cellulose
B) chitin
C) glucose
D) glycogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The configuration at which carbon of a pentose determines if the pentose has the D or L configuration?
A) C-1
B) C-3
C) C-4
D) C-5
A) C-1
B) C-3
C) C-4
D) C-5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Carbohydrates account for approximately what percentage of the dry weight of plants?
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
A) 10%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is the Fischer projection of L-glyceraldehyde?
A)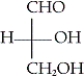
B)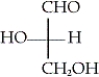
C)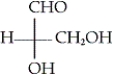
D)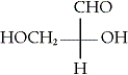
A)
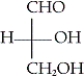
B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How many chiral carbons are present in the open-chain form of an aldopentose?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How many different D-aldohexoses are there?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which are the most abundant organic compounds in the plant world?
A) alcohols
B) amino acids
C) carbohydrates
D) proteins
A) alcohols
B) amino acids
C) carbohydrates
D) proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Including pairs of enantiomers, how many different 2-ketohexoses are there?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How many amino sugars are common in nature?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The cyclic structures of monosaccharides are which of the following?
A) acetals
B) hemiacetals
C) ethers
D) esters
A) acetals
B) hemiacetals
C) ethers
D) esters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is a generally mild disease?
A) galactosemia
B) galactosuria
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b
A) galactosemia
B) galactosuria
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For the solvents water, ethanol, and benzene which gives the correct order of solubility of monosaccharides?
A) benzene > ethanol > water
B) benzene > water > ethanol
C) water > ethanol > benzene
D) water > benzene > ethanol
A) benzene > ethanol > water
B) benzene > water > ethanol
C) water > ethanol > benzene
D) water > benzene > ethanol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The sugars in RNA and DNA are ribose and deoxyribose respectively. Which of the following describes the relationship between these two sugars?
A) In deoxyribose the oxygen lost is from the hydroxyl on C-1 of ribose.
B) In deoxyribose the oxygen lost is from the hydroxyl on C-2 of ribose.
C) In deoxyribose the oxygen lost is from the hydroxyl on C-3 of ribose.
D) In deoxyribose the oxygen lost is from the hydroxyl on C-4 of ribose.
A) In deoxyribose the oxygen lost is from the hydroxyl on C-1 of ribose.
B) In deoxyribose the oxygen lost is from the hydroxyl on C-2 of ribose.
C) In deoxyribose the oxygen lost is from the hydroxyl on C-3 of ribose.
D) In deoxyribose the oxygen lost is from the hydroxyl on C-4 of ribose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The D-form of which of the following amino sugars is not commonly found naturally?
A) galactosamine
B) glucosamine
C) mannosamine
D) ribosamine
A) galactosamine
B) glucosamine
C) mannosamine
D) ribosamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following functional groups is present in N-acetylglucosamine?
A) amide
B) 1° amine
C) 2° amine
D) 3° amine
A) amide
B) 1° amine
C) 2° amine
D) 3° amine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When an aldohexose such as glucose adopts the pyranose structure which atoms are connected by an oxygen atom?
A) C-1 and C-5
B) C-1 and C-6
C) C-2 and C-5
D) C-2 and C-6
A) C-1 and C-5
B) C-1 and C-6
C) C-2 and C-5
D) C-2 and C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following occurs when a monosaccharide is converted to an amino sugar?
A) An amino group replaces an aldehyde carbonyl.
B) An amino group replaces a ketone carbonyl.
C) An amino group replaces a hydroxyl group.
D) Any of the above, it depends on the identity of the monosaccharide.
A) An amino group replaces an aldehyde carbonyl.
B) An amino group replaces a ketone carbonyl.
C) An amino group replaces a hydroxyl group.
D) Any of the above, it depends on the identity of the monosaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When fructose adopts a furanose structure which carbon is the anomeric carbon?
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When glucose adopts a pyranose structure which carbon is the anomeric carbon?
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a severe disease?
A) galactosemia
B) galactosuria
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b
A) galactosemia
B) galactosuria
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the relationship between the number of stereocenters in a monosaccharide in its open-chain and ring structures?
A) The two structures contain the same number of stereocenters.
B) The open-chain form contains one less stereocenter than does the ring.
C) The open-chain form contains one more stereocenter than does the ring.
D) There is no general relationship, each case must be considered separately.
A) The two structures contain the same number of stereocenters.
B) The open-chain form contains one less stereocenter than does the ring.
C) The open-chain form contains one more stereocenter than does the ring.
D) There is no general relationship, each case must be considered separately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
To which carbon of a monosaccharide is the amino group bound in the amino sugars commonly found in nature?
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How many chiral carbons are present in the open-chain form of a ketopentose?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Approximately how many infants are born with galactosemia?
A) 1 in 1.8 × 102
B) 1 in 1.8 × 104
C) 1 in 1.8 × 103
D) 1 in 1.8 × 105
A) 1 in 1.8 × 102
B) 1 in 1.8 × 104
C) 1 in 1.8 × 103
D) 1 in 1.8 × 105

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When a ketohexose such as fructose adopts the furanose structure which atoms are connected by an oxygen atom?
A) C-1 and C-5
B) C-1 and C-6
C) C-2 and C-5
D) C-2 and C-6
A) C-1 and C-5
B) C-1 and C-6
C) C-2 and C-5
D) C-2 and C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
How many chiral carbons are present in the open-chain form of a ketohexose?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The D-form of which of the following amino sugars is commonly found naturally?
A) allosamine
B) althrosamine
C) mannosamine
D) none of these
A) allosamine
B) althrosamine
C) mannosamine
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is associated with the projections commonly used to illustrate furanoses and pyranoses?
A) E. Fischer
B) W. Haworth
C) L. Pauling
D) L. Pasteur
A) E. Fischer
B) W. Haworth
C) L. Pauling
D) L. Pasteur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is true of glucitol?
A) It exists only as an open-chain structure.
B) It exists only as a ring structure.
C) It exists as both ring and open-chain structures with the open-chain structure predominating.
D) It exists as both ring and open-chain structures with the ring structure predominating.
A) It exists only as an open-chain structure.
B) It exists only as a ring structure.
C) It exists as both ring and open-chain structures with the open-chain structure predominating.
D) It exists as both ring and open-chain structures with the ring structure predominating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which carbon is the site of reaction when glucose reacts to form a glucoside?
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which sugar is the starting material used by plants to synthesize vitamin C?
A) D-fructose
B) L-fructose
C) D-glucose
D) L-glucose
A) D-fructose
B) L-fructose
C) D-glucose
D) L-glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What reaction occurs when glucose is converted to gluconate?
A) reduction at C-1
B) oxidation at C-1
C) reduction at C-6
D) oxidation at C-6
A) reduction at C-1
B) oxidation at C-1
C) reduction at C-6
D) oxidation at C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following explains why glycosides do not undergo mutarotation?
A) There is no longer an anomeric carbon.
B) There are no longer any stereocenters.
C) The ring structure does not open to become the open-chain structure.
D) None of the above is correct.
A) There is no longer an anomeric carbon.
B) There are no longer any stereocenters.
C) The ring structure does not open to become the open-chain structure.
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is true of the spatial distribution of the hydroxyl groups of α-D-glucopyranose?
A) They are all in axial positions.
B) They are all in equatorial positions.
C) The hydroxyl on C-1 is axial, those on C-2, C-3 and C-4 are equatorial.
D) The hydroxyl on C-1 is equatorial, those on C-2, C-3 and C-4 are axial.
A) They are all in axial positions.
B) They are all in equatorial positions.
C) The hydroxyl on C-1 is axial, those on C-2, C-3 and C-4 are equatorial.
D) The hydroxyl on C-1 is equatorial, those on C-2, C-3 and C-4 are axial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The formation of a glycoside from a sugar is which of the following reactions?
A) condensation
B) hydrolysis
C) reduction
D) oxidation
A) condensation
B) hydrolysis
C) reduction
D) oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What reaction occurs when glucose is converted to glucuronic acid?
A) reduction at C-1
B) oxidation at C-1
C) reduction at C-6
D) oxidation at C-6
A) reduction at C-1
B) oxidation at C-1
C) reduction at C-6
D) oxidation at C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following explains why ketoses are reducing sugars?
A) Under acidic conditions they are converted to aldoses.
B) Under basic conditions they are converted to aldoses.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b
A) Under acidic conditions they are converted to aldoses.
B) Under basic conditions they are converted to aldoses.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is true of the spatial distribution of the hydroxyl groups of β-D-glucopyranose?
A) They are all in axial positions.
B) They are all in equatorial positions.
C) The hydroxyl on C-1 is axial, those on C-2, C-3 and C-4 are equatorial.
D) The hydroxyl on C-1 is equatorial, those on C-2, C-3 and C-4 are axial.
A) They are all in axial positions.
B) They are all in equatorial positions.
C) The hydroxyl on C-1 is axial, those on C-2, C-3 and C-4 are equatorial.
D) The hydroxyl on C-1 is equatorial, those on C-2, C-3 and C-4 are axial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Under which of the following conditions can monosaccharides be oxidized to aldonic acids?
A) acidic
B) basic
C) neutral
D) all of these
A) acidic
B) basic
C) neutral
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is true of the α and β anomers of glucose?
A) They have equal but opposite optical rotations.
B) They are equally stable.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b
A) They have equal but opposite optical rotations.
B) They are equally stable.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following reagents is capable of hydrolyzing glycosides?
A) acids
B) bases
C) water
D) all of these
A) acids
B) bases
C) water
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of following describes a solution in which the α and β anomers of glucose have reached equilibrium?
A) There are equal amounts of the two anomers.
B) The solution shows no optical activity.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b
A) There are equal amounts of the two anomers.
B) The solution shows no optical activity.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What reaction occurs when glucose is converted to glucitol?
A) reduction at C-1
B) oxidation at C-1
C) reduction at C-6
D) oxidation at C-6
A) reduction at C-1
B) oxidation at C-1
C) reduction at C-6
D) oxidation at C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following reacts with sugars to form glycosides?
A) alcohols
B) amines
C) hemiacetals
D) water
A) alcohols
B) amines
C) hemiacetals
D) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is true of the α and β anomers of glucose?
A) They both rotate light to the right (i.e. +), but not to the same extent.
B) They are equally stable.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b
A) They both rotate light to the right (i.e. +), but not to the same extent.
B) They are equally stable.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of following describes a solution in which the α and β anomers of glucose have reached equilibrium?
A) There is more β anomer present than α anomer.
B) The solution shows no optical activity.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b
A) There is more β anomer present than α anomer.
B) The solution shows no optical activity.
C) both a and b
D) neither a nor b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When ribose adopts a furanose structure which carbon is the anomeric carbon?
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6
A) C-1
B) C-2
C) C-5
D) C-6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Glycosides are examples of which class of compounds?
A) acetals
B) hemiacetals
C) ethers
D) esters
A) acetals
B) hemiacetals
C) ethers
D) esters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The reaction of monosaccharides to form a disaccharide is an example of which of the following reactions?
A) condensation
B) hydrolysis
C) reduction
D) oxidation
A) condensation
B) hydrolysis
C) reduction
D) oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the charge on glucose 6-phosphate?
A) 0
B) −1
C) −2
D) −3
A) 0
B) −1
C) −2
D) −3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following determines blood type O in the ABO blood typing system?
A) the presence of only N-acetyl-D-galactosamine antigen
B) the presence of only N-acetyl-D-galactose antigen
C) the presence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and N-acetyl-D-galactose antigens
D) the absence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and N-acetyl-D-galactose antigens
A) the presence of only N-acetyl-D-galactosamine antigen
B) the presence of only N-acetyl-D-galactose antigen
C) the presence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and N-acetyl-D-galactose antigens
D) the absence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and N-acetyl-D-galactose antigens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is true of glucose 6-phosphate?
A) It is a cationic species with a charge of +1.
B) It is an electrically neutral molecule.
C) It is an anionic species with a charge of −1.
D) It is an anionic species with a charge of −2.
A) It is a cationic species with a charge of +1.
B) It is an electrically neutral molecule.
C) It is an anionic species with a charge of −1.
D) It is an anionic species with a charge of −2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is the sweetest?
A) fructose
B) honey
C) maltose
D) sucrose
A) fructose
B) honey
C) maltose
D) sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In sucrose, which of the following describes the glycosidic bond between C-1 of glucose and C-2 of fructose?
A) for both fructose and glucose it is α
B) for both fructose and glucose it is β
C) for fructose it is α and for glucose it is β
D) for fructose it is β and for glucose it is α
A) for both fructose and glucose it is α
B) for both fructose and glucose it is β
C) for fructose it is α and for glucose it is β
D) for fructose it is β and for glucose it is α

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Complete hydrolysis of which of the following disaccharides yields a single monosaccharide?
A) lactose
B) maltose
C) sucrose
D) none of these
A) lactose
B) maltose
C) sucrose
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the test for blood glucose which of the following is formed?
A) D-glucitol
B) D-gluconic acid
C) D-glucuronic acid
D) methyl-α-D-glucopyranoside
A) D-glucitol
B) D-gluconic acid
C) D-glucuronic acid
D) methyl-α-D-glucopyranoside

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
An α(1 → 2) glycosidic bond is found in which of the following?
A) lactose
B) maltose
C) sucrose
D) none of these
A) lactose
B) maltose
C) sucrose
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Under which of the following conditions can monosaccharides be oxidized to uronic acids?
A) basic
B) enzymatic
C) acidic
D) none of these
A) basic
B) enzymatic
C) acidic
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is true about the reducing properties of sugars?
A) All monosaccharides and all disaccharides are nonreducing sugars.
B) All monosaccharides and all disaccharides are reducing sugars.
C) All disaccharides and some monosaccharides are nonreducing sugars.
D) All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars.
A) All monosaccharides and all disaccharides are nonreducing sugars.
B) All monosaccharides and all disaccharides are reducing sugars.
C) All disaccharides and some monosaccharides are nonreducing sugars.
D) All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A β(1 → 4) glycosidic bond is found in which of the following?
A) lactose
B) maltose
C) sucrose
D) all of these
A) lactose
B) maltose
C) sucrose
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An α(1 → 4) glycosidic bond is found in which of the following?
A) lactose
B) maltose
C) sucrose
D) all of these
A) lactose
B) maltose
C) sucrose
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following determines blood type A in the ABO blood typing system?
A) the presence of only N-acetyl-D-galactosamine antigen
B) the presence of only D-galactose antigen
C) the presence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and D-galactose antigens
D) the absence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and D-galactose antigens
A) the presence of only N-acetyl-D-galactosamine antigen
B) the presence of only D-galactose antigen
C) the presence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and D-galactose antigens
D) the absence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and D-galactose antigens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is obtained as a result of the complete hydrolysis of starch?
A) D-glucose
B) lactose
C) maltose
D) sucrose
A) D-glucose
B) lactose
C) maltose
D) sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Approximately what percentage of plant starch is amylopectin?
A) 10 to 15%
B) 20 to 25%
C) 75 to 80%
D) 85 to 90%
A) 10 to 15%
B) 20 to 25%
C) 75 to 80%
D) 85 to 90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Approximately what percentage of plant starch is amylose?
A) 10 to 15%
B) 20 to 25%
C) 75 to 80%
D) 85 to 90%
A) 10 to 15%
B) 20 to 25%
C) 75 to 80%
D) 85 to 90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
How many monosaccharide units are in molecules called oligosaccharides?
A) 3 to 6
B) 6 to 10
C) 10 to 15
D) 15 to 20
A) 3 to 6
B) 6 to 10
C) 10 to 15
D) 15 to 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following determines blood type B in the ABO blood typing system?
A) the presence of only N-acetyl-D-galactosamine antigen
B) the presence of only D-galactose antigen
C) the presence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and D-galactose antigens
D) the absence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and D-galactose antigens
A) the presence of only N-acetyl-D-galactosamine antigen
B) the presence of only D-galactose antigen
C) the presence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and D-galactose antigens
D) the absence of both N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and D-galactose antigens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is true of amylose?
A) It consists of as many as 4000 D-glucose units linearly linked by α(1 → 4) glycosidic bonds.
B) It consists of as many as 4000 D-glucose units linearly linked by β(1 → 4) glycosidic bonds.
C) It consists of as many as 10,000 D-glucose units linearly linked by α(1 → 4) glycosidic bonds and there are branches every 24-30 units via α(1 → 6) glycosidic bonds.
D) It consists of as many as 10,000 D-glucose units linearly linked by β(1 → 4) glycosidic bonds and there are branches every 24-30 units via β(1 → 6) glycosidic bonds.
A) It consists of as many as 4000 D-glucose units linearly linked by α(1 → 4) glycosidic bonds.
B) It consists of as many as 4000 D-glucose units linearly linked by β(1 → 4) glycosidic bonds.
C) It consists of as many as 10,000 D-glucose units linearly linked by α(1 → 4) glycosidic bonds and there are branches every 24-30 units via α(1 → 6) glycosidic bonds.
D) It consists of as many as 10,000 D-glucose units linearly linked by β(1 → 4) glycosidic bonds and there are branches every 24-30 units via β(1 → 6) glycosidic bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 103 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



