Deck 12: Dna Replication and Manipulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/169
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Dna Replication and Manipulation
1
Which of the following enzymes is the FIRST to bind to the DNA sequences at the origin of replication?
A)DNA polymerase
B)DNA helicase
C)DNA primase
D)single-strand binding protein
E)DNA ligase
A)DNA polymerase
B)DNA helicase
C)DNA primase
D)single-strand binding protein
E)DNA ligase
B
2
In observing DNA replication in the lab, you notice that in some cells, a defect occurs where DNA replication proceeds, but the RNA primers are not removed and replaced with DNA. Which enzyme is MOST likely to be defective in this system?
A)RNA primase
B)helicase
C)single-strand binding protein
D)DNA polymerase
E)DNA ligase
A)RNA primase
B)helicase
C)single-strand binding protein
D)DNA polymerase
E)DNA ligase
D
3
Consider a cell in which one of the proteins or enzymes involved in DNA replication is altered in a way that results in an increased rate of single-base changes in the newly synthesized DNA strand. Which function of which protein is MOST likely disrupted in this situation?
A)the unwinding function of helicase
B)the winding stress relief function of topoisomerase II
C)the fragment joining function of DNA ligase
D)the proofreading function of DNA polymerase
E)the strand separation function of single-stranded binding protein
A)the unwinding function of helicase
B)the winding stress relief function of topoisomerase II
C)the fragment joining function of DNA ligase
D)the proofreading function of DNA polymerase
E)the strand separation function of single-stranded binding protein
D
4
The lagging strand is the daughter strand that has its _____ end pointed toward the replication fork and is therefore synthesized _____.
A)3'; in a series of segments
B)3'; continuously
C)5'; in a series of segments
D)5'; continuously
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)3'; in a series of segments
B)3'; continuously
C)5'; in a series of segments
D)5'; continuously
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What feature of double-stranded DNA makes it necessary to have a leading strand and a lagging strand during replication?
A)the hydrogen bonding between bases
B)the base stacking of the bases
C)the negative charge on the sugar-phosphate backbone
D)the antiparallel orientation of the strands
A)the hydrogen bonding between bases
B)the base stacking of the bases
C)the negative charge on the sugar-phosphate backbone
D)the antiparallel orientation of the strands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A new nucleotide can only be added to the _____ end of a growing DNA strand. DNA therefore always grows in the _____ direction.
A)3'; 5' to 3'
B)5'; 5' to 3'
C)3'; 3' to 5'
D)5'; 3' to 5'
A)3'; 5' to 3'
B)5'; 5' to 3'
C)3'; 3' to 5'
D)5'; 3' to 5'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You discover a virus with a number of unusual properties, and decide to assign it the name virus U238. The genome of U238 consists of double-stranded DNA. To study the mode of DNA replication in U238, you carry out a Meselson-Stahl type of experiment, and first observe that viral DNA containing only normal "light" nitrogen (14N) has a density of 1.715 gm/cm3. You then allow the virus to replicate in the presence of nucleotides containing "heavy" nitrogen (15N) until both strands of its genome are "heavy." At this point the density of the viral DNA is 1.722 gm/cm3. You allow the virus with "heavy" DNA to undergo one round of replication in the presence of only "light" nucleotides, and you observe that half of the viral progeny have DNA with a density of 1.722 gm/cm3 and the other half of the viral progeny have DNA with a density of 1.715 gm/cm3. How would you interpret these results?
A)The viral DNA is replicated like any other double-stranded DNA molecule.
B)The viral DNA is replicated in very short pieces that reassociate at random.
C)After replication, pairing of the parental strands is restored.
D)This result is impossible and is therefore most likely due to an error.
A)The viral DNA is replicated like any other double-stranded DNA molecule.
B)The viral DNA is replicated in very short pieces that reassociate at random.
C)After replication, pairing of the parental strands is restored.
D)This result is impossible and is therefore most likely due to an error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A cell with a defect in the proofreading function of DNA polymerase is observed to have a rate of incorporation of incorrect bases into newly synthesized DNA that is 100 times greater than a cell with a nondefective, normal DNA polymerase. Estimate from this number what fraction of incorrect nucleotide incorporations are corrected by the proofreading function of DNA polymerase in the cell with normal DNA polymerase.
A)0)9 percent
B)9)0 percent
C)99.0 percent
D)99.9 percent
A)0)9 percent
B)9)0 percent
C)99.0 percent
D)99.9 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
To cells that are defective in primer removal, you add fluorescent ribonucleotides when the cells are undergoing DNA replication. In this case, you observe that one strand glows more than the other not only near the replication fork but also at intervals along its length. Which strand glows in this way and why?
A)The leading strand glows in this way because it is synthesized continuously.
B)The leading strand glows in this way because its RNA primers are widely spaced.
C)The lagging strand glows in this way because it is synthesized continuously.
D)The lagging strand glows in this way because its RNA primers are closely spaced.
A)The leading strand glows in this way because it is synthesized continuously.
B)The leading strand glows in this way because its RNA primers are widely spaced.
C)The lagging strand glows in this way because it is synthesized continuously.
D)The lagging strand glows in this way because its RNA primers are closely spaced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
To follow up on your previous experiment with DNA replication in virus U238, conduct another Meselson-Stahl type experiment, again allowing a virus to replicate in the presence of "heavy" nitrogen until both strands of its genome are "heavy." In this experiment, you allow virus U238 to undergo two complete rounds of replication in the presence of "light" nitrogen. What ratio of "heavy" to "light" viral DNA would you expect to find at the end of two complete rounds of replication?
A)1:3
B)2:2
C)3:1
D)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)1:3
B)2:2
C)3:1
D)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The enzyme responsible for replacing RNA primers with DNA is a type of:
A)DNA polymerase.
B)helicase.
C)topoisomerase II.
D)DNA ligase.
E)DNA replicase.
A)DNA polymerase.
B)helicase.
C)topoisomerase II.
D)DNA ligase.
E)DNA replicase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What would happen to the variation between organisms in a population if their DNA polymerase did NOT have a proofreading function?
A)The amount of variation would increase.
B)The amount of variation would decrease.
C)The amount of variation would stay the same.
A)The amount of variation would increase.
B)The amount of variation would decrease.
C)The amount of variation would stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
During DNA replication in a cell, RNA primase synthesizes a primer that is complementary to the region in the sequence below shown in bold.
What is the primer sequence?
A)5'-CTTTGGATGTTG-3'
B)5'-GTTGTAGGTTTC-3'
C)5'-CUUUGGAUGUUG-3'
D)5'-GUUGUAGGUUUC-3'
What is the primer sequence?
A)5'-CTTTGGATGTTG-3'
B)5'-GTTGTAGGTTTC-3'
C)5'-CUUUGGAUGUUG-3'
D)5'-GUUGUAGGUUUC-3'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The fact that DNA replication occurs in virtually the same way in all organisms reflects:
A)its origin early in the history of life.
B)its multiple origins in different lineages of organisms.
C)the laws of thermodynamics.
D)the fact that mutations are generally harmful.
E)the universal genetic code.
A)its origin early in the history of life.
B)its multiple origins in different lineages of organisms.
C)the laws of thermodynamics.
D)the fact that mutations are generally harmful.
E)the universal genetic code.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The leading strand is the daughter strand that has its _____ end pointed toward the replication fork and is therefore synthesized _____.
A)3'; in a series of segments
B)3'; continuously
C)5'; in a series of segments
D)5'; continuously
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)3'; in a series of segments
B)3'; continuously
C)5'; in a series of segments
D)5'; continuously
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Incorrect nucleotides are sometimes incorporated into DNA during the process of replication. In the sequences shown here, the template strand is shown on top and the replicating daughter strand at the bottom. The nucleotide shown in bold is incorrect in that its base does not undergo pairing with the base in the template strand. In the situation shown in (A) the proofreading function of DNA polymerase removes the incorrect nucleotide from the daughter strand and replaces it with the correct one, but in situation (B) the polymerase has moved on and the incorrect nucleotide cannot be repaired. Can you explain why the error in situation (B) cannot be fixed by DNA polymerase?
(A)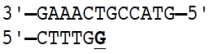 (B)
(B) 
(A)
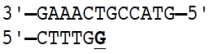 (B)
(B) 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When we say that DNA replication is semiconservative, we mean that:
A)only half of an organism's DNA is replicated during each cell division.
B)when DNA is replicated, each new double helix contains one parental strand and one newly synthesized daughter strand.
C)when DNA is replicated, one double helix contains both parental strands and one contains two newly synthesized daughter strands.
D)parental DNA stays in the parent cell and daughter DNA ends up in the daughter cell.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)only half of an organism's DNA is replicated during each cell division.
B)when DNA is replicated, each new double helix contains one parental strand and one newly synthesized daughter strand.
C)when DNA is replicated, one double helix contains both parental strands and one contains two newly synthesized daughter strands.
D)parental DNA stays in the parent cell and daughter DNA ends up in the daughter cell.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
As additional evidence that U238 has an unusual mode of DNA replication, you conduct still another Meselson-Stahl type experiment, again allowing the virus to replicate in the presence of "heavy" nitrogen until both strands of its genome are "heavy." This time you allow U238 to undergo three complete rounds of replication in the presence of "light" nitrogen. What ratio of "heavy" to "light" viral DNA would you expect to find after three complete rounds of replication?
A)1:7
B)2:6
C)4:4
D)6:2
E)7:1
A)1:7
B)2:6
C)4:4
D)6:2
E)7:1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The enzyme responsible for proofreading a growing DNA strand and for replacing mismatched nucleotides is:
A)DNA polymerase.
B)helicase.
C)topoisomerase II.
D)DNA ligase.
E)DNA replicase.
A)DNA polymerase.
B)helicase.
C)topoisomerase II.
D)DNA ligase.
E)DNA replicase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose you add fluorescent ribonucleotides to a cell undergoing DNA replication so that the RNA primers used in DNA synthesis glow when viewed with a fluorescent microscope. You notice that, near each replication fork, one strand glows more than the other. Which strand is it that glows more, and why?
A)The leading strand glows more because it is elongated nearest the replication fork.
B)The leading strand glows more because it forms the "trombone loop."
C)The lagging strand glows more because its RNA primer is nearer the replication fork.
D)The lagging strand glows more because it forms the "trombone loop."
A)The leading strand glows more because it is elongated nearest the replication fork.
B)The leading strand glows more because it forms the "trombone loop."
C)The lagging strand glows more because its RNA primer is nearer the replication fork.
D)The lagging strand glows more because it forms the "trombone loop."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the result of DNA ligase's action?
A)DNA is broken up at specific sites.
B)DNA fragments are joined together.
C)DNA translation occurs.
D)DNA transcription occurs.
E)DNA is condensed to chromosomes.
A)DNA is broken up at specific sites.
B)DNA fragments are joined together.
C)DNA translation occurs.
D)DNA transcription occurs.
E)DNA is condensed to chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is the function of the enzyme DNA polymerase?
A)to synthesize a strand of DNA using DNA as a template
B)to synthesize a strand of DNA using a polypeptide as a template
C)to synthesize a strand of mRNA using DNA as a template
D)to synthesize a strand of mRNA using mRNA as a template
E)to synthesize a polypeptide using DNA as a template
A)to synthesize a strand of DNA using DNA as a template
B)to synthesize a strand of DNA using a polypeptide as a template
C)to synthesize a strand of mRNA using DNA as a template
D)to synthesize a strand of mRNA using mRNA as a template
E)to synthesize a polypeptide using DNA as a template

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements about the strands of a newly replicated DNA molecule is CORRECT?
A)Both strands are made up of newly assembled nucleotides.
B)One strand is new and the other is from the original molecule.
C)Both strands contain some nucleotides from the original molecule.
D)The sugar-phosphate chains are conserved and new bases are inserted between them.
E)The base pairs are conserved and new sugar-phosphate backbones are built up on them.
A)Both strands are made up of newly assembled nucleotides.
B)One strand is new and the other is from the original molecule.
C)Both strands contain some nucleotides from the original molecule.
D)The sugar-phosphate chains are conserved and new bases are inserted between them.
E)The base pairs are conserved and new sugar-phosphate backbones are built up on them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
_____ relieves the tension on the double helix during DNA replication.
A)Helicase
B)Topoisomerase
C)DNA polymerase
D)A single-stranded binding protein
E)An RNA primer
A)Helicase
B)Topoisomerase
C)DNA polymerase
D)A single-stranded binding protein
E)An RNA primer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication?
A)ribosomes
B)DNA
C)nucleotides
D)enzymes
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)ribosomes
B)DNA
C)nucleotides
D)enzymes
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In DNA replication, each individual parent strand acts as a _____ strand for the synthesis of a _____ strand.
A)template; duplicate
B)duplicate; daughter
C)daughter; template
D)template; daughter
E)daughter; duplicate
A)template; duplicate
B)duplicate; daughter
C)daughter; template
D)template; daughter
E)daughter; duplicate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The enzyme that catalyzes the addition of new nucleotides to a growing DNA strand is:
A)DNA polymerase.
B)helicase.
C)topoisomerase II.
D)DNA ligase.
E)DNA replicase.
A)DNA polymerase.
B)helicase.
C)topoisomerase II.
D)DNA ligase.
E)DNA replicase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The enzyme responsible for joining Okazaki fragments together during DNA replication is:
A)DNA polymerase.
B)helicase.
C)topoisomerase II.
D)DNA ligase.
E)DNA replicase.
A)DNA polymerase.
B)helicase.
C)topoisomerase II.
D)DNA ligase.
E)DNA replicase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why are single-stranded binding proteins necessary for DNA replication?
A)They provide the energy necessary to separate the two strands of DNA.
B)They prevent the two parental strands from coming together again.
C)They direct the primase where to lay down the primer.
D)They direct where replication will start.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)They provide the energy necessary to separate the two strands of DNA.
B)They prevent the two parental strands from coming together again.
C)They direct the primase where to lay down the primer.
D)They direct where replication will start.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Why is DNA ligase important for a cell?
A)It joins Okazaki fragments.
B)It relieves the stress of DNA unwinding.
C)It joins DNA together from different origins of replication.
D)It unwinds DNA.
A)It joins Okazaki fragments.
B)It relieves the stress of DNA unwinding.
C)It joins DNA together from different origins of replication.
D)It unwinds DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
During DNA replication, the leading strand contains Okazaki fragments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Synthesis of nucleic acids always occurs in the 5' 3' direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The semiconservative model of DNA replication means that each DNA strand consists of some newly synthesized DNA and some parental DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Energy is required in order to add a nucleotide to the growing strand of DNA during replication. From where does that energy come?
A)DNA polymerase
B)DNA ligase
C)helicase
D)primase
E)the incoming nucleotide
A)DNA polymerase
B)DNA ligase
C)helicase
D)primase
E)the incoming nucleotide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following would block the process of DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase?
A)removal of the 3'-OH from the last nucleotide of the daughter strand
B)removal of the 5'triphosphate from the nucleotides used by DNA polymerase
C)removal of the base from the nucleotides used by DNA polymerase
D)removal of DNA ligase from the DNA replication process
A)removal of the 3'-OH from the last nucleotide of the daughter strand
B)removal of the 5'triphosphate from the nucleotides used by DNA polymerase
C)removal of the base from the nucleotides used by DNA polymerase
D)removal of DNA ligase from the DNA replication process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following enzymes is responsible for unwinding the double helix at the replication fork?
A)ligase
B)DNA polymerase
C)primase
D)helicase
E)topoisomerase
A)ligase
B)DNA polymerase
C)primase
D)helicase
E)topoisomerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A eukaryotic chromosome has _____ origin(s) of replication, and a bacterial chromosome has _____ origin(s) of replication.
A)one; one
B)many; one
C)one; many
D)many; two
E)many; three
A)one; one
B)many; one
C)one; many
D)many; two
E)many; three

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
DNA polymerase is the enzyme that separates the two strands of DNA during DNA replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the name of the enzyme that separates the two strands of DNA during replication?
A)DNA polymerase
B)DNA ligase
C)primase
D)helicase
E)topoisomerase
A)DNA polymerase
B)DNA ligase
C)primase
D)helicase
E)topoisomerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
As a piece of linear DNA is replicated, the leading strand will have _____ RNA primer(s) and the lagging strand will have _____ RNA primer(s).
A)one; one
B)one; two
C)one; many
D)many; one
E)many; many
A)one; one
B)one; two
C)one; many
D)many; one
E)many; many

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Given that a chromosome is 60,000,000 bases in length, and DNA polymerase functions at a rate of 50 base pairs per second, what is the minimum number of origins of replication required on that chromosome to allow replication to complete if S phase lasts for 5.5 hours?
A)one
B)about 30
C)about 300
D)about 3000
E)about 30,000
A)one
B)about 30
C)about 300
D)about 3000
E)about 30,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If you were able to find a drug that could inhibit the reactivation of telomerase activity in cancer cells, the cancer cells would:
A)stop dividing immediately.
B)become less invasive.
C)eventually die from lack of energy.
D)slowly erode their chromosome ends.
E)gradually revert to normal cells.
A)stop dividing immediately.
B)become less invasive.
C)eventually die from lack of energy.
D)slowly erode their chromosome ends.
E)gradually revert to normal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
_____ is the first enzyme to synthesize a nucleic acid at a replication fork.
A)RNA primase
B)Helicase
C)Topoisomerase II
D)DNA polymerase
A)RNA primase
B)Helicase
C)Topoisomerase II
D)DNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The enzyme _____ compensates for chromosomes shortening at the tips after each round of DNA replication.
A)DNA polymerase
B)telomerase
C)topoisomerase II
D)DNA ligase
E)DNA replicase
A)DNA polymerase
B)telomerase
C)topoisomerase II
D)DNA ligase
E)DNA replicase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The main function of DNA polymerase is to add new nucleotides to the 3'-end of a growing chain. What is the second role of this enzyme in DNA replication?
A)synthesis of RNA primer
B)unwinding of the DNA duplex
C)proofreading
D)stabilizing strands of DNA at replication fork
E)joining Okazaki fragments
A)synthesis of RNA primer
B)unwinding of the DNA duplex
C)proofreading
D)stabilizing strands of DNA at replication fork
E)joining Okazaki fragments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider the end of a DNA strand in a double-stranded molecule that has become shorter as a result of DNA replication. This same end will be shortened still further in:
A)every round of DNA replication.
B)alternate rounds of DNA replication.
C)every third round of DNA replication.
D)every fourth round of DNA replication.
A)every round of DNA replication.
B)alternate rounds of DNA replication.
C)every third round of DNA replication.
D)every fourth round of DNA replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In contrast to linear DNA replication, circular DNA replication typically:
A)has a single origin of replication.
B)does not produce a replication bubble.
C)occurs only at a single replication fork.
D)does not produce Okazaki fragments.
E)All of these choices are correct.
A)has a single origin of replication.
B)does not produce a replication bubble.
C)occurs only at a single replication fork.
D)does not produce Okazaki fragments.
E)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
DNA replication in human cells occurs at a rate of about 50 base pairs per second, and the length of the longest human chromosome (chromosome 1) is 249 Mb. If DNA replication took place continuously from one end of chromosome 1 to the other, it would take approximately:
A)2 seconds.
B)2 minutes.
C)2 hours.
D)2 days.
E)2 months.
A)2 seconds.
B)2 minutes.
C)2 hours.
D)2 days.
E)2 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The presence of Okazaki fragments demonstrates the antiparallel nature of the double helix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In replication of a linear double-stranded DNA molecule, one end of each strand becomes shorter in each round of replication. This happens because:
A)each replicated DNA strand requires an RNA primer.
B)the RNA primer cannot be replaced at the very end of a DNA strand.
C)DNA polymerase elongates a growing DNA strand at only the 3' end.
D)All of these choices are correct.
A)each replicated DNA strand requires an RNA primer.
B)the RNA primer cannot be replaced at the very end of a DNA strand.
C)DNA polymerase elongates a growing DNA strand at only the 3' end.
D)All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
DNA replication of small circular molecules usually starts at a single origin of replication and proceeds bidirectionally (that is, with two replication forks proceeding in opposite directions from the origin of replication). How would the time required for replication be affected if replication of such a molecule were unidirectional rather than bidirectional?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
_____ moves outward from the origin of replication and breaks hydrogen bonds between DNA nucleotides.
A)RNA primase
B)Helicase
C)Topoisomerase II
D)DNA polymerase
A)RNA primase
B)Helicase
C)Topoisomerase II
D)DNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
RNA is involved in which of the following cellular processes?
A)transcription
B)transcription and translation
C)translation and DNA replication
D)DNA replication and transcription
E)DNA replication, transcription, and translation
A)transcription
B)transcription and translation
C)translation and DNA replication
D)DNA replication and transcription
E)DNA replication, transcription, and translation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A lack of telomerase activity limits what?
A)the rate of DNA replication
B)the number of replication bubbles that form during replication
C)the number of times a cell can divide
D)the number of Okazaki fragments that can be linked together
E)the rate of meiosis
A)the rate of DNA replication
B)the number of replication bubbles that form during replication
C)the number of times a cell can divide
D)the number of Okazaki fragments that can be linked together
E)the rate of meiosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Okazaki fragments are found on _____ strand of DNA.
A)the lagging
B)the leading
C)the parental
D)both the leading and lagging
A)the lagging
B)the leading
C)the parental
D)both the leading and lagging

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
_____ requires both a template and a free 3' end to elongate a nucleotide chain.
A)RNA primase
B)Helicase
C)Topoisomerase II
D)DNA polymerase
A)RNA primase
B)Helicase
C)Topoisomerase II
D)DNA polymerase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Why are primers needed for DNA replication?
A)They help with the joining of Okazaki fragments.
B)A tiny amount of RNA is needed to tell the cell where genes are located.
C)DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to an existing chain.
D)The primers help with the proofreading function of DNA polymerase.
E)They help direct the placement of the telomeres.
A)They help with the joining of Okazaki fragments.
B)A tiny amount of RNA is needed to tell the cell where genes are located.
C)DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to an existing chain.
D)The primers help with the proofreading function of DNA polymerase.
E)They help direct the placement of the telomeres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Given that the rate of DNA synthesis of a plasmid in yeast is 50 nucleotides per second and the circular plasmid replicates in 20 minutes, what is the approximate maximum size of the plasmid?
A)30,000 bp
B)60,000 bp
C)120,000 bp
A)30,000 bp
B)60,000 bp
C)120,000 bp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An organism is found in which the template RNA sequence in the telomerase is 5'-CCAUAA-3'.
What is the DNA sequence of the organism's telomeres?
A)
B)
C)
D)
What is the DNA sequence of the organism's telomeres?
A)
B)
C)
D)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The following enzymes play important roles in DNA replication: DNA polymerase, primase, ligase, helicase. In what order do they work during replication?
A)DNA polymerase, primase, ligase, helicase
B)primase, helicase, ligase, DNA polymerase
C)DNA polymerase, helicase, primase, ligase
D)helicase, primase, DNA polymerase, ligase
E)ligase, helicase, DNA polymerase, primase
A)DNA polymerase, primase, ligase, helicase
B)primase, helicase, ligase, DNA polymerase
C)DNA polymerase, helicase, primase, ligase
D)helicase, primase, DNA polymerase, ligase
E)ligase, helicase, DNA polymerase, primase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The point at which DNA synthesis is initiated is called the:
A)primer.
B)primase.
C)start codon.
D)replication fork.
E)origin of replication.
A)primer.
B)primase.
C)start codon.
D)replication fork.
E)origin of replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why are telomeres a necessary component of linear chromosomes?
A)They direct where DNA synthesis will begin.
B)They fix mistakes that are made during DNA replication.
C)They maintain the length of a chromosome because DNA is shortened every time it is replicated.
D)They direct where DNA synthesis will end.
E)None of the answer options is correct.
A)They direct where DNA synthesis will begin.
B)They fix mistakes that are made during DNA replication.
C)They maintain the length of a chromosome because DNA is shortened every time it is replicated.
D)They direct where DNA synthesis will end.
E)None of the answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following reasons explains why bacteria can continually divide?
A)because they are so simple
B)because their DNA is circular so the DNA never shortens after replication
C)because DNA replication is much quicker in bacteria than in eukaryotes
D)because they have plasmids
E)because they only have one chromosome
A)because they are so simple
B)because their DNA is circular so the DNA never shortens after replication
C)because DNA replication is much quicker in bacteria than in eukaryotes
D)because they have plasmids
E)because they only have one chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What would happen if telomerase stopped working in a cell in which it normally functions at high levels?
A)The cells would be able to divide indefinitely.
B)Cancer would be the result.
C)The cell would die immediately.
D)The cell would eventually die as the DNA continued to shorten.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)The cells would be able to divide indefinitely.
B)Cancer would be the result.
C)The cell would die immediately.
D)The cell would eventually die as the DNA continued to shorten.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Each end of a eukaryotic chromosome is capped by a repeating DNA sequence called the _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Stem cells located in the gastrointestinal tract would possess more inactive telomerase compared to the amount of telomerase activity in mature neurons of the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A daughter strand of DNA produced during chromosome replication can be composed of leading and lagging strands from different replication bubbles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Mitochondria contain their own double-stranded, circular DNA and replicate on their own. Why don't they suffer the same consequences as our cells in terms of limited division?
A)Because they have high telomerase activity.
B)Shortening of the DNA is only a problem with nuclear DNA; shortening of mitochondrial DNA isn't catastrophic.
C)Because mitochondrial DNA is circular, it doesn't shorten when it replicates.
D)Since mitochondrial DNA only contains a few genes, it can last a lot longer.
E)Because they have high telomerase activity and their DNA is circular and so doesn't shorten in replication.
A)Because they have high telomerase activity.
B)Shortening of the DNA is only a problem with nuclear DNA; shortening of mitochondrial DNA isn't catastrophic.
C)Because mitochondrial DNA is circular, it doesn't shorten when it replicates.
D)Since mitochondrial DNA only contains a few genes, it can last a lot longer.
E)Because they have high telomerase activity and their DNA is circular and so doesn't shorten in replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding origins of replication?
A)Circular DNA always has between two and three origins of replication.
B)Eukaryotic DNA always has one origin of replication.
C)The replication bubbles associated with different origins of replication never fuse.
D)Origins of replication are synonymous with replication forks.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)Circular DNA always has between two and three origins of replication.
B)Eukaryotic DNA always has one origin of replication.
C)The replication bubbles associated with different origins of replication never fuse.
D)Origins of replication are synonymous with replication forks.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Each DNA parent strand within a replication bubble acts as a template strand that produces:
A)either a leading strand or a lagging strand.
B)two leading strands or two lagging strands.
C)one leading strand and one lagging strand.
D)only leading strands.
E)only lagging strands.
A)either a leading strand or a lagging strand.
B)two leading strands or two lagging strands.
C)one leading strand and one lagging strand.
D)only leading strands.
E)only lagging strands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Okazaki fragments are ligated into a continuous DNA molecule after replication is completed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding DNA replication?
A)Only the lagging strand gets shortened during replication.
B)Only the leading strand gets shortened during replication.
C)Both strands get shortened at the same end during replication.
D)Both strands get shortened at opposite ends during replication.
E)Only the lagging strand gets shortened after every other round of replication.
A)Only the lagging strand gets shortened during replication.
B)Only the leading strand gets shortened during replication.
C)Both strands get shortened at the same end during replication.
D)Both strands get shortened at opposite ends during replication.
E)Only the lagging strand gets shortened after every other round of replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In circular DNA, the DNA molecule is not shortened during replication.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding chromosome replication in eukaryotes?
A)During chromosome replication, multiple origins of replication form for all DNA in a cell.
B)Replication bubbles remain distinct, isolated structures during chromosome replication and never fuse with one another.
C)In humans, it takes several days to replicate an entire chromosome.
D)Replication begins at one end of the chromosome and proceeds until it reaches the opposite end.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)During chromosome replication, multiple origins of replication form for all DNA in a cell.
B)Replication bubbles remain distinct, isolated structures during chromosome replication and never fuse with one another.
C)In humans, it takes several days to replicate an entire chromosome.
D)Replication begins at one end of the chromosome and proceeds until it reaches the opposite end.
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding telomeres?
A)Telomeres are enzymes that repair telomerases (which cap the end of linear chromosomes).
B)Telomeres contain nonessential genes that are not necessary for cell survival.
C)Telomeres are typically only a few base pairs in size.
D)Telomeres can contain repeated base sequences.
E)Telomeres are repaired to the same extent in germ cells and somatic cells.
A)Telomeres are enzymes that repair telomerases (which cap the end of linear chromosomes).
B)Telomeres contain nonessential genes that are not necessary for cell survival.
C)Telomeres are typically only a few base pairs in size.
D)Telomeres can contain repeated base sequences.
E)Telomeres are repaired to the same extent in germ cells and somatic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Telomerase is fully active in _____ and _____ cells, but almost completely inactive in _____ cells.
A)germ; somatic; stem
B)germ; stem; somatic
C)stem; blood; germ
D)somatic; blood; germ
E)somatic; germ; stem
A)germ; somatic; stem
B)germ; stem; somatic
C)stem; blood; germ
D)somatic; blood; germ
E)somatic; germ; stem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Imagine that a doctor is culturing cells from a malignant melanoma and from a normal skin sample. How would you expect these two cell populations to differ?
A)Malignant melanoma cells would have telomeres that do not shorten during successive rounds of replication.
B)Normal skin cells would have telomeres that do not shorten during successive rounds of replication.
C)Malignant melanoma cells would have inactive telomerases and so their telomeres would shorten during successive rounds of replication.
D)Normal skin cells would have active telomerases that constantly replenish and lengthen telomeres.
E)Malignant melanoma cells would have active telomerases that constantly replenish and lengthen telomeres.
A)Malignant melanoma cells would have telomeres that do not shorten during successive rounds of replication.
B)Normal skin cells would have telomeres that do not shorten during successive rounds of replication.
C)Malignant melanoma cells would have inactive telomerases and so their telomeres would shorten during successive rounds of replication.
D)Normal skin cells would have active telomerases that constantly replenish and lengthen telomeres.
E)Malignant melanoma cells would have active telomerases that constantly replenish and lengthen telomeres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In a long DNA molecule, each origin of replication produces a _____ with a _____ on each side.
A)replication bubble; replication fork
B)replication fork; replication bubble
C)replication bubble; DNA ligase
D)replication fork; DNA ligase
E)None of the other answer options is correct.
A)replication bubble; replication fork
B)replication fork; replication bubble
C)replication bubble; DNA ligase
D)replication fork; DNA ligase
E)None of the other answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Telomerase activity in stem cells is very low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If a restriction enzyme has a cleavage site consisting of six nucleotide pairs, what is the chance that six adjacent nucleotides in a random sequence of double-stranded DNA will match the restriction site?
A)(1/2)4 = 1/16
B)(1/2)6 = 1/64
C)(1/4)4 = 1/256
D)(1/4)6 = 1/4096
A)(1/2)4 = 1/16
B)(1/2)6 = 1/64
C)(1/4)4 = 1/256
D)(1/4)6 = 1/4096

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 169 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



