Deck 14: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/135
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Chemical Equilibrium
1
The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction at 673 K are [H₂] = 0.63 M, [N₂] = 0.45 M, and [NH₃] = 0.24 M. The value of Keq is ________. N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) ![<strong>The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction at 673 K are [H₂] = 0.63 M, [N₂] = 0.45 M, and [NH₃] = 0.24 M. The value of Keq is ________. N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) 2NH₃ (g)</strong> A) 0.85 B) 1.18 C) 0.51 D) 1.96](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_9738_be6e_03fa135e519b_TB6848_11.jpg) 2NH₃ (g)
2NH₃ (g)
A) 0.85
B) 1.18
C) 0.51
D) 1.96
![<strong>The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction at 673 K are [H₂] = 0.63 M, [N₂] = 0.45 M, and [NH₃] = 0.24 M. The value of Keq is ________. N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) 2NH₃ (g)</strong> A) 0.85 B) 1.18 C) 0.51 D) 1.96](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_9738_be6e_03fa135e519b_TB6848_11.jpg) 2NH₃ (g)
2NH₃ (g)A) 0.85
B) 1.18
C) 0.51
D) 1.96
0.51
2
For which of the following values of an equilibrium constant, Keq, would you expect the equilibrium to lie farthest to the right?
A) 0.491, at 20 °C
B) 1.04, at 20 °C
C) 10.6, at 20 °C
D) 1.46 × 10-4 , at 20 °C
A) 0.491, at 20 °C
B) 1.04, at 20 °C
C) 10.6, at 20 °C
D) 1.46 × 10-4 , at 20 °C
10.6, at 20 °C
3
Which statement is true about equilibrium?
A) The forward reaction rate is greater than the reverse reaction rate.
B) The reverse reaction rate is greater than the forward reaction rate.
C) The forward reaction rate is equal to the reverse reaction rate.
D) Either A or B depending on the reaction.
A) The forward reaction rate is greater than the reverse reaction rate.
B) The reverse reaction rate is greater than the forward reaction rate.
C) The forward reaction rate is equal to the reverse reaction rate.
D) Either A or B depending on the reaction.
The forward reaction rate is equal to the reverse reaction rate.
4
For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant, Keq, is equal to 53.3. What is the concentration of I₂ at equilibrium, if the concentrations of HI and H2 are 0.212 M and 1.576 M, respectively? H₂ + I₂  2HI
2HI
A) 1.576 M
B) 0.000535 M
C) 0.212 M
D) 0.314 M
 2HI
2HIA) 1.576 M
B) 0.000535 M
C) 0.212 M
D) 0.314 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
For which of the following values of an equilibrium constant, Keq, would you expect the equilibrium to lie farthest to the left?
A) 0.491, at 20 °C
B) 1.04, at 20 °C
C) 10.6, at 20 °C
D) 1.46 × 10-4 , at 20 °C
A) 0.491, at 20 °C
B) 1.04, at 20 °C
C) 10.6, at 20 °C
D) 1.46 × 10-4 , at 20 °C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Calculate the equilibrium concentration of N₂ for the following reaction. 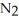 +
+ 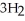

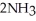 The equilibrium constant Keq is 0.055 and the concentrations of
The equilibrium constant Keq is 0.055 and the concentrations of 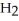 and
and 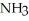 are 1.20 M and 0.225 M, respectively.
are 1.20 M and 0.225 M, respectively.
A) 0.0915 M
B) 0.533 M
C) 0.915 M
D) 3.41 M
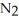 +
+ 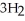

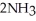 The equilibrium constant Keq is 0.055 and the concentrations of
The equilibrium constant Keq is 0.055 and the concentrations of 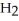 and
and 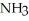 are 1.20 M and 0.225 M, respectively.
are 1.20 M and 0.225 M, respectively.A) 0.0915 M
B) 0.533 M
C) 0.915 M
D) 3.41 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
For this chemical reaction at equilibrium: N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)  2NH₃ (g)
2NH₃ (g)
Which of the following statements is true of the reaction rate?
A) The forward rate is faster than the reverse rate.
B) The reverse rate is faster than the forward rate.
C) Both the forward and reverse rates are zero.
D) The forward and reverse rates are the same.
 2NH₃ (g)
2NH₃ (g)Which of the following statements is true of the reaction rate?
A) The forward rate is faster than the reverse rate.
B) The reverse rate is faster than the forward rate.
C) Both the forward and reverse rates are zero.
D) The forward and reverse rates are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction at 300 K are [CL₂] = 0.75 M, [PCl3] = 0.45 M and [PCl5] = 0.73 M. Based on the calculated value of the equilibrium constant, the reaction is ________. CL₂ (g) + PCL₃ (g) ![<strong>The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction at 300 K are [CL₂] = 0.75 M, [PCl<sub>3</sub>] = 0.45 M and [PCl<sub>5</sub>] = 0.73 M. Based on the calculated value of the equilibrium constant, the reaction is ________. CL₂ (g) + PCL₃ (g) PCl<sub>5</sub> (g)</strong> A) favorable B) unfavorable C) temperature dependent D) temperature independent](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63ef_107d_be6e_eda8272eaa99_TB6848_11.jpg) PCl5 (g)
PCl5 (g)
A) favorable
B) unfavorable
C) temperature dependent
D) temperature independent
![<strong>The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction at 300 K are [CL₂] = 0.75 M, [PCl<sub>3</sub>] = 0.45 M and [PCl<sub>5</sub>] = 0.73 M. Based on the calculated value of the equilibrium constant, the reaction is ________. CL₂ (g) + PCL₃ (g) PCl<sub>5</sub> (g)</strong> A) favorable B) unfavorable C) temperature dependent D) temperature independent](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63ef_107d_be6e_eda8272eaa99_TB6848_11.jpg) PCl5 (g)
PCl5 (g)A) favorable
B) unfavorable
C) temperature dependent
D) temperature independent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The equilibrium constant is equal to which of the following?
A) kforward / kreverse
B) kreverse / kforward
C) kforward × kreverse
D) 1 / (kforward/kreverse)
A) kforward / kreverse
B) kreverse / kforward
C) kforward × kreverse
D) 1 / (kforward/kreverse)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction is ________. N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) ![<strong>The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction is ________. N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) 2NH₃ (g)</strong> A) Keq = [N₂] [3H₂]3 / [2NH₃]2 B) Keq = [NH₃]2 / [N₂] [H₂]3 C) Keq = [N₂] [H₂]3 / [NH₃]2 D) Keq = [2NH₃]2 / [N₂] [3H₂]3](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_7026_be6e_1d44b462e822_TB6848_11.jpg) 2NH₃ (g)
2NH₃ (g)
A) Keq = [N₂] [3H₂]3 / [2NH₃]2
B) Keq = [NH₃]2 / [N₂] [H₂]3
C) Keq = [N₂] [H₂]3 / [NH₃]2
D) Keq = [2NH₃]2 / [N₂] [3H₂]3
![<strong>The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction is ________. N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g) 2NH₃ (g)</strong> A) Keq = [N₂] [3H₂]3 / [2NH₃]2 B) Keq = [NH₃]2 / [N₂] [H₂]3 C) Keq = [N₂] [H₂]3 / [NH₃]2 D) Keq = [2NH₃]2 / [N₂] [3H₂]3](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_7026_be6e_1d44b462e822_TB6848_11.jpg) 2NH₃ (g)
2NH₃ (g)A) Keq = [N₂] [3H₂]3 / [2NH₃]2
B) Keq = [NH₃]2 / [N₂] [H₂]3
C) Keq = [N₂] [H₂]3 / [NH₃]2
D) Keq = [2NH₃]2 / [N₂] [3H₂]3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is true for a chemical reaction that has not reached an equilibrium?
A) The "reverse" reaction rate is zero.
B) The "forward" reaction rate is zero.
C) The "forward" and "reverse" reaction rates are equal.
D) Both A and B are true statements.
E) None of the above are true statements.
A) The "reverse" reaction rate is zero.
B) The "forward" reaction rate is zero.
C) The "forward" and "reverse" reaction rates are equal.
D) Both A and B are true statements.
E) None of the above are true statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Increasing the pressure will ________. 2 HCl (g)  CL₂ (g) + H₂ (g)
CL₂ (g) + H₂ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 CL₂ (g) + H₂ (g)
CL₂ (g) + H₂ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction is ________. 2SO₃ (g) + 2CL₂ (g) ![<strong>The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction is ________. 2SO₃ (g) + 2CL₂ (g) 2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)</strong> A) Keq = [SO₂CL₂] [O₂] / [SO₃] [CL₂] B) Keq = [SO₃] [CL₂] / [SO₂CL₂] [O₂] C) Keq = [SO₂CL₂]2[O₂] / [SO₃]2[CL₂]2 D) Keq = [SO₃]2[CL₂]2 / [SO₂CL₂]2[O₂]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_7027_be6e_85e49af4ff1a_TB6848_11.jpg) 2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
A) Keq = [SO₂CL₂] [O₂] / [SO₃] [CL₂]
B) Keq = [SO₃] [CL₂] / [SO₂CL₂] [O₂]
C) Keq = [SO₂CL₂]2[O₂] / [SO₃]2[CL₂]2
D) Keq = [SO₃]2[CL₂]2 / [SO₂CL₂]2[O₂]
![<strong>The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction is ________. 2SO₃ (g) + 2CL₂ (g) 2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)</strong> A) Keq = [SO₂CL₂] [O₂] / [SO₃] [CL₂] B) Keq = [SO₃] [CL₂] / [SO₂CL₂] [O₂] C) Keq = [SO₂CL₂]2[O₂] / [SO₃]2[CL₂]2 D) Keq = [SO₃]2[CL₂]2 / [SO₂CL₂]2[O₂]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_7027_be6e_85e49af4ff1a_TB6848_11.jpg) 2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)A) Keq = [SO₂CL₂] [O₂] / [SO₃] [CL₂]
B) Keq = [SO₃] [CL₂] / [SO₂CL₂] [O₂]
C) Keq = [SO₂CL₂]2[O₂] / [SO₃]2[CL₂]2
D) Keq = [SO₃]2[CL₂]2 / [SO₂CL₂]2[O₂]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The following chemical reaction has reached equilibrium. 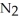
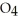 (g)
(g) 
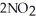 (g) Calculate the equilibrium constant, Keq, if the concentrations of
(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant, Keq, if the concentrations of 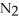
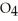 and
and 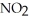 are 0.0238 M and 0.196 M, respectively.
are 0.0238 M and 0.196 M, respectively.
A) 8.34
B) 346
C) 0.621
D) 1.61
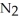
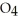 (g)
(g) 
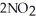 (g) Calculate the equilibrium constant, Keq, if the concentrations of
(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant, Keq, if the concentrations of 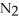
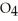 and
and 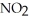 are 0.0238 M and 0.196 M, respectively.
are 0.0238 M and 0.196 M, respectively.A) 8.34
B) 346
C) 0.621
D) 1.61

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The following chemical reaction has reached equilibrium. 2NO (g) + O₂ (g)  2NO₂ (g)
2NO₂ (g)
Calculate the equilibrium constant, Keq, if the concentrations of reactants and products are 1.26 × 10-10 M for NO, 2.28 × 10-3 M for O₂, and 9.32 × 10-6 M for NO₂.
A) 2.40 × 10-12
B) 3.28 × 10-7
C) 2.61 × 10-17
D) 2.40 × 1012
 2NO₂ (g)
2NO₂ (g)Calculate the equilibrium constant, Keq, if the concentrations of reactants and products are 1.26 × 10-10 M for NO, 2.28 × 10-3 M for O₂, and 9.32 × 10-6 M for NO₂.
A) 2.40 × 10-12
B) 3.28 × 10-7
C) 2.61 × 10-17
D) 2.40 × 1012

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements best describes the rate of the forward reaction as it approaches equilibrium?
A) The rate increases as equilibrium is approached.
B) The rate decreases as equilibrium is approached.
C) The rate remains constant.
D) The rate slows down, then increases, as equilibrium is approached.
A) The rate increases as equilibrium is approached.
B) The rate decreases as equilibrium is approached.
C) The rate remains constant.
D) The rate slows down, then increases, as equilibrium is approached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When a reaction shows one arrow pointing from left to right, this means ________.
A) the reaction has reached equilibrium
B) the reaction favors the right direction
C) there is practically no reactant left
D) both B and C
A) the reaction has reached equilibrium
B) the reaction favors the right direction
C) there is practically no reactant left
D) both B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the value of the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction is 2.5 × 10-6, the value of the equilibrium constant for the forward reaction is ________.
A) -2.5 × 10-6
B) 4.0 × 105
C) 2.5 × 106
D) 4.0 × 107
A) -2.5 × 10-6
B) 4.0 × 105
C) 2.5 × 106
D) 4.0 × 107

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the value of the equilibrium constant for the forward reaction is 5.0 × 1010, the value of the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction is ________.
A) -5.0 × 1030
B) 5.0 × 10-10
C) 2.0 × 10-11
D) 2.0 × 10-10
A) -5.0 × 1030
B) 5.0 × 10-10
C) 2.0 × 10-11
D) 2.0 × 10-10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements about the equilibrium constant is incorrect?
A) If Keq > 1 the reaction favors product formation.
B) If Keq > 1 the reaction does not favor product formation.
C) If Keq = 1 the reaction is at equilibrium.
D) If Keq < 1 the reaction does not favor product formation.
A) If Keq > 1 the reaction favors product formation.
B) If Keq > 1 the reaction does not favor product formation.
C) If Keq = 1 the reaction is at equilibrium.
D) If Keq < 1 the reaction does not favor product formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Increasing the concentration of hydrogen gas will ________. O₂ (g) + 2H₂ (g)  2H₂O (g)
2H₂O (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2H₂O (g)
2H₂O (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction at 300 K are [CL₂] = 0.75 M, [PCL₃] = 0.45 M, and [PCl5] = 0.73 M. The value of Keq is ________. CL₂ (g) + PCL₃ (g) ![<strong>The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction at 300 K are [CL₂] = 0.75 M, [PCL₃] = 0.45 M, and [PCl5] = 0.73 M. The value of Keq is ________. CL₂ (g) + PCL₃ (g) PCl5 (g)</strong> A) 2.2 B) 0.15 C) 0.048 D) 4.7](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_9739_be6e_cf42dcc266f2_TB6848_11.jpg) PCl5 (g)
PCl5 (g)
A) 2.2
B) 0.15
C) 0.048
D) 4.7
![<strong>The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction at 300 K are [CL₂] = 0.75 M, [PCL₃] = 0.45 M, and [PCl5] = 0.73 M. The value of Keq is ________. CL₂ (g) + PCL₃ (g) PCl5 (g)</strong> A) 2.2 B) 0.15 C) 0.048 D) 4.7](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_9739_be6e_cf42dcc266f2_TB6848_11.jpg) PCl5 (g)
PCl5 (g)A) 2.2
B) 0.15
C) 0.048
D) 4.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Adding iron(III) chloride will ________. FeCL₃ (aq) + KSCN (aq) ![<strong>Adding iron(III) chloride will ________. FeCL₃ (aq) + KSCN (aq) 3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq) Yellow colorless red colorless</strong> A) turn the solution more red. B) turn the solution less red. C) turn the solution clear. D) have no effect on the color.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f1_cec6_be6e_45a3d390a7ca_TB6848_11.jpg) 3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)
3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)
Yellow colorless red colorless
A) turn the solution more red.
B) turn the solution less red.
C) turn the solution clear.
D) have no effect on the color.
![<strong>Adding iron(III) chloride will ________. FeCL₃ (aq) + KSCN (aq) 3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq) Yellow colorless red colorless</strong> A) turn the solution more red. B) turn the solution less red. C) turn the solution clear. D) have no effect on the color.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f1_cec6_be6e_45a3d390a7ca_TB6848_11.jpg) 3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)
3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)Yellow colorless red colorless
A) turn the solution more red.
B) turn the solution less red.
C) turn the solution clear.
D) have no effect on the color.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Adding a couple of drops of an aqueous KCl solution will ________. FeCL₃ (aq) + KSCN (aq) ![<strong>Adding a couple of drops of an aqueous KCl solution will ________. FeCL₃ (aq) + KSCN (aq) K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq) Yellow colorless red colorless</strong> A) turn the solution more red. B) turn the solution less red. C) turn the solution clear. D) have no effect on the color.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f1_f5d8_be6e_bbed82f4d490_TB6848_11.jpg) K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)
K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)
Yellow colorless red colorless
A) turn the solution more red.
B) turn the solution less red.
C) turn the solution clear.
D) have no effect on the color.
![<strong>Adding a couple of drops of an aqueous KCl solution will ________. FeCL₃ (aq) + KSCN (aq) K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq) Yellow colorless red colorless</strong> A) turn the solution more red. B) turn the solution less red. C) turn the solution clear. D) have no effect on the color.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f1_f5d8_be6e_bbed82f4d490_TB6848_11.jpg) K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)
K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)Yellow colorless red colorless
A) turn the solution more red.
B) turn the solution less red.
C) turn the solution clear.
D) have no effect on the color.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Removing sulfur dioxide as it is formed will ________. 2H₂S (g) + 3O₂ (g)  2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Increasing the volume will ________. 2NH₃ (g)  N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)
N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)
N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Increasing the pressure will ________. 2NH₃ (g)  N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)
N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)
N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Decreasing the volume will ________. 2SO₃ (g) + 2CL₂ (g)  2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Removing product will ________. 2SO₂ (g) + O₂ (g)  2SO₃ (g)
2SO₃ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₃ (g)
2SO₃ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Equal numbers of moles for A and B are added to the reaction vessel and equilibrium established. At that point ________. A + 3B ![<strong>Equal numbers of moles for A and B are added to the reaction vessel and equilibrium established. At that point ________. A + 3B 2C</strong> A) [A] < [B] B) [A] > [B] C) [A] = [B] D) One cannot say unless the equilibrium constant value is known.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_be4b_be6e_4948be4db48b_TB6848_11.jpg) 2C
2C
A) [A] < [B]
B) [A] > [B]
C) [A] = [B]
D) One cannot say unless the equilibrium constant value is known.
![<strong>Equal numbers of moles for A and B are added to the reaction vessel and equilibrium established. At that point ________. A + 3B 2C</strong> A) [A] < [B] B) [A] > [B] C) [A] = [B] D) One cannot say unless the equilibrium constant value is known.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_be4b_be6e_4948be4db48b_TB6848_11.jpg) 2C
2CA) [A] < [B]
B) [A] > [B]
C) [A] = [B]
D) One cannot say unless the equilibrium constant value is known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Increasing the pressure will ________. 2SO₂ (g) + O₂ (g)  2SO₃ (g)
2SO₃ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₃ (g)
2SO₃ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Decreasing the pressure will ________. 2SO₃ (g) + 2CL₂ (g)  2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
2SO₂CL₂ (g) + O₂ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Adding more oxygen will ________. 2SO₂ (g) + O₂ (g)  2SO₃ (g)
2SO₃ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₃ (g)
2SO₃ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Removing ammonia as soon as it is formed will ________. N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)  2NH₃ (g)
2NH₃ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2NH₃ (g)
2NH₃ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Adding helium to the reaction vessel will ________. 2H₂S (g) + 3O₂ (g)  2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Adding H₂O to the reaction vessel will ________. 2H₂S (g) + 3O₂ (g)  2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the reaction with Kc = 0.211. Which of the following pairs of concentrations indicate that the system is not at equilibrium? N₂O₄ (g) ![<strong>Consider the reaction with Kc = 0.211. Which of the following pairs of concentrations indicate that the system is not at equilibrium? N₂O₄ (g) 2NO₂ (g)</strong> A) [N₂O₄] = 0.00140 M; [NO₂] = 0.0172 M B) [N₂O₄] = 0.00280 M; [NO₂] = 0.0243 M C) [N₂O₄] = 0.00452 M; [NO₂] = 0.0309 M D) [N₂O₄] = 0.00840 M; [NO₂] = 0.0572 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_973a_be6e_c965bc07b9d6_TB6848_11.jpg) 2NO₂ (g)
2NO₂ (g)
A) [N₂O₄] = 0.00140 M; [NO₂] = 0.0172 M
B) [N₂O₄] = 0.00280 M; [NO₂] = 0.0243 M
C) [N₂O₄] = 0.00452 M; [NO₂] = 0.0309 M
D) [N₂O₄] = 0.00840 M; [NO₂] = 0.0572 M
![<strong>Consider the reaction with Kc = 0.211. Which of the following pairs of concentrations indicate that the system is not at equilibrium? N₂O₄ (g) 2NO₂ (g)</strong> A) [N₂O₄] = 0.00140 M; [NO₂] = 0.0172 M B) [N₂O₄] = 0.00280 M; [NO₂] = 0.0243 M C) [N₂O₄] = 0.00452 M; [NO₂] = 0.0309 M D) [N₂O₄] = 0.00840 M; [NO₂] = 0.0572 M](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f0_973a_be6e_c965bc07b9d6_TB6848_11.jpg) 2NO₂ (g)
2NO₂ (g)A) [N₂O₄] = 0.00140 M; [NO₂] = 0.0172 M
B) [N₂O₄] = 0.00280 M; [NO₂] = 0.0243 M
C) [N₂O₄] = 0.00452 M; [NO₂] = 0.0309 M
D) [N₂O₄] = 0.00840 M; [NO₂] = 0.0572 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Increasing the pressure will ________. 2H₂S (g) + 3O₂ (g)  2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Adding KSCN will ________. FeCL₃ (aq) + KSCN (aq) ![<strong>Adding KSCN will ________. FeCL₃ (aq) + KSCN (aq) K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq) Yellow colorless red colorless</strong> A) turn the solution more red. B) turn the solution less red. C) turn the solution clear. D) have no effect on the color.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f1_f5d7_be6e_09bd0d251dcd_TB6848_11.jpg) K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)
K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)
Yellow colorless red colorless
A) turn the solution more red.
B) turn the solution less red.
C) turn the solution clear.
D) have no effect on the color.
![<strong>Adding KSCN will ________. FeCL₃ (aq) + KSCN (aq) K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq) Yellow colorless red colorless</strong> A) turn the solution more red. B) turn the solution less red. C) turn the solution clear. D) have no effect on the color.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f1_f5d7_be6e_09bd0d251dcd_TB6848_11.jpg) K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)
K3[Fe(SCN)6] (aq) + 3KCl (aq)Yellow colorless red colorless
A) turn the solution more red.
B) turn the solution less red.
C) turn the solution clear.
D) have no effect on the color.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Decreasing the concentration of ammonia gas will ________. 2NH₃ (g)  N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)
N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)
N₂ (g) + 3H₂ (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
For the following endothermic reaction, what condition will increase the yield of product? N₂ (g) + 2H₂ (g)  N₂H₄ (g)
N₂H₄ (g)
A) high temperature, high pressure
B) high temperature, low pressure
C) low temperature, high pressure
D) low temperature, low pressure
 N₂H₄ (g)
N₂H₄ (g)A) high temperature, high pressure
B) high temperature, low pressure
C) low temperature, high pressure
D) low temperature, low pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Adding a catalyst will ________. FeCL₃ + KSCN ![<strong>Adding a catalyst will ________. FeCL₃ + KSCN K3[Fe(SCN)6] + 3KCl Yellow colorless red colorless</strong> A) turn the solution red. B) turn the solution less red. C) turn the solution clear. D) have no effect on the color.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f2_b933_be6e_891bb00e8084_TB6848_11.jpg) K3[Fe(SCN)6] + 3KCl
K3[Fe(SCN)6] + 3KCl
Yellow colorless red colorless
A) turn the solution red.
B) turn the solution less red.
C) turn the solution clear.
D) have no effect on the color.
![<strong>Adding a catalyst will ________. FeCL₃ + KSCN K3[Fe(SCN)6] + 3KCl Yellow colorless red colorless</strong> A) turn the solution red. B) turn the solution less red. C) turn the solution clear. D) have no effect on the color.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f2_b933_be6e_891bb00e8084_TB6848_11.jpg) K3[Fe(SCN)6] + 3KCl
K3[Fe(SCN)6] + 3KClYellow colorless red colorless
A) turn the solution red.
B) turn the solution less red.
C) turn the solution clear.
D) have no effect on the color.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following will shift the reaction to the right? CH₄ (g) + 2O₂ (g)  CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) adding excess oxygen
B) removing carbon dioxide as soon as it is formed
C) increasing the pressure
D) both A and B
 CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) adding excess oxygen
B) removing carbon dioxide as soon as it is formed
C) increasing the pressure
D) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In an exothermic reaction, adding heat will ________.
A) increase the amount of products
B) decrease the amount of reactants
C) decrease the amount of products
D) both A and B
A) increase the amount of products
B) decrease the amount of reactants
C) decrease the amount of products
D) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Increasing the volume of the system will ________. 2H₂S (g) + 3O₂ (g)  2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the solubility of calcium fluoride is 2.0 × 10-4 M, the solubility product value is ________.
A) 1.6 × 10-12
B) 3.2 × 10-11
C) 4.0 × 10-8
D) 8.0 × 10-12
A) 1.6 × 10-12
B) 3.2 × 10-11
C) 4.0 × 10-8
D) 8.0 × 10-12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the solubility of a certain salt A2B is 1.4 × 10-4 M, the value of the solubility product will be ________.
A) 2.7 × 10-12
B) 1.1 × 10-11
C) 1.6 × 10-11
D) 3.6 × 10-12
A) 2.7 × 10-12
B) 1.1 × 10-11
C) 1.6 × 10-11
D) 3.6 × 10-12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The solubility product expression for silver(I) sulfate is ________.
A) Ksp = [Ag+] [SO₄-2]
B) Ksp = [2 Ag+] [SO₄-2]
C) Ksp = [Ag+]2[SO₄-2]
D) Ksp = [2Ag+]2[SO₄-2]
A) Ksp = [Ag+] [SO₄-2]
B) Ksp = [2 Ag+] [SO₄-2]
C) Ksp = [Ag+]2[SO₄-2]
D) Ksp = [2Ag+]2[SO₄-2]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
At equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products are always exactly the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If oxygen is removed this will ________. CH₄ (g) + 2O₂ (g)  CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the reaction vessel is expanded, this will ________. CH₄ (g) + 2O₂ (g)  CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown
 CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is unknown

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For an exothermic reaction, lowering the temperature of the reaction will ________.
A) increase the amount of products
B) decrease the amount of reactants
C) decrease the amount of products
D) both A and B
A) increase the amount of products
B) decrease the amount of reactants
C) decrease the amount of products
D) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Adding excess oxygen will ________. CH₄ (g) + 2O₂ (g)  CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is not known
 CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
CO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) shift the reaction to the right
B) shift the reaction to the left
C) have no effect
D) cannot be determined, since the temperature is not known

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
At equilibrium, the amount of product present is always greater than the amount of reactant present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
For an endothermic reaction, lowering the temperature of the reaction will ________.
A) increase the amount of products
B) decrease the amount of reactants
C) decrease the amount of products
D) both A and B
A) increase the amount of products
B) decrease the amount of reactants
C) decrease the amount of products
D) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
For the following exothermic reaction, what condition will increase the yield of product? C₂H₂ (g) + H₂O (g)  CH₃CHO (g)
CH₃CHO (g)
A) high temperature, high pressure
B) high temperature, low pressure
C) low temperature, high pressure
D) low temperature, low pressure
 CH₃CHO (g)
CH₃CHO (g)A) high temperature, high pressure
B) high temperature, low pressure
C) low temperature, high pressure
D) low temperature, low pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In an endothermic reaction, adding heat will ________.
A) increase the amount of products
B) decrease the amount of reactants
C) decrease the amount of products
D) both A and B
A) increase the amount of products
B) decrease the amount of reactants
C) decrease the amount of products
D) both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The solubility of SrF₂ in water (given Ksp = 2.6 × 10-9 ) is ________.
A) 4.3 × 10-4 M
B) 1.2 × 10-4 M
C) 7.6 × 10-5 M
D) 8.7 × 10-4 M
A) 4.3 × 10-4 M
B) 1.2 × 10-4 M
C) 7.6 × 10-5 M
D) 8.7 × 10-4 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following will shift the equilibrium to the left? 2H₂S (g) + 3O₂ (g)  2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
A) adding sulfur dioxide
B) adding hydrogen sulfide
C) decreasing the pressure
D) both A and C
 2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)
2SO₂ (g) + 2H₂O (g)A) adding sulfur dioxide
B) adding hydrogen sulfide
C) decreasing the pressure
D) both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the solubility of copper(II) sulfate is 4.9 × 10-3 M, the solubility product is ________.
A) 2.4 × 10-5
B) 9.6 × 10-5
C) 1.2 × 10-2
D) 8.7 × 10-8
A) 2.4 × 10-5
B) 9.6 × 10-5
C) 1.2 × 10-2
D) 8.7 × 10-8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Reducing the pressure will shift the equilibrium to the right.
N₂ (g) + O₂ (g) ⇔ 2NO (g)
N₂ (g) + O₂ (g) ⇔ 2NO (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Decreasing the concentration of nitrogen will shift the equilibrium to the left.
N₂ (g) + 2O₂ (g) ⇔ 2NO₂ (g)
N₂ (g) + 2O₂ (g) ⇔ 2NO₂ (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The concentrations of reactants and products do not change as equilibrium is approached, only the rate at which products are formed and reactants are consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The double arrow in a chemical reaction indicates that the equilibrium is established since the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If more reactants are added to a chemical reaction already at equilibrium, a shift to the products is required to restore an equilibrium condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
At equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Reducing the pressure will shift the equilibrium to the left.
N₂ (g) + 2O₂ (g) ⇔ 2NO₂ (g)
N₂ (g) + 2O₂ (g) ⇔ 2NO₂ (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Among the two reactions whose equilibrium constants are 0.003 and 30, the one that will produce greater quantities of products is the one whose equilibrium constant is 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Removing ozone as soon as it is formed will shift the equilibrium to the right.
3O₂ (g) ⇔ 2O₃ (g)
3O₂ (g) ⇔ 2O₃ (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a chemical reaction at an equilibrium state is disturbed, the reaction will compensate for the disturbance in some way so that equilibrium can be restored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Expanding the reaction vessel will shift the equilibrium to the right.
3O₂ (g) ⇔ 2O₃ (g)
3O₂ (g) ⇔ 2O₃ (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If the value of the equilibrium constant for the forward reaction is 2.5 × 1030, the value of the equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction is 4.0 × 10-30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For the following reaction at 1500 K, the equilibrium concentrations of each species are, ![For the following reaction at 1500 K, the equilibrium concentrations of each species are, [N₂] = 0.10 M, and [N₂H₄] = 0.10 M. The equilibrium constant value is 0.04. N₂H₄ (g) ⇔ 2 H₂ (g) + N₂ (g)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f3_7c86_be6e_df8f041afda1_TB6848_11.jpg) [N₂] = 0.10 M, and [N₂H₄] = 0.10 M. The equilibrium constant value is 0.04.
[N₂] = 0.10 M, and [N₂H₄] = 0.10 M. The equilibrium constant value is 0.04.
N₂H₄ (g) ⇔ 2 H₂ (g) + N₂ (g)
![For the following reaction at 1500 K, the equilibrium concentrations of each species are, [N₂] = 0.10 M, and [N₂H₄] = 0.10 M. The equilibrium constant value is 0.04. N₂H₄ (g) ⇔ 2 H₂ (g) + N₂ (g)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6848/11eab3b7_63f3_7c86_be6e_df8f041afda1_TB6848_11.jpg) [N₂] = 0.10 M, and [N₂H₄] = 0.10 M. The equilibrium constant value is 0.04.
[N₂] = 0.10 M, and [N₂H₄] = 0.10 M. The equilibrium constant value is 0.04.N₂H₄ (g) ⇔ 2 H₂ (g) + N₂ (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An equilibrium condition can be achieved only when 100% of the reactants have been converted to products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A reaction is close to equilibrium when a rapid reverse reaction slows down and a slower forward reaction speeds up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A reaction that favors products has a Keq > 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
At 500 K, the equilibrium concentrations of each species are [PCl5] = 0.008 M, [PCL₃] = 0.02 M, and [CL₂] = 0.02 M. The equilibrium constant value is 0.5.
PCl5 ⇔ PCL₃ + CL₂
PCl5 ⇔ PCL₃ + CL₂

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A product favored reaction has Keq = 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A reaction is approaching equilibrium when the rate of a forward reaction slows down and the rate of a reverse reaction speeds up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Reducing the pressure will shift the equilibrium to the right.
CL₂ (g) + 3F₂ (g) ⇔ 2ClF3 (g)
CL₂ (g) + 3F₂ (g) ⇔ 2ClF3 (g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 135 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



