Deck 12: The Aggregate Demand and Supply Model
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/87
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: The Aggregate Demand and Supply Model
1
If for any given inflation rate, the federal government lowered taxes, ________.
A) it would have a similar qualitative result on output as an increase in government purchases
B) it would raise disposable income leading to higher consumption spending
C) the aggregate demand curve would shift to the right
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) it would have a similar qualitative result on output as an increase in government purchases
B) it would raise disposable income leading to higher consumption spending
C) the aggregate demand curve would shift to the right
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
all of the above
2
In the short run, as output rises above potential ________.
A) inflation will fall from its current level which explains the upward-sloping nature of the Phillips curve
B) inflation will rise from its current level which explains the upward-sloping nature of the aggregate supply curve
C) unemployment will rise above the natural rate which explains the upward-sloping nature of both the Phillips curve and the AS curve
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) inflation will fall from its current level which explains the upward-sloping nature of the Phillips curve
B) inflation will rise from its current level which explains the upward-sloping nature of the aggregate supply curve
C) unemployment will rise above the natural rate which explains the upward-sloping nature of both the Phillips curve and the AS curve
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
inflation will rise from its current level which explains the upward-sloping nature of the aggregate supply curve
3
A change in the output gap is likely to lead to ________.
A) a change in inflation
B) a change in expected inflation
C) a shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) a change in inflation
B) a change in expected inflation
C) a shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
all of the above
4
In the short run, ________.
A) cost push shocks can cause firms to raise prices
B) workers pushing for higher wages may lead to increases in inflation
C) the aggregate supply curve may shift to the left with increases in expected inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) cost push shocks can cause firms to raise prices
B) workers pushing for higher wages may lead to increases in inflation
C) the aggregate supply curve may shift to the left with increases in expected inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The aggregate demand curve shifts to the left when there is ________.
A) autonomous tightening of monetary policy
B) an increase in the nominal interest rate
C) an increase in inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) autonomous tightening of monetary policy
B) an increase in the nominal interest rate
C) an increase in inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Under a favorable business environment and if the economic outlook of the future looked promising ________.
A) firms might spend more for any given inflation rate
B) planned investment might increase leading to a higher equilibrium level of output
C) the aggregate demand curve would likely shift to the right
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) firms might spend more for any given inflation rate
B) planned investment might increase leading to a higher equilibrium level of output
C) the aggregate demand curve would likely shift to the right
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The endogenous variable in the aggregate supply curve is ________.
A) output
B) the real interest rate
C) inflation
D) planned expenditure
E) none of the above
A) output
B) the real interest rate
C) inflation
D) planned expenditure
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If consumers suddenly became more optimistic ________.
A) they would spend more at any given inflation rate
B) planned expenditures would decline
C) the aggregate demand curve would shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) they would spend more at any given inflation rate
B) planned expenditures would decline
C) the aggregate demand curve would shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the long run, we typically assume that ________.
A) capital, labor, and technology are independent of the level of inflation
B) the natural rate of unemployment is independent of the level of inflation
C) aggregate supply is fixed and independent of the level of inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) capital, labor, and technology are independent of the level of inflation
B) the natural rate of unemployment is independent of the level of inflation
C) aggregate supply is fixed and independent of the level of inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the short run, ________.
A) when expected inflation rises, there is a movement up along the AS curve
B) workers pushing for higher wages causes output to rise
C) the aggregate supply curve may shift to the right with increases in output
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) when expected inflation rises, there is a movement up along the AS curve
B) workers pushing for higher wages causes output to rise
C) the aggregate supply curve may shift to the right with increases in output
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The endogenous variable in the aggregate demand curve is ________.
A) the real interest rate
B) output
C) inflation
D) planned expenditure
E) none of the above
A) the real interest rate
B) output
C) inflation
D) planned expenditure
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which equation is a plausible aggregate demand curve?
A) π = 2 + 0.3Y
B) Y = 50 - 1.25π
C) Y = 250 - 80r
D) π = 5 - 0.4 (U - 6)
E) none of the above
A) π = 2 + 0.3Y
B) Y = 50 - 1.25π
C) Y = 250 - 80r
D) π = 5 - 0.4 (U - 6)
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the Federal Reserve raises the real interest rate for any given inflation rate ________.
A) investment spending would increase
B) it would lead to higher consumption spending and net exports
C) the aggregate demand curve would shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) investment spending would increase
B) it would lead to higher consumption spending and net exports
C) the aggregate demand curve would shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The short-run aggregate supply curve shows how ________ cause output to rise.
A) increases in inflation
B) decreases in unemployment
C) decreases in nominal interest rates
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) increases in inflation
B) decreases in unemployment
C) decreases in nominal interest rates
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right when there is ________.
A) a negative price shock
B) a decrease in the nominal interest rate
C) a decrease in inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) a negative price shock
B) a decrease in the nominal interest rate
C) a decrease in inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The aggregate demand curve has a negative slope, because households and businesses respond to an increase in ________ by reducing their expenditures.
A) the inflation rate
B) output
C) the real interest rate
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) the inflation rate
B) output
C) the real interest rate
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Rising inflation causes quantity demanded to decline, because ________.
A) the central bank raises the nominal interest rate by more than the increase in expected inflation
B) households and businesses are reluctant to spend when prices rise
C) higher inflation causes the IS curve to shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) the central bank raises the nominal interest rate by more than the increase in expected inflation
B) households and businesses are reluctant to spend when prices rise
C) higher inflation causes the IS curve to shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The assumption that in the long run prices and wages are fully flexible implies that the long-run aggregate supply curve is determined by ________.
A) capital and labor inputs
B) technology
C) the natural rate of unemployment
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) capital and labor inputs
B) technology
C) the natural rate of unemployment
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An autonomous increase in net exports for any given inflation rate ________.
A) would add directly to planned expenditures
B) would raise the equilibrium level of output
C) the aggregate demand curve would shift to the right
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) would add directly to planned expenditures
B) would raise the equilibrium level of output
C) the aggregate demand curve would shift to the right
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which equation is a plausible aggregate supply curve?
A) Y = 50 - 1.25π
B) π = 2 + 0.3 (Y - 75)
C) Y = 250 - 80r
D) π = 5 - 0.4 (U - 6)
E) none of the above
A) Y = 50 - 1.25π
B) π = 2 + 0.3 (Y - 75)
C) Y = 250 - 80r
D) π = 5 - 0.4 (U - 6)
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the unemployment rate is below its natural rate, then ________.
A) output is below its potential level
B) there is excess tightness in the labor market
C) the AS curve will shift to the right
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) output is below its potential level
B) there is excess tightness in the labor market
C) the AS curve will shift to the right
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An economy is in long-run equilibrium when output equals potential output. Why is there no long-run equilibrium rate of "potential inflation"?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The aggregate demand curve is Y = 75 - 3π, and the short-run aggregate supply curve is π = 6.2 + 0.8(Y - 70). Assuming adaptive expectations, calculate the inflation rate and output for the next period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
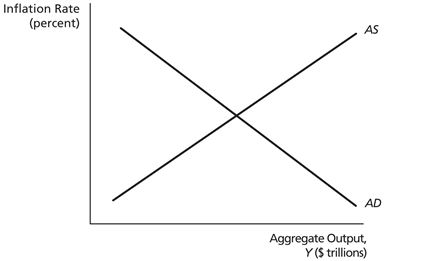
On the graph above, if inflation is rising, while the quantity demanded and output are rising, the economy may be at a point on ________.
A) the aggregate supply curve above the aggregate demand curve
B) the aggregate supply curve below the aggregate demand curve
C) the aggregate demand curve above the aggregate supply curve
D) the aggregate demand curve below the aggregate supply curve
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25

According to the "self-correcting mechanism" in the AD-AS framework, ________.
A) the aggregate demand curve shifts up or down as needed to bring the economy to full employment
B) the inflation rate changes as needed to move the economy along the short-run aggregate supply curve until output is at potential output
C) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts until it intersects both the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply curves at a single point
D) inflation and expected inflation are unaffected by deviations of output from potential output
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

In the AD-AS framework, long-run equilibrium implies that ________.
A) quantity demanded equals quantity supplied at a moderate level of equilibrium inflation
B) quantity demanded equals quantity supplied at a point consistent with the short-run equilibrium level of inflation
C) quantity demanded equals quantity supplied at a point consistent with the natural rate of unemployment
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
By the time Paul Volcker took office as the new Federal Reserve chairman in 1979, the inflation rate exceeded 10%. By the end of 1986 the inflation rate had been brought down to 1.9%. Which of the following is true about the Volcker Disinflation?
A) lower inflation resulted from a tightening of monetary policy
B) by raising the federal funds rate to over 20%, the Federal Reserve stimulated the economy resulting in lower levels of both inflation and the unemployment rate by the early 1980s
C) the unemployment rate was brought down by 1982 but it took longer to reach lower inflation rates
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) lower inflation resulted from a tightening of monetary policy
B) by raising the federal funds rate to over 20%, the Federal Reserve stimulated the economy resulting in lower levels of both inflation and the unemployment rate by the early 1980s
C) the unemployment rate was brought down by 1982 but it took longer to reach lower inflation rates
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

On the graph above, if inflation is falling, while the quantity demanded and output are rising, the economy may be at a point on ________.
A) the aggregate supply curve above the aggregate demand curve
B) the aggregate supply curve below the aggregate demand curve
C) the aggregate demand curve above the aggregate supply curve
D) the aggregate demand curve below the aggregate supply curve
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the unemployment rate is above its natural rate, then ________.
A) output is below its potential level
B) there is excess slack in the labor market which will dive down wages
C) inflation will decline until equilibrium output reaches its potential level
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) output is below its potential level
B) there is excess slack in the labor market which will dive down wages
C) inflation will decline until equilibrium output reaches its potential level
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

On the graph above, if output is falling, while the quantity demanded is rising, the economy may be at a point on ________.
A) the aggregate supply curve above the aggregate demand curve
B) the aggregate supply curve below the aggregate demand curve
C) the aggregate demand curve above the aggregate supply curve
D) the aggregate demand curve below the aggregate supply curve
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How does the aggregate supply curve differ from a supply curve for, say, bananas?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

On the graph above, at the point where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied (let's call it point A), the economy has reached its ________.
A) general equilibrium, and barring any shocks, it will not move from A
B) long-run equilibrium, and barring any shocks, it will not move from A
C) short-run equilibrium, and even without any shocks, it may move away from A
D) short-run equilibrium, and barring any shocks, it will not move from A
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the unemployment rate is above its natural rate, then ________.
A) output is below its potential level
B) there is excess tightness in the labor market
C) wages and prices will rise more rapidly and the AS curve will shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) output is below its potential level
B) there is excess tightness in the labor market
C) wages and prices will rise more rapidly and the AS curve will shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Picture an economy that is in general equilibrium. What would happen if the natural rate of unemployment were to experience a decrease?
A) according to the Phillips curve, the ensuing negative unemployment gap would exert inflationary pressures
B) according to Okun's Law, the ensuing negative unemployment gap would be consistent with a positive output gap
C) according to the AD-AS framework, the LRAS curve would shift to the right and the ensuing output gap would have to be closed by subsequent rightward shifts in the AS curve to a lower equilibrium level of inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) according to the Phillips curve, the ensuing negative unemployment gap would exert inflationary pressures
B) according to Okun's Law, the ensuing negative unemployment gap would be consistent with a positive output gap
C) according to the AD-AS framework, the LRAS curve would shift to the right and the ensuing output gap would have to be closed by subsequent rightward shifts in the AS curve to a lower equilibrium level of inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

On the graph above, consider a point A on the aggregate supply curve and above the aggregate demand curve. At this point, ________.
A) quantity demanded equals output, but the inflation rate will fall, so output will rise
B) quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied, so the inflation rate will rise
C) output is greater than the quantity demanded, so output will fall
D) the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right until quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How does the aggregate demand curve differ from a demand curve for, say, bananas?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the unemployment rate is below its natural rate, then ________.
A) output is above its potential level
B) there is excess tightness in the labor market
C) wages and prices will rise more rapidly and the AS curve will shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) output is above its potential level
B) there is excess tightness in the labor market
C) wages and prices will rise more rapidly and the AS curve will shift to the left
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

On the graph above, consider a point A at which output is greater than potential output. At this point, ________.
A) the inflation rate will rise
B) output will rise
C) potential output will rise
D) the aggregate demand curve will shift to the left
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Picture an economy that is in general equilibrium. What would happen if the natural rate of unemployment were to experience an increase?
A) according to the Phillips curve, the ensuing negative unemployment gap would exert inflationary pressures
B) according to Okun's Law, the ensuing negative unemployment gap would be consistent with a positive output gap
C) according to the AD-AS framework, the LRAS curve would shift to the left and the ensuing positive output gap would be closed by subsequent leftward shifts in the AS curve to higher equilibrium levels of inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) according to the Phillips curve, the ensuing negative unemployment gap would exert inflationary pressures
B) according to Okun's Law, the ensuing negative unemployment gap would be consistent with a positive output gap
C) according to the AD-AS framework, the LRAS curve would shift to the left and the ensuing positive output gap would be closed by subsequent leftward shifts in the AS curve to higher equilibrium levels of inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

On the graph above, consider a point A on the aggregate demand curve and above the aggregate supply curve. At this point, ________.
A) quantity demanded equals output, but the inflation rate will fall, so output will rise
B) quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied, so the inflation rate will rise
C) output is greater than the quantity demanded, so output will fall
D) the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right until quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
AD - AS Shocks
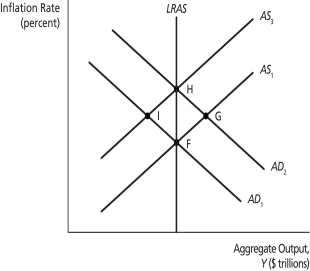
On the graph above, suppose point G is on the short-run aggregate supply curve π = 2.5 + 2∗(Y - 22) and aggregate demand curve Y = 29.25 - 0.5π. If output at point G is 25, and inflation expectations are adaptive, then the inflation rate next period will be ________.
A) 11.5
B) 14.5
C) 8.5
D) 2.5
E) none of the above

On the graph above, suppose point G is on the short-run aggregate supply curve π = 2.5 + 2∗(Y - 22) and aggregate demand curve Y = 29.25 - 0.5π. If output at point G is 25, and inflation expectations are adaptive, then the inflation rate next period will be ________.
A) 11.5
B) 14.5
C) 8.5
D) 2.5
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
By the time Paul Volcker took office as the new Federal Reserve chairman in 1979, the inflation rate exceeded 10%. By 1982 the unemployment rate soared to 9.7% and inflation was cut to 6.2%. By the end of 1986 the unemployment rate was brought down to 7% and the inflation rate was brought further down to 1.9%. Which of the following is an appropriate description of the mechanism behind the Volcker Disinflation?
A) The AD curve shifted right due to the autonomous tightening of monetary policy which explains the lowering of the unemployment rate between 1982 and 1986
B) With the Federal Reserve raising interest rates, the AD curve shifted to the left lowering the equilibrium level of inflation but inducing a negative output gap, which explains the lower inflation rate between 1979 and 1982 at the cost of a higher unemployment rate over the same period
C) The LRAS curve shifted left due to the tightening of monetary policy generating a positive output gap or a negative unemployment gap which explains the lowering of the unemployment rate between 1982 and 1986
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The AD curve shifted right due to the autonomous tightening of monetary policy which explains the lowering of the unemployment rate between 1982 and 1986
B) With the Federal Reserve raising interest rates, the AD curve shifted to the left lowering the equilibrium level of inflation but inducing a negative output gap, which explains the lower inflation rate between 1979 and 1982 at the cost of a higher unemployment rate over the same period
C) The LRAS curve shifted left due to the tightening of monetary policy generating a positive output gap or a negative unemployment gap which explains the lowering of the unemployment rate between 1982 and 1986
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
By the time Paul Volcker took office as the new Federal Reserve chairman in 1979, both the inflation and unemployment rates were higher than during most of the 1950s, 60s and early 70s. The Federal Reserve implemented an autonomous tightening of monetary policy that resulted in the famous Volker Disinflation which was successful in bringing both problems under control. What would have been a likely long-run result had Mr. Volker conducted an expansionary monetary policy instead?
A) Eventually, inflation would have been made worse but unemployment would have been lowered
B) Eventually, both the inflation and unemployment rates would have declined
C) Eventually, both inflation and unemployment would have been made worse
D) There would have been no effect on the unemployment and inflation rates
E) none of the above
A) Eventually, inflation would have been made worse but unemployment would have been lowered
B) Eventually, both the inflation and unemployment rates would have declined
C) Eventually, both inflation and unemployment would have been made worse
D) There would have been no effect on the unemployment and inflation rates
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What was(were) the effect(s) of the Enron Bankruptcy in late 2001 and other corporate scandals in 2002?
A) An ensuing lack of confidence in financial accounting
B) The value of corporate bonds declined
C) It became more expensive for firms to finance their investments
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) An ensuing lack of confidence in financial accounting
B) The value of corporate bonds declined
C) It became more expensive for firms to finance their investments
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the main difference between a demand shock stemming from monetary policy and a demand shock that comes from a change in spending?
A) In the short-run, an autonomous monetary policy easing lowers real interest rates and raises aggregate output whereas a positive spending shock has the opposite effect on both variables
B) An autonomous monetary policy easing raises inflation permanently whereas a positive spending shock only raises inflation temporarily
C) An autonomous monetary policy easing has a temporary effect on the real interest rate whereas a positive spending shock has a permanent effect on the real interest rate
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) In the short-run, an autonomous monetary policy easing lowers real interest rates and raises aggregate output whereas a positive spending shock has the opposite effect on both variables
B) An autonomous monetary policy easing raises inflation permanently whereas a positive spending shock only raises inflation temporarily
C) An autonomous monetary policy easing has a temporary effect on the real interest rate whereas a positive spending shock has a permanent effect on the real interest rate
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
By the time Paul Volcker took office as the new Federal Reserve chairman in 1979, the inflation rate exceeded 10%. By 1982 the unemployment rate soared to 9.7% and inflation was cut to 6.2%. By the end of 1986 the unemployment rate was brought down to 7% and the inflation rate was brought further down to 1.9%. Which of the following is an appropriate description of the mechanism behind the Volcker Disinflation?
A) The AD curve likely shifted left due to the autonomous tightening of monetary policy which explains the lowering of the inflation rate between 1979 and 1982
B) Due to the autonomous tightening of monetary policy, a negative output gap ensued which explains the increase in the unemployment rate between 1979 and 1982
C) By 1982, it is likely that equilibrium output was lower than potential leading the AS curve to shift to the right to close the output gap toward a general equilibrium which explains the reduction in the unemployment rate and the further reduction in inflation between 1982 and 1986
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The AD curve likely shifted left due to the autonomous tightening of monetary policy which explains the lowering of the inflation rate between 1979 and 1982
B) Due to the autonomous tightening of monetary policy, a negative output gap ensued which explains the increase in the unemployment rate between 1979 and 1982
C) By 1982, it is likely that equilibrium output was lower than potential leading the AS curve to shift to the right to close the output gap toward a general equilibrium which explains the reduction in the unemployment rate and the further reduction in inflation between 1982 and 1986
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The March 2000 "tech bubble" burst caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left by ________.
A) causing an upward spike in the real interest rate
B) reducing autonomous spending by households and businesses
C) reducing government spending on high-tech equipment
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) causing an upward spike in the real interest rate
B) reducing autonomous spending by households and businesses
C) reducing government spending on high-tech equipment
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
By the time Paul Volcker took office as the new Federal Reserve chairman in 1979, both the inflation and unemployment rates were higher than during most of the 1950s, 60s and early 70s. The Federal Reserve implemented an autonomous tightening of monetary policy that resulted in the famous Volker Disinflation which was successful in bringing both problems under control. What would have been a likely short-run result had Mr. Volker conducted an expansionary monetary policy instead?
A) Inflation would have been made worse right away but unemployment would have been lowered
B) Both inflation and unemployment would have declined
C) Both inflation and unemployment would have been made worse
D) There would have been no effect on the unemployment and inflation rates
E) none of the above
A) Inflation would have been made worse right away but unemployment would have been lowered
B) Both inflation and unemployment would have declined
C) Both inflation and unemployment would have been made worse
D) There would have been no effect on the unemployment and inflation rates
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
By the time Paul Volcker took office as the new Federal Reserve chairman in 1979, both the inflation and unemployment rates were higher than during most of the 1950s, 60s and early 70s. The Federal Reserve implemented an autonomous tightening of monetary policy that resulted in the famous Volker Disinflation which was successful in bringing both problems under control. Which of the following is an appropriate description had Mr. Volker conducted an expansionary monetary policy instead?
A) The AD curve would have likely shifted right due to the Federal Reserve lowering of interest rates which might have resulted in a temporary decline in the unemployment rate but at the cost of skyrocketing inflation
B) Due to the autonomous expansion of monetary policy, a temporary positive output gap might have ensued thereby decreasing the unemployment rate while exerting huge inflationary pressures in the economy
C) Due to the autonomous expansion of monetary policy the unemployment rate might have artificially declined. However, the AS curve would then have shifted left to close the ensuing positive output gap thereby returning the unemployment rate to the levels prior to the Fed's action while, likely, making inflation even worse than before Mr. Volker took office
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The AD curve would have likely shifted right due to the Federal Reserve lowering of interest rates which might have resulted in a temporary decline in the unemployment rate but at the cost of skyrocketing inflation
B) Due to the autonomous expansion of monetary policy, a temporary positive output gap might have ensued thereby decreasing the unemployment rate while exerting huge inflationary pressures in the economy
C) Due to the autonomous expansion of monetary policy the unemployment rate might have artificially declined. However, the AS curve would then have shifted left to close the ensuing positive output gap thereby returning the unemployment rate to the levels prior to the Fed's action while, likely, making inflation even worse than before Mr. Volker took office
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A likely result of the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks was ________.
A) weaker consumer confidence
B) lower business confidence
C) a leftward shift of the AD curve
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) weaker consumer confidence
B) lower business confidence
C) a leftward shift of the AD curve
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
By the time Paul Volcker took office as the new Federal Reserve chairman in 1979, both the inflation and unemployment rates were higher than during most of the 1950s, 60s and early 70s. The Federal Reserve implemented an autonomous tightening of monetary policy that resulted in the famous Volker Disinflation which was successful in bringing both problems under control. What would have been a likely result had Mr. Volker conducted an expansionary monetary policy instead?
A) Inflation would have been made worse right away but unemployment would have been permanently lowered
B) In the long run the unemployment problem would not have been fixed and the inflation problem would have been made much worse
C) In the short-run both inflation and unemployment would have declined but in the long-run unemployment would have been worse than before the Fed's action
D) In the short-run both inflation and unemployment would have been made worse but both would have been lowered in the long-run
E) none of the above
A) Inflation would have been made worse right away but unemployment would have been permanently lowered
B) In the long run the unemployment problem would not have been fixed and the inflation problem would have been made much worse
C) In the short-run both inflation and unemployment would have declined but in the long-run unemployment would have been worse than before the Fed's action
D) In the short-run both inflation and unemployment would have been made worse but both would have been lowered in the long-run
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
By the time Paul Volcker took office as the new Federal Reserve chairman in 1979, both the inflation and unemployment rates were higher than during most of the 1950s, 60s and early 70s. The Federal Reserve implemented an autonomous tightening of monetary policy that resulted in the famous Volker Disinflation which was successful in bringing both problems under control. What would have been a likely long-run result had Mr. Volker conducted an expansionary monetary policy instead?
A) Eventually, inflation would have been made worse and unemployment would not have been fixed
B) Eventually, both the inflation and unemployment rates would have declined
C) Eventually, inflation would have been fixed and unemployment would have been made worse
D) There would have been no effect on the unemployment and inflation rates
E) none of the above
A) Eventually, inflation would have been made worse and unemployment would not have been fixed
B) Eventually, both the inflation and unemployment rates would have declined
C) Eventually, inflation would have been fixed and unemployment would have been made worse
D) There would have been no effect on the unemployment and inflation rates
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The "tech bubble" burst of 2000, the terrorist attacks of 2001 and the corporate scandals of 2001 and 2002 all had similar qualitative effects on the economy. Which of the following is an appropriate description of the mechanism that would have ensued?
A) Household and business spending would have been eroded shifting the AD curve to the left
B) Unemployment would have risen and inflation would have fallen
C) Output would have declined below potential but through shifts in the AS curve, the self-correcting mechanism of the AD-AS framework would have brought the unemployment rate down to the lower levels we saw by 2004
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) Household and business spending would have been eroded shifting the AD curve to the left
B) Unemployment would have risen and inflation would have fallen
C) Output would have declined below potential but through shifts in the AS curve, the self-correcting mechanism of the AD-AS framework would have brought the unemployment rate down to the lower levels we saw by 2004
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
According to the economy's self-correcting mechanism, how does the economy return to potential output following a negative demand shock? How is the recovery process different, if the government implements a policy of economic stimulus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider an economy in a long-run equilibrium with Y = 40 and π = 3. A demand shock in period one causes output to rise to 45 and inflation rises to 4. Then, the updating of expected inflation to equal 4 causes output in period two to decline to 43.85, and inflation to rise to 4.77. Assuming no further shocks, calculate the values of output and inflation for period three.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
AD - AS Shocks

On the graph above, movement from point ________ to point ________ might occur if there is a negative demand shock, followed by updating of expected inflation.
A) F; G
B) H; I
C) H; F
D) F; H
E) none of the above

On the graph above, movement from point ________ to point ________ might occur if there is a negative demand shock, followed by updating of expected inflation.
A) F; G
B) H; I
C) H; F
D) F; H
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
AD - AS Shocks

On the graph above, an example of a positive demand shock is the movement from point ________ to point ________.
A) F; G
B) H; I
C) F; H
D) H; F
E) none of the above

On the graph above, an example of a positive demand shock is the movement from point ________ to point ________.
A) F; G
B) H; I
C) F; H
D) H; F
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Suppose that households and businesses increase autonomous expenditures, driving output well above potential. Describe, in detail, how monetary policy might react to minimize the increase in inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
By the time Paul Volcker took office as the new Federal Reserve chairman in 1979, the inflation rate exceeded 10%. By the end of 1986 the inflation rate had been brought down to 1.9%. Which of the following is true about the Volcker Disinflation?
A) lower inflation resulted from a tightening of monetary policy
B) by raising the federal funds rate to over 20%, the Federal Reserve slowed the economy and was able to cut inflation in half by 1982 at the cost of a substantial hike in the unemployment rate causing a recession
C) this policy induced a substantial negative output gap
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) lower inflation resulted from a tightening of monetary policy
B) by raising the federal funds rate to over 20%, the Federal Reserve slowed the economy and was able to cut inflation in half by 1982 at the cost of a substantial hike in the unemployment rate causing a recession
C) this policy induced a substantial negative output gap
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
AD - AS Shocks

On the graph above, an example of a negative demand shock is the movement from point ________ to point ________.
A) F; G
B) H; I
C) F; H
D) H; F
E) none of the above

On the graph above, an example of a negative demand shock is the movement from point ________ to point ________.
A) F; G
B) H; I
C) F; H
D) H; F
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
AD - AS Shocks
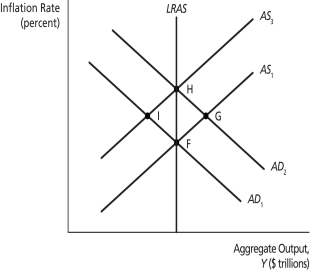
On the graph above, a movement from point ________ to point ________ might represent a negative supply shock.
A) H: G
B) H: F
C) F; I
D) F; G
E) none of the above

On the graph above, a movement from point ________ to point ________ might represent a negative supply shock.
A) H: G
B) H: F
C) F; I
D) F; G
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When a temporary shock in the economy involves a restriction in supply ________.
A) we refer to it as a negative supply shock
B) a rise in commodity prices typically follows
C) a reduction in output typically ensues
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) we refer to it as a negative supply shock
B) a rise in commodity prices typically follows
C) a reduction in output typically ensues
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
AD - AS Shocks

On the graph above, a movement from point ________ to point ________ might represent a positive supply shock.
A) F; I
B) H: G
C) H: F
D) F; G
E) none of the above

On the graph above, a movement from point ________ to point ________ might represent a positive supply shock.
A) F; I
B) H: G
C) H: F
D) F; G
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
AD - AS Shocks

On the graph above, suppose the economy has moved from point H to point G. If the shock was temporary and inflation expectations are adaptive, the economy will next ________.
A) return to point H
B) move to point F
C) move to a point between points G and H
D) remain at point G
E) none of the above

On the graph above, suppose the economy has moved from point H to point G. If the shock was temporary and inflation expectations are adaptive, the economy will next ________.
A) return to point H
B) move to point F
C) move to a point between points G and H
D) remain at point G
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose there is a temporary supply shock because of a war in the Middle East, then ________.
A) this would constitute a cost push shock due to a restriction in the supply of oil
B) the AS curve would shift to the left
C) this could theoretically lead to stagflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) this would constitute a cost push shock due to a restriction in the supply of oil
B) the AS curve would shift to the left
C) this could theoretically lead to stagflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
AD - AS Shocks

On the graph above, suppose the economy is at point F when there is a temporary negative supply shock. The new long-run equilibrium is at point ________.
A) H
B) I
C) F
D) G
E) none of the above

On the graph above, suppose the economy is at point F when there is a temporary negative supply shock. The new long-run equilibrium is at point ________.
A) H
B) I
C) F
D) G
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Suppose there is a temporary supply shock because of a war in the Middle East, then, ceteris paribus, the ensuing cost push shock ________.
A) would lead to a temporary increase in prices but a permanent reduction in output
B) would lead to a temporary increase in output but a permanent increase in inflation
C) would lead to a temporary decrease in output but a permanent increase in inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) would lead to a temporary increase in prices but a permanent reduction in output
B) would lead to a temporary increase in output but a permanent increase in inflation
C) would lead to a temporary decrease in output but a permanent increase in inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
AD - AS Shocks

A fall in import prices or an increase in productivity ________.
A) constitute a positive supply shock
B) typically leads to a rise in commodity prices
C) typically comes with a reduction in output
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

A fall in import prices or an increase in productivity ________.
A) constitute a positive supply shock
B) typically leads to a rise in commodity prices
C) typically comes with a reduction in output
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the 1960s and 1970s, research funding by the U.S. government and some universities led to revolutionary advances in network computing. These advances in communication and network technology remained largely isolated to governmental and academic use. By the mid-to-late 1990s, the Internet began to be widely adopted with massive increases in productivity (which journalists dubbed the "new economy"). Which of the following is an appropriate description of the mechanism behind this supply shock?
A) Since this "new economy" was a new paradigm, the transition from a pre-internet to an internet economy was initially costly. Thus, the AS curve likely shifted to the left and unemployment likely increased in the short-run
B) The ensuing increase in productive capacity led to the rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the unemployment rate of the 1990s
C) A negative output gap would have resulted in the short-run, but it was eventually closed by a rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the inflation rate of the 1990s
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) Since this "new economy" was a new paradigm, the transition from a pre-internet to an internet economy was initially costly. Thus, the AS curve likely shifted to the left and unemployment likely increased in the short-run
B) The ensuing increase in productive capacity led to the rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the unemployment rate of the 1990s
C) A negative output gap would have resulted in the short-run, but it was eventually closed by a rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the inflation rate of the 1990s
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is (are) linked to (an) adverse supply shock(s)?
A) The terrorist attacks of 2001
B) Collective bargaining that followed the termination of U.S. wage and price controls in 1973
C) The corporate scandals of 2002
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The terrorist attacks of 2001
B) Collective bargaining that followed the termination of U.S. wage and price controls in 1973
C) The corporate scandals of 2002
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the main difference between a temporary and permanently negative supply shock?
A) The real interest rate immediately decreases after a temporary shock while it eventually increases after a permanent shock
B) Output increases right away after a temporary shock but the impact does not last whereas for a permanent shock output permanently decreases
C) A temporary shock will see a permanent increase in inflation while inflation will only rise temporarily after a permanent shock
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The real interest rate immediately decreases after a temporary shock while it eventually increases after a permanent shock
B) Output increases right away after a temporary shock but the impact does not last whereas for a permanent shock output permanently decreases
C) A temporary shock will see a permanent increase in inflation while inflation will only rise temporarily after a permanent shock
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a new government adopted some ill-advised regulations causing the economy to be less efficient ________.
A) the ensuing negative supply shock would lead to an immediate rise in inflation
B) in the short-run this would create a negative output gap but eventually the previous general equilibrium would be restored by subsequent rightward shifts of the AS curve
C) there would be no permanent changes in output and inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) the ensuing negative supply shock would lead to an immediate rise in inflation
B) in the short-run this would create a negative output gap but eventually the previous general equilibrium would be restored by subsequent rightward shifts of the AS curve
C) there would be no permanent changes in output and inflation
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the adoption of a new technology led to gains in productivity ________.
A) the ensuing positive supply shock would lead to an immediate increase in output
B) in the short-run, the ensuing increase in supply would lower inflation
C) and if this new technology permanently altered the productive capacity of the economy then the increase in output and decrease in inflation would be permanent as well
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) the ensuing positive supply shock would lead to an immediate increase in output
B) in the short-run, the ensuing increase in supply would lower inflation
C) and if this new technology permanently altered the productive capacity of the economy then the increase in output and decrease in inflation would be permanent as well
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
AD - AS Shocks

On the graph above, suppose the economy is at point F when there is a temporary positive supply shock. The new long-run equilibrium is at point ________.
A) H
B) I
C) F
D) G
E) none of the above

On the graph above, suppose the economy is at point F when there is a temporary positive supply shock. The new long-run equilibrium is at point ________.
A) H
B) I
C) F
D) G
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is (are) linked to (an) adverse supply shock(s)?
A) The Arab-Israeli war of 1973
B) the Iranian revolution of 1979
C) The wage renegotiations that followed the termination of U.S. wage and price controls in 1973
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The Arab-Israeli war of 1973
B) the Iranian revolution of 1979
C) The wage renegotiations that followed the termination of U.S. wage and price controls in 1973
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
AD - AS Shocks

On the graph above, suppose the economy is at point F when there is a permanent positive supply shock. The new long-run equilibrium is at point ________.
A) F
B) H
C) I
D) G
E) none of the above

On the graph above, suppose the economy is at point F when there is a permanent positive supply shock. The new long-run equilibrium is at point ________.
A) F
B) H
C) I
D) G
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the mid-to-late 1990s, changes in the health care industry, substantially reduced health care costs relative to other goods and services. Which of the following is an appropriate description of the mechanism behind this supply shock?
A) The AS curve likely shifted to the right which likely explains the short-run fall in unemployment
B) The ensuing increase in productive capacity led to the rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the unemployment rate of the 1990s
C) A positive output gap would have resulted in the short-run but it was eventually closed by a rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the inflation rate of the 1990s
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The AS curve likely shifted to the right which likely explains the short-run fall in unemployment
B) The ensuing increase in productive capacity led to the rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the unemployment rate of the 1990s
C) A positive output gap would have resulted in the short-run but it was eventually closed by a rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the inflation rate of the 1990s
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In 1973, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) engineered a quadrupling of oil prices by restricting oil production. Which of the following is an appropriate description of this negative supply shock?
A) The AS curve likely shifted to the left and output likely fell because of this adverse shock
B) In the short-run there was a movement out of general equilibrium leading to an increase in inflation as a likely result of this adverse shock
C) In the short-run there was a movement out of general equilibrium leading to an increase in unemployment as a likely result of this adverse shock
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) The AS curve likely shifted to the left and output likely fell because of this adverse shock
B) In the short-run there was a movement out of general equilibrium leading to an increase in inflation as a likely result of this adverse shock
C) In the short-run there was a movement out of general equilibrium leading to an increase in unemployment as a likely result of this adverse shock
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Describe how changes in expected inflation impact an economy in the wake of a temporary negative supply shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Suppose there is a temporary supply shock because of a war in the Middle East, then, ceteris paribus, the ensuing cost push shock ________.
A) would lead to a temporary increase in prices due to a restriction in the supply of oil
B) would lead to a temporary decrease in output as the AS curve would shift to the left
C) would lead to a temporary shift in the AS curve but ultimately output and inflation would return to the original long-run values
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) would lead to a temporary increase in prices due to a restriction in the supply of oil
B) would lead to a temporary decrease in output as the AS curve would shift to the left
C) would lead to a temporary shift in the AS curve but ultimately output and inflation would return to the original long-run values
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



