Deck 14: Sales and Operations Planning
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Sales and Operations Planning
1
Atlas Inc. produces product A and product B. Each product must go through two processes. Each A produced requires two hours in process 1 and five hours in process 2. Each B produced requires six hours in process 1 and three hours in process 2. There are 80 hours of capacity available each week in each process. Each A produced generates $6.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $9.00 in profit for the company. The company's objective function is
A) Maximize Z = $6.00A + $9.00B.
B) Maximize Z = $9.00A + $6.00B.
C) Minimize Z = $6.00A + $9.00B.
D) Minimize Z = $6.00A +$9.00B.
A) Maximize Z = $6.00A + $9.00B.
B) Maximize Z = $9.00A + $6.00B.
C) Minimize Z = $6.00A + $9.00B.
D) Minimize Z = $6.00A +$9.00B.
A
2
The feasible solution space contains the values for the decision variables that satisfy the linear programming model's constraints.
True
3
A linear programming model's constraints are nonlinear relationships that describe the restrictions placed on the decision variables.
False
4
Because linear programming provides an optimal solution, sensitivity analysis is never an important consideration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
While all linear programming problems have a single objective function, very few, if any, have constraints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
TicToc produces product A and product B. These products have the following resource requirements. 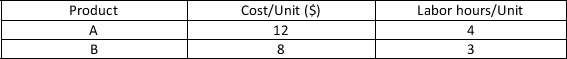 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The company's objective function is
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The company's objective function is
A) Maximize Z = $35.00A + $25.00B.
B) Minimize Z = $12A + 8B.
C) Minimize Z = 4A + 3B.
D) None of these answer choices is correct.
 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The company's objective function is
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The company's objective function isA) Maximize Z = $35.00A + $25.00B.
B) Minimize Z = $12A + 8B.
C) Minimize Z = 4A + 3B.
D) None of these answer choices is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The objective function in a linear programming formulation defines the feasible solution space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The objective function is a linear relationship that either minimizes or maximizes some value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
_____________ represent a restriction on decision variable values for a linear programming problem.
A) Surpluses
B) Constraints
C) Extreme points
D) Optimal points
A) Surpluses
B) Constraints
C) Extreme points
D) Optimal points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The formulation for a linear programming problem cannot include more than one decision variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Atlas Inc. produces product A and product B. Each product must go through two processes. Each A produced requires two hours in process 1 and five hours in process 2. Each B produced requires six hours in process 1 and three hours in process 2. There are 80 hours of capacity available each week in each process. Each A produced generates $6.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $9.00 in profit for the company. The capacity constraint for Process 2 is
A) 5A + 3B > 80
B) 6A + 3 B < 80
C) 5A + 3B < 80
D) 5A + 3B < 80
A) 5A + 3B > 80
B) 6A + 3 B < 80
C) 5A + 3B < 80
D) 5A + 3B < 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Linear programming problems with three decision variables can be solved graphically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In general, the objective function for linear programming problems in operations is one of minimizing costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Most real-world linear programming problems cannot be solved graphically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Operations mangers find very few types of linear program models applicable today because finding an optimal solution is no longer a concern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A formulation for a linear programming model consists of a decision variable, a constraint and several objective functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Atlas Inc. produces product A and product B. Each product must go through two processes. Each A produced requires two hours in process 1 and five hours in process 2. Each B produced requires six hours in process 1 and three hours in process 2. There are 80 hours of capacity available each week in each process. Each A produced generates $6.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $9.00 in profit for the company. The constraint for process 1 is represented by
A) 2A + 5B < 80.
B) 2A + 6B > 80.
C) 2A + 6B < 80.
D) 2A + 6B < 80.
A) 2A + 5B < 80.
B) 2A + 6B > 80.
C) 2A + 6B < 80.
D) 2A + 6B < 80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The simplex method used for solving linear programming problems uses matrix algebra to solve simultaneous equations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The optimal solution for a linear programming problem will always occur at an extreme point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Linear programming is a mathematical modeling technique based on linear relationships

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
TicToc produces product A and product B. These products have the following resource requirements. 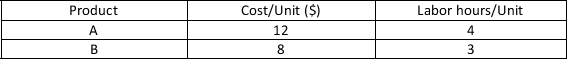 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 100 units of A and 200 units of B the value of the objective function is equal to
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 100 units of A and 200 units of B the value of the objective function is equal to
A) $2,800.
B) $8,500.
C) $9,500.
D) $11,800.
 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 100 units of A and 200 units of B the value of the objective function is equal to
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 100 units of A and 200 units of B the value of the objective function is equal toA) $2,800.
B) $8,500.
C) $9,500.
D) $11,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is meant by the term "shadow price" in linear programming?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How is linear programming useful to an operations manager?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
TicToc produces product A and product B. These products have the following resource requirements. 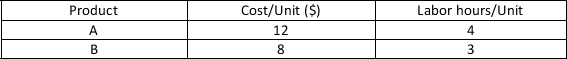 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The capacity constraint for labor is
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The capacity constraint for labor is
A) 12A + 8B > 1000.
B) 12A + 8B < 1000.
C) 4A + 3B < 1000.
D) 4A + 3B > 1000.
 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The capacity constraint for labor is
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The capacity constraint for labor isA) 12A + 8B > 1000.
B) 12A + 8B < 1000.
C) 4A + 3B < 1000.
D) 4A + 3B > 1000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The simplex method is a solution method used for linear programming problems that have
A) no constraints.
B) at least one constraint.
C) at least two constraints.
D) at least three constraints.
A) no constraints.
B) at least one constraint.
C) at least two constraints.
D) at least three constraints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Atlas Inc. produces product A and product B. Each product must go through two processes. Each A produced requires two hours in process 1 and five hours in process 2. Each B produced requires six hours in process 1 and three hours in process 2. There are 80 hours of capacity available each week in each process. Each A produced generates $6.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $9.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 6 units of A and 9 units of B the amount of slack (in hours) for process 1 is
A) 0 hours.
B) 14 hours.
C) 66 hours.
D) 80 hours.
A) 0 hours.
B) 14 hours.
C) 66 hours.
D) 80 hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The constraint 3x1 + 6x2 > 48 is converted to an equality by
A) adding a slack variable.
B) subtracting a surplus variable.
C) adding both a slack variable and a surplus variable.
D) subtracting both a slack variable and a surplus variable.
A) adding a slack variable.
B) subtracting a surplus variable.
C) adding both a slack variable and a surplus variable.
D) subtracting both a slack variable and a surplus variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Atlas Inc. produces product A and product B. Each product must go through two processes. Each A produced requires two hours in process 1 and five hours in process 2. Each B produced requires six hours in process 1 and three hours in process 2. There are 80 hours of capacity available each week in each process. Each A produced generates $6.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $9.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 6 units of A and 9 units of B the value of the objective function is equal to
A) $36.
B) $81.
C) $108.
D) $117.
A) $36.
B) $81.
C) $108.
D) $117.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
TicToc produces product A and product B. These products have the following resource requirements. 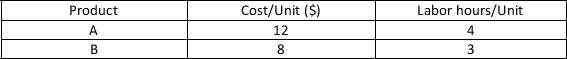 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The constraint for the budget is represented by
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The constraint for the budget is represented by
A) $35A + $25B < $3,000.
B) $35A + $25B > $3,000.
C) $12A + $8B > $3,000.
D) $12A + $8B < $3,000.
 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The constraint for the budget is represented by
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. The constraint for the budget is represented byA) $35A + $25B < $3,000.
B) $35A + $25B > $3,000.
C) $12A + $8B > $3,000.
D) $12A + $8B < $3,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
TicToc produces product A and product B. These products have the following resource requirements. 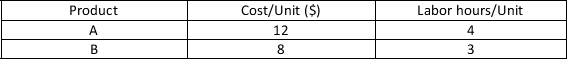 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 100 units of A and 200 units of B the amount of slack (in hours) for labor is
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 100 units of A and 200 units of B the amount of slack (in hours) for labor is
A) 0 hours.
B) 14 hours.
C) 66 hours.
D) 80 hours.
 The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 100 units of A and 200 units of B the amount of slack (in hours) for labor is
The firm has a weekly production budget of $3000 and a maximum of 1000 hours of labor per week. Each A produced generates $35.00 in profit for the company. Each B produced generates $25.00 in profit for the company. If the company produces 100 units of A and 200 units of B the amount of slack (in hours) for labor isA) 0 hours.
B) 14 hours.
C) 66 hours.
D) 80 hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The optimal solution for a linear programming problem will always occur
A) when the slack price equals the surplus price.
B) when the surplus price equals the slack price.
C) at an extreme point.
D) at a non-extreme point.
A) when the slack price equals the surplus price.
B) when the surplus price equals the slack price.
C) at an extreme point.
D) at a non-extreme point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Briefly define the components that comprise a linear programming model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
For a less than or equal to (<) constraint the shadow price represents the
A) amount you would be willing to pay for one additional unit of a resource.
B) amount you at which you would be willing to sell one additional unit of a resource.
C) difference between the slack price and the surplus price.
D) difference between the surplus price and the slack price.
A) amount you would be willing to pay for one additional unit of a resource.
B) amount you at which you would be willing to sell one additional unit of a resource.
C) difference between the slack price and the surplus price.
D) difference between the surplus price and the slack price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The area that contains the values that satisfies all the constraints in a linear programming problem is known as the _________________ space.
A) optimal solution
B) non-optimal solution
C) feasible solution
D) infeasible solution.
A) optimal solution
B) non-optimal solution
C) feasible solution
D) infeasible solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



