Deck 15: Neuropsychology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/151
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Neuropsychology
1
A brain injury known as a cerebral hemorrhage results in
A) blockage from material that doesn't move from its point of origin.
B) blockage from material that travels to smaller diameter blood vessels until it has to stop.
C) bleeding in the brain.
D) an area of dead neurons.
A) blockage from material that doesn't move from its point of origin.
B) blockage from material that travels to smaller diameter blood vessels until it has to stop.
C) bleeding in the brain.
D) an area of dead neurons.
bleeding in the brain.
2
The herpes simplex virus responsible for cold sores and genital herpes can produce a type of secondary encephalitis.
True
3
The Halstead-Reitan battery is used to assess
A) cognitive function.
B) reflexes.
C) sensation.
D) coma.
A) cognitive function.
B) reflexes.
C) sensation.
D) coma.
cognitive function.
4
It is estimated that half the people over 75 will suffer from Alzheimer's disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Most neuropsychologists are
A) specialists among psychiatrists who have medical doctor (M.D.) degrees.
B) specialists among neurologists who have M.D. degrees.
C) licensed clinical psychologists who have special training in the neurosciences.
D) masters level psychologists who hold licenses in counseling.
A) specialists among psychiatrists who have medical doctor (M.D.) degrees.
B) specialists among neurologists who have M.D. degrees.
C) licensed clinical psychologists who have special training in the neurosciences.
D) masters level psychologists who hold licenses in counseling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Oligodendrocytes are destroyed by the autoimmune disease of multiple sclerosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Partial seizures are frequently accompanied by an aura, but generalized seizures typically occur without an aura.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Kennard Principle appears to predict recovery of language functions, but not necessarily other types of cognitive function, following brain damage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When low oxygen levels result from insufficiency in the blood supply to the brain, the resulting condition is known as
A) ischemia.
B) aneurysm.
C) arteriovenous malformation.
D) cavernous malformation.
A) ischemia.
B) aneurysm.
C) arteriovenous malformation.
D) cavernous malformation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Strokes occur when the blood supply is affected by
A) low blood pressure (hypotension).
B) hemorrhage or blockage.
C) death of adjacent neurons.
D) the presence of infarcts.
A) low blood pressure (hypotension).
B) hemorrhage or blockage.
C) death of adjacent neurons.
D) the presence of infarcts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An aneurysm can be the cause of
A) an open head injury.
B) thrombosis.
C) a concussion.
D) a cerebral hemorrhage.
A) an open head injury.
B) thrombosis.
C) a concussion.
D) a cerebral hemorrhage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Larger numbers of strokes result from ischemia than from cerebral hemorrhages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Among the primary risk factors for stroke are
A) low blood pressure and sodium insufficiency.
B) sleep deprivation.
C) obesity and the use of alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs.
D) unusually low cholesterol levels.
A) low blood pressure and sodium insufficiency.
B) sleep deprivation.
C) obesity and the use of alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs.
D) unusually low cholesterol levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An open head injury is another name for a concussion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Migraine headaches can result from information carried by the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V) from the brainstem to the meninges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) can be transmitted from one patient to another in spite of typical hospital sterilization methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Joseph is 78 years of age, and the recent appearance of certain cognitive symptoms has led his physician to diagnose him with Alzheimer's disease. Which of the following statements would be the most accurate with regard to Joseph's situation?
A) Joseph should begin receiving passive chemotherapy treatment, as this has been found to reverse the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
B) Joseph should be very concerned that his wife will develop the same symptoms, as the disease has been found to be contagious.
C) The risk of his symptoms getting worse will decrease the longer Joseph survives.
D) A definitive diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease will not be possible until an autopsy is conducted after Joseph's death.
A) Joseph should begin receiving passive chemotherapy treatment, as this has been found to reverse the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
B) Joseph should be very concerned that his wife will develop the same symptoms, as the disease has been found to be contagious.
C) The risk of his symptoms getting worse will decrease the longer Joseph survives.
D) A definitive diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease will not be possible until an autopsy is conducted after Joseph's death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The vast majority of those diagnosed with dementia-between 60 and 90 percent-suffer from ________ disease.
A) Huntington's
B) Klinefelter's
C) Parkinson's
D) Alzheimer's
A) Huntington's
B) Klinefelter's
C) Parkinson's
D) Alzheimer's

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Reactive neuroplasticity involves structural changes in the brain due to learning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Alzheimer's disease involves several changes in the brain. Which of the following is NOT one of the affected structures?
A) neurofibrillary tangles
B) beta amyloid proteins
C) extrapyramidal cells
D) tau proteins
A) neurofibrillary tangles
B) beta amyloid proteins
C) extrapyramidal cells
D) tau proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Following ischemia, neural damage is found
A) equally distributed throughout the brain.
B) primarily in the hippocampus and in middle layers of the cortex.
C) primarily in the hippocampus and inner layers of the cortex.
D) primarily in subcortical areas.
A) equally distributed throughout the brain.
B) primarily in the hippocampus and in middle layers of the cortex.
C) primarily in the hippocampus and inner layers of the cortex.
D) primarily in subcortical areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Phencyclidine (PCP) is a potent glutamate antagonist that is known to produce psychotic behavior in humans. Given what you know about stroke, what would happen if somebody used PCP right after a stroke?
A) It would increase the damage initiated by the stroke.
B) It might have a protective effect against further cell death, but the psychotic side effects would be problematic.
C) It would not produce any psychotic symptoms due to stroke-related changes in brain biochemistry.
D) It would have no observable effects on cell health or psychotic behavior.
A) It would increase the damage initiated by the stroke.
B) It might have a protective effect against further cell death, but the psychotic side effects would be problematic.
C) It would not produce any psychotic symptoms due to stroke-related changes in brain biochemistry.
D) It would have no observable effects on cell health or psychotic behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The area of neural tissue that dies following a stroke or other interruption of cerebral blood flow is known as the
A) infarct.
B) aneurysm.
C) thrombosis.
D) embolism.
A) infarct.
B) aneurysm.
C) thrombosis.
D) embolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
While a large stroke can cause long-term damage, multiple small strokes
A) typically are no cause for concern.
B) are not predictive of later larger strokes.
C) can also produce significant damage.
D) do not produce true infarcts.
A) typically are no cause for concern.
B) are not predictive of later larger strokes.
C) can also produce significant damage.
D) do not produce true infarcts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In cultures of rat hippocampal cells, cell death due to oxygen deprivation can be reduced by application of
A) kainate.
B) magnesium.
C) N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA).
D) GABA.
A) kainate.
B) magnesium.
C) N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA).
D) GABA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Olney's concept of excitotoxicity suggests that most neural death in ischemia is due to
A) excess cholinergic activity.
B) insufficient gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) activity.
C) insufficient glutamate activity.
D) excess glutamate activity.
A) excess cholinergic activity.
B) insufficient gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) activity.
C) insufficient glutamate activity.
D) excess glutamate activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Oxygen deprivation in neurons leads to a "cascade" of enzyme activity triggered by abnormally
A) high levels of sodium activity.
B) low levels of sodium activity.
C) high levels of calcium activity.
D) high levels of potassium activity.
A) high levels of sodium activity.
B) low levels of sodium activity.
C) high levels of calcium activity.
D) high levels of potassium activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An embolism is
A) a blockage resulting from material that doesn't move from its point of origin.
B) a blockage resulting from material that travels to smaller diameter blood vessels until it has to stop.
C) bleeding in the brain.
D) an area of dead neurons.
A) a blockage resulting from material that doesn't move from its point of origin.
B) a blockage resulting from material that travels to smaller diameter blood vessels until it has to stop.
C) bleeding in the brain.
D) an area of dead neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An injury with penetration of the skull is termed
A) a concussion.
B) a subdural hematoma.
C) a meningioma.
D) an open head injury.
A) a concussion.
B) a subdural hematoma.
C) a meningioma.
D) an open head injury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Major causes of open head injuries in the United States include
A) boxing and playing football.
B) gunshot wounds and skull fractures.
C) playing soccer.
D) aneurysms.
A) boxing and playing football.
B) gunshot wounds and skull fractures.
C) playing soccer.
D) aneurysms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The area of neural tissue surrounding an infarct is known as the
A) embolism.
B) thrombosis.
C) penumbra.
D) aneurysm.
A) embolism.
B) thrombosis.
C) penumbra.
D) aneurysm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
A) produce symptoms of stroke lasting less than 24 hours.
B) produce very mild stroke symptoms that last indefinitely.
C) are typically fatal within a few hours.
D) are very common and do not require medical treatment.
A) produce symptoms of stroke lasting less than 24 hours.
B) produce very mild stroke symptoms that last indefinitely.
C) are typically fatal within a few hours.
D) are very common and do not require medical treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A thrombosis is
A) a blockage resulting from material that doesn't move from its point of origin.
B) a blockage resulting from material that travels to smaller diameter blood vessels until it has to stop.
C) bleeding in the brain.
D) an area of dead neurons.
A) a blockage resulting from material that doesn't move from its point of origin.
B) a blockage resulting from material that travels to smaller diameter blood vessels until it has to stop.
C) bleeding in the brain.
D) an area of dead neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Cells in culture that are deprived of oxygen are more likely to survive in the presence of
A) GABA agonists.
B) GABA antagonists.
C) glutamate agonists.
D) glutamate antagonists.
A) GABA agonists.
B) GABA antagonists.
C) glutamate agonists.
D) glutamate antagonists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A cerebral hemorrhage
A) usually does not cause much damage.
B) produces milder symptoms than ischemia.
C) usually does not produce noticeable behavioral symptoms.
D) is frequently fatal due to interfering with the blood supply to neurons and leading to neuron dehydration.
A) usually does not cause much damage.
B) produces milder symptoms than ischemia.
C) usually does not produce noticeable behavioral symptoms.
D) is frequently fatal due to interfering with the blood supply to neurons and leading to neuron dehydration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An infarct of brain tissue
A) seldom produces any noticeable symptoms.
B) always triggers unconsciousness or coma.
C) contributes to the development of epilepsy.
D) produces different symptoms that depend on the size and location.
A) seldom produces any noticeable symptoms.
B) always triggers unconsciousness or coma.
C) contributes to the development of epilepsy.
D) produces different symptoms that depend on the size and location.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following symptoms of stroke are part of the American Heart Association's "FAST" acronym?
A) Arm weakness
B) Tripping or stumbling
C) Total loss of consciousness
D) Tingling in the extremities
A) Arm weakness
B) Tripping or stumbling
C) Total loss of consciousness
D) Tingling in the extremities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A balloon-like bulge in an artery is known as a(n)
A) aneurysm.
B) embolism.
C) thrombosis.
D) cerebrovascular accident (CVA).
A) aneurysm.
B) embolism.
C) thrombosis.
D) cerebrovascular accident (CVA).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Closed head injuries, or concussions, are characterized by
A) injury without penetration of the skull.
B) lack of a coup and countercoup.
C) penetration of the skull.
D) no loss of consciousness.
A) injury without penetration of the skull.
B) lack of a coup and countercoup.
C) penetration of the skull.
D) no loss of consciousness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
While TIAs often do not have long-term effects, they are
A) rarely predictive of later strokes.
B) strong predictors of later strokes.
C) predictive of further TIAs but not full strokes.
D) negatively correlated with the occurrence of later strokes.
A) rarely predictive of later strokes.
B) strong predictors of later strokes.
C) predictive of further TIAs but not full strokes.
D) negatively correlated with the occurrence of later strokes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Among the symptoms of a TSE in humans is (are)
A) convulsions.
B) paranoia.
C) inflammation of the meninges.
D) a stiff neck and aversion to lights.
A) convulsions.
B) paranoia.
C) inflammation of the meninges.
D) a stiff neck and aversion to lights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Bleeding between the membranes covering the brain (that is, under the dura mater) following a closed head injury is known as
A) thrombosis.
B) subdural hematoma.
C) coup.
D) countercoup.
A) thrombosis.
B) subdural hematoma.
C) coup.
D) countercoup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The site of a blow to the head in a closed head injury is known as
A) thrombosis.
B) hematoma.
C) coup.
D) countercoup.
A) thrombosis.
B) hematoma.
C) coup.
D) countercoup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following individuals is the most likely to have ongoing symptoms of traumatic brain injury?
A) Guillaume, who is an Olympic sprinter
B) George, who has been a professional American football player for many years
C) Michael, who has been an Olympic swimmer for years
D) Samuel, who has been a professional ballet dancer for years
A) Guillaume, who is an Olympic sprinter
B) George, who has been a professional American football player for many years
C) Michael, who has been an Olympic swimmer for years
D) Samuel, who has been a professional ballet dancer for years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
(see Figure 15.6) In this illustration of a closed head injury, the area indicated by the #2 is known as a(n)
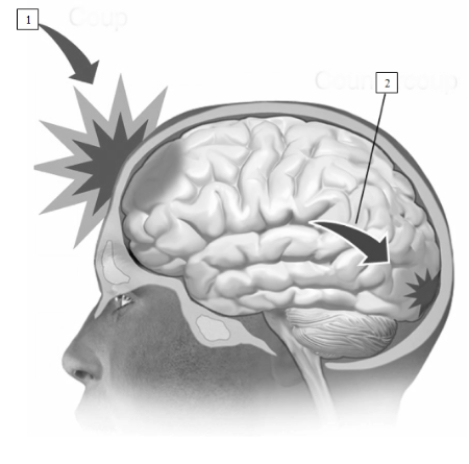
A) embolism.
B) thrombosis.
C) coup.
D) countercoup.

A) embolism.
B) thrombosis.
C) coup.
D) countercoup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An injury that produces a concussion
A) is a mild injury that does not require medical attention.
B) is a type of open head injury.
C) can produce symptoms that range from mild to a coma.
D) does not produce unconsciousness.
A) is a mild injury that does not require medical attention.
B) is a type of open head injury.
C) can produce symptoms that range from mild to a coma.
D) does not produce unconsciousness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is one of the three leading causes of traumatic brain injuries in the United States?
A) playing football
B) traffic accidents
C) playing soccer
D) boxing
A) playing football
B) traffic accidents
C) playing soccer
D) boxing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Symptoms that occur following a concussion
A) occur only in cases in which unconsciousness lasts for more than a day.
B) occur only in cases in which bleeding has required surgery.
C) can produce lack of concentration and memory loss.
D) are usually so mild that the patient does not notice any changes.
A) occur only in cases in which unconsciousness lasts for more than a day.
B) occur only in cases in which bleeding has required surgery.
C) can produce lack of concentration and memory loss.
D) are usually so mild that the patient does not notice any changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
So-called mad cow disease is a type of
A) TSE.
B) encephalitis.
C) meningitis.
D) kuru.
A) TSE.
B) encephalitis.
C) meningitis.
D) kuru.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The autopsy results from cases of dementia pugilistica, or boxer's syndrome, most closely resemble
A) open head injuries.
B) Alzheimer's disease.
C) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD).
D) meningitis.
A) open head injuries.
B) Alzheimer's disease.
C) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD).
D) meningitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is there about a concussion that may cause the cognitive symptoms seen in some people following their injury?
A) When you are unconscious, your brain is not getting enough nutrients, so the longer you are unconscious, the more apt you are to have problems.
B) When you have a concussion, there is a very good probability that the brain is actually injured either by compression or some similar trauma.
C) Concussions will not cause any problems unless you are unconscious for a while, which results in loss of blood supply to the brain.
D) Concussions will not cause cognitive problems unless the damage is accompanied by bleeding.
A) When you are unconscious, your brain is not getting enough nutrients, so the longer you are unconscious, the more apt you are to have problems.
B) When you have a concussion, there is a very good probability that the brain is actually injured either by compression or some similar trauma.
C) Concussions will not cause any problems unless you are unconscious for a while, which results in loss of blood supply to the brain.
D) Concussions will not cause cognitive problems unless the damage is accompanied by bleeding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The best predictor of the development of chronic traumatic brain injury in boxers is
A) the use of protective headgear.
B) the weight class of the boxer.
C) their genetic makeup.
D) the win-loss record of the boxer.
A) the use of protective headgear.
B) the weight class of the boxer.
C) their genetic makeup.
D) the win-loss record of the boxer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Symptoms of dementia pugilistica, or boxer's syndrome, can include
A) an inability to feel pain.
B) unrealistically euphoric mood.
C) slurred speech and personality changes.
D) high blood pressure.
A) an inability to feel pain.
B) unrealistically euphoric mood.
C) slurred speech and personality changes.
D) high blood pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Infection from HIV results in the virus
A) invading neurons, killing them.
B) invading a variety of cells in the nervous system, which release chemicals that trigger apoptosis.
C) interfering with the NMDA glutamate receptor, which then no longer allows calcium to enter neurons.
D) having no direct effect on the cells of the nervous system but allows opportunistic viruses to thrive.
A) invading neurons, killing them.
B) invading a variety of cells in the nervous system, which release chemicals that trigger apoptosis.
C) interfering with the NMDA glutamate receptor, which then no longer allows calcium to enter neurons.
D) having no direct effect on the cells of the nervous system but allows opportunistic viruses to thrive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In which of the following ways does HIV-associated neurocognitive disease (HAND) differ in children versus in adults?
A) HIV effects on the nervous system are seen quickly in children, but appear only at later stages of the disease in adults.
B) HIV does not affect the nervous system in children, but does affect the nervous system in adults.
C) HIV effects on the nervous system occur at late stages of the disease in children, but appear right away in adults.
D) HIV affects the nervous systems of children, but has no impact on the nervous system in adults.
A) HIV effects on the nervous system are seen quickly in children, but appear only at later stages of the disease in adults.
B) HIV does not affect the nervous system in children, but does affect the nervous system in adults.
C) HIV effects on the nervous system occur at late stages of the disease in children, but appear right away in adults.
D) HIV affects the nervous systems of children, but has no impact on the nervous system in adults.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The site of damage on the opposite side of an initial blow in a closed head injury is known as
A) thrombosis.
B) hematoma.
C) coup.
D) countercoup.
A) thrombosis.
B) hematoma.
C) coup.
D) countercoup.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Having the E4 variant of the APOE gene increases a boxer's risk for
A) stroke.
B) brain tumors.
C) aneurysms.
D) dementia pugilistica.
A) stroke.
B) brain tumors.
C) aneurysms.
D) dementia pugilistica.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Symptoms that occur following a concussion
A) are only seen when subdural bleeding has occurred.
B) are always seen.
C) occur in some but not all cases of open head injury.
D) occur in some but not all cases of concussion.
A) are only seen when subdural bleeding has occurred.
B) are always seen.
C) occur in some but not all cases of open head injury.
D) occur in some but not all cases of concussion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Open head injuries are most likely to be fatal when the damage
A) involves both hemispheres of the brain.
B) is localized in one hemisphere of the brain.
C) does not involve the ventricles.
D) affects a single lobe rather than multiple lobes.
A) involves both hemispheres of the brain.
B) is localized in one hemisphere of the brain.
C) does not involve the ventricles.
D) affects a single lobe rather than multiple lobes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Initial symptoms of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND) may mimic
A) meningitis.
B) West Nile virus infection.
C) depression.
D) schizophrenia.
A) meningitis.
B) West Nile virus infection.
C) depression.
D) schizophrenia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Independent growths of new tissue that lack purpose are known as
A) tumors.
B) arteriovenous malformations.
C) cavernous malformations.
D) aneurysms.
A) tumors.
B) arteriovenous malformations.
C) cavernous malformations.
D) aneurysms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Meningiomas typically arise from
A) neurons.
B) astrocytes and oligodendrocytes or a combination of the two.
C) Schwann and amacrine cells.
D) the membranes covering the brain.
A) neurons.
B) astrocytes and oligodendrocytes or a combination of the two.
C) Schwann and amacrine cells.
D) the membranes covering the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In studies of prion proteins in cell culture, the abnormal prions
A) "hijack" deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in order to produce more abnormal prions.
B) convert normal prions into the abnormal form.
C) increase calcium influx, which triggers apoptosis.
D) enhance the expression of death genes that produce caspases.
A) "hijack" deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in order to produce more abnormal prions.
B) convert normal prions into the abnormal form.
C) increase calcium influx, which triggers apoptosis.
D) enhance the expression of death genes that produce caspases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following could NOT be an accurate statement?
A) Tom has been hospitalized due to lung cancer that has metastasized to his brain.
B) Tom has been hospitalized due to a glioma that has caused him to have seizures.
C) Tom has been hospitalized due to a benign tumor that has spread to his liver.
D) Tom has been hospitalized due to a meningioma that will be removed from his brain tomorrow.
A) Tom has been hospitalized due to lung cancer that has metastasized to his brain.
B) Tom has been hospitalized due to a glioma that has caused him to have seizures.
C) Tom has been hospitalized due to a benign tumor that has spread to his liver.
D) Tom has been hospitalized due to a meningioma that will be removed from his brain tomorrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Symptoms of tumors include
A) general symptoms due to increased pressure and specific symptoms related to the location of the tumor.
B) increased heart rate.
C) increased amounts of cerebrospinal fluid.
D) loss of the ability to plan behavior.
A) general symptoms due to increased pressure and specific symptoms related to the location of the tumor.
B) increased heart rate.
C) increased amounts of cerebrospinal fluid.
D) loss of the ability to plan behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following factors is responsible for some cases of CJD?
A) eating infected beef
B) cannibalism
C) contamination of surgical instruments
D) eating sheep meat infected with "scrapie"
A) eating infected beef
B) cannibalism
C) contamination of surgical instruments
D) eating sheep meat infected with "scrapie"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A meningioma is a cancer that
A) cannot be removed surgically due to the location.
B) is typically malignant.
C) is typically benign.
D) produces a serious risk of metastasis.
A) cannot be removed surgically due to the location.
B) is typically malignant.
C) is typically benign.
D) produces a serious risk of metastasis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The process in which malignant tumors shed cells that travel to another part of the body, where they initiate new tumor growth, is known as
A) infiltration.
B) encapsulation.
C) malformation.
D) metastasis.
A) infiltration.
B) encapsulation.
C) malformation.
D) metastasis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Recovery from substance/medication-induced neurocognitive disorder is more likely when people
A) have been using alcohol or anti-anxiety medications instead of cocaine and methamphetamine.
B) begin abstaining before the age of 30 years.
C) begin abstaining before the age of 50 years.
D) experience milder withdrawal syndromes after abstaining from their drug of choice.
A) have been using alcohol or anti-anxiety medications instead of cocaine and methamphetamine.
B) begin abstaining before the age of 30 years.
C) begin abstaining before the age of 50 years.
D) experience milder withdrawal syndromes after abstaining from their drug of choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Tumors in the nervous system arise from
A) neurons and glia.
B) neurons and cells of the meninges.
C) glia and cells of the meninges.
D) neurons, glia, and cells of the meninges.
A) neurons and glia.
B) neurons and cells of the meninges.
C) glia and cells of the meninges.
D) neurons, glia, and cells of the meninges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Most cases of new variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) probably resulted from
A) contamination from instruments used in surgical procedures.
B) cannibalism.
C) eating steak (muscle meat) from infected cattle.
D) eating meat from infected cattle that contained nervous system tissue.
A) contamination from instruments used in surgical procedures.
B) cannibalism.
C) eating steak (muscle meat) from infected cattle.
D) eating meat from infected cattle that contained nervous system tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Your physician somberly informs you that you have been diagnosed with a Grade I tumor and will require surgery. What does this mean?
A) You may want to pass up the surgery and concentrate on enjoying your remaining time, as Grade I tumors are typically rapidly fatal with or without treatment.
B) You should ask for a second opinion, as Grade I tumors are benign and do not need to be removed through surgery.
C) You can feel mildly optimistic, as Grade I tumors tend to recur after surgery, but they also grow slowly.
D) Your chances of survival are relatively good, as Grade I tumors are usually benign, slow-growing, and respond well to surgery.
A) You may want to pass up the surgery and concentrate on enjoying your remaining time, as Grade I tumors are typically rapidly fatal with or without treatment.
B) You should ask for a second opinion, as Grade I tumors are benign and do not need to be removed through surgery.
C) You can feel mildly optimistic, as Grade I tumors tend to recur after surgery, but they also grow slowly.
D) Your chances of survival are relatively good, as Grade I tumors are usually benign, slow-growing, and respond well to surgery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The sheep disease "scrapie" can spread to
A) humans but not to cows.
B) cows but not to humans.
C) both cows and humans.
D) neither cows nor humans.
A) humans but not to cows.
B) cows but not to humans.
C) both cows and humans.
D) neither cows nor humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Tumors that lack boundaries and are likely to recur following removal are known as
A) benign.
B) malignant.
C) Encapsulated.
D) recursive.
A) benign.
B) malignant.
C) Encapsulated.
D) recursive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Kuru, a disease found among the Fore people of New Guinea, virtually died out after
A) beef consumption was outlawed.
B) people changed to vegetarian diets.
C) consumption of monkeys was outlawed.
D) cannibalism was outlawed.
A) beef consumption was outlawed.
B) people changed to vegetarian diets.
C) consumption of monkeys was outlawed.
D) cannibalism was outlawed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Most gliomas develop in
A) neurons.
B) astrocytes and oligodendrocytes or a combination of the two.
C) Schwann and amacrine cells.
D) the membranes covering the brain.
A) neurons.
B) astrocytes and oligodendrocytes or a combination of the two.
C) Schwann and amacrine cells.
D) the membranes covering the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The outbreak of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in Great Britain and other countries during the 1990s probably resulted from
A) spontaneous genetic mutations.
B) housing cattle in too close proximity to infected sheep.
C) the use of ground bone and meat in animal feed.
D) the use of hormones to promote growth in cattle.
A) spontaneous genetic mutations.
B) housing cattle in too close proximity to infected sheep.
C) the use of ground bone and meat in animal feed.
D) the use of hormones to promote growth in cattle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The prions believed to cause TSEs
A) normally perform important functions in their host animal, and only cause problems if they are transmitted to another species.
B) differ from normal versions of proteins due to their increased length.
C) show different forms in different species.
D) show identical forms in all species.
A) normally perform important functions in their host animal, and only cause problems if they are transmitted to another species.
B) differ from normal versions of proteins due to their increased length.
C) show different forms in different species.
D) show identical forms in all species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The sheep disease "scrapie"
A) caused an epidemic among humans in nineteenth century Great Britain.
B) is responsible for causing kuru in humans.
C) does not pass directly to humans, although it can pass to other animals like cows.
D) passes frequently to humans in countries that consume a lot of sheep.
A) caused an epidemic among humans in nineteenth century Great Britain.
B) is responsible for causing kuru in humans.
C) does not pass directly to humans, although it can pass to other animals like cows.
D) passes frequently to humans in countries that consume a lot of sheep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Tumors that are contained within their own membrane are unlikely to recur following removal are known as
A) infiltrating.
B) malignant.
C) benign.
D) metastatic.
A) infiltrating.
B) malignant.
C) benign.
D) metastatic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 151 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



