Deck 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
1
Provide the proper IUPAC name for the compound below. 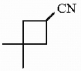

3,3-dimethylcyclobutanecarbonitrile
2
Provide the IUPAC name of the following compound. 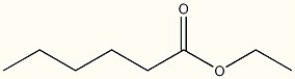

ethyl hexanoate
3
Cyclic amides are called:
A) lactones.
B) lactams.
C) aminals.
D) animals.
E) imines.
A) lactones.
B) lactams.
C) aminals.
D) animals.
E) imines.
lactams.
4
The correct priority of functional groups in IUPAC nomenclature is:
A) ester > amide > ketone > acid.
B) ketone > acid > ester > amide.
C) acid > ester > amide > ketone.
D) amide > acid > ester > ketone.
E) amide > ester > acid > ketone.
A) ester > amide > ketone > acid.
B) ketone > acid > ester > amide.
C) acid > ester > amide > ketone.
D) amide > acid > ester > ketone.
E) amide > ester > acid > ketone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Provide the structure of cyclohexyl formate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Provide the proper IUPAC name for ClCH2CH2CONHCH3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Provide the proper IUPAC name for the compound below. 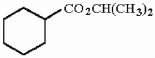
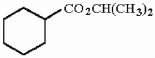

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Provide the name of the compound shown below. 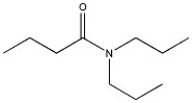


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Provide the structure of trifluoroacetic anhydride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Provide the structure of propanoic anhydride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Amides are less basic than amines because:
A) the carbonyl group donates electrons by resonance.
B) the carbonyl group withdraws electrons by resonance.
C) the nitrogen does not have a lone pair of electrons.
D) the nitrogen has a full positive charge.
E) amides do not contain nitrogen.
A) the carbonyl group donates electrons by resonance.
B) the carbonyl group withdraws electrons by resonance.
C) the nitrogen does not have a lone pair of electrons.
D) the nitrogen has a full positive charge.
E) amides do not contain nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
N-Methylacetamide is an example of:
A) a primary amide.
B) a secondary amide.
C) a tertiary amide.
D) an N, N-disubstituted amide.
E) an imine
A) a primary amide.
B) a secondary amide.
C) a tertiary amide.
D) an N, N-disubstituted amide.
E) an imine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Provide the name of the compound shown below. 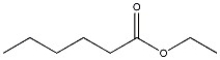


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following structures are carboxylic acid derivatives? 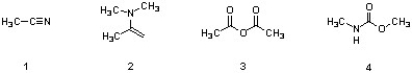
A) 3
B) 1 & 3
C) 1, 2, & 3
D) 4
E) All are carboxylic acid derivatives.

A) 3
B) 1 & 3
C) 1, 2, & 3
D) 4
E) All are carboxylic acid derivatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Provide the structure of (R)-4-ethoxypentanenitrile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Provide the structure of o-bromobenzoyl chloride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Provide the structure of γ-butyrolactam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Provide the proper IUPAC name for the compound below. 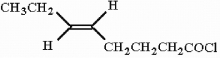


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Cyclic esters are called:
A) lactones.
B) lactams.
C) lacrimals.
D) imides.
E) enamines.
A) lactones.
B) lactams.
C) lacrimals.
D) imides.
E) enamines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Provide the IUPAC name of the following compound. 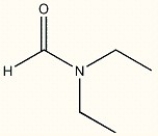


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Provide the structure of 3-oxobutanenitrile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Provide the name of the compound shown below. 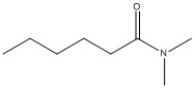


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Provide the name of CH3O2CH2CH2CH2CH3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Provide the name of the compound shown below. 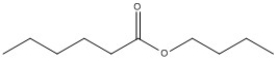


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the common name for the following carboxylic acid derivative? 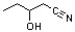
A) β-hydroxybutyronitrile
B) 1-cyano-2-butanol
C) β-hydroxyvaleronitrile
D) γ-hydroxyvaleronitrile
E) 2-hydroxypentane nitrile

A) β-hydroxybutyronitrile
B) 1-cyano-2-butanol
C) β-hydroxyvaleronitrile
D) γ-hydroxyvaleronitrile
E) 2-hydroxypentane nitrile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Provide the structure of N,N-diethylbutanamide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the correct IUPAC name for the following compound? 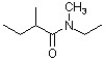
A) N-ethyl-2,N-dimethylbutanamide
B) N-ethyl-N-methylisobutyramide
C) 2,N-dimethyl-N-ethylbutanamide
D) 1-(ethylmethylamino)-2-methylbutanamide

A) N-ethyl-2,N-dimethylbutanamide
B) N-ethyl-N-methylisobutyramide
C) 2,N-dimethyl-N-ethylbutanamide
D) 1-(ethylmethylamino)-2-methylbutanamide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Provide the IUPAC name for HCONHCH2CH2CH3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing boiling point: acetic acid, propanenitrile, butane, and acetamide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
List the following five compounds, ethanamide, 1-propanol, methyl formate, acetic acid, and propanenitrile, in order of increasing boiling point. Start with the lowest boiling compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Arrange the following three amides in order of increasing boiling point: propanamide, N-methylacetamide, and N,N-dimethylformamide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In 1H NMR, the chemical shifts for protons α to a carbonyl group:
A) are similar for all acid derivatives.
B) are farthest downfield for carboxylic acids.
C) are farther downfield than those α to a nitrile.
D) fall between δ 3.1 and δ 4.2 (ppm).
E) fall between δ 1.3 and δ 1.8 (ppm).
A) are similar for all acid derivatives.
B) are farthest downfield for carboxylic acids.
C) are farther downfield than those α to a nitrile.
D) fall between δ 3.1 and δ 4.2 (ppm).
E) fall between δ 1.3 and δ 1.8 (ppm).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
While the carbonyl stretching frequency for simple aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids is about 1710 cm-1, the carbonyl stretching frequency for acid chlorides is about ________.
A) 1700 cm-1
B) 1735 cm-1
C) 1800 cm-1
D) 1660 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1
A) 1700 cm-1
B) 1735 cm-1
C) 1800 cm-1
D) 1660 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the proton NMR spectrum of a secondary amide, the amide proton's signal is:
A) sharp, around δ 5.0 (ppm).
B) sharp, around δ 10.0 (ppm).
C) broad, around δ 9.0 (ppm).
D) broad, around δ 7.0 (ppm).
E) usually not observed.
A) sharp, around δ 5.0 (ppm).
B) sharp, around δ 10.0 (ppm).
C) broad, around δ 9.0 (ppm).
D) broad, around δ 7.0 (ppm).
E) usually not observed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Provide the proper IUPAC name for NCCH2CH2CH2CH2CO2CH3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify the correct IUPAC systematic name for the structure below. 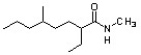
A) N-methyl-2-ethyl-5-methyloctanamide
B) 6,N-dimethylnonane-3-carboxamide
C) 5,N-dimethyl-2-ethyloctanamide
D) 2-ethyl-5,N-dimethyloctanamide

A) N-methyl-2-ethyl-5-methyloctanamide
B) 6,N-dimethylnonane-3-carboxamide
C) 5,N-dimethyl-2-ethyloctanamide
D) 2-ethyl-5,N-dimethyloctanamide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
While the carbonyl stretching frequency for simple aldeydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids is about 1710 cm-1, the carbonyl stretching frequency for esters is about ________.
A) 1660 cm-1
B) 1700 cm-1
C) 1735 cm-1
D) 1800 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1
A) 1660 cm-1
B) 1700 cm-1
C) 1735 cm-1
D) 1800 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Provide the structure of 2-bromo-2-methylbutanoyl chloride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
While the carbonyl stretching frequency for simple aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids is about 1710 cm-1, the carbonyl stretching frequency for amides is about ________.
A) 1700 cm-1
B) 1735 cm-1
C) 1800 cm-1
D) 1660 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1
A) 1700 cm-1
B) 1735 cm-1
C) 1800 cm-1
D) 1660 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following are strongly hydrogen bonded in the liquid phase?
A) nitriles
B) esters
C) secondary amides
D) tertiary amides
E) acid chlorides
A) nitriles
B) esters
C) secondary amides
D) tertiary amides
E) acid chlorides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A correct order of reactivity of acid derivatives towards nucleophilic attack is:
A) esters > acid anhydrides > amides.
B) anhydrides > amides > esters.
C) carboxylates > esters > amides.
D) anhydrides > acids > acid chlorides.
E) anhydrides > amides > carboxylates.
A) esters > acid anhydrides > amides.
B) anhydrides > amides > esters.
C) carboxylates > esters > amides.
D) anhydrides > acids > acid chlorides.
E) anhydrides > amides > carboxylates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The following compound is a tumor growth inhibitor (J. Med. Chem. 2011, 1789). Circle all carbon centers that are at the same oxidation state as a carboxylic acid. 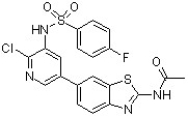


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What compound results when ethyl benzoate is stirred in methanol containing a trace of HCl and by what name is this process known?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Name the compound which results when δ-valerolactone is heated in a large excess of methanol in the presence of catalytic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which compound has a carbonyl stretch in its IR spectrum at the lowest wavenumber?
A) acetic anhydride
B) formamide
C) cyclohexanone
D) propanoyl chloride
E) ethyl acetate
A) acetic anhydride
B) formamide
C) cyclohexanone
D) propanoyl chloride
E) ethyl acetate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The most characteristic IR stretch of butanenitrile occurs at approximately what wavenumber?
A) 3500 cm-1
B) 3100 cm-1
C) 2600 cm-1
D) 2200 cm-1
E) 1750 cm-1
A) 3500 cm-1
B) 3100 cm-1
C) 2600 cm-1
D) 2200 cm-1
E) 1750 cm-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Provide a detailed, stepwise mechanism for the acid-catalyzed transesterification of ethyl acetate with n-propanol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Using the two key resonance structures for an ester, show how resonance stabilization is lost when an ester is attacked by a nucleophile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is the most reactive carboxylic acid derivative?
A) ester
B) anhydride
C) nitrile
D) acid chloride
E) amide
A) ester
B) anhydride
C) nitrile
D) acid chloride
E) amide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Using potential energy diagrams, explain why alkoxides act as leaving groups in nucleophilic acyl substitutions but not in SN2 reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Provide a detailed, stepwise mechanism for the base-mediated transesterification of methyl benzoate with sodium ethoxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
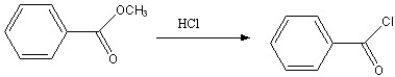
Which of the following reactions is favorable, in the direction indicated, under fairly "normal" laboratory conditions?
A)
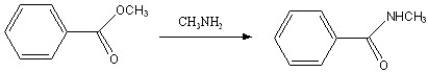
B)
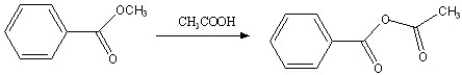
C)
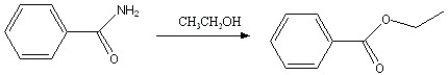
D)
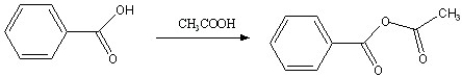
E)
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In nucleophilic acyl substitution,
A) protonation of the carbonyl is followed immediately by loss of the leaving group.
B) loss of the leaving group is followed by rearrangement of the carbocation.
C) addition to the carbonyl by a nucleophile is followed by loss of the leaving group.
D) ester hydrolysis is followed by deprotonation.
E) an SN2 reaction occurs.
A) protonation of the carbonyl is followed immediately by loss of the leaving group.
B) loss of the leaving group is followed by rearrangement of the carbocation.
C) addition to the carbonyl by a nucleophile is followed by loss of the leaving group.
D) ester hydrolysis is followed by deprotonation.
E) an SN2 reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Name the compound which results when propyl benzoate is heated in a large excess of ethanol in the presence of catalytic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Predict the major product of the following reaction. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Arrange the carboxylic acid derivatives below in order of increasing reactivity towards nucleophilic acyl substitution. 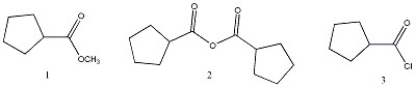
A) 1 < 2 <3
B) 1 < 3 < 2
C) 2 < 1 < 3
D) 2 < 3 < 1
E) 3 < 2 < 1

A) 1 < 2 <3
B) 1 < 3 < 2
C) 2 < 1 < 3
D) 2 < 3 < 1
E) 3 < 2 < 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Provide an arrow pushing mechanism for the following reaction. Show all
intermediate structures and formal charges. You do not need to show resonance structures.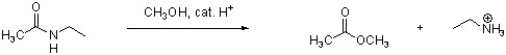
intermediate structures and formal charges. You do not need to show resonance structures.
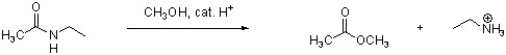

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
List the following four carboxylic acid derivatives, ester, anhydride, amide, and acid halide, in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions. Start with the least reactive derivative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Describe, in short phrases, the three step mechanism by which hexanoyl chloride reacts with dimethylamine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Draw the product resulting from the following reaction. Indicate any relevant stereochemistry. 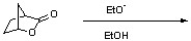


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Distamycin and derivatives have exhibited antiviral, antibiotic, and antitumor activity by binding to the minor groove of DNA (J. Med. Chem. 2004, 2133). Place a line through each bond of distamycin that would be cleaved by acid hydrolysis. 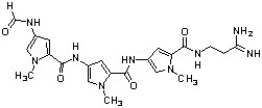


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following compounds is(are) hydrolyzed to butanoic acid upon heating in H2O, H2SO4?
A) ethyl butanoate
B) butyl acetate
C) N-methylbutanamide
D) both A and B
E) both A and C
A) ethyl butanoate
B) butyl acetate
C) N-methylbutanamide
D) both A and B
E) both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Acids can be converted to primary amines by:
A) conversion to the nitrile followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
B) conversion to the diazonium salt followed by treatment with NaBH4.
C) conversion to the primary amide followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
D) both A and B.
E) both A and C.
A) conversion to the nitrile followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
B) conversion to the diazonium salt followed by treatment with NaBH4.
C) conversion to the primary amide followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
D) both A and B.
E) both A and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Acids can be reduced to aldehydes by:
A) treatment with LiAlH4.
B) conversion to the acid chloride followed by treatment with LiAlH[OC(CH3)3]3.
C) conversion to the amide followed by treatment with NaBH4.
D) conversion to the ester followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
E) conversion to the anhydride followed by treatment with Mg and H3O+.
A) treatment with LiAlH4.
B) conversion to the acid chloride followed by treatment with LiAlH[OC(CH3)3]3.
C) conversion to the amide followed by treatment with NaBH4.
D) conversion to the ester followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
E) conversion to the anhydride followed by treatment with Mg and H3O+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Provide the major organic product in the reaction shown below. 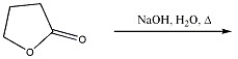
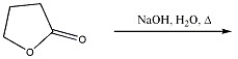

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which sequence ranks the following carboxylic acid derivatives in order of increasing rate of hydrolysis? 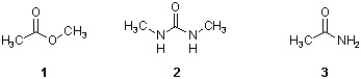
A) 2 < 3 < 1
B) 3 < 2 < 1
C) 2 < 1 < 3
D) 1 < 3 < 2

A) 2 < 3 < 1
B) 3 < 2 < 1
C) 2 < 1 < 3
D) 1 < 3 < 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Lithium aluminum hydride reduces carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, and esters to:
A) aldehydes.
B) primary alcohols.
C) secondary alcohols.
D) tertiary alcohols.
E) ketones.
A) aldehydes.
B) primary alcohols.
C) secondary alcohols.
D) tertiary alcohols.
E) ketones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Provide the major organic product in the reaction shown below. 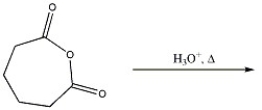


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The hydrolysis of esters in base is called:
A) the Fischer esterification.
B) the Hunsdiecker reaction.
C) the Dieckmann condensation.
D) transesterification.
E) saponification.
A) the Fischer esterification.
B) the Hunsdiecker reaction.
C) the Dieckmann condensation.
D) transesterification.
E) saponification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following are intermediates in the acid hydrolysis of an amide? 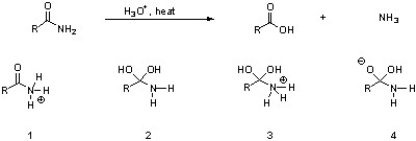
A) 1
B) 2
C) 2 & 3
D) 4
E) 1, 2, & 3

A) 1
B) 2
C) 2 & 3
D) 4
E) 1, 2, & 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What compound is produced when N,N-dimethylpropanamide is treated with LiAlH4?
A) CH3CH2CONH2
B) CH3CH2CH2NH2
C) CH3CH2CH2OH
D) CH3CH2CH2N(CH3)2
E) CH3CH2N(CH3)2
A) CH3CH2CONH2
B) CH3CH2CH2NH2
C) CH3CH2CH2OH
D) CH3CH2CH2N(CH3)2
E) CH3CH2N(CH3)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which sequence correctly lists the following structures in order of increasing rate of hydrolysis to a carboxylic acid under basic conditions? 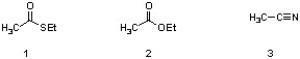
A) 1 < 2 < 3
B) 2 < 3 < 1
C) 3 < 1 < 2
D) 3 < 2 < 1
E) 2 < 1 < 3

A) 1 < 2 < 3
B) 2 < 3 < 1
C) 3 < 1 < 2
D) 3 < 2 < 1
E) 2 < 1 < 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Typically, amides will hydrolyze under ________ conditions than esters.
A) stronger
B) more dilute
C) milder
D) less vigorous
E) more saline
A) stronger
B) more dilute
C) milder
D) less vigorous
E) more saline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Predict the major product of the following reaction. 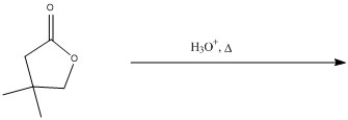


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Predict the major product of the following reaction. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Two equivalents of methyl magnesium bromide will add to:
A) lactones.
B) aldehydes.
C) ketones.
D) imines.
E) secondary amines.
A) lactones.
B) aldehydes.
C) ketones.
D) imines.
E) secondary amines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Predict the major product of the following reaction. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The hydrolysis of esters, amides, and nitriles:
A) can be carried out under acidic or basic conditions.
B) must be acid-catalyzed.
C) must be base-catalyzed.
D) should be carried out at pH 7.0 for optimum efficiency.
E) is not pH dependent.
A) can be carried out under acidic or basic conditions.
B) must be acid-catalyzed.
C) must be base-catalyzed.
D) should be carried out at pH 7.0 for optimum efficiency.
E) is not pH dependent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Provide the major organic product in the reaction of CH3CH2CONH2 with hot aqueous acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Predict the major product of the following reaction. 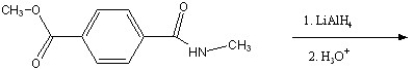


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



